Abstract
Large-scale transcriptome and methylome data analyses obtained by high-throughput technologies have been enabling the identification of novel imprinted genes. We investigated genome-wide DNA methylation patterns in multiple human tissues, using a high-resolution microarray to uncover hemimethylated CpGs located in promoters overlapping CpG islands, aiming to identify novel candidate imprinted genes. Using our approach, we recovered ~30% of the known human imprinted genes, and a further 168 candidates were identified, 61 of which with at least three hemimethylated CpGs shared by more than two tissue types. Thirty-four of these candidate genes are members of the protocadherin cluster on 5q31.3; in mice, protocadherin genes have non-imprinted random monoallelic expression, which might also be the case in humans. Among the remaining 27 genes, ZNF331 was recently validated as an imprinted gene, and six of them have been reported as candidates, supporting our prediction. Five candidates (CCDC166, ARC, PLEC, TONSL, and VPS28) map to 8q24.3, and might constitute a novel imprinted cluster. Additionally, we performed a comprehensive compilation of known human and mice imprinted genes from literature and databases, and a comparison among high-throughput imprinting studies in humans. The screening for hemimethylated CpGs shared by multiple human tissues, together with the extensive review, appears to be a useful approach to reveal candidate imprinted genes.
1. Introduction
The appropriate gene expression of each cell type is controlled by several mechanisms, and for most genes, both or neither of the alleles are expressed, depending on the state or identity of a given cell. However, many genes are monoallelically expressed, such as the majority of those on the inactive X chromosome, autosomal genes exhibiting random monoallelic expression, those regulated by polymorphisms in cis-regulatory elements, and imprinted genes (IG) [1].
The most important epigenetic modification at imprinted loci is DNA methylation, that is, the addition of methyl groups in CG dinucleotides, known as CpG sites. Genomic segments presenting with a higher density of CpGs compared to the whole genome are known as CpG islands; these segments constitute 1–2% of the mammalian genome, and are associated with most promoters in both human and mouse genomes [2]. Imprinted genes are rich in CpG islands, and acquire methylation according to the parental origin of the allele, leading to differential expression. Two types of differentially methylated regions (DMRs) have been described in imprinting: germline (or primary) DMRs, whose pattern of methylation is established during gametogenesis, and is maintained through the wave of demethylation and remethylation that occurs at the early stages of mammalian embryo development; and somatic (or secondary) DMRs, which become differentially methylated in the promoters of some IGs, after egg fertilization, and can be tissue-specific [3]. Once established, the cells and their descendants have the same methylated allele at a given IG.
About one-third of known IGs are non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), many of which are small RNAs [4]. Although some IGs occur isolated or in pairs, the majority of human IGs (~65%) are arranged in clusters of three or more genes in segments up to 2.3 Mb in size, that are structurally conserved between humans and mice. Ten human imprinted clusters have been characterized so far, mapping to 2q33.3, 6q24.2, 7q21.3, 7q32.2, 11p15.5p15.4, 14q32.2, 15q11.2, 19q13.43, and 20q13.32. Most clusters consist of both maternally and paternally imprinted genes, at least one imprinted ncRNA (microRNA, snoRNA, or lncRNA), as well as non-imprinted genes [3]. In order to achieve parental specific expression, each cluster is controlled by a master cis-acting element, the imprinting control region (ICR). The ICR control mechanisms might differ from one cluster to another, but typically include promoter or intergenic methylation, insulators and ncRNA transcripts [5,6,7,8]. The ICRs harbor parent-specific DMRs and regulate allelic expression of many genes across long distances within the imprinted cluster. Promoters of singleton IGs are also differentially methylated, frequently acting as ICRs [9]. Despite DNA methylation being the best-known epigenetic mark found in IGs, ICRs also show allelic differences in chromatin structure, involving histone modifications [10].
Most human IGs were identified in familial studies of morbid conditions with manifestation dependent on maternal or paternal transmission, or otherwise, by comparison to mouse IGs. In general, the approaches used to identify novel IGs are based on three main features: presence of an epigenetic signature, monoallelic expression dependent on parental origin, and specific characteristics of the DNA sequence (such as Short interspersed nuclear elements—SINE—exclusion) [3]. Currently, large-scale transcriptome and methylome analyses of data obtained by high-throughput technologies, such as microarrays and next-generation sequencing, are enabling the identification of new candidate IGs [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
In the present study, we investigated the genome-wide DNA methylation pattern of hundreds of thousands of CpG sites in multiple human tissues, using the high-resolution Infinium 450K array platform (HM450K, Illumina, Inc, San Diego, CA, USA). We applied stringent criteria that allowed robust identification of genomic hemimethylated CpG sites, and a surrogate marker for monoallelic methylation, thus disclosing candidate IGs. In addition, we performed a comprehensive compilation of all known IGs in both human and mice, based on pertinent literature and databases.
2. Results
2.1. Compilation of Known Imprinted Genes in Human and Mice
Using two available imprinting public databases, the Catalogue of Imprinted Genes and Parent-of-Origin Effects in Humans and Animals [21] and Geneimprint [22], all genes classified as “imprinted” in at least one of the databases were selected, resulting in a list of 103 known IGs in humans (Table S1), and 150 in mice (Table S2). Most IGs are conserved between humans and mice; however, excluding those that have no orthologs between the two species, 62 are specific to mice and only 27 to humans, which may reflect the difficulty in identifying IGs in humans. Only one gene (DLX5) has a contradictory imprinting status in humans between both databases; given that this gene is not imprinted in mouse, its imprinting status needs to be better characterized in human. A growing number of putative IGs, in which allele-specific expression (ASE) has been demonstrated in one or more human tissues, have been described in the past few years using genome-wide methodologies—ARMC3, WDR27, WRB, NHP2L1, AGBL3, MCCC1, MIR512-1, MX2, NOTCH3, NDUFB, FAM19A5, RMI2, HERC3, SORCS2, ANTXR1, PTPRN2, PMF1, PRSS50, THEGL, UGT2B4, FRG1, DHFR, KIF25, NAPRT1, INTS4, AMPD3, LPAR6, MEG9, RP11-7F17.7, SNHG14, GNG7, and CST1 [11,15,16,17,18,19,20] (all known and candidate IGs are listed and compared in Table S3). ASE in some tissues and/or differential methylation patterns are indicative of imprinting, but, for validating candidate IGs, the analysis of ASE in family trios is necessary to exclude random monoallelic expression and to distinguish the candidates from possible cis-regulatory elements [23]. More recently, novel IGs have been described, after validation using familial data—ZNF331, RHOBTB3, PAPPA2, UTS2, PSCA, PPIEL, ENST00000393177, PAX8, PAX8-AS1, PID1, HM13, and ZNF595 [17,19,20]. The ZNF331, RHOBTB3, and PAPPA2 genes have a “provisional” status in the Catalogue of Imprinted Genes and Parent-of-Origin Effects in Humans and Animals, and the other genes were not included in the two public databases, and therefore, were not listed in Table S1.
