Friction and Wear Pattern of Silica-Reinforced Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in Sliding Contact with a Blade Indenter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
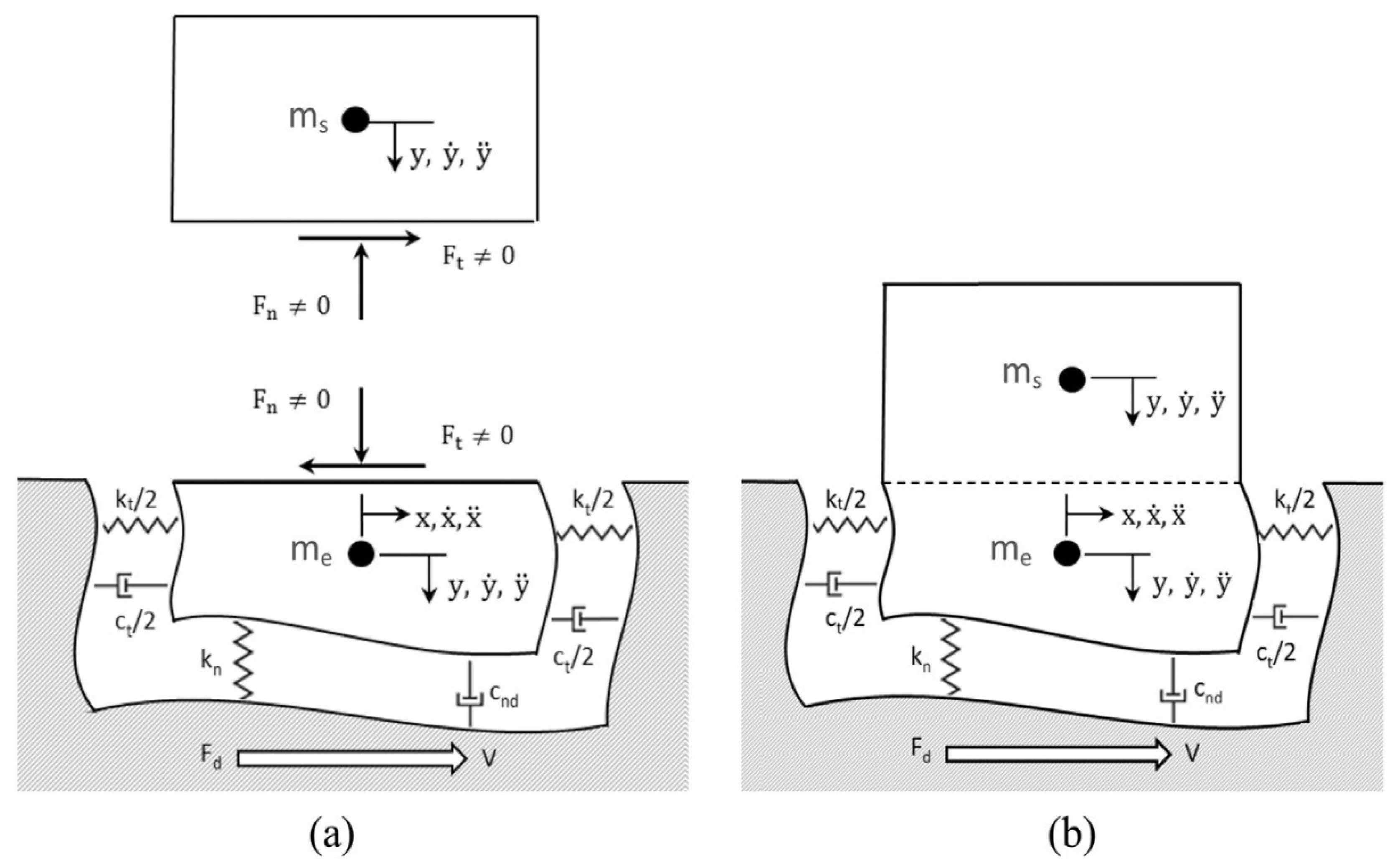
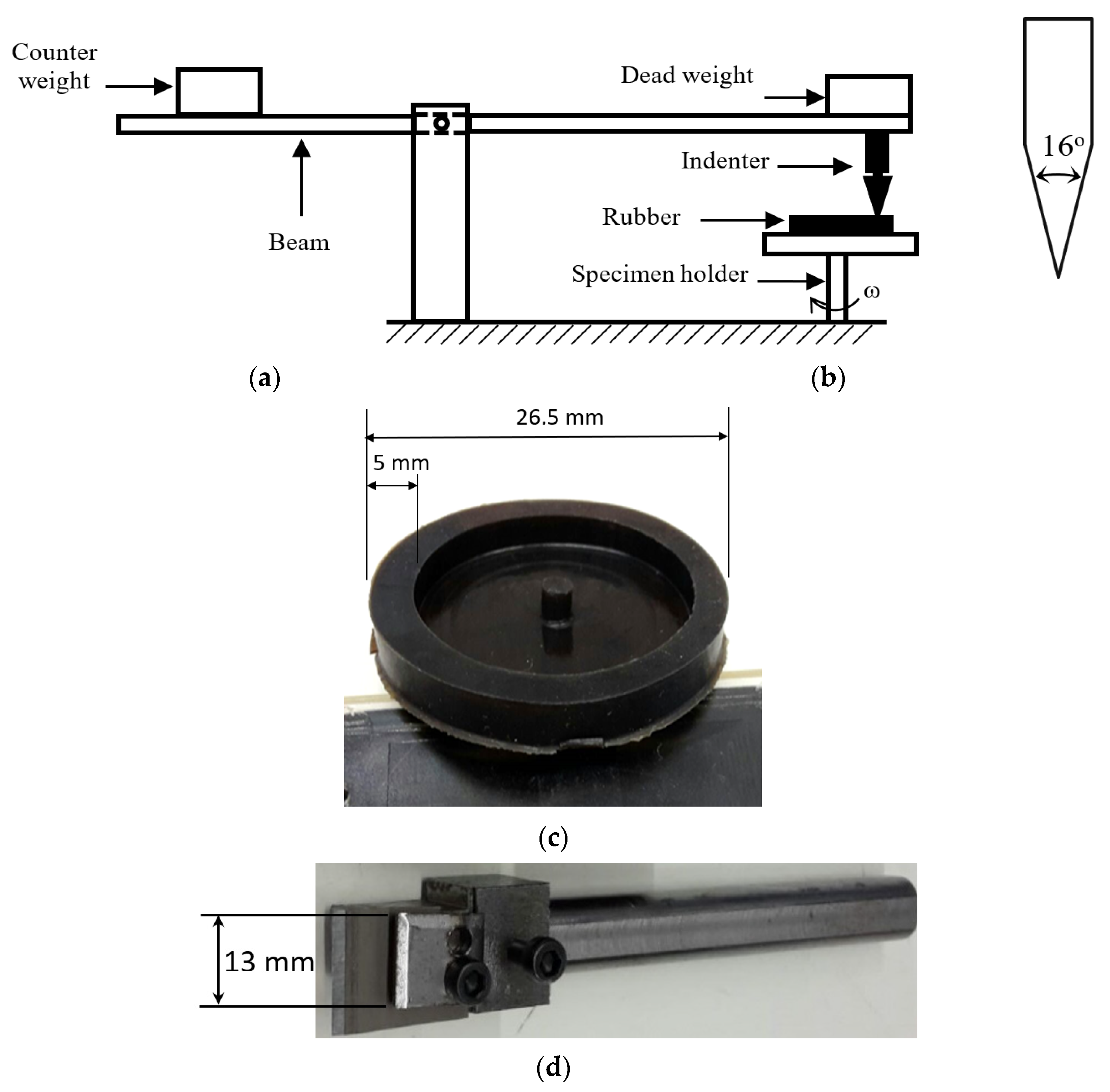
2.2. Methods
3. Results and Discussion
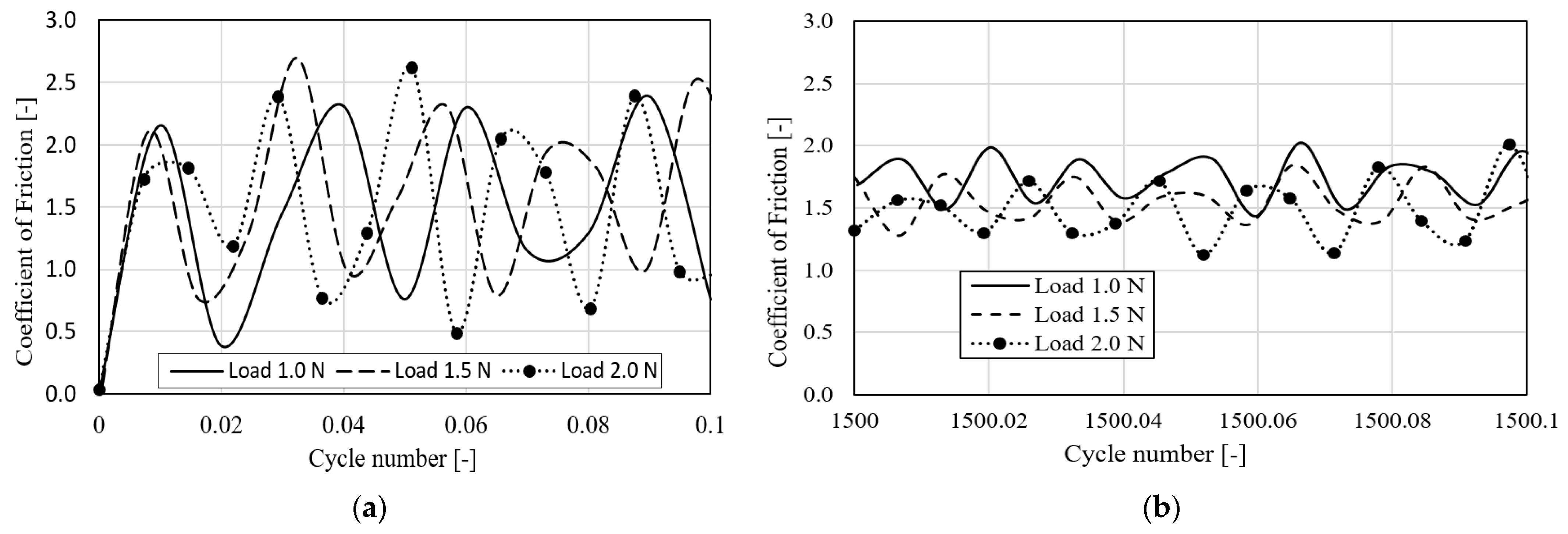
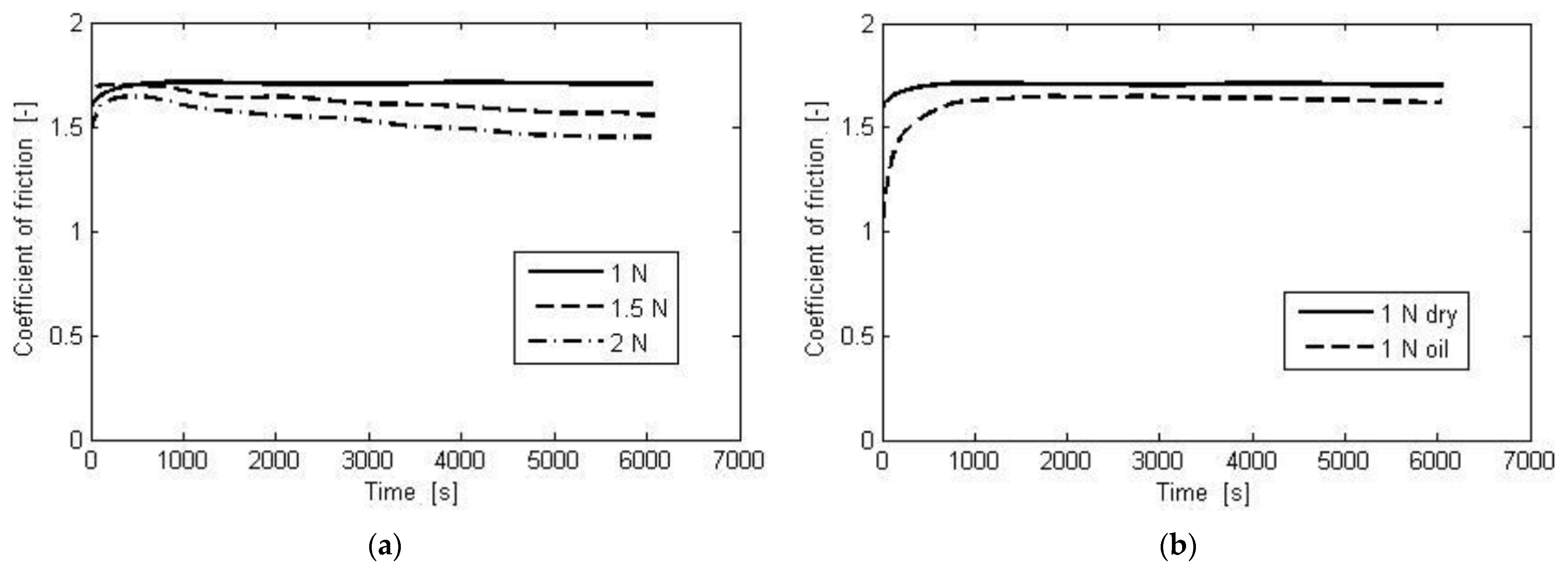
3.1. Experimental Results
3.2. Coefficient of Friction Analysis
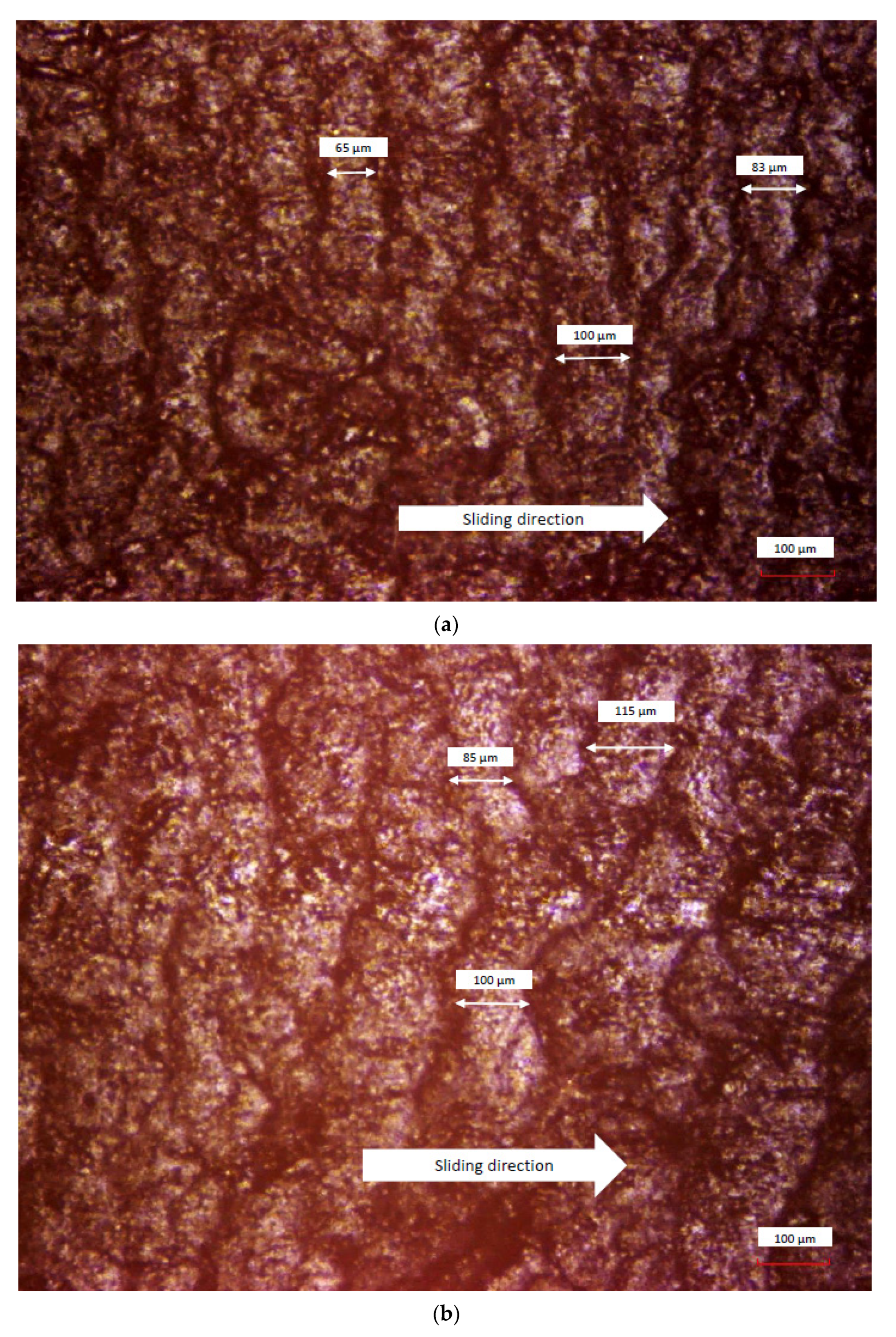
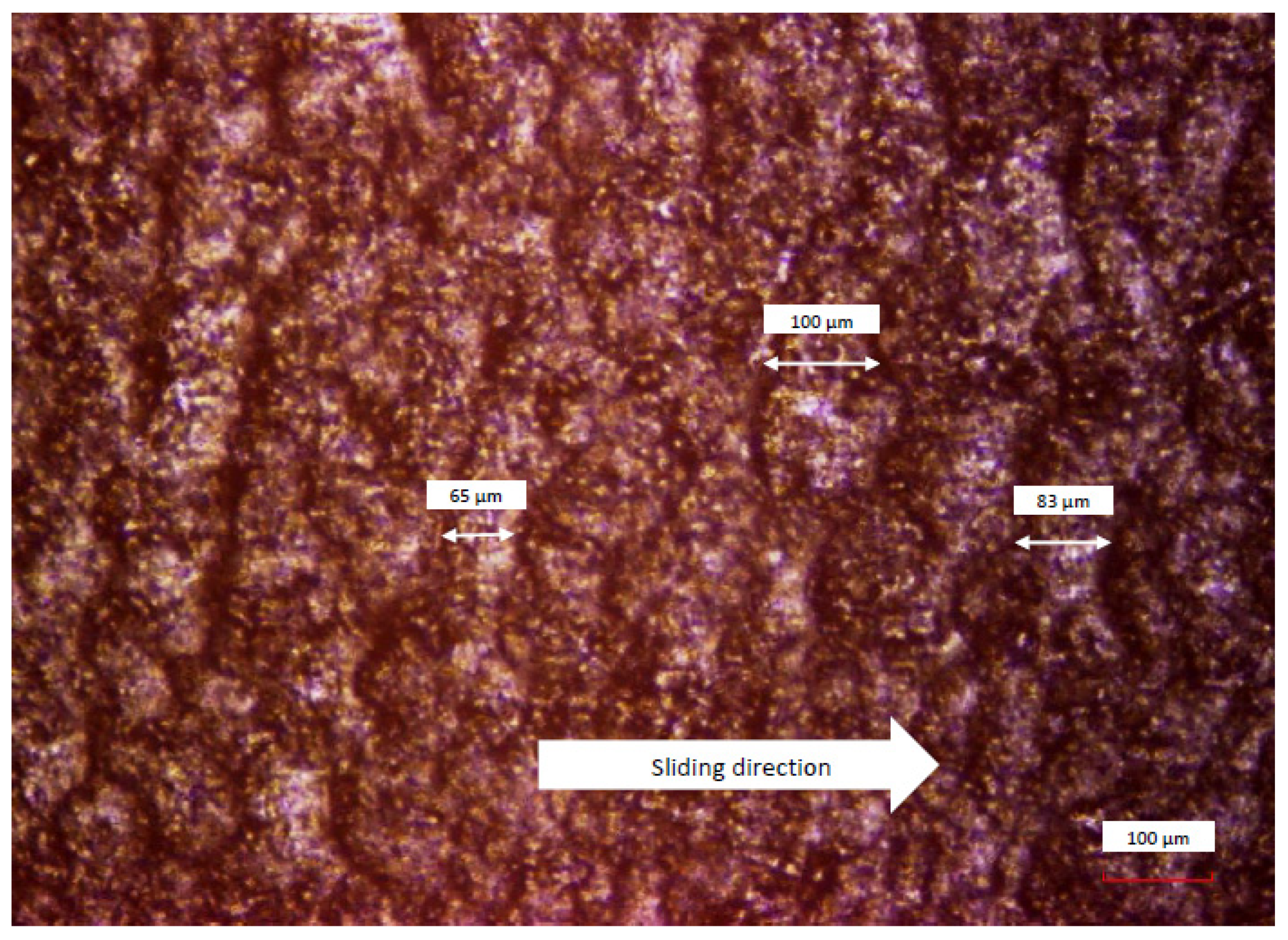
3.3. Wear Pattern Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| g | Gravity acceleration [m/s2] |
| H | Rubber hardness [MPa] |
| Constants [-] | |
| kn | Normal stiffness of the rubber [N/m] |
| Fn | Total normal load [N] |
| mdw | Dead mass [kg] |
| mif | Inertia mass of the indenter system [kg] |
| mdwg | Dead weight or static load [N] |
| mifg | Dynamic load or inertia force of the indenter system [N] |
| Loss factor, depend on the rubber properties [-] | |
| V | Sliding velocity [m/s] |
| Length of the wear pattern spacing [m] | |
| Friction coefficient due to point contact [-] | |
| Coefficient of friction due to sliding [-] | |
