Synergistic Lubrication Mechanism of Nano-Fluid and Grinding Wheel Prepared by CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and Characterization of CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules
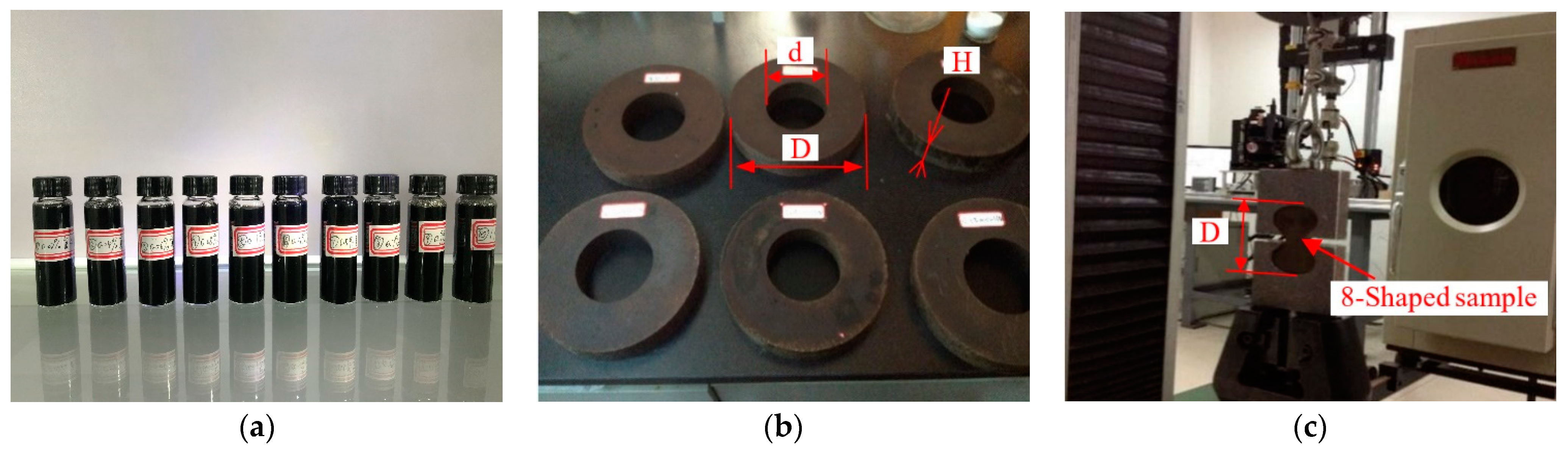
2.2. Preparation of Nanofluids and Nano-Capsule Grinding Wheels
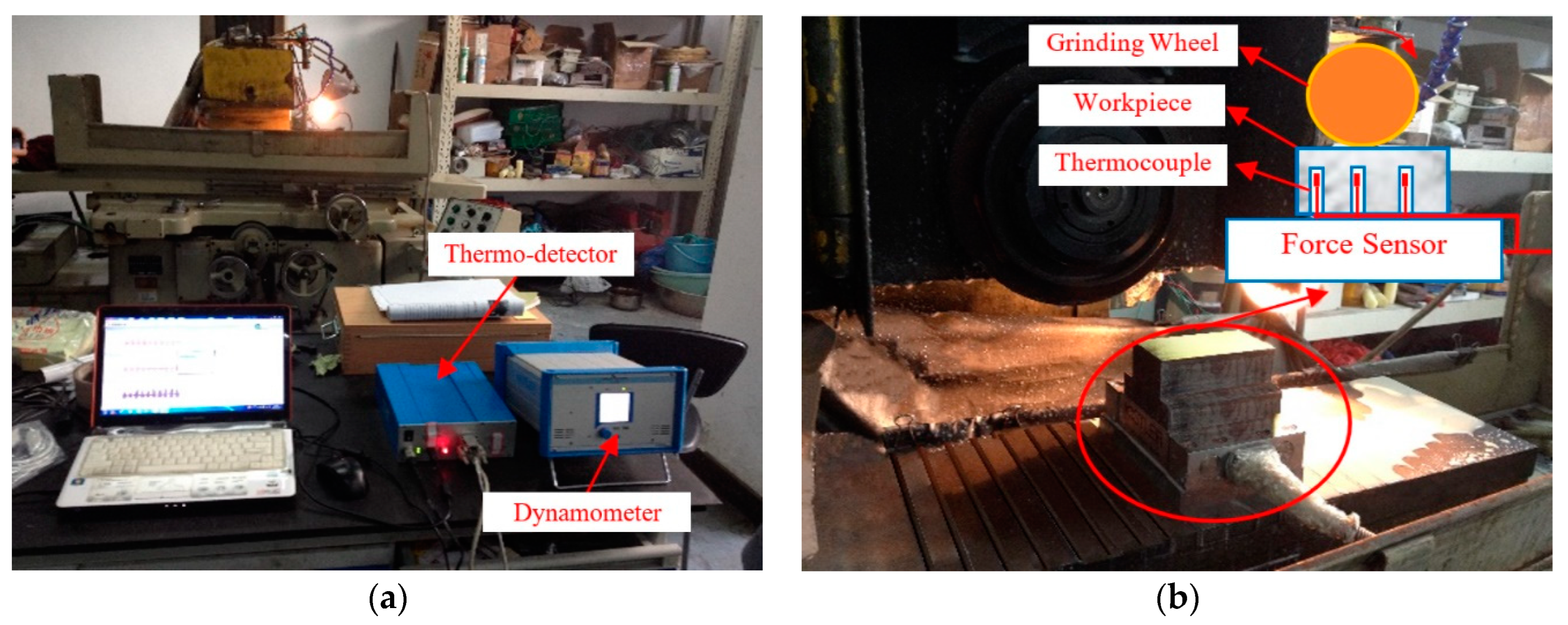
2.3. Grinding Test Scheme
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Characterization of Nano-Capsules
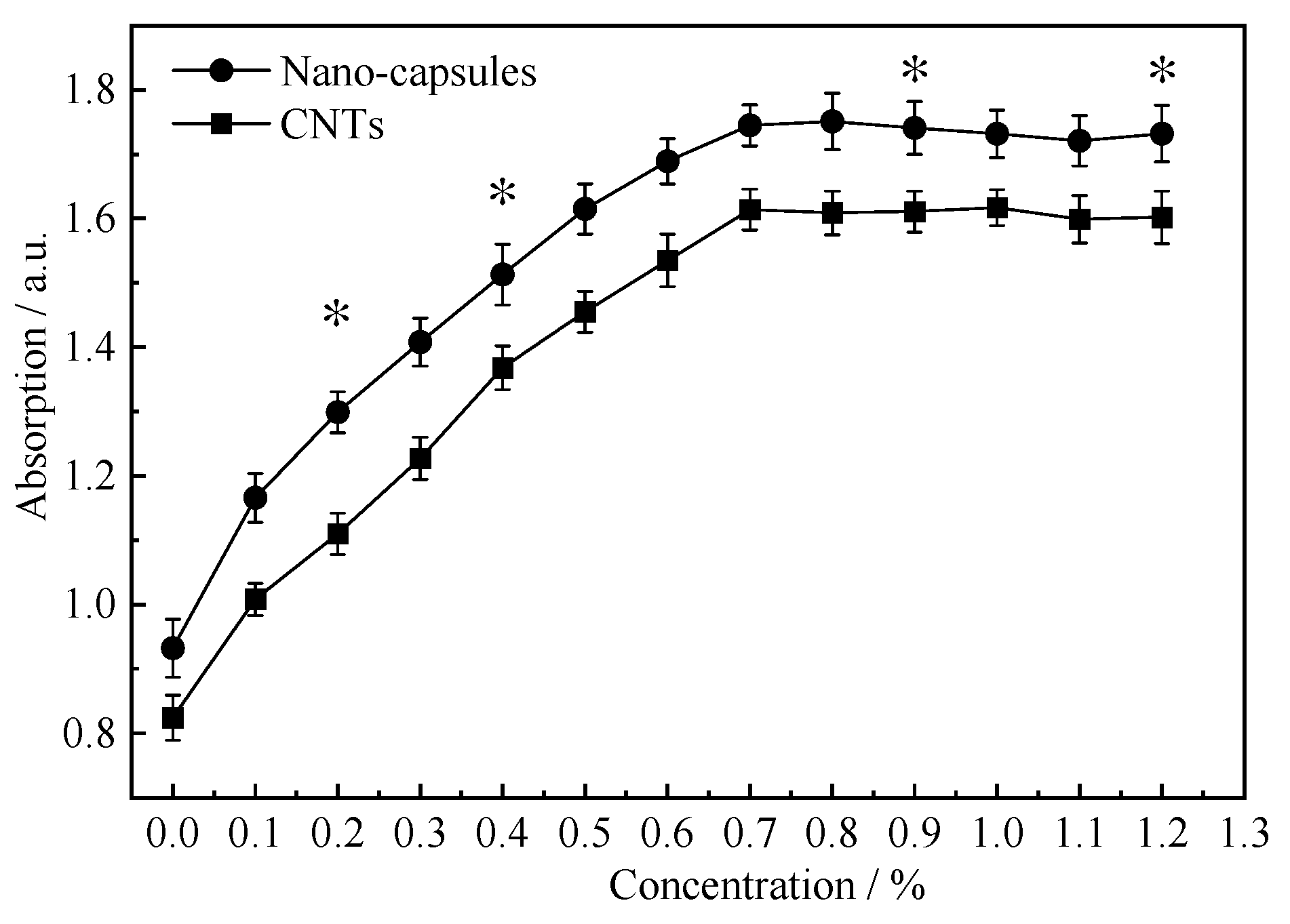
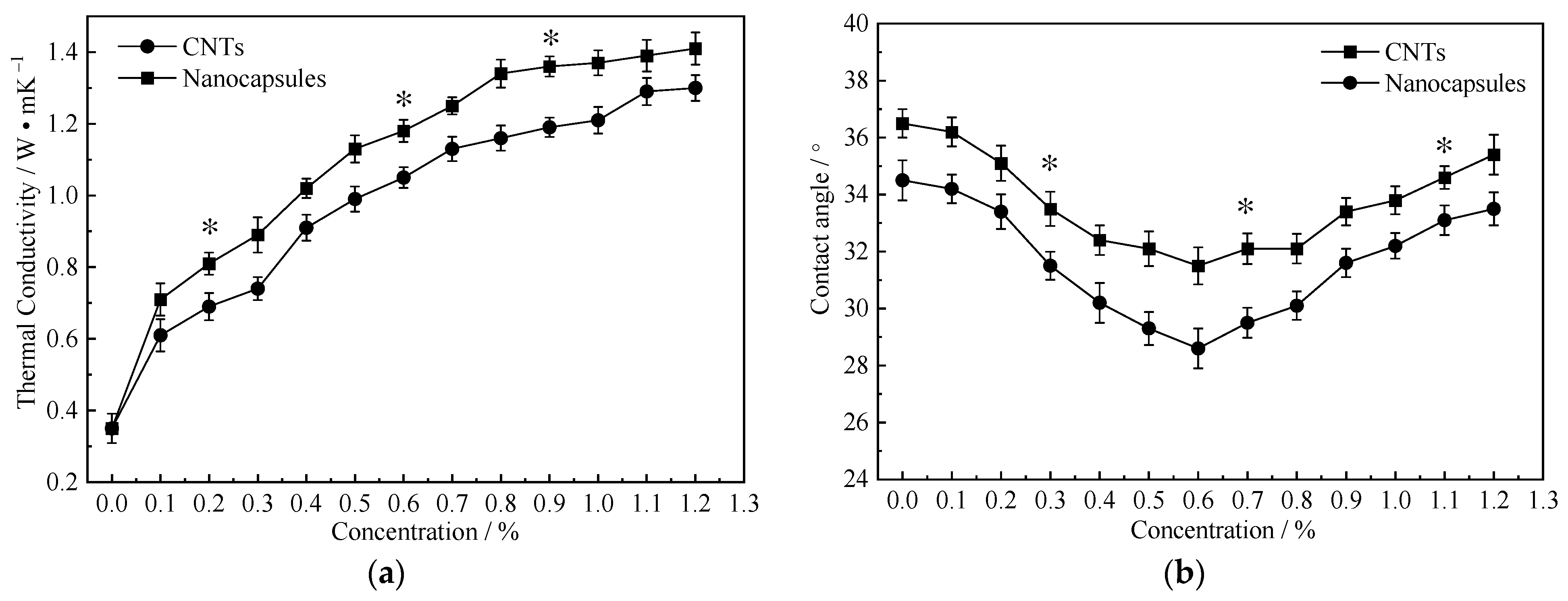
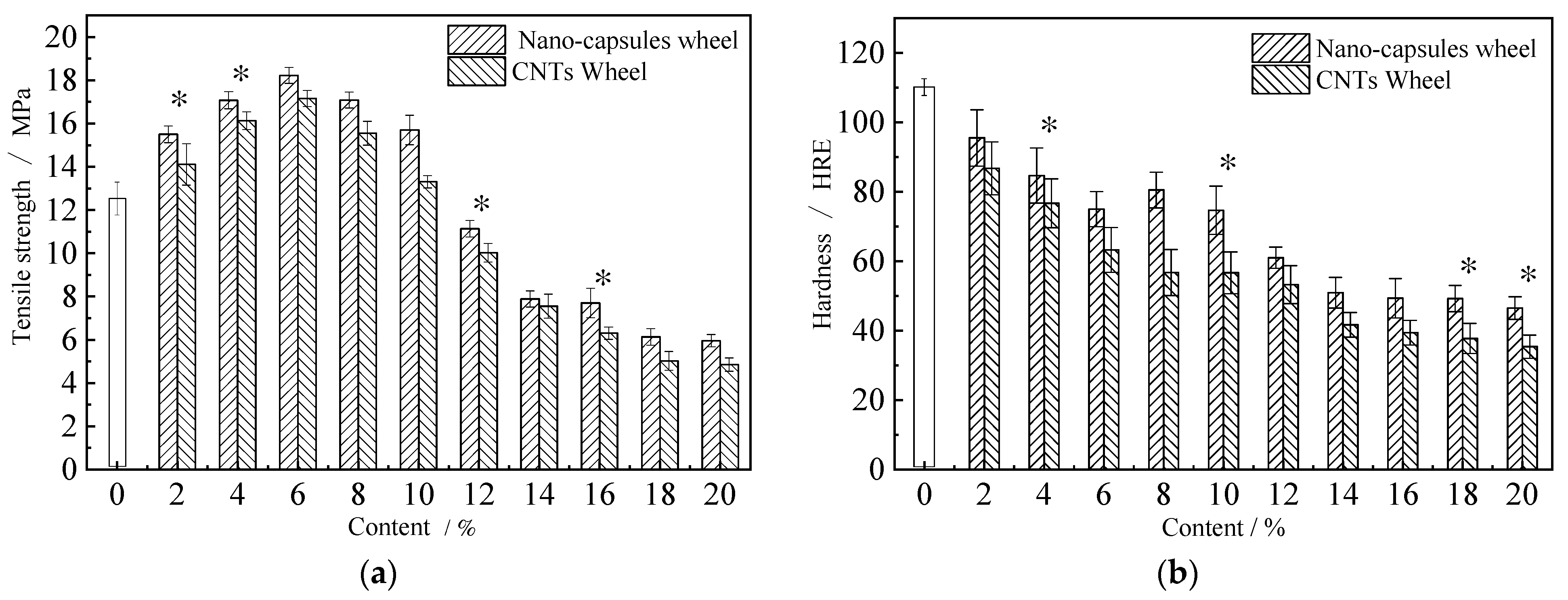
3.2. Performance Testing of Nanofluid and Nano-Capsule Grinding Wheels
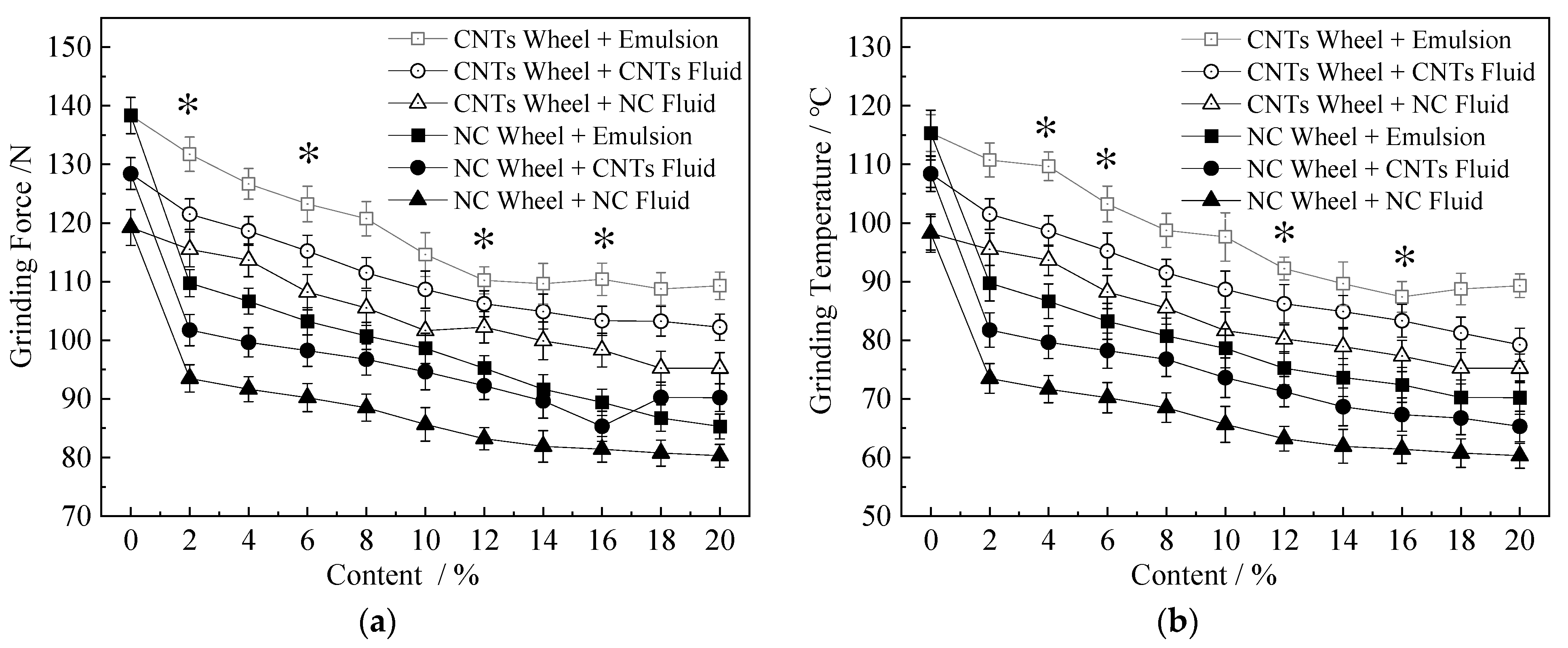
3.3. Grinding Force and Grinding Temperature
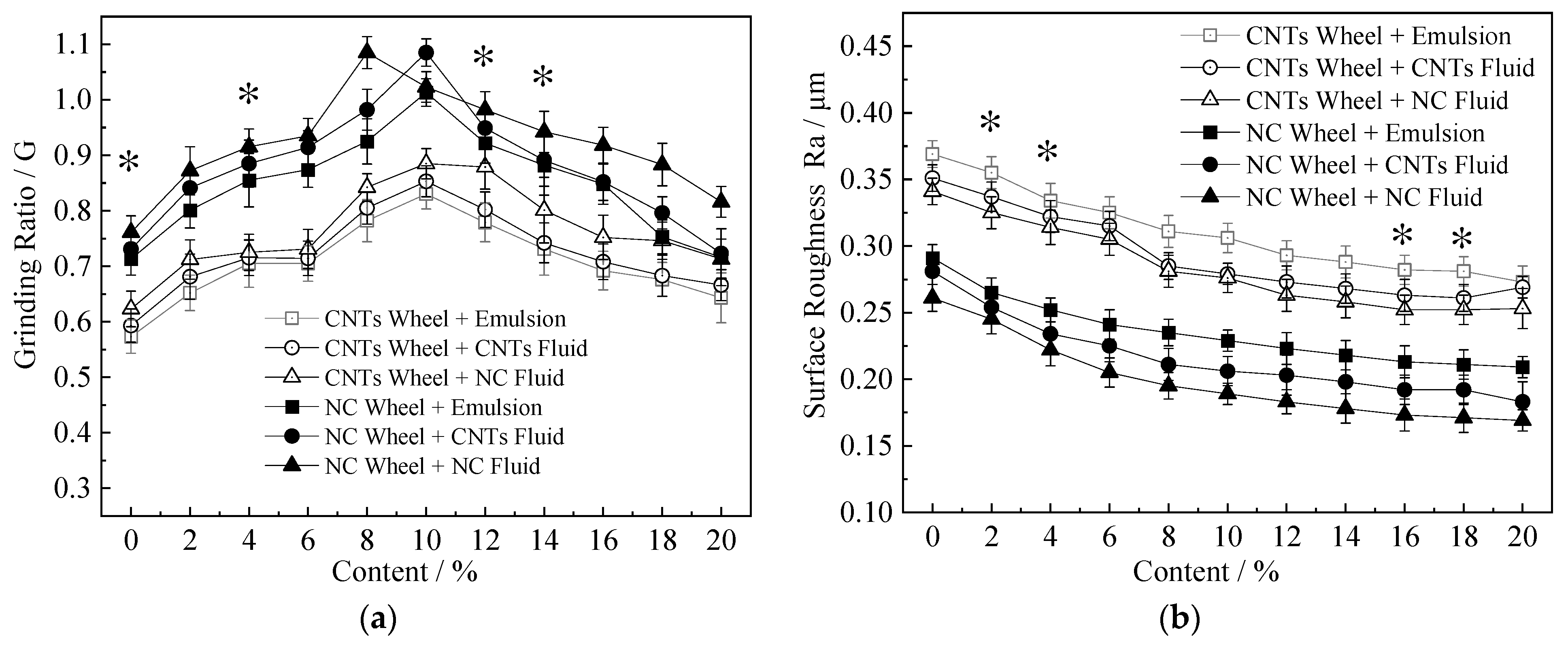
3.4. Grinding Ratio and Workpiece Surface Roughness
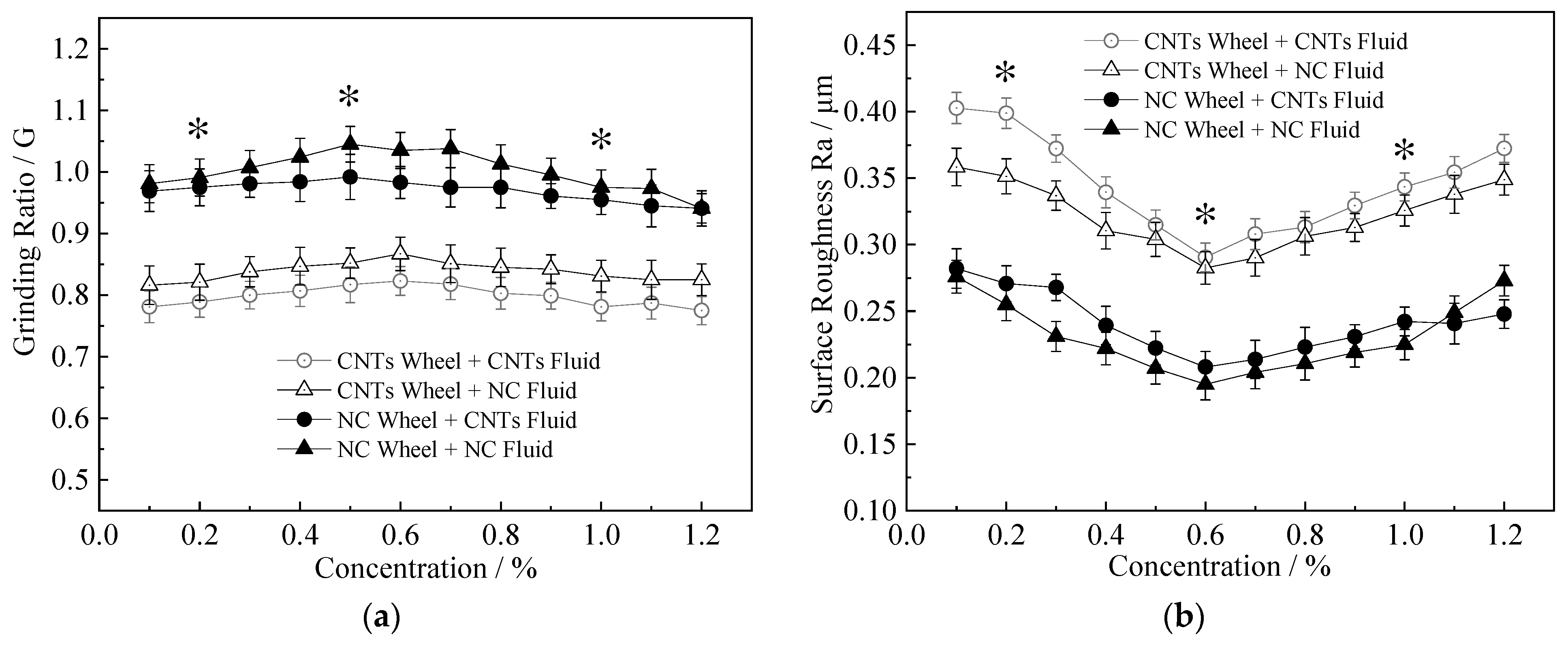
3.5. Effect of Grinding Speed on Grinding Performance
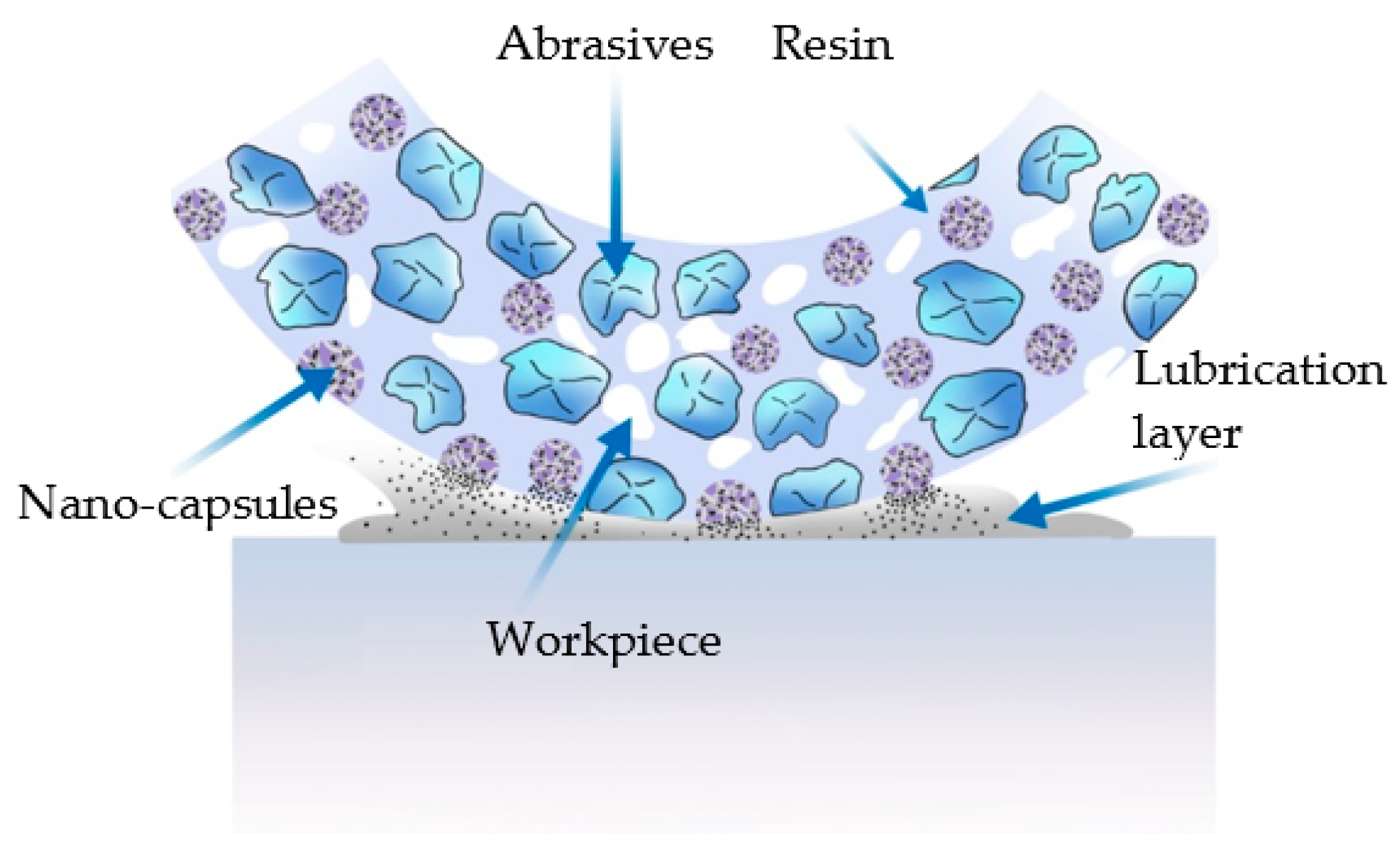
4. Discussion of Lubrication Mechanism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abrão, B.S.; Pereira, M.F.; da Silva, L.R.R.; Machado, Á.R.; Gelamo, R.V.; de Freitas, F.M.C.; Mia, M.; da Silva, R.B. Improvements of the MQL Cooling-Lubrication Condition by the Addition of Multilayer Graphene Platelets in Peripheral Grinding of SAE 52,100 Steel. Lubricants 2021, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanapriyan, S.N.A.; Vijayaraghavan, V.; Krishnamurthy, R. Significance of grinding burn on high speed steel tool performance. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2003, 134, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, S.S.; Balguri, P.K.; Govardhan, D. Optimization of grinding depth to avoid grind-induced burns in 35NCD16 alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 62, 2739–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightstone, M.; Koshy, P.; Tullis, S. High-coherence jets for focused fluid delivery in grinding. CIRP Ann. 2021, 70, 293–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, R.; Zhao, L.; Tang, X.; Xiao, X.; Gao, J. Heat transfer performance assessment of abrasive phyllotaxy arrangement in internal cooling grinding. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 197, 123317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Shirvani, K.A.; Przyborowski, A.; Pai, N.; Mosleh, M. Role of Nanofluid Minimum Quantity Lubrication (NMQL) in Machining Application. Lubricants 2022, 10, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.d.J.; Guermandi, L.G.; Bianchi, E.C.; Diniz, A.E.; de Aguiar, P.R.; Canarim, R.C. Improving minimum quantity lubrication in CBN grinding using compressed air wheel cleaning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2012, 212, 2559–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Malshe, A.P.; Kalita, P.; Shih, A.J. Performance of novel MoS2 nanoparticles based grinding fluids in minimum quantity lubrication grinding. Trans. NAMRI/SME 2008, 36, 357–364. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D. Experimental evaluation of the lubrication performance of MoS2/CNT nanofluid for minimal quantity lubrication in Ni-based alloy grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. Des. Res. Appl. 2015, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Jia, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, X. Experimental evaluation of MoS2 nanoparticles in jet MQL grinding with different types of vegetable oil as base oil. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 87, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, M.; Zhang, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, G. Experimental evaluation of the lubrication properties of the wheel/workpiece interface in MQL grinding with different nanofluids. Tribol. Int. 2016, 99, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, C.H.; Jung, Y.M.; Cheong, S.I.; Lee, C.G.; Ku, B.C.; Jang, S.P. Stability and thermal conductivity characteristics of nanofluids. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 455, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, J.-K.; Lee, J.