2.2. Methylation Array Data Processing and Selection Criteria of IGs
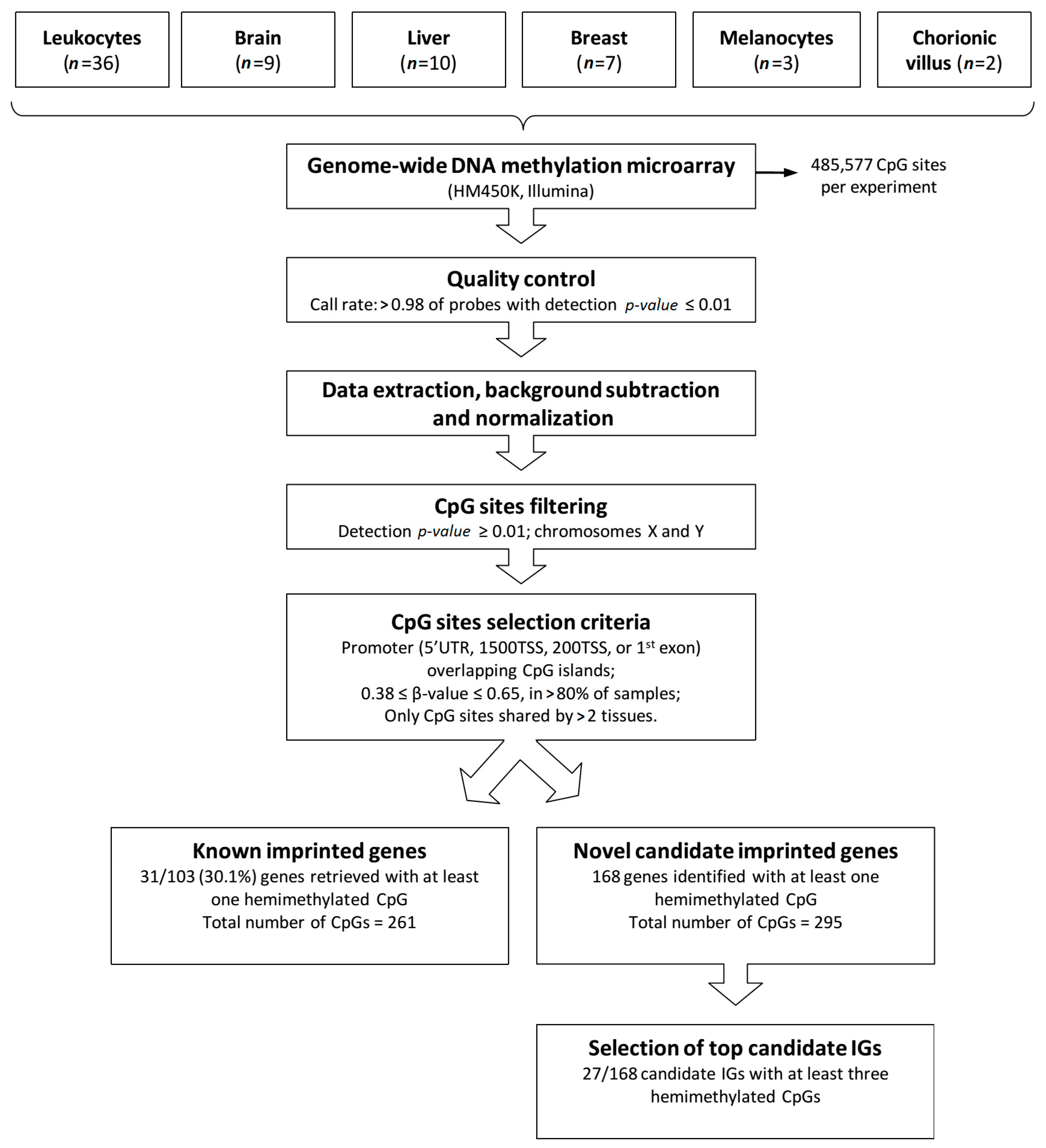
A flow diagram depicting the stages of the analysis shown in Figure 1. Genomic methylation data were generated from 67 samples from different normal human tissues (leukocyte, brain frontal cortex, liver, breast, melanocyte and chorionic villus), using the HM450K platform (Illumina). A total of 485,577 CpG sites were investigated per experiment. All samples met quality control parameters, data was extracted and normalized, and CpG sites with detection p-value ≥ 0.01 as well as those mapped to the X and Y chromosomes were excluded, reducing by ~15,000 the number of probes per experiment.
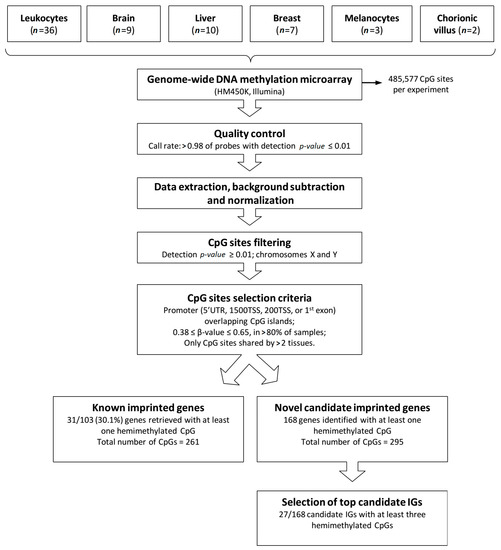
Figure 1.
Methodology applied to identify novel candidate imprinted genes. The flow diagram shows tissue types, steps of methylation array data processing, selection criteria for screening candidate imprinted genes (IG) and results obtained.