| Coefficient of friction due to rupturing [-] | |
| ρ | Proportional parameter [m/N1/2] |
| Damping factor for abrasion tester [-] | |
| Maximum elastic stress [N/m2] | |
| Breaking stress of the rubber chain [N/m2] | |
| Apex angle of cone tip [deg] |
Appendix A
References
- Hokkirigawa, K.; Kato, K. An experimental and theoretical investigation of ploughing, cutting and wedge formation during abrasive wear. Tribol. Int. 1998, 88, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallamach, A. Abrasion of rubber by a needle. J. Polym. Sci. 1954, 9, 385–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schallamach, A. Friction and abrasion of rubber. Wear 1958, 1, 384–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern, E.; Thomas, A.C. Studies of rubber abrasion. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1979, 52, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, M.; Anil, K.; Bhowmick, A.K. Analysis of wear characteristics of natural rubber nanocomposites. Wear 2010, 269, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, A.N.; Pulford, C.T.R. Mechanisms of Rubber Abrasion. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 1983, 28, 943–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gent, A.N.; Nah, C. Abrasion of rubber by a blade abrader: Effect of blade sharpness and test temperature for selected compounds. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1996, 69, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Yamazaki, H. Mechanism of rubber abrasion—Part 1: Abrasion pattern formation in natural rubber vulcanizate. Wear 1994, 171, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Yamazaki, H. Mechanism of rubber abrasion—Part 2: General rule in abrasion pattern formation in rubber-like materials. Wear 1994, 178, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukahori, Y.; Yamazaki, H. Mechanism of rubber abrasion—Part 3: How is friction linked to fracture in rubber abrasion? Wear 1995, 188, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchiyama, Y.; Ishino, Y. Pattern abrasion mechanism of rubber. Wear 1992, 158, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coveney, C.; Menger, C. Initiation and development of wear of an elastomeric surface by a blade abrader. Wear 1999, 233–235, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosch, K.A.; Scallamach, A. Relation between abrasion and strength of rubber. Trans. Inst. Rubber