Enhanced Lymph Node Detection in Colon Cancer Using Indocyanine Green Fluorescence: A Systematic Review of Studies from 2020 Onwards
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
- In vitro, cadaveric, or animal studies.
- No full text available. Restricted access.
- Other publication type (review, meta-analysis, questionnaire-based study, case report or case series, etc.).
- Other diseases or studies that focused on the surgical treatment of metastasis from colon cancer.
- Foreign language (not in English).
- No data of interest for the current review.
- Rectal cancer and studies that grouped rectal and colon cancer.
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Assessment
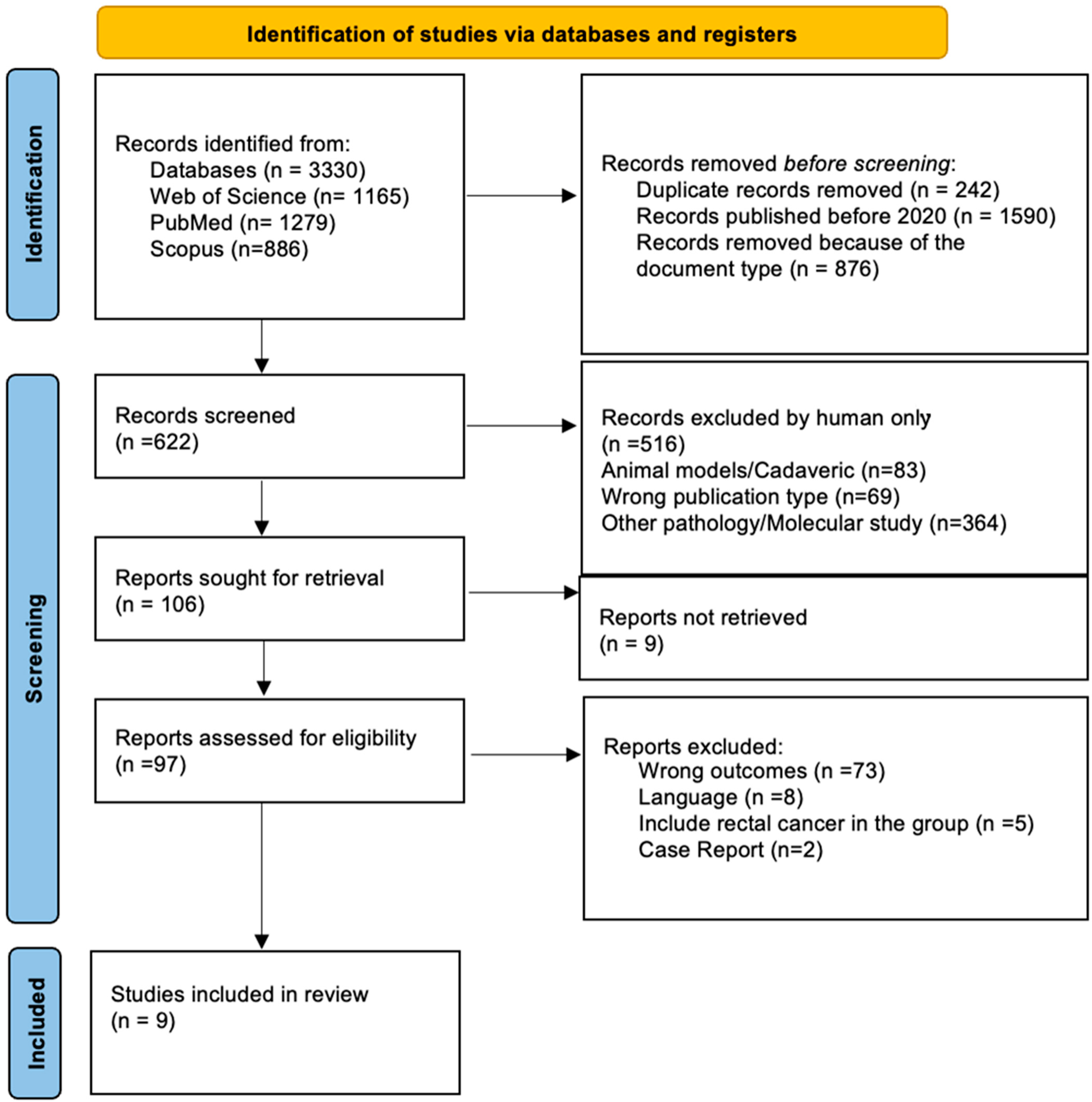
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Risk of Bias
3.3. Studies Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Hida, K.; Deguchi, Y.; Oshima, N.; Mizuno, R.; Wada, T.; Okada, T.; Sakai, Y. Laparoscopic left hemicolectomy with regional lymph node navigation and intracorporeal anastomosis for splenic flexure colon cancer. Int. Cancer Conf. J. 2020, 9, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohenberger, W.; Weber, K.; Matzel, K.; Papadopoulos, T.; Merkel, S. Standardized surgery for colonic cancer: Complete mesocolic excision and central ligation—Technical notes and outcome. Color. Dis. 2009, 11, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberale, G.; Lasser, P.; Sabourin, J.-C.; Malka, D.; Duvillard, P.; Elias, D.; Boige, V.; Goéré, D.; Ducreux, M.; Pocard, M. Sentinel lymph nodes of colorectal carcinoma: Reappraisal of 123 cases. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2007, 31, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberale, G.; Vankerckhove, S.; Bouazza, F.; Galdon, M.G.; Larsimont, D.; Moreau, M.; Bourgeois, P.; Donckier, V. Systemic Sentinel Lymph Node Detection Using Fluorescence Imaging After Indocyanine Green Intravenous Injection in Colorectal Cancer: Protocol for a Feasibility Study. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2020, 9, e17976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Bilchik, A.; Wiese, D.; Espinosa, M.; Badin, J.; Ganatra, B.K.; Desai, D.; Kaushal, S.; Singh, T.; Arora, M. Ultrastaging of colorectal cancer by sentinel lymph node mapping technique—A multicenter trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2001, 8, 94S–98S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van der Stok, E.P.; Spaander, M.C.W.; Grünhagen, D.J.; Verhoef, C.; Kuipers, E.J. Surveillance after curative treatment for colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elferink, M.A.G.; de Jong, K.P.; Klaase, J.M.; Siemerink, E.J.; de Wilt, J.H.W. Metachronous metastases from colorectal cancer: A population-based study in North-East Netherlands. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2015, 30, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberale, G.; Galdon, M.G.; Moreau, M.; Vankerckhove, S.; El Nakadi, I.; Larsimont, D.; Donckier, V.; Bourgeois, P. Ex vivo detection of tumoral lymph nodes of colorectal origin with fluorescence imaging after intraoperative intravenous injection of indocyanine green. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 114, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberale, G.; Vankerckhove, S.; Galdon, M.; Donckier, V.; Larsimont, D.; Bourgeois, P. Fluorescence imaging after intraoperative intravenous injection of indocyanine green for detection of lymph node metastases in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 41, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Q.; Butch, C.J.; Guissi, N.E.I.; You, Q.; Cai, H.; Ding, Y.; et al. A pilot study of near-infrared fluorescence guided surgery for primary tumor localization and lymph node mapping in colorectal cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021, 9, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan—A web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomized studies of interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munn, Z.; Stone, J.; Aromataris, E.; Klugar, M.; Sears, K.; Leonardi-Bee, J.; Barker, T.H. Assessing the risk of bias of quantitative analytical studies: Introducing the vision for critical appraisal within JBI systematic reviews. JBI Évid. Synth. 2023, 21, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. 2014. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Sikkenk, D.J.; Sterkenburg, A.J.; Burghgraef, T.A.; Akol, H.; Schwartz, M.P.; Arensman, R.; Verheijen, P.M.; Nagengast, W.B.; Consten, E.C.J. Robot-assisted fluorescent sentinel lymph node identification in early-stage colon cancer. Surg. Endosc. 2023, 37, 8394–8403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Patil, S.M.; Sekaran, A.; Rebala, P.; Rao, G. Indocyanine green guided sentinel lymph node biopsy may have a high sensitivity for early (T1/T2) colon cancer: A prospective study in Indian patients. Turk. J. Surg. 2023, 39, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.M.; Li, Q.M.; Sheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, W.M. Quantitative analysis of peri-intestinal lymph node metastasis using indocyanine green fluorescence imaging technology. Medicine 2024, 103, e39240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sollazzo, B.M.; Cassini, D.; Biacchi, D.; Sammartino, P.; Baldazzi, G. ICG-assisted D3 lymphadenectomy in right colectomy for cancer. Ann. Laparosc. Endosc. Surg. 2020, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, G.M.; Kim, T.U.; Yun, M.S.; Kim, C.; Lee, I.Y.; Park, S.B.; Shin, D.-H.; Ha, G.W. Effect of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping on Improving Diagnostic Values of CT D3 Lymph Node Staging for Right-Sided Colon Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.M.; Yun, M.S.; Lee, I.Y.; Bin Im, S.; Kim, K.H.; Park, S.B.; Kim, T.U.; Shin, D.-H.; Nazir, A.M.; Ha, G.W. Clinical Effectiveness of Fluorescence Lymph Node Mapping Using ICG for Laparoscopic Right Hemicolectomy: A Prospective Case–Control Study. Cancers 2023, 15, 4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, H.; Kawada, K.; Itatani, Y.; Okamura, R.; Oshima, N.; Okada, T.; Hida, K.; Obama, K. Timing of real-time indocyanine green fluorescence visualization for lymph node dissection during laparoscopic colon cancer surgery. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2023, 408, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushijima, H.; Kawamura, J.; Ueda, K.; Yane, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Daito, K.; Tokoro, T.; Hida, J.-I.; Okuno, K. Visualization of lymphatic flow in laparoscopic colon cancer surgery using indocyanine green fluorescence imaging. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fen, X.; Li, H.; Lu, X.; Yi, X.; Wan, J.; Liao, W.; Wang, J.; Ke, Y.; Tan, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Regional lymph nodes distribution pattern in central area of right-sided colon cancer: In-vivo detection and the update on the clinical exploration. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021, 11, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Porritt, K.; Pilla, B.; Jordan, Z. (Eds.) JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2024; ISBN 978-0-6488488-2-0. Available online: https://synthesismanual.jbi.global (accessed on 20 November 2024). [CrossRef]
- Egloff-Juras, C.; Bezdetnaya, L.; Dolivet, G.; Lassalle, H.-P. NIR fluorescence-guided tumor surgery: New strategies for the use of indocyanine green. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 7823–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaafsma, B.E.; Mieog, J.S.D.; Hutteman, M.; van der Vorst, J.R.; Kuppen, P.J.; Löwik, C.W.; Frangioni, J.V.; van de Velde, C.J.; Vahrmeijer, A.L. The clinical use of indocyanine green as a near-infrared fluorescent contrast agent for image-guided oncologic surgery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 104, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serban, D.; Dascalu, A.M.; Tribus, L.; Alius, C.; Cristea, B.M.; Suceveanu, A.I.; Voiculescu, D.; Dumitrescu, D.; Bobirca, F.; Suceveanu, A.P.; et al. Factors Affecting the Efficiency of Near-Infrared Indocyanine Green (NIR/ICG) in Lymphatic Mapping for Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e55290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, M.B.; Huntington, C.R.; Blair, L.J.; Heniford, B.T.; Augenstein, V.A. Indocyanine Green: Historical Context, Current Applications, and Future Considerations. Surg. Innov. 2016, 23, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5282412, Indocyanine Green. 2024. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Indocyanine-Green (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Markuszewski, M.; Buszewska-Forajta, M.; Artymowicz, M.; Połom, W.; Roslan, M.; Markuszewski, M. Binding indocyanine green to human serum albumin potentially enhances the detection of sentinel lymph nodes. An initial step for facilitating the detection of first-station nodes in penile and other urological cancers. Arch. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sánchez, J.; Garrosa-Muñoz, S.; Pardo-Aranda, F.; Zarate, A.; López-Pérez, R.; Rodríguez-Fortúnez, P.; Sánchez-Santos, J.M.; Esteban, C.; Quiñones, J.; Iglesias, M.; et al. DOse and administration time of indocyanine green in near-infrared fluorescence cholangiography during laparoscopic cholecystectomy (DOTIG): Study protocol for a randomised clinical trial. Surgery Endosc. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Endo, S.; Hidaka, E.; Tanaka, J.-I.; Kudo, S.-E.; Shiokawa, A. Laparoscopic sentinel node mapping for colorectal cancer using infrared ray laparoscopy. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 2307–2311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kusano, M.; Tajima, Y.; Yamazaki, K.; Kato, M.; Watanabe, M.; Miwa, M. Sentinel node mapping guided by indocyanine green fluorescence imaging: A new method for sentinel node navigation surgery in gastrointestinal cancer. Dig. Surg. 2008, 25, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirche, C.; Mohr, Z.; Kneif, S.; Doniga, S.; Murawa, D.; Strik, M.; Hünerbein, M. Ultrastaging of colon cancer by sentinel node biopsy using fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2012, 27, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrara, A.; Motter, M.; Amabile, D.; Pellecchia, L.; Moscatelli, P.; Pertile, R.; Barbareschi, M.; Decarli, N.L.; Ferrari, M.; Tirone, G. Predictive value of the sentinel lymph node procedure in the staging of non-metastatic colorectal cancer. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2020, 35, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noura, S.; Ohue, M.; Seki, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Idota, A.; Fujii, J.; Yamasaki, T.; Nakajima, H.; Murata, K.; Kameyama, M.; et al. Evaluation of the lateral sentinel node by indocyanine green for rectal cancer based on micrometastasis determined by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noura, S.; Ohue, M.; Seki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Motoori, M.; Kishi, K.; Miyashiro, I.; Ohigashi, H.; Yano, M.; Ishikawa, O.; et al. Feasibility of a lateral region sentinel node biopsy of lower rectal cancer guided by indocyanine green using a near-infrared camera system. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, R.A.; Anderson, M.; Wang, L.M.; Lindsey, I.; Cunningham, C.; Mortensen, N.J. Near-infrared (NIR) laparoscopy for intraoperative lymphatic road-mapping and sentinel node identification during definitive surgical resection of early-stage colorectal neoplasia. Surg. Endosc. 2012, 26, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handgraaf, H.J.; Boogerd, L.S.; Verbeek, F.P.; Tummers, Q.R.; Hardwick, J.C.; Baeten, C.I.; Frangioni, J.V.; van de Velde, C.J.; Vahrmeijer, A.L. Intraoperative fluorescence imaging to localize tumors and sentinel lymph nodes in rectal cancer. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2016, 25, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishigori, N.; Koyama, F.; Nakagawa, T.; Nakamura, S.; Ueda, T.; Inoue, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Obara, S.; Nakamoto, T.; Fujii, H.; et al. Visualization of Lymph/Blood Flow in Laparoscopic Colorectal Cancer Surgery by ICG Fluorescence Imaging (Lap-IGFI). Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23 (Suppl. S2), S266–S274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pas, M.H.; Ankersmit, M.; Stockmann, H.B.; Silvis, R.; van Grieken, N.C.; Bril, H.; Meijerink, W.J. Laparoscopic sentinel lymph node identification in patients with colon carcinoma using a near-infrared dye: Description of a new technique and feasibility study. J. Laparoendosc. Adv. Surg. Tech. 2013, 23, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, J.; Ota, M.; Suwa, Y.; Ishibe, A.; Masui, H.; Nagahori, K. Real-Time Indocyanine Green Fluorescence Imaging–Guided Complete Mesocolic Excision in Laparoscopic Flexural Colon Cancer Surgery. Dis. Colon Rectum 2016, 59, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garijo, P.D.; Sáez, O.M.; Caldera, M.; López, A.; Lacy, A.M.; de Lacy, F.B. Applications of indocyanine green fluorescence imaging in colorectal surgery: A narrative review. Ann. Laparosc. Endosc. Surg. 2022, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Satoyoshi, T.; Okita, K.; Kyuno, D.; Hamabe, A.; Okuya, K.; Nishidate, T.; Akizuki, E.; Ishii, M.; Yamano, H.