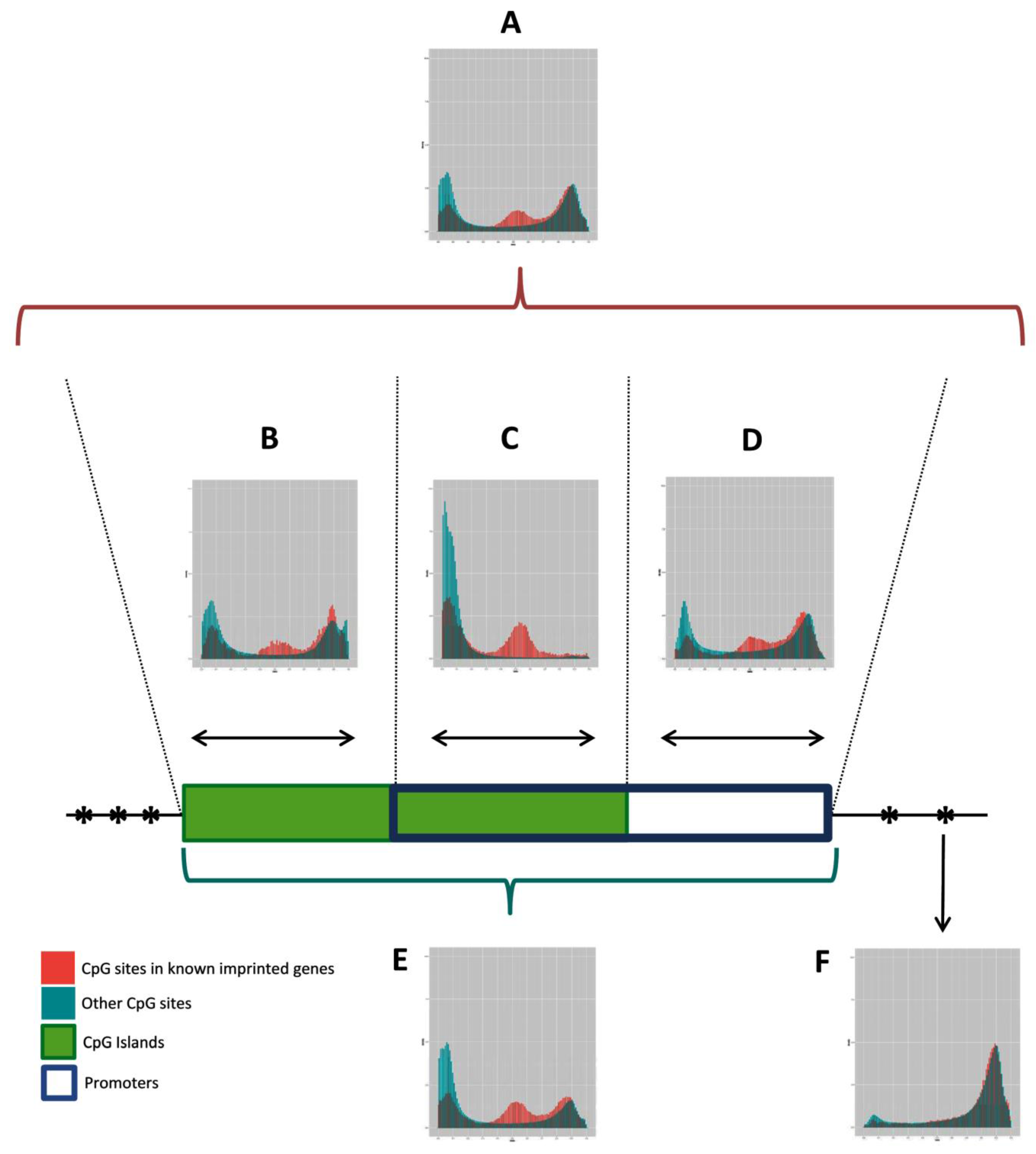
To search candidate IGs, we first analyzed the methylation pattern of the known human IGs in relation to all CpG sites covered by the HM450K, using array data from leukocytes of 36 healthy donors. The DNA methylation pattern of DMRs in blood has been reported to be robust and representative of DMRs in other human tissues [24], supporting the use of blood methylation data to define the selection criteria. The graphs presented in Figure 2 show the density of β-values measured for CpG sites associated or not with known IGs, grouped according to their genomic context (Figure 2A–F). CpG islands (Figure 2B) or promoter regions (promoter, 1500TSS, 200TSS, and first exon; Figure 2D) have similar methylation profiles, with CpGs associated with known IGs that are either hypo, hemi, or hypermethylated. In both cases, we observe an enrichment of CpGs associated with known IGs in intermediate ratios of methylation (hemimethylated regions), compared to other CpG sites in the genome. The greatest enrichment was observed on the overlapping regions of CpG islands and promoters, with a methylation ratio interval of 0.38–0.65 (Figure 2C). Thus, the combination of these genomic features was defined as the most suitable criteria to search for novel IGs in our analysis.
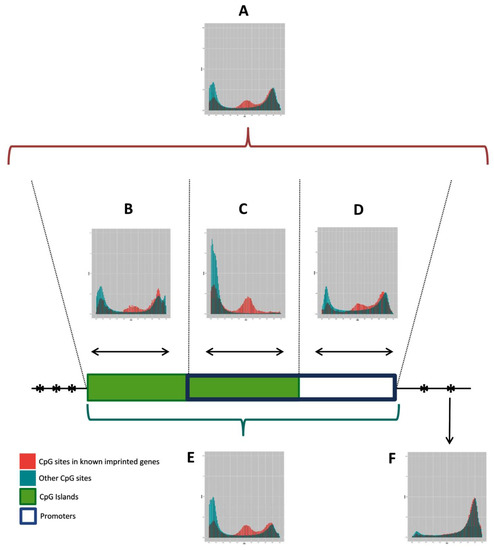
Figure 2.
Methylation pattern of CpGs of known human IGs relative to CpGs covered by the HM450K. The histograms show the density of CpG sites (y axis) and their respective β values (x axis) ranging from 0 (unmethylated) to 1 (fully methylated), grouped according to their genomic context. (A) All CpG sites; (B) CpG sites in CpG islands, only; (C) CpG sites overlapping promoter regions (promoter, 1500TSS, 200TSS, and 1st exon) and CpG islands; (D) CpG sites in promoter regions, only; (E) CpG sites in promoter regions or CpG islands; (F) All CpG sites, except CpG islands or promoter regions. Histogram C recovered a better profile of known imprinted genes (IG) in this platform, with methylation ratios in the range 0.38–0.65. Data was generated from leukocytes of 36 healthy donors.
Epigenetic marks are usually maintained throughout the body in known imprinted regions [3,24]. Based on this fact, we retrieved hemimethylated CpG sites of islands mapped to promoters and selected those shared by at least three different human tissue types. The overlap of hemimethylated CpG sites in multiple human tissues was applied, aiming to detect more generally expressed IGs, but not the tissue-specific ones. In order to detect tissue specificity of imprinting would require screening many more tissue types, which was not the purpose of the study. Our selection criteria were applied to the whole data to call hemimethylated CpG sites that could be associated with both known IGs (positive control) and novel candidate IGs.
2.3. Known Imprinted Gene Cpgs Retrieved from the HM450K Methylation Data
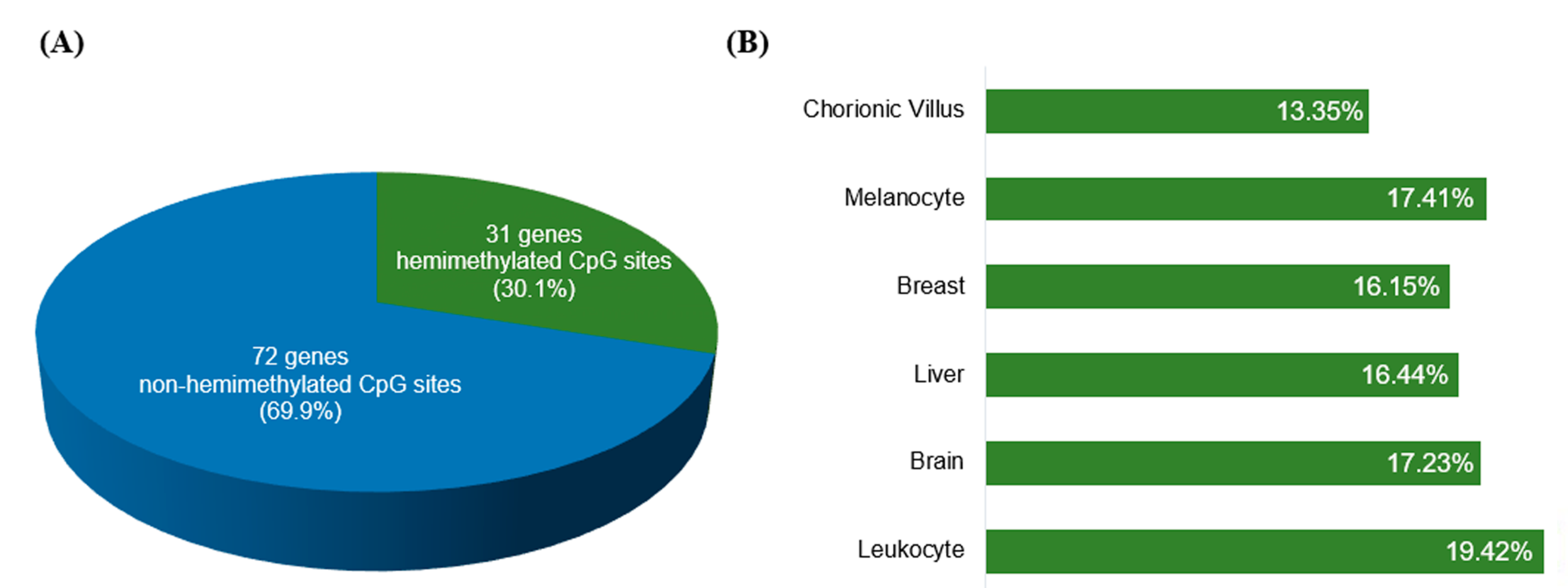
We evaluated how many of the known IGs (listed in Table S1) were retrieved, by applying the selection criteria described above. Thirty-one of the 103 IGs (30.1%; Figure 3A) were recovered for presenting at least one hemimethylated CpG site shared by ≥3 tissue types (Table S4; Figure 3B), validating our method for recovering known IGs. Thus, our approach might have the potential to identify novel candidate IGs.
