Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
3. Results
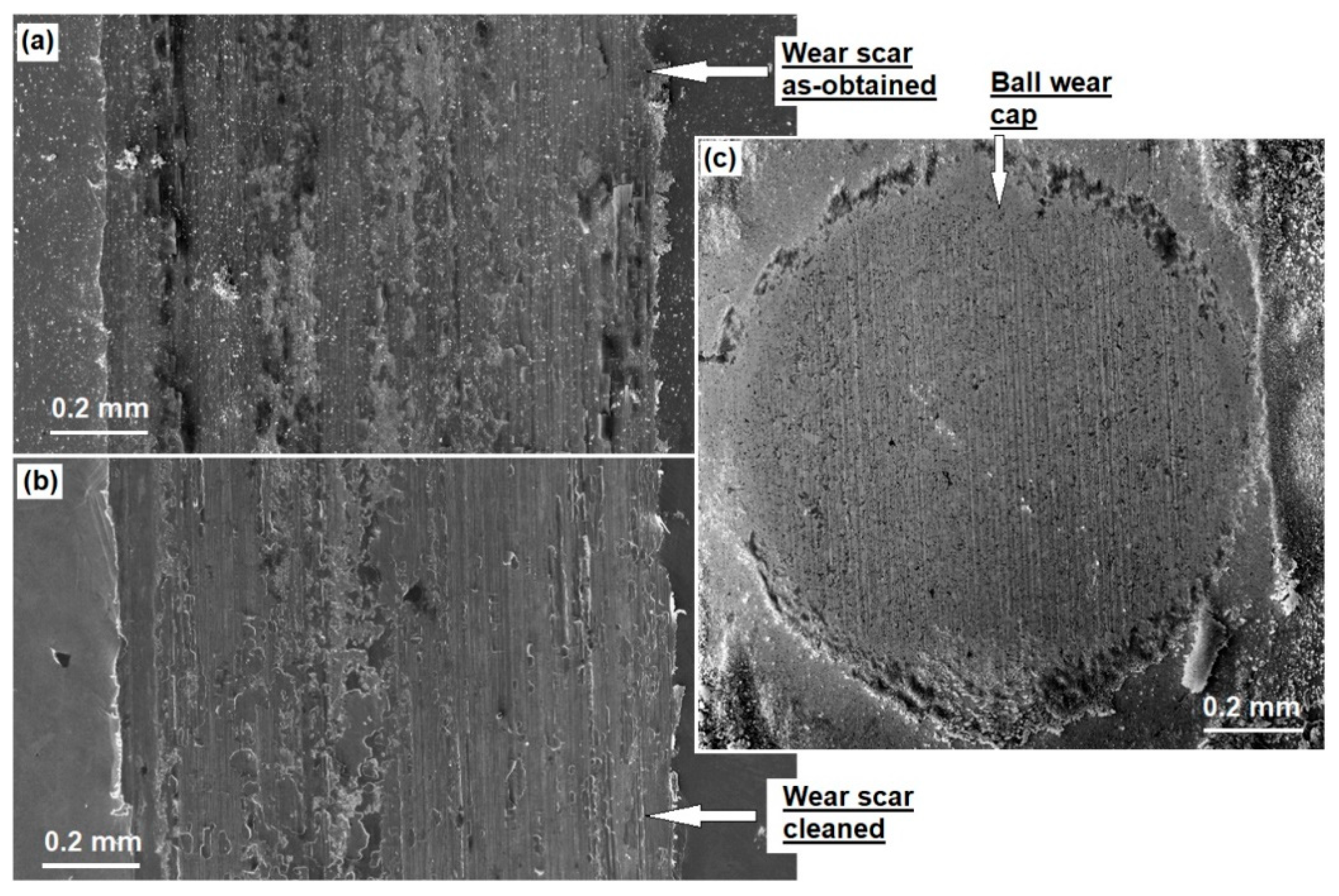
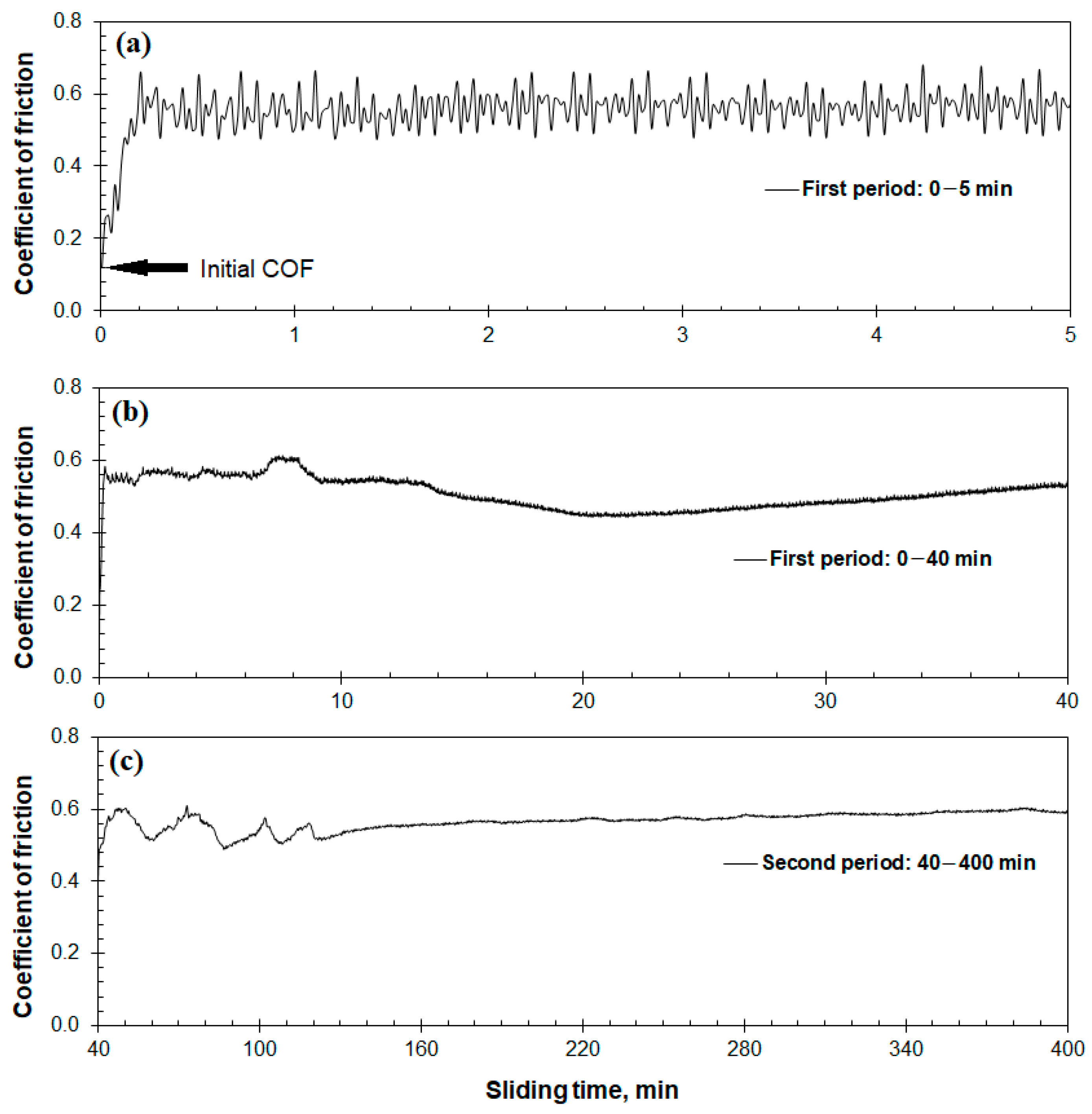
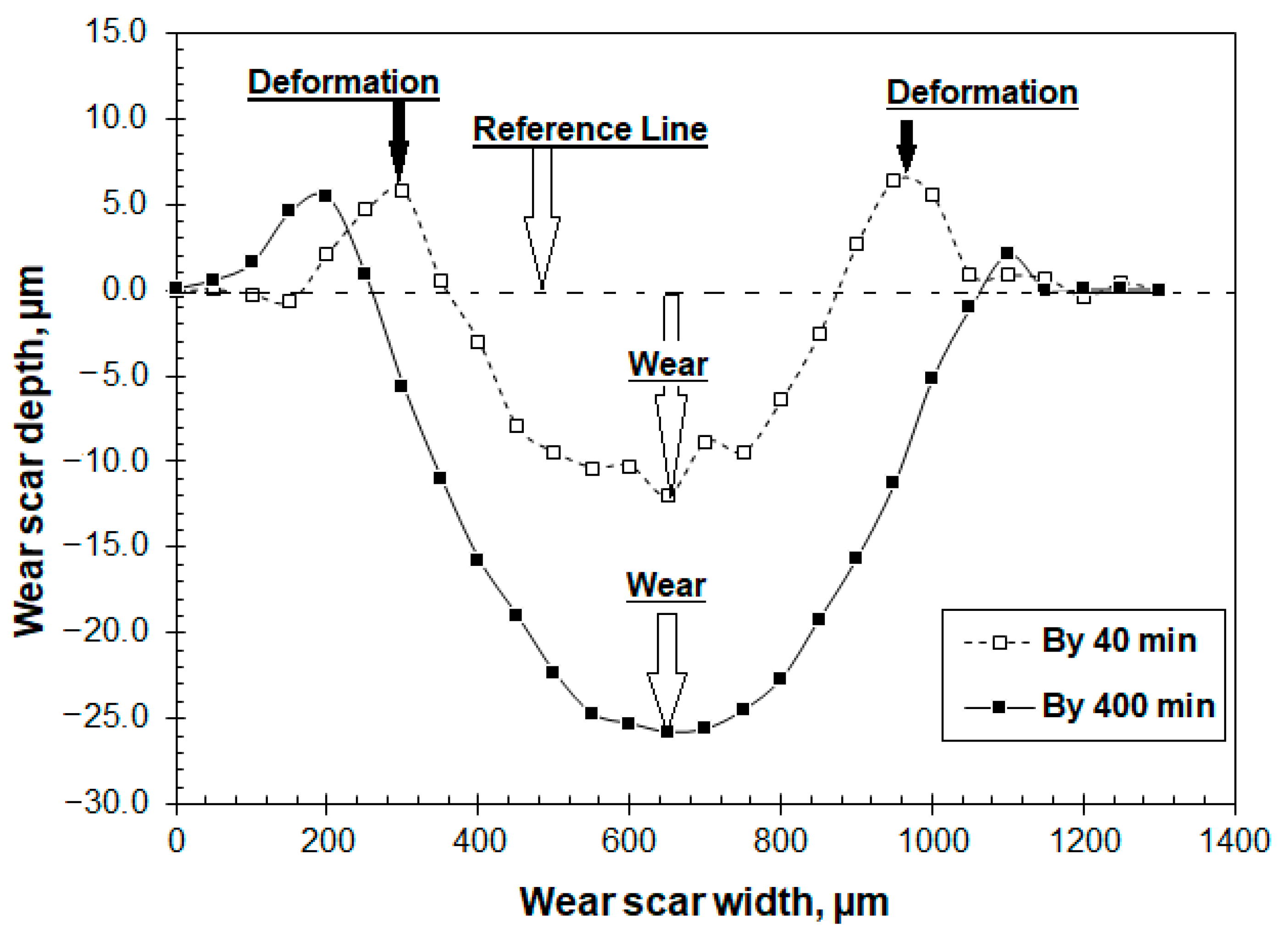
3.1. The Friction and Wear Properties
