Pathology Laboratory Archives: Conservation Quality of Nucleic Acids and Proteins for NSCLC Molecular Testing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. FFPE Blocks
| Annual Group Progressive Number # | Number of Cases | Year of Storage Initiation | Storage Time (Years) |
|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 15 | 2006–2012 | >10 |
| #2 | 15 | 2015–2017 | 6–8 |
| #3 | 15 | 2021–2022 | <3 |
2.2. Nucleic Acids Concentration and Fragmentation Testing
2.3. Protein Antigens Analysis: IHC and MALDI-MSI Approaches
3. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
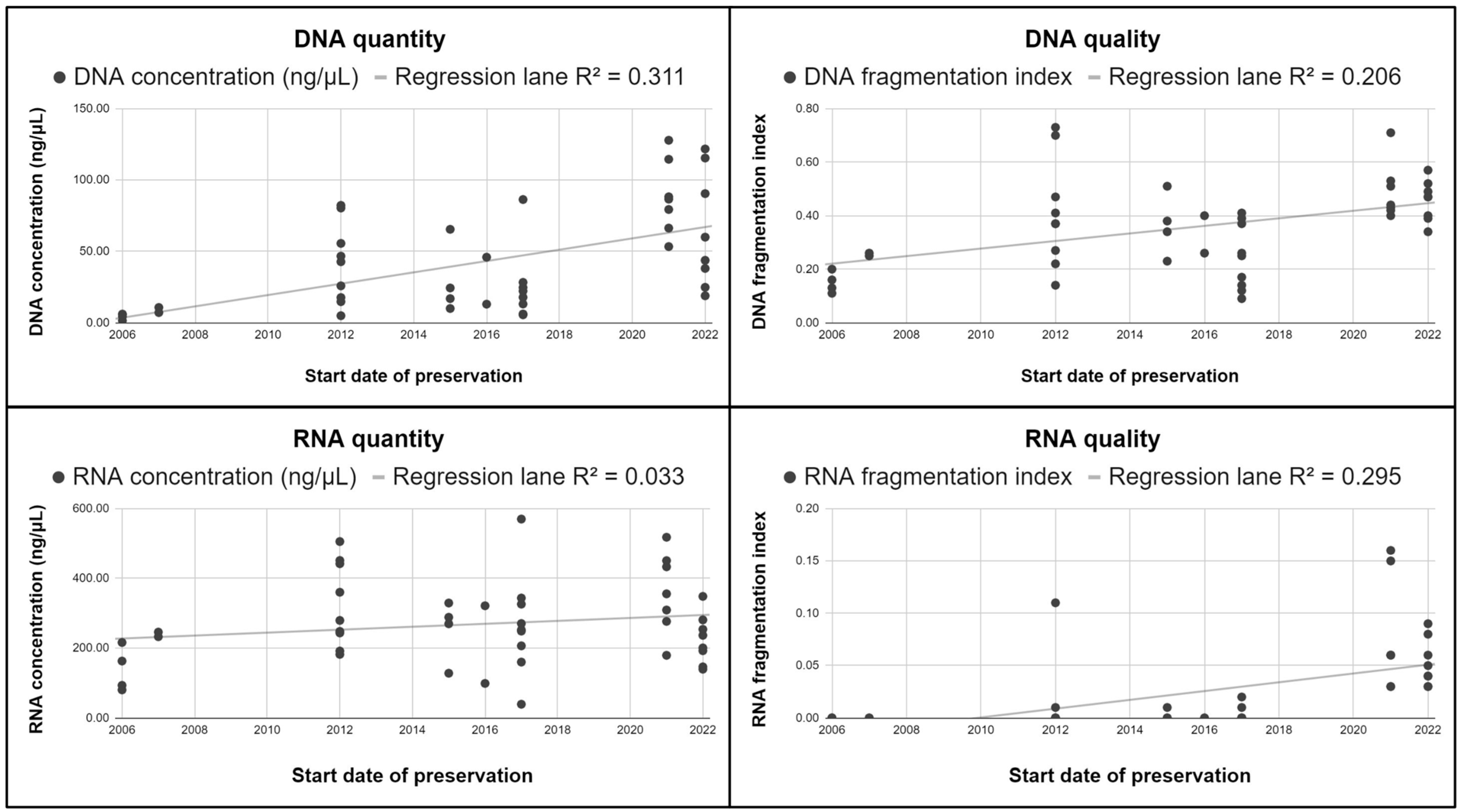
4.1. Nucleic Acids Raw Data Results
4.2. Annual Groups Evaluation
4.3. Nucleic Acids Results According to Molecular Adequacy Criteria
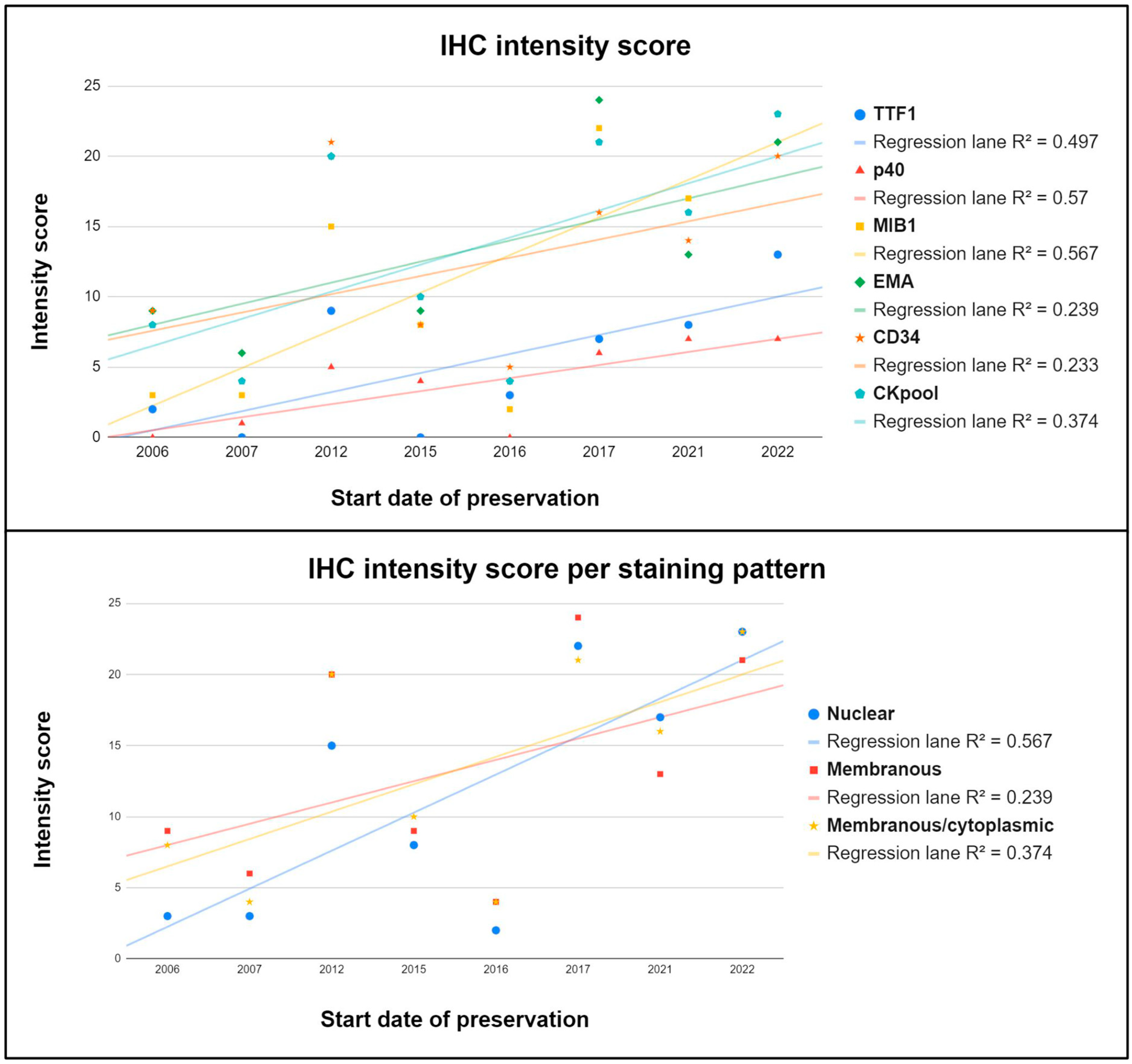
4.4. IHC Results
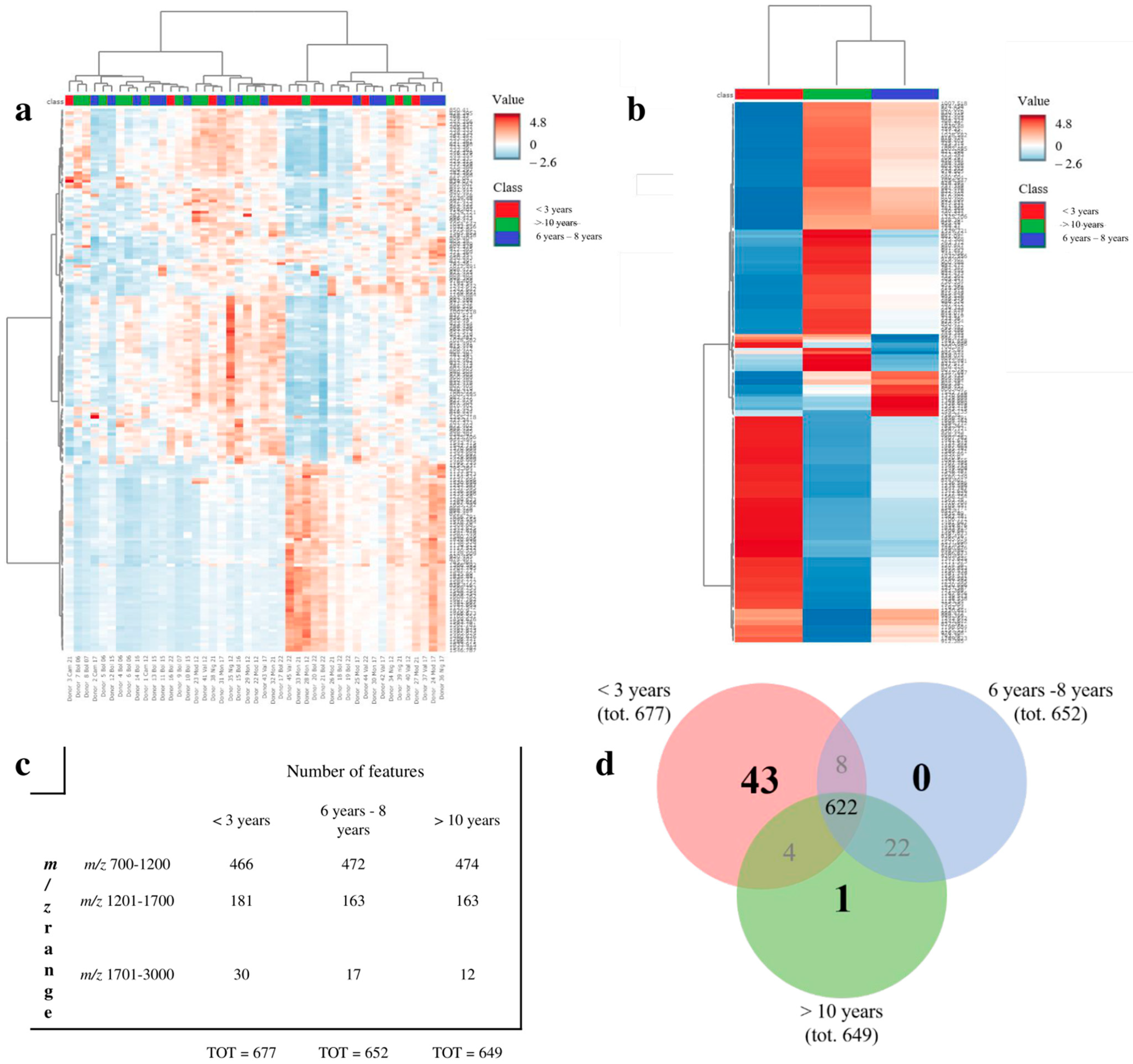
4.5. MALDI-MSI Proteomic Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eccher, A.; Dei Tos, A.P.; Scarpa, A.; L’Imperio, V.; Munari, E.; Troncone, G.; Naccarato, A.G.; Seminati, D.; Pagni, F. Cost Analysis of Archives in the Pathology Laboratories: From Safety to Management. J. Clin. Pathol. 2023, 76, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malapelle, U.; Parente, P.; Pepe, F.; De Luca, C.; Cerino, P.; Covelli, C.; Balestrieri, M.; Russo, G.; Bonfitto, A.; Pisapia, P.; et al. Impact of Pre-Analytical Factors on MSI Test Accuracy in Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma: A Multi-Assay Concordance Study. Cells 2020, 9, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaratone, L.; De Palma, G.; Bonizzi, G.; Sapino, A.; Botti, G.; Berrino, E.; Mannelli, C.; Arcella, P.; Di Martino, S.; Steffan, A.; et al. Basic Principles of Biobanking: From Biological