The Effect of Probiotics on the Prognostication of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Severe Multi-Trauma Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Neutrophils
3.2. Lymphocytes
3.3. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio
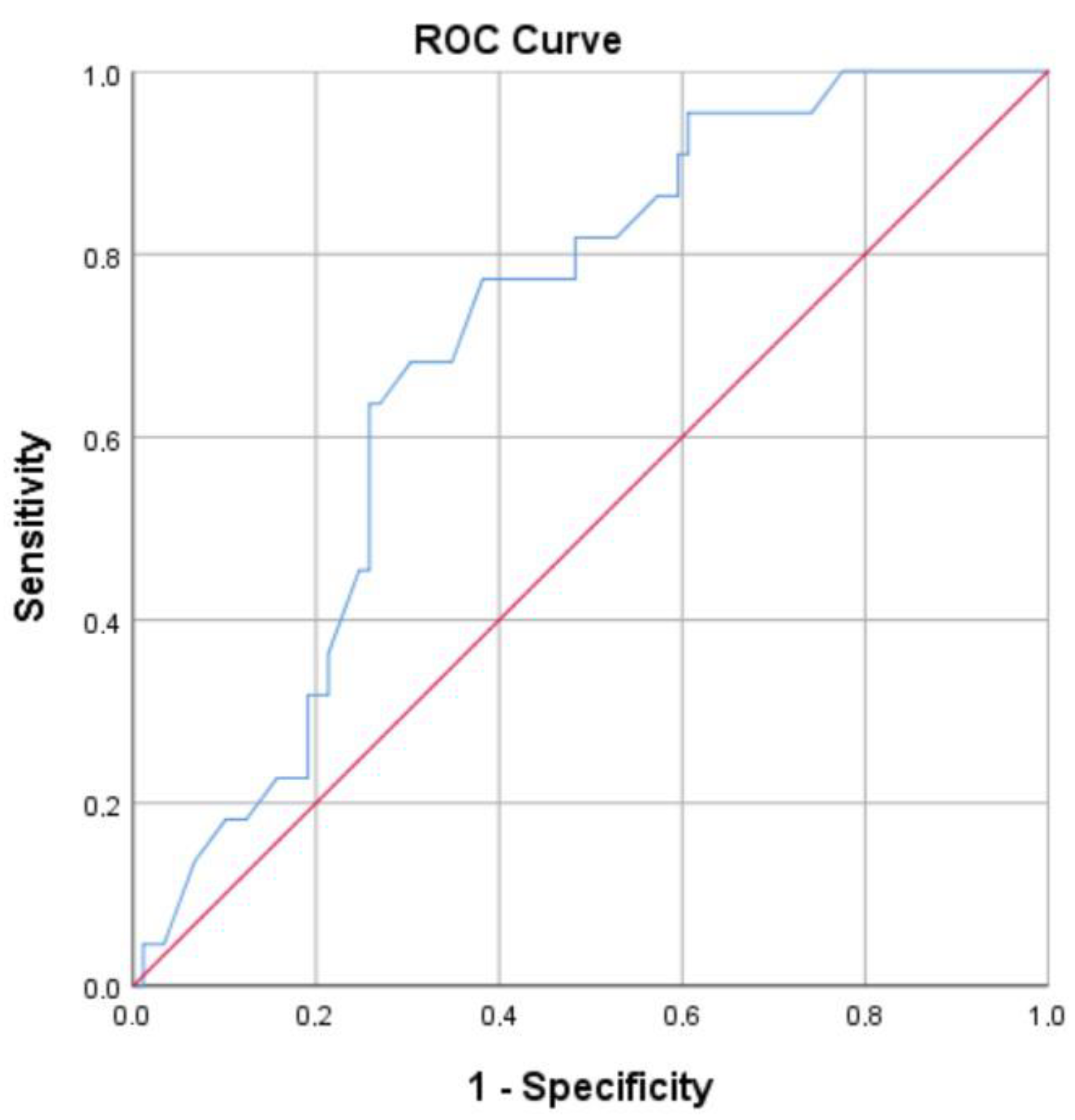
3.4. ROC Curve and Optimal Cut-Off Points
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robateau, Z.; Lin, V.; Wahlster, S. Acute Respiratory Failure in Severe Acute Brain Injury. Crit. Care Clin. 2024, 40, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iddagoda, M.T.; Trevenen, M.; Meaton, C.; Etherton-Beer, C.; Flicker, L. Identifying factors predicting outcomes after major trauma in older patients: Prognostic systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, S.; Jeong, T.; Park, B. Evaluation of the sequential organ failure assessment score and newly introduced criteria-Traumasis-in traffic collision patients. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 51, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou-Olivgeris, M.; Panteli, E.; Koutsileou, K.; Boulovana, M.; Zotou, A.; Marangos, M.; Fligou, F. Predictors of mortality of trauma patients admitted to the ICU: A retrospective observational study☆. Braz. J. Anesthesiol. 2021, 71, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieler, D.; Paffrath, T.; Schmidt, A.; Völlmecke, M.; Lefering, R.; Kulla, M.; Kollig, E.; Franke, A. Why do some trauma patients die while others survive? A matched-pair analysis based on data from Trauma Register DGU®. Chin. J. Traumatol. 2020, 23, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, T.M.; Tracy, J.K.; Dunne, J.R.; Pasquale, M.; Napolitano, L.M. Epidemiology of sepsis in patients with traumatic injury. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, E.; Amram, O.; Baer, H.J.; Hameed, S.M.; Griesdale, D.E.G. Transport Time and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients with Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 48, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, D.; Ackermann, G.; Khailova, L.; Baird, C.; Heyland, D.; Kozar, R.; Lemieux, M.; Derenski, K.; King, J.; Vis-Kampen, C.; et al. Extreme Dysbiosis of the Microbiome in Critical Illness. mSphere 2016, 1, e00199-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Ge, Q.; Fei, A.; Pan, S. Prognostic Significance of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Sepsis: A Prospective Observational Study. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 8191254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts--rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Heffernan, D.S.; Monaghan, S.F.; Thakkar, R.K.; Machan, J.T.; Cioffi, W.G.; Ayala, A. Failure to normalize lymphopenia following trauma is associated with increased mortality, independent of the leukocytosis pattern. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, D.; Andersson, H.; Kihlberg, P.; Olson, S.; Ziegler, I.; Rasmussen, G.; Källman, J.; Cajander, S.; Mölling, P.; Sundqvist, M. Early prediction of blood stream infection in a prospectively collected cohort. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert consensus document. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Bengmark, S.; Kanellakopoulou, K.; Kotzampassi, K. Pro- and synbiotics to control inflammation and infection in patients with multiple injuries. J. Trauma 2009, 67, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengmark, S. Pro- and synbiotics to prevent sepsis in major surgery and severe emergencies. Nutrients 2012, 4, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Ojima, M.; Ogura, H. Gut Microbiota and Probiotics/Synbiotics for Modulation of Immunity in Critically Ill Patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, C. Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Immune System by Probiotics, Pre-biotics, and Post-biotics. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 634897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotou, D.; Filidou, E.; Gaitanidou, M.; Tarapatzi, G.; Spathakis, M.; Kandilogiannakis, L.; Stavrou, G.; Arvanitidis, K.; Tsetis, J.K.; Gionga, P.; et al. Role of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum UBLP-40, Lactobacillus rhamnosus UBLR-58 and Bifidobacterium longum UBBL-64 in the Wound Healing Process of the Excisional Skin. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menni, A.; Moysidis, M.; Tzikos, G.; Stavrou, G.; Tsetis, J.K.; Shrewsbury, A.D.; Filidou, E.; Kotzampassi, K. Looking for the Ideal Probiotic Healing Regime. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzikos, G.; Tsalkatidou, D.; Stavrou, G.; Thoma, G.; Chorti, A.; Tsilika, M.; Michalopoulos, A.; Papavramidis, T.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Kotzampassi, K. A Four-Probiotic Regime to Reduce Surgical Site Infections in Multi-Trauma Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzampassi, K.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Voudouris, A.; Kazamias, P.; Eleftheriadis, E. Benefits of a synbiotic formula (Synbiotic 2000Forte) in critically Ill trauma patients: Early results of a randomized controlled trial. World J. Surg. 2006, 30, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsilika, M.; Thoma, G.; Aidoni, Z.; Tsaousi, G.; Fotiadis, K.; Stavrou, G.; Malliou, P.; Chorti, A.; Massa, H.; Antypa, E.; et al. A four-probiotic preparation for ventilator-associated pneumonia in multi-trauma patients: Results of a randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2022, 59, 106471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilberberg, M.D.; Shorr, A.F. Ventilator-associated pneumonia: The clinical pulmonary infection score as a surrogate for diagnostics and outcome. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51 (Suppl. 1), S131–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, N.J.; Schisterman, E.F. The Inconsistency of “Optimal” Cutpoints Obtained using Two Criteria based on the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youden, W.J. Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 1950, 3, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekmekciu, I.; von Klitzing, E.; Fiebiger, U.; Neumann, C.; Bacher, P.; Scheffold, A.; Bereswill, S.; Heimesaat, M.M. The Probiotic Compound VSL#3 Modulates Mucosal, Peripheral, and Systemic Immunity Following Murine Broad-Spectrum Antibiotic Treatment. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finamore, A.; Roselli, M.; Donini, L.; Brasili, D.E.; Rami, R.; Carnevali, P.; Mistura, L.; Pinto, A.; Giusti, A.; Mengheri, E. Supplementation with Bifidobacterium longum Bar33 and Lactobacillus helveticus Bar13 mixture improves immunity in elderly humans (over 75 years) and aged mice. Nutrition 2019, 63–64, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, M.A.; Haseeb, A.; Asghar, B.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhry, E.R.; Mustafa, M.S. Assessing the impact of pre-hospital airway management on severe traumatic Brain injury: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 78, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. Pathophysiology of acute lung injury in patients with acute brain injury: The triple-hit hypothesis. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robba, C.; Bonatti, G.; Pelosi, P.; Citerio, G. Extracranial complications after traumatic brain injury: Targeting the brain and the body. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2020, 26, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, S.J.; Sharkey, J.M.; Sun, M.; Kaukas, L.M.; Shultz, S.R.; Turner, R.J.; Leonard, A.V.; Brady, R.D.; Corrigan, F. Beyond the Brain: Peripheral Interactions after Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2020, 37, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musleh-Vega, S.; Ojeda, J.; Vidal, P.M. Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis as a Potential Modulator of Psychological Stress after Spinal Cord Injury. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, M.T.; Cryan, J.F. The microbiome as a key regulator of brain, behavior and immunity: Commentary on the 2017 named series. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, A.K.; Behera, J.; Homme, R.P.; Tyagi, N.; Tyagi, S.C.; Singh, M. Rebuilding Microbiome for Mitigating Traumatic Brain Injury: Importance of Restructuring the Gut-Microbiome-Brain Axis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 3614–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghakhani, N. Relationship between mild traumatic brain injury and the gut microbiome: A scoping review. J. Neurosci. Res. 2022, 100, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, T.W.; Putnam, J.G.; Sawada, R.; Baird, A.; Loomis, W.H.; Eliceiri, B.P.; Bansal, V.; Coimbra, R. Targeting the gut barrier: Identification of a homing peptide sequence for delivery into the injured intestinal epithelial cell. Surgery 2009, 146, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, E.L.; Smith, A.D.; Desai, N.; Cheung, L.; Hanscom, M.; Stoica, B.A.; Loane, D.J.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Faden, A.I. Bidirectional brain-gut interactions and chronic pathological changes after traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, M.; Exadaktylos, A. ARDS associated acute brain injury: From the lung to the brain. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erfani, Z.; Jelodari Mamaghani, H.; Rawling, J.A.; Eajazi, A.; Deever, D.; Mirmoeeni, S.; Azari Jafari, A.; Seifi, A. Pneumonia in Nervous System Injuries: An Analytic Review of Literature and Recommendations. Cureus 2022, 14, e25616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, C.; Khurana, S.; Kapoor, I.; Sokhal, S.; Kumar, S.; Prabhakar, H.; Mathur, P.; Mani, K. Characteristics of Gut Microbiome After Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurosurg. Anesthesiol. 2023, 35, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoia, A.; Paradiso, R.; Ferrara, G.; Borriello, G.; Santoro, F.; Spina, I.; Mirabella, L.; Mariano, K.; Fusco, G.; Cinnella, G.; et al. Modifications of lung microbiota structure in traumatic brain injury ventilated patients according to time and enteral feeding formulas: A prospective randomized study. Crit. Care 2023, 27, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, S.D.; Olwenyi, O.A.; Bhyravbhatla, N.; Thurman, M.; Pandey, K.; Klug, E.A.; Johnston, M.; Dyavar, S.R.; Acharya, A.; Podany, A.T.; et al. Therapeutic implications of SARS-CoV-2 dysregulation of the gut-brain-lung axis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 4763–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, M.; Klingensmith, N.J.; Coopersmith, C.M. New insights into the gut as the driver of critical illness and organ failure. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2017, 23, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rosa, S.; Battaglini, D.; Llompart-Pou, J.A.; Godoy, D.A. Ten good reasons to consider gastrointestinal function after acute brain injury. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2024, 38, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Z.; Pei, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Z. Investigation of Gut Microbiota Disorders in Sepsis and Sepsis Complicated with Acute Gastrointestinal Injury Based on 16S rRNA Genes Illumina Sequencing. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 7389–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Chen, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Shang, X.; Huang, T.; Huang, G.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota composition reflects disease progression, severity and outcome, and dysfunctional immune responses in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 869846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingensmith, N.J.; Coopersmith, C.M. The Gut as the Motor of Multiple Organ Dysfunction in Critical Illness. Crit. Care Clin. 2016, 32, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.H.; Shim, H.J.; Hwang, E.C.; Choi, Y.D.; Bang, H.; Cho, S.H.; Chung, I.J.; Hwang, J.E.; Lee, M.A.; et al. Prognostic Significance of the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-Lymphocyte Ratio in Neuroendocrine Carcinoma. Chonnam Med. J. 2022, 58, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunoda, J.; Shigeta, K.; Matsui, S.; Seishima, R.; Okabayashi, K.; Kitagawa, Y. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio is a Useful Biomarker for Predicting Postoperative Complications in Crohn’s Disease. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2022, 26, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, T.; Teli, S.; Rijal, J.; Bhat, H.; Raza, M.; Khoueiry, G.; Meghani, M.; Akhtar, M.; Costantino, T. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and cardiovascular diseases: A review. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2013, 11, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Hirooka, M.; Kariyama, K.; Tani, J.; Atsukawa, M.; Takaguchi, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Fukunishi, S.; et al. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts early outcomes in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab: A multicenter analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 34, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Dong, J.; Sun, Q.; Lu, N.; Pan, Y.; Han, X. Role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic biomarker in patients with breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e047957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, H.K.S.; Davis, G.N.; Trejo-Avila, M.; Igwe, P.O.; Garcia-Marín, A. Prognostic and predictive value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio after curative rectal cancer resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 37, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzikos, G.; Alexiou, I.; Tsagkaropoulos, S.; Menni, A.E.; Chatziantoniou, G.; Doutsini, S.; Papavramidis, T.; Grosomanidis, V.; Stavrou, G.; Kotzampassi, K. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as Predictive Factors for Mortality and Length of Hospital Stay after Cardiac Surgery. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, C.D.; Parajuli, A.; Gale, H.J.; Bulteel, N.S.; Schuetz, P.; de Jager, C.P.C.; Loonen, A.J.M.; Merekoulias, G.I.; Baillie, J.K. The utility of peripheral blood leucocyte ratios as biomarkers in infectious diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2019, 78, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djordjevic, D.; Rondovic, G.; Surbatovic, M.; Stanojevic, I.; Udovicic, I.; Andjelic, T.; Zeba, S.; Milosavljevic, S.; Stankovic, N.; Abazovic, D.; et al. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio, and Mean Platelet Volume-to-Platelet Count Ratio as Biomarkers in Critically Ill and Injured Patients: Which Ratio to Choose to Predict Outcome and Nature of Bacteremia? Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3758068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haran, C.; Gimpel, D.; Clark, H.; McCormack, D.J. Preoperative Neutrophil and Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality and Morbidity After Cardiac Surgery. Heart Lung Circ. 2021, 30, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larmann, J.; Handke, J.; Scholz, A.S.; Dehne, S.; Arens, C.; Gillmann, H.-J.; Uhle, F.; Motsch, J.; Weigand, M.A.; Janssen, H. Preoperative neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio are associated with major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events in coronary heart disease patients undergoing non-cardiac surgery. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méndez Hernández, R.; Ramasco Rueda, F. Biomarkers as Prognostic Predictors and Therapeutic Guide in Critically Ill Patients: Clinical Evidence. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Tinsley, K.W.; Swanson, P.E.; Schmieg, R.E., Jr.; Hui, J.J.; Chang, K.C.; Osborne, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Cobb, J.P.; Buchman, T.G.; et al. Sepsis-induced apoptosis causes progressive profound depletion of B and CD4+ T lymphocytes in humans. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 6952–6963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewry, A.M.; Samra, N.; Skrupky, L.P.; Fuller, B.M.; Compton, S.M.; Hotchkiss, R.S. Persistent lymphopenia after diagnosis of sepsis predicts mortality. Shock 2014, 42, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.A.; Brain, S.D.; Pearson, J.D.; Edgeworth, J.D.; Lewis, S.M.; Treacher, D.F. Neutrophils in development of multiple organ failure in sepsis. Lancet 2006, 368, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Yao, K.; Syeda, M.Z.; Wan, J.; Cheng, Q.; You, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; et al. Neutrophil Targeting Platform Reduces Neutrophil Extracellular Traps for Improved Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke Theranostics. Adv. Sci. 2024, e2308719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelekanou, A.; Tsangaris, I.; Kotsaki, A.; Karagianni, V.; Giamarellou, H.; Armaganidis, A.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. Decrease of CD4-lymphocytes and apoptosis of CD14-monocytes are characteristic alterations in sepsis caused by ventilator-associated pneumonia: Results from an observational study. Crit. Care 2009, 13, R172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Liang, B.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Tong, Q.; Yi, J.; Zhao, L.; et al. Longitudinal characteristics of lymphocyte responses and cytokine profiles in the peripheral blood of SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. eBioMedicine 2020, 55, 102763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Colaci, M.; Malatino, L. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio: An Emerging Marker of the Relationships between the Immune System and Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahorec, R. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio. Sixteen-year-long history since publication of our article in Bratislava Medical Journal. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2017, 118, 321–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konieczna, P.; Akdis, C.A.; Quigley, E.M.; Shanahan, F.; O’Mahony, L. Portrait of an immunoregulatory Bifidobacterium. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotoia, A.; Spadaro, S.; Gambetti, G.; Koulenti, D.; Cinnella, G. Pathogenesis-Targeted Preventive Strategies for Multidrug Resistant Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia: A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Roock, S.; van Elk, M.; van Dijk, M.E.; Timmerman, H.M.; Rijkers, G.T.; Prakken, B.J.; Hoekstra, M.O.; de Kleer, I.M. Lactic acid bacteria differ in their ability to induce functional regulatory T cells in humans. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2010, 40, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifi, N.; Sedaghat, A.; Nematy, M.; Khadem-Rezaiyan, M.; Shirazinezhad, R.; Ranjbar, G.; Safarian, M. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on the serum endotoxin level, inflammatory status, and clinical outcomes of adult patients with critical illness: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2022, 37, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Padilla, Á.; Morales-Martín, G.; Pérez-Quintero, R.; Gómez-Salgado, J.; Ruiz-Frutos, C. Serological Biomarkers and Diversion Colitis: Changes after Stimulation with Probiotics. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.H.; Cámara, M.; Verma, C.; Eremin, O.; Kulkarni, A.D.; Lobo, D.N. Modulation of T Regulatory and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes Following Ingestion of Bifidobacterium longum, AHCC(®) and Azithromycin in Healthy Individuals. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olimpio, F.; Carvalho, J.; Kaminsky, V.; Aimbire, F. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus attenuates acute lung inflammation in a murine model of acute respiratory distress syndrome: Relevance to cytokines associated to STAT4/T-bet and STAT3/RORɣt″. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 173, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzampassi, K.; Stavrou, G.; Damoraki, G.; Georgitsi, M.; Basdanis, G.; Tsaousi, G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J. A Four-Probiotics Regimen Reduces Postoperative Complications After Colorectal Surgery: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 2776–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapatzi, G.; Filidou, E.; Kandilogiannakis, L.; Spathakis, M.; Gaitanidou, M.; Arvanitidis, K.; Drygiannakis, I.; Valatas, V.; Kotzampassi, K.; Manolopoulos, V.G.; et al. The Probiotic Strains Bifidοbacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces boulardii Regulate Wound Healing and Chemokine Responses in Human Intestinal Subepithelial Myofibroblasts. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Groups | Day 0 | Day 7 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 53) | 6.94 ± 2.28 | 12.68 ± 5.43 | <0.001 |
