The Value of Fournier’s Gangrene Scoring Systems on Admission to Predict Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
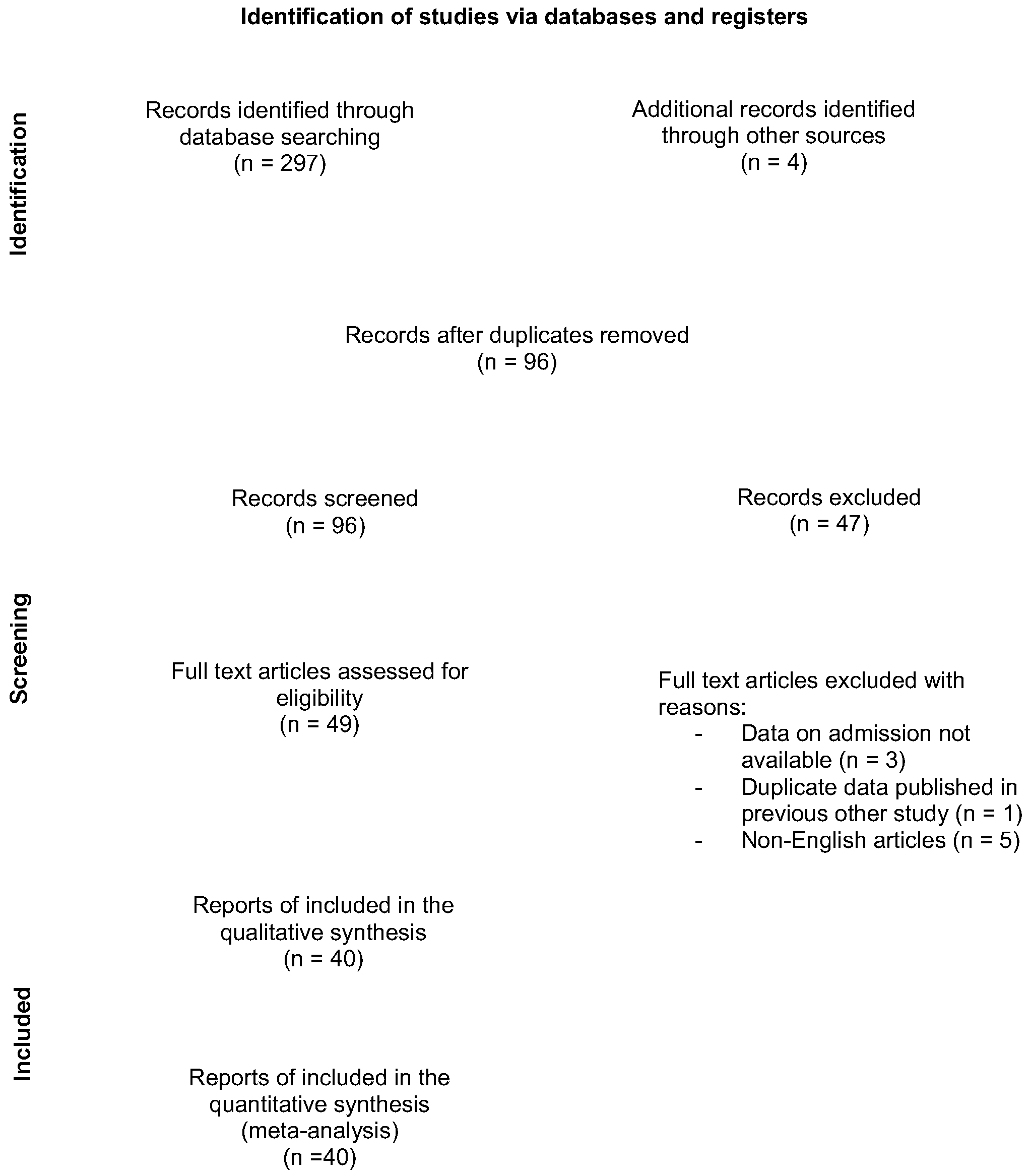
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction and Management
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Data Synthesis
3. Results
3.1. Included Studies and Study Characteristics
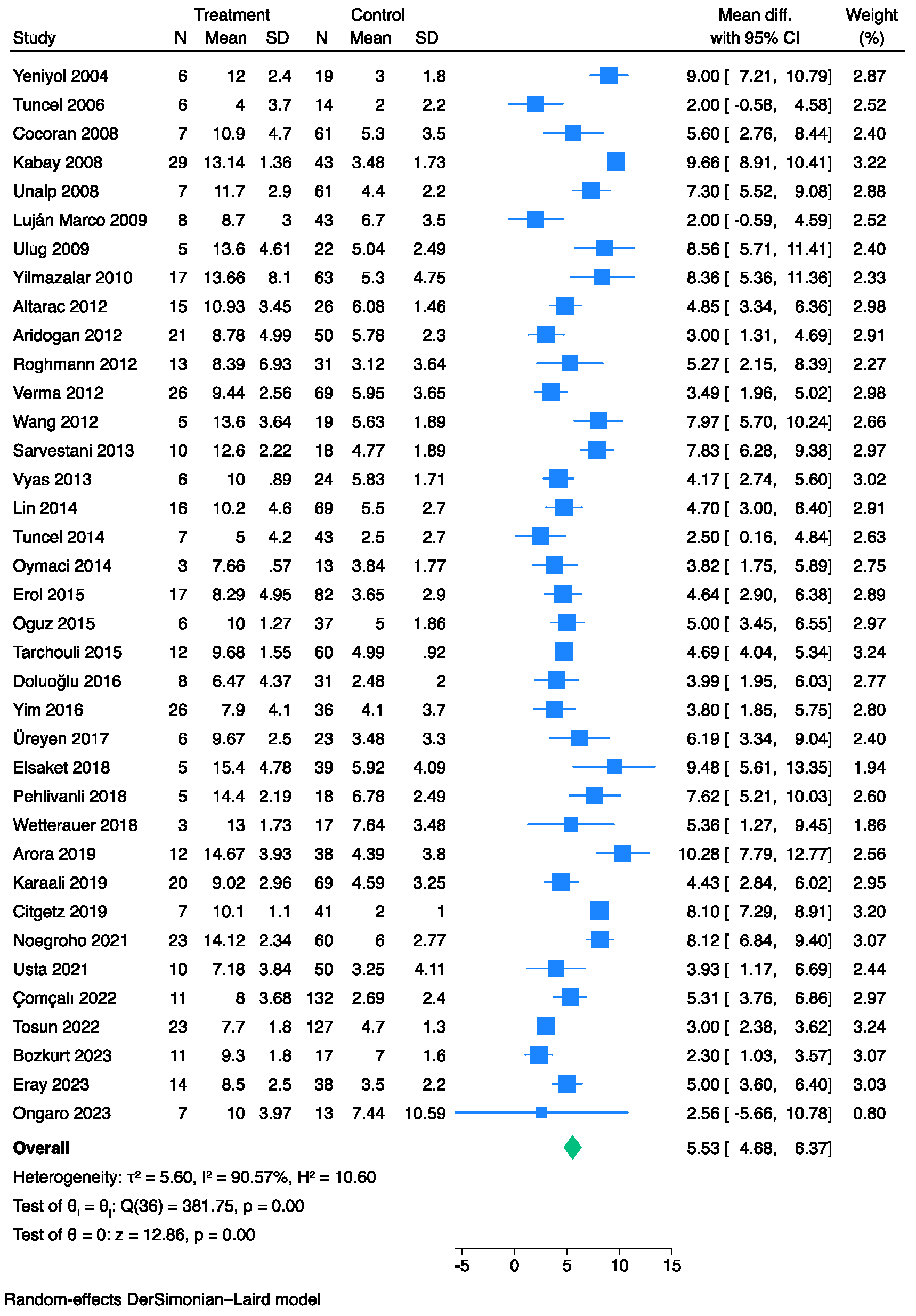
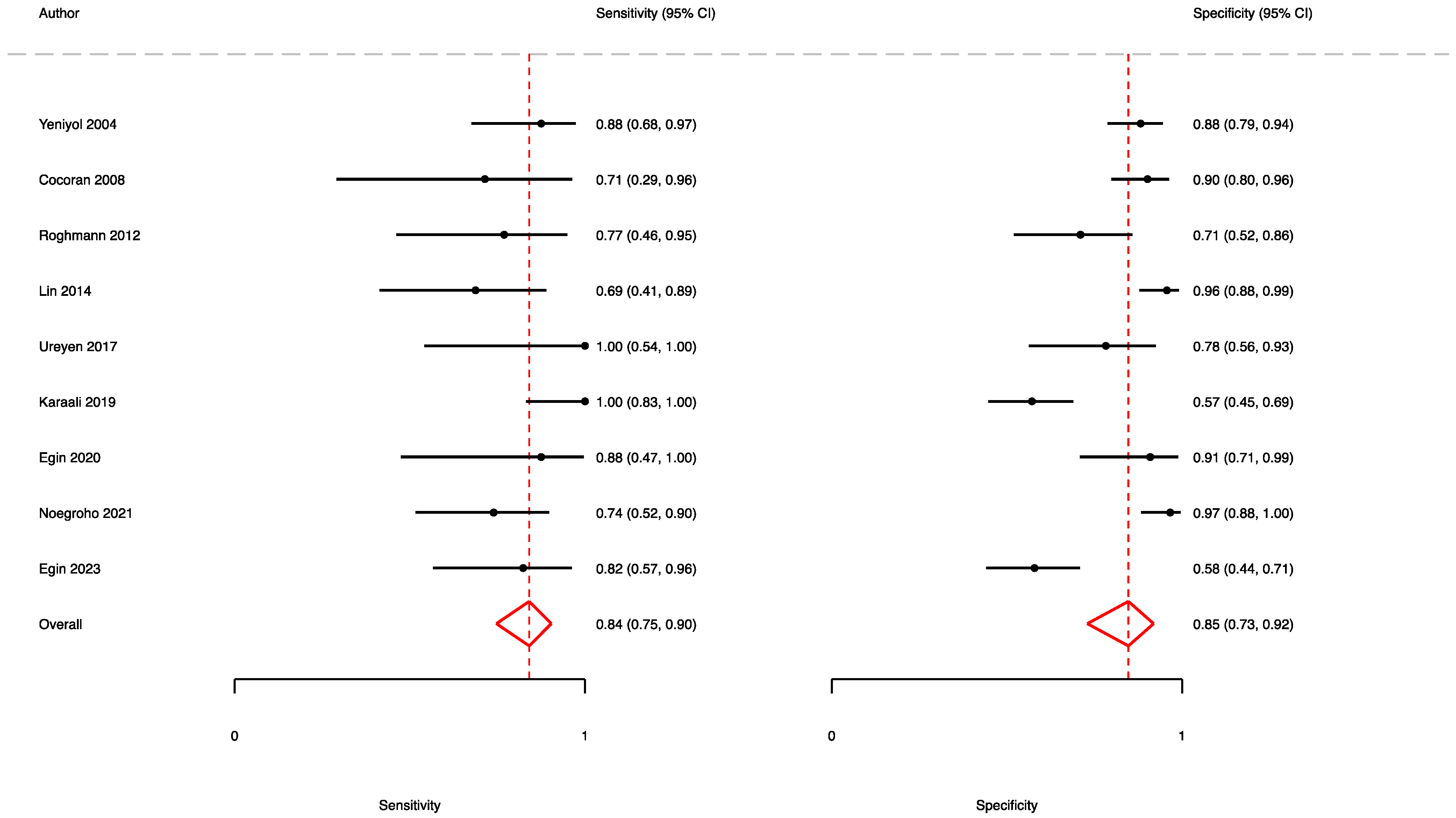
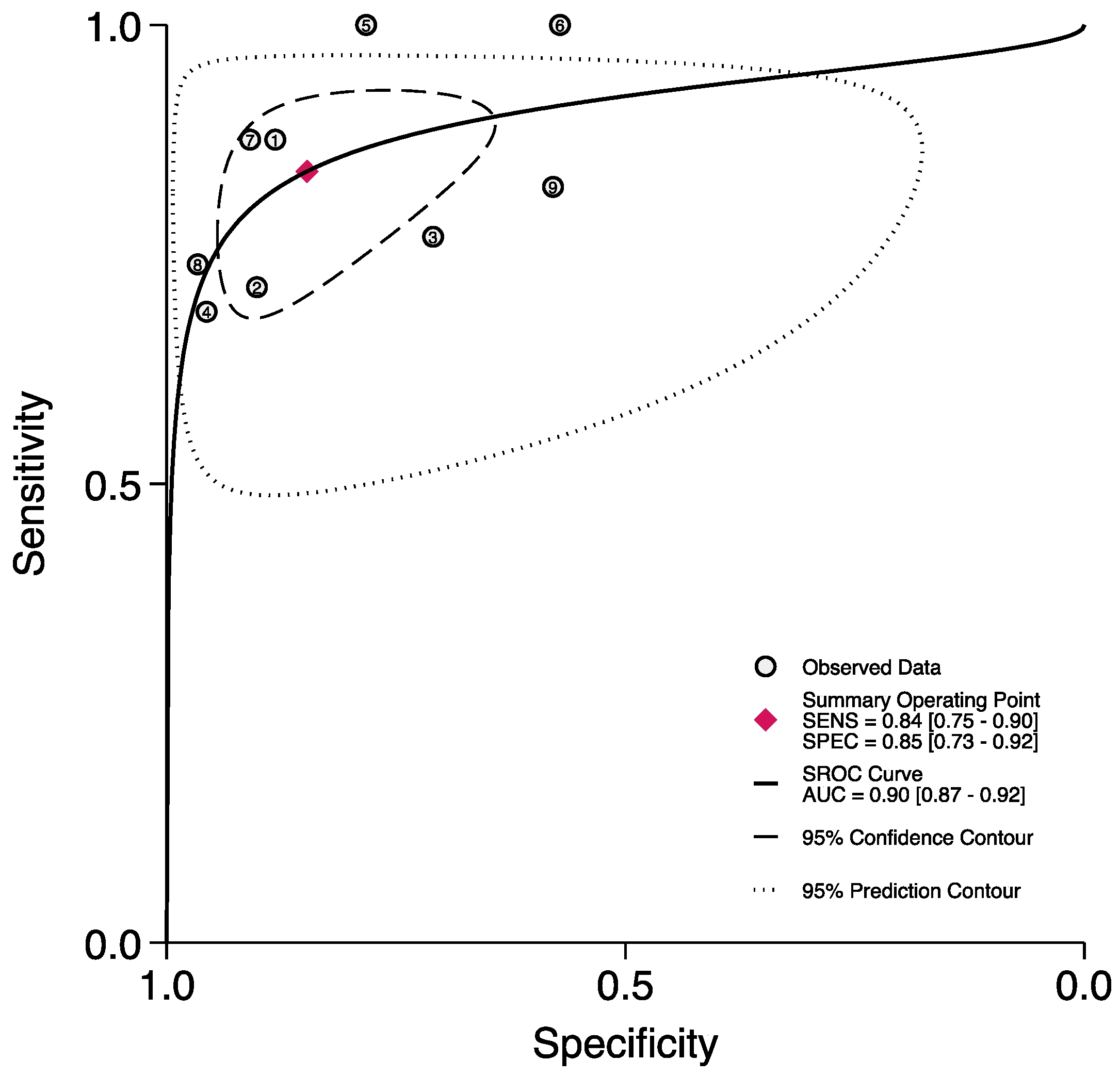
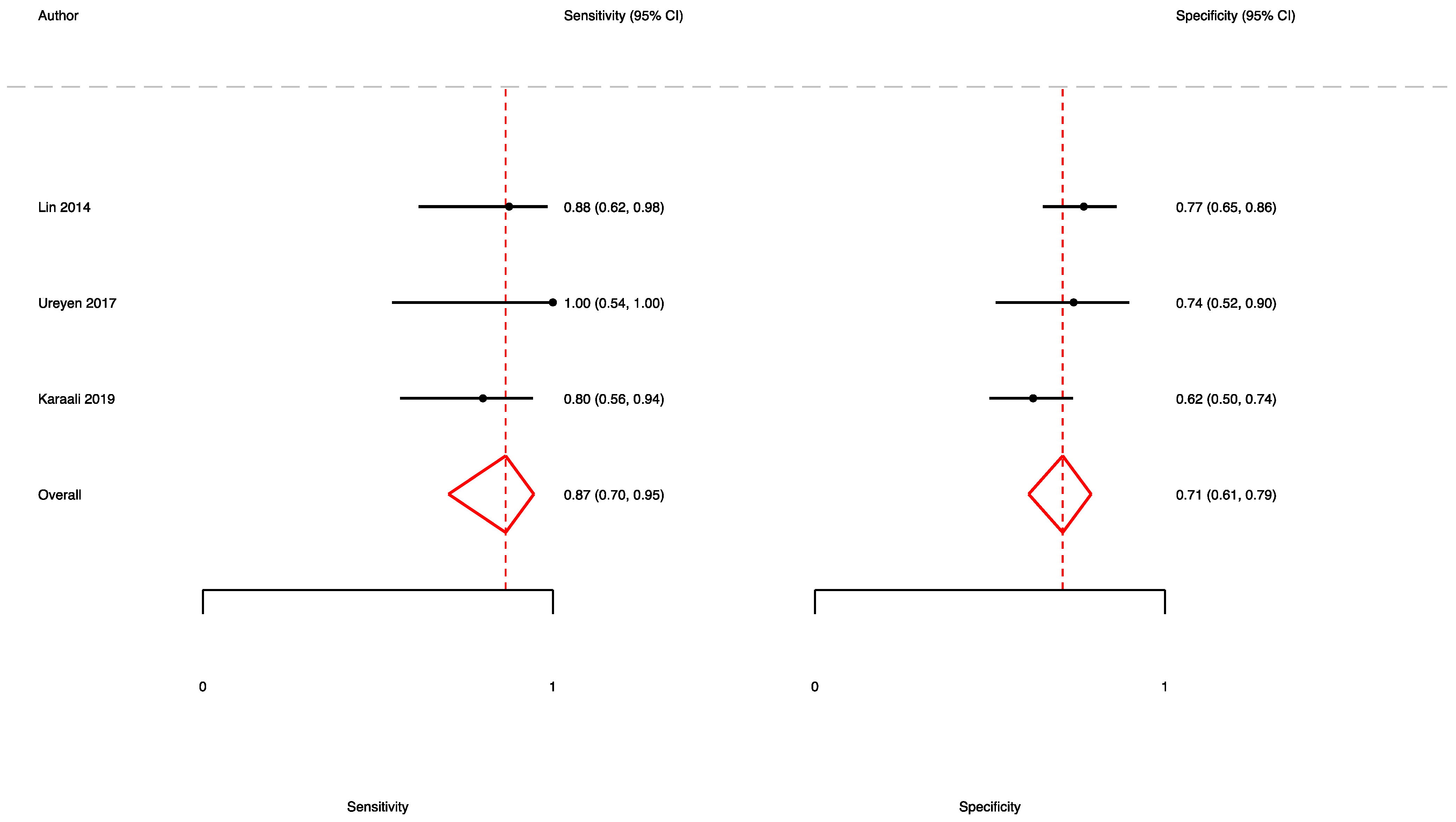
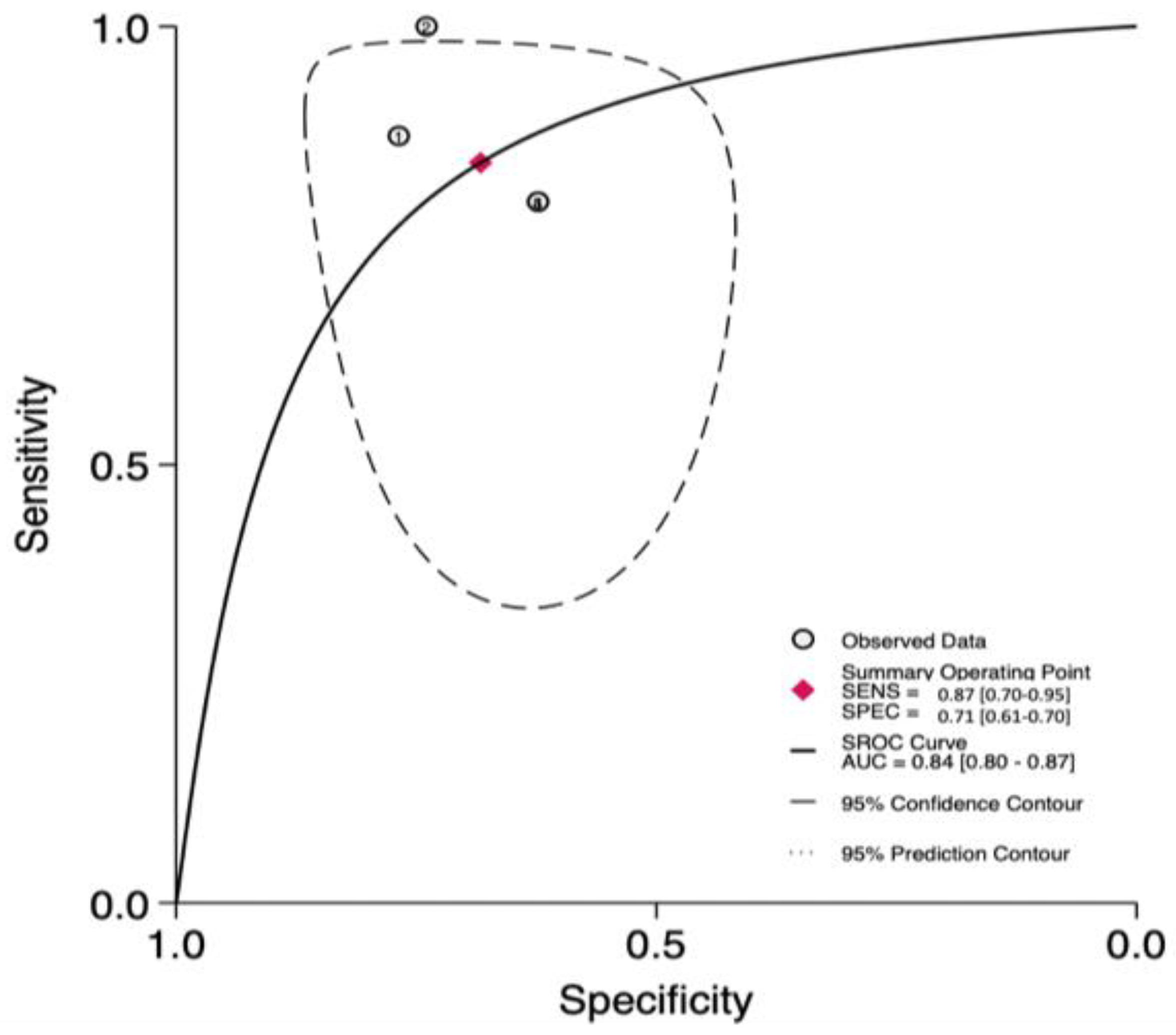
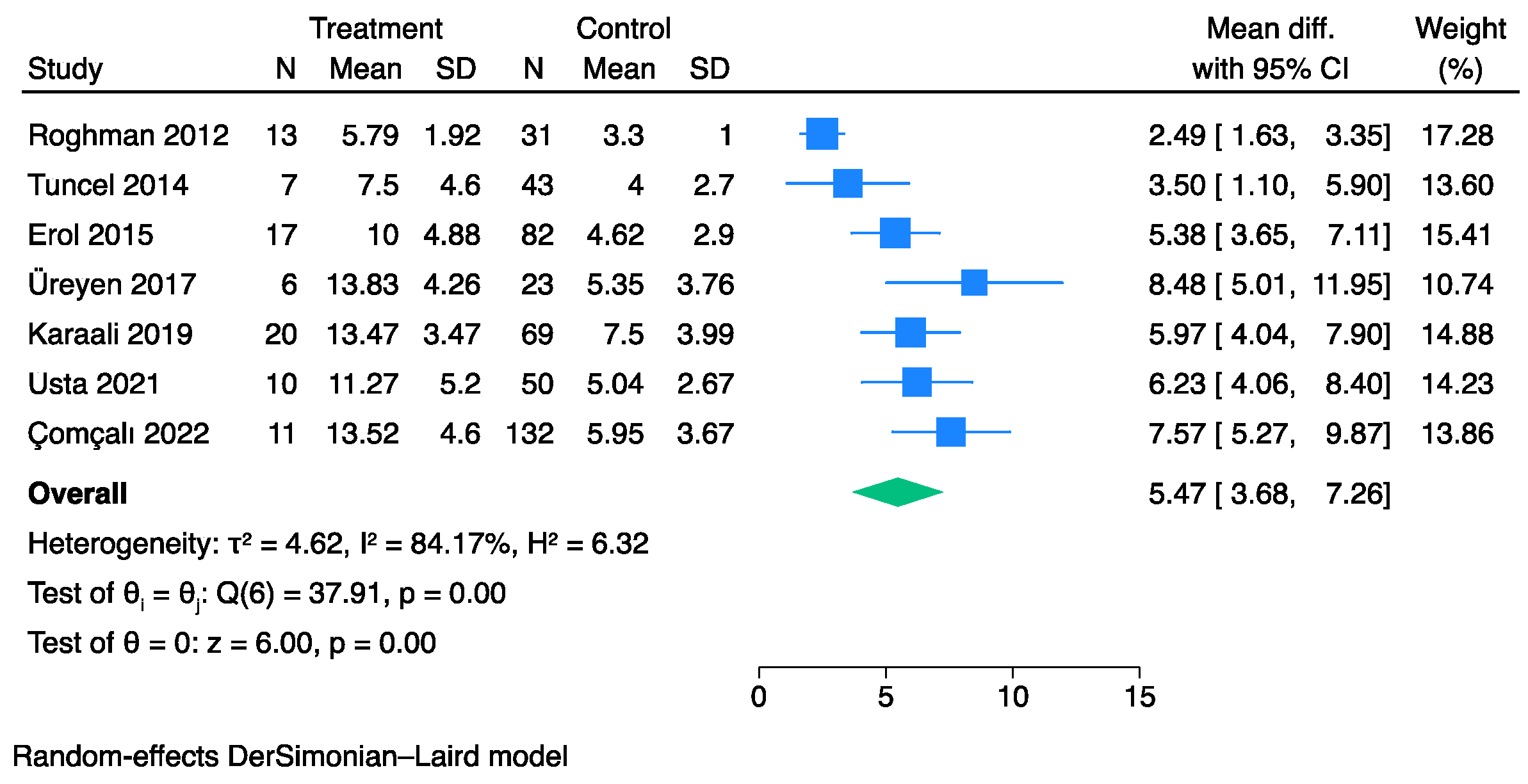
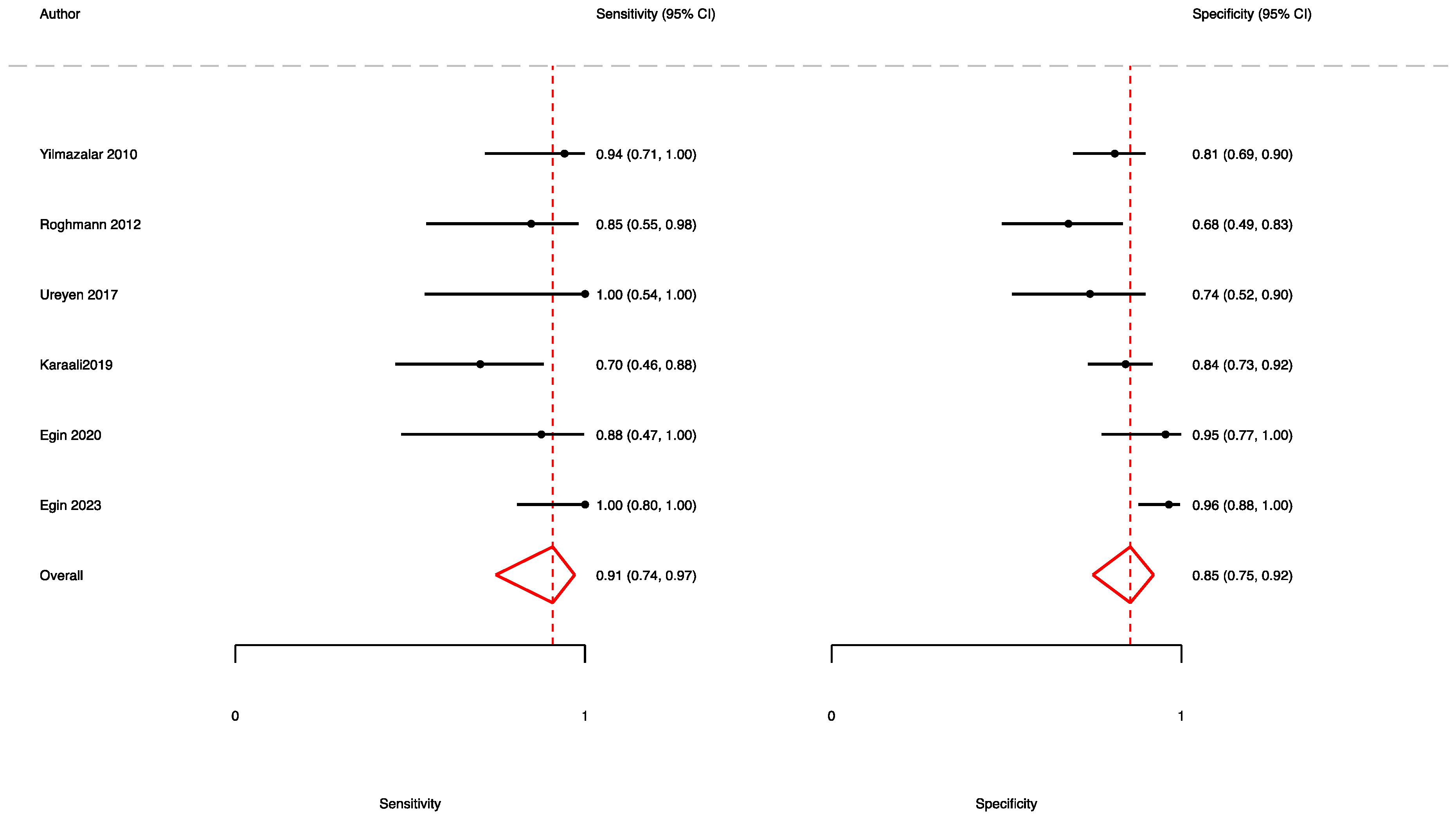
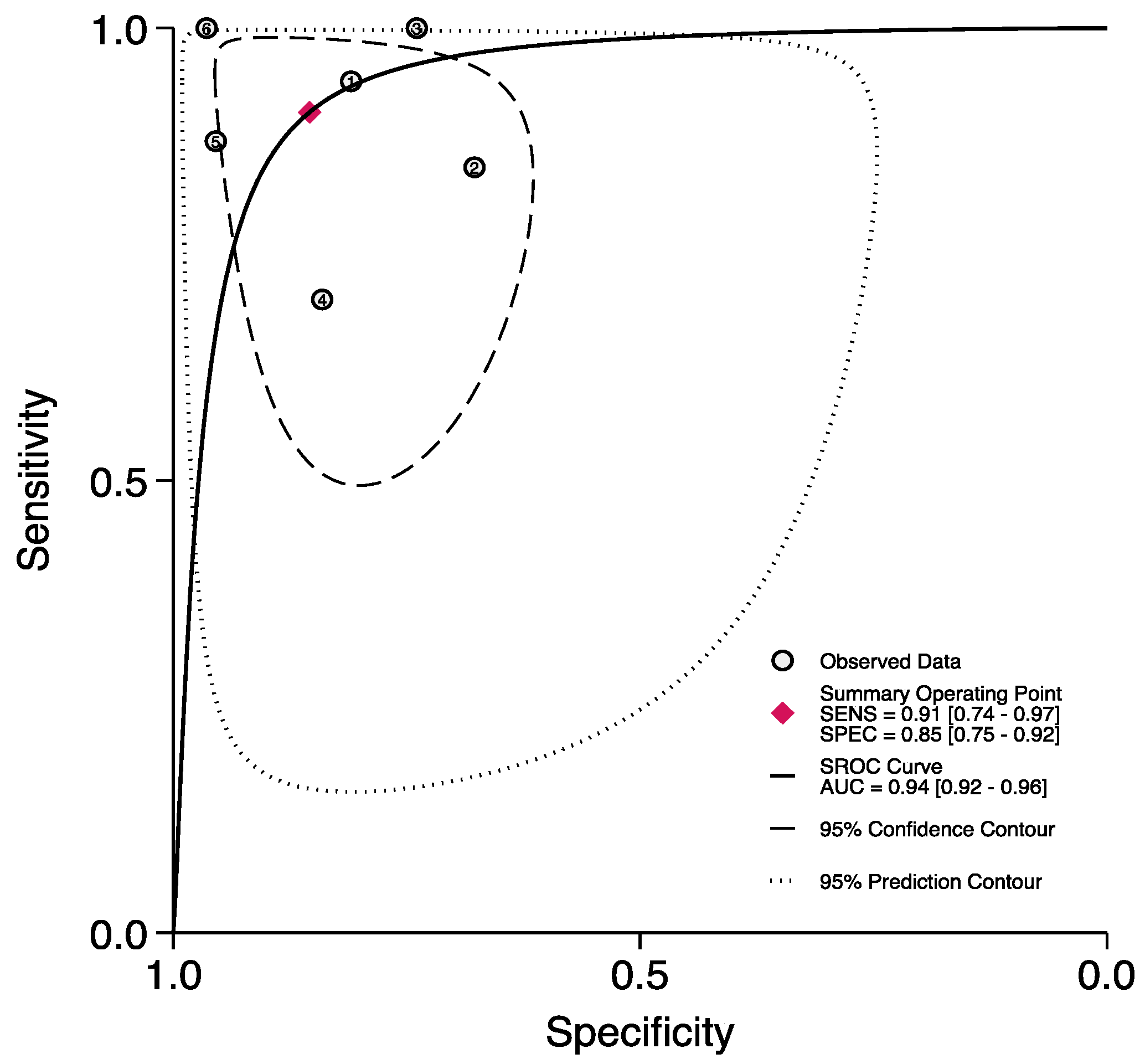
3.2. The Prognostic Value of FGSI
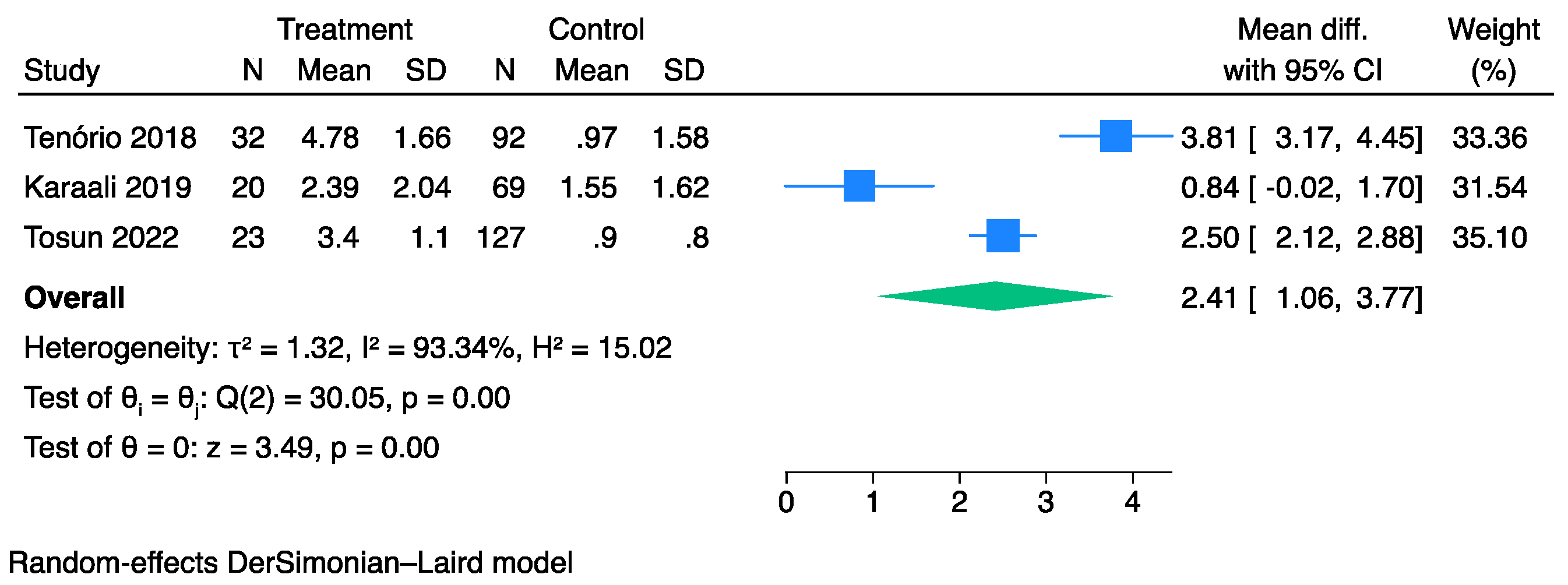
3.3. The Prognostic Value of SFGSI
3.4. The Prognostic Value of UFGSI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sorensen, M.D.; Krieger, J.N.; Rivara, F.P.; Broghammer, J.A.; Klein, M.B.; Mack, C.D.; Wessells, H. Fournier’s Gangrene: Population based epidemiology and outcomes. J. Urol. 2009, 181, 2120–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecker, K.W.; Baars, A.; Töpfer, J.; Frank, J. Necrotizing Fasciitis of the Perineum and the Abdominal Wall-Surgical Approach. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2008, 34, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkut, M.; Içöz, G.; Dayangaç, M.; Akgün, E.; Yeniay, L.; Erdoğan, O.; Cal, C. Outcome analysis in patients with Fournier’s gangrene: Report of 45 cases. Dis. Colon. Rectum. 2003, 46, 649–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raizandha, M.A.; Hidayatullah, F.; Kloping, Y.P.; Rahman, I.A.; Djatisoesanto, W.; Rizaldi, F. The role of hyperbaric oxygen therapy in Fournier’s Gangrene: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2022, 48, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laor, E.; Palmer, L.S.; Tolia, B.M.; Reid, R.E.; Winter, H.I. Outcome prediction in patients with Fournier’s gangrene. J. Urol. 1995, 154, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmazlar, T.; Ozturk, E.; Ozguc, H.; Ercan, I.; Vuruskan, H.; Oktay, B. Fournier’s gangrene: An analysis of 80 patients and a novel scoring system. Tech. Coloproctol. 2010, 14, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.Y.; Ou, C.H.; Tzai, T.S.; Tong, Y.C.; Chang, C.C.; Cheng, H.L.; Yang, W.H.; Lin, Y.M. Validation and simplification of Fournier’s gangrene severity index. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health NIo. Quality Assessment Tool for Observational Cohort and Cross-Sectional Studies. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 2014. Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeniyol, C.O.; Suelozgen, T.; Arslan, M.; Ayder, A.R. Fournier’s gangrene: Experience with 25 patients and use of Fournier’s gangrene severity index score. Urology 2004, 64, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, A.; Aydin, O.; Tekdogan, U.; Nalcacioglu, V.; Capar, Y.; Atan, A. Fournier’s gangrene: Three years of experience with 20 patients and validity of the Fournier’s Gangrene Severity Index Score. Eur. Urol. 2006, 50, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcoran, A.T.; Smaldone, M.C.; Gibbons, E.P.; Walsh, T.J.; Davies, B.J. Validation of the Fournier’s gangrene severity index in a large contemporary series. J. Urol. 2008, 180, 944–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabay, S.; Yucel, M.; Yaylak, F.; Algin, M.C.; Hacioglu, A.; Kabay, B.; Muslumanoglu, A.Y. The clinical features of Fournier’s gangrene and the predictivity of the Fournier’s Gangrene Severity Index on the outcomes. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2008, 40, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unalp, H.R.; Kamer, E.; Derici, H.; Atahan, K.; Balci, U.; Demirdoven, C.; Nazli, O.; Onal, M.A. Fournier’s gangrene: Evaluation of 68 patients and analysis of prognostic variables. J. Postgrad. Med. 2008, 54, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luján Marco, S.; Budía, A.; Di Capua, C.; Broseta, E.; Jiménez Cruz, F. Evaluation of a severity score to predict the prognosis of Fournier’s gangrene. BJU Int. 2010, 106, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluğ, M.; Gedik, E.; Girgin, S.; Celen, M.K.; Ayaz, C. The evaluation of microbiology and Fournier’s gangrene severity index in 27 patients. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 13, e424–e430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altarac, S.; Katušin, D.; Crnica, S.; Papeš, D.; Rajković, Z.; Arslani, N. Fournier’s gangrene: Etiology and outcome analysis of 41 patients. Urol. Int. 2012, 88, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aridogan, I.A.; Izol, V.; Abat, D.; Karsli, O.; Bayazit, Y.; Satar, N. Epidemiological characteristics of Fournier’s gangrene: A report of 71 patients. Urol. Int. 2012, 89, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghmann, F.; von Bodman, C.; Löppenberg, B.; Hinkel, A.; Palisaar, J.; Noldus, J. Is there a need for the Fournier’s gangrene severity index? Comparison of scoring systems for outcome prediction in patients with Fournier’s gangrene. BJU Int. 2012, 110, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Sayana, A.; Kala, S.; Rai, S. Evaluation of the Utility of the Fournier’s Gangrene Severity Index in the Management of Fournier’s Gangrene in North India: A Multicentre Retrospective Study. J. Cutan. Aesthet. Surg. 2012, 5, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Han, X.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Li, B.; Pan, F.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Chen, Z.; et al. Experience in management of Fournier’s gangrene: A report of 24 cases. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 2012, 32, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzi Sarvestani, A.; Zamiri, M.; Sabouri, M. Prognostic Factors for Fournier’s Gangrene; A 10-year Experience in Southeastern Iran. Bull. Emerg. Trauma. 2013, 1, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vyas, H.G.; Kumar, A.; Bhandari, V.; Kumar, N.; Jain, A.; Kumar, R. Prospective evaluation of risk factors for mortality in patients of Fournier’s gangrene: A single center experience. Indian J. Urol. 2013, 29, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oymacı, E.; Coşkun, A.; Yakan, S.; Erkan, N.; Uçar, A.D.; Yıldırım, M. Evaluation of factors affecting mortality in Fournier’s Gangrene: Retrospective clinical study of sixteen cases. Ulus. Cerrahi. Derg. 2014, 30, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuncel, A.; Keten, T.; Aslan, Y.; Kayali, M.; Erkan, A.; Koseoglu, E.; Atan, A. Comparison of different scoring systems for outcome prediction in patients with Fournier’s gangrene: Experience with 50 patients. Scand. J. Urol. 2014, 48, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, B.; Tuncel, A.; Tok, A.; Hanci, V.; Sari, U.; Sendogan, F.; Budak, S.; Aydemir, H.; Amasyali, A.S.; Yildirim, A.; et al. Low magnesium levels an important new prognostic parameter can be overlooked in patients with Fournier’s gangrene: A multicentric study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oguz, A.; Gümüş, M.; Turkoglu, A.; Bozdağ, Z.; Ülger, B.V.; Agaçayak, E.; Böyük, A. Fournier’s Gangrene: A Summary of 10 Years of Clinical Experience. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarchouli, M.; Bounaim, A.; Essarghini, M.; Ratbi, M.B.; Belhamidi, M.S.; Bensal, A.; Zemmouri, A.; Ali, A.A.; Sair, K. Analysis of prognostic factors affecting mortality in Fournier’s gangrene: A study of 72 cases. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2015, 9, E800–E804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doluoğlu, Ö.G.; Karagöz, M.A.; Kılınç, M.F.; Karakan, T.; Yücetürk, C.N.; Sarıcı, H.; Özgür, B.C.; Eroğlu, M. Overview of different scoring systems in Fournier’s Gangrene and assessment of prognostic factors. Turk. J. Urol. 2016, 42, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, S.U.; Kim, S.W.; Ahn, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Chung, H.; Hwang, E.C.; Yu, H.S.; Oh, K.J.; Kim, S.O.; Jung, S.I.; et al. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratios Are More Effective than the Fournier’s Gangrene Severity Index for Predicting Poor Prognosis in Fournier’s Gangrene. Surg. Infect. 2016, 17, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Üreyen, O.; Acar, A.; Gökçelli, U.; Atahan, M.K.; İlhan, E. Usefulness of FGSI and UFGSI scoring systems for predicting mortality in patients with Fournier’s gangrene: A multicenter study. Ulus. Travma. Acil. Cerrahi. Derg. 2017, 23, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Elsaket, A.E.; Maharajh, S.; Urry, R.J. The presentation, management and outcomes of Fournier’s gangrene at a tertiary urology referral centre in South Africa. S. Afr. Med. J. 2018, 108, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pehlivanlı, F.; Aydin, O. Factors Affecting Mortality in Fournier Gangrene: A Single Center Experience. Surg. Infect. 