Influence of Prenatal Methamphetamine Abuse on the Brain
Abstract
:1. Introduction/Background
1.1. Drug Dependence
1.2. Stimulant Drugs: Characteristics and the General Mechanism of its Effect
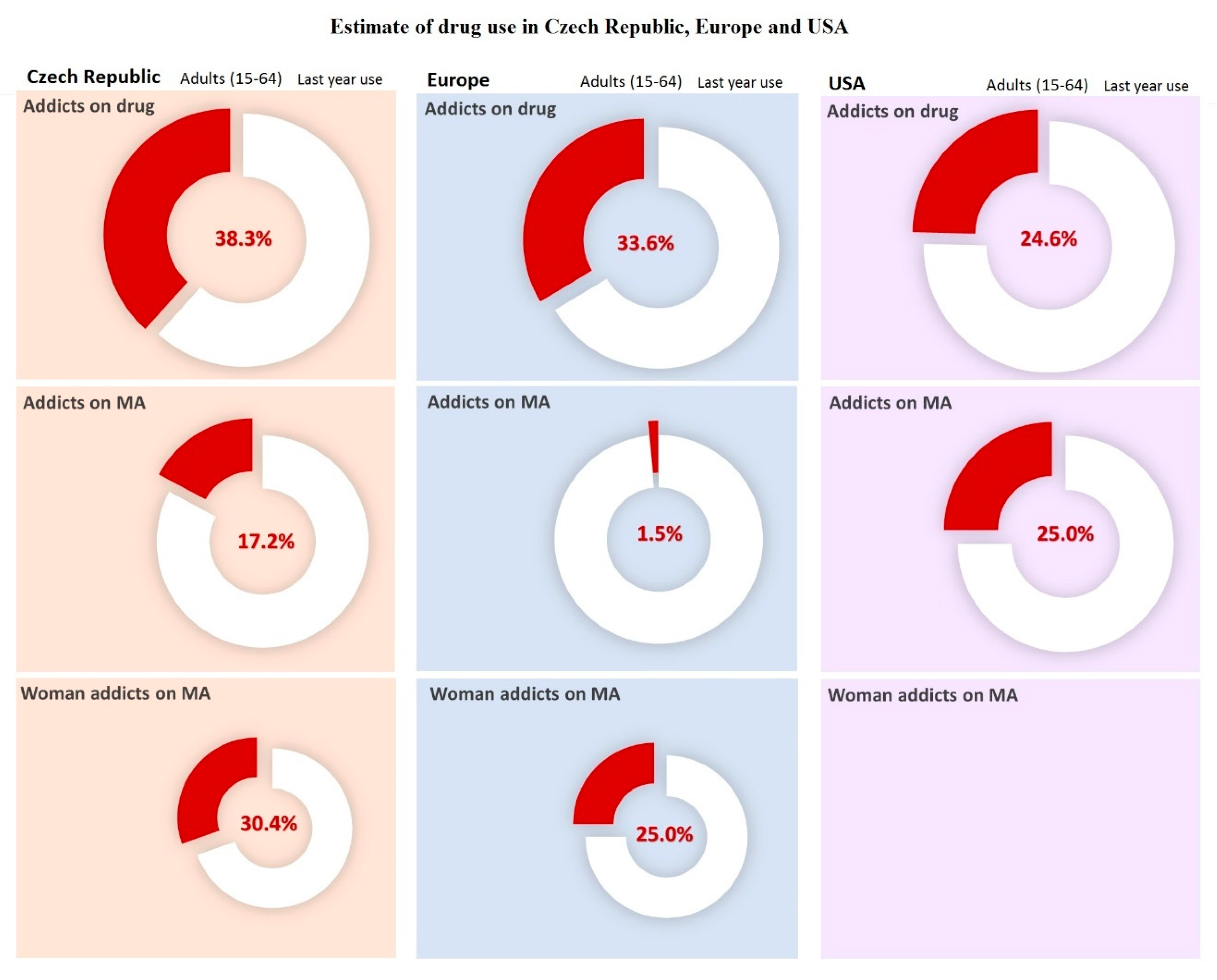
2. Methamphetamine
3. Influence of Methamphetamine on the CNS and on Selected Parts of the Brain
3.1. Dopaminergic System
3.2. Serotoninergic System
3.3. The Striatum
3.4. The Prefrontal Cortex
3.5. Hippocampus
4. Methamphetamine Use by Pregnant Addicted Women
5. Methamphetamine: Prenatal Influence on the Child
Tests of MA Prenatal Influence on Offspring
6. Epigenetics of Methamphetamine-Induced Changes
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Segal, B.; Morral, A.R.; Stevens, S.J. Adolescent Substance Abuse Treatment in the United States: Exemplary Models from a National Evaluation Study; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office of the Government of the Czech Republic. Annual Report on the State of the Drugs Problem for the European Monitoring Center for Drugs and Drug Addiction: Czech Republic; Office of the Government of the Czech Republic: Prague, Czech Republic, 2018; ISBN 978-80-7440-219-7. [Google Scholar]
- Staeheli, S.N.; Veloso, V.P.; Bovens, M.; Bissig, C.; Kraemer, T.; Poetzsch, M. LC-MS/MS Screening Method Using Information-Dependent Acquisition of Enhanced Product Ion Mass Spectra for Synthetic Cannabinoids Including Metabolites in Urine. Drug Test. Anal. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIDA. Methamphetamine. Retrieved. Available online: https://www.drugabuse.gov/drugs-abuse/methamphetamine (accessed on 5 November 2019).
- Walsh, N. Harm Reduction: Focal Point for Viral Hepatitis; World Health Organization: København, Denmark, 2019; Available online: https://www.who.int/hepatitis/news-events/03_prevention-preventing-infection.pdf?ua=1 (accessed on 9 May 2019).
- Vindenes, V.; Yttredal, B.; Øiestad, E.L.; Waal, H.; Bernard, J.P.; Mørland, J.G.; Christophersen, A.S. Oral fluid is a viable alternative for monitoring drug abuse: Detection of drugs in oral fluid by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and comparison to the results from urine samples from patients treated with methadone or buprenorphine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindsay, M.K.; Burnett, E. The use of narcotics and street drugs during pregnancy. Clin. Obstet. Gynekol. 2013, 56, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobell, L.C.; Sobell, M.B.; Ward, E. Evaluating Alcohol and Drug Abuse Treatment Effectiveness: Recent Advances; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Švestka, J.; Češková, E.; Náhunek, K. Psychofarmaka V Klinické Praxi; Grada Publishing: Prague, Czech Republic, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, R.D.; Potter, J.S.; Griffin, M.L.; Provost, S.E.; Fitzmaurice, G.M.; McDermott, K.A.; Carroll, K.M. Long-Term outcomes from the national drug abuse treatment clinical trials network prescription opioid addiction treatment study. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015, 150, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKetin, R.; Dawe, S.; Burns, R.A.; Hides, L.; Kavanagh, D.J.; Teesson, M.; Saunders, J.B. The profile of psychiatric symptoms exacerbated by methamphetamine use. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2016, 161, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birbaumer, N.; Veit, R.; Lotze, M.; Erb, M.; Hermann, C.; Grodd, W.; Flor, H. Deficient fear conditioning in psychopathy: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2005, 62, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebb, D.O. Textbook of Psychology, 3rd ed.; W.B. Saunders Company: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- McCusker, J.; Bigelow, C.; Vickers-Lahi, M.; Spotts, D.; Garfield, F.; Frost, R. Planned duration of residential drug abuse treatment: Efficasy versus effectiveness. Addiction 1997, 92, 1467–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefunková, M. Metamfetamin (Pervitin): Situace v eu a Její Globální Kontext; Centrum adiktologie, Psychiatrická klinika 1. LF UK a VFN v Praze: Praha, Czech Republic, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Mayer-Blackwell, B.; Schlussman, S.D.; Randesi, M.; Butelman, E.R.; Ho, A.; Kreek, M.J. Extended access oxycodone self-administration and neurotransmitter receptor gene expression in the dorsal striatum of adult C57BL/6 J mice. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fumagalli, F.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Valenzano, K.J.; Caron, M.G. Role of dopamine transporter in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity: Evidence from mice lacking the transporter. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 4861–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessinger, M.A. Prenatal exposure to amphetamines. Risks and adverse outcomes in pregnancy. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 1998, 25, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubertret, C.; Gorwood, P.; Ades, J.; Feingold, J.; Schwartz, J.C.; Sokoloff, P. Meta-Analysis of DRD3 gene and schizophrenia: Ethnic heterogeneity and significant association in caucasians. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A. 1998, 81, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Santos, A.M.; Kelly, J.P.; Doyle, K.M. Dose-Dependent effects of binge-like methamphetamine dosing on dopamine and neurotrophin levels in rat brain. Neuropsychobiology 2017, 75, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camp, D.M.; Browman, K.E.; Robinson, T.E. The effects of methamphetamine and cocaine on motor behavior and extracellular dopamine in the ventral striatum of Lewis versus Fischer 344 rats. Brain Res. 1994, 668, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Numachi, N.; Ohara, A.; Yamashita, M.; Fukushima, S.; Kobayashi, K.; Hata, H.; Watanabe, H.; Hall, F.S.; Lesch, K.P.; Murphy, D.L.; et al. Methamphetamine-Induced hyperthermia and lethal toxicity: Role of the dopamine and serotonin transporters. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 572, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šlamberová, R. Drug in pregnancy: The Effects on mother and her progeny. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, B.I. Methamphetamine abuse: Epidemiologic issues and implications. NIDA Res. Monogr. 1991, 115, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Thrash, B.; Thiruchelvan, K.; Ahuja, M.; Suppiramaniam, V.; Dhanasekaran, M. Methamphetamine-Induced neurotoxicity: The road to Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampert, S.M.; Kaye, A.D.; Urman, R.D.; Manchikanti, L. Drug testing and adherence monitoring in substance abuse patients. In Substance Abuse; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, K.; Ikemoto, S.; Goto, K.; Nishijima, K.; Yoshino, T.; Ishiguro, T. Spontaneous Recurrence of Methamphetamine-Lnduced Paranoid-Hallucinatory States in Female Subjects: Susceptibility to Psychotic States and Implications for Relapse of Schizophrenia. Pharmacopsychiatry 2002, 35, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavříková, B.; Binder, T.; Živný, J. Characteristics of a population of drug dependent pregnant women in Czech Republic. Čes. Gynekol. 2001, 66, 285–291. [Google Scholar]
- Sipes, T.E.; Geyer, M.A. DOI disruption of prepulse inhibition of startle in the rat is mediated by 5-HT2A and not by 5-HT2C receptors. Behav. Pharnmacol. 1995, 6, 839–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavříková, B.; Binder, T.; Živný, J.; Vítková, I. Placental and umbilical cord changes in drug-addicted women. Čes. Gynekol. 2001, 66, 345–349. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, C.R.; Shankaran, S.; Bada, H.S.; Lester, B.; Wright, L.L.; Krause-Steinrauf, H.; Smeriglio, V.L.; Finnegan, L.P.; Maza, P.L.; Verter, J. The Maternal Lifestyle Study: Drug exposure during pregnancy and short-term maternal outcomes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2002, 186, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Alicata, D.; Ernst, T.; Volkow, N. Structural and metabolic brain changes in the striatum associated with methamphetamine abuse. Addict. Soc. Study Addict. 2007, 102, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anckarsater, H. Central nervous changes in social dysfunction: Autism, aggression, and psychopathy. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, F.; Xie, H.; Dong, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wu, G.C. Expression of ORL 1 mRNA in some brain nuclei in neuropathic pain rats. Brain Res. 2005, 1043, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, J.C.; Cuellar, H.; Vargas, D.; Riascos, R. PET and SPECT in drug and substance abuse. Top. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2005, 16, 253–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raine, A.; Yang, Y. The neuroanatomical bases of psychopathy: A review of brain imaging findings. In Handbook of Psychopathy; Patrick, C.J., Ed.; Guilford: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bechara, A. The role of emotion in decision making: Evidence from neurological patients with orbitofrontal damage. Brain Cognit. 2004, 55, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amen, D.G.; Stubblefield, M.; Carmicheal, B.; Thisted, R. Brain SPECT findings and aggressiveness. Ann. Clin. Psychiatry 1996, 8, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, S.A.; Altman, J.; Russo, R.J.; Zhang, X. Timetables of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neurotoxicology 1993, 14, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Rolls, E.T.; Treves, A. Neural Networks and Brain Function; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bullmore, E.; Sporns, O. Complex brain networks: Graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maren, S.; Phan, K.L.; Liberzon, I. The contextual brain: Implications for fear conditioning, extinction and psychopathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Scholl, J.L.; Tu, W.; Hassell, J.E.; Watt, M.J.; Forster, G.L.; Renner, K.J. Serotonergic responses to stress are enhanced in the central amygdala and inhibited in the ventral hippocampus during amphetamine withdrawal. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2014, 40, 3684–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krugel, L.K.; Biele, G.; Mohr, P.N.C.; Li, S.C.; Heekeren, H.R. Genetic variation in dopaminergic neuromodulation influences the ability to rapidly and flexibly adapt decisions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17951–17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mansour, A.; Meador-Woodruff, J.H.; Bunzow, J.R.; Civelli, O.; Akil, H.; Watson, S.J. Localization of dopamine D2 receptor mRNA and D1 and D2 receptor binding in the rat brain and pituitary: An in situ hybridization-receptor autoradiographic analysis. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 2587–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bourque, M.; Liu, B.; Dluzen, D.E.; Di Paolo, T. Sex differences in methamphetamine toxicity in mice: Effect on brain dopamine signalling pathways. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, J.; Padungchaichot, P.; Accili, D.; Fuchs, S. Dopamine receptors and dopamine transporter in brain function and addictive behaviors: Insights from targeted mouse mutants. Dev. Neurosci. 1998, 20, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollerman, J.R.; Schultz, W. Dopamine neurons report an error in the temporal prediction of reward during learning. Nat. Neurosci. 1998, 1, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, K.A.; Lee, D.C.; Hen, R.; Dulawa, S.C. Behavioral effects of chronic fluoxetine in BALB/cJ mice do not require adult hippocampal neurogenesis or the serotonin 1A receptor. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankle, W.G.; Lombardo, I.; New, A.S.; Goodman, M.; Talbot, P.S.; Huang, Y.; Hwang, D.; Slifstein, M.; Curry, S.; Abi-Dargham, A.; et al. Brain serotonin transporter distribution in subjects with impulsive aggressivity: A positron emission study with [11C] McN 5652. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, L.; Bubula, N.; McCoy, H.; Heller, A. Methamphetamine concentrations in fetal and maternal brain following prenatal exposure. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2001, 23, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, K.E.; Barman, S.M.; Boitano, S.; Brooks, H.L. Ganong’s Review of Medical Physiology, 23rd ed.; McGraw-Hill Medical: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Guyton, A.C.; Hall, J.E. Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, T.G. The best of a bas bunch: The ventromedial prefrontal cortex and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in decision-making. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 447–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waberžinek, G.; Krajíčková, D. Základy Speciální Neurologie; Karolinum: Praha, Czech Republic, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Apergis-Schoute, A.M.; Gillan, C.M.; Fineberg, N.A.; Fernandez-Egea, E.; Sahakian, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Neural basis of impaired safety signaling in obsessive compulsive disorder. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 3216–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillan, C.M.; Apergis-Schoute, A.M.; Morein-Zamir, S.; Urcelay, C.P.; Sule, A.; Fineberg Sahakian, B.J.; Robbins, T.W. Functional neuroimaging of avoidance habits in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, R.J. Neurocognitive models of aggression, the antisocial personality disorders, and psychopathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brower, M.C.; Price, B.H. Neuropsychiatry of frontal lobe dysfunction in violent and criminal behavior: A critical review. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 71, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, N.; Maguire, E.A.; O’Keefe, J. The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron 2002, 35, 625–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuchlik, A. Dynamic learning and memory, synaptic plasticity and neurogenesis: An update. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakazawa, K.; Quirk, M.C.; Chitwood, R.A.; Watanabe, M.; Yeckel, M.F.; Sun, L.D.; Tonegawa, S. Requirement for hippocampal CA3 NMDA receptors in associative memory recall. Science 2002, 297, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesner, R.P.; Gilbert, P.E.; Barua, L.A. The role of the hippocampus in memory for the temporal order of a sequence of odors. Behav. Neurosci. 2002, 116, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerman, D.M.; Sprengel, R.; Sanderson, D.J.; McHugh, S.B.; Rawlins, J.N.P.; Monyer, H.; Seeburg, P.H. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2014, 15, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simões, P.F.; Silva, A.P.; Pereira, F.C.; Grade, S.; Milhazes, N.; Borges, F.; Ribeiro, C.F.; Macedo, T.R. Methamphetamine induces alternations on hippocampal NMDA and AMPA receptor subunit levels and impairs spatial working memory. Neuroscience 2007, 150, 433–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honey, R.C.; Good, M. Associative modulation of the orienting response: Distinct effects revealed by hippocampal lesions. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 2000, 26, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bannerman, D.M.; Rawlins, J.N.P.; Good, M.A. The drugs don’t work—or do they? Pharmacological and transgenic studies of the contribution of NMDA and GluR-A-containing AMPA receptors to hippocampal-dependent memory. Psychopharmacology 2006, 188, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutcheon, J.E.; Marinelli, M. Age matters. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 997–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, L.R. Memory and the hippocampus: A synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychol. Rev. 1992, 99, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caputi, A.; Fuchs, E.C.; Allen, K.; Le Magueresse, C.; Monyer, H. Selective reduction of AMPA currents onto hippocampal interneurons impairs network oscillatory activity. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Keefe, J.; Nadel, L. The Hippocampus as a Cognitive Map; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins, J.N.; Olton, D.S. The septo-hippocampal system and cognitive mapping. Behav. Brain Res. 1982, 5, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, J.; Dostrovsky, J. The hippocampus as a spatial map. Preliminary evidence from unit activity in the freely-moving rat. Brain Res. 1971, 34, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, T.Y.; Bannerman, D.M.; McHugh, S.B.; Preston, T.J.; Rudebeck, P.H.; Rudebeck, S.R.; Campbell, T.G. Impulsive choice in hippocampal but not orbitofrontal cortex-lesioned rats on a nonspatial decision-making maze task. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 30, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pothuizen, H.H.; Zhang, W.N.; Jongen-Relo, A.L.; Feldon, J.; Yee, B.K. Dissociation of function between the dorsal and the ventral hippocampus in spatial learning abilities of the rat: A within-subject, within-task comparison of reference and working spatial memory. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuchlik, A.; Rehakova, L.; Rambousek, L.; Svoboda, J.; Vales, K. Manipulation of D2 receptors with quinpirole and sulpiride affects locomotor activity before spatial behavior of rats in an active place avoidance task. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 58, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, J.S.; Muller, R.U.; Ranck, J.B. Head-Direction cells recorded from the postsubiculum in freely moving rats. I. Description and quantitative analysis. J. Neurosci. 1990, 10, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuchlik, A.; Rezacova, L.; Vales, K.; Bubenikova, V.; Kubik, S. Application of a novel Active Allothetic Place Avoidance task (AAPA) in testing a pharmacological model of psychosis in rats: Comparison with the Morris Water Maze. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 366, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barkus, C.; McHugh, S.B.; Sprengel, R.; Seeburg, P.H.; Rawlins, J.N.P.; Bannerman, D.M. Hippocampal NMDA receptors and anxiety: At the interface between cognition and emotion. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 626, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pentkowski, N.S.; Blanchard, D.C.; Lever, C.; Litvin, Y.; Blanchard, R.J. Effects of lesions to the dorsal and ventral hippocampus on defensive behaviors in rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 23, 2185–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deacon, R.M.; Bannerman, D.M.; Rawlins, J.N. Anxiolytic effects of cytotoxic hippocampal lesions in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2002, 116, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, H.; Cruz, C.; Camarena, B.; Orozco, B.; Kennedy, J.L.; King, N.; Sidenberg, D. DRD2, DRD3 and 5HT2A receptor genes polymorphisms in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 1996, 1, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Macúchová, M.; Šlamberová, R. Gender differences in the effect of adult amphetamine on cognitive functions of rats prenatally exposed to methamphetamine. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 270, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlamberová, R.; Charousová, P.; Pometlová, M. Methamphetamine Administration during Gestation Impairs Maternal Behavior. Dev. Psychobiol. J. Int. Soc. Dev. Psychobiol. 2005, 46, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnke, M.; Smith, V.C. Committee on Substance Abuse; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Prenatal Substance Abuse: Short- and Long-term Effects on the Exposed Fetus. Pediatrics 2013, 131, 1009–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuczkowski, K.M. The effects of drug abuse on pregnancy. Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 19, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotka, J.; Narkowicz, S.; Polkowska, Z.; Biziuk, M.; Namiesnik, J. Effects of addictive substances during pregnancy and infancy and their analysis in biological materials: Reviews. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; Volume 227, pp. 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambousek, L.; Kacer, P.; Syslová, K.; Bumba, J.; Bubeníková-Valesová, V.; Šlamberová, R. Sex differences in methamphetamine pharmacokinetics in adult rats and its transfer to pups through the placental membrane and breast milk. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2014, 139, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Derauf, C.; Grant, P.; Shah, R.; Arria, A.; Fallone, M. Prenatal methamphetamine use and neonatal neurobehavioral outcome. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2008, 30, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dattel, B.J. Substance abuse in pregnancy. Semin. Perinatol. 1990, 14, 179–187. [Google Scholar]
- Neri, M.; Bello, S.; Turillazzi, E.; Riezzo, I. Drugs of abuse in pregnancy, poor neonatal development, and future neurodegeneration. Is oxidative stress the culprit? Curr. Pharmaceutical Design. 2015, 21, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, P.G.; Bhatia, S.; Drake, D.M.; Miller-Pinsler, L. Fetal oxidative stress mechanisms of neurodevelopmental deficits and exacerbation by ethanol and methamphetamine. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2016, 108, 108–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Sakata-Haga, H.; Ohta, K.I.; Nishida, M.; Yashiki, M.; Sawada, K.; Fukui, Y. Histological brain alterations following prenatal methamphetamine exposure in rats. Congenit. Anomalies 2006, 46, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.; Costa, L.; Crofton, K.; Frank, D.; Fried, P.; Gladen, B.; Rowland, A. NTP-CERHR Expert Panel Report on the reproductive and developmental toxicity of amphetamine and methamphetamine. Birth Defects Res. Part B Dev. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 74, 471–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.; Hohman, M. The impact of methamphetamine use on parenting. J. Soc. Work Pract Addict. 2006, 6, 63–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, J.P.; Llorente, A.M.; Black, M.M.; Ackerman, C.S.; Mayes, L.A.; Nair, P. The effect of prenatal drug exposure and caregiving context on children’s performance on a task of susteined visual attention. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. 2008, 29, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šlamberová, R.; Macúchová, E.; Nohejlová, K.; Štofková, A.; Juroviová, J. Effect of amphetamine on adult male and female rats prenatally exposed to methamphetamine. Prague Med. Rep. 2014, 115, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šlamberová, R.; Pometlová, M.; Charousová, P. Postnatal development of rat pups is altered by prenatal mathamphetamine exposure. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. A Biol. Psychiatr. 2006, 30, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šlamberová, R.; Charousová, P.; Pometlová, M. Maternal behavior is impaired by methamphetamine administered during pre-mating, gestation and lactation. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vrajová, M.; Schutová, B.; Klaschka, J.; Štěpánková, H.; Řípová, D.; Šlamberová, R. Age-Related differences in NMDA receptor subunits of prenatally MA—Exposed male rats. Neurochem. Res. 2014, 39, 2040–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schutová, B.; Hrubá, L.; Rokyta, R.; Šlamberová, R. Gender differences in behavioral changes elicited by prenatal methamphetamine exposure and application of the same drug in adulthood. Dev. Psychobiol. 2013, 55, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinsley, C.H.; Turco, D.; Bauer, A.; Beverly, M.; Wellman, J.; Graham, A.L. Cocaine alters the onset and maintenance of maternal behavior in lactating rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1994, 47, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassoler, F.M.; Byrnes, E.M.; Pierce, R.C. The impact of exposure to addictive drugs on future generations: Physiological and behavioral effects. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, J.; Rajabzadeh, A.; Baei, F.; Jalayeri, Z.; Ebrahimzadeh-Bideskan, A. The effect of maternal exposure to methamphetamine during pregnancy and lactation period on hippocampal neurons apoptosis in rat offspring. Toxin Rev. 2017, 36, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, E.; Villen, T.; Hallberg, M.; Rane, A. Amphetamine secretion in breast milk. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1984, 27, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Derauf, C.; Grant, P.; Shah, R.; Arria, A.; Liu, J. The infant development, environment, and lifestyle study: Effects of prenatal methamphetamine exposure, polydrug exposure, and poverty on intrauterine growth. Pediatrics 2006, 118, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.M.; Yonekura, M.L.; Wallace, T.; Berman, N.; Kuo, J.; Berkowitz, C. Effects of prenatal methamphetamine exposure on fetal growth and drug withdrawal symptoms in infants born at term. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatri. 2003, 24, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyler, F.D.; Behnke, M. Early development of infants exposed to drug prenataly. Clin. Perinatol. 1999, 26, 107–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Baar, A.L.; Fleury, P.; Soepatmi, S.; Ultee, C.A.; Wesselman, P.J.M. Neonatal behaviour after drug dependent pregnancy. Arch. Dis. Child. 1989, 64, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, B.B.; Snell, L.M.; Gilstrap, L.C. Methamphetamine abuse during pregnancy: Outcome and fetal effects. Obstetri. Gynecol. 1988, 72, 541–544. [Google Scholar]
- Eze, N.; Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Derauf, C.; Newman, E.; Arria, A.; Lester, B.M. School-Aged outcomes following prenatal methamphetamine exposure: 7.5-year follow-up from the infant development, environment, and lifestyle study. J. Pediatri. 2016, 170, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, D.; Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Derauf, C.; Grant, P.; Shah, R.; Della Grotta, S. Intrauterine growth of infants exposed to prenatal methamphetamine: Results from the infant development, environment, and lifestyle study. J. Pediatri. 2010, 157, 337–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, R.; Diaz, S.D.; Arria, A. Prenatal methamphetamine exposure and short-term maternal and infant medical outcomes. Am. J. Perinatol. 2012, 29, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Šlamberová, R. Review of Long-Term Consequences of Maternal Methamphetamine Exposure. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, S219–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behnke, M.; Eyler, F.D. The Consequences of Prenatal Substance Use for the Developing Fetus, Newborn, and Young Child. Int. J. Addict. 1993, 28, 1341–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derauf, C.; LaGasse, L.; Smith, L.; Newman, E.; Shah, R.; Arria, A.; Dansereau, L. Infant temperament and high risk environment relate to behavior problems and language in toddlers. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatri. JDBP 2011, 32, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Covington, S.S. Women and addiction: A trauma-informed approach. J. Psychoact. Drugs 2008, 40, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiblawi, Z.N.; Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Diaz, S.D.; Derauf, C.; Newman, E.; Strauss, A. Prenatal methamphetamine exposureand neonatal and infant neurobehavioral outcome: Results from the IDEAL study. Subst. Abus. 2014, 35, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, A.; Anstice, N.S.; Jacobs, R.J.; LaGasse, L.L.; Lester, B.M.; Wouldes, T.A.; Thompson, B. Prenatal exposure to recreational drugs affects global motion perception in preschool children. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zabaneh, R.; Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Derauf, C.; Newman, E.; Shah, R.; Della Grotta, S. The effects of prenatal methamphetamine exposure on childhood growth patterns from birth to 3 years of age. Am. J. Perinatol. 2012, 29, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cernerud, L.; Eriksson, M.; Jonsson, B.; Steneroth, G.; Zetterstrom, R. Amphetamine addiction during pregnancy: 14-year follow-up of growth and school performance. Acta Paediatr. 1996, 85, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Santos, L.C. Prenatal exposure: The effects of prenatal cocaine and methamphetamine exposure on the developing child. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2016, 108, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonski, S.A.; Williams, M.T.; Vorhees, C.V. Neurobehavioral effects from developmental methamphetamine exposure. In Neurotoxin Modeling of Brain Disorders—Life-Long Outcomes in Behavioral Teratology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 183–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Smith, L.M.; LoPresti, C.; Yonekura, M.L.; Kuo, J.; Walot, I.; Ernst, T. Smaller subcortical volumes and cognitive deficits in children with prenatal methamphet-amine exposure. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2004, 132, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.H.; Ross, L. Consequences of prenatal toxin exposure for mental health in children and adolescents. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2007, 16, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Chen, A. Neonatal amphetamine exposure and hippocampus-mediated behaviors. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 91, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jablonski, S.A.; Williams, M.T.; Vorhees, C.V. Mechanisms involved in the neurotoxic and cognitive effects of developmental methamphetamine exposure. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2016, 108, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billing, L.; Eriksson, M.; Jonsson, B.; Steneroth, G.; Zetterström, R. The influence of environmental factors on behavioural problems in 8-year-old children exposed to amphetamine during fetal life. Child Abus. Negl. 1994, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiblawi, Z.N.; Smith, L.M.; LaGasse, L.L.; Diaz, S.D.; Newman, E.; Shah, R.; Neal, C. The effect of prenatal methamphetamine exposure on attention as assessed by continuous performance tests: Results from the infant development, environment, and lifestyle (IDEAL) study. J. Dev. Behav. Pediatr. JDBP 2013, 34, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abar, B.; LaGasse, L.L.; Derauf, C.; Newman, E.; Shah, R.; Smith, L.M.; Arria, A.; Huestis, M.; Della, G.S.; Dansereau, L.M.; et al. Examining the relationships between prenatal methamphetamine exposure, early adversity, and child neurobehavioral disinhibition. Psychol. Addict. Behav. 2013, 27, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spurlock, G.; Williams, J.; McGuffin, P.; Aschauer, H.N.; Lenzinger, E.; Fuchs, K.; Mallet, J. European Multicentre Association Study of Schizophrenia: A study of the DRD2 Ser311Cys and DRD3 Ser9Gly polymorphisms. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 81, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, A.; Yang, Y. Neural foundations to moral reasoning and antisocial behavior. Soc. Cognit. Affect. Neurosci. 2006, 1, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, S.E.; Slaughter, J.R.; Kashani, J. Risk factors in childhood that lead to the development of conduct disorder and antisocial personality disorder. Child Psychiatry Human Dev. 2001, 31, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raine, A.; Lencz, T.; Bihrle, S.; LaCasse, L.; Colletti, P. Reduced prefrontal gray matter volume and reduced autonomic activity in antisocial personality disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2000, 57, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leech, S.L.; Richardson, G.A.; Goldschmidt, L.; Day, N.L. Prenatal substance exposure: Effects on attention and impulsivity of 6-year-olds. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1999, 21, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.J.; Putnam, K.M.; Larson, C.L. Dysfunction in the neural circuitry of emotion regulation—A possible prelude to violence. Science 2000, 289, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irner, T.B. Substance exposure in utero and developmental consequences in adolescence: A systematic review. Child Neuropsychol. 2012, 18, 521–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilling, P.D.; Kuczenski, R.; Segal, D.S.; Barrett, T.B.; Kelsoe, J.R. Differential regulation of immediate-early gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of rat with a high vs. low behavioral response to methamphetamine. Neuropsychopharm 2006, 31, 2359–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujáková-Lipski, M.; Kaping, D.; Sirová, J.; Šlamberová, R. Transgenerational neurobiochemical modulation of methamphetamine in the adult brain of the Wistar rat. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3373–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šlamberová, R.; Pometlová, M.; Rokyta, R. Effect of methamphetamine exposure during prenatal and preweaning periods lasts for generations in rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2007, 49, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westerga, J.; Gramsbergen, A. The development of locomotion in the rat. Dev. Brain Res. 1990, 57, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altman, J.; Sudarshan, K. Postnatal development of locomotion in the laboratory rat. Anim. Behav. 1975, 23, 896–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinay, L.; Ben-Mabrouk, F.; Brocard, F.; Clarac, F.; Jean-Xavier, C.; Pearlstein, E.; Pflieger, J.F. Perinatal development of the motor systems involved in postural control. Neural Plast. 2005, 12, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P. The laboratory rat: Relating its age with human’s. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2013, 4, 624. [Google Scholar]
- Petríková, I.; Šlamberová, R. Critical neurodevelopmental periods for the effect of methamphetamine. Cesk. Fysiol. 2018, 67, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, D.; Baron, S. Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous systém: Evidence from humans and animal models. Environ. Healt Perspect. 2000, 108, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křeček, J. Effect of ovarectomy of females and oestrogen administration to males during the neonatal critical period on salt intake in adulthood in rats. Physiol. Bohemoslov. 1978, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Křeček, J. The theory of critical developmental periods and postnatal development of endocrine functions. Biopsychol. Dev. 1971, 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Information Processing in Animals: Memory Mechanisms; Spear, N.E.; Miller, R.R. (Eds.) Psychology Press: New Brunswick, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 5–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wiltgen, B.J.; Royle, G.A.; Gray, E.E.; Abdipranoto, A.; Thangthaeng, N.; Jacobs, N.; Fanselow, M.S. A role for calcium-permeable AMPA receptors in synaptic plasticity and learning. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, P.G.; McCallum, G.P.; Chen, C.S.; Henderson, J.T.; Lee, C.J.; Perstin, J.; Wong, A.W. Oxidative stress in developmental origins of disease: Teratogenesis, neurodevelopmental deficits, and cancer. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silva, A.J. Molecular and cellular cognitive studies of the role of synaptic plasticity in memory. J. Neurobiol. 2003, 54, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, M.S.; Yamamoto, B.K. Causes and consequences of methamphetamine and MDMA toxicity. AAPS J. 2006, 8, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pometlová, M.; Hrubá, L.; Slamberová, R.; Rokyta, R. Cross-Fostering effect on postnatal development of rat pups exposed to methamphetamine during gestation and preweaning periods. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2009, 27, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuff-Smith, K.D.; Schilling, M.A.; Fisher, J.E.; Vorhees, C.V. Stage-Specific effects of prenatal d-methamphetamine exposure on behavioral and eye development in rats. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 1996, 18, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.C.; Ellinwood, E.H. Conditioned aversion in spatial paradigms following methamphetamine injection. Psychopharmacology 1974, 36, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlamberová, R.; Vrajová, M.; Schutová, B.; Mertlová, M.; Macúchová, E.; Nohejlová, K.; Hrubá, L.; Puskarčíková, J.; Bubeníková-Valešová, V.; Yamamotová, A. Prenatal methamphetamine exposure induces long-lasting alterations in memory and development of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamotová, A.; Šlamberová, R. Behavioral and antinoticeptive effects of different psychostimulant drugs in parentally methamphetamine-exposed rats. Physiol. Res. 2012, 61, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Fowler, J.S.; Volkow, N.D.; Logan, J. Fast uptake and long-lasting binding of methamphetamine in the human brain: Comparison with cocaine. NeuroImage 2008, 43, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Volkow, N.D.; Fowler, J.S.; Wang, G.J. Distribution and pharmacokinetics of methamphetamine in the human body: Clinical implications. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Girault, J.; Valjent, E.; Caboche, J.; Herve, D. ERK2: A logical AND gate critical for drug-induced plasticity? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Curley, J.P.; Champagne, F.A.; Bateson, P.; Keverne, E.B. Transgenerational effects of impaired maternal care on behaviour of offspring and grandoffspring. Anim. Behav. 2008, 75, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldji, C.; Diorio, J.; Anisman, H.; Meaney, M.J. Maternal behavior regulates benzodiazepine/GABAA receptor subunit expression in brain regions associated with fear in BALB/c and C57BL/6 mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2004, 29, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Homer, B.D.; Solomon, T.M.; Moeller, R.W.; Mascia, A.; DeRaleau, L.; Halkitis, P.N. Methamphetamine abuse and impairment of social functioning: A review of the underlying neurophysiological causes and behavioural implications. Psychol. Bull. 2008, 134, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, F.; Diorio, J.; Sharma, S.; Meaney, M.J. Naturally occurring variations in maternal behavior in the rat are associated with differences in estrogen-inducible central oxytocin receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 12736–12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benoit, D.; Parker, K.C. Stability and transmission of attachment across three generations. Child Dev. 1994, 65, 1444–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itzhak, Y.; Ergui, I.; Young, J.I. Long-term parental methamphetamine exposure of mice influences behavior and hippocampal DNA methylation of the offspring. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lester, B.M.; LaGasse, L.L. Children of addicted women. J. Addict Dis. 2010, 29, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ary, T.E.; Komiskey, H.L. Basis of phencyclidine’s ability to decrease the synaptosomal accumulation of 3Hcatecholamines. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1980, 61, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagioni, F.; Ferese, R.; Limanaqi, F.; Madonna, M.; Lenzi, P.; Gambardella, S.; Fornai, F. Methamphetamine persistently increases alpha-synuclein and suppresses gene promoter methylation within striatal neurons. Brain Res. 2019, 1719, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohesara, S.; Ghadirivasfi, M.; Barati, M. Methamphetamine-induced psychosis is associated with DNA hypomethylation and increased expression of AKT1 and key dopaminergic genes. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2016, 171, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šagud, M.; Mück-Seler, D.; Mihaljević-Peles, A. Catechol-O-methyl transferase and schizophrenia. Psychiatr. Danub. 2010, 22, 270–274. [Google Scholar]
- Pregelj, P. Neurobiological aspects of psychosis and gender. Psychiatr. Danub. 2010, 21, 128–131. [Google Scholar]
- Fraga, M.F.; Esteller, M. Epigenetics and ageing: The targets and the marks. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasnova, I.N.; Chiflikyan, M.; Justinova, Z.; McCoy, M.T.; Ladenheim, B.; Jayanthi, S. CREB phosphorylation regulates striatal transcriptional responses in the self-administration model of methamphetamine addiction in the rat. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 58, 132–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renthal, W.; Maze, I.; Krishnan, V.; Covington, H.E., 3rd; Xiao, G.; Kumar, A. Histone deacetylase 5 epigenetically controls behavioral adaptations to chronic emotional stimuli. Neuron 2007, 56, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, Y.Y.; Wu, L.; Zhao, Z.B.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Ma, J.F.; Chen, S.D. Methylation of alpha-synuclein and leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 in leukocyte DNA of Parkinson’s disease patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desplats, P.; Spencer, B.; Coffee, E.; Patel, P.; Michael, S.; Patrick, C.; Adame, A.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E. Alpha-Synuclein sequesters Dnmt1 from the nucleus: A novel mechanism for epigenetic alterations in Lewy body diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 9031–9037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z. Epigenetic upregulation of alpha-synuclein in the rats exposed to methamphetamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 745, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mark, K.A.; Soghomonian, J.J.; Yamamoto, B.K. Highdose methamphetamine acutely activates the striatonigral pathway to increase striatal glutamate and mediate longterm dopamine toxicity. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 11449–11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marshall, J.F.; O’Dell, S.J.; Weihmuller, F.B. Dopamineglutamate interactions in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. J. Neural Transm. 1993, 91, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayanthi, S.; McCoy, M.T.; Chen, B.; Britt, J.P.; Kourrich, S.; Yau, H.J.; Cadet, J.L. Methamphetamine downregulates striatal glutamate receptors via diverse epigenetic mechanisms. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cadet, J.L.; Ali, S.; Epstein, C. Involvement of oxygenbased radicals in methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity: Evidence from the use of CuZnSOD transgenic micea. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1994, 738, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hřebíčková, I.; Ševčíková, M.; Macúchová, E.; Šlamberová, R. How methamphetamine exposure during different neurodevelopmental stages affects social behavior of adult rats? Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hřebíčková, I.; Malinová-Ševčíková, M.; Macúchová, E.; Nohejlová, K.; Šlamberová, R. Exposure to methamphetamine during first and second half of prenatal period and its consequences on cognition after long-term application in adulthood. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Ševčíková, M.; Hrebíčková, I.; Macúchová, E.; Šlamberová, R. The influence of methamphetamine on maternal behavior and development of the pups during the neonatal period. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2017, 59, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šlamberová, R.; Mikulecká, A.; Pometlová, M.; Schutová, B.; Hrubá, L.; Deykun, K. Sex differences in social interaction of methamphetamine-treated rats. Behav. Pharmacol. 2011, 22, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holubová, A.; Ševčíková, M.; Macúchová, E.; Hrebíčková, I.; Pometlová, M.; Šlamberová, R. Effects of perinatal stress and drug abuse on maternal behavior and sensorimotor development of affected progeny. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matějovská, I.; Bernášková, K.; Šlamberová, R. Effect of prenatal methamphetamine exposure and challenge dose of the same drug in adulthood on epileptiform activity induced by electrical stimulation in female rats. Neuroscience 2014, 257, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, O.; Wee, S.; Specio, S.E.; Koob, G.F.; Pulvirenti, L. Escalation of methamphetamine self-administration in rats: A dose–effect function. Psychopharmacology 2006, 186, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrod, S.B.; Dwoskin, L.P.; Crooks, P.A.; Klebaur, J.E.; Bardo, M.T. Lobeline attenuates d-methamphetamine self-administration in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 298, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- van Thriel, C.; Westerink, R.H.S.; Beste, C.; Bale, A.S.; Lein, P.J.; Leist, M. Translating neurobehavioural endpoints of developmental neurotoxicity tests into in vitro assays and readouts. Neurotoxicology 2012, 33, 911–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van Thriel, C.; Quetscher, C.; Pesch, B.; Lotz, A.; Lehnert, M.; Casjens, S.; Beste, C. Are multitasking abilities impaired in welders exposed to manganese? Translating cognitive neuroscience to neurotoxicology. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 2865–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, A. Executive functions. Ann. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Life Period | Rat | Man | Influence of MA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Life expectancy | 2–3 years | 75–85 years | Highest addiction in the 15–34 age range [2,3,4] |
| Weaning | week 3–4 | after 6–12 months | MA passes into the milk [88,105] |
| Prepubertal period | 4th week | Between 8–10 years | The influence of environment on the psycho-motoric development of the child [31,33,87,106,111,112,116,128,129,133,135] |
| Adolescence | week 5–10 | 10–20 years | First use of addictive substance [2,24,133,137] |
| Adulthood | From week 10 to 12 | From year 20 | Period of sexual maturity—pregnant addicted woman [2,7,18,23,31,135] |
| Late age | From 20th month | From the 60th year |
| Brain Development | Rat | Man |
|---|---|---|
| Neurulation and development of neural tube | 9–11 ED (half of pregnancy) | 24–28 ED (3rd week of pregnancy) |
| Cell proliferating process | 10.5–11 ED | From 4th week of pregnancy |
| Serotoninergic cells | 9–11 ED | 5th week of pregnancy |
| Striatum, nucleus accumbens, basal ganglia | 12–13 ED | 5th week of pregnancy |
| Noradrenergic neurons | 12–14 ED | 5th–6th week of pregnancy |
| Dopaminergic neurons | 10–15 ED | 6th–8th week of pregnancy |
| Hippocampus, amygdala, limbic system | From 14 ED (about 15% of granular cells are created in the postnatal period) | 8th week of pregnancy (about 80% of granular cells are created in the 40th week, i.e., right before labor) |
| Maturation of synaptic connections | 18–21 ED (last prenatal days) | 34th–36th week of pregnancy |
| The peak of neurogenesis | 1st and 2nd week postnatal | 40th week of pregnancy |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tomášková, A.; Šlamberová, R.; Černá, M. Influence of Prenatal Methamphetamine Abuse on the Brain. Epigenomes 2020, 4, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4030014
Tomášková A, Šlamberová R, Černá M. Influence of Prenatal Methamphetamine Abuse on the Brain. Epigenomes. 2020; 4(3):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4030014
Chicago/Turabian StyleTomášková, Anežka, Romana Šlamberová, and Marie Černá. 2020. "Influence of Prenatal Methamphetamine Abuse on the Brain" Epigenomes 4, no. 3: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4030014
APA StyleTomášková, A., Šlamberová, R., & Černá, M. (2020). Influence of Prenatal Methamphetamine Abuse on the Brain. Epigenomes, 4(3), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/epigenomes4030014