| Probiotics (n = 59) | 6.21 ± 2.00 | 11.68 ± 5.05 | <0.001 |
| p Value ** | 0.07 | 0.2 |
| Groups | Sub-Groups | Day 0 | Day 7 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 53) | no-VAP (n = 38) | 7.20 ± 2.22 | 13.08 ± 6.16 | <0.001 |
| VAP (n = 15) | 6.31 ± 2.37 | 11.70 ± 6.14 | 0.012 | |
| p Value ** | 0.2 | 0.4 | ||
| Probiotics (n = 59) | no-VAP (n = 52) | 6.28 ± 1.96 | 11.31 ± 5.09 | <0.001 |
| VAP (n = 7) | 5.71 ± 2.38 | 14.32 ± 4.09 | <0.001 | |
| p Value ** | 0.02 | 0.14 |
| Groups | Day 0 | Day 7 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 53) | 1.30 ± 0.37 | 0.86 ± 0.43 | <0.001 |
| Probiotics (n = 59) | 1.23 ± 0.29 | 2.95 ± 1.23 | <0.001 |
| p Value ** | 0.3 | <0.001 |
| Groups | Sub-Groups | Day 0 | Day 7 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 53) | no-VAP (n = 38) | 1.33 ± 0.36 | 0.88 ± 0.41 | <0.001 |
| VAP (n = 15) | 1.22 ± 0.41 | 0.81 ± 0.50 | 0.06 | |
| p Value ** | 0.3 | 0.6 | ||
| Probiotics (n = 59) | no-VAP (n = 52) | 1.24 ± 0.29 | 3.02 ± 1.21 | <0.001 |
| VAP (n = 7) | 1.16 ± 0.33 | 2.41 ± 1.28 | 0.03 | |
| p Value ** | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Groups | Day 0 | Day 7 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Placebo (n = 53) | 5.61 ± 2.06 | 16.15 ± 5.81 | <0.001 |
| Probiotics (n = 59) | 5.18 ± 1.62 | 4.71 ± 3.44 | 0.066 |
| p Value ** | 0.2 | <0.001 |
| Groups | Sub-Groups | Day 0 | Day 7 | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
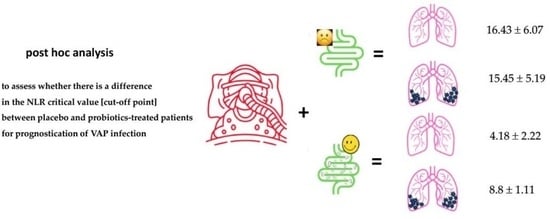
| Placebo (n = 53) | no-VAP (n = 38) | 5.74 ± 1.65 | 16.43 ± 6.07 | <0.001 |
| VAP (n = 15) | 5.29 ± 1.65 | 15.45 ± 5.19 | 0.001 | |
| p Value ** | 0.4 | 0.3 | ||
| Probiotics (n = 59) | no-VAP (n = 52) | 5.19 ± 1.61 | 4.18 ± 2.22 | 0.01 |
| VAP (n = 7) | 5.12 ± 1.77 | 8.8 ± 1.11 | 0.018 | |
| p Value ** | 0.98 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menni, A.-E.; Tzikos, G.; Fyntanidou, B.; Ioannidis, A.; Loukipoudi, L.; Grosomanidis, V.; Chorti, A.; Shrewsbury, A.; Stavrou, G.; Kotzampassi, K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Prognostication of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Severe Multi-Trauma Patients. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040419
Menni A-E, Tzikos G, Fyntanidou B, Ioannidis A, Loukipoudi L, Grosomanidis V, Chorti A, Shrewsbury A, Stavrou G, Kotzampassi K. The Effect of Probiotics on the Prognostication of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Severe Multi-Trauma Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2024; 14(4):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040419
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenni, Alexandra-Eleftheria, Georgios Tzikos, Barbara Fyntanidou, Aristeidis Ioannidis, Lamprini Loukipoudi, Vasilis Grosomanidis, Angeliki Chorti, Anne Shrewsbury, George Stavrou, and Katerina Kotzampassi. 2024. "The Effect of Probiotics on the Prognostication of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Severe Multi-Trauma Patients" Journal of Personalized Medicine 14, no. 4: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040419
APA StyleMenni, A.-E., Tzikos, G., Fyntanidou, B., Ioannidis, A., Loukipoudi, L., Grosomanidis, V., Chorti, A., Shrewsbury, A., Stavrou, G., & Kotzampassi, K. (2024). The Effect of Probiotics on the Prognostication of the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Severe Multi-Trauma Patients. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 14(4), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm14040419