Dynamic Response and Lubrication Performance of Spur Gear Pair Under Time-Varying Rotation Speeds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
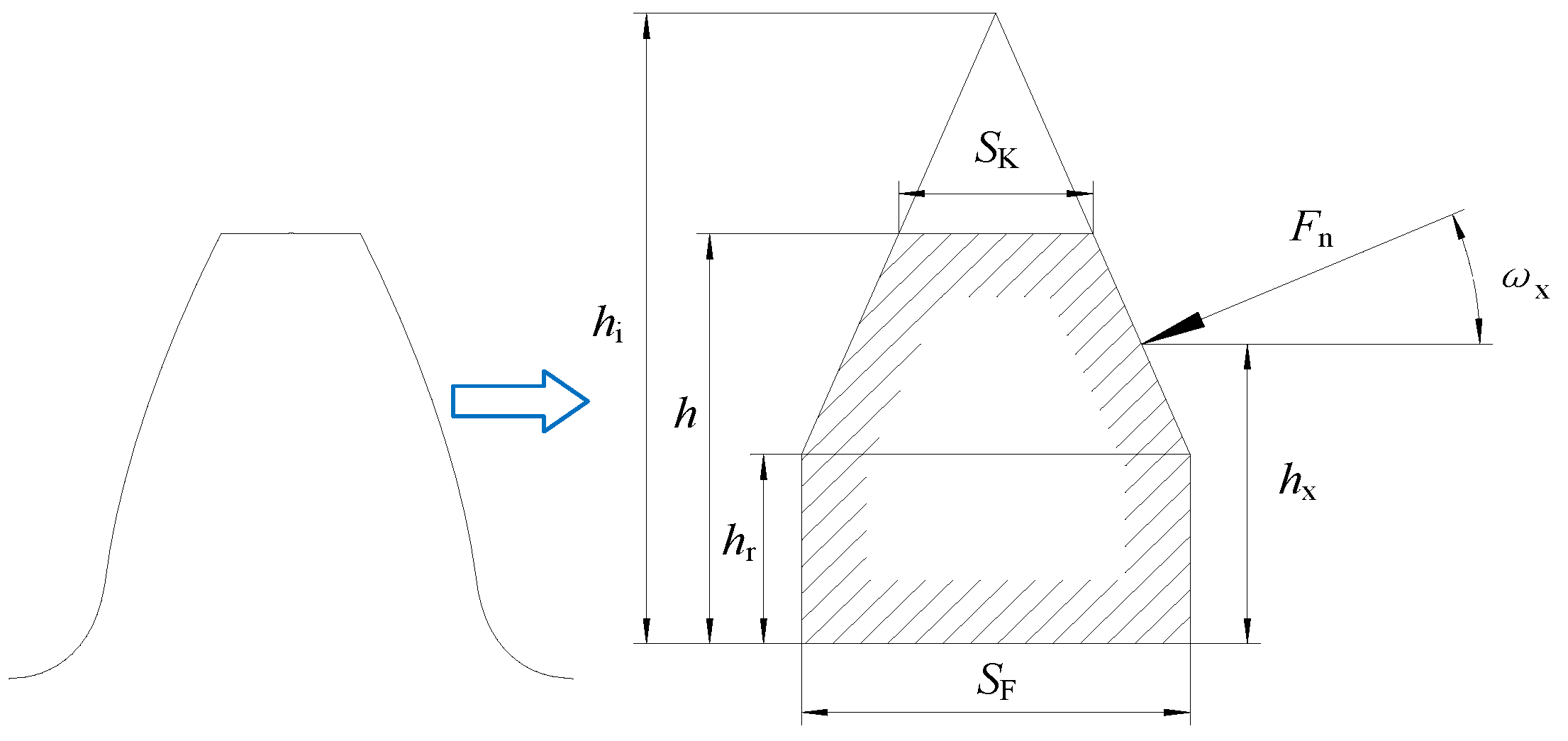
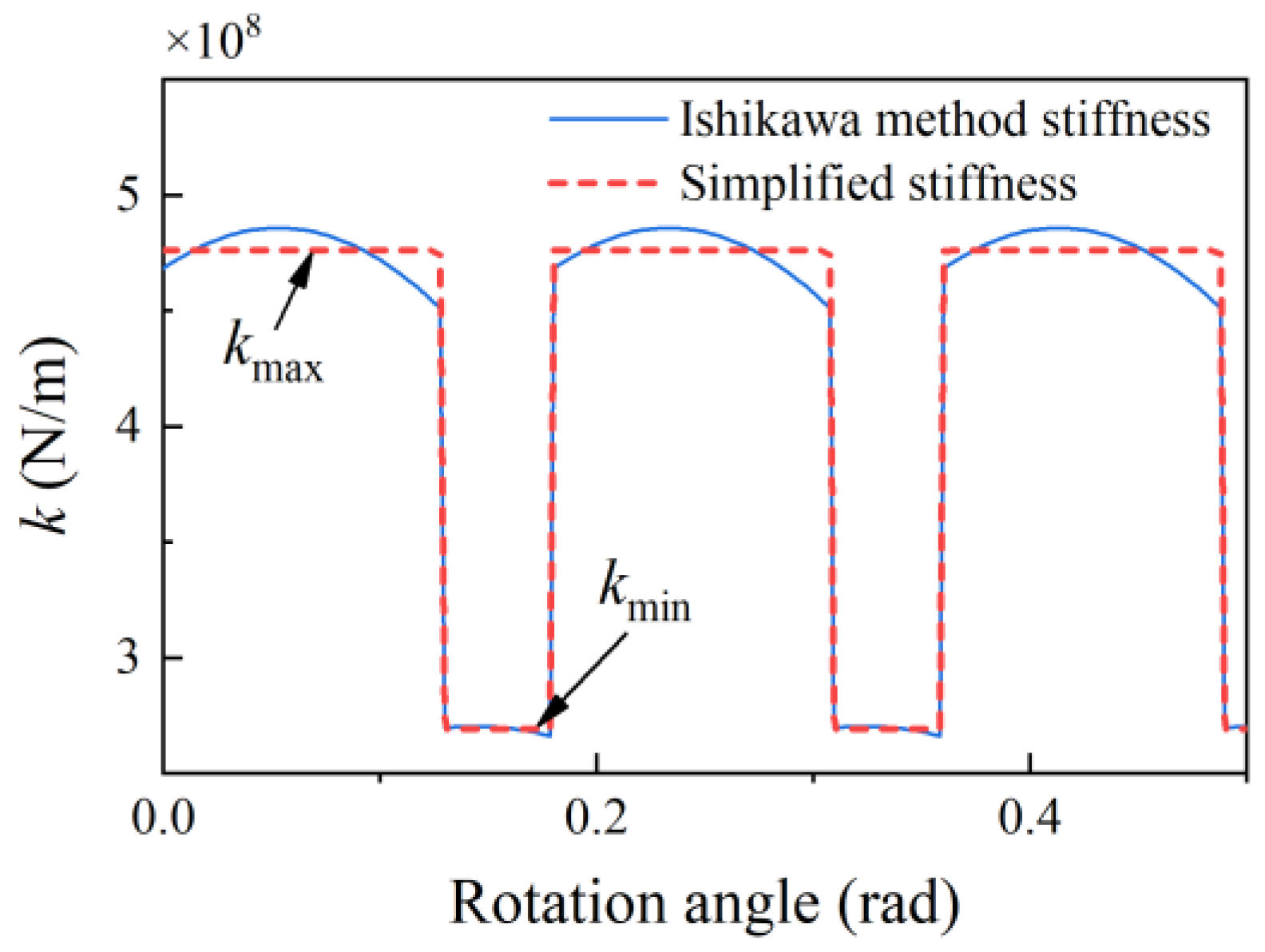