-K.; Jeong, Y.-M.; Cheong, S.-i.; Ahn, Y.-C.; Kim, S.H. Production and dispersion stability of nanoparticles in nanofluids. Powder Technol. 2008, 186, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, S.; Radhakrishnan, V. An investigation on solid lubricant moulded grinding wheels. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2003, 43, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshiyuki, E.; Yutaka, S.; Yasuhiro, T. Mechanical-chemical finishing using a lapping stone including microcapsules. Trans. Jpn. Soc. Mech. Eng. Ser. 1999, 65, 394–399. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Huang, S.; Guan, J.; Hu, J.; Peng, W. Grinding performance and self–lubrication mechanism of phenolic resin-bonded grinding wheel filled with inclusion complex of β-cyclodextrin and dialkyl pentasulfide. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 221, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, J. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thostenson, E.T.; Ren, Z.; Chou, T.W. Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1899–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Liu, C.; Sun, R.; Yu, T.; Li, Y.; Yang, G. Carbon nanofiber activated by molybdenum disulfide as an effective binder-free composite anode for highly reversible lithium storage. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; He, X.; Chen, J.; Tao, S.; Luo, H. Hierarchical Ni(HCO3)2 Nanosheets Anchored on Carbon Nanofibers as Binder-Free Anodes for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energy Technol. 2019, 7, 1900094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, B.-K.; Sakka, Y. Dispersion and Shortening of Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes by Size Modification. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehhef, K.A.; Siba, M.A.A.A. Effect of surfactant addition on the nanofluids properties: A review. Acta Mech. Malays. 2019, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huaxu, L.; Fuqiang, W.; Dong, L.; Jie, Z.; Jianyu, T. Optical properties and transmittances of ZnO-containing nanofluids in spectral splitting photovoltaic/thermal systems. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 128, 668–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safiei, W.; Rahman, M.M.; Yusoff, A.R.; Radin, M.R. Preparation, stability and wettability of nanofluid: A review. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 14, 7244–7257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Yang, L.; Xiong, Y. Microstructure and shear property of Ni-coated carbon nanotubes reinforced InSn-50Ag composite solder joints prepared by transient liquid phase bonding. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 73, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Feng, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, H.; Qin, Y.; Jia, X. Experimental study on longitudinal-torsional ultrasonic vibration drilling of carbon fiber–reinforced plastics/titanium alloy stacks. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 124, 527–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, K.; Sørby, K. A measuring method for micro force based on MEMS planar torsional spring. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2020, 32, 035002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, K.; Wu, S. Grinding performance of micro-texured grinding wheel on different ceramic materials. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2022, 42, 290–299. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhu, T.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, C.; An, Z. Influence of grinding lubrication methods on surface integrity of nickel-based single crystal superalloy. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2022, 42, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Feng, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Qin, Y.; Jia, X. Experimental research on new hole-making method assisted with asynchronous mixed frequency vibration in TiBw/TC4 composites. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 125, 543–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, C.; Song, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Yang, J.; Song, Y. Optical limiting properties of hybrid nickel naphthalocyanine-titania nanoparticals thin films. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 112, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhao, S.; Xu, G.; Wang, Z. Effect of dimethyl carbonate on the micromorphology and structure of combustion particles from diesel engines. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 42, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dujardin, E.; Ebbesen, T.W.; Hiura, H.; Tanigaki, K. Capillarity and Wetting of Carbon Nanotubes. Science 1994, 265, 1850–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babita, S.S.; Gupta, S.M. Synergic effect of SDBS and GA to prepare stable dispersion of CNT in water for industrial heat transfer applications. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 055511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, M.; Chen, Q. Effects of exhaust gas recirculation composition and temperature on microscopic mechanical properties of particles in a diesel engine. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2018, 38, e13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Y.; Li, Q. Heat transfer enhancement of nanofluids. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2000, 21, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Ma, H. A Hierarchical Conical Array with Controlled Adhesion and Drop Bounce Ability for Reducing Residual Non-Newtonian Liquids. J. Bionic Eng. 2021, 18, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, S.; Li, Q. Surface Tension of Nanofluid-type Fuels containing Suspended Nanomaterials. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Kuang, Y.; Hong, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X. Plasmon enhancement of optical absorption in ultra-thin film solar cells by rear located aluminum nanodisk arrays. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleduzzaman, S.S.; Mahbubul, I.M.; Shahrul, I.M.; Saidur, R. Effect of particle concentration, temperature and surfactant on surface tension of nanofluids. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. Rapid Commun. J. 2013, 49, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Hong, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J. Scattering of light into thin film solar cells by rear located hemispherical silver nanoparticles. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2016, 48, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C. Research on abrasive wear dress of CBN honing tool based on single abrasive cutting. Diam. Abras. Eng. 2022, 42, 728–737. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Lin, L.; Hu, Y. Effects of the lubricating oil and diesel mixture combustion on the oxidation and microphysical properties of particulate matter. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Liu, T.; Yu, N.; Cao, J.; Wang, K.; Sørby, K. A Pin-on-Disk Tribometer for Friction and Lubricating Performance in mm-Scale. Tribol. Lett. 2021, 69, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, G.; Li, M.; Chen, Q. The evolution of the micro-morphology and micro-structure of particles from diesel engine in combination with exhaust gas recirculation. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2018, 40, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Yan, Y.; Guo, R.; Guan, W.; Guo, G. Microstructure characterization and mechanical behavior of dissimilar friction stir welded Al/Cu couple with different joint configurations. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 94, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Yuan, H.; Dang, Q.; Wang, T.; Pang, T.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, K.; Wu, X.; Shao, M. Quantitative evaluation of synergistic effects for Pt nanoparticles embedded in N-enriched carbon matrix as an efficient and durable catalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction and their PEMWE performance. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 31121–31128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Geng, F.; Fan, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, H. Effect of preparation process on elevated temperature tribological properties of composite polyurea grease. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2016, 68, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Lin, L.; Hu, Y. Effects of Lubricating Oil Additives on the Microphysical Properties of Diesel Exhaust Particulate Matter. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2020, 193, 1718–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Li, J.; She, T.; Ma, S.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, P.; Wei, W.; Xia, D.; Leung, D.Y.C. Study on the Photocatalysis Mechanism of the Z-Scheme Cobalt Oxide Nanocubes/Carbon Nitride Nanosheets Heterojunction Photocatalyst with High Photocatalytic Performances. J. Hazard Mater. 2021, 402, 123839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, X.; Pang, Y.; Gao, X.; Kou, Z.; Tang, J.; Wang, J. Unlocking the synergy of interface and oxygen vacancy by core-shell nickel phosphide@oxyhydroxide nanosheets arrays for accelerating alkaline oxygen evolution kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oumahi, C.; Mogne, T.L.; Aguilar-Tapia, A.; Charrin, C.; Geantet, C.; Afanasiev, P.; Thiebaut, B.; De Barros-Bouchet, M.I. Impact of Fatty Triamine on Friction Reduction Performance of MoDTC Lubrication Additive. Lubricants 2022, 10, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Composition | Content | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Deionized water | 97.3–98.4 wt.% | Base fluid |
| CNTs or nano-capsules | 0.1–1.2 wt.% | Lubricating additive |
| TW-80/SDBS | 0.5 wt.% | Active agent |
| Triethanolamine | 0.5 wt.% | Rust inhibitor |
| Sodium benzoate | 0.5 wt.% | Antiseptic |
| No. | Resin | Abrasive | CNTs | CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A0 (Common Wheel) | 15 wt.% | 85 wt.% | — | — |
| B2-B20 (CNT Wheel) | 15 wt.% | 83–65 wt.% | 2–20 wt.% | — |
| C2-C20 (NC Wheel) | 15 wt.% | 83–65 wt.% | — | 2–20 wt.% |
| Machine Tool | Grinding Wheel | Workpiece | Cooling Conditions | Grinding Speed (m/s) | Feed Speed (m/s) | Grinding Depth (μm) | Total Grinding Depth (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M7140 | 2–20 wt.% wheel | GCr15 steel (HRC60-62), 100 × 50 × 50 mm | Nanofluid under MQL, 50 mL/min | 4.45, 8.9, 13.35, 17.8, 22.25, 26.7 | 0.2 | 10 | 300 |
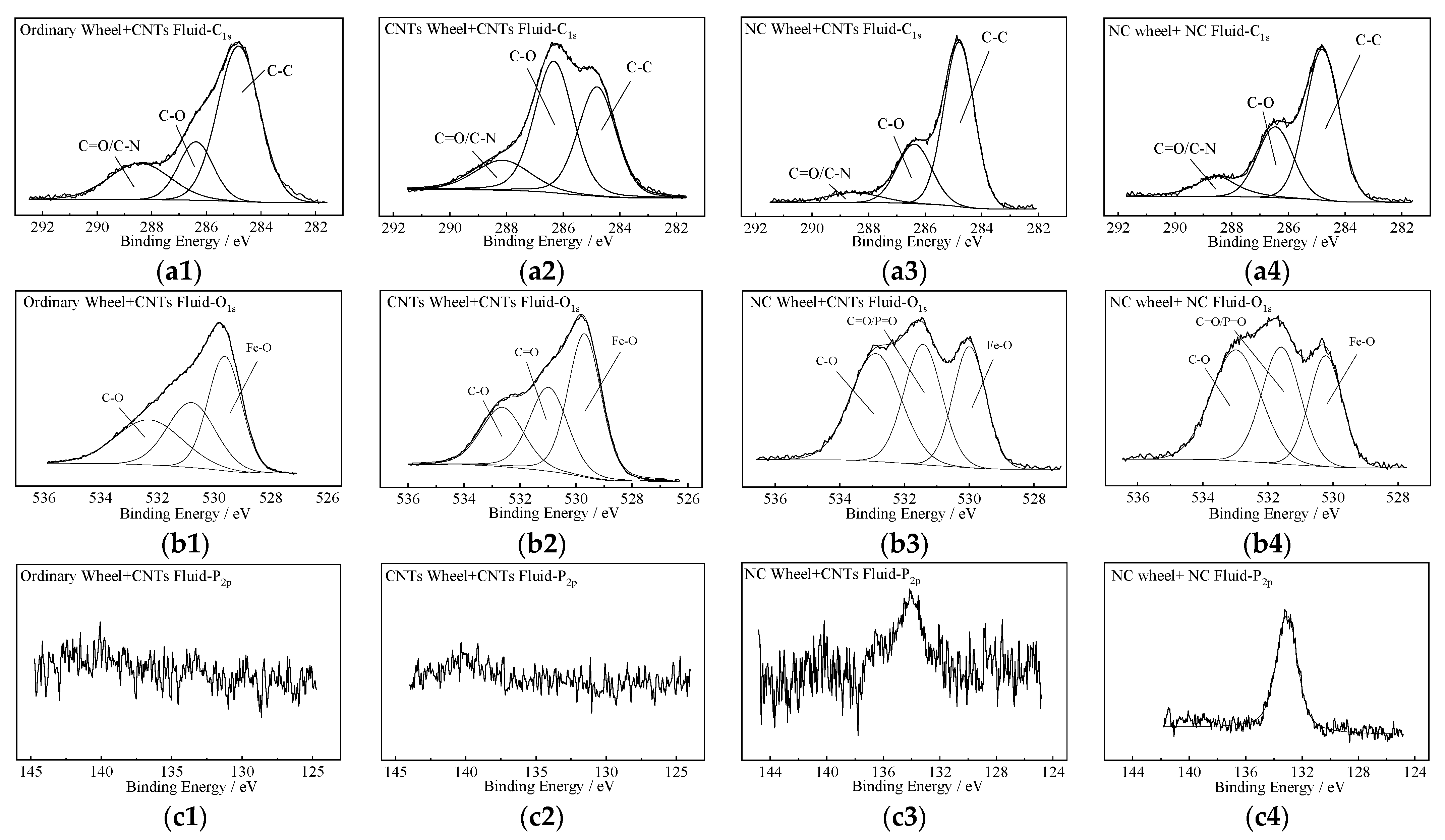
| Type of Steel Surface | Relative Content/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Fe | P | |
| Common Wheel + CNT Fluid | 20.31 | 35.13 | 44.56 | — |
| CNT Wheel + CNT Fluid | 30.17 | 29.76 | 40.07 | — |
| NC Wheel + CNT Fluid | 25.18 | 28.33 | 44.51 | 1.95 |
| NC wheel + NC Fluid | 27.86 | 32.71 | 37.05 | 2.38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guan, J.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, L.; Xia, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, S. Synergistic Lubrication Mechanism of Nano-Fluid and Grinding Wheel Prepared by CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules. Lubricants 2023, 11, 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11060244
Guan J, Zhu Z, Yang L, Xia Y, Xu X, Huang S. Synergistic Lubrication Mechanism of Nano-Fluid and Grinding Wheel Prepared by CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules. Lubricants. 2023; 11(6):244. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11060244
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuan, Jiju, Zhengbing Zhu, Lanyu Yang, Yu Xia, Xuefeng Xu, and Shuiquan Huang. 2023. "Synergistic Lubrication Mechanism of Nano-Fluid and Grinding Wheel Prepared by CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules" Lubricants 11, no. 6: 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11060244
APA StyleGuan, J., Zhu, Z., Yang, L., Xia, Y., Xu, X., & Huang, S. (2023). Synergistic Lubrication Mechanism of Nano-Fluid and Grinding Wheel Prepared by CNTs@T304 Nano-Capsules. Lubricants, 11(6), 244. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants11060244