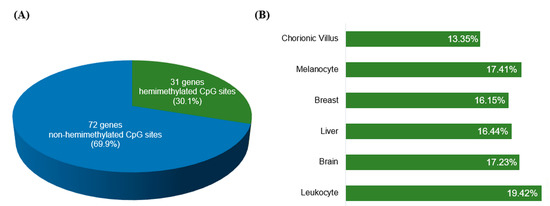
Figure 3.
Hemimethylated CpG sites on known imprinted genes retrieved from the HM450K methylation data obtained for six different tissues. (A) In 31 of the 103 known imprinted genes, we identified at least one hemimethylated CpG site common to ≥3 tissue types; (B) A total of 2292 hemimethylated CpG sites were recovered on the 103 known imprinted genes; the bar chart indicates the distribution of the hemimethylated sites per tissue.
2.4. Mining Novel Candidate Imprinted Genes Using the HM450K Methylation Data
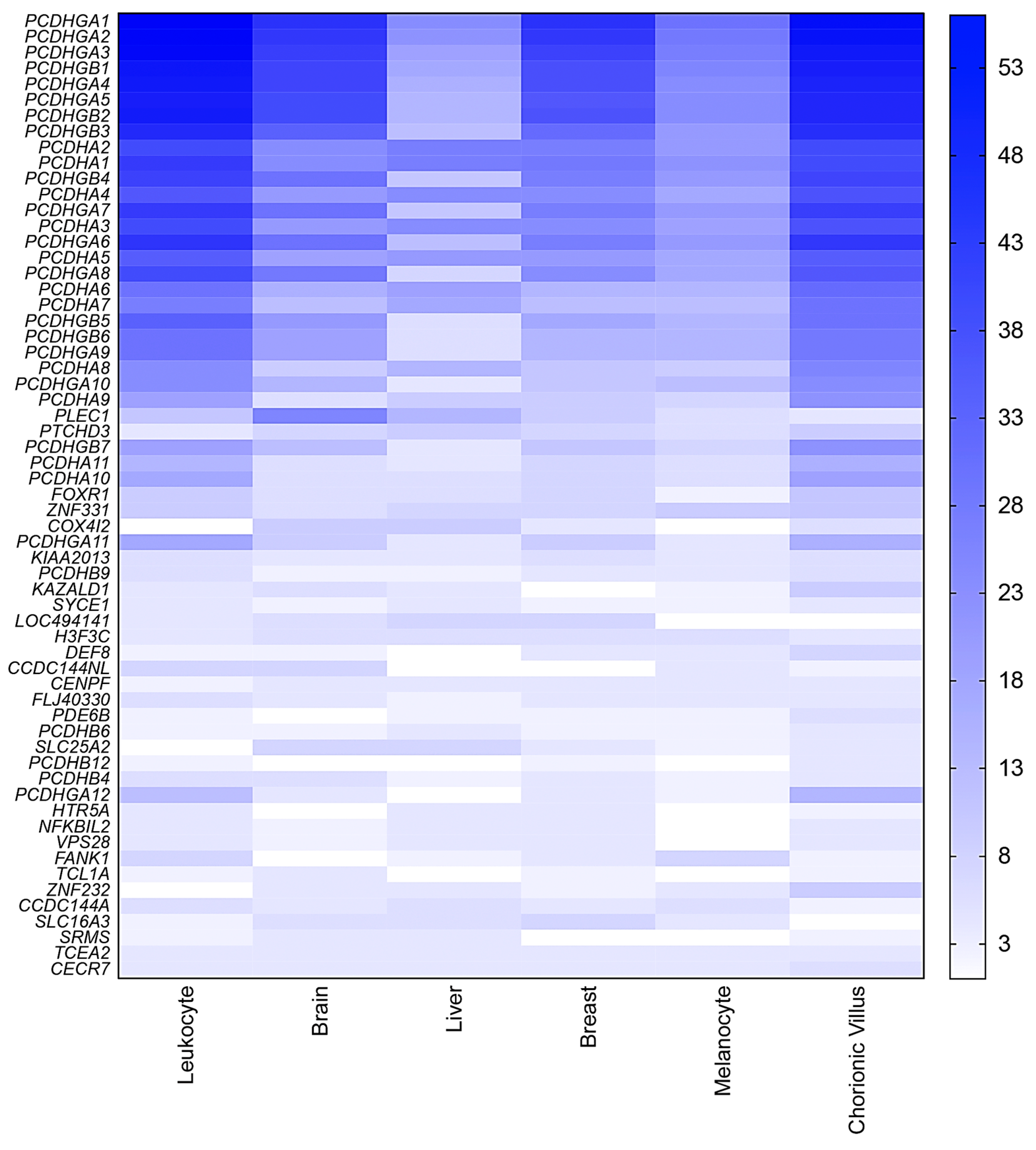
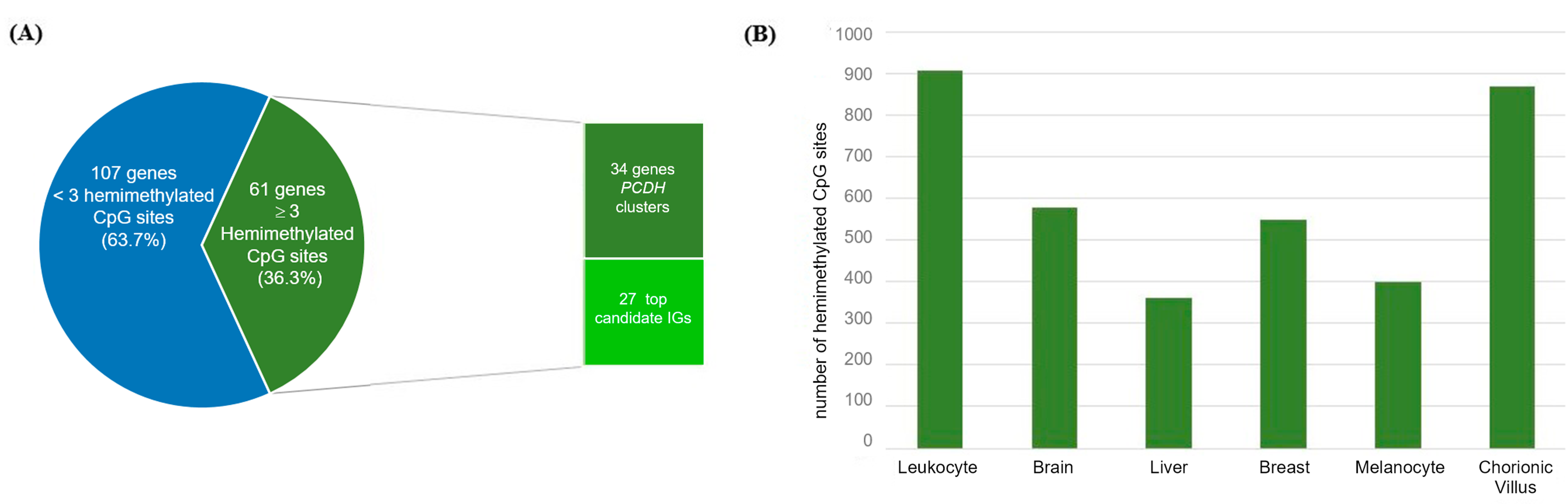
The screening for hemimethylated CpG sites fulfilling our selection criteria identified 295 hemimethylated CpG sites common to ≥3 tissue types (Table S5). The total number of retrieved hemimethylated CpG sites per tissue ranged from 720 (melanocytes) to 2640 (chorionic villus) (Figure 4). These 295 shared CpGs correspond to 168 candidate IGs, 61 of which hadat least three hemimethylated CpG sites shared by more than two tissue types (Figure 5). Thirty-four of these 61 genes are members of the PCDH gene cluster located on chromosome 5q31.3, which are known to have random monoallelic expression in mice. The remaining 27 genes were considered the top candidates for novel IGs from the present work (Table 1).
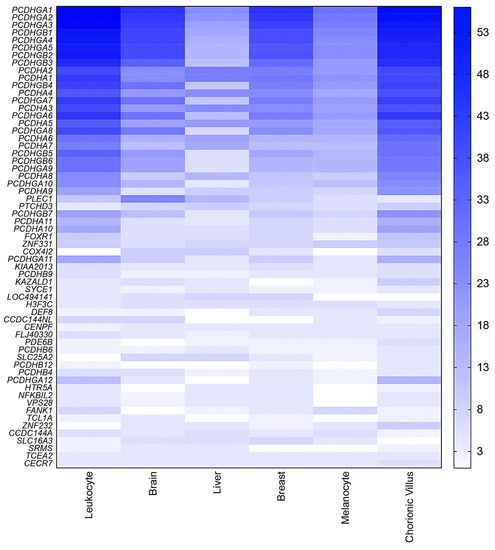
Figure 4.
Heatmap showing the average probe density for each novel candidate imprinted gene for all tested tissues. The novel candidate imprinted genes are displayed in horizontal lines (gene symbols at left), and the columns show the distribution of the number of hemimethylated CpG sites identified for each gene per tissue type. At right, the blue vertical bar indicates the range of hemimethylated CpGs number, starting from 3.
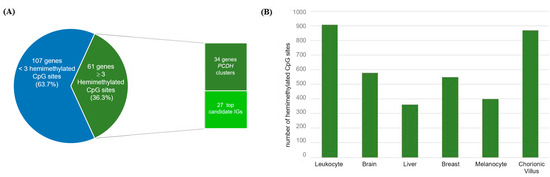
Figure 5.
Mining novel candidate imprinted genes using the methylation data obtained for six different tissues. (A) Classification of the 168 identified candidate imprinted genes according to the number of hemimethylated sites observed in ≥3 tissue types; (B) In the y axis, number of hemimethylated CpG sites on the novel candidate imprinted genes per tissue type (vertical bars).

Table 1.
Top candidate imprinted genes. The 27 genes exhibit at least three hemimethylated CpGs in promoter regions overlapping CpG islands, shared by at least three human tissue types.
2.5. Characterization of Human Orthologues of Known Mouse IGs, Using the HM450K Human Methylation Data
Human orthologues of 49 known mouse IGs have no evidence of imprinting and were considered in the literature as possible candidate IGs (Table S2). However, none of these genes were retrieved in the screening for hemimethylated CpG sites under our selection criteria. We searched for hemimethylated CpG sites shared by at least three human tissue types, irrespective of their genomic localization. We detected 61 hemimethylated CpG sites mapped to 13 genes of these human orthologues of the known mouse IGs (Table S6).
2.6. Comparison of Known and Candidate IGs Detected in Human Imprinting Studies Using High-Throughput Technologies