2.1. Time-Varying Stiffness
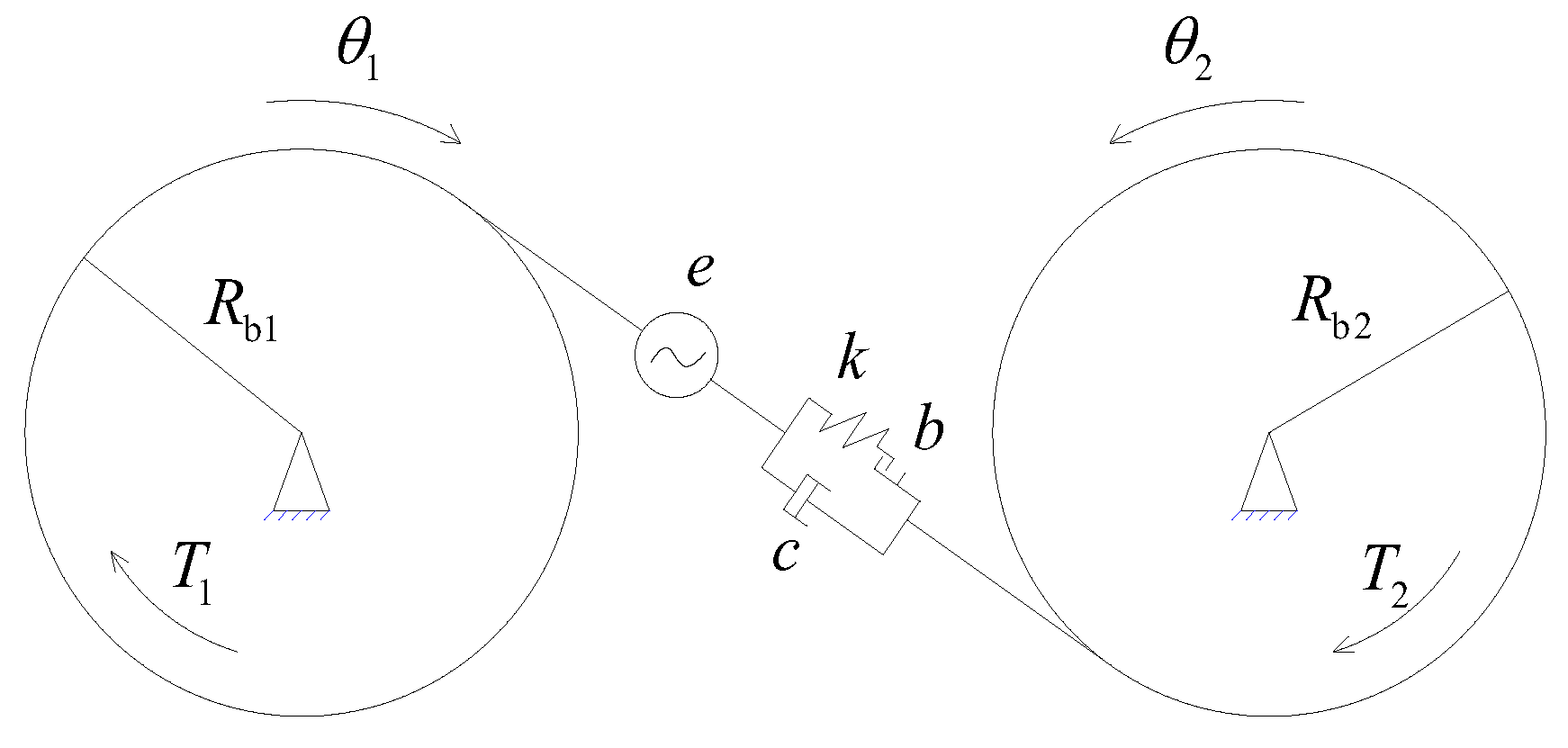
2.2. The Dynamics Model of the Gear Pair
2.3. Geometry and Kinematics Analysis
2.4. The Transient EHL Model
2.5. The Numerical Procedure
