Effect of Micro- and Nano-Sized Carbonous Solid Lubricants as Oil Additives in Nanofluid on Tribological Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Works
3. Results and Discussions
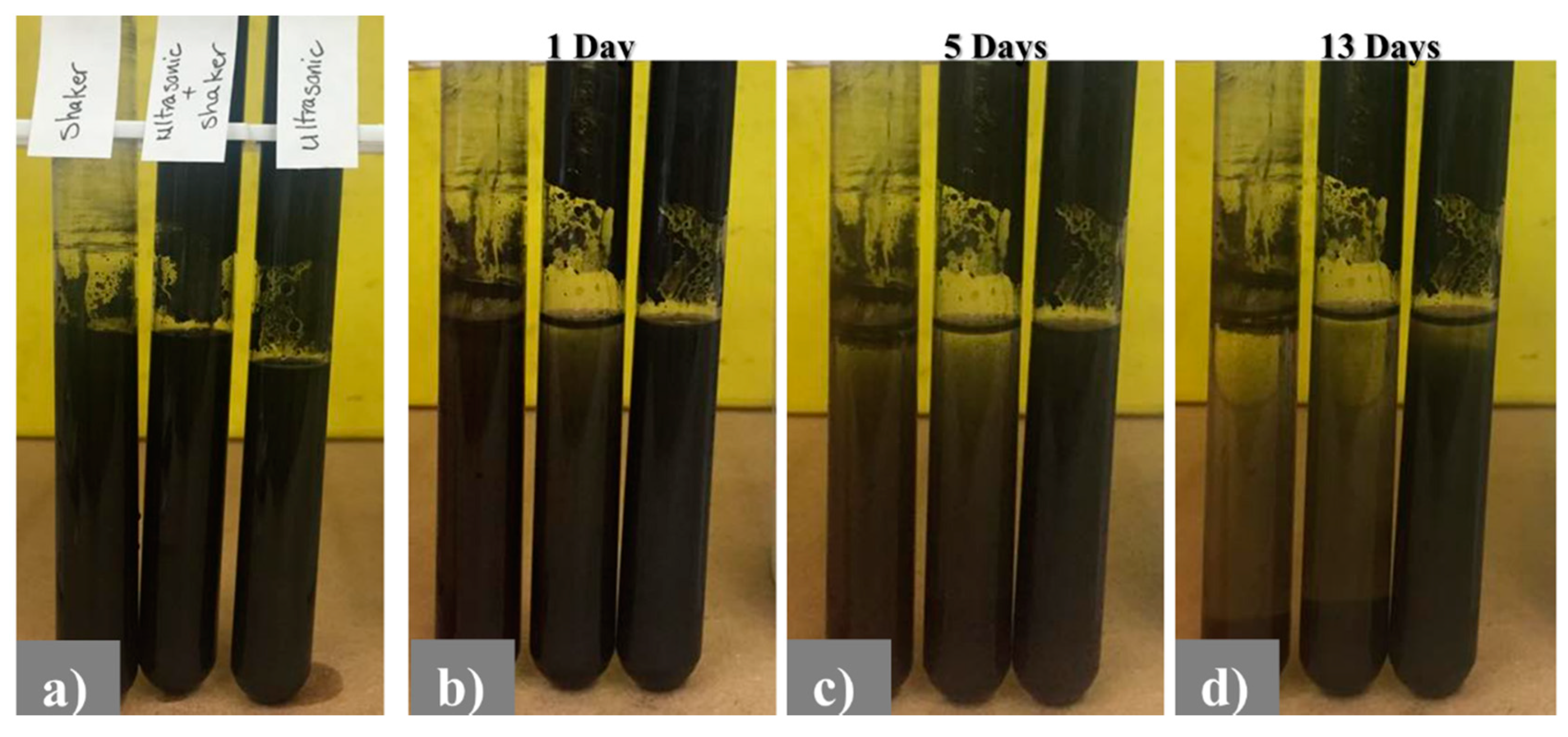
3.1. Dispersion Stability
3.2. Tribological Performance
3.3. Surface Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, J.; Luedtke, W.; Gourdon, D.; Ruths, M.; Israelachvili, J.; Landman, U. Frictional forces and Amontons’ law: From the molecular to the macroscopic scale. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3410–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, W.; Xue, Q. Tribological behavior and lubricating mechanism of Cu nanoparticles in oil. Tribol. Lett. 2000, 8, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, R.; Halperin, G.; Etsion, I.; Tenne, R. The effect of WS2 nanoparticles on friction reduction in various lubrication regimes. Tribol. Lett. 2004, 17, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tu, J.; Zou, T.; Zhang, L.; He, D. Friction and wear properties of IF–MoS 2 as additive in paraffin oil. Tribol. Lett. 2005, 20, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, S.; Kolubaev, A.; Belyaev, S.; Lerner, M.; Tepper, F. Study of friction reduction by nanocopper additives to motor oil. Wear 2002, 252, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhao, J.; Xu, K.; Xue, Q. Study on the tribological properties of ultradispersed diamond containing soot as an oil additive©. Tribol. Trans. 1997, 40, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, S. An investigation of the tribological behaviour of surface-modified ZnS nanoparticles in liquid paraffin. Wear 2000, 238, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, W.; Yu, L. Preparation of DDP-coated PbS nanoparticles and investigation of the antiwear ability of the prepared nanoparticles as additive in liquid paraffin. Wear 1998, 218, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Z. Friction and wear properties of a surface-modified TiO 2 nanoparticle as an additive in liquid paraffin. Wear 1997, 213, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, H.-Z.; Hu, K.-H.; Hu, X.-G. Tribological Properties of MoS~ 2 Nanoparticles as Additive in a Machine Oil. Tribology 2004, 24, 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Thakre, A.A.; Thakur, A.; Taylor, J. Study of behaviour of aluminium oxide nanoparticles suspended in SAE20W40 oil under extreme pressure lubrication. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2015, 67, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, Y.-R.; Huang, Y.-H.; Tsai, P.-C.; Hwang, G.-L. Tribological Performance of Oil-Based Lubricants with Carbon-Fe Nanocapsules Additive. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunn, N.; Mahbooba, Z.; Ivanov, M.; Ivanov, D.; Brenner, D.; Shenderova, O. Tribological properties of polyalphaolefin oil modified with nanocarbon additives. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2015, 54, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X. On the size effect of molybdenum disulfide particles on tribological performance. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2005, 57, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Hwang, Y.-J.; Choi, Y.-M.; Lee, J.-K.; Choi, C.; Oh, J.-M. A study on the tribological characteristics of graphite nano lubricants. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2009, 10, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Modification of graphene platelets and their tribological properties as a lubricant additive. Tribol. Lett. 2011, 41, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, E.; Moghadam, A.D.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Influences of graphite reinforcement on the tribological properties of self-lubricating aluminum matrix composites for green tribology, sustainability, and energy efficiency—A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 83, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.D.; Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Mechanical and tribological properties of self-lubricating metal matrix nanocomposites reinforced by carbon nanotubes (CNTs) and graphene—A review. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 77, 402–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, A.D.; Schultz, B.F.; Ferguson, J.; Omrani, E.; Rohatgi, P.K.; Gupta, N. Functional metal matrix composites: Self-lubricating, self-healing, and nanocomposites-an outlook. JOM 2014, 66, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tu, J.; Gan, L.; Li, C. An investigation on tribological properties of graphite nanosheets as oil additive. Wear 2006, 261, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaraiah, V.; Sankaranarayanan, V.; Ramaprabhu, S. Graphene-based engine oil nanofluids for tribological applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2011, 3, 4221–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, W.; Alpas, A.T. Wear mechanisms in hybrid composites of graphite-20 Pct SiC in A356 aluminum alloy (Al-7 Pct Si-0.3 Pct Mg). Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.R.; Alpas, A.T. The role of tribo-layers on the sliding wear behavior of graphite aluminum matrix composites. Wear 2001, 251, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.L.T.; Tsao, C.Y.A. Tribological behavior of aluminum/SiC/nickel-coated graphite hybrid composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2002, 333A, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshminarayanan, P.A.; Nayak, N.S. Tribological tests to simulate wear on piston rings. In Critical Component Wear in Heavy Duty Engines; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Singapore, 2011; pp. 167–195. [Google Scholar]
- Akhlaghi, F.; Zare-Bidaki, A. Influence of graphite content on the dry sliding and oil impregnated sliding wear behavior of Al 2024-graphite composites produced by in situ powder metallurgy method. Wear 2009, 266, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani1, E.; Moghadam, A.D.; Algazzar, M.; Moghadam, A.D.; Algazzar, M.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Effect of graphite particles on improving tribological properties Al-16Si-5Ni-5Graphite self-lubricating composite under fully flooded and starved lubrication conditions for transportation applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 87, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranganathan, N.; Bijwe, J. Comparative performance evaluation of NAO friction materials containing natural graphite and thermo-graphite. Wear 2016, 358–359, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Wei, X.D.; Li, Q.Y.; Wei, X.; Li, Q.; Carpick, R.