2019, 20, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenório, C.E.L.; Lima, S.V.C.; Albuquerque, A.V.; Cavalcanti, M.P.; Teles, F. Risk factors for mortality in Fournier’s gangrene in a general hospital: Use of simplified founier gangrene severe index score (SFGSI). Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetterauer, C.; Ebbing, J.; Halla, A.; Kuehl, R.; Erb, S.; Egli, A.; Schaefer, D.J.; Seifert, H.H. A contemporary case series of Fournier’s gangrene at a Swiss tertiary care center-can scoring systems accurately predict mortality and morbidity? World J. Emerg. Surg. 2018, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Rege, S.; Surpam, S.; Gothwal, K.; Narwade, A. Predicting Mortality in Fournier Gangrene and Validating the Fournier Gangrene Severity Index: Our Experience with 50 Patients in a Tertiary Care Center in India. Urol. Int. 2019, 102, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çitgez, S.; Demirdağ, Ç.; Özkaya, M.; Selçuk, S.; Erözenci, A. Fournier’s gangrene: Analysis of risk factors affecting mortality in a tertiary urology referral center. J. Urol. Surg. 2019, 6, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaali, C.; Salimoglu, S.; Emiroglu, M.; Budak, G.G.; Calik, B.; Aydin, C. Is it possible to estimate the mortality rate of Fournier Gangrene with new parameters? Kuwait Med. J. 2019, 52, 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Egin, S.; Kamali, S.; Hot, S.; Gökçek, B.; Yesiltas, M. Comparison of Mortality in Fournier’s Gangrene with the Two Scoring Systems. J. Coll. Physicians Surg. Pak. 2020, 30, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noegroho, B.S.; Siregar, S.; Mustafa, A.; Rivaldi, M.A. Validation of FGSI Scores in Predicting Fournier Gangrene in Tertiary Hospital. Res. Rep. Urol. 2021, 13, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usta, M.A.; Ulusahin, M.; Tayar, S.; Cekic, A.B.; Kazaz, I.O.; Guner, A.; Turkyilmaz, S. Scoring Systems for the Prediction of Mortality in Patient with Fournier’s Gangrene: An Analysis of 60 Patients. Indian J. Surg. 2021, 83, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çomçalı, B.; Ceylan, C.; Altun Özdemir, B.; Ağaçkıran, İ.; Akıncı, F. Comparison of the newly developed Fournier’s gangrene mortality prediction model with existing models. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022, 28, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tosun, Y.; Akıncı, O.; Küçük, H.F. Risk factors for mortality in Fournier’s gangrene of anorectal origin. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2022, 28, 1128–1133. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, F.T.; Öncel, H.F.; Salar, R. Predictive factors for mortality in intensive care patients with Fournier’s gangrene: Five years’ experience from a single center in Turkey. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eğin, S.; Kamalı, S.; Hot, S.; Gökçek, B.; Yeşiltaş, M.; Duman, M.G.; Alemdar, A. The importance of the scoring system in Fournier’s gangrene. Ulus. Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2023, 29, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eray, I.C.; Dalci, K.; Gumus, S.; Yalav, O.; Saritas, A.G.; Boz, A.; Rencuzogullari, A. The role of C-reactive protein ratio in predicting mortality in patients with Fournier gangrene. Ann. Coloproctol. 2023, 39, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, L.; Claps, F.; Rizzo, M.; Di Cosmo, G.; Traunero, F.; D’Andrea, E.; Garaffa, G.; Cai, T.; Zucchi, A.; Trombetta, C.; et al. Procalcitonin as prognostic factor in patients with Fournier’s gangrene. Urol. J. 2023, 90, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Gidda, H.; Murphy, N.; Alshanqeeti, S.; Singh, I.; Wasay, A.; Haseeb, M. An Unusual Bacterial Etiology of Fournier’s Gangrene in an Immunocompetent Patient. Cureus 2022, 14, e26616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Qushayri, A.E.; Khalaf, K.M.; Dahy, A.; Mahmoud, A.R.; Benmelouka, A.Y.; Ghozy, S.; Mahmoud, M.U.; Bin-Jumah, M.; Alkahtani, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M. Fournier’s gangrene mortality: A 17-year systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 92, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammia, R.S.; Tufano, A.; Proietti, F.; Gerolimetto, C.; DENunzio, C.; Franco, G.; Leonardo, C. Renal surgery for kidney cancer: Is preoperative proteinuria a predictor of functional and survival outcomes after surgery? A systematic review of the literature. Minerva Urol. Nephrol. 2022, 74, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirklbauer, M. Hemodialysis treatment in patients with severe electrolyte disorders: Management of hyperkalemia and hyponatremia. Hemodial. Int. 2020, 24, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Bates, D.W.; Kuperman, G.J.; Curhan, G.C. Relationship between hematocrit and renal function in men and women. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, M.D.; Krieger, J.N.; Rivara, F.P.; Klein, M.B.; Wessells, H. Fournier’s gangrene: Management and mortality predictors in a population based study. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yücel, B.; Ustun, B. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, platelet to lymphocyte ratio, mean platelet volume, red cell distribution width and plateletcrit in preeclampsia. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2017, 7, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L. Bias caused by sampling error in meta-analysis with small sample sizes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| FGSI | High | Normal | Low | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +4 | +3 | +2 | +1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | |
| Temp. °C | >41 | 39–40.9 | - | 38.5–38.9 | 36–38.4 | 34–35.9 | 32–33.9 | 30–31.9 | <39.9 |
| Heart rate | >180 | 140–179 | 110–139 | - | 70–109 | - | 55–69 | 40–54 | <39 |
| Respiratory rate | >50 | 35–49 | - | 25–34 | 12–24 | 10–11 | 6–9 | - | <5 |
| Serum sodium mmol/L | >180 | 160–179 | 155–159 | 150–154 | 130–149 | - | 120–129 | 111–119 | <110 |
| Serum potassium mmol/L | >7 | 6–6.9 | - | 5.5–5.9 | 3.5–5.4 | 3–3.4 | 2.5–2.9 | - | <2.5 |
| Serum creatinine mg/100 mL | >3.5 | 2–3.4 | 1.5–1.9 | - | 0.6–1.4 | - | <0.6 | - | - |
| Hematocrit (HT) | >60 | - | 50–59.9 | 46–49.9 | 30–45.9 | - | 20–29.9 | - | <20 |
| Leukocytes total/mm3 × 1000 | >40 | - | 20–39.9 | 15–19.9 | 3–14.9 | - | 1–2.9 | - | <1 |
| Serum bicarbonate mmol/L | >52 | 41–51.9 | - | 32–40.9 | 22–31.9 | - | 18–21.9 | 15–17.9 | <15 |
| UFGSI | High | Normal | Low | ||||||
| +4 | +3 | +2 | +1 | 0 | +1 | +2 | +3 | +4 | |
| Temp. °C | >41 | 39–40.9 | - | 38.5–38.9 | 36–38.4 | 34–35.9 | 32–33.9 | 30–31.9 | <39.9 |
| Heart rate | >180 | 140–179 | 110–139 | - | 70–109 | - | 55–69 | 40–54 | <39 |
| Respiratory rate | >50 | 35–49 | - | 25–34 | 12–24 | 10–11 | 6–9 | - | <5 |
| Serum sodium mmol/L | >180 | 160–179 | 155–159 | 150–154 | 130–149 | - | 120–129 | 111–119 | <110 |
| Serum potassium mmol/L | >7 | 6–6.9 | - | 5.5–5.9 | 3.5–5.4 | 3–3.4 | 2.5–2.9 | - | <2.5 |
| Serum creatinine mg/100 mL | >3.5 | 2–3.4 | 1.5–1.9 | - | 0.6–1.4 | - | <0.6 | - | - |
| Hematocrit (HT) | >60 | - | 50–59.9 | 46–49.9 | 30–45.9 | - | 20–29.9 | - | <20 |
| Leukocytes total/mm3 × 1000 | >40 | - | 20–39.9 | 15–19.9 | 3–14.9 | - | 1–2.9 | - | <1 |
| Serum bicarbonate mmol/L | >52 | 41–51.9 | - | 32–40.9 | 22–31.9 | - | 18–21.9 | 15–17.9 | <15 |
| Dissemination score |
| ||||||||
| Age score |
| ||||||||
| SFGSI | High | Normal | Low | ||||||
| Serum potassium mmol/L | >7 | 6–6.9 | - | 5.5–5.9 | 3.5–5.4 | 3–3.4 | 2.5–2.9 | - | <2.5 |
| Serum creatinine mg/100 mL | >3.5 | 2–3.4 | 1.5–1.9 | - | 0.6–1.4 | - | <0.6 | - | - |
| Hematocrit (HT) | >60 | - | 50–59.9 | 46–49.9 | 30–45.9 | - | 20–29.9 | - | <20 |
| Study, Year | Study Design | Single/Multi-Center | Sample, N | Gender, M/F | Mortality, % | Age, (Years) Mean ± SD/ Median (IQR) | Survivors’ Age, (Years) Mean ± SD/ Median (IQR) | Non-Survivors’ Age, (Years) Mean ± SD/ Median (IQR) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yeniyol et al., 2004 [11] | Retrospective | Single-center | 25 | 25/0 | 24.0% | 61.7 ± 13.4 | 58.9 ± 12.5 | 70.6 ± 13.4 |
| Tuncel et al., 2006 [12] | Retrospective | Single-center | 20 | 20/0 | 30.0% | N.R. | 60.0 ± 12.9 | 64.5 ± 6.5 |
| Cocoran et al., 2008 [13] | Retrospective | Single-center | 68 | 54/14 | 10.3% | 55.8 ± 15.2 | 59.3 ± 11.8 | 55.4 ± 15.6 |