Samples to Precision Medicine for Patients. Virchows Arch. 2021, 479, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arreaza, G.; Qiu, P.; Pang, L.; Albright, A.; Hong, L.Z.; Marton, M.J.; Levitan, D. Pre-Analytical Considerations for Successful Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): Challenges and Opportunities for Formalin-Fixed and Paraffin-Embedded Tumor Tissue (FFPE) Samples. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, S.E.; Han, G.; Mani, N.; Beruti, S.; Nerenberg, M.; Rimm, D.L. Loss of Antigenicity with Tissue Age in Breast Cancer. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groelz, D.; Viertler, C.; Pabst, D.; Dettmann, N.; Zatloukal, K. Impact of Storage Conditions on the Quality of Nucleic Acids in Paraffin Embedded Tissues. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkat, T.J.; Patel, M.S.; McGarvey, D.; LiVolsi, V.A.; Baloch, Z.W. Archived Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Blocks: A Valuable Underexploited Resource for Extraction of DNA, RNA, and Protein. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2013, 11, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Chung, J.-Y.; Ylaya, K.; Williams, R.L.; Guerrero, N.; Nakatsuka, N.; Badie, C.; Hewitt, S.M. Factors Influencing the Degradation of Archival Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Sections. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- della Salute, M. Linee Guida Tracciabilità, Raccolta, Trasporto, Conservazione e Archiviazione di Cellule e Tessuti per Indagini Diagnostiche di Anatomia Patologica. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/portale/documentazione/p6_2_2_1.jsp?lingua=italiano&id=2369 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Andreasson, A.; Kiss, N.B.; Juhlin, C.C.; Höög, A. Long-Term Storage of Endocrine Tissues at −80 °C Does Not Adversely Affect RNA Quality or Overall Histomorphology. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2013, 11, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuovo, A.J.; Garofalo, M.; Mikhail, A.; Nicol, A.F.; Vianna-Andrade, C.; Nuovo, G.J. The Effect of Aging of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissues on the in Situ Hybridization and Immunohistochemistry Signals in Cervical Lesions. Diagn. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 22, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrick, D.M.; Mehaffey, M.G.; Sachs, M.C.; Altekruse, S.; Camalier, C.; Chuaqui, R.; Cozen, W.; Das, B.; Hernandez, B.Y.; Lih, C.-J.; et al. Robustness of Next Generation Sequencing on Older Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Webster, J.D.; DuSold, D.; Miller, M.A. Immunohistochemical Evaluation of the Effects of Paraffin Section Storage on Biomarker Stability. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillo, F.; Pigozzi, S.; Ceriolo, P.; Calamaro, P.; Fiocca, R.; Mastracci, L. Factors Affecting Immunoreactivity in Long-Term Storage of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Tissue Sections. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2015, 144, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahashi, M.; Shimada, Y.; Ichikawa, H.; Nakagawa, S.; Sato, N.; Kaneko, K.; Homma, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Kodama, K.; Lyle, S.; et al. Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Sample Conditions for Deep next Generation Sequencing. J. Surg. Res. 2017, 220, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieson, W.; Thomas, G. Using FFPE Tissue in Genomic Analyses: Advantages, Disadvantages and the Role of Biospecimen Science. Curr. Pathobiol. Rep. 2019, 7, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwata, T.; Wakabayashi, M.; Hatanaka, Y.; Morii, E.; Oda, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Noguchi, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Nakajima, T.; Sekine, S.; et al. Impact of DNA Integrity on the Success Rate of Tissue-Based next-Generation Sequencing: Lessons from Nationwide Cancer Genome Screening Project SCRUM-Japan GI-SCREEN. Pathol. Int. 2020, 70, 932–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- della Salute, M. Proposta di Regolamentazione per L’appropriatezza dell’utilizzo dei Test Multigenici NGS Predittivi e Prognostici Nella Pratica Clinica. Available online: https://www.salute.gov.it/portale/documentazione/p6_2_2_1.jsp?lingua=italiano&id=3358testmultigenici (accessed on 18 September 2023).
- WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board Thoracic Tumours; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2021; ISBN 9789283245063.
- Myriapod NGS: Local Analysis of Sequencing Data Using Dedicated Software. Available online: https://www.diatechpharmacogenetics.com/en/myriapod-ngs-line-dry/ (accessed on 18 December 2023).
- Chougule, A.; Jagtap, V.; Nikam, A.; Kale, S.; Nambiar, K.; Bagayatkar, P.; Chandrani, P.; Kaushal, R.; Noronha, V.; Patil, V.; et al. Comprehensive Development and Implementation of Good Laboratory Practice for NGS Based Targeted Panel on Solid Tumor FFPE Tissues in Diagnostics. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, I.; L’Imperio, V.; Principi, L.; Bellevicine, C.; Fusco, N.; Maffini, F.; Venetis, K.; Ivanova, M.; Seminati, D.; Casati, G.; et al. Spatially Resolved Molecular Approaches for the Characterisation of Non-Invasive Follicular Tumours with Papillary-like Features (NIFTPs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalystR: An R Package for Flexible and Reproducible Analysis of Metabolomics Data. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 4313–4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohalm, M.; Hassman, M.; Kosata, B.; Kodícek, M. mMass Data Miner: An Open Source Alternative for Mass Spectrometric Data Analysis. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 22, 905–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldron, L.; Ogino, S.; Hoshida, Y.; Shima, K.; McCart Reed, A.E.; Simpson, P.T.; Baba, Y.; Nosho, K.; Segata, N.; Vargas, A.C.; et al. Expression Profiling of Archival Tumors for Long-Term Health Studies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6136–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blow, N. Tissue Preparation: Tissue Issues. Nature 2007, 448, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, F.; Bruzzone, M.; Pigozzi, S.; Prosapio, S.; Migliora, P.; Fiocca, R.; Mastracci, L. Immunohistochemistry on Old Archival Paraffin Blocks: Is There an Expiry Date? J. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 70, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, R.A.; Cairns, D.A.; Zougman, A.; Harnden, P.; Selby, P.J.; Banks, R.E. Proteomic Analysis of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Renal Tissue Samples by Label-Free MS: Assessment of Overall Technical Variability and the Impact of Block Age. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2013, 7, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, A.; Bitzios, A.; Kassa, E.; Shevchenko, G.; Falk, A.; Malmström, P.-U.; Dragomir, A.; Segersten, U.; Lind, S.B. Proteomic Comparison between Different Tissue Preservation Methods for Identification of Promising Biomarkers of Urothelial Bladder Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
