Abstract
Creative social enterprises are increasingly emerging in rural regions, motivated by a desire to take social responsibility through creative approaches. These enterprises integrate entrepreneurial activities with creative social attributes and are sometimes set in rural collaborative workspaces (CWSs) facilitating entrepreneurial activities. Under the frame of entrepreneurial ecosystems (EEs), we argue that CWSs can be seen as brokers, who (1) link resources as liaisons, (2) hold and pass resources as gatekeepers, (3) enhance resource flows as coordinators, and (4) reproduce experiences as representatives. Against this backdrop, this paper presents a case study of two creative social enterprises in a CWS with a cooperative structure in rural Upper Austria by analyzing entrepreneurial biographies about the demand and use of entrepreneurial resources. Through a comparison between before and after the emergence of the CWS, the findings suggest that the EE for creative and social entrepreneurship undergoes two different types of transformation, a radical and a gradual one. The brokerage process of the CWS enhances local resource networks’ transformation of EE and brings the transformation in terms of translocal resources and integral EE of enterprises in the CWS. Additionally, the CWS generates social impacts on the local community through social enterprises. This paper contributes to ecosystem literature by introducing an actor-centric perspective and giving new insights into social entrepreneurship and the transformative power of CWSs as brokers.
1. Introduction
Due to limited profitability, rural areas are often unable to attract private services, and economic non-viability leads to the withdrawal of public services [1,2,3]. Yet, social enterprises are about to fill this gap, and the creation and development of such entities are widely supported across the EU [4]. Despite these disadvantages, local communities are willing to “buy local products” and to “support local enterprises”, and the social responsibility of the rural social enterprise provides feasibility [5,6]. Several scholars define the social enterprise as a business that sees solving social problems with entrepreneurial approaches as a mission, and the social impact of activities is prioritized to an equal or greater extent than making a profit [7,8]. Examples of such social enterprises offering solutions to local challenges are care service providers and agricultural marketing companies.
Some social enterprises in rural areas act as context-specific initiatives within the creative industries. Within our specific area of investigation, creative industries officially refer to those businesses that are engaged in the creation, production, and (media) distribution of creative and cultural goods and services, including architecture, the music industry, books and publishing, radio and TV, design, software and games, film and photography, advertising and the performing arts market [9]. Numerous studies show that creative industries play an essential role in fostering innovation processes in rural areas, not only with technological innovations, but also in rethinking the design of products or services, the organizational aspect, or the business model, as a vehicle of cultural development or culture-led and creativity-led local development [10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. Creative industries in the rural region enhance the identity of a community and place as “creative” [17,18] to attract creative professionals [19], which provides favorable conditions for the emergence of shared identity, increases trust and collaboration, and thus fosters social participation, innovation, inclusion, accessibility, and cooperation [20,21]. This supports the social and community core of social enterprises. Rural enterprises in creative industries sometimes claim their social missions, such as social and environmental goals of design projects, media focusing on community cohesion, and software/advertising on agriculture marketing and development. Furthermore, there are some key features that make the concept of the creative industry and the social enterprise compatible, especially when referring to small enterprises in rural areas: the creative and social sides of the enterprises prefer to be among like-minded people, which can help them become more visible and accessible for concrete intervention and support by the public. It is also vital for both sides to have direct contact with their audiences and consumers to provide practices that are suitable for public consumption, which, in terms of social and creative impact generation, potentially transforms the place into a more attractive site. On the basis of these reflections, we decided to focus our investigation specifically on social enterprises engaged in creative industries (from now on simply referred to as “creative social enterprises”) for the following two reasons: social enterprises play an important role in the wider rural development, and their creative practices are important to the quality of life of people living in rural areas as they facilitate ways to express the community’s identity and cohesion and can foster social and economic value creation [22,23].
In rural areas, typically, many of these social enterprises engaged in creative industries are micro and small businesses [23], in the form of one-person enterprises, small studios, or small cooperatives. They often have limited profit and resource networks [24,25]. With the emergence of rural collaborative workspaces (hereinafter CWSs), some of the creative social enterprises have started joining them to obtain support, e.g., the provision of offices, activity space, or other types of resource management. CWSs in rural areas include different organizational formats ranging from coworking spaces, creative hubs, open labs, and maker spaces to incubators. They can be registered as a limited liability company, cooperative, non-profit organization, association, or welfare organization, with different advantages. Despite these structural differences, rural CWSs usually have a clear social ethos, and facilitating creative social entrepreneurship is an important way for CWSs to create social impact [26,27].
The unfolding of creative social entrepreneurship and how it generates the expected social impacts depend largely on whether or not access is given to the needed entrepreneurial resources. Hence, a perspective of the supportive resources system for creative social enterprises, namely, the entrepreneurial ecosystem (hereinafter EE), is applied to study entrepreneurship. We argue that CWSs bring added value to this perspective as they link wider entrepreneurial resources and make them more accessible to entrepreneurs [28,29,30]. With the CWSs, the resources are co-located in a space and become more visible and reachable. According to the literature, there is also more intensive communication and collaboration among the enterprises inside the CWS [31,32]. Based on these features, we claim that CWSs function as brokers within the entrepreneurial ecosystem [33,34].
An analysis of the situation before and after the emergence of CWSs in the entrepreneurial ecosystem provides insights into entrepreneurial support for creative social enterprises and gives, especially, insights into the role and impact of CWSs. There is a theoretical gap regarding how we can frame CWSs’ position in the EE and whether/how we could employ the broker concept to better understand CWS functions. Empirically, the enterprise-support roles of CWSs for creative social enterprises are underexplored, especially in rural contexts, though it is an emerging practice. Therefore, this paper aims to answer the following research question: what are the broker roles and brokerage processes of CWSs in the entrepreneurial ecosystem for creative social entrepreneurship? After answering the question, the impact of the broker CWS on the EE and local community is revealed.
The goal of this paper is to highlight the broker roles of CWSs in the entrepreneurial ecosystem and stress the importance of including a bottom-up and actor-centered perspective in ecosystem research, which has not yet been covered in the top-down EE discussion and CWS function studies. The investigation reveals that entrepreneurial ecosystems undergo radical and gradual changes, which, together with the temporal explanation of the CWS’s functions, describes a transformative process. Our empirical data show that due to the broker roles of the rural CWS, the transformation occurring in the creative and social enterprises’ EE impacts the enterprises’ development and the way their entrepreneurial activities are being carried out. In addition, the coevolution between EEs, CWSs, and social enterprises in rural areas, leads to the establishment of a strong and active socially oriented entrepreneurial ecosystem. The innovative approach of the CWS in our case, including the broker functions with its cooperative structure, brings the transformation of EE and social impact to the local community by fostering social enterprises. Our empirical evidence contributes to the discussion about the impacts of social innovation on the local community and its development.
