Combination of Tractography, Intraoperative Computed Tomography and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Fluorescence in Stereotactic Brain Biopsies: A Case Series
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bex, A.; Mathon, B. Advances, Technological Innovations, and Future Prospects in Stereotactic Brain Biopsies. Neurosurg. Rev. 2022, 46, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, S.; He, Y.; Bartek, J.; Alattar, A.A.; Chen, C.C. Comparison of Frame-Based Versus Frameless Intracranial Stereotactic Biopsy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, 607–616.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesserwan, M.A.; Shakil, H.; Lannon, M.; McGinn, R.; Banfield, L.; Nath, S.; Alotaibi, M.; Kasper, E.; Sharma, S. Frame-Based versus Frameless Stereotactic Brain Biopsies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodworth, G.F.; McGirt, M.J.; Samdani, A.; Garonzik, I.; Olivi, A.; Weingart, J.D. Frameless Image-Guided Stereotactic Brain Biopsy Procedure: Diagnostic Yield, Surgical Morbidity, and Comparison with the Frame-Based Technique. J. Neurosurg. 2006, 104, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riche, M.; Amelot, A.; Peyre, M.; Capelle, L.; Carpentier, A.; Mathon, B. Complications after Frame-Based Stereotactic Brain Biopsy: A Systematic Review. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balducci, M.; Chiesa, S.; Diletto, B.; D’Agostino, G.R.; Mangiola, A.; Manfrida, S.; Mantini, G.; Albanese, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Frascino, V.; et al. Low-Dose Fractionated Radiotherapy and Concomitant Chemotherapy in Glioblastoma Multiforme with Poor Prognosis: A Feasibility Study. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizobuchi, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Fujihara, T.; Matsuzaki, K.; Mure, H.; Nagahiro, S.; Takagi, Y. The Risk of Hemorrhage in Stereotactic Biopsy for Brain Tumors. J. Med. Investig. 2019, 66, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Zhu, C.X.L.; Chan, D.T.M.; Cheung, T.C.Y.; Ng, H.-K.; Mok, V.C.T.; Poon, W.S. Diagnostic Accuracy and Field for Improvement of Frameless Stereotactic Brain Biopsy: A Focus on Nondiagnostic Cases. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2024, 85, 048–061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riche, M.; Marijon, P.; Amelot, A.; Bielle, F.; Mokhtari, K.; de Chambrun, M.P.; Joncour, A.L.; Idbaih, A.; Touat, M.; Do, C.