The Power of Customized Clear Aligners in Closing Molar Edentulous Spaces: Clinical and Medico-Legal Considerations in a Scoping Review and Case Report
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Scoping Review
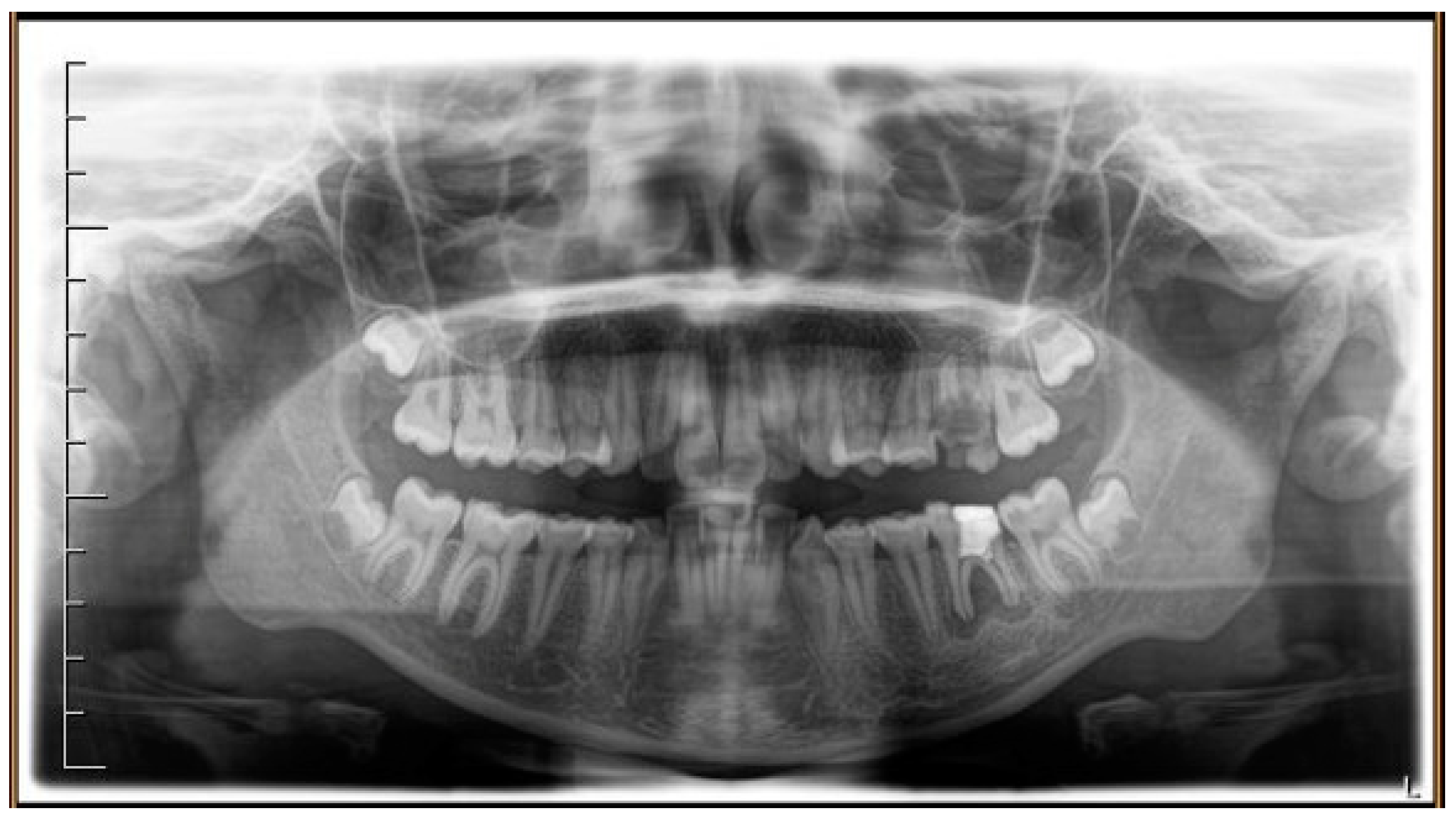
2.2. Case Report
3. Results
Scoping Review
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhan, B.; Huang, X.; Huo, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Z. Effect of clear aligners on oral health-related quality of life: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yan, X.; Zhao, R.; Shan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jian, F.; Long, H.; Lai, W. Comparison of pain perception, anxiety, and impacts on oral health-related quality of life between patients receiving clear aligners and fixed appliances during the initial stage of orthodontic treatment. Eur. J. Orthod. 2021, 43, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putrino, A.; Marinelli, E.; Raso, M.; Calace, V.; Zaami, S. Clear Aligners and Smart Eye Tracking Technology as a New Communication Strategy between Ethical and Legal Issues. Life 2023, 13, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, M.; Arqub, S.A. Biomechanics of clear aligners: Hidden truths & first principles. J. World. Fed. Orthod. 2022, 11, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M. A comparison of treatment effectiveness between clear aligner and fixed appliance therapies. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putrino, A.; Barbato, E.; Galluccio, G. Clear Aligners: Between Evolution and Efficiency-A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Kaur, H.; Fagundes, N.C.F.; Romanyk, D.; Major, P.; Flores Mir, C. Effectiveness of clear aligner therapy for orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galan-Lopez, L.; Barcia-Gonzalez, J.; Plasencia, E. A systematic review of the accuracy and efficiency of dental movements with Invisalign®. Korean J. Orthod. 2019, 49, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auladell, A.; De La Iglesia, F.; Quevedo, O.; Walter, A.; Puigdollers, A. The efficiency of molar distalization using clear aligners and mini-implants: Two clinical cases. Int. Orthod. 2022, 20, 100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brugnami, F.; Meuli, S.; Caiazzo, A.; Marrocco, S.; Scopelliti, D. Three-dimensional digital planning of class III decompensation with clear aligners: Hard and soft tissue augmentation with concomitant corticotomy to stretch the limits of safe orthodontic treatment. J. Oral Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2021, 11, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Pepe, F.; Carlucci, A.; Cremonini, F. A hybrid approach to clear aligner therapy in lower-incisor extraction cases. J. Clin. Orthod. 2022, 55, 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Palone, M.; Brucculeri, L.; Cremonini, F.; Albertini, P.; Lombardo, L. Treatment of severe Class II skeletal malocclusion in a hyperdivergent adult patient via hybrid clear aligner approach: A case report of successful camouflage therapy. J. Orthod. 