This research is organized as a qualitative case study in Upper Austria with a rural CWS and two of its local social enterprises engaged in distinct sectors of creative industries. This paper first employs the theory of EE to understand the specific ecosystem of social enterprises in creative industries (Section 2.1) and, then, frames the broker roles of CWSs in the EE perspective (Section 2.2). After describing the research design (Section 3), we reveal the empirical findings through a temporal perspective and by organizing the interview contents of the entrepreneurs and the manager according to the four broker roles of CWSs (Section 4). Finally, we discuss how the transformation of the EE for social enterprises in creative industries occurs and what roles the CWS plays in it (Section 5).
2. Literature Review
2.1. Rural Entrepreneurial Ecosystems of Social Enterprises
The entrepreneurial ecosystem emphasizes the interacting resource elements between interconnected actors that support start-ups and moderates the impact of entrepreneurship on economic growth [35,36,37,38]. An entrepreneurial ecosystem contains two bodies of knowledge: the main elements, and how these elements influence and interact with each other, which is the source of entrepreneurial opportunities [39]. Based on the knowledge gained from the urban context, the discussion of rural EE undergoes a bias. To check the sufficiency of interacting resources in rural EE through the urban experience is inappropriate, since social norms, local markets, and local connections may be the outstanding elements in the rural areas, unlike the vital EE actors in cities [40]. Further, an urban focus on technical and innovative companies is not suitable for the rural economy [41,42]. The enterprises, which includes social enterprises, that fit into the rural society and economy and make a difference for the local community, and their EE should be the focus of rural EE arguments.
Rural social enterprises emphasize the social attributes of the enterprises, enabling them to be embedded in the local EE, meet the local needs, and contribute to the local community [3,43]. They mix and overlap the “hard” business and “softer” social interests [44], running activities to provide services or goods that combine the goal of benefiting the community and society, while pursuing financial sustainability [4,43]. The literature on social entrepreneurship ventures appears to mostly focus on the social entrepreneurs themselves, e.g., individual motivations and logic of action, or the internal organizational structure of the firms [45,46]. Though social entrepreneurship is essentially the process by which entrepreneurs acquire entrepreneurial assets to pursue their social ventures [47], so far, little attention has been given to their EE and how this ecosystem can provide advantages to social enterprises [48]. There are many studies on entrepreneurial ecosystems but little knowledge of social EEs. A perspective of social entrepreneurial ecosystems would highlight the resources and resource interactions that facilitate social entrepreneurship and generate transferable insights [39]. When it comes to how to position social EE in the general discourse of EE, we do not support the idea that social EE is a subtype of EE [49]: the core actors switch to social enterprises; the most crucial entrepreneurial resources in social EEs are different from the ones of general EE discussions; and both the interactions and action modes of these elements change [48]. Accordingly, the approach to studying social EE differs from how EEs are usually analyzed.
A strong presence of social enterprises in the EE transforms the EE to become socially oriented. There are some characteristics of social EEs that are relevant to our perspective: in social EEs, the social side of the resource elements is indispensable, including self-organization, local trust, local connection, visibility, and recognition [50]. Bottom-up day-to-day activities at the individual level, rather than exogenous top-down actions by governments and powerful players, are critical to the formation and durability of resources in their interactions [51,52]. For a better understanding, given its complexity, it is thus convenient to apply an actor-centric approach to social EEs and focus on micro-dynamics and the strategic organization of ecosystems [51]. There is a temporal dimension of the entrepreneurship process included in the entrepreneurs’ actions [53,54]. For this reason, it appears easier to describe the functioning resource interactions through the lens of the entrepreneurs, by seeing the social EE as a boundary object [55], influenced by individual social norms, societal goals, and business culture [56]. A last characteristic of social EEs that is relevant is the translocality of entrepreneurial resources, which are prominent in social EEs. Translocality originates from social proximity to see whether the resources are within personal connections [57].
Coming to the application and significance of the study of social EEs, it appears that a more focused approach is relevant for today’s local development programs in general and, specifically, for social innovation processes, based on the assumption that participative and collective approaches of creative social enterprises are significant in enhancing transformation. As some scholars argue, social entrepreneurship is, indeed, an action under the collective background [58,59]. Following this perspective, social entrepreneurs are key players in the entrepreneurial ecosystem, and attributes like their community belonging are part of the positive externalities of success, driving the social outcomes of social entrepreneurship to be meaningful in local communities [60]. The social EE underscores a community logic that focuses on community needs, development, prosperity, trust, and cooperation [61,62]. It engages in social responsibility and focuses on community microeconomic initiatives [63]. Different from focusing on scaling-up businesses and the growth economy [64], economic vitality with stable employment and unique processes with value-added opportunities, community cohesion, and social elevation are the contributions from social EEs to community development [65].
The social EE is an ever more prevalent phenomenon in the countryside. It is crucial to know how CWSs can support creative social enterprises from an EE perspective. Since the CWSs organize events, take the initiative to reach out to new contacts, build up local trust, and promote visibility [32,66], they are the nodes and brokers of the entrepreneurial resources network, taking on various supporting actors and translocal resources and facilitating cooperation with the enterprises inside the space [67,68].
2.2. CWSs as Brokers in Entrepreneurial Ecosystems
CWSs, the co-localization of a group of individuals in the same rural work environment, which often has community- or business-focused functions [31,69,70], are interpreted as an integral part and functional infrastructure for entrepreneurial ecosystems [71,72]. In social EEs, having an ethos of entrepreneurship and social impact, CWSs work on both practical support and knowledge exchange for social enterprises, e.g., suppliers, supportive companies, and tax advisors, as well as facilitating mentorship and discussion [73,74]. Against this background and according to the current literature, CWSs are recognized as organizations on and beyond the local scale that bring the following advantages to social entrepreneurship: (1) they facilitate the social enterprises to embed in the local community by establishing connections and linking local entrepreneurial resources [56]; (2) they grasp translocal resources with external linkages [7,63], which is especially important for social enterprises in the creative industries with limited profitability, needing socio-economic visibility and profiting from idea exchange [75]. In this sense, the resource networks that CWSs offer (3) reduce the possible entrepreneurial frailties and are one of the determining factors of success [76]. Furthermore, with regard to their general approach and social impact, CWSs (4) act as collective organizations that leverage strengths in linking resources, whether as a bottom-up practice [77] or as a policy tool [78].
