Possibilities of Dry and Lubricated Friction Modification Enabled by Different Ultrashort Laser-Based Surface Structuring Methods
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
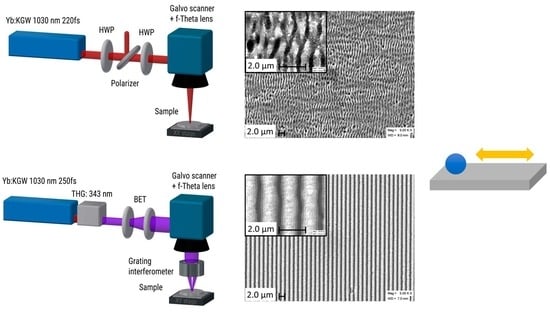
2.1. Laser Surface Texturing
2.1.1. LSFL
2.1.2. LBIA
2.2. Surface Analysis
2.3. Tribological Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Laser Surface Texturing
3.2. Friction Measurement
3.2.1. Dry Test 100Cr6 on 100Cr6
3.2.2. Dry Test Tungsten Carbide on 100Cr6
3.2.3. Lubricated Test 100Cr6 on 100Cr6
3.2.4. Lubricated Test Tungsten Carbide on 100Cr6
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holmberg, K.; Erdemir, A. Influence of tribology on global energy consumption, costs and emissions. Friction 2017, 5, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancona, A.; Carbone, G.; Scaraggi, M.; Mezzapesa, F.P.; Sorgente, D.; Lugarà, P.M. Laser surface micro-texturing to enhance the frictional behavior of lubricated steel. In Proceedings of the SPIE Laser-Based Micro- and Nanoprocessing VIII, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–6 February 2014; Volume 8968, p. 896806. [Google Scholar]
- Scaraggi, M.; Mezzapesa, F.P.; Carbone, G.; Ancona, A.; Tricarico, L. Friction Properties of Lubricated Laser-MicroTextured-Surfaces: An Experimental Study from Boundary- to Hydrodynamic-Lubrication. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Honda, T.; Kikuchi, J.; Iwai, Y.; Yasumaru, N.; Miyazaki, K. Friction Properties of the DLC Film with Periodic Structures in Nano-scale. Tribol. Online 2006, 1, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnilitskyi, I.; Rotundo, F.; Martini, C.; Pavlov, I.; Ilday, S.; Vovk, E.; Ilday, F.Ö.; Orazi, L. Nano patterning of AISI 316L stainless steel with Nonlinear Laser Lithography: Sliding under dry and oil-lubricated conditions. Tribol. Int. 2016, 99, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichstädt, J.; Römer, G.; Huis in’tVeld, A.J. Towards Friction Control using laser-induced periodic Surface Structures. Phys. Procedia 2011, 12, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Koter, R.; Hartelt, M.; Spaltmann, D.; Pentzien, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Tribological performance of sub-100-nm femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on titanium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Kirner, S.V.; Rosenfeld, A.; Kruger, J. Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures—A Scientific Evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 9000615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekesi, J.; Meinertz, J.; Ihlemann, J.; Simon, P. Fabrication of large-area grating structures through laser ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2008, 93, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, B.K.; Gupta, M.C. Self-organized micro/nano structures in metal surfaces by ultrafast laser irradiation. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2010, 48, 940–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Rung, S.; Hellmann, R. Generation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on transparent material-fused silica. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 181607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.J.Y.; Krüger, J.; Itina, T.E.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Bonse, J. Rippled area formed by surface plasmon polaritons upon femtosecond laser double-pulse irradiation of silicon: The role of carrier generation and relaxation processes. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 117, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Chu, J.; Huang, W. Femtosecond laser color marking stainless steel surface with different wavelengths. Appl. Phys. A 2015, 118, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rung, S.; Schwarz, S.; Götzendorfer, B.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Time Dependence of Wetting Behavior Upon Applying Hierarchic Nano-Micro Periodic Surface Structures on Brass Using Ultra Short Laser Pulses. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ta, D.; Dunn, A.; Wasley, T.J.; Li, J.; Kay, R.W.; Stringer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Esenturk, E.; Connaughton, C.; Shephard, J.D. Laser textured surface gradients. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 371, 583–589. [Google Scholar]
- Raimbault, O.; Benayoun, S.; Anselme, K.; Mauclair, C.; Bourgade, T.; Kietzig, A.M.; Girard-Lauriault, P.L.; Valette, S.; Donnet, C. The effects of femtosecond laser-textured Ti-6Al-4V on wettability and cell response. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 69, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallat, K.; Dörr, D.; Le Harzic, R.; Stracke, F.; Sauer, D.; Neumeier, M.; Kovtun, A.; Zimmermann, H.; Epple, M. Cellular reactions toward nanostructured silicon surfaces created by laser ablation. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 042016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Rosenkranz, A.; Reinert, L.; Ramos-Moore, E.; Souza, N.; Müser, M.H.; Mücklich, F. Dry Friction Between Laser-Patterned Surfaces: Role of Alignment, Structural Wavelength and Surface Chemistry. Tribol. Lett. 2013, 49, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancona, A.; Carbone, G.; de Filippis, M.; Volpe, A.; Lugarà, P.M. Femtosecond laser full and partial texturing of steel surfaces to reduce friction in lubricated contact. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2014, 3, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rung, S.; Bokan, K.; Rutsch, K.; Schwarz, S.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Laser Induced Periodic Surface Structures on 100Cr6 Steel for Modification of Friction Demonstrated with Stribeck Test. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2018, 13, 160–165. [Google Scholar]