2022, 16, 14653125221138588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nadawi, M.; Kravitz, N.D.; Hansa, I.; Makki, L.; Ferguson, D.J.; Vaid, N.R. Effect of clear aligner wear protocol on the efficacy of tooth movement. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakdach, W.M.M.; Haiba, M.; Hadad, R. Changes in surface morphology, chemical and mechanical properties of clear aligners during intraoral usage: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. Orthod. 2022, 20, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barreda, G.J.; Dzierewianko, E.A.; Muñoz, K.A.; Piccoli, G.I. Surface wear of resin composites used for Invisalign® attachments. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2017, 30, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhan, Q.; Zhou, J.; Kuang, Q.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Y.; Li, X.; Lai, W.; Long, H. Effectiveness of an anterior mini-screw in achieving incisor intrusion and palatal root torque for anterior retraction with clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, M.; Rossini, G.; Rombolà, A. G-Block: Posterior anchorage device tads-supported after molar distalization with aligners: An adult case report. Int. Orthod. 2022, 20, 100687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, S.; Darvizeh, A.; Zema, S.; Gatto, R.; Nota, A. Management of a Facilitated Aesthetic Orthodontic Treatment with Clear Aligners and Minimally Invasive Corticotomy. Dent. J. 2020, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannequin, R.; Ouadi, E.; Racy, E.; Moreau, N. Clinical follow-up of corticotomy-accelerated Invisalign orthodontic treatment with Dental Monitoring. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial. Orthop. 2020, 158, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, A.; Figueiredo, D.S.F.; Jeremiah, H.G.; Oliveira, D.D.; Freitas, L.R.P.; Chahoud, M.; Soares, R.V.; Cobourne, M.T. The effect of social media on patient acceptance of temporary anchorage devices. Angle Orthod. 2021, 91, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapetanović, A.; Noverraz, R.R.M.; Listl, S.; Bergé, S.J.; Xi, T.; Schols, J.G.J.H. What is the Oral Health-related Quality of Life following Miniscrew-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion (MARPE)? A prospective clinical cohort study. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Attar, A.M.; Al-Shaham, S.; Abid, M. Perception of Iraqi Orthodontists and Patients toward Accelerated Orthodontics. Int. J. Dent. 2021, 2021, 5512455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haliloğlu Özkan, T.; Dursun, D. The Perception of Adults and Adolescents of Undergoing and Paying for Tooth Movement Acceleration Procedures in Turkey. Turk. J. Orthod. 2022, 35, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroflorio, T.; Sedran, A.; Parrini, S.; Garino, F.; Reverdito, M.; Capuozzo, R.; Mutinelli, S.; Grybauskas, S.; Vaitiekūnas, M.; Deregibus, A. Predictability of orthodontic tooth movement with aligners: Effect of treatment design. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, E.D.; de Araújo, N.S. Brazilian orthodontists and the legal issues involving their professional activity: A legal and behavioral proposal. Dental Press J. Orthod. 2013, 18, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouradian, W.E.; Omnell, M.L.; Williams, B. Ethics for orthodontists. Angle Orthod. 1999, 69, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corte-Real, A.; Caetano, C.; Alves, S.; Pereira, A.D.; Rocha, S.; Nuno Vieira, D. Patient Safety in Dental Practice: Lessons to Learn About the Risks and Limits of Professional Liability. Int. Dent. J. 2021, 71, 378–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Kochhar, A.S.; Gupta, H.; Singh, G.; Kubavat, A. Appropriate orthodontic appliances during the COVID-19 pandemic: A scoping review. J. Oral. Biol. Craniofac. Res. 2020, 10, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marya, A.; Venugopal, A.; Vaid, N.; Alam, M.K.; Karobari, M.I. Essential Attributes of Clear Aligner Therapy in terms of Appliance Configuration, Hygiene, and Pain Levels during the Pandemic: A Brief Review. Pain Res. Manag. 2020, 2020, 6677929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putrino, A.; Caputo, M.; Giovannoni, D.; Barbato, E.; Galluccio, G. Impact of the sars-cov2 pandemic on orthodontic therapies: An italian experience of teleorthodontics. Pesqui. Bras. Odontopediatria Clin. Integr. 2020, 20, e0100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliliwi, M.; ElShebiny, T.; de Menezes, L.M.; Stefanovic, N.; Palomo, J.M. Comparing virtual setup software programs for clear aligner treatment. J. World Fed. Orthod. 2023, 12, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adel, S.M.; Vaid, N.R.; El-Harouni, N.; Kassem, H.; Zaher, A.R. TIP, TORQUE & ROTATIONS: How accurately do digital superimposition software packages quantify tooth movement? Prog. Orthod. 2022, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, H.; Heger, S.M.; Stocker, T.; Baumert, U.; Wichelhaus, A.; Hoffmann, L. Accuracy of 3D Tooth Movements in the Fabrication of Manual Setup Models for Aligner Therapy. Materials 2022, 15, 3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, H.; Subramani, K.; Stevens, R.; Sinha, P. An overview of orthodontic malpractice liability based on a survey and case assessment review. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2022, 14, e694–e704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putrino, A.; Abed, M.R.; Lilli, C. Clear aligners with differentiated thickness and without attachments—A case report. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2022, 14, e514–e519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, A.; Mousoulea, S.; Gkantidis, N.; Kloukos, D. Clinical effectiveness of Invisalign® orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, J.J.L.; Tai, S.K.; Huang, G. Torque recovery of the maxillary incisors with a modified double J retractor in a Class II division 2 case treated with clear aligners. Angle Orthod. 