Brokers are considered actors with ties to disconnected individuals, communities, and collaborators [79,80,81], taking structural holes (non-tie condition) to define brokerage [82,83,84]. However, Obstfeld suggests that brokerage can take many forms of activities and does not require strict prerequisites of disconnected structural patterns [85]. Further, from a functional perspective, Fernandez and Gould elaborate that the broker, as the actor, mediates the flow of resources and information [34]. This argument explains the roles of CWSs in linking different resource networks to promote entrepreneurial behaviors in the EE and that CWSs can establish, enhance, or simply reduce impediments in the resource flow process by a variety of means. The more bridging relationships there are, the more opportunities the creative social enterprises can receive to recombine resources for entrepreneurship [85,86]. These are the brokerage orientations we highlight, that the CWS is taking resources from EEs and giving them to enterprises. We are aware that there are also negative notions or interpretations attached to the concept of brokerage, e.g., leveraging one actor against another [87]. However, in our perception and use, it is treated as a neutral concept that brings the advantages we described before and helps to understand relationships, collaborations, and transactions between the various actors involved in the study.
Based on what has been exposed so far, we now describe how CWSs utilize their brokerage role, arguing that they have different ways in which they prove to do so. Instead of focusing on the broker’s position in the network structure, we are interested in highlighting their actions, which we interpret as brokerage processes [88]. We agree with the literature claiming that brokers act proactively in identifying entrepreneurial opportunities, creatively synthesizing different information, and providing a social entrepreneurial vision [89]. This is in line with the actor-centric approach of entrepreneurs’ actions in social EEs. The actions of brokers and the actions of entrepreneurs are interactive and intertwined. Brokers can be (a) coordinators, who enhance interaction between group members (integrate internal resource networks, reorganize resources, strengthen internal communication and cooperation); (b) gatekeepers, who take resources from an external network and forward them onto a social venture through organization and relationship network (hold and pass the resources to the social entrepreneurship); (c) liaisons, if brokers mediate between different resource networks (link resources, build connections); or (d) representatives, when the broker spreads the broker’s own acquired prior knowledge experience to a new social venture (reproduce useful features and tools through organizational structures) [33,34].
To complete the picture and help address the CWSs’ general approach in social EEs, the broker role of CWSs take place at different levels: First, for each enterprise, it connects other resources (networks) to the social enterprise. Second, for each enterprise, it links the local and translocal ecosystems. Third, it links the ecosystems of enterprises to jointly reveal the integral ecosystem. These networks of resources grow and evolve over time, fueled by the CWS, the broker, which ultimately shapes the configuration of the EE [90,91].
3. Research Design
The purpose of this investigation is to interpret the brokerage roles and practices of rural CWSs in the frame of entrepreneurial ecosystems. Being especially interested in analyzing creative social EEs in rural areas, we selected a CWS with a cooperative structure in the rural area of Upper Austria that claims a creative and social ethos. We then picked two social enterprises in the field of creative industries. The two social enterprises are members and users of this CWS. Altogether, this represents our single case study with multiple perspectives of entrepreneurs and the CWS’s manager [92]. We applied an actor-centric perspective and compared the empirical data against the theoretical background of the broker role of CWSs in creative social EEs, which finally led us to a plausible conclusion and to further research prospects.
3.1. Research Methods
The research is qualitative [93], with a multimethod approach [94] of qualitative interviews, participatory observation, and document analysis. We combine the deductive approach of broker concepts from the literature with the inductive approach of empirical evidence and, then, compare and develop the broker concept to reach a conclusion. Documents include web pages, reports, and local materials like flyers. The observations were taken at both the office table and the CWS’s common area, for instance, in the conference room, kitchen, and terrace. The authors spent ten weeks (March, June, and July of 2023) in the field and conducted 12 interviews using a semi-structured interview guideline, in German and English language. The interview partners included various typologies, ranging from entrepreneurs, CWS employees, former employees, interns, and the manager. Three of the interviews were selected for the discussion of this paper and reflected the perspective of the CWS manager and of two CWS users/members, that is, of two local social enterprises of the creative industries: a photographer/filmmaker and a product designer. The enterprises were identified using the snowball method and finally selected for the present analysis because of their specificities responding to the criteria of local social enterprises engaged in the creative industries. The photographer/filmmaker makes videos for social or environmental purposes or projects/businesses with similar missions. The product designer’s business focuses on projects with social value, that is, following educational and environmental aims. The CWS we selected is known for promoting social enterprise development and has a cooperative structure, which provides exploratory insights into how the innovative approaches and functions of a CWS can generate social impact through social entrepreneurship. Additionally, for our selection, we prioritized a balance of gender and diversity in the creative industry sectors. To retrace the entrepreneurship process, the enterprise biography was applied by the retrospective description of entrepreneurship from entrepreneurs [95]. Accordingly, the relevance of the enterprises’ biography was investigated in light of the CWSs’ activities and, vice versa, the relevance of the CWS’s biography in light of the enterprises’ activities.
Finally, interviews allowed for the expression of subjective ideas from entrepreneurs and managers, which is crucial for studying social enterprises.
3.2. Data Collection and Data Analysis
As shown in the overview of Table 1, we collected empirical data about two social enterprises in the creative industries and the rural CWS they collaborate with. In concrete terms, our sample consists of a two-person cooperative in video-making (enterprise 1), a one-person company in product design (enterprise 2), and the founder and manager of a rural cooperative based on a sociocracy structure (CWS manager). First, we conducted a ground-laying interview with the CWS manager which we followed up, in a second moment, in between the interviews with the two enterprises. This allowed us to fine-tune our conversation with him and clarify details we had learned from the enterprises’ perspective. At the same time, it provided us with further inputs about the CWS’s overall context, which were useful for understanding how to frame the EE.

Table 1.
Overview of interviews: Type of interviewees, main features, and interview duration.
The questions for the entrepreneurs included the stages they went through in their enterprise’s development and the social and business side of their resources, especially, how they find and obtain resources. Therein, the analysis of our research was focused on the processes the two enterprises are exposed to when providing, facilitating, and procuring their resources and—according to their perspective—what role the rural CWS plays over time in these regards.
The questions for the CWS manager included the resources the CWS provides during different stages of the enterprises, the structure of its cooperative, and how it sets up linkages to resources and networks.