| Kabay et al., 2008 [14] | Retrospective | Multi-center | 72 | 67/5 | 40.3% | 61 (24–87) | 61 (27–87) | 62 (42–87) |
| Unalp et al., 2008 [15] | Retrospective | Single-center | 68 | 59/9 | 10.3% | 54.7 ± 15.6 | 53.3 ± 15.8 | 66.7 ± 5.6 |
| Luján Marco et al., 2009 [16] | Retrospective | Single-center | 51 | 48/3 | 15.7% | 63 (17–85) | 60 (17–81) | 73.5 (50–85) |
| Ulug et al., 2009 [17] | Retrospective | Single-center | 20 | 20/7 | 18.5% | N.R. | 53.9 ± 21.5 | 57.2 ± 12.9 |
| Yilmazlar et al., 2010 [6] | Retrospective | Single-center | 80 | 57/23 | 21.2% | 57 (24–85) | 55 (24–85) | 62 (47–77) |
| Altarac et al., 2012 [18] | Retrospective | Single-center | 41 | 39/2 | 36.6% | 59 (51–69) | 58 (47–66) | 69 (45–78) |
| Aridogan et al., 2012 [19] | Retrospective | Single-center | 71 | 71/0 | 29.6% | 61.3 ± 12.3 | 61.2 ± 12.1 | 66.2 ± 12.4 |
| Roghmann et al., 2012 [20] | Retrospective | Single-center | 44 | 44/0 | 29.5% | 59 (48–65) | 52 (43–64) | 62 (52–71) |
| Verma et al., 2012 [21] | Retrospective | Multi-center | 95 | 81/14 | 27.4% | 46.5 ± 15.6 | N.R. | N.R. |
| Wang et al., 2012 [22] | Retrospective | Single-center | 24 | 20/4 | 20.8% | N.R. | 48.9 ± 12.9 | 46.6 ± 14.1 |
| Sarvestani et al., 2013 [23] | Retrospective | Single-center | 28 | 28/0 | 35.7% | 44.6 ± 8.5 | 39.4 ± 8.9 | 54.1 ± 7.8 |
| Vyas et al., 2013 [24] | Prospective | Single-center | 30 | 30/0 | 20.0% | N.R. | 35.7 ± 9.4 | 55.0 ± 9.5 |
| Lin et al., 2014 [7] | Retrospective | Single-center | 65 | 85/0 | 18.8% | N.R. | 57.8 ± 14.4 | 62.3 ± 13.0 |
| Oymaci et al., 2014 [25] | Retrospective | Single-center | 16 | 10/6 | 18.7% | 61.2 ± 12.3 | 61.7± 12.7 | 59.0 ± 12.1 |
| Tuncel et al., 2014 [26] | Retrospective | Single-center | 50 | 50/0 | 14.0% | 61 (35–79) | 58 (35–79) | 68.5 (58–77) |
| Erol et al., 2015 [27] | Retrospective | Multi-center | 99 | 99/0 | 17.2% | N.R. | 60.9 ± 13.1 | 68.1 ± 12.6 |
| Oguz et al., 2015 [28] | Retrospective | Single-center | 43 | 34/9 | 13.9% | 53.3 ± 16.1 | 50.1 ± 14.1 | 63.0 ± 18.6 |
| Trachouli et al., 2015 [29] | Retrospective | Single-center | 72 | 64/8 | 16.7% | 51 (23–75) | N.R. | N.R. |
| Doluoğlu et al., 2016 [30] | Retrospective | Single-center | 39 | N.R. | 20.5% | N.R. | 65 (43–83) | 52 (30–90) |
| Yim et al., 2016 [31] | Retrospective | Single-center | 62 | 61/1 | 41.9% | N.R. | 57.1 ± 14.4 | 56.2 ± 13.0 |
| Üreyen et al., 2017 [32] | Retrospective | Multi-center | 29 | 18/11 | 20.7% | 51.5 ± 13.4 | 51.9 ± 13.5 | 50.0 ± 13.9 |
| Elsaket et al., 2018 [33] | Retrospective | Single-center | 44 | 43/1 | 11.4% | 51 (28–82) | N.R. | N.R. |
| Pehlivanli et al., 2018 [34] | Retrospective | Single-center | 23 | 19/4 | 21.7% | 65.9 ± 16.3 | 63.0 ± 16.3 | 78.0 ± 10.8 |
| Tenório et al., 2018 [35] | Retrospective | Single-center | 124 | N.R. | 25.8% | 50.8 ± 19.5 | 48.1 ± 18.6 | 58.5 ± 20.1 |
| Watterauer et al., 2018 [36] | Retrospective | Single-center | 20 | 20/0 | 15.0% | 66 (46–73) | 64 (43–72) | 84 (67–94) |