2022, 93, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.J.; Celenza, F.; Sparaga, J.; Papadopoulos, M.A.; Ojima, K.; Lin, J.C. Creative adjuncts for clear aligners, part 3: Extraction and interdisciplinary treatment. J. Clin. Orthod. 2015, 49, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Bollen, A.M.; Huang, G.; King, G.; Hujoe, P.; Ma, T. Activation time and material stiffness of sequential removable orthodontic appliances. Part 1: Ability to complete treatment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2003, 124, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravera, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Garino, F.; Daher, S.; Cugliari, G.; Deregibus, A. Maxillary molar distalization with aligners in adult patients: A multicenter retrospective study. Prog. Orthod. 2016, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corte-Real, A.; Caetano, C.; Dias Pereira, A.; Rocha, S.; Alves, S.; Nuno-Vieira, D. Risk and limits in dental practice: A Portuguese approach to medical-legal evaluation and professional liability. J. Forensic Odontostomatol. 2020, 38, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perrenoud, B.; Velonaki, V.S.; Bodenmann, P.; Ramelet, A.S. The effectiveness of health literacy interventions on the informed consent process of health care users: A systematic review protocol. JBI Database Syst. Rev. Implement Rep. 2015, 13, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelkarim, A.; Jerrold, L. Litigation and Legislation. Risk management strategies in orthodontics. Part 1: Clinical considerations. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 148, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conduru Fernandes Moreira, N.; Keenan, L.; Cummings, G.; Flores-Mir, C. Informed consent challenges and strategies: A qualitative study of the orthodontists’ perspective. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2022, 25, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanari Vergallo, G.; Zaami, S. Guidelines and best practices: Remarks on the Gelli-Bianco law. Clin. Ter. 2018, 169, e82–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolford, L.M. Comprehensive Post Orthognathic Surgery Orthodontics: Complications, Misconceptions, and Management. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 135–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Population/Problem | Orthodontic Patients |
|---|---|
| Concept | Clear aligners efficiently close edentulous spaces |
| Context | Congenitally missing or lost for diseases upper and/or lower molars |
| Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|
| Randomized and non-randomized clinical, observational studies | In vitro and in vivo (animal) studies, finite element studies, case reports/case series, reviews, commentaries, letters to editors |