Additional interviews with other people connected to the CWS helped us to gain a more integral understanding of the EE. In this case, the interview questions included their daily duty and contributions to the CWS, especially activities related to the two enterprises under analysis, and all of them were put into a temporal order.
For data analysis, we took the qualitative content analysis with deductive categories (the broker roles) [96]. We first reorganized all the interview materials into a temporal order to compare the enterprises’ stages before and after joining the CWS. After that, we assembled the content according to the theoretical frame of the broker roles of the CWS and the social EE, that is, we organized the content according to the four broker roles of (a) coordinators (enhance); (b) gatekeepers (hold and pass); (c) liaisons (link and build); (d) representatives (reproduce). Then, we adopted an inductive approach to conclusively emphasize the different networks of resources, the local/translocal resources, and the resources in the integral ecosystem.
The resources are seen as components that directly influence entrepreneurship, for instance, entrepreneurs’ skills and idea exchange among colleagues, instead of people [97,98,99], and investments, conference rooms, tools as concrete materials, instead of supporting organizations [97]. Conclusively, the results are discussed in light of what are claimed to be the advantages of a CWS’s broker roles.
4. Results
We start with outlining the development of the enterprises in order to better understand the functions and roles of the rural CWS, as reported by the two creative social enterprises. They both developed their desire of pursuing their profession during their studies and started entrepreneurship on their own. They both found out about the CWS through local connections and joined the CWS to continue their business further.
Both entrepreneurs run their social enterprises with a clear social mission. E1 wants to return benefits to the community with his abilities, as he claims that his business uses social and ecological values to change people’s mindsets: “I’m a kind of self-defined social entrepreneur” (E1). E2 also set the goal to “have a social impact to improve the local inhabitants’ life” (E2) at the very beginning, and they both adhere to these visions throughout the entrepreneurship.
4.1. EE before Joining of the CWS
For E1, the idea of social entrepreneurship came from a positive experience with yoga courses, along with support from family and friends. These were entrepreneurial role models who were inspiring for E1 regarding the expression of videos and the philosophical background. E1 developed video-making skills while in school. At a later stage, the CWS, which he joined afterward, became a client. Though E1 was not a member of the CWS, during this collaboration, the discussion with the people from the CWS turned out to be very helpful.
Material support is the basis for practical actions. E1 had the financial means to buy his first camera from a paid project by using equipment from the university. Subsequently, his skills also brought him some extra financial support from a part-time job in the television station.
There are also some supportive policies. At the time E1 could not receive any commissions, it was possible to receive money from the state government. “That (unemployment money) is also kind of a support for you, continuing your interest” (E1). During this period, E1 had many clients from different sectors and institutions: museums, nature reserves, sports clubs, art associations, climate projects, and with disabled people, among others. The CWS was one of them. All of them were from personal efforts. “Five years working by myself; it’s a one-man enterprise” (E1).
E2 stayed on the learning-career path with ecological product design. Motivated by the design offices working for the local community, her idea came up about starting a social business. Working for a design studio abroad, E2 set up connections and accumulated more knowledge. After returning to Austria, E2 explains, “I had kind of my own business registered for these two years” (E2). This is a stage in which she was registered as a one-person company. The business was primarily art and crafts, shop design, and exhibition design. The designer friends were still in contact for exchanging ideas and discussions.
Building on ideas and personal competence, material support was crucial. There was a company that offered materials for a leather upcycling project. The relatives taking care of E2’s kids were important in this stage of life. There was further policy and organizational support. Maternity leave provided time and financial support for starting her entrepreneurship. The “Creative Austria” program for creative industry networks and “Frau Wirtschaft”, both organized by the regional government, were events in which she could share experiences.
The clients during this period, which was before joining the CWS, included E2’s former boss, the owner of an advertisement company who was known by E2 from an English class. Additionally, E2 did the shop design for a biological farm, which called her up in response to her newspaper announcement. From there, the relatives of the first client became involved, which led to another shop design and a project for house interior design. Generally, E2’s clients were the result of her efforts to reach out to the people, and bit by bit, she gained visibility within the community.
4.2. EE with CWS
The reason why E1 joined the CWS was that he reached a business level in which he had to pay a lot more insurance than before as a start-up; therefore, it made sense to get into the CWS. Then, the creative social enterprise became a label in the CWS. “I don’t feel like it is my social enterprise only; it feels more like that’s a collective social enterprise. My part is like a label” (E1). However, it is still an independent creative social business. He reaches out to his own clients and does the projects, with an independent income, only under the name of the CWS. “Officially, I am employed. I’m also an entrepreneur” (E1).
E2 worked for a project of the CWS for a while, then took a leave, and later went back to join the CWS since she wanted a more stable and safe business. When referring to staying in the CWS, E2 explains that it was like “you are acting like an entrepreneur, but you are employed” (E2). Same as E1, the business of E2 became a label in the CWS, yet it was independent.
The following section elaborates on the broker roles and brokerage process of the CWS for the two enterprises during this stage of entrepreneurship, which is once they joined the CWS.
4.2.1. The Power to Link and Build
By building connections and linking entrepreneurial resource networks to social enterprises, the brokerage process of the CWS is acting as a liaison.
In the video-making business, besides E1’s own clients, there are also a number of clients from the CWS network, linked to the enterprise. “I made a lot of projects with the people connected to the CWS. So, there we had a really intense cooperation going on” (E1). The CWS also brings big clients for E1, through the reputation of the CWS, from where the income helps to work further on social goals. They are not merely clients; they bring with them the corresponding technical support, revenue, prestige, and snowball potential for new clients, which altogether is a whole network of resources.
In an art project promoting a particular kind of paper as environment-friendly material, the CWS built connections and linked various resources for E2. Through the network of the CWS, E2 attended events in another coworking space and met one graphic designer who also contributed to the project. Additionally, E2 received funds from the LEADER program, with the help of the reputation of the CWS. There was another artist in the CWS, through whose well-connected network, E2 could reach out to other artists to do this project together, whom E2 did not know before. “I think most of the recommendations were based on her (the artist in the CWS) recommendations” (E2). One of the collaborators of E2 was from the local museum, which is also an extension of the CWS network. A fisherman was helping to transport the materials since the exhibition was on the river. The photographer agreed to join with a lower budget, thanks to the good reputation of the CWS. Furthermore, E2 can use spaces from another coworking space that connects to the CWS manager in addition to the CWS’s offices and conference room.