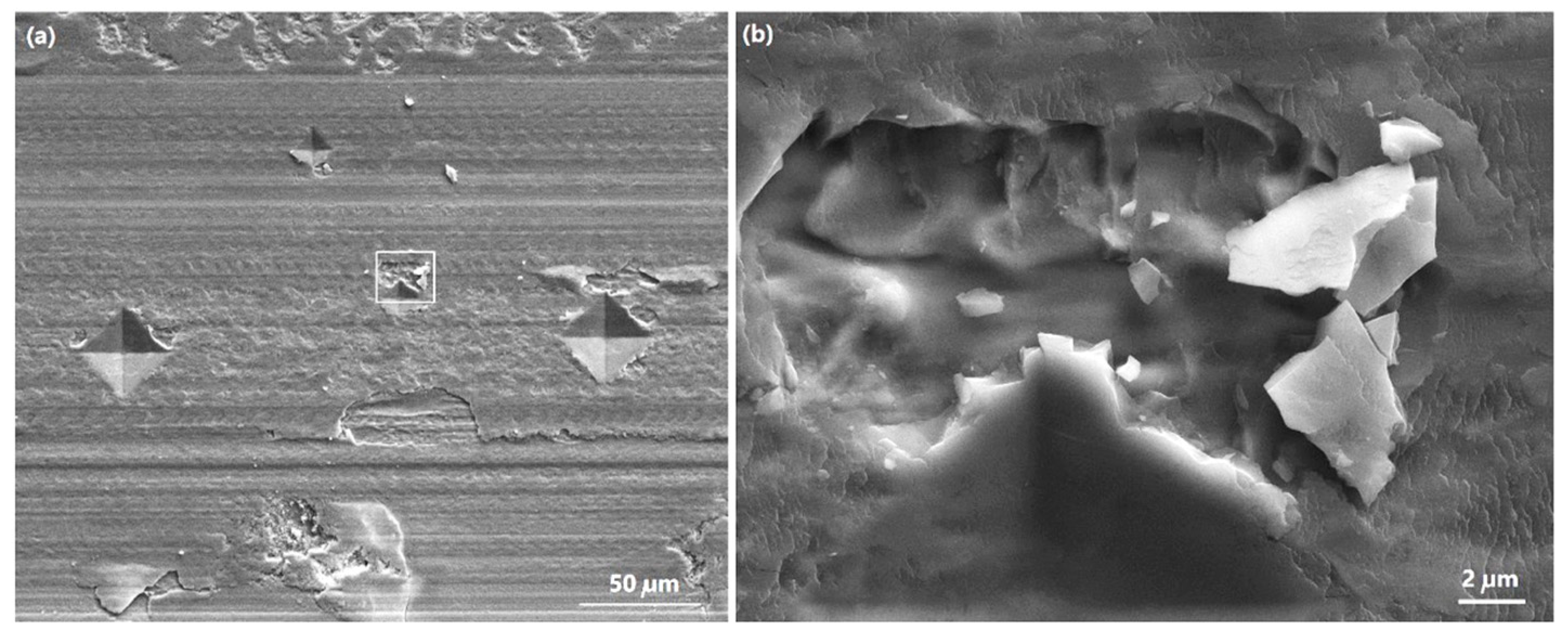
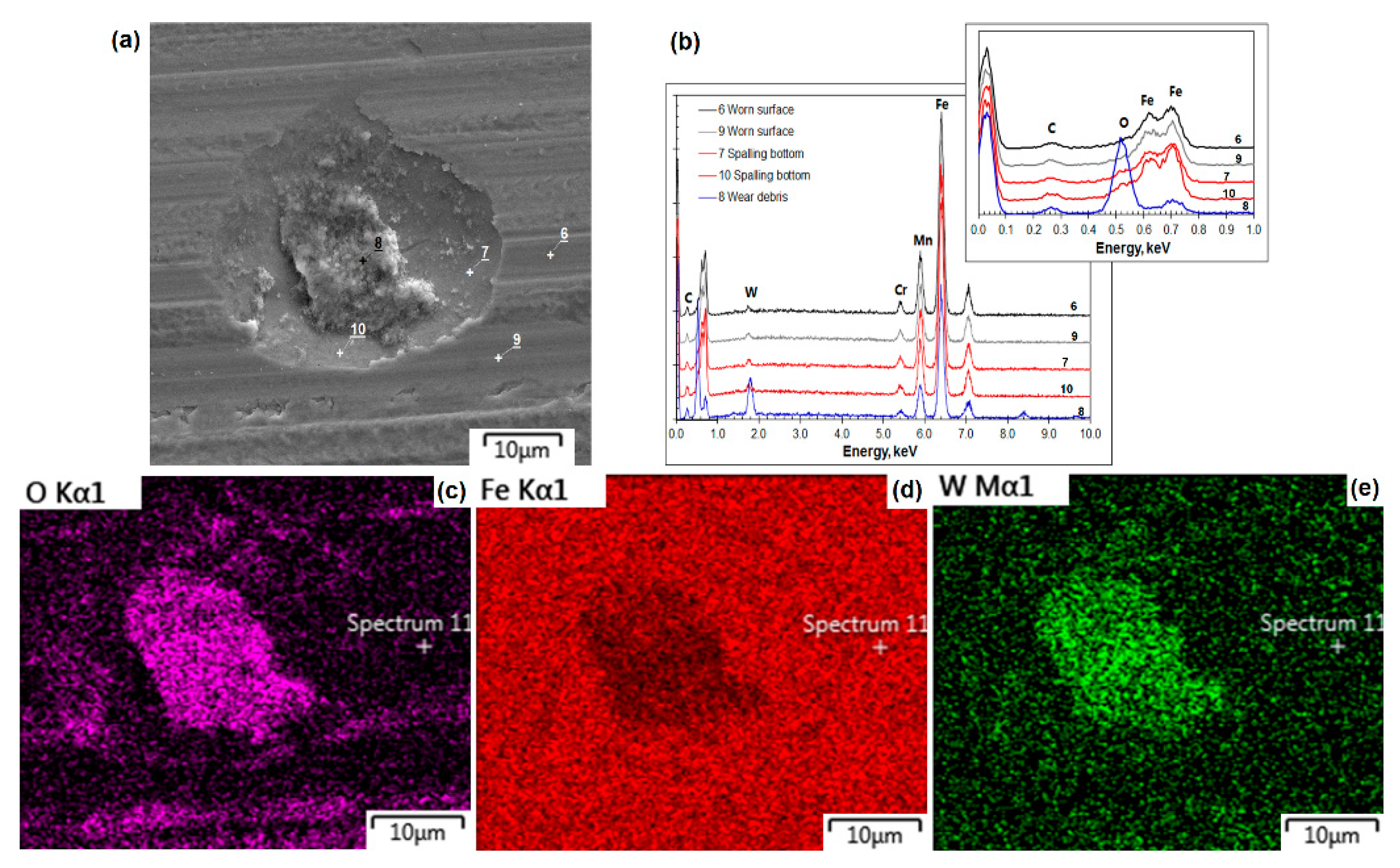
3.2. SEM and EDX Analyses of Worn Surfaces
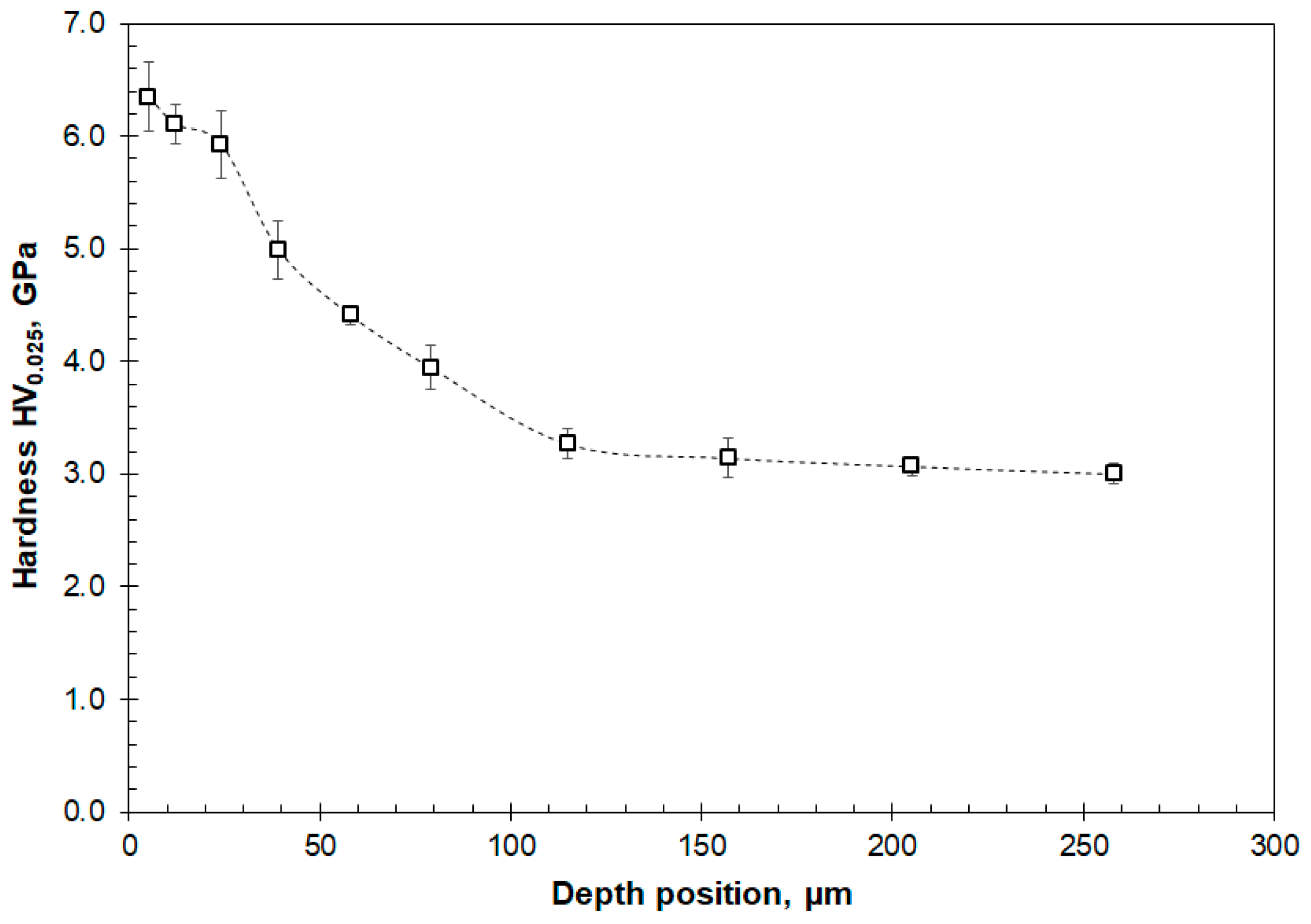
3.3. Cross-Sectional SEM, Microhardness and TEM Analyses of Worn Surfaces