Ind. 1965, 41, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhr, A.H.; Roberts, A.D. Rubber abrasion and wear. Wear 1992, 158, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Theory of rubber friction and contact mechanics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Busse, L.; Le Gal, A.; Kluppel, M. Modelling of Dry and Wet Friction of Silica Filled Elastomers on Self-Affine Road Surfaces. LNACM 2009, 51, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Schallamach, A. Recent advances in knowledge of rubber friction and tire wear. Rubber Chem. Technol. 1968, 41, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.F. Principles and Alication of Tribology, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, D.F. The Friction and Lubrication of Elastomer, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Setiyana, B.; Ismail, R.; Jamari, J.; Schipper, D.J. An analytical study of the wear pattern of an abraded rubber surface: The interaction model. Tribol.–Mater. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 12, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafidh, M.; Setiyana, B.; Jamari, J.; Masen, M.A.; Schipper, D.J. Understanding the occurrence of a wavy wear track on elastomeric materials. Wear 2018, 412–413, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vieira, T.; Ferreira, R.P.; Kuchiishi, A.K.; Bernucci, L.L.B.; Sinatora, A. Evaluation of friction mechanisms and wear rates on rubber tire materials by low-cost laboratory tests. Wear 2015, 328–329, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauline, R. Rubber Compound and Tires Based on such a Compound. Google Patents. 1995. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0501227A1/en (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Hintze, C. Influence of processing on morphology in short aramid fiber reinforced elastomer compounds. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 130, 1682–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiyana, B.; Ismail, R.; Jamari, J.; Schipper, D.J. Stick-slip behaviour of a viscoelastic flat sliding against a rigid indenter. Tribol. Online 2016, 11, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mané, Z.; Loubet, J.L.; Guerret, C.; Guy, L.; Sanseau, O.; Odoni, L.; Vanel, L.; Long, D.R.; Sotta, P. A new rotary tribometer to study the wear of reinforced rubber materials. Wear 2013, 306, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ingredients | [in phr] | Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| SBR | 97.3 | Arlanxeo, Leverkusen, Germany |
| BR | 30.0 | Kumho, Seoul, Korea |
| Silica | 80.0 | Evonik Industries AG, Essen, Germany |
| Zinc oxide (ZnO) | 2.5 | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA |
| Stearic acid (SA) | 2.5 | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA |
| Treated Distillate Aromatic Extract (TDAE) | 6.7 | Hansen & Rosenthal, Hamburg, Germany |
| TESPT | 7.0 | Evonik Industries AG, Essen, Germany |
| 6PPD | 2.0 | Flexsys, Brussels, Belgium |
| TMQ | 2.0 | Flexsys, Brussels, Belgium |
| Sulfur | 1.4 | Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA |
| N-Cyclohexyl Benzothiazole Sulfenamide (CBS) | 1.7 | Flexsys, Brussels, Belgium |
| Di-Phenyl Guanidine (DPG) | 2.0 | Flexsys, Brussels, Belgium |
| Fn (N) | (µm) | Average (µm) | ρ (µm/) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 65–100 | 83 | 77.1 |
| 1.5 | 85–115 | 100 | 77.6 |
| 2.0 | 100–130 | 115 | 78.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Setiyana, B.; Khafidh, M.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Ismail, R.; Jamari; Schipper, D.J. Friction and Wear Pattern of Silica-Reinforced Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in Sliding Contact with a Blade Indenter. Lubricants 2021, 9, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9110110
Setiyana B, Khafidh M, Tauviqirrahman M, Ismail R, Jamari, Schipper DJ. Friction and Wear Pattern of Silica-Reinforced Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in Sliding Contact with a Blade Indenter. Lubricants. 2021; 9(11):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9110110
Chicago/Turabian StyleSetiyana, Budi, Muhammad Khafidh, Mohammad Tauviqirrahman, Rifky Ismail, Jamari, and Dirk Jan Schipper. 2021. "Friction and Wear Pattern of Silica-Reinforced Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in Sliding Contact with a Blade Indenter" Lubricants 9, no. 11: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9110110
APA StyleSetiyana, B., Khafidh, M., Tauviqirrahman, M., Ismail, R., Jamari, & Schipper, D. J. (2021). Friction and Wear Pattern of Silica-Reinforced Styrene-Butadiene Rubber (SBR) in Sliding Contact with a Blade Indenter. Lubricants, 9(11), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/lubricants9110110