Recent studies in humans used a variety of tissues, whole-genome methodologies, and different approaches to search for novel IGs [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. These studies detected, with variable efficiency, a fraction of the known IGs, and some of them revealed novel putative IGs, or validated novel IGs. Summarizing these imprinting studies in humans since 2011, including our data, a total of 383 genes were retrieved (Table S3). Sixty-one of them were known IGs, which correspond to 59.2% of all known human IGs (Table S1). Fifty-six of the 383 genes (14.6%) were reported in at least two studies, including 36 (36/56; 64.3%) known IGs. Three genes have been recently validated after ASE analysis in family trios (3/56; 5.4%); seven genes (7/56; 12.5%) have been described as putative IGs, after ASE analysis, but lack familial confirmation; for nine genes (9/56; 16.1%), expression analysis was not conclusive or not performed; and the remaining gene (1/56; 1.8%), IGF1R, has been described as non-imprinted in humans.
3. Discussion
Recent studies have applied different strategies to search for novel IGs in humans. One successful approach is based on monoallelic expression using microarray or RNA-seq [14,17,19,20,25]. However, the downside of this methodology is that non-imprinted genes may also show monoallelic expression [1,26], and imprinted expression is mostly tissue-specific [20,27]. Another approach that has been extensively explored is the search for epigenetic signature of imprinted regions, using methylation microarrays or next generation sequencing [11,12,13,15,16,18]. Although methylation array does not provide data of allelic methylation, the advantage of this approach is that, in most tissues, DNA methylation of IGs is preserved throughout development and adult life, irrespective of their expression status [3,24].
As most imprinted DMRs co-localize with CpG islands, our approach focused on promoter regions overlapping CpG islands, genomic features that are well represented on the HM450K microarray. The methodology used here proved to be appropriate, since it allowed the identification of 30.1% of all known IGs. In fact, other groups searching for novel human IGs have obtained similar or lower rates of retrieved known IGs (Table S3). We did not expect to retrieve all of them, considering the stringency of our selection criteria and other aspects: (1) many IGs are known to be tissue-specific [20,27], and might not undergo genomic imprinting in the tissue types that we investigated; (2) whole-genome methylation analysis by microarray is restrictive to the sequences interrogated in the platform, which covers each gene with different quantities of probes; (3) the databases we used to list all known IGs are derived from heterogeneous sources, and can include some false positives [20]; (4) the intermediate levels of methylation can be a result of mixed cellular composition, which could introduce false positive results in our data. Given all these facts, we considered our detection rate of known IGs to be reasonable.