| English language | Other languages |
| Abstract and full-text reading available | No abstracts and/or full-text reading |
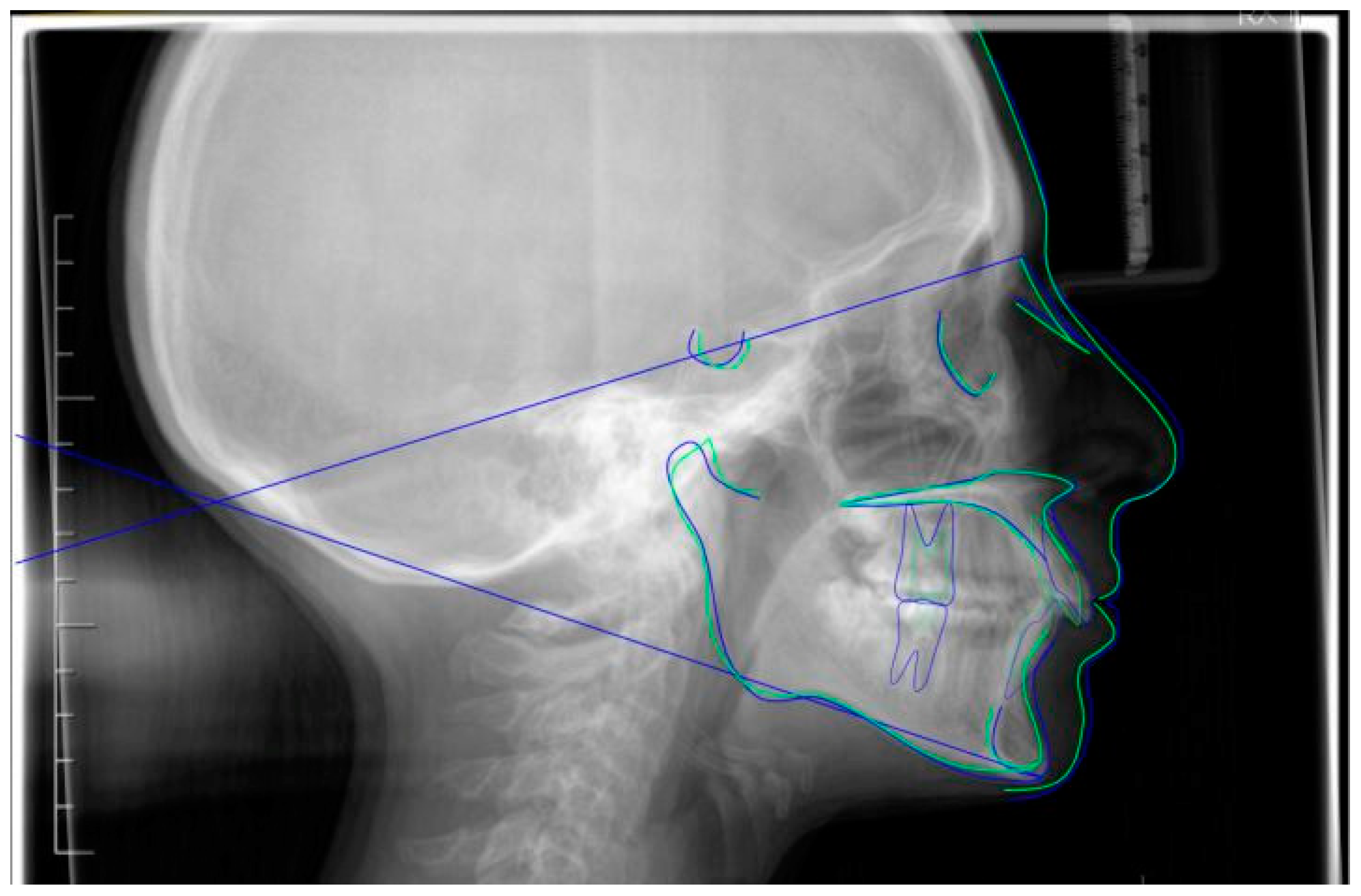
| Cephalometric Landmarks | Pre-Treatment | Post-Treatment | Normal Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| SNA | 80° | 78.5° | 82 ± 2° |
| SNB | 74.6° | 73.8° | 80 ± 2° |
| ANB | 5.4° | 4.8° | 2 ± 2° |
| OP-SNP | 21.1° | 21.6° | 14 ± 2° |
| MP(GoGn)-SNP | 35.4° | 34° | 32 ± 3° |
| +1- NA | 14.1° | 17.4° | 22 ± 2° |
| +1: NA (mm) | 4.1 mm | 4.8 mm | 4 ± 2 mm |
| −1- NB | 28.4° | 25.4° | 25 ± 2° |
| −1: NB (mm) | 4.7 mm | 5 mm | 4 ± 1 mm |
| Interincisal Angle | 132.1° | 132.4° | 131 ± 8° |
| FMA | 26.2° | 27.5° | 22 ± 5° |
| FMIA | 57.7° | 57.7° | 68 ± 7° |
| IMPA | 96.1° | 94.8° | 90 ± 5° |
| SNPog | 76.2° | 75.6° | 81 ± 3° |
| Saddle Angle (N-S-Ar) | 125.1° | 122.6° | 123 ± 5° |
| Articular Angle (S-Ar-Go) | 142.5° | 145.9° | 143 ± 6° |
| Gonial Angle (Ar-Go-Me) | 127.8° | 125.5° | 130 ± 7° |
| Upper Gonial Angle | 53.3° | 53.4° | 52°–55° |
| Lower Gonial Angle | 74.4° | 72.1° | 70°–75° |
| Bjork’s sum | 395.4° | 394° | 396 ± 6° |
| Anterior Cranial Base (N-S) | 59.9 mm | 63 mm | 71 ± 3 mm |
| Posterior Cranial Base (S-Ar) | 29.2 mm | 32.2 mm | 32 ± 3 mm |
| Ramus Height (Ar-Go) | 37.1 mm | 35.1 mm | 44 ± 5 mm |
| Mandibular Body (Go-Gn) | 61.1 mm | 64.6 mm | 71 ± 5 mm |
| Posterior Face Height (S-Go) | 62.8 mm | 64.4 mm | 70–85 mm |
| Anterior Face Height (N-Me) | 100.2 mm | 103 mm | 105–120 mm |
| Facial Height Index | 61.5% | 61.5% | Clock < 65; Anti-clock > 65 |
| Upper Lip | 0 mm | 0 mm | 0 mm |
| Lower Lip | 2.4 mm | 2 mm | 0 mm |
| Overjet | 6 mm | 3 mm | 2.5 ± 2.5 mm |
| Overbite | 7 mm | 3 mm | 2.5 ± 2.5 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Putrino, A.; Marinelli, E.; Zaami, S. The Power of Customized Clear Aligners in Closing Molar Edentulous Spaces: Clinical and Medico-Legal Considerations in a Scoping Review and Case Report. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091389
Putrino A, Marinelli E, Zaami S. The Power of Customized Clear Aligners in Closing Molar Edentulous Spaces: Clinical and Medico-Legal Considerations in a Scoping Review and Case Report. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2023; 13(9):1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091389
Chicago/Turabian StylePutrino, Alessandra, Enrico Marinelli, and Simona Zaami. 2023. "The Power of Customized Clear Aligners in Closing Molar Edentulous Spaces: Clinical and Medico-Legal Considerations in a Scoping Review and Case Report" Journal of Personalized Medicine 13, no. 9: 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091389
APA StylePutrino, A., Marinelli, E., & Zaami, S. (2023). The Power of Customized Clear Aligners in Closing Molar Edentulous Spaces: Clinical and Medico-Legal Considerations in a Scoping Review and Case Report. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 13(9), 1389. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm13091389