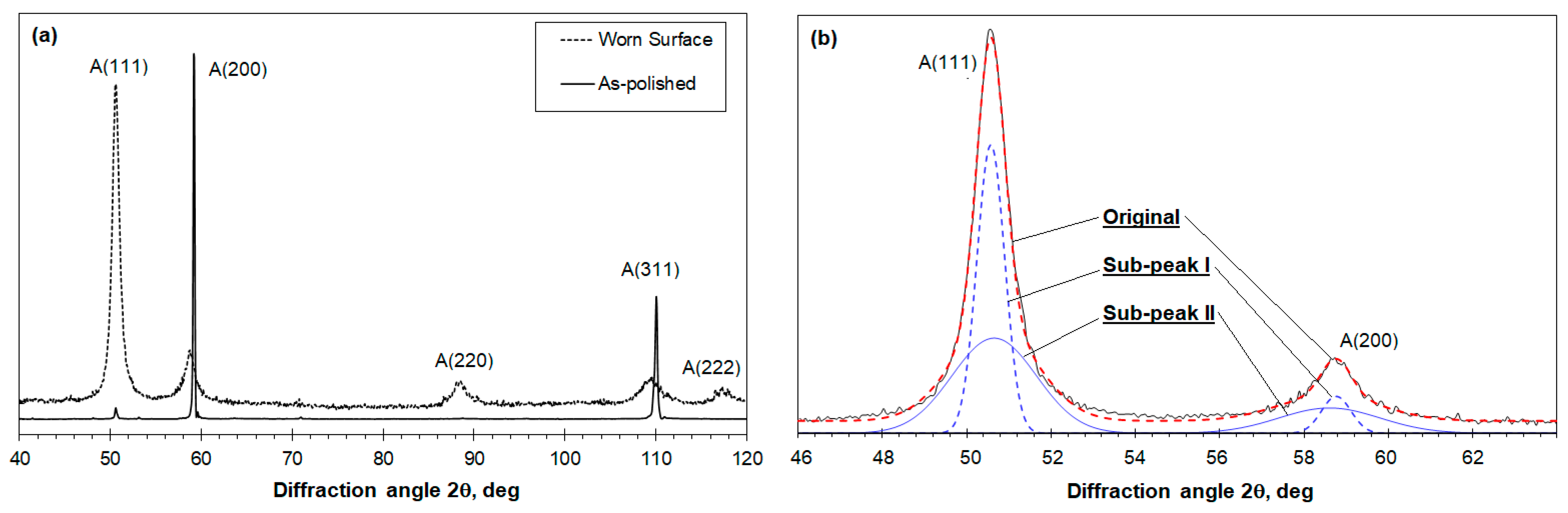
3.4. X-ray Diffraction Analyses of Worn Surfaces
4. Discussion
4.1. The Friction and Wear Properties of Hadfield Steel
4.2. Sliding-Induced Microstructure Evolution and Strain Hardening
4.3. Spalling Wear and Its Relation to the Sliding-Induced Surface Embrittlement
5. Conclusions
- The Hadfield steel showed a coefficient of wear in the scale of 10−14 m3·N−1·m−1 and a coefficient of friction of 0.5–0.6.
- The steel still retained its austenitic structure in the sliding wear without any detectable evidence of deformation-induced martensite transformation.
- The steel encountered severe plastic deformation beneath the worn surface. The deformation led to significant work hardening and surface embrittlement. Deformation-induced spalling wear was found as the predominant wear mechanism. Tribo-oxidation was also observed in the resultant wear debris.
- The surface embrittlement and spalling wear was associated with the deformation-induced nano-heterogeneous microstructure including nano-laminate, nanotwins, and nanocrystalline beneath the worn surface.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gauzzi, F.; Rossi, M.; Verdini, B. Cold-Working induced martensitic transformation in 12 percent Mn austenitic steel (Hadfield steel). Metall. Ital. 1971, 63, 555. [Google Scholar]
- Tweedale, G.; Paton, W.D.M. Sir Robert Abbott Hadfield F.R.S (1858–1940) and the discovery of manganese steel, Notes and Records. R. Soc. J. Hist. Sci. 1985, 40, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Dastur, Y.N.; Leslie, W.C. Mechanism of work-hardening in Hadfield manganese steel. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.P.; Wang, W.Y.; Li, J.W.; Wang, A.Q.; Zhao, Y.R.; Li, L.L. Wear Resistant Austenitic Manganese Steels; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Harzallah, R.; Mouftiez, A.; Felder, E.; Harriri, S.; Maujean, J.P. Rolling contact fatigue of Hadfield steel X120Mn12. Wear 2010, 269, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, R.; Das, S.; Das, K. Effect of thermo-mechanical processing on the low impact abrasion and low stress sliding wear resistance of austenitic high manganese steels. Wear 2019, 420, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, F.; Zhu, R.; Lei, T. On the impact abrasive wear of super-high manganese steel. Acta Metall. Sinica 1999, 35, 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, C.; Song, R.; Liu, S.; Feng, Y.; Pei, Z. Wear behaviour and subsurface layer work hardening mechanism of Fe-24. 1Mn-1.21C-0.48Si steel. Procedia Eng. 2017, 207, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, P.C.; Pereira, J.I.; Sinatora, A. Abrasive wear of austenitic manganese steels via jaw crusher test. Wear 2021, 476, 203726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, P.C.; Pereira, J.I.; Sinatora, A. Subsurface microstructural dynamic recrystallization in multiscale abrasive wear. Wear 2021, 486–487, 204111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiou, C.; Sehitoglu, H. Strain hardening and heterogeneous deformation during twinning in Hadfield steel. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 1479–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allende-Seco, R.; Artigas, A.; Bruna, H.; Carvajal, L.; Monsalve, A.; Sklate-Boja, M.F. Hardening by Transformation and Cold Working in a Hadfield Steel Cone Crusher Liner. Metals 2021, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychagin, D.V.; Filippov, A.V.; Novitskaya, O.S.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kolubaev, E.A.; Lychagina, L.L. Deformation of Hadfield steel single crystals by dry sliding friction with the normal load/friction force orientations []/[10] and []/[001]. Tribo. Int. 2020, 147, 106284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lychagin, D.V.; Filippov, A.V.; Novitskaya, O.S.; Kolubaev, A.V.; Moskvichev, E.N.; Fortuna, S.V.; Chumlyakov, Y.I. Deformation and wera of Hadfield steel single crystals under dry sliding friction. Wear 2022, 488–489, 204126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lv, B.; Wang, T.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, M.; Luo, H.; Liu, H. Microstructure and properties of purity high Mn steel crossing explosion hardened. ISIJ Int. 2008, 48, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, W.; Fang, L.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y. Effect of surface nanocrystallization on abrasive wear properties in Hadfield steel. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2007, 41, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Fang, L.; Sun, K.; Xu, Y. Effect of surface hardening on wear behaviour of Hadfield steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2007, 460–461, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, I.A.; Datta, P.K.; Du, H.L.; Burnell-Gray, J.S.; Pierzgalski, S.; Luo, Q. Studies of high temperature sliding wear of metallic dissimilar interfaces. Tribo Int. 2005, 38, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.G.; Yin, C.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Tang, S.H. Lowering the coefficient of martensitic steel by forming a self-lubricating layer in dry sliding wear. Mater. Res. Exp. 2019, 6, 055024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Li, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Kitchen, M.; Bowen, L.; Farmilo, N.; Ding, Y. Sliding wear of medium-carbon bainitic/martensitic/austenitic steel treated by short-term low-temperature austempering. Wear 2021, 476, 203732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Deng, X.; Wang, Z. Friction behaviour and self-lubricating mechanism of low alloy martensitic steel during reciprocating sliding. Wear 2021, 482–483, 203972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.H.; Liang, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, M.; Long, S.L. Formation of nano-laminated structures in a dry sliding wear induced layer under different wear mechanisms of 20CrNi2Mo steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 423, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.S.; Li, S.X.; Gao, Q.Y.; Jiang, H.; Lu, S.Y.; Yu, F.; Shu, X.D. Evolution of nano-laminated structure formed by the thermally-assisted plastic deformation in dry sliding wear. Tribo Int. 2019, 140, 105846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariff, S.M.; Pal, T.K.; Padmanabham, G.; Joshi, S.V. Comparative study on dry sliding wear behaviour of various railroad steels. Trans. ASME J. Tribo 2011, 133, 021602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korshunov, L.G.; Chernenko, N.L. Effect of aluminium on the structural transitions and the wear resistance of Hadfield steel under friction. Phys. Met. Metall. 2018, 119, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lv, B.; Ma, H.; Sun, D.; Zhang, F. Wear behaviour and the corresponding work hardening characteristics of Hadfield steel. Tribo Int. 2018, 121, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. A modified X-ray diffraction method to measure residual normal and shear stresses of machined surfaces. Int. J. Adv. Manufact. Technol. 2022, 119, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullity, B.D.; Stock, S.R. Elements of X-ray Diffraction; Pearson Education Ltd.: Harlow, UK, 2014; p. 379. [Google Scholar]
- Lahrman, D.F.; Field, R.D.; Darolia, R.; Fraser, H.L. Investigation of techniques for measuring lattice mismatch in a rhenium containing nickel based superalloy. Acta Metall. 1988, 36, 1309–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, D.; Gilles, R.; Barbier, B.; Del Genovese, D.; Hasse, B.; Strunz, P.; Wroblewski, T.; Fuess, H.; Rösler, J. Lattice misfit measurement in Inconel 706 containing coherent γ’ and γ” precipitates. Scrip. Mater. 2003, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Chi, K.; Li, S.; Barnard, P. Microstructural Stability and Lattice Misfit Characterisations of Nimonic 263. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 Pressure Vessels & Piping Division Conference (PVP2012), Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 July 2012; Volume 6, PTS A & B. pp. 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q. A new XRD method to quantify plate and lath martensites of hardened medium-carbon steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 2170–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Q. Characterization of short-range ordered domains using quantitative X-ray diffraction. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. Lett. 2018, 10, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Oluwafemi, O.; Kitchen, M.; Yang, S. Tribological properties and wear mechanisms of DC pulse plasma nitrided austenitic stainless steel in dry reciprocating sliding tests. Wear 2017, 376–377, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, E.A.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Mostafa, A.; Abdel-Rahman, M. Determination of the crystallite size and micro-strain by novel method from XRD profile. Appl. Phys. 2019, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Shafi, P.M.; Bose, A.C. Impact of crystalline defects and size on X-ray line broadening: A phenomenological approach for tetragonal SnO2 nanocrystals. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 057137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q. Electron microscopy and spectroscopy in the analysis of friction and wear mechanisms. Lubricants 2018, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Q. Origin of friction in running-in sliding wear of nitride coatings. Tribo Lett. 2010, 37, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Lv, B.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, M.; Yang, S.; Yan, Z. Failure mechanism and worn surface microstructure of high manganese steel and bainite steel crossings. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2008, 44, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emurlaev, K.; Gerasimenko, T.; Abdimazhan, D. Nondestructive evaluation of material state near the friction interface under dry sliding. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 1526–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.M.; Polycarpou, A.A. Wear of conventional pearlitic and improved bainitic steels. Wear 2005, 259, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Mei, H.J.; Kitchen, M.; Gao, Y.; Bowen, L. Effect of short-term low-temperature austempering on the microstructure and abrasive wear of medium-carbon low-alloy stee. Met. Mater. Int. 2021, 27, 3115–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Method | C * | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OES | 1.29 ± 0.01 | 17.93 ± 0.06 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.01 ± 0.00 | 1.87 ± 0.01 | In balance |
| EDX | 1.29 ± 0.01 | 17.88 ± 0.18 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 1.43 ± 0.04 | In balance |
| Time Period | Volume Loss [10−12 m3] | Wear Coefficient [10−16 m3·N−1·m−1] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | WC | Steel | WC | |
| 0–40 min | 20.3 ± 2.6 | 1.2 ± 0.3 | 275.1 ± 35.5 | 15.5 ± 3.5 |
| 40–400 min | 83.7 ± 5.0 | 6.2 ± 1.0 | 126.3 ± 6.8 | 9.1 ± 1.4 |
| 0–400 min | 104.0 ± 5.0 | 7.3 ± 1.0 | 141.2 ± 6.8 | 9.7 ± 1.4 |
| Property | Position | Mean | Stdev | Diffraction Peak | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A(111) | A(200) | A(220) | A(311) | A(222) | |||||
| β, deg | Bulk | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.27 | |||
| Worn surface | I | 1.22 | 0.45 | 0.80 | 0.85 | 1.17 | 1.91 | 1.38 | |
| II | 3.33 | 0.75 | 2.33 | 2.81 | 3.55 | 4.19 | 3.76 | ||
| ε, % | Bulk | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.23 | 0.15 | 0.07 | |||
| Worn surface | I | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.73 | 0.93 | 0.52 | 0.59 | 0.37 | |
| II | 1.34 | 0.57 | 2.15 | 0.66 | 1.59 | 1.29 | 0.99 | ||
| t, nm | Bulk | 49 | 11 | 38 | 50 | 59 | |||
| Worn surface | I | 11 | 2 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 8 | 12 | |
| II | 3 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, Q.; Zhu, J. Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding. Lubricants 2022, 10, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037
Luo Q, Zhu J. Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding. Lubricants. 2022; 10(3):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Quanshun, and Jingzhi Zhu. 2022. "Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding" Lubricants 10, no. 3: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037
APA StyleLuo, Q., & Zhu, J. (2022). Wear Property and Wear Mechanisms of High-Manganese Austenitic Hadfield Steel in Dry Reciprocal Sliding. Lubricants, 10(3), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants10030037