In sum, it was the CWS that set up initial linkages with the participating artists, the fisherman, the photographer, and the museum, as well as with the LEADER region, and then, the cooperation took place. These were the local exhibition resource networks. In these processes, the brokerage brings demand and offer sides together, and then, the cooperation is to negotiate between them.
4.2.2. The Power to Hold and Pass
As a cooperative, in addition to creating connections between networks of resources, the CWS can hold some entrepreneurial resources that are well coordinated and have been readily called on, as a gatekeeper.
Switching to the education and exhibition projects, E2 received funding from the Chamber of Commerce, with the help of the CWS manager, under the name of the cooperative. The Chamber of Commerce also helped in contacting the kindergartens as well as mayors for the education project. The wooden boxes they needed for the education project were provided by a person from the nearby city, and an external person was helping with the distribution website. Both of them had worked with the CWS cooperative before. An advertising company painted the delivery truck for a better price in the education project, through the connection of the CWS manager. All of these resources were already connected with the CWS cooperative and came in use when needed. There was “a host in internal CWS groups, a kind of janitor” (C), who knew exactly where the tools, contacts, and resources are in the place and needed for activities and special events, as explained by the CWS manager.
Being a registered cooperative, the CWS could also hold and pass policy and organizational support. The parental leave and leave for health issues were covered by the government and the Chamber of Commerce because the two entrepreneurs were employed by the CWS cooperative. During the pandemic, the CWS as a cooperative received money from the state for all entrepreneurs, as well as social business funds in Austria. Since entrepreneurs are employed in the CWS, they have the chance to do further education while being paid. In the CWS, “there is a financier in charge to find paying members” (C). “(Being) employed is a huge resource” (E1).
Besides policies, there are further programs that the CWS joins as a collective entity by its organizational advantage of a cooperative. The sociocracy approach of the foundation behind the CWS allows collaborations with other initiatives. The European Capital of Culture program of 2024, which the CWS is part of, brings many offers through its visibility. E2 planned to repeat the art project under this program. For a future project of E2 with the European Capital of Culture, a Japanese company is already on board. Thanks to the openness and free access to the CWS, there is more space for spontaneous opportunities by meeting people. In this sense, “(CWS) is as a playground, for pop-up activities” (C). The CWS cooperative is the entity that is aware of these resources held by the authorities and larger programs, and it obtains them by handling all the required administrative work and bringing them down to the enterprises. “As such, social enterprises belonging to a CWS can use the contacts of the CWS network for their own development” (C). These brokerages of the gatekeeper are exclusively accessible with the CWS cooperative.
4.2.3. The Power to Enhance
The CWS integrates internal resources as a coordinator, especially for collaboration between enterprises within it.
The idea exchange and entrepreneurial atmosphere are typical resources brought by the coordination brokerage. For the people inside the CWS, there are physical meetings and online discussions organized once a month. “They were really inspiring and giving good feedback. So, I had a lot of new ideas. That is quite valuable” (E1). For the people doing other social businesses, they share the same values and sometimes have the same problems. Specifically, for reaching out to the participating artists in an art project, E2 discussed it with others in the CWS. The idea of the education project of E2 derived from a discussion with everyone in the CWS. There were also network meetings with other CWS branches, through which E2 found a collaborator for a future project. “That is how the networking happens” (E2). Further, the CWS regularly organizes social events, in which entrepreneurs can get to know other external people, e.g., “in community education program the CWS finds people in the village who are willing to share their topic and skills” (C), as well as the international exchanges brought by the international project of the CWS. “There is a scouting competence in the CWS, allocated explicitly for local, topic-specific, and international network meetings” (C).
Collaborating with others in the CWS, entrepreneurs can manage to do bigger and more diverse projects. In the education project of E2, there were technical parts, financial parts, bigger stations, and packaging; someone from the CWS helped each of them with their specialties, “Everybody is kind of involved” (E2). E2 also hired a person to do the logistics and the maintenance work by putting a notice in the newspaper. Further, E1 made videos for the CWS, working with the other social entrepreneurs in the CWS, while E2 helped others in the CWS with graphic design and did the refurbishment of the space by making use of her interior design expertise. “Often somebody is offering help whenever somebody has the capability or capacity” (E2). “I like the collaborative spirit that we have, and the trying to find a new way of work” (E2). The collective identity of being part of the cooperative further fosters collaboration. From the CWS’s perspective, members need to be active on the cooperative level and not only get paid and dedicate time to their own enterprise. “Do not abuse the CWS as a vehicle” (C). The peer resources are reorganized and made visible to entrepreneurs, and the collaborative spirit of the CWS facilitates interactions between internal resource networks.
Moreover, the CWS offers a proper working environment to work with the materials. The time and spaciousness that the CWS provides helps. “In order to fulfill the social enterprise’s needs and be effective as a broker…, it needs to be clear how to make use of the space” (C). For all the activities happening in the CWS, “…the spatial space is really also quite important” (E2). With physical co-location, it is possible to send the message across faster.
4.2.4. The Power to Reproduce
The CWS is also more of a representative that uses its structure and strengths to provide entrepreneurial experience and help with the entrepreneurial process.
Within this cooperative model, the CWS takes care of the income for entrepreneurs, and does the work of accounting, tax, insurance, and website maintenance. The way the CWS is organized as a cooperative invoked E1’s thoughts about doing some social work and broadening the business to better realize social-ecological aspects. The ethos and philosophy of the CWS also gave E1 some new approaches to carrying out social business. Additionally, the manager of the CWS acted as a mentor who monitored and supported the project of E2 along the way. “(Name of the manager) is my main mentor; from him I learned a lot about how to initiate projects” (E2).
Another large advantage of joining the CWS cooperative is strategic and organizational support. “The top function of the CWS (is), so the diversity and also keep(ing) the stable income” (E2). Flexibility is also a merit of the CWS cooperative: besides the fact that the work can be performed anywhere and anytime, the evaluation is about the actual job performed other than the working time. The CWS is vital in providing visibility: “It helped me a lot to get a better standing in my field I think, to get more professional, easier to promote yourself” (E2).
This is the entrepreneurial knowledge that the CWS has accumulated and reproduced for every entrepreneur. This is also a bidirectional result of the collaborative work of all CWS participants. The CWS keeps growing with its members and, thus, knowledge experience can be reproduced, both within entrepreneurs of the CWS and its cooperative and towards a new social venture. Yet, reproducing values and principles does not always go smoothly and can be difficult. As the manager highlights, “personal clashes played a role in how the structure behind the CWS continues to develop” (C), which are about how to promote the social enterprise, how to model the development, and how to offer a fellowship.