Among our 27 top candidate genes, seven have been previously reported in human imprinting studies, supporting the hypothesis of these genes being imprinted: PLEC, PTCHD3, ZNF331, KIAA2013, SYCE1, HTR5A, and ZNF232 (Table 1) [11,13,15,16]. The ZNF331 (zinc finger protein 331) gene has provisional imprinted status in the Catalogue of Imprinted Genes and Parent-of-Origin Effects in Humans and Animals [28,29,30], and has been recently confirmed to have expression consistent with imprinting in a isoform-specific manner [16,19,20]. The putative imprinted gene SYCE1 (synaptonemal complex central element protein 1) had the ASE demonstrated in multiple human tissues [20]. Four hypomethylated CpG sites were found in the PTCHD3 (patched domain containing 3) promoter region in patients with Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome and multilocus hypomethylation [15]; moreover, an allele-specific methylation region in PTCHD3 exon 1 has been recently reported in human breast and blood samples [31], reinforcing the hypothesis of imprinting. Apart from ZNF331, the other genes have not yet been validated.
As most known human IGs occur in clusters spanning up to 2.3 Mb (Table S1), and typically share common regulatory mechanisms, we looked for retrieved genes mapped closer to known IGs or to each other. Among the 27 top candidates, PLEC (plectin), TONSL (tonsoku-like, DNA repair protein), and VPS28 [vacuolar protein sorting 28 homolog (S. cerevisiae)] mapped to a 665 kb segment on 8q24.3, and might constitute a novel imprinted cluster. Two other genes among the 168 candidates also mapped to this same region 8q24.3, ARC (activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein) and CCDC166 (coiled-coil domain containing 166; alias LOC100130274), which are located ~200 kb and ~1.3 Mb proximal to PLEC, respectively. Three hypomethylated CpG sites were found in the PLEC promoter region in patients with Beckwith–Wiedemann syndrome and multilocus hypomethylation [15], which support our findings. However, there is no evidence in the literature for TONSL, VPS28, ARC, and CCDC166 being imprinted. Additionally, the COX4I2 [cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV isoform 2 (lung)] gene is mapped only 90 kb from the known imprinted gene MCTS2P (malignant T cell amplified sequence 2, pseudogene), raising the possibility that it might be imprinted.
The 34 members of protocadherin (PCDH) genes that we retrieved belong to 53 related genes clustered in three major groups, PCDH-α, PCDH-β, and PCDH-γ, which are tandemly arranged. Protocadherins are diversified receptor proteins that play an important role in specific cell–cell connections in the brain [32]. In mice, most Pcdh isoforms display a random combinatorial monoallelic expression in individual neurons, a mechanism supposed to specify neuron identity [33,34,35]. Recently, it has been demonstrated that the promoter regions of most Pcdh-α and Pcdh-γ variable exons are differentially methylated in mosaic by the de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3b, during early embryonic development, both in mice brain and liver [36]. However, the Pcdh-associated CpG islands do not show uniparental methylation patterns, in contrast to the observed pattern at the DMRs of IGs [37]. We show that promoter regions of PCDH variable exons have hemimethylated CpGs in multiple human tissues; three allele-independent methylation regions have been recently reported in PCDH-α, in adult human blood, and breast samples [31]. Pcdh non-imprinted monoallelic and random isoform expression has been previously demonstrated in mice; given the evolutionarily conserved organization of the PCDH clusters, this unique type of monoallelic expression might be present in human tissues as well, although this assumption needs validation.
Our screening for hemimethylated CpGs in human orthologues of known mouse IGs, with no imprinting data in humans, retrieved 13 genes; six of them are localized within imprinted clusters in mice, and are within or close to imprinted clusters in human as well—CD81, NAP1L4, USP29, ZIM3, BEGAIN, and MIR379. CD81 gene is listed as non-imprinted in Geneimprint database, but the only evidence against its imprinting status comes from a report of biallelic expression in somatic cell hybrids [38]. In mice, Nap1l4 has controversial imprinting status between databases (Table S2); NAP1L4 is biallelically expressed in embryonic and trophoblast stem cells [39], being a weak candidate in humans. Currently, imprinting evidence for USP29 and ZIM3 is lacking; they are both expressed only in testis [40,41], but there are no data about their expression pattern. A DMR was described in the USP29 promoter region [42], while ZIM3 promoter is unmethylated in adult human tissues.
We compared the high-throughput imprinting studies in human reported since 2011 (Table S3) [11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. Different methods were designed to screen novel candidate IGs. Combining these studies, 59.2% of known IGs were recovered. The missing half could be genes with tissue-specific or isoform-specific expression, genes presenting intergenic DMRs, or even genes excluded due to the type of analysis that was made. It is noteworthy that our screening retrieved five known IGs not detected by other groups—TP73, SLC22A3, MESTIT1, KCNQ1DN, and MIMT1, which demonstrates the potential of our method. The status of most genes reported in at least two studies are known (64.3%), recently validated (5.4%) or putative IGs (12.5%), indicating the strength of overlapping of genes to reveal novel candidate IGs, which should be prioritized for validation. In nine overlapping candidate genes, including five of our 27 top candidates discussed above, expression analysis for validation was not conclusive or not performed. Monoallelic expression has been reported for ERLIN2 and LEP genes in leukocyte and placenta, respectively, but confirmation of ASE according to parental origin is still needed [11,16]. SORD gene was considered a candidate IG in two studies [11,13], but allele-specific bisulphite PCR analysis revealed a mosaic methylated profile in its promoter, arguing against the possibility of SORD being imprinted. ZNF396 gene was also considered a candidate IG in two studies [11,16]; a maternally methylated DMR restricted to placenta was detected in the promoter of ZNF396 [16]. A DMR has been reported more than once in the overlapping gene IGF1R [15,16,43], although it was shown not to be imprinted in human embryonic and adult tissues [44].
4. Materials and Methods
The material and analysis procedures are summarized in the flow diagram in Figure 1.
4.1. Human Tissue Samples
DNA was extracted using a standard phenol–chloroform protocol from normal human samples: 36 leukocyte samples (provided by the Brain Bank of the Brazilian Aging Brain Study Group, São Paulo, Brazil) [45], two chorionic villi samples (provided by the Institute of Biosciences, University of São Paulo), 17 frozen samples from tumor adjacent normal liver (n = 10) and breast (n = 7) (provided by the Biobank of the A. C. Camargo Cancer Center), nine frozen postmortem brain frontal cortex samples (provided by the Brain Bank of the Brazilian Aging Brain Study Group) [45], and three primary cultures of melanocytes (provided by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, University of São Paulo). The study was approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of the Institute of Biosciences of the University of São Paulo (protocol no 124/2011-FR.450069), AC Camargo Cancer Center Ethics Committee (protocols 768/06 and 1448/10) and Research Ethics Committee of the University of São Paulo Hospital (protocol HU/USP 943/09). Written informed consent was obtained from all participants for the publication of data.