-H.; et al. Severity, Timeline, and Management of Complications after Stereotactic Brain Biopsy. J. Neurosurg. 2022, 136, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoeller, G.K.; Benveniste, R.J.; Landy, H.; Morcos, J.J.; Jagid, J. Outcomes and Management Strategies after Nondiagnostic Stereotactic Biopsies of Brain Lesions. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2009, 87, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regragui, A.; Amarti Riffi, A.; Maher, M.; El Khamlichi, A.; Saidi, A. Accuracy of intraoperative diagnosis in central nervous system tumors: Report of 1315 cases. Neurochirurgie 2003, 49, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walter, S.; Susanne, S.; Simon, W.; Herbert, S.; Clemens, F.; Claudia, G.; Alwin, E.G.; Rainer, K.; Hans, J.R. Intraoperative Detection of Malignant Gliomas by 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Induced Porphyrin Fluorescence. Neurosurgery 1998, 42, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjipanayis, C.G.; Stummer, W. 5-ALA and FDA Approval for Glioma Surgery. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, K.; Garvey, K.L.; Bouras, A.; Cramer, G.; Stepp, H.; Jesu Raj, J.G.; Bozec, D.; Busch, T.M.; Hadjipanayis, C.G. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Photodynamic Therapy for the Treatment of High-Grade Gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 141, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibson, S.L.; Nguyen, M.L.; Havens, J.J.; Barbarin, A.; Hilf, R. Relationship of δ-Aminolevulinic Acid-Induced Protoporphyrin IX Levels to Mitochondrial Content in Neoplastic Cells in Vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 265, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, S.; Eljamel, M.S. Fluorescence Image-Guided Neurosurgery. Future Oncol. 2017, 13, 2341–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, F.; Takahashi, H.; Teramoto, A. Photodiagnosis for Frameless Stereotactic Biopsy of Brain Tumor. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2007, 4, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinova, V.; von Eckardstein, K.; Mielke, D.; Rohde, V. Diagnostic Yield of Fluorescence-Assisted Frame-Based Stereotactic Biopsies of Intracerebral Lesions in Comparison with Frozen-Section Analysis. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 149, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesel, B.; Wadiura, L.I.; Mischkulnig, M.; Makolli, J.; Sperl, V.; Borkovec, M.; Freund, J.; Lang, A.; Millesi, M.; Berghoff, A.S.; et al. Efficacy, Outcome, and Safety of Elderly Patients with Glioblastoma in the 5-ALA Era: Single Center Experience of More Than 10 Years. Cancers 2021, 13, 6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marbacher, S.; Klinger, E.; Schwyzer, L.; Fischer, I.; Nevzati, E.; Diepers, M.; Roelcke, U.; Fathi, A.-R.; Coluccia, D.; Fandino, J. Use of Fluorescence to Guide Resection or Biopsy of Primary Brain Tumors and Brain Metastases. Neurosurg. Focus 2014, 36, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shofty, B.; Richetta, C.; Haim, O.; Kashanian, A.; Gurevich, A.; Grossman, R. 5-ALA-Assisted Stereotactic Brain Tumor Biopsy Improve Diagnostic Yield. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 45, 2375–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Campe, G.; Moschopulos, M.; Hefti, M. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Induced Protoporphyrin IX Fluorescence as Immediate Intraoperative Indicator to Improve the Safety of Malignant or High-Grade Brain Tumor Diagnosis in Frameless Stereotactic Biopsies. Acta Neurochir. 2012, 154, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widhalm, G.; Minchev, G.; Woehrer, A.; Preusser, M.; Kiesel, B.; Furtner, J.; Mert, A.; Di Ieva, A.; Tomanek, B.; Prayer, D.; et al. Strong 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Induced Fluorescence Is a Novel Intraoperative Marker for Representative Tissue Samples in Stereotactic Brain Tumor Biopsies. Neurosurg. Rev. 2012, 35, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Ishikawa, E.; Miki, S.; Sakamoto, N.; Zaboronok, A.; Matsuda, M.; Akutsu, H.; Nakai, K.; Tsuruta, W.; Matsumura, A. Photodynamic Diagnosis Using 5-Aminolevulinic Acid in 41 Biopsies for Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 1452–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, N.; Katayama, Y.; Kawabata, S.; Furuse, M.; Tsuji, Y.; Nonoguchi, N.; Yagi, R.; Kameda, M.; Takami, T.; Kuroiwa, T.; et al. Frameless Stereotactic Biopsy with Intraoperative Computed Tomography “Assessment of Efficacy and Real Target Registration Error”. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2022, 62, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hefti, M.; von Campe, G.; Moschopulos, M.; Siegner, A.; Looser, H.; Landolt, H. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Induced Protoporphyrin IX Fluorescence in High-Grade Glioma Surgery: A One-Year Experience at a Single Institutuion. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2008, 138, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriuchi, S.; Yamada, K.; Dehara, M.; Teramoto, Y.; Soda, T.; Imakita, M.; Taneda, M. Use of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for the Confirmation of Deep-Seated Brain Tumors during Stereotactic Biopsy: Report of 2 Cases. J. Neurosurg. 2011, 115, 278–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.; Gallieni, M.; Zaed, I.; Samii, A. Use of Frameless Stereotactic Navigation System Combined with Intraoperative Magnetic Resonance Imaging and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid. World Neurosurg. 2019, 131, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchi, E.; La Rocca, G.; Ius, T.; Sabatino, G.; Della Pepa, G.M. Multimodality Imaging Techniques to Assist Surgery in Low-Grade Gliomas. World Neurosurg. 2020, 133, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzucchi, E.; La Rocca, G.; Hiepe, P.; Pignotti, F.; Galieri, G.; Policicchio, D.; Boccaletti, R.; Rinaldi, P.; Gaudino, S.; Ius, T.; et al. Intraoperative Integration of Multimodal Imaging to Improve Neuronavigation: A Technical Note. World Neurosurg. 2022, 164, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Pepa, G.M.; Ius, T.; La Rocca, G.; Gaudino, S.; Isola, M.; Pignotti, F.; Rapisarda, A.; Mazzucchi, E.; Giordano, C.; Dragonetti, V.; et al. 5-Aminolevulinic Acid and Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: The Combination of the Two Techniques to Optimize the Extent of Resection in Glioblastoma Surgery. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, E529–E540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbassani, H.J.; Nishio, S.; Sweeney, K.M.; Bakay, R.A.; Takei, Y. CT-Assisted Stereotactic Brain Biopsy: Value of Intraoperative Frozen Section Diagnosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millesi, M.; Kiesel, B.; Wöhrer, A.; Mercea, P.A.; Bissolo, M.; Roetzer, T.; Wolfsberger, S.; Furtner, J.; Knosp, E.; Widhalm, G. Is Intraoperative Pathology Needed If 5-Aminolevulinic-Acid-Induced Tissue Fluorescence Is Found in Stereotactic Brain Tumor Biopsy? Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slof, J.; Díez Valle, R.; Galván, J. Cost-Effectiveness of 5-Aminolevulinic Acid-Induced Fluorescence in Malignant Glioma Surgery. Neurología 2015, 30, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
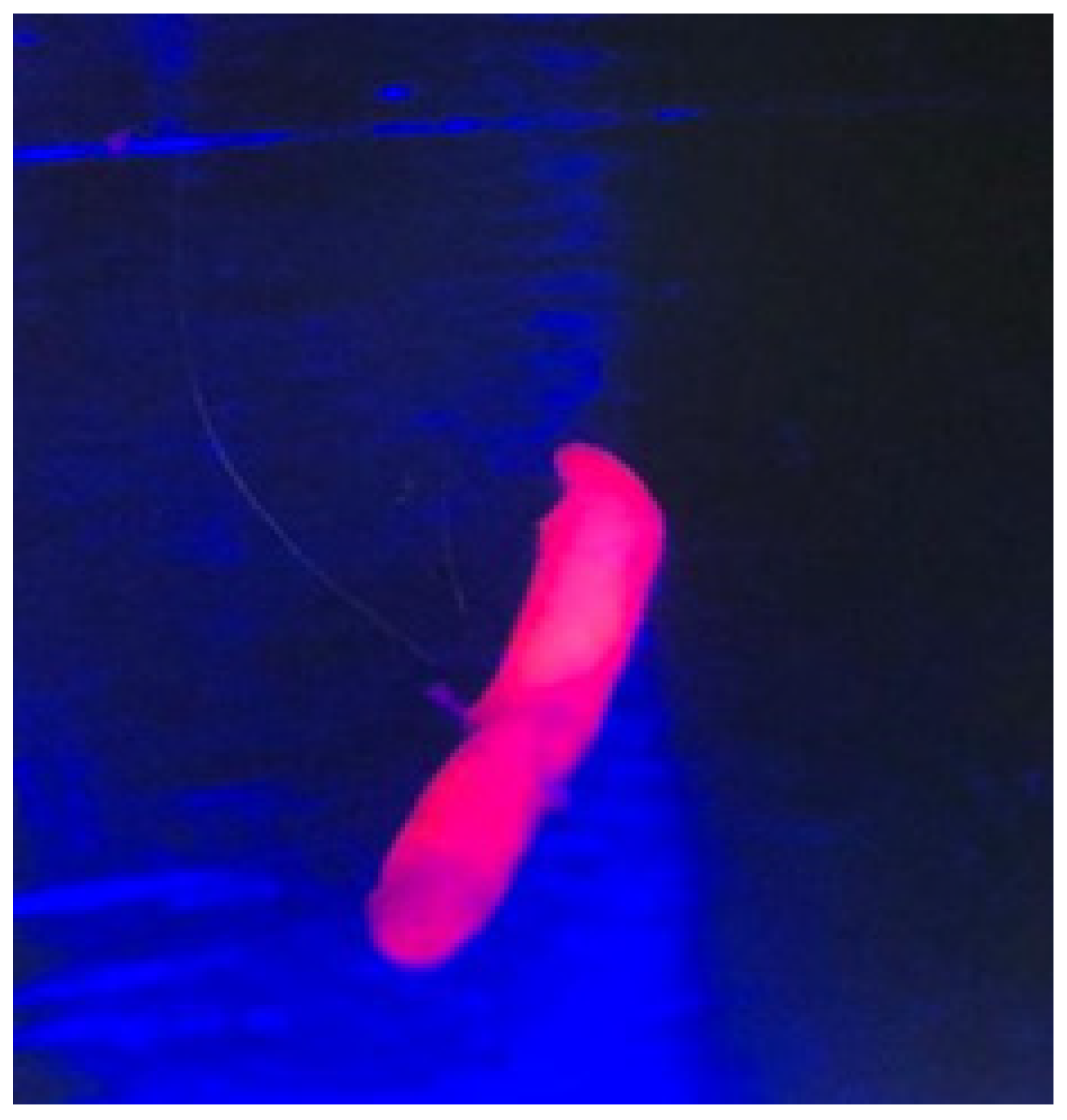
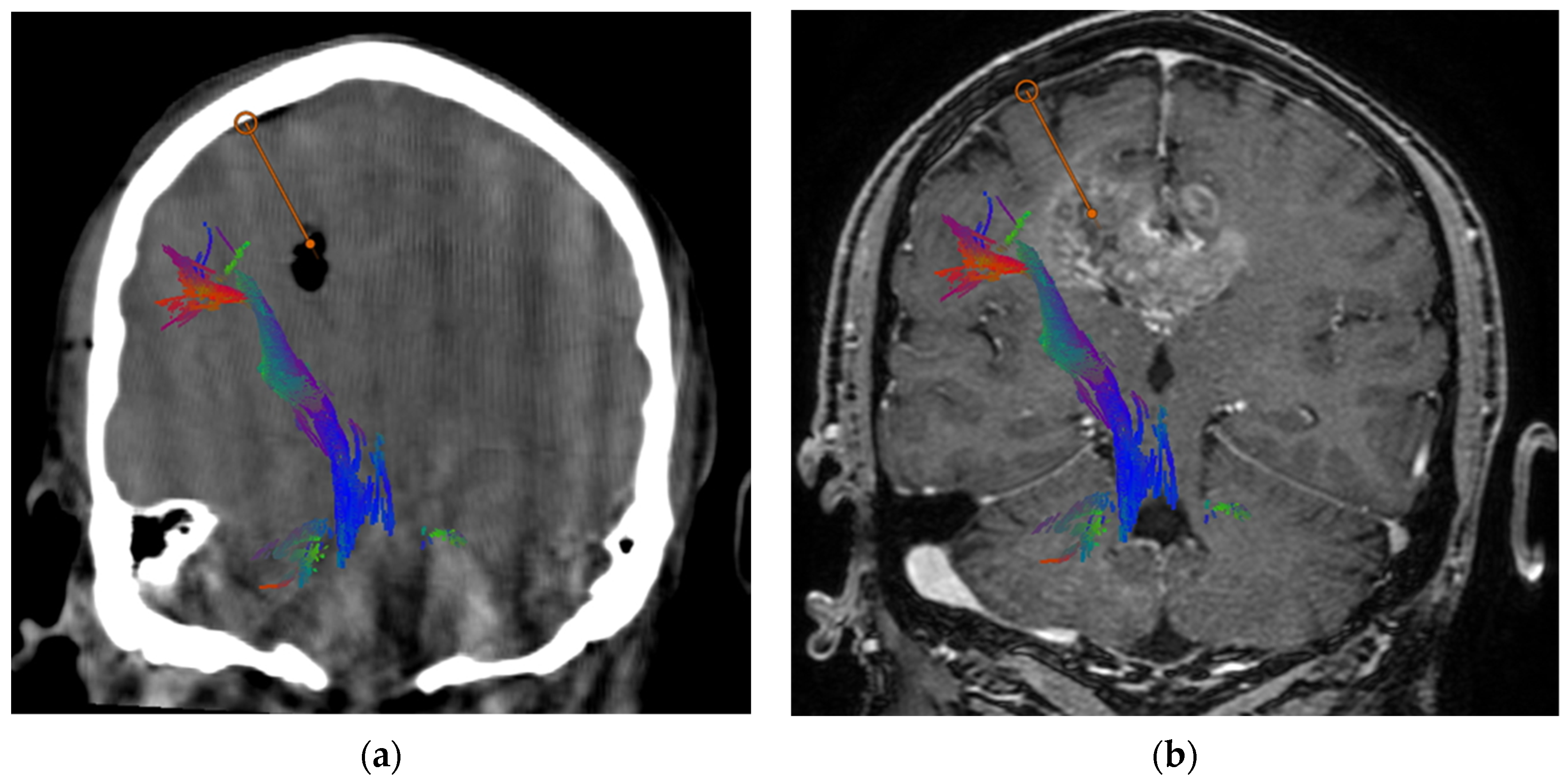
| Patient ID | Tumor Location | 5-ALA Fluorescence | Intra-Operative Pathology | Final Pathology | Complication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Right parietal and CC | Yes | No | Glioblastoma IDH-wt | None |
| 2 | Right parietal | Yes | Yes (malignant glioma) | Glioblastoma IDH-wt | Worsening of left arm motor function |
| 3 | Bilateral frontal and CC | Yes | No | Glioblastoma IDH-wt | None |
| 4 | Bilateral frontal and CC | Yes | No | DLBCL | None |
| 5 | Bilateral frontal and CC | Yes | No | Glioblastoma IDH-wt | None |
| 6 | Left temporal and insular | Yes | No | Glioblastoma IDH-wt | None |
| 7 | Bilateral parietal and CC | Yes | No | Glioblastoma IDH-wt | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazzucchi, E.; Galieri, G.; Pignotti, F.; Rinaldi, P.; Sabatino, G.; La Rocca, G. Combination of Tractography, Intraoperative Computed Tomography and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Fluorescence in Stereotactic Brain Biopsies: A Case Series. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040357
Mazzucchi E, Galieri G, Pignotti F, Rinaldi P, Sabatino G, La Rocca G. Combination of Tractography, Intraoperative Computed Tomography and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Fluorescence in Stereotactic Brain Biopsies: A Case Series. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(4):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040357
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazzucchi, Edoardo, Gianluca Galieri, Fabrizio Pignotti, Pierluigi Rinaldi, Giovanni Sabatino, and Giuseppe La Rocca. 2024. "Combination of Tractography, Intraoperative Computed Tomography and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Fluorescence in Stereotactic Brain Biopsies: A Case Series" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 4: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040357
APA StyleMazzucchi, E., Galieri, G., Pignotti, F., Rinaldi, P., Sabatino, G., & La Rocca, G. (2024). Combination of Tractography, Intraoperative Computed Tomography and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid Fluorescence in Stereotactic Brain Biopsies: A Case Series. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040357