4.3. The Broker Roles of the CWS
According to our data, there are many resources available; however, enterprises do not access them directly. The CWS makes these resources accessible to them: it serves as the entity that is aware of the resources; it can set up linkages; it has its own resource networks; it is able to manage the required administrative work and, finally, transfer the resources to the enterprises; it utilizes its organizational advantages. The CWS is far more than just a passive provider of workspace; it is a proactive provider and facilitator of various resources. It responds to the demands of the enterprises inside but also actively builds networks and offers more additional opportunities. Throughout our interviews, there were no negative comments from entrepreneurs about the functions of the CWS. This might be because they have a say in the CWS’s cooperative organization, and the CWS shares the resources with all the entrepreneurs. However, it can be observed that creative social enterprises in the CWS are less flexible in choosing their own clients/projects, as they might prioritize the projects that the CWS brings to them. Sometimes, creative social enterprises take advantage of the CWS’s label and reputation, without returning much to the CWS. Nevertheless, on the one hand, the broker functions of the CWS are from the key persons inside, e.g., the CWS manager and entrepreneurs; on the other hand, they also originate from the organizational structure of a cooperative and the CWS label as a whole.
The CWS can link, hold, reorganize, and reproduce entrepreneurial resources, as various brokerage actions, referring to the broker roles of liaisons, gatekeepers, coordinators, and representatives. For different entrepreneurial resources, different actions are required from the CWS to fulfill entrepreneurial needs. In the EE, the brokerages of the CWS are important drivers in activating and facilitating the interaction of resources, and the interaction of these components is the source of social entrepreneurship.
5. Discussion
5.1. The Transformation of EE
5.1.1. Radical Change of the EE with the Emergence of CWSs
With the joining of the CWS, the broker CWS takes over the majority of resources, which is shown in Figure 1 as many resources going through the CWS (the intermittent arrows) in phase 2 for both cases. The colored squares in phase 2 refer to the resources that are taken in by the CWS through different broker functions, and the circle with gray-filling represents the resources directly accessed by the enterprise. The CWS links clients, collaborators, and supporters for the enterprises; the CWS holds and passes otherwise unreachable policy support and readily available actors to the enterprises; the CWS enhances the discussions and idea exchanges, as well as collaborations inside the CWS, e.g., joint ideation phase, offering skill sets to each other, and further practicing joint work in projects; the CWS reproduces the prior experience to help entrepreneurship by its organizational structure. The CWS also greatly increases the translocal resources for entrepreneurship. Through its cooperative structure, the CWS can pass policy and regional funds down to the enterprises; through the CWS, enterprises can take advantage of the better visibility, gaining cooperators and clients beyond personal connections.
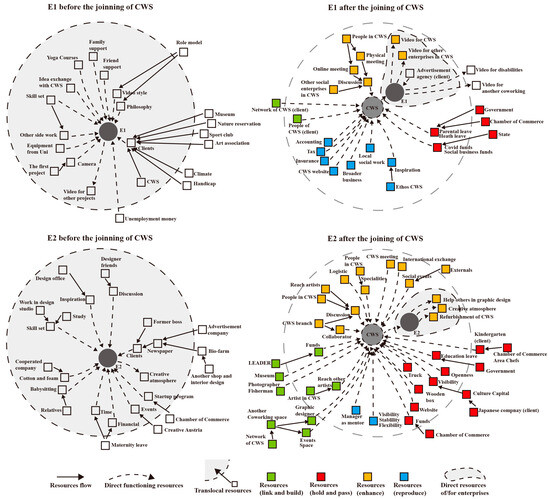
Figure 1.
Transformation of EE.
The EE for creative social enterprises moves to primarily having resources brokered by the CWS. The richness of entrepreneurial resources has increased, and the interactions of resources has changed from loose to tight. The CWS itself provides lots of assets, such as financial management and mentorship. Together with enterprises, the CWS can receive a lot of support, such as policies and funds. Through the needs of enterprises, CWS and enterprises work together to acquire further collaborators and clients, mainly through network and visibility. As shown in the resource quantities of Figure 1, EEs with CWSs have more resources coming into the ventures and really play a role in entrepreneurship. More resources also mean that creative social enterprises can undertake more diverse and larger projects, in terms of both more clients and better organizational structure support. In addition to the amount of resources, resource interactions are also more intense, which are the short solid arrows in the figure. External resources brought by the CWS will collide with internal ones to generate new resources. Internal resources also have more interactions, especially mutual help and cooperation among in-house entrepreneurs. Considering the spontaneous property of entrepreneurship, interacting resources are a source of entrepreneurial opportunities.
The way that entrepreneurs grab resources has also switched. Before, it was more about personal connections and personal efforts to connect through involvement in organizations and meetings. After joining the CWS, some resources are held by the CWS and only need to be used passively; some resources exist in the CWS’s network, and linking to them is very efficient and straightforward, while some CWS events bring resources to the space. Further, in contrast to the previous need for enterprises to pitch themselves, the CWS brings collective visibility, making it easier to reach out to resources outside of personal connections. In other words, entrepreneurs access most of their resources by utilizing, facilitating, and accelerating brokerage processes based on their entrepreneurial needs through the broker functions of the CWS.
5.1.2. Gradual Change Brought by Social Enterprises
Apart from the radical change of having a CWS brokering in the EE, there are also gradual changes in the EE brought by entrepreneurship on a daily basis. As a forwarding process, the EE takes changes from entrepreneurial activities that are embedded in it. This is the coevolution between social enterprises and the EE, originating from the knowledge spillover, entrepreneurial model, and the atmosphere. For instance, the exchange and discussion not only happen in the CWS but are also disseminated to a wider audience through events organized by the CWS that include outsiders, e.g., the state education administration sends someone to the CWS to learn the “Robots” and plans to broadly replicate the project, which E2 is currently in charge of. E1 made many videos for other social enterprises, e.g., disabilities, natural reservation, and education activities, which helped other social entrepreneurs and was a contribution to the EE. Jointly, the CWS and social enterprises have become models for others, and their path is reproduced by other branches of the CWS and social ventures. On the local level, mutual assistance and resource sharing are favorable among entrepreneurs. Beyond the local level, by the incremental visibility, there is a growing entrepreneurial climate that believes in citizen spontaneity because they know “how to give back something or payback.” (C). “I think it’s a little bit shift in the culture in the way of thinking and also in the way of trusting citizens.” (C) states the CWS manager and adds the importance of letting citizens act and create.