3. Results and Discussions
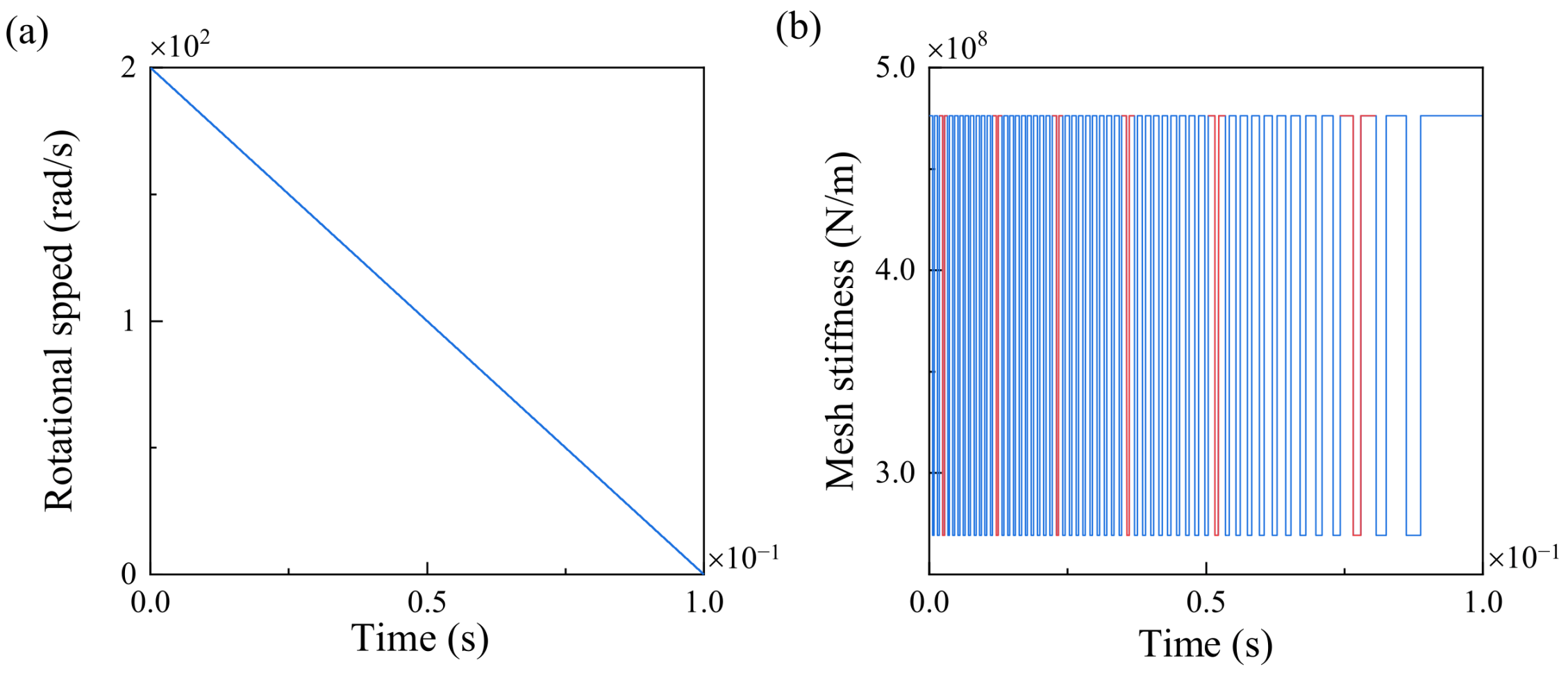
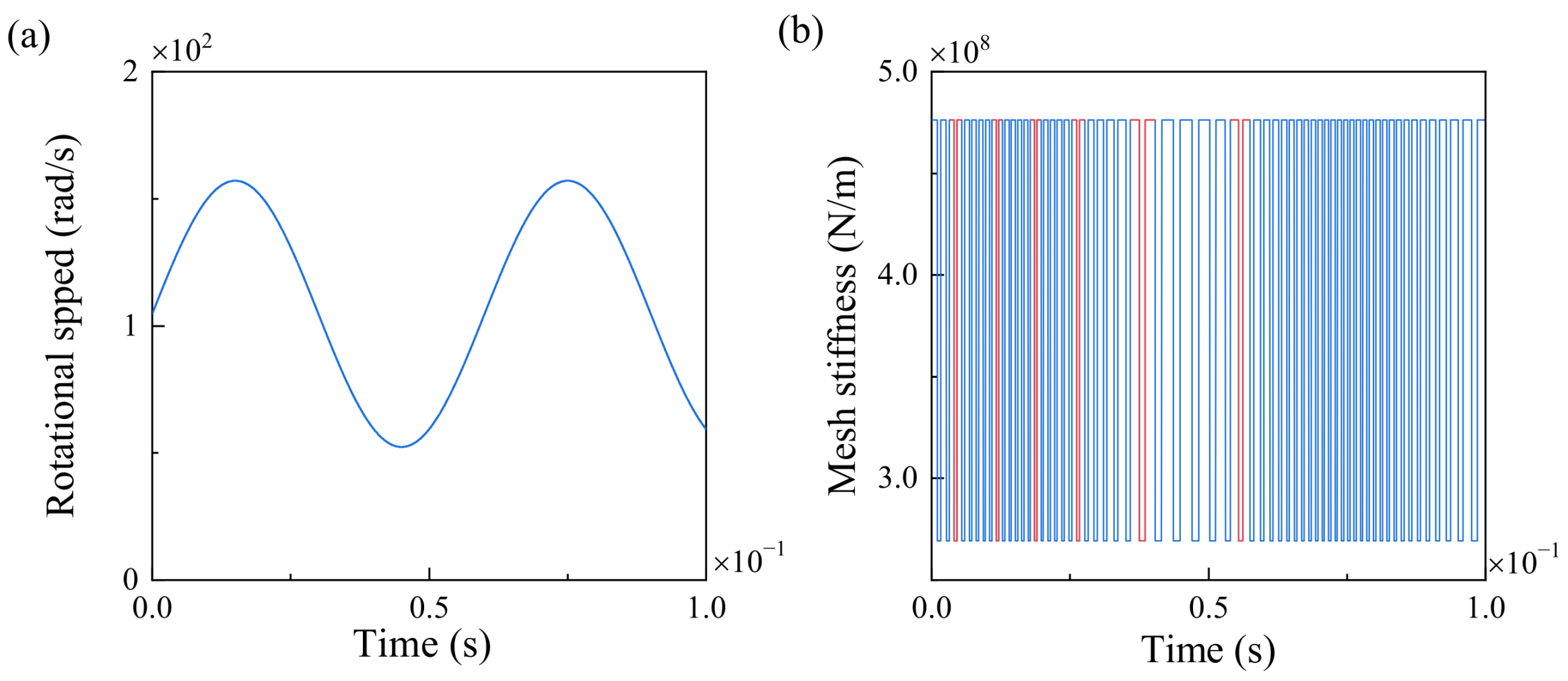
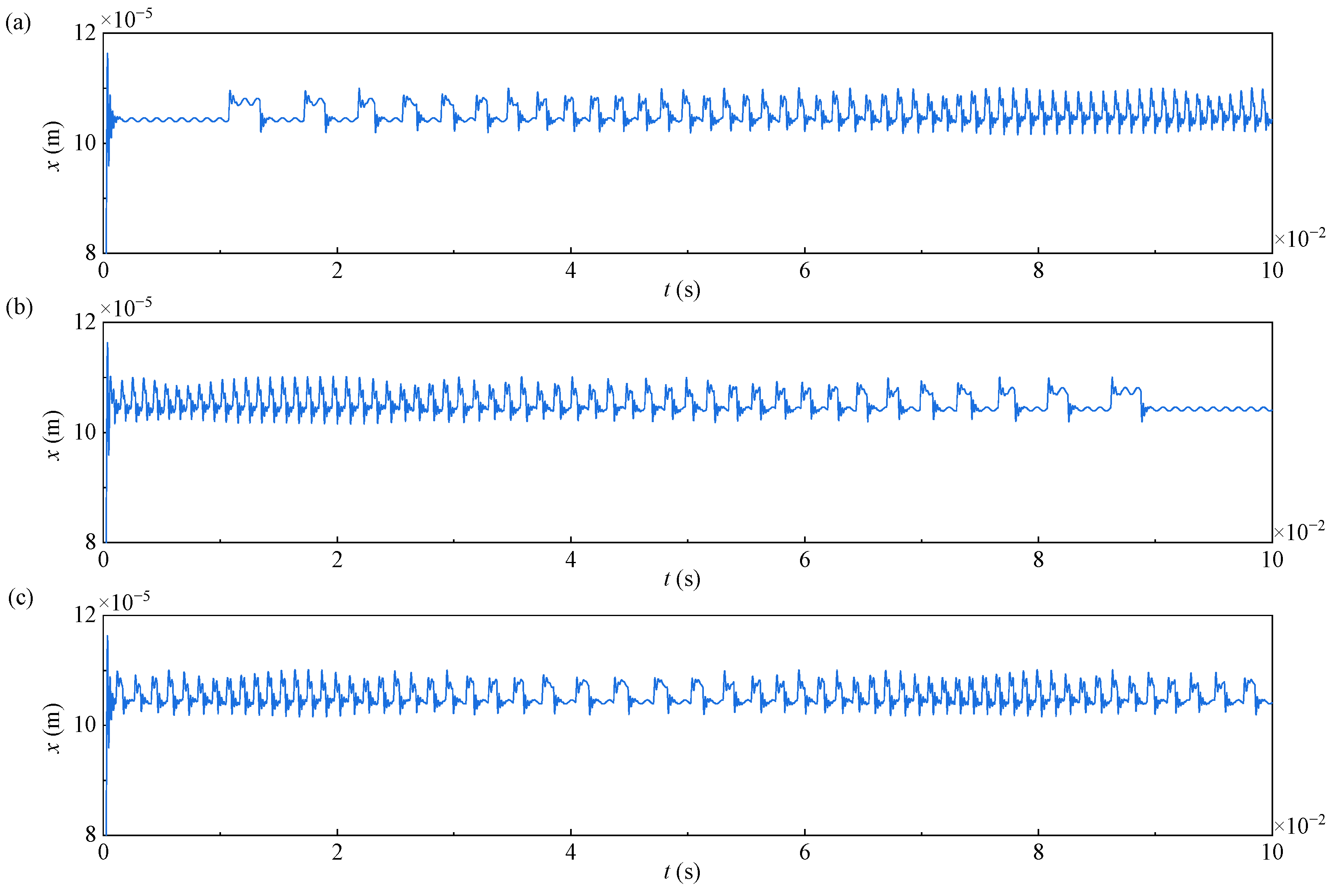
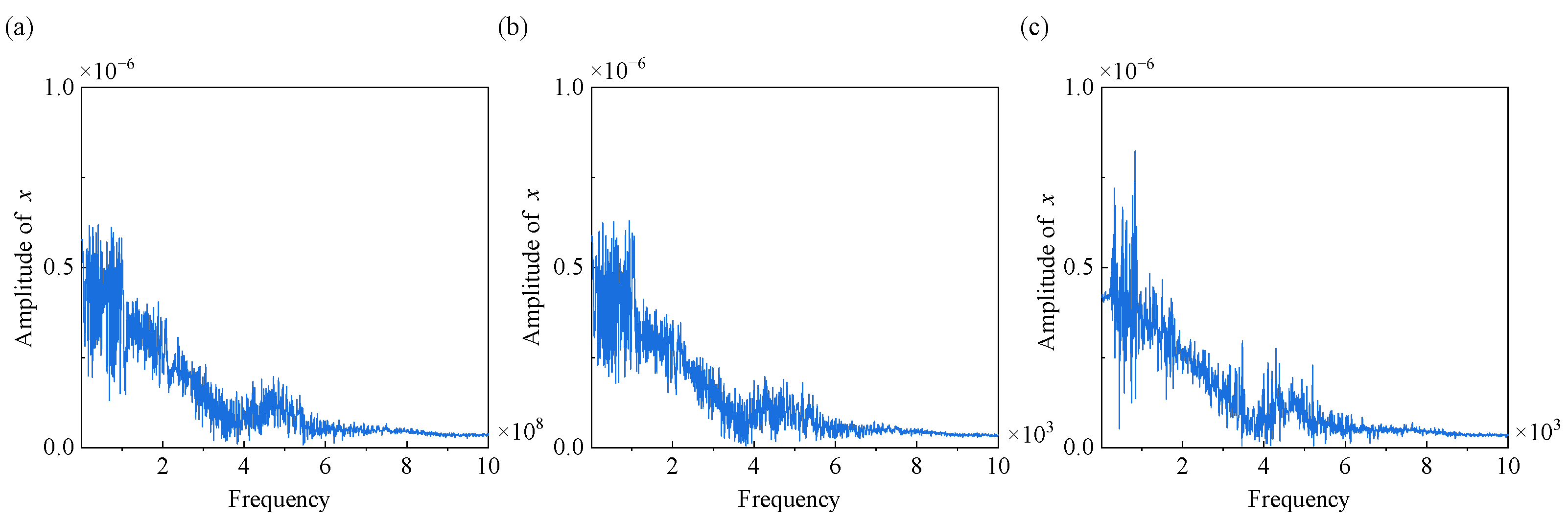