| Arora et al., 2019 [37] | Prospective | Single-center | 50 | 50/0 | 24.0% | 53 ± 16.8 | 47.9 ± 14.4 | 69.9 ± 11.1 |
| Citigez et al., 2019 [38] | Retrospective | Single-center | 48 | 48/0 | 14.6% | 53.9 ± 12.6 | 50.5 ± 9.8 | 73.4 ± 8.6 |
| Karaali et al., 2019 [39] | Retrospective | Single-center | 89 | 58/31 | 22.5% | 60.2 ± 12.7 | 53.9 ± 13.6 | 67.6 ± 11.5 |
| Egin et al., 2020 [40] | Retrospective | Single-center | 30 | 16/14 | 26.7% | 58.7 ± 11.5 | 55.1 ± 9.17 | 68.5 ± 12.1 |
| Noegroho et al., 2021 [41] | Retrospective | Single-center | 83 | N.R. | 27.7% | N.R. | 45.9 ± 11.8 | 55.9 ± 13.6 |
| Usta et al., 2021 [42] | Retrospective | Single-center | 60 | 45/15 | 16.7% | 61.4 ± 16.0 | 59.9 ± 16.1 | 68.5 ± 14.1 |
| Çomçalı et al., 2022 [43] | Retrospective | Single-center | 144 | 101/43 | 7.6% | 55 (19–80) | 61 (38–80) | 53 (19–78) |
| Tosun et al., 2022 [44] | Retrospective | Single-center | 150 | 123/27 | 15.3% | 57.9 ± 13.2 | 56.0 ± 12.8 | 68.5 ± 10.4 |
| Bozkurt et al., 2023 [45] | Retrospective | Single-center | 28 | 28/0 | 39.3% | 62.0 ± 18.7 | 54.5 ± 17.3 | 73.4 ±15.2 |
| Egin et al., 2023 [46] | Retrospective | Single-center | 73 | 42/31 | 23.3% | 57.3 ± 13.4 | 69.2 ± 13.3 | 53.7 ± 11.2 |
| Eray et al., 2023 [47] | Retrospective | Single-center | 52 | 30/22 | 26.9% | 54.3 ± 13.4 | 52.9 ± 13.6 | 57.9 ± 12.8 |
| Ongaro et al., 2023 [48] | Retrospective | Single-center | 20 | 20/0 | 35.0% | 58 (51–88) | N.R. | N.R. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tufano, A.; Dipinto, P.; Passaro, F.; Anceschi, U.; Franco, G.; Flammia, R.S.; Proietti, F.; Antonelli, L.; Di Pierro, G.B.; Prata, F.; et al. The Value of Fournier’s Gangrene Scoring Systems on Admission to Predict Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091283
Tufano A, Dipinto P, Passaro F, Anceschi U, Franco G, Flammia RS, Proietti F, Antonelli L, Di Pierro GB, Prata F, et al. The Value of Fournier’s Gangrene Scoring Systems on Admission to Predict Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(9):1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091283
Chicago/Turabian StyleTufano, Antonio, Piervito Dipinto, Francesco Passaro, Umberto Anceschi, Giorgio Franco, Rocco Simone Flammia, Flavia Proietti, Luca Antonelli, Giovanni Battista Di Pierro, Francesco Prata, and et al. 2023. "The Value of Fournier’s Gangrene Scoring Systems on Admission to Predict Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 9: 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091283
APA StyleTufano, A., Dipinto, P., Passaro, F., Anceschi, U., Franco, G., Flammia, R. S., Proietti, F., Antonelli, L., Di Pierro, G. B., Prata, F., Rullo, R., Perdonà, S., & Leonardo, C. (2023). The Value of Fournier’s Gangrene Scoring Systems on Admission to Predict Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(9), 1283. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091283