Therefore, through this gradual change, we see that the CWS’s brokerage process is bilateral. It is not only that the CWS brings entrepreneurial resources from the EE to the enterprises, which is one direction, but it also brings the experience and paths collected along the entrepreneurial process to EE. When others learn and reproduce the entrepreneurial expertise of the broker CWS, the brokerage process goes from the internal interaction network to the ecosystem and, finally, through there to other creative social actions.
5.2. CWSs as Driving Forces for Transformation
In terms of the local resource networks, the CWS does not cover all the aspects that social enterprises need; for example, E1 contacted his friends without the help of the CWS, and they divided the work and expanded the business. In addition, the resources brought by the CWS are not irreplaceable. For instance, E1 had a nearly saturated order book before joining CWS, and the CWS brought in a different set of customers; in the small community of the countryside, E2 also knew other artists and project collaborators, but the CWS could make the contacting process easier. Thus, for local resource networks, the CWS fosters the transformation of the EE for creative social enterprises rather than bringing novel development.
Translocal resources are a different matter. Apart from unemployment benefits, maternity leave, and events of the Chamber of Commerce for entrepreneurs, all remaining translocal resources came from the CWS. Because of the cooperative structure of the CWS, entrepreneurs enjoy employment benefits such as COVID funds and education leave, and also the European Capital of Culture program could only be realized through the collective efforts of CWS. In addition to this, small enterprises have a limited outreach, whereas the CWS is well placed to help them connect with previously inaccessible collaborators, as well as to access regional resources through collective visibility.
Likewise, the integral EE of different enterprises, including the internal exchanges and collaborations of enterprises in the CWS, as well as the well-connected resources of the CWS, is exclusively brought by CWS, e.g., mentorship, website maintenance, and monthly meetings. The aim of the CWS is to establish internal contracts to integrate the competencies of each CWS member, that is, creative social enterprise, into the CWS network. These resource interactions can occur only within the frame of the CWS, since there are dedicated persons to arrange the physical space, who are responsible for exchange activities and in charge of resource networking; the CWS not only provides a co-location site but also transmits an ethos and atmosphere of cooperation. Therefore, regarding the translocal resources and integral EE, the CWS brings transformation to the EE.
5.3. Integral Impact on the Local Community
The innovative approach of the rural CWS comprises its four broker roles of offering various entrepreneurial resources in the social EE. Therein, its specific organizational structure of a cooperative brings distinct functions, such as connecting external funds, authorities, policies, and programs as a gatekeeper, fostering internal collaboration as a coordinator, taking care of administrative tasks, and providing flexibility and stability as a representative. Besides its impact on the transformation of the social EE, the CWS also generates impacts on the local community through the social entrepreneurship it promotes.
If a rural CWS manages to attract creative social enterprises to the rural area and offers them suitable conditions to combine their private life with their professional ambitions, then this is already a first example of how impactful the CWS can be with regard to the economic vitality of the place in terms of the creation of a stable business environment. Further, the social enterprises also provide additional employment, such as the E2 hiring a truck driver and facility maintenance people as shown in our case.
Besides their impacts on the local market and labor force, the creative social enterprises brought awareness changes through their environmental protection and educational projects. The promotion of an environment-friendly paper from E2’s project called on people to slow down and rethink their lifestyles, while education programs offered opportunities for kids to experience science and technologies to better set their career goals. The communication approaches from the videos of E1 highlighted ecological rural lives and new models of work.
During some of the projects of social enterprises, new infrastructures were established. The educational program came along with a mobile station for technology experience, which could be taken further to various places. E1’s video helped another coworking space to establish and operate. The renovated exhibition hall in the school also remained an asset for the local community, being available for future activities.
Through the development of the creative social enterprises supported by the CWS, there are more artists in the region, as observed by E2 referring to the creative atmosphere in the local community. Additionally, more funds are going into the local community, the European Capital of Culture program, for instance, which is the hotbed for new projects. New initiatives are already flourishing, e.g., the replication of E2’s art project and the education authority’s wish to reproduce the “Robots” program.
The innovative approaches of the rural CWS fostered social enterprises, in terms of both their stable operation and further project development and, through the social enterprises’ actions, generated a wide range of social impact on the local community.
6. Conclusions
Our example shows how the innovative approaches of a rural CWS, comprising its broker roles with a cooperative structure, generate impacts on the social EE and the local community through the social enterprises engaged in creative industries in rural areas. The entrepreneurship processes these enterprises undergo are largely dependent on the resource networks of the social EE in which they are embedded. Therein, the rural CWS acts as a broker of resource networks that brings entrepreneurial resources to the single enterprise and to the larger entrepreneurial ecosystem and, while doing so, facilitates the unfolding and establishment of social entrepreneurship in the area. The broker CWS links, holds, reorganizes, and reproduces entrepreneurial resources, as brokerage actions, in which the broker roles of liaisons, gatekeepers, coordinators, and representatives connect various local networks, bridge translocal networks, and integrate new available networks to the integral entrepreneurial ecosystem.
With the emergence of the broker CWS, the social EE undergoes a transformation from scattered resources to major resources brokered by the CWS. The interactions of the resources in the social EE change from loose to tight connections. Additionally, there is also a gradual change brought by daily activities of social enterprises as the coevolution progresses.