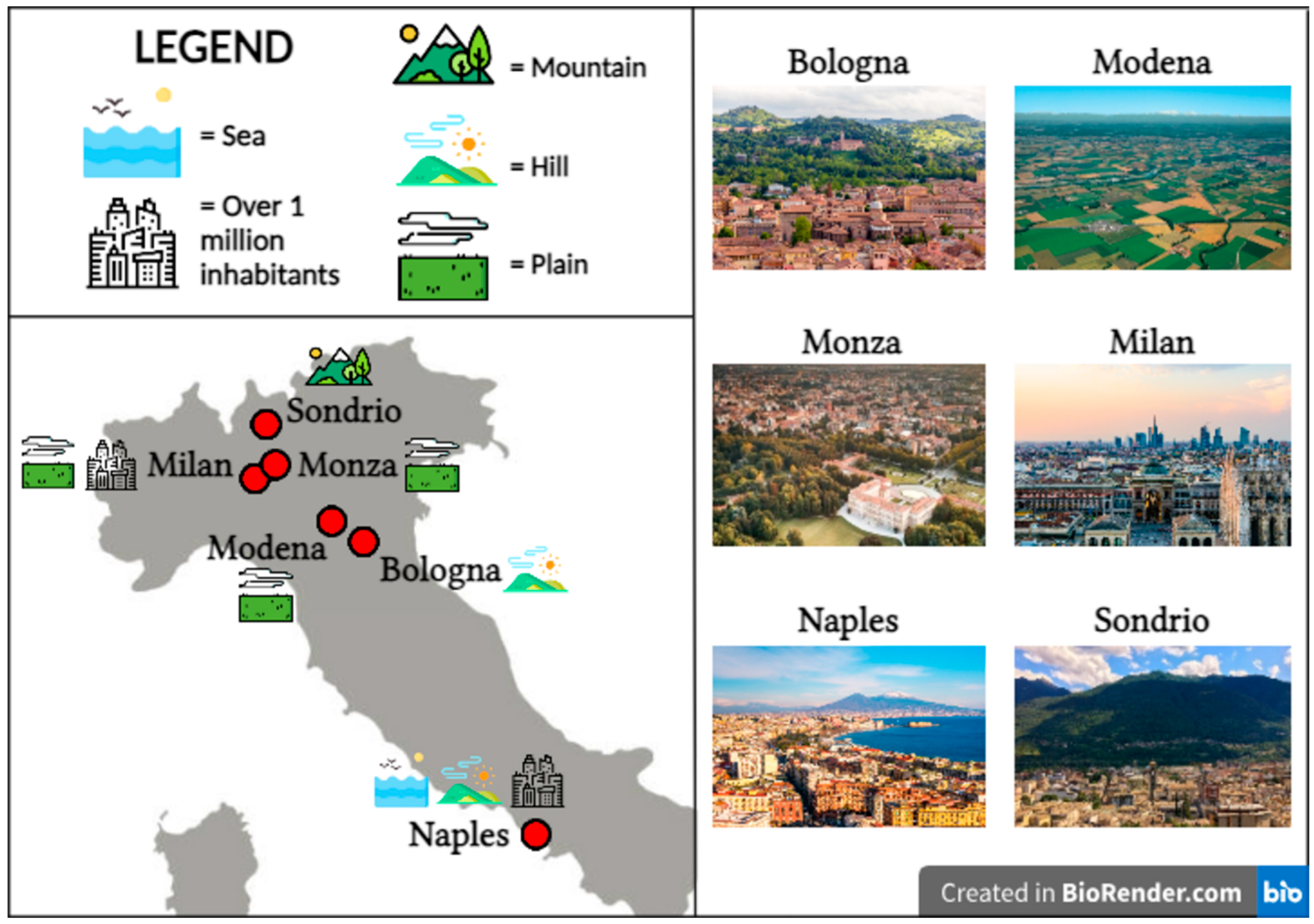
| Center Progressive Number # | Center | Geographic Coordinates | Altitude (m a.s.l.) | Range of Start Year of Storage | N° of FFPE Blocks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | Bologna | 44°29′38″ N 11°20′34″ E | 54 | 2006–2022 | 18 |
| #2 | Milan | 45°28′01″ N 9°11′24″ E | 120 | 2012–2021 | 6 |
| #3 | Modena | 44°38′52″ N 10°55′31″ E | 34 | 2012–2021 | 6 |
| #4 | Monza | 45°35′01″ N 9°16′25″ E | 162 | 2012–2021 | 6 |
| #5 | Naples | 40°51’46″80 N 14°14′47″ E | 17 | 2012–2021 | 3 |
| #6 | Sondrio | 46°10′06″ N9°52′16″ E | 360 | 2012–2022 | 6 |
| DNA Fragmentation Index | RNA Fragmentation Index | Nucleic Acid Fragmentation Level |
|---|---|---|
| >0.5 | >0.7 | Low |
| 0.3–0.5 | 0.05–0.7 | Medium |
| <0.3 | <0.05 | High: suboptimal for molecular analysis |
| Staining Intensity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Absent | Barely Perceptible/Weak | Moderate | Strong | |
| IHC intensity score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Average | Median | Minimum | Maximum | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleic Acid | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA |
| Concentration | 42.68 | 269.16 | 25.83 | 252.41 | 1.46 | 39.27 | 127.84 | 569.94 |
| Fragmentation index | 0.36 | 0.025 | 0.38 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 0.73 | 0.16 |
| Quantity | Quality | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleic Acid | DNA | RNA | DNA | RNA |
| Suboptimal rate | 6.6% | 0% | 37.7% | 77.7% |