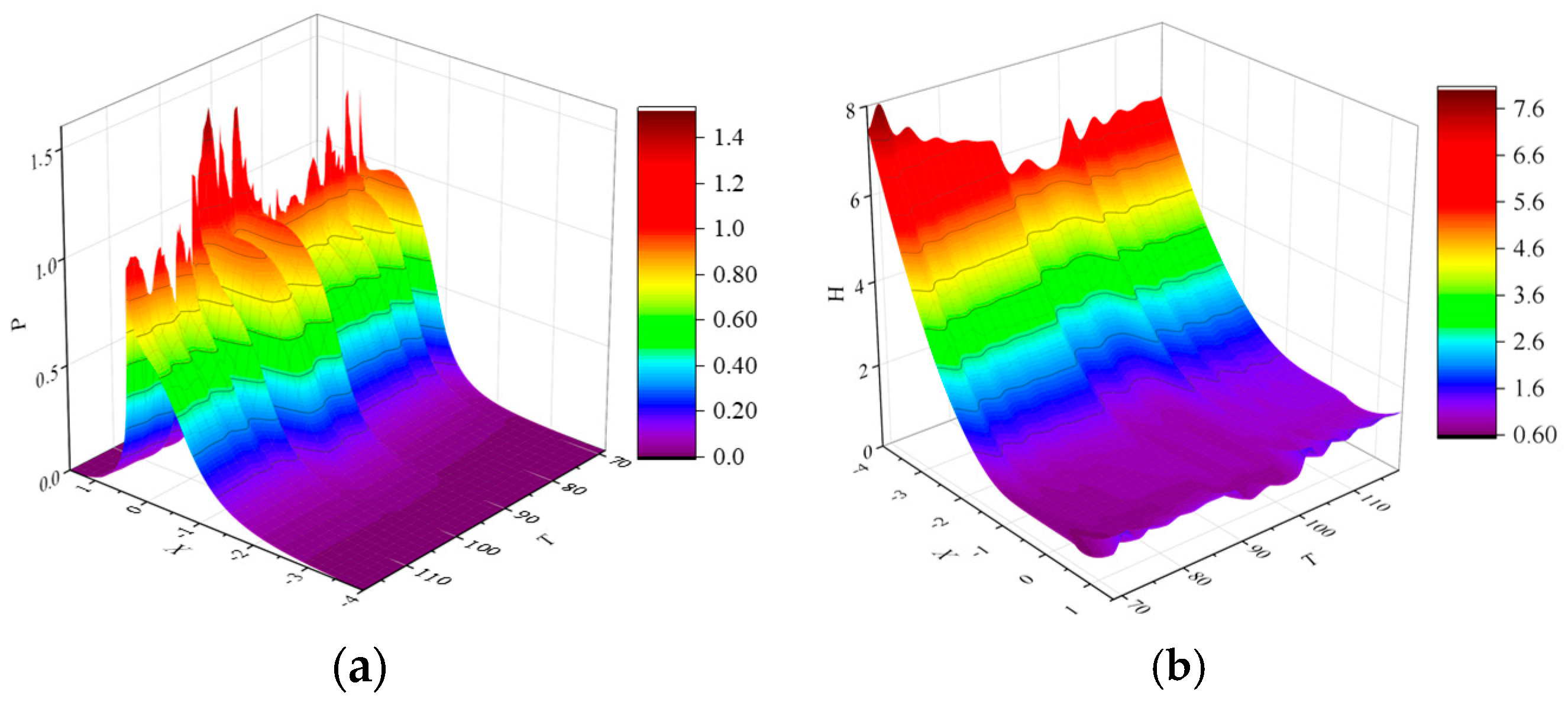
3.1. Dynamic Response of the Gear System with Time-Varying Rotation Speeds
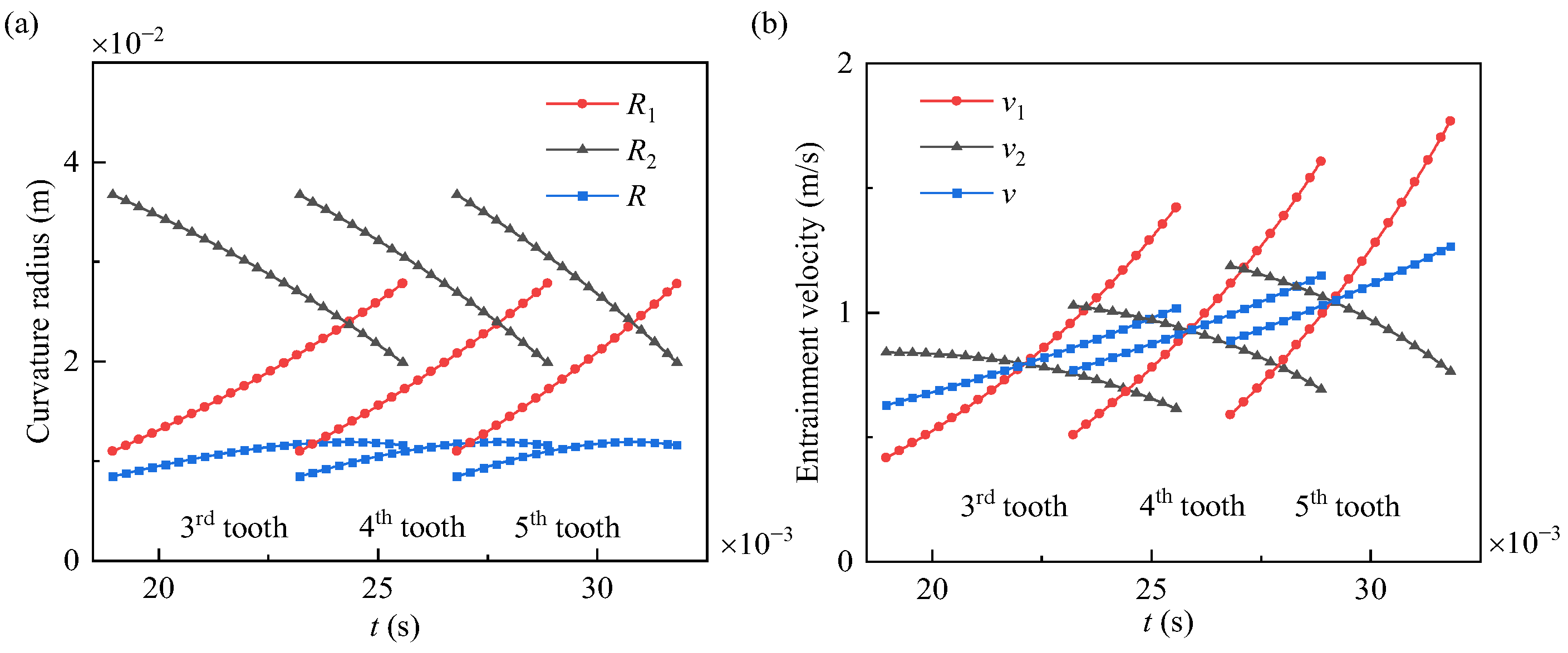
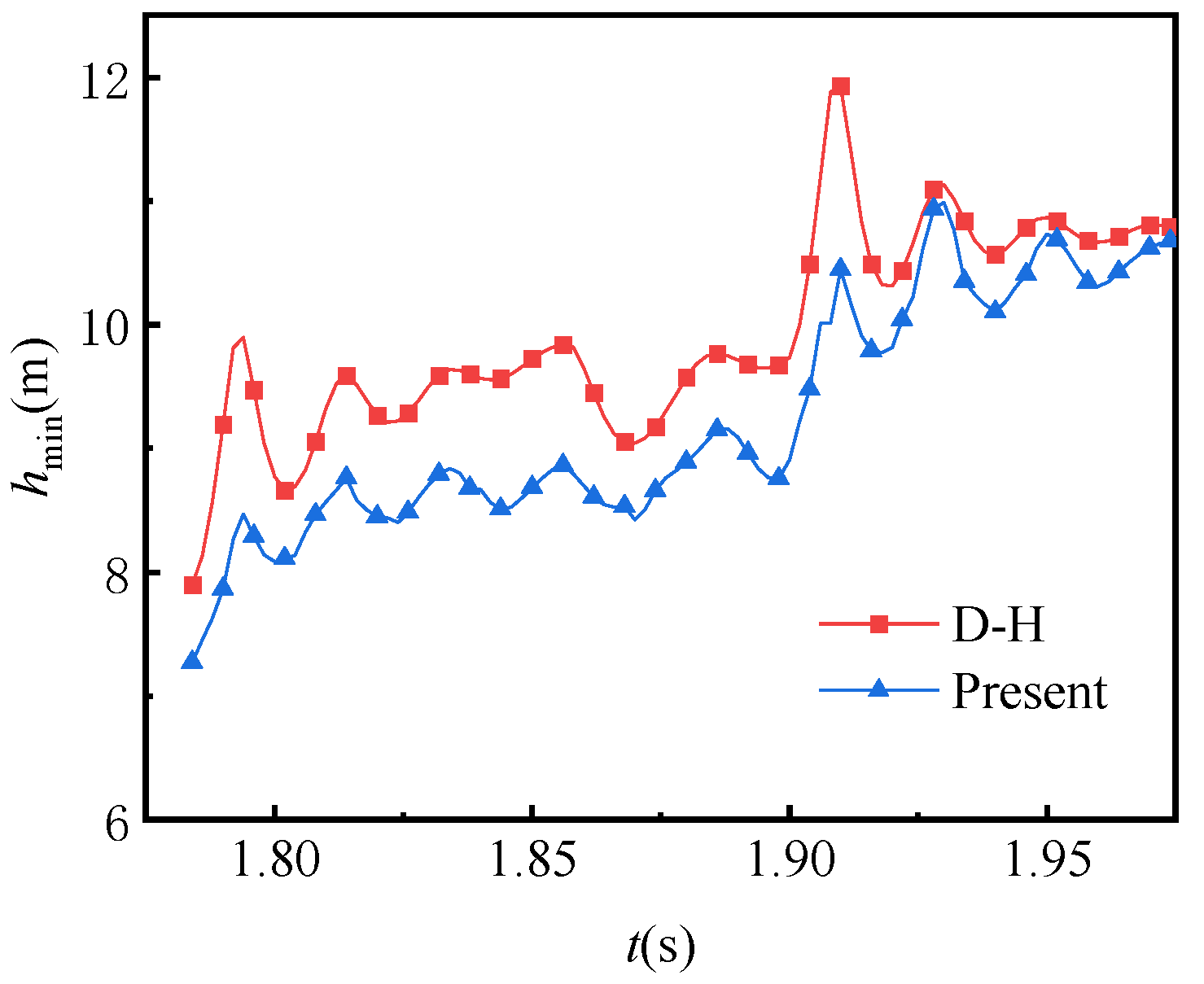
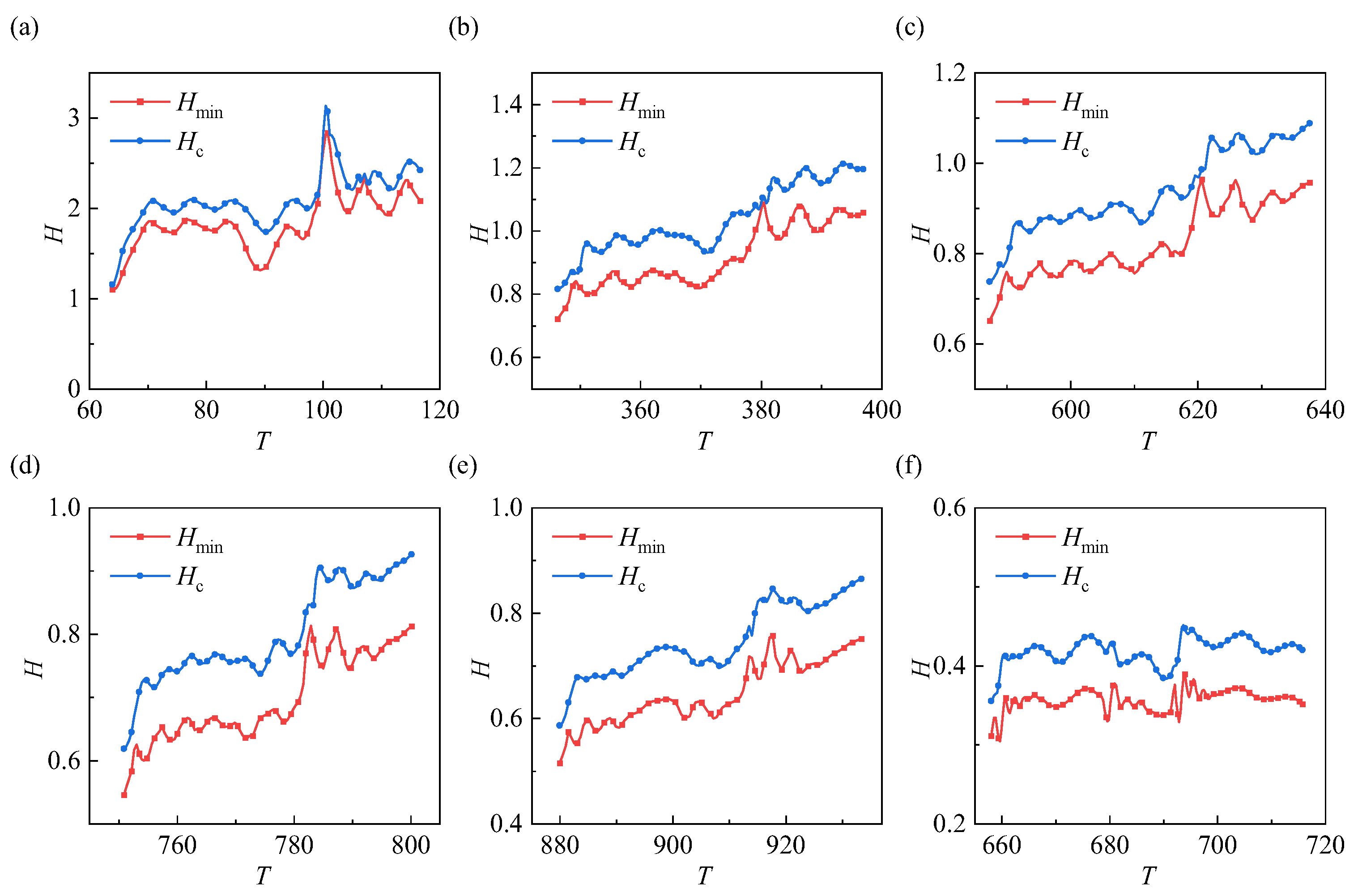