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Elastic and frictional properties of graphene. Phys. Status Solidi B 2009, 246, 2562–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, Y.J.; Stromberg, R.; Nay, R.; Stromberg, R.; Nay, R.; Huang, H.; Wee, A.T.S.; Yang, H.; Bhatia, C.S. Frictional characteristics of exfoliated and epitaxial graphene. Carbon 2011, 49, 4059–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoz-Rosado, E.J.; Tertuliano, O.A.; Terrell, E.J. An atomistic study of the abrasive wear and failure of graphene sheets when used as a solid lubricant and a comparison to diamond-like-carbon coatings. Carbon 2012, 50, 4078–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetto, D.; Held, C.; Hausen, F. Friction and wear on single-layer epitaxial graphene in multi-asperity contacts. Tribol. Lett. 2012, 48, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Few layer graphene to reduce wear and friction on sliding steel surfaces. Carbon 2013, 54, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arwin, G.Z.; Rashmi, G.W. Tribological Evaluation of nano graphene Platelets as an additive to biolubricant base fluid. In EURECA 2013; Taylor’s University: Subang Jaya, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, H.W. Tribological properties of oleic acid-modified graphene as lubricant oil additives. J. Phys. D 2011, 44, 205303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, S.; Mungse, H.P.; Khatri, O.P. Dispersion of alkylated graphene in organic solvents and its potential for lubrication applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21032–21039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Menezes, P.L.; Lovell, M.R.; Jen, T.-C. The influence of surface roughness and particulate size on the tribological performance of bio-based multi-functional hybrid lubricants. Tribol. Int. 2015, 88, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, C.J.; Menezes, P.L.; Jen, T.-C.; Lovell, M.R. The influence of fatty acids on tribological and thermal properties of natural oils as sustainable biolubricants. Tribol. Int. 2015, 90, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, K.K.; Pol, V.G.; Thackeray, M.M.; Wen, J.; Miller, D.J.; Erdemir, A. Synthesis and tribology of micro-carbon sphere additives for enhanced lubrication. Tribol. Trans. 2015, 58, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omrani, E.; Menezes, P.L.; Rohatgi, P.K. Effect of Micro- and Nano-Sized Carbonous Solid Lubricants as Oil Additives in Nanofluid on Tribological Properties. Lubricants 2019, 7, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030025
Omrani E, Menezes PL, Rohatgi PK. Effect of Micro- and Nano-Sized Carbonous Solid Lubricants as Oil Additives in Nanofluid on Tribological Properties. Lubricants. 2019; 7(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmrani, Emad, Pradeep L. Menezes, and Pradeep K. Rohatgi. 2019. "Effect of Micro- and Nano-Sized Carbonous Solid Lubricants as Oil Additives in Nanofluid on Tribological Properties" Lubricants 7, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030025
APA StyleOmrani, E., Menezes, P. L., & Rohatgi, P. K. (2019). Effect of Micro- and Nano-Sized Carbonous Solid Lubricants as Oil Additives in Nanofluid on Tribological Properties. Lubricants, 7(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7030025