-O.; et al. Snapshots of lymphatic pathways in colorectal cancer surgery using near-infrared fluorescence, in vivo and ex vivo. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 3130–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakizoe, M.; Watanabe, J.; Suwa, Y.; Nakagawa, K.; Suwa, H.; Ozawa, M.; Ishibe, A.; Masui, H.; Nagahori, K. The histopathological evaluation based on the indocyanine green fluorescence imaging of regional lymph node metastasis of splenic flexural colon cancer by near-infrared observation. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Ushijima, H.; Kawamura, J. Lymphatic flow mapping during colon cancer surgery using indocyanine green fluorescence imaging. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied Technol. 2023, 32, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Article | Study Type | Assessment Tool | Bias Domains Assessed | Overall Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daan J. Sikkenk et al. [17] | Prospective Pilot Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Zeeshan Ahmed et al. [18] | Prospective Cohort Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Hokuto Ushijima et al. [24] | Observational Study | JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist for Case Series | Inclusion Criteria, Outcome Measurement, Consecutive Participants, Demographics, Statistical Analysis | Moderate |
| Weiyang Lin et al. [19] | Prospective Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Bianca Maria Sollazzo et al. [20] | Non-Randomized Prospective Pilot Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Gyung Mo Son et al. [21] | Non-Randomized Cohort Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Xiaochuang Feng et al. [25] | Retrospective Study | NOS | Selection, Comparability, Outcome | Moderate |
| Gyung Mo Son et al. [22] | Prospective Case–Control Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Hiromitsu Kinoshita et al. [23] | Prospective Study | ROBINS-I | Confounding, Selection, Classification, Deviations, Missing Data, Outcome Measurement, Reported Results | Moderate |
| Article | Year | Country | Study Design | Surgical Intervention | Tracer | Number of Participants | Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daan J. Sikkenk et al. [17] | 2023 | The Netherland | Prospective | Robot-assisted | ICG | 10 | cT1-2N0M0 |
| Zeeshan Ahmed et al. [18] | 2023 | India | Prospective cohort | Laparoscopic/ Open | ICG | 48 | T1-4aN0-2b |
| Hokuto Ushijima et al. [24] | 2020 | Japan | Prospective cohort | Laparoscopic | ICG | 57 | Any stage |
| Weiyang Lin et al. [19] | 2024 | China | Prospective | Not mentioned | ICG and Nanocarbon | 30 | Any stage |
| Bianca Maria Sollazzo et al. [20] | 2020 | Italy | Prospective | Laparoscopic | ICG | 20 | Any stage Right-sided colon cancer |
| Gyung Mo Son et al. [21] | 2024 | South Korea | Unclear | Laparoscopic | ICG | 218 | Any stage Right-sided colon cancer |
| Xiaochuang Feng et al. [25] | 2021 | China | Retrospective | Laparoscopic | ICG | 143 | Any stage Right-sided colon cancer |
| Gyung Mo Son et al. [22] | 2023 | South Korea | Prospective | Laparoscopic | ICG | 291 | Any stage Right-sided colon cancer |
| Hiromitsu Kinoshita et al. [23] | 2023 | Japan | Prospective | Laparoscopic | ICG | 56 | Any stage |
| Article | Intervention Description | Surgical Technique | Additional Notes | Detection Rate | Sensitivity | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daan J. Sikkenk et al. [17] | Robot assisted SLNi with submucosal ICG | Segmental colectomy | SLNs ultra staged with IHC | 100% SLN detection | High | None |
| Zeeshan Ahmed et al. [18] | Colonoscopic ICG injection during surgery | Laparoscopic/open resection | Separate protocols for laparoscopic and open injections | 93.75% SLN detection | 77.77%; higher for T1-2 | Four false negative SLNs |
| Hokuto Ushijima et al. [24] | Lymphatic flow visualization with ICG imaging | Laparoscopic resections | Real-time imaging used to guide resection | A 75.4% lymphatic flow visualization | Higher in early stage cancer | None |
| Weiyang Lin et al. [19] | Comparison of ICG vs. nanocarbon | Standard colon surgery | Dual tracers analyzed for node detection | Varied (ICG superior to nanocarbon) | ICG Strong correlation with metastasis | None |
| Bianca Maria Sollazzo et al. [20] | Fluorescence guided D3 lymphadenectomy | CME with CVL | Intraoperative changes made based on lymphatic flow visualization | A 55% higher incidence of lymph node metastasis | Improved compared to non ICG | None |
| Gyung Mo Son et al. [21] | FLNM using ICS for real-time visualization | Laparoscopic right colectomy | FLNM performed after endoscopic submucosal ICG injection | Improved detection of D3 nodes | High for D3 LN staging | None |
| Xiaochuang Feng et al. [25] | Preoperative ICG tattooing | SMA oriented colectomy | Mapping includes anterior/posterior to SMA lymph nodes | 81.5% mapping of SMA-related lymph node | Variable | None |
| Gyung Mo Son et al. [22] | FLNM for improved DT dissection | Laparoscopic right colectomy | Enhanced oncological dissection using ICG | 50% increase in harvested D3 nodes | High for metastatic nodes | None |
| Hiromitsu Kinoshita et al. [23] | Real-time ICG | CME with CVL | Lymphatic flow patterns to optimize dissection | 20.9% cases showed ICG beyond standard dissection | High | None |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negrut, R.L.; Cote, A.; Feder, B.; Bodog, F.D.; Maghiar, A.M. Enhanced Lymph Node Detection in Colon Cancer Using Indocyanine Green Fluorescence: A Systematic Review of Studies from 2020 Onwards. J. Pers. Med. 2025, 15, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15020054
Negrut RL, Cote A, Feder B, Bodog FD, Maghiar AM. Enhanced Lymph Node Detection in Colon Cancer Using Indocyanine Green Fluorescence: A Systematic Review of Studies from 2020 Onwards. Journal of Personalized Medicine. 2025; 15(2):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15020054
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegrut, Roxana Loriana, Adrian Cote, Bogdan Feder, Florian Dorel Bodog, and Adrian Marius Maghiar. 2025. "Enhanced Lymph Node Detection in Colon Cancer Using Indocyanine Green Fluorescence: A Systematic Review of Studies from 2020 Onwards" Journal of Personalized Medicine 15, no. 2: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15020054
APA StyleNegrut, R. L., Cote, A., Feder, B., Bodog, F. D., & Maghiar, A. M. (2025). Enhanced Lymph Node Detection in Colon Cancer Using Indocyanine Green Fluorescence: A Systematic Review of Studies from 2020 Onwards. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 15(2), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpm15020054