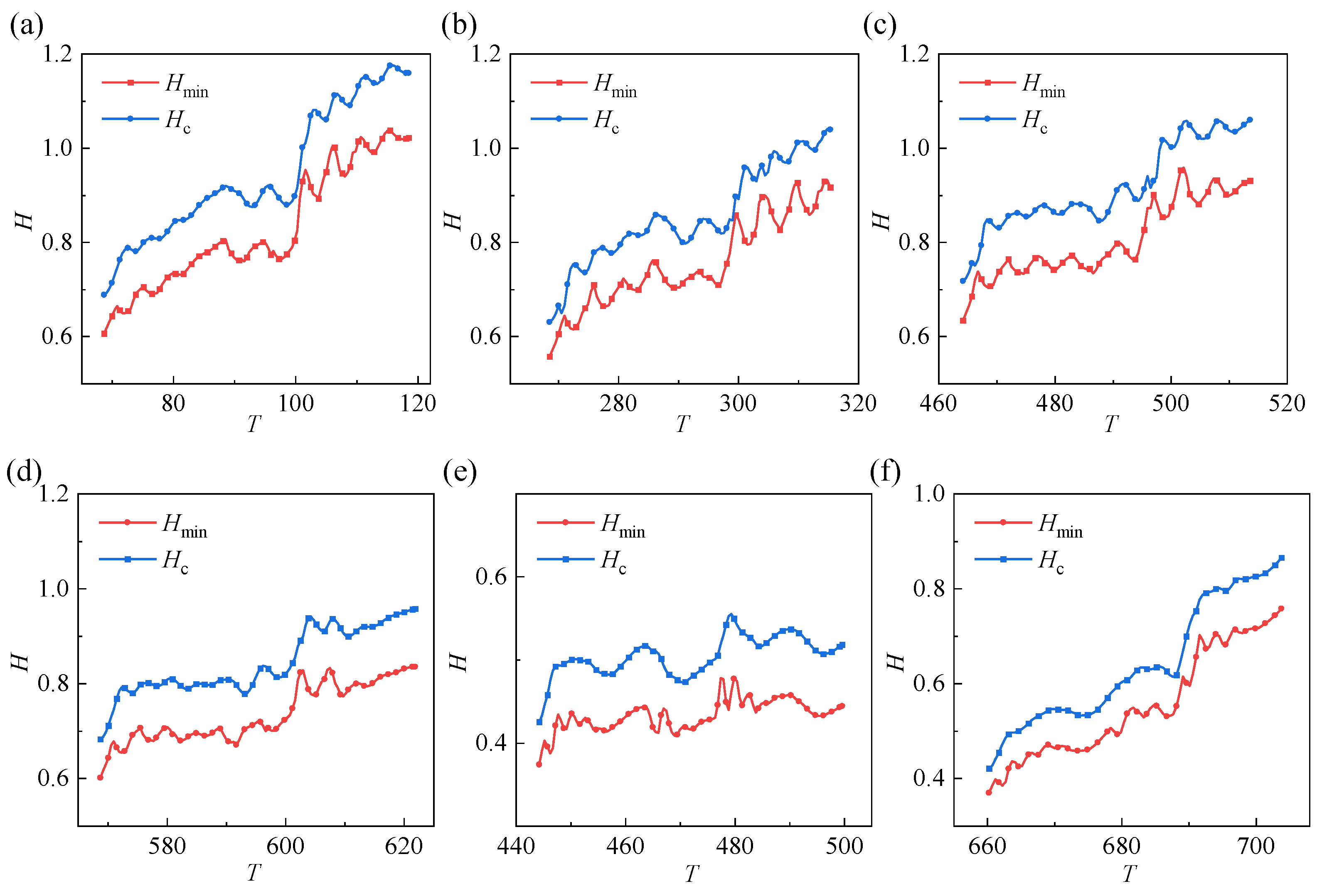
3.2. Effect of Time-Varying Rotation Speeds on Gear Lubrication
4. Conclusions
- The time-varying rotation speeds affect the meshing stiffness due to the variation in the rotation time per tooth. The type of time-varying rotation plays a significant role in the shape of the meshing stiffness of the gear pair.
- The time-varying rotation speeds induce chaotic motion of the gear pair. The vibration is higher when the frequency of the rotation speed is lower, and the amplitude of the rotation speed primarily influences the fluctuation range of the dynamic transmission error.