Through the insights of the two social enterprises engaged in creative industries that have been analyzed in this paper, the entrepreneurial functions of the rural broker CWS are revealed under the social EE. As an integral part of the EE, the CWS changes the configuration of resources, which expands the opportunities and borders of social entrepreneurship. The non-physical connection among individuals and enterprises in the ecosystem of a rural CWS is characterized by a strong interpersonal bond and an increased awareness and social responsibility towards the place in which the CWS and the creative social enterprises are embedded. The key persons and organizational structure of a cooperative of the CWS are vital in its broker functions and underpin the EE’s transformation into a more vibrant, stable support for rural creative social enterprises, especially for small businesses. By knowing this, further local strategies of the CWS and policy backup can be proposed, which are based on a more informed understanding of social EEs in rural regions. Examples of such recommendations are the following: the CWS should rearrange and utilize the internal resources among members; the CWS should set up resource networks by its reputation and visibility; the CWS should actively link the government and authorities to hold administrative resources for the possible use of enterprises. If these circumstances are provided, the CWS can operate spontaneously as a kind of spin-off for short-term implementation while also following its own long-term goals as a broker within and for the local and translocal creative and social entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Although we analyzed the entrepreneurial process of the two social enterprises in detail and compared them against the CWS manager’s information, some parts of the picture may be missing due to the fact that the data relied on retrospective descriptions. Ongoing follow-up surveys, such as entrepreneurs’ start-up diaries or regular return visits, could help to obtain more thorough information. In addition, more cases of social enterprises in creative industries, as well as of different CWS structures in rural regions, would provide further insights into social EEs and broker CWSs. As a last remark, it appears from our empirical evidence that the four functions are non-exclusive; the CWS can act at the same time as a liaison, as a gatekeeper, as a coordinator, and as a representative by alternately or contemporarily linking, holding, and reorganizing the resources and reproducing processes that are either established over time so to respond to recurring demands or set up ad hoc to respond to emerging needs in the ecosystem. Whether the four broker functions are generally non-exclusive, and to what extent or under which circumstances, has not been further investigated in this contribution and, thus, presents a limitation. Finally, another limitation that, at the same time, offers a potential research outlook is the ongoing discussion about urban and rural distinctions and their impact on the CWS and its broker roles for creative and social EEs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.G. and E.P.; Methodology, C.G. and E.P.; Software, C.G.; Validation, C.G. and E.P.; Formal Analysis, C.G. and E.P.; Investigation, C.G. and E.P.; Resources, C.G. and E.P.; Data Curation, C.G.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, C.G. and E.P.; Writing –Review & Editing, C.G. and E.P.; Visualization, C.G.; Supervision, C.G. and E.P.; Project Administration, C.G. and E.P.; Funding Acquisition, C.G. and E.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This paper has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 955907, project CORAL (Exploring the impacts of collaborative workspaces in rural and peripheral areas in the EU).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study is approved by the Ethics Committee of Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin on 6 October 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data include personal information and thus cannot be publicly available.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Galloway, L. Can broadband access rescue the rural economy? J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2007, 14, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, H.; Carson, D.; Carson, D.; Newman, L.; Garrett, J. Using Internet technologies in rural communities to access services: The views of older people and service providers. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 54, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.; Teasdale, S. Unlocking the potential of rural social enterprise. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 70, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defourny, J.; Nyssens, M. Social enterprise in Europe: Recent trends and developments. Soc. Enterp. J. 2008, 4, 202–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosworth, G. Characterising rural businesses—Tales from the paperman. J. Rural Stud. 2012, 28, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saffu, K.; Walker, J. The Country-of-Origin Effect and Consumer Attitudes to “Buy Local” Campaign: The Ghanaian Case. J. Afr. Bus. 2006, 7, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.; Evans, R.; Fetzer, E.; Higgings, A.; Lähdesmäki, M.; Linno, K.; Matilainen, A.; Păunescu, C.; Rinne-Koski, K.; Staicu, D.; et al. The Rural Social Enterprise Guidebook of Good Practice: Experience from Estonia, Finland, Germany, Romania and Scotland; University of Helsinki, Ruralia Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Vincze, M.; Birkhölzer, K.; Kaepplinger, S.; Gollan, A.K.; Richter, A. A Map of Social Enterprises and Their Ecosystems in Europe; Country Report for Germany; Europäische Kommission: Brüssel, Belgium, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kreativwirtschaft Austria. Preparations of SME Research Austria for the 7th Austrian Creative Industries Report 2017. 2016. Available online: https://www.kreativwirtschaft.at/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/7KWB-barrierefrei.pdf (accessed on 28 May 2024).
- Parkman, I.D.; Holloway, S.S.; Sebastiao, H. Creative Industries: Aligning Entrepreneurial Orientation and Innovation Capacity. J. Res. Mark. Entrep. 2012, 14, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubareva, I.; Benghozi, P.J.; Fidele, T. Online Business Models in Creative Industries: Diversity and Structure. Int. Stud. Manag. Organ. 2014, 44, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grantham, A.; Kaplinsky, R. Getting the Measure of the Electronic Games Industry: Development and the Management of Innovation. Int. J. Innov. Manag. 2005, 9, 183–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, E.; De Jong, J.P.; Marlet, G. Creative Industries in the Netherlands: Structure, Development, Innovativeness and Effects on Urban Growth. Geogr. Ann. B Hum. 2008, 90, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañer, X.; Campos, L. Determinants of Artistic Innovation: Bringing in the Role of Organizations. J. Cult. Econ. 2002, 26, 29–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handke, C. Promises and Challenges in Innovation Surveys of the Media Industries. In Management and Innovation in the Media Industry; van Kranenburg, H., Dal Zotto, C., Eds.; Edward Elgar: Cheltenham, UK, 2007; pp. 123–152. [Google Scholar]
- Innocenti, N.; Lazzeretti, L. Do the creative industries support growth and innovation in the wider economy? Industry relatedness and employment growth in Italy. Ind. Innov. 2019, 26, 1152–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, P.; Schwartz, D. (Eds.) Creative Regions: Technology, Culture and Knowledge Entrepreneurship; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Cooke, P.N.; Lazzeretti, L. (Eds.) Creative Cities, Cultural Clusters and Local Economic Development; Edward Elgar Publishing: Cheltenham, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Florida, R. Cities and the Creative Class; Routledge: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sacco, P.L. Culture as an Engine of Local Development Processes: System-wide Cultural Districts. J. Arts Manag. Law Soc. 2009, 39, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, G. Designing creative places: The role of creative tourism. Ann. Tour. Res. 2020, 85, 102922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazana, V.; Kazaklis, A. Exploring quality of life concerns in the context of sustainable rural development at the local level: A Greek case study. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2009, 9, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Townsend, L.; Wallace, C.; Fairhurst, G.; Anderson, A. Broadband and the creative industries in rural Scotland. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 54, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barraket, J.; Eversole, R.; Luke, B.; Barth, S. Resourcefulness of locally-oriented social enterprises: Implications for rural community development. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 70, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, A.M.; Robinson, J.A.; Shapira, Z. Serving rural low-income markets through a social entrepreneurship approach: Venture creation and growth. Strateg. Entrep. J. 2022, 16, 826–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouncken, R.B.; Laudien, S.M.; Fredrich, V.; Görmar, L. Coopetition in coworking-spaces: Value creation and appropriation tensions in an entrepreneurial space. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2018, 12, 385–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surman, T. Building Social Entrepreneurship through the Power of Coworking. Innov. Technol. Gov. Glob. 2013, 8, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, M.; Lyon-Hill, S.; Tate, S. It takes all kinds: Understanding diverse entrