Optical Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation, Emitted by Particles or Stars Moving near Supermassive Black Hole
Abstract
:1. Introduction
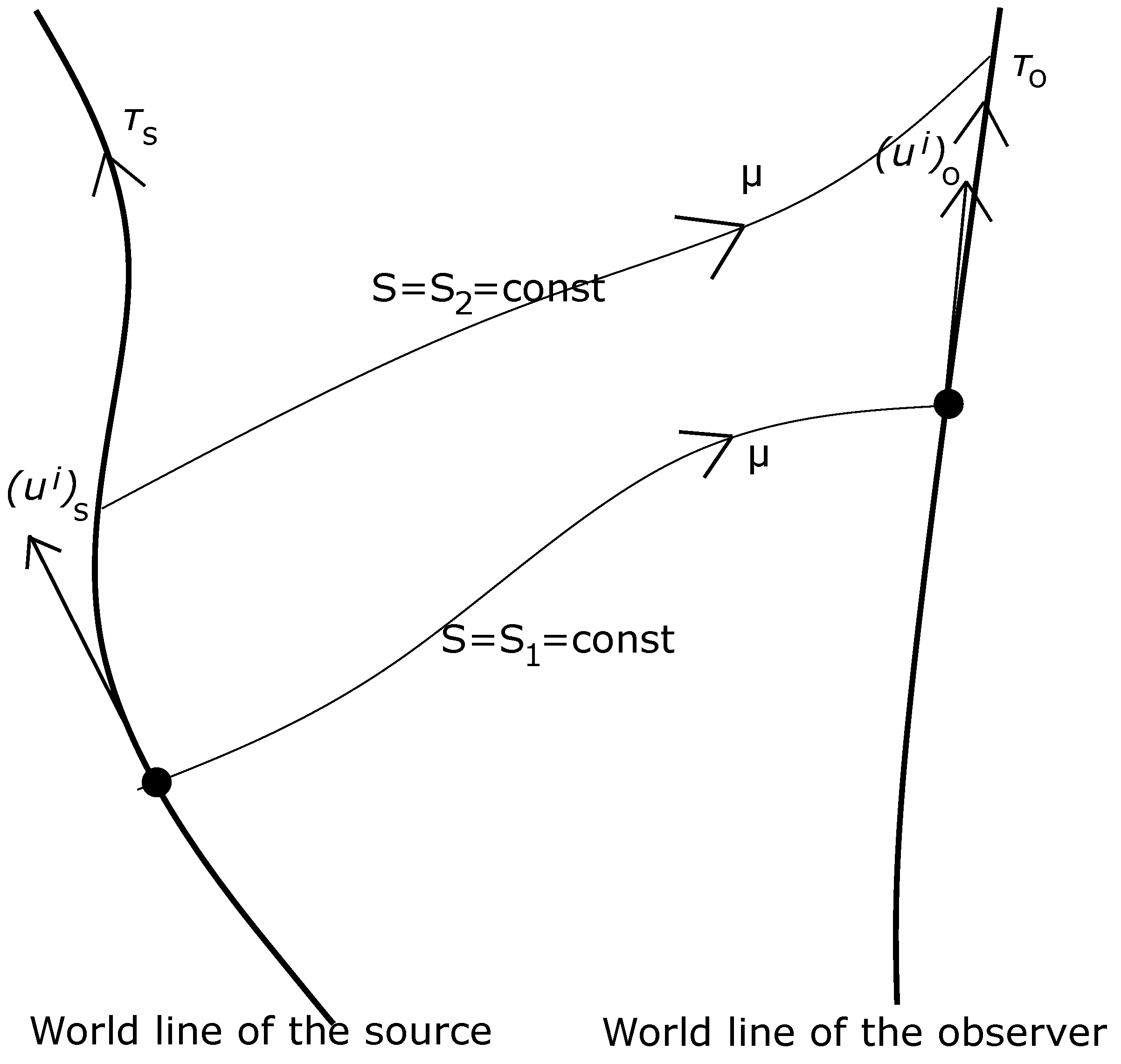
2. Geometrical Optics
3. Redshift of the Spectrum of Electromagnetic Radiation
4. Luminous Intensity
5. Polarization Plane
6. Inverse Problem
6.1. General Approaches
6.2. Reconstruction of the Motion of the Source Using Redshift and Luminous Intensity
6.3. Reconstruction of the Motion of the Components of a Binary Star That Moves in the Vicinity of a Black Hole
- —orbital inclination is the angle between the picture plane and the plane of the orbit;
- —pericentre longitude, counted along the orbital plane;
- —position angle, counted along the picture plane.
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, B.P.; Abbott, R.; Abbott, T.D.; Abernathy, M.R.; Acernese, F.; Ackley, K.; Adams, C.; Adams, T.; Addesso, P.; Adhikari, R.X.; et al. Tests of general relativity with gw150914. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 221101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.-K.; Ball, D.; Baloković, M.; Barrett, J.; et al. First M87 event horizon telescope results. I. the shadow of the supermassive black hole. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.11238. [Google Scholar]
- The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration; Akiyama, K.; Alberdi, A.; Alef, W.; Asada, K.; Azulay, R.; Baczko, A.-K.; Ball, D.; Baloković, M.; Barrett, J.; et al. First M87 event horizon telescope results. iv. imaging the central supermassive black hole. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 875, L4. [Google Scholar]
- Westphal, T.; Hepach, H.; Pfaff, J.; Aspelmeyer, M. Measurement of gravitational coupling between millimetre-sized masses. Nature 2021, 591, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuchlík, Z.; Kološ, M. Acceleration of the charged particles due to chaotic scattering in the combined black hole gravitational field and asymptotically uniform magnetic field. Eur. Phys. J. C 2016, 76, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biteau, J.; Prandini, E.; Costamante, L.; Lemoine, M.; Padovani, P.; Pueschel, E.; Resconi, E.; Tavecchio, A.; Taylor, A.; Zech, A. Progress in unveiling extreme particle acceleration in persistent astrophysical jets. Nat. Astron. 2020, 4, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruffini, R.; Rueda, J.A.; Moradi, R.; Wang, Y.; Xue, S.S.; Becerra, L.; Bianco, C.L.; Chen, Y.C.; Cherubini, C.; Vereshchagin, G.V.; et al. The inner engine of gev-radiation-emitting gamma-ray bursts. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.01839v4. [Google Scholar]
- Genzel, R.; Eisenhauer, F.; Gillessen, S. The galactic center massive black hole and nuclear star cluster. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 3121–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillessen, S.; Plewa, P.M.; Eisenhauer, F.; Sari, R.E.; Waisberg, I.; Habibi, M.; Pfuhl, O.; George, E.; Dexter, J.; Genzel, R.; et al. An update on monitoring stellar orbits in the galactic center. Astrophys. J. 2017, 837, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsa, M.; Eckart, A.; Shahzamanian, B.; Karas, V.; Zajaček, M.; Zensus, J.A.; Straubmeier, C. Investigating the relativistic motion of the stars near the supermassive black hole in the galactic center. Astrophys. J. 2017, 845, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, S.; Lu, J.R.; Sakai, S.; Gautam, A.K.; Do, T.; Hosek, M.W.; Service, M.; Ghez, A.M.; Gallego-Cano, E.; Matthews, K. The galactic center: Improved relative astrometry for velocities, accelerations, and orbits near the supermassive black hole. Astrophys. J. 2019, 873, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuter, R.; Amorim, A.; Anugu, N.; Bauböck, M.; Benisty, M.; Berger, J.P.; Blind, N.; Bonnet, H.; Brandner, W.; Buron, A.; et al. Detection of the gravitational redshift in the orbit of the star S2 near the galactic centre massive black hole. Astron. Astrophys. 2018, 615, L5. [Google Scholar]
- Abuter, R.; Amorim, A.; Bauböck, M.; Berger, J.P.; Bonnet, H.; Brandner, W.; Cardoso, V.; Clénet, Y.; de Zeeuw, P.T.; Zins, G.; et al. Detection of the schwarzschild precession in the orbit of the star S2 near the galactic centre massive black hole. Astron. Astrophys. 2020, 636, L5. [Google Scholar]
- Iorio, L. Post-keplerian effects on radial velocity in binary systems and the possibility of measuring general relativity with the star S2 in 2018. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2017, 472, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peibker, F.; Eckart, A.; Parsa, M. S62 on a 9.9 yr orbit around Sgr A*. Astrophys. J. 2020, 889, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Paumard, T.; Grould, M.; Vincent, F.H.; Perrin, G. General relativistic effects on the orbit of the s2 star with gravity. Astron. Astrophys. 2017, 608, A60. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Q. On testing the Kerr metric of the massive black hole in the Galactic Center via stellar orbital motion: Full general relativistic treatment. Astrophys. J. 2015, 809, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Angélil, R.; Saha, P.; Merritt, D. Toward relativistic orbit fitting of galactic center stars and pulsars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 720, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Saha, P. Probing the spinning of the massive black hole in the Galactic Center via pulsar timing: A full relativistic treatment. Astrophys. J. 2017, 849, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grasso, M.; Korzyński, M.; Serbenta, J. Geometric optics in general relativity using bilocal operators. Phys. Rev. D 2019, 99, 064038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, T. Equivalence of Gibbons-Werner method to geodesics method in the study of gravitational lensing. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 044043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gralla, S.E.; Lupsasca, A. Lensing by Kerr black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 044031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gralla, S.E.; Lupsasca, A. Null geodesics of the Kerr exterior. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 044032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsiao, Y.-W.; Lee, D.-S.; Lin, C.-Y. Equatorial light bending around Kerr–Newman black holes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 064070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korzyński, M.; Villa, E. Geometric optics in relativistic cosmology: New formulation and a new observable. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 063506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Angelil, R.; Saha, P. Relativistic redshift effects and the galactic-center stars. Astrophys. J. 2010, 711, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Creighton, T.; Price, R.H.; Jenet, F.A. Strong field effects on pulsar arrival times: General orientations. Astrophys. J. 2009, 705, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stovall, K.; Creighton, T.; Price, R.H.; Jenet, F.A. Observability of pulsar beam bending by the Sgr A* black hole. Astrophys. J. 2012, 744, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, S.O. Observability time for the pulsar that is moves in external strong gravitational field. J. Belarusian State Univ. Phys. 2018, 2, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Stephani, H. 21.3 Electrodynamics in vacuo. In Relativity: An Introduction to Special and General Relativity, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004; pp. 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Tarasenko, A. Reconstruction of a compact object motion in the vicinity of a black hole by its electromagnetic radiation. Phys. Rev. D 2010, 81, 123005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misner, C.W.; Thorne, K.S.; Wheeler, J.A. §32.1 Relevance of Schwarzschild Geometry. In Gravitation; W. H. Freeman and Company: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1973; pp. 842–843. [Google Scholar]
- Korn, G.A.; Korn, T.M. 21.6 Elliptic Functions, Elliptic Integrals and Related Functions. In Mathematical Handbook for Scientists and Engineers; Definitions, Theorems and Formulas; for Reference and Review; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA; San Francisco, CA, USA; Toronto, ON, Canada; London, UK; Sidney, Australia, 1968; pp. 827–847. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasechar, S. The Mathematical Theory of Black Holes; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. 131–141. [Google Scholar]
- Santana, L.T.; Lobato, J.C.; Matos, I.S.; Calvão, M.O.; Reis, R.R. Evolution of the electric field along null rays for arbitrary observers and spacetimes. Phys. Rev. D 2020, 101, 081501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hastings, W.K. Monte carlo sampling methods using markov chains and their applications. Biometrica 1970, 57, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisnovatyi-Kogan, G.S.; Tsupko, O.Y. Strong gravitational lensing by schwarzschild black holes. Astrophysics 2008, 51, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komarov, S.; Gorbatsievich, A. Reconstruction of relative motion of a binary star in the vicinity of black hole by its redshift. Int. J. Mod. Phys. A 2020, 35, 2040052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitskievich, V.N.; Efremov, A.P.; Nesterov, A.I. Dynamics of Fields in General Relativity; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1985; pp. 115–129. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Fortini, P.; Gualdi, C. Fermi normal co-ordinate system and electromagnetic detectors of gravitational waves. Nuovo Cimento 1982, 71, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komarov, S.; Gorbatsievich, A.; Tarasenko, A. Redshift of a compact binary star in the neighborhood of a supermassive black hole. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 2015, 50, 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepaschuck, A.M. Close Binary Stars; Fizmatlit: Moscow, Russia, 2013; pp. 50–123. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komarov, S. Optical Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation, Emitted by Particles or Stars Moving near Supermassive Black Hole. Galaxies 2021, 9, 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030057
Komarov S. Optical Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation, Emitted by Particles or Stars Moving near Supermassive Black Hole. Galaxies. 2021; 9(3):57. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomarov, Stanislav. 2021. "Optical Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation, Emitted by Particles or Stars Moving near Supermassive Black Hole" Galaxies 9, no. 3: 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030057
APA StyleKomarov, S. (2021). Optical Characteristics of Electromagnetic Radiation, Emitted by Particles or Stars Moving near Supermassive Black Hole. Galaxies, 9(3), 57. https://doi.org/10.3390/galaxies9030057