- Bonse, J.; Kirner, S.V.; Griepentrog, M.; Spaltmann, D.; Krüger, J. Femtosecond Laser Texturing of Surfaces for Tribological Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voyer, J.; Klien, S.; Ausserer, F.; Velkavrh, I.; Ristow, A.; Diem, A. Friction Reduction Through Sub-Micro Laser Surface Modifications. Tribologie Schmierungstechnik 2015, 62, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kasem, H.; Stav, O.; Grützmacher, P.; Gachot, C. Effect of Low Depth Surface Texturing on Friction Reduction in Lubricated Sliding Contact. Lubricants 2018, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gachot, C.; Grützmacher, P.; Rosenkranz, A. Laser Surface Texturing of TiAl Multilayer Films—Effects of Microstructure and Topography on Friction and Wear. Lubricants 2018, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golosov, E.V.; Emel’yanov, V.I.; Ionin, A.A.; Kolobov, Y.R.; Kudryashov, S.I.; Ligachev, A.E.; Novoselov, Y.N.; Seleznev, L.V.; Sinitsyn, D.V. Femtosecond laser writing of subwave one-dimensional quasiperiodic nanostructures on a titanium surface. JETP Lett. 2009, 90, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamuro, K.; Hashida, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ikuta, Y.; Tokita, S.; Sakabe, S. Laser fluence dependence of periodic grating structures formed on metal surfaces under femtosecond laser pulse irradiation. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 165417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J. Pulse number dependence of laser-induced periodic surface structures for femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 034903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preusch, F.; Rung, S.; Hellmann, R. Influence of Polishing Orientation on the Generation of LIPSS on Stainless Steel. J. Laser Micro/Nanoeng. 2016, 11, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekesi, J.; Simon, P.; Ihlemann, J. Deterministic sub-micron 2D grating structures on steel by UV-fs-laser interference patterning. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 114, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirner, S.V.; Slachciak, N.; Elert, A.M.; Griepentrog, M.; Fischer, D.; Hertwig, A.; Sahre, M.; Dörfel, I.; Sturm, H.; Pentzien, S.; et al. Tribological performance of titanium samples oxidized by fs-laser radiation, thermal heating, or electrochemical anodization. Appl. Phys. A 2018, 124, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czichos, H.; Habig, K.H. Tribologie-Handbuch: Tribometrie, Tribomaterialien, Tribotechnik, 4th ed.; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.J. On the Stribeck Curves for Lubricated Counterformal Contacts of Rough Surfaces. J. Tribol. 2015, 137, 021501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelinck, E.; Schipper, D.J. Calculation of Stribeck curves for line contacts. Tribol. Int. 2000, 33, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Q.J. On the lambda ratio range of mixed lubrication. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2012, 226, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, O.; Fineberg, J. Static friction coefficient is not a material constant. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2011, 106, 254301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; de Rooij, M.; Schipper, D. A load dependent friction model for fully plastic contact conditions. Wear 2010, 269, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Q.J. Effect of Roughness Orientation on the Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication Film Thickness. J. Tribol. 2013, 135, 031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Tribometer Ball | Load/mN | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 100 | 200 | 500 | 1000 | |
| 100Cr6 steel | 20.2 µm | 25.6 µm | 32.0 µm | 43.4 µm | 54.7 µm |
| Tungsten carbide | 17.8 µm | 22.4 µm | 28.3 µm | 38.4 µm | 48.3 µm |
| Sliding Regime | Test Methode | Substrate | Tribometer Ball | Load Force | Velocity | Cycles | Lubricant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| dry | Ball-on-disc | 100Cr6 | 100Cr6 tungsten carbide | 50 mN 200 mN | 4 mm/s | 500 | - |
| lubrication | Ball-on-disc | 100Cr6 | 100Cr6 tungsten carbide | 100 mN 500 mN 1000 mN | 4 mm/s | 1000 | 5W40 |
| Ball | Dry | Lubricated | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LBIA | LSFL | LBIA | LSFL | |||||
| 90 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 90 | 0 | |
| Steel | 0 | - - | + | + | ++ | + | 0 | - |
| WC | - | - - | ++ | + | + | ++ | - - | - - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rung, S.; Bokan, K.; Kleinwort, F.; Schwarz, S.; Simon, P.; Klein-Wiele, J.-H.; Esen, C.; Hellmann, R. Possibilities of Dry and Lubricated Friction Modification Enabled by Different Ultrashort Laser-Based Surface Structuring Methods. Lubricants 2019, 7, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7050043
Rung S, Bokan K, Kleinwort F, Schwarz S, Simon P, Klein-Wiele J-H, Esen C, Hellmann R. Possibilities of Dry and Lubricated Friction Modification Enabled by Different Ultrashort Laser-Based Surface Structuring Methods. Lubricants. 2019; 7(5):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7050043
Chicago/Turabian StyleRung, Stefan, Kevin Bokan, Frederick Kleinwort, Simon Schwarz, Peter Simon, Jan-Hendrik Klein-Wiele, Cemal Esen, and Ralf Hellmann. 2019. "Possibilities of Dry and Lubricated Friction Modification Enabled by Different Ultrashort Laser-Based Surface Structuring Methods" Lubricants 7, no. 5: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7050043
APA StyleRung, S., Bokan, K., Kleinwort, F., Schwarz, S., Simon, P., Klein-Wiele, J.-H., Esen, C., & Hellmann, R. (2019). Possibilities of Dry and Lubricated Friction Modification Enabled by Different Ultrashort Laser-Based Surface Structuring Methods. Lubricants, 7(5), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants7050043