- The time-varying rotation speed influences the lubrication characteristics through changes in the curvature radius, entrainment velocity, and meshing force. The film thickness of each tooth is different, which makes it difficult to predict the lubricant and wear performance of the gear pair.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Özgüven, H.N.; Houser, D.R. Dynamic Analysis of High Speed Gears by Using Loaded Static Transmission Error. J. Sound Vib. 1988, 125, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, A.; Singh, R. Non-linear Dynamics of a Spur Gear Pair. J. Sound Vib. 1990, 142, 49–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, A.; Blankenship, W. Interactions between commensurate parametric and forcing excit-tions in a system with clearance. J. Sound Vib. 1996, 194, 317–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, A.; Blankeship, G.W. Experiments on nonlinear dynamic behavior of an oscillator with clearance and periodically time-varying parameters. J. Appl. Mech. 1997, 64, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y. Study on the dynamic characteristics of gears considering surface topography in a mixed lubrication state. Lubricants 2024, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zuo, M.; Parey, A. Simulation of spur gear dynamics and estimation of fault growth. J. Sound Vib. 2008, 317, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Huang, K.; Xiong, Y.; Sang, M. Nonlinear dynamic modelling and analysis for a spur gear system with time-varying pressure angle and gear backlash. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2019, 132, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharagozloo, M.; Shahmansoorian, A. Chaos control in gear transmission system using GPC and SMC controllers. J. Appl. Comput. Mech. 2022, 8, 545–556. [Google Scholar]
- Shams, Z.; Shahmansoorian, A. Fault estimation based on observer for chaotic Lorenz system with bifurcation problem. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2020, 42, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Goua, X.; Zhu, L. Modeling and analysis of a spur gear pair considering multi-state mesh with time-varying parameters and backlash. Mech. Mach. Theory 2019, 134, 582–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Kong, Y.; Xiao, K. Nonlinear Dynamic analysis of a spur gear pair system with wear considering the meshing position. Lubricants 2024, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, H. Nonlinear dynamics of a spur gear pair with force-dependent mesh stiffness. Nonlinear Dyn. 2020, 99, 1227–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnijeh, S.G.; Poursina, M.; Leira, B.J.; Karimpour, H.; Chai, W. Stochastic dynamics of a nonlinear time-varying spur gear model using an adaptive time-stepping path integration method. J. Sound Vib. 2019, 447, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khabou, M.T.; Bouchaala, N.; Chaari, F.; Fakhfakh, T.; Haddar, M. Study of a spur gear dynamic behavior in transient regime. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 125, 3089–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kahraman, A. A transient mixed elastohydrodynamic lubrication model for spur gear pairs. ASME J. Tribol. 2010, 132, 011501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kahraman, A. Influence of dynamic behaviour on elastohydrodynamic lubrication of spur gears. Proc. I. Mech. E. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2011, 225, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Kahraman, A. prediction of spur gear mechanical power losses using a transient elastohydrodynamic lubrication model. Tribol. Trans. 2010, 53, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjelm, R.; Wahlström, J. Influence of manufacturing error tolerances on thermal EHL behavior of gears. Lubricants 2022, 10, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhou, C. Oil film damping analysis in non-Newtonian transient thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication for gear transmission. J. Appl. Mech.-Trans. ASME 2018, 85, 035001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.U.; Aljibori, H.S.S.; Jweeg, M.J.; Abdullah, O.I.; Ruggiero, A. An investigation on the teeth crowning effects on the transient EHL performance of large-scale wind turbine spur gears. Lubricants 2023, 11, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gong, J. Study on TEHL flash temperature of helical gear pair considering profile modification. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2023, 75, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.B.; Yang, B.T.; Wang, Y.Q. Influences of transient impact and vibration on the lubrication performance of spur gears. Proc. I Mech. E. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2021, 235, 274–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wang, M. Thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication characteristics of double involute gears at the graded position of tooth waist. Tribol. Int. 2020, 144, 106028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, C.; Zang, S. Meshing stiffness analysis of gear using the Ishikawa method. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 401–403, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Y. Nonlinear dynamics analysis of the spur gear system for railway locomotive. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2017, 85, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Han, X.; Tao, Y.; Feng, S. Lubrication reliability analysis of spur gear systems based on random dynamics. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, R. Transient non-Newtonian elastohydrodynamic lubrication analysis of an involute spur gear. Wear 1997, 207, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masjedi, M.; Khonsari, M.M. Film thickness and asperity load formulas for line-contact elastohydrodynamic lubrication with provision for surface roughness. J. Tribol. 2012, 134, 011503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Meng, X.; Wang, S.; Ding, X. Research on mixed lubrication problems of the non-gaussian rough textured surface with the influence of stochastic roughness in consideration. J. Tribol. 2019, 141, 121501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Han, X.; Tao, Y.; Feng, S. Mixed elastohydrodynamic lubrication analysis of line contact with non-gaussian surface roughness. Tribol. Int. 2020, 151, 106449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Symbol, Unit | Gear Pair |
|---|---|
| Number of teeth, z1:z2 | 35:58 |
| Pressure angle, ° | 20 |
| Module, mm | 3 |
| Face width, mm | 20 |
| Rotational inertia, kg∙mm2 | 1860/13,590 |
| Constant component of rotation speed, rad/min | 2000 |
| Center distance, mm | 139.5 |
| Modulus of elasticity, GPa | 206 |
| Damping ratio | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pei, J.; Tian, Y.; Hou, H.; Tao, Y.; Wu, M.; Guan, Z. Dynamic Response and Lubrication Performance of Spur Gear Pair Under Time-Varying Rotation Speeds. Lubricants 2025, 13, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13010015
Pei J, Tian Y, Hou H, Tao Y, Wu M, Guan Z. Dynamic Response and Lubrication Performance of Spur Gear Pair Under Time-Varying Rotation Speeds. Lubricants. 2025; 13(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13010015
Chicago/Turabian StylePei, Jiaxing, Yuanyuan Tian, Hongjuan Hou, Yourui Tao, Miaojie Wu, and Zhigang Guan. 2025. "Dynamic Response and Lubrication Performance of Spur Gear Pair Under Time-Varying Rotation Speeds" Lubricants 13, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13010015
APA StylePei, J., Tian, Y., Hou, H., Tao, Y., Wu, M., & Guan, Z. (2025). Dynamic Response and Lubrication Performance of Spur Gear Pair Under Time-Varying Rotation Speeds. Lubricants, 13(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants13010015