| IHC Intensity Score | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Annual Group Progressive Number # | Sum | Median | Average |
| #1 | 139 | 2 | 1.54 |
| #2 | 153 | 2 | 1.7 |
| #3 | 182 | 3 | 2.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eccher, A.; Seminati, D.; L’Imperio, V.; Casati, G.; Pilla, D.; Malapelle, U.; Piga, I.; Bindi, G.; Marando, A.; Bonoldi, E.; et al. Pathology Laboratory Archives: Conservation Quality of Nucleic Acids and Proteins for NSCLC Molecular Testing. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040333
Eccher A, Seminati D, L’Imperio V, Casati G, Pilla D, Malapelle U, Piga I, Bindi G, Marando A, Bonoldi E, et al. Pathology Laboratory Archives: Conservation Quality of Nucleic Acids and Proteins for NSCLC Molecular Testing. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(4):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040333
Chicago/Turabian StyleEccher, Albino, Davide Seminati, Vincenzo L’Imperio, Gabriele Casati, Daniela Pilla, Umberto Malapelle, Isabella Piga, Greta Bindi, Alessandro Marando, Emanuela Bonoldi, and et al. 2024. "Pathology Laboratory Archives: Conservation Quality of Nucleic Acids and Proteins for NSCLC Molecular Testing" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 4: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040333
APA StyleEccher, A., Seminati, D., L’Imperio, V., Casati, G., Pilla, D., Malapelle, U., Piga, I., Bindi, G., Marando, A., Bonoldi, E., Dainese, E., Riefolo, M., D’Errico, A., Costantini, M., Lugli, A., Grassi, S., Scarpa, A., Dei Tos, A. P., & Pagni, F. (2024). Pathology Laboratory Archives: Conservation Quality of Nucleic Acids and Proteins for NSCLC Molecular Testing. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040333