4.2. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Analysis
Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles were obtained using the Infinium Human Methylation 450K BeadChips (Illumina, Inc.), following manufacturer’s instructions. These microarrays interrogate the DNA methylation status across 485,577 CpG loci distributed along the genome at single-nucleotide resolution. Briefly, a total of 1µg of each DNA sample was bisulfite-converted (EZ DNA methylation kit; Zymo Research, Irvine, CA, EUA), amplified, fragmented, and hybridized to Bead Chips. Microarray images were captured by the iScan SQ scanner (Illumina, Inc.).
4.3. Array Quality Control and Data Processing
The data discussed in this publication have been deposited in NCBI's Gene Expression Omnibus and are accessible through GEO Series accession number GSE103413 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc =GSE103413).
Only experiments exhibiting a call rate > 0.98 of probes with detection p-value ≤ 0.01 were considered for data analysis. Microarray data were extracted using the GenomeStudio software (v.2011.1; Illumina) with the methylation module (v.1.9.0). DNA methylation level of each CpG was obtained in β values (β = intensity of the methylated allele (M)/intensity of the unmethylated allele (U) + intensity of the M + 100) ranging from 0 to 1, with 0 indicating unmethylated sites and 1, fully methylated sites. Background subtraction and normalization of data were performed using the Illumina default protocol with internal controls. CpG sites with detection p-value ≥ 0.01, as well as those mapped at X and Y chromosomes, were excluded from further analysis.
We implemented two Perl scripts for the in silico analysis. The first script used data from the Genome Studio software to create a table containing the following columns: (i) TargetID—probe identification; (ii) Sample_Name; (iii) Beta—β value of the probe; (iv) Imprint—associated or not with a known human imprinted gene; (v) Island—annotation of CpG island region according to UCSC; (vi) Promoter—genomic localization at 5’UTR, 1500TSS, 200TSS, or first exon, according to UCSC; (vii) Genes—genes associated with the probe. The data output was used to generate histograms with the package ggplot2 [46] from the R statistical software. The second script received the data from the GenomeStudio software and returned the list of genes containing at least one CpG site mapped in promoter regions overlapping CpG islands, with β values between 0.38–0.65. Only CpG sites fulfilling these criteria in at least 80% of samples in each tissue type were retrieved from the processed data. Genes presenting at least one hemimethylated CpG site in more than two different human tissue types were retrieved. Perl scripts used for the in silico analysis are available upon request.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the screening for hemimethylated CpG sites shared by multiple tissue types was a useful approach for identifying novel candidate IGs. Further studies should be undertaken to validate the identified candidate loci. Some of our top candidate IGs have also been reported as candidates by other groups. We showed that promoter regions of PCDH genes, located on chromosome 5q31.3, are hemimethylated in multiple human tissue types, which might be related to the transcriptional regulation of these genes. Our compilation of all known human and mouse IGs, combined with the comparison of the recently published imprinting data, will be valuable in future studies of genomic imprinting.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at www.mdpi.com/2075-4655/1/2/13/s1. Table S1: Compilation of known human imprinted genes (IGs) based on the Catalogue of Imprinted Genes and Parent-of-Origin Effects in Humans and Animals and Geneimprint databases; Table S2: Compilation of known mouse imprinted genes based on the Catalogue of Imprinted Genes and Parent-of-Origin Effects in Humans and Animals and Geneimprint databases; Table S3: Comparison of all known and candidate imprinted genes detected in human imprinting studies using high-throughput technologies, including this present study; Table S4: Hemimethylated CpG sites of known human imprinted genes recovered from different human tissue types; Table S5: Identification of candidate imprinted genes based on 450K methylation array data; Table S6: Search for hemimethylated CpG sites in human orthologues of known mouse imprinted genes, based on 450K methylation array data.
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Paula Pennacchi, Ligia Vieira and Dimitrius T. Pramio for technical assistance. This study was carried out only with funding from FAPESP (2009/00898-1; 2013/07480-8; 2013/08028-1) and CNPq (470446_2013-7) agencies.
Author Contributions
L.R.V. and A.K. conceived the study, and participated in its design and coordination; A.B., M.P.R., E.S.S.A. and D.V. designed and performed the experiments; A.B., M.B.A. and A.Y.K. analyzed the data; A.Y.K., H.B. and A.R.P. performed bioinformatics analysis; A.M.V.M., C.R., C.K.S., C.A.P., L.T.G. and D.M.C. assessed the clinical data and selected individuals; S.S.M.E. established primary cultures of melanocytes; A.B., M.P.R., E.S.S.A. and L.R.V. wrote and edited the manuscript; A.M.V.M., A.K., L.V.P. and C.R. critically revised the manuscript; all authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chess, A. Mechanisms and consequences of widespread random monoallelic expression. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxonov, S.; Berg, P.; Brutlag, D.L. A genome-wide analysis of CpG dinucleotides in the human genome distinguishes two distinct classes of promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henckel, A.; Arnaud, P. Genome-wide identification of new imprinted genes. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2010, 9, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morison, I.M.; Ramsay, J.P.; Spencer, H.G. A census of mammalian imprinting. Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reik, W.; Walter, J. Genomic imprinting: parental influence on the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, A.; Reik, W. How imprinting centres work. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2006, 113, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, H.; Cavaillé, J. Non-coding RNAs in imprinted gene clusters. Biol. Cell 2008, 100, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.T.; Bartolomei, M.S. X-inactivation, imprinting, and long noncoding RNAs in health and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1308–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, C.A.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C. Mechanisms regulating imprinted genes in clusters. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, J.R.; Bartolomei, M.S. Chromatin regulators of genomic imprinting. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Gene Regul. Mech. 2014, 1839, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, R.K.; Jiang, R.; Peñaherrera, M.S.; McFadden, D.E.; Robinson, W.P. Genome-wide mapping of imprinted differentially methylated regions by DNA methylation profiling of human placentas from triploidies. Epigenet. Chromatin 2011, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choufani, S.; Shapiro, J.S.; Susiarjo, M.; Butcher, D.T.; Grafodatskaya, D.; Lou, Y.; Ferreira, J.C.; Pinto, D.; Scherer, S.W.; Shaffer, L.G.; et al. A novel approach identifies new differentially methylated regions (DMRs) associated with imprinted genes. Genome Res. 2011, 21, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakabayashi, K.; Trujillo, A.M.; Tayama, C.; Camprubi, C.; Yoshida, W.; Lapunzina, P.; Sanchez, A.; Soejima, H.; Aburatani, H.; Nagae, G.; et al. Methylation screening of reciprocal genome-wide UPDs identifies novel human-specific imprinted genes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3188–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbaux, S.; Gascoin-Lachambre, G.; Buffat, C.; Monnier, P.; Mondon, F.; Tonanny, M.-B.; Pinard, A.; Auer, J.; Bessières, B.; Barlier, A.; et al. A genome-wide approach reveals novel imprinted genes expressed in the human placenta. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1079–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Docherty, L.E.; Rezwan, F.I.; Poole, R.L.; Jagoe, H.; Lake, H.; Lockett, G.A.; Arshad, H.; Wilson, D.I.; Holloway, J.W.; Temple, I.K.; et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis of patients with imprinting disorders identifies differentially methylated regions associated with novel candidate imprinted genes. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Court, F.; Tayama, C.; Romanelli, V.; Martin-Trujillo, A.; Iglesias-Platas, I.; Okamura, K.; Sugahara, N.; Simon, C.; Moore, H.; Harness, J.V.; et al. Genome-wide parent-of-origin DNA methylation analysis reveals the intricacies of human imprinting and suggests a germline methylation-independent mechanism of establishment. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metsalu, T.; Viltrop, T.; Tiirats, A.; Rajashekar, B.; Reimann, E.; Kõks, S.; Rull, K.; Milani, L.; Acharya, G.; Basnet, P.; et al. Using RNA sequencing for identifying gene imprinting and random monoallelic expression in human placenta. Epigenetics 2014, 9, 1397–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steyaert, S.; Van Criekinge, W.; De Paepe, A.; Denil, S.; Mensaert, K.; Vandepitte, K.; Vanden Berghe, W.; Trooskens, G.; De Meyer, T. SNP-guided identification of monoallelic DNA-methylation events from enrichment-based sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babak, T.; DeVeale, B.; Tsang, E.K.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Smith, K.S.; Kukurba, K.R.; Zhang, R.; Li, J.B.; van der Kooy, D.; et al. Genetic conflict reflected in tissue-specific maps of genomic imprinting in human and mouse. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 544–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baran, Y.; Subramaniam, M.; Biton, A.; Tukiainen, T.; Tsang, E.K.; Rivas, M.A.; Pirinen, M.; Gutierrez-Arcelus, M.; Smith, K.S.; Kukurba, K.R.; et al. The landscape of genomic imprinting across diverse adult human tissues. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalogue of Imprinted Genes and Parent-of-Origin Effects in Humans and Animals. Available online: http://igc.otago.ac.nz/home.html (accessed on 27 July 2017).
- Geneimprint. Available online: http://www.geneimprint.com/ (accessed on 3 August 2017).
- Wang, X.; Clark, A.G. Using next-generation RNA sequencing to identify imprinted genes. Heredity 2014, 113, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodfine, K.; Huddleston, J.E.; Murrell, A. Quantitative analysis of DNA methylation at all human imprinted regions reveals preservation of epigenetic stability in adult somatic tissue. Epigenet. Chromatin 2011, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornsson, H.; Albert, T. SNP-specific array-based allele-specific expression analysis. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarutani, Y.; Takayama, S. Monoallelic gene expression and its mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 608–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abramowitz, L.K.; Bartolomei, M.S. Genomic imprinting: Recognition and marking of imprinted loci. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2012, 22, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pant, P.V.K.; Tao, H.; Beilharz, E.J.; Ballinger, D.G.; Cox, D.R.; Frazer, K.A. Analysis of allelic differential expression in human white blood cells. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, N.D.; Chen, J.; Stuart, R.K.; Fan, J.B.; Ren, B. Genome-wide mapping of allele-specific protein-DNA interactions in human cells. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, K.S.; Serre, D.; Wang, X.; Tao, H.; Grundberg, E.; Hudson, T.J.; Clark, A.G.; Frazer, K. A genome-wide approach to identifying novel-imprinted genes. Hum. Genet. 2008, 122, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, G.; Hong, C.; Xing, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, D.; Coarfa, C.; Bell, R.J.A.; Maire, C.L.; Ligon, K.L.; Sigaroudinia, M.; et al. Intermediate DNA methylation is a conserved signature of genome regulation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Maniatis, T. A striking organization of a large family of human neural cadherin-like cell adhesion genes. Cell 1999, 97, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esumi, S.; Kakazu, N.; Taguchi, Y.; Hirayama, T.; Sasaki, A.; Hirabayashi, T.; Koide, T.; Kitsukawa, T.; Hamada, S.; Yagi, T. Monoallelic yet combinatorial expression of variable exons of the protocadherin-alpha gene cluster in single neurons. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, R.; Kato, H.; Kawamura, Y.; Esumi, S.; Hirayama, T.; Hirabayashi, T.; Yagi, T. Allelic gene regulation of Pcdh-α and Pcdh-γ clusters involving both monoallelic and biallelic expression in single Purkinje cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 30551–30560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K.; Kaneko, R.; Izawa, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kitsukawa, T.; Yagi, T. Single-neuron diversity generated by Protocadherin-β cluster in mouse central and peripheral nervous systems. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Tarusawa, E.; Toyama, T.; Okano, M.; Oda, M.; Nakauchi, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Sanbo, M.; et al. Developmental epigenetic modification regulates stochastic expression of clustered protocadherin genes, generating single neuron diversity. Neuron 2014, 82, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendrel, A.V.; Tang, Y.A.; Suzuki, M.; Godwin, J.; Nesterova, T.B.; Greally, J.M.; Heard, E.; Brockdorff, N. Epigenetic functions of Smchd1 repress gene clusters on the inactive X chromosome and on autosomes. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 33, 3150–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, J.M.; Higgins, M.J.; Gebuhr, T.C.; Shows, T.B.; Saitoh, S.; Nicholls, R.D. A model system to study genomic imprinting of human genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14857–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, J.M.; Udayashankar, R.; Moore, H.D.; Moore, G.E. Telomeric NAP1L4 and OSBPL5 of the KCNQ1 cluster, and the DECORIN gene are not imprinted in human trophoblast stem cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Noskov, V.N.; Lu, X.; Bergmann, A.; Ren, X.; Warth, T.; Richardson, P.; Kouprina, N.; Stubbs, L. Discovery of a novel, paternally expressed ubiquitin-specific processing protease gene through comparative analysis of an imprinted region of mouse chromosome 7 and human chromosome 19q13.4. Genome Res. 2000, 10, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Bergmann, A.; Wehri, E.; Lu, X.; Stubbs, L. Imprinting and evolution of two Kruppel-type zinc-finger genes, ZIM3 and ZNF264, located in the PEG3/USP29 imprinted domain. Genomics 2001, 77, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.M.; Kim, J. DNA methylation analysis of the mammalian PEG3 imprinted domain. Gene 2009, 442, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, A.J.; Migliavacca, E.; Dupre, Y.; Stathaki, E.; Sailani, M.R.; Baumer, A.; Schinzel, A.; Mackay, D.J.; Robinson, D.O.; Cobellis, G.; et al. Methylation profiling in individuals with uniparental disomy identifies novel differentially methylated regions on chromosome 15. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, O.; McNoe, L.A.; Eccles, M.R.; Morison, I.M. Reeve AEHuman insulin-like growth factor type I and type II receptors are not imprinted. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993, 2, 2163–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinberg, L.T.; Lucena Ferretti, R.E.; Farfel, J.M.; Leite, R.; Pasqualucci, C.A.; Rosemberg, S.; Nitrini, R.; Saldiva, P.H.N.; Jacob Filho, W. Brain bank of the Brazilian aging brain study group-A milestone reached and more than 1,600 collected brains. Cell Tissue Bank. 2007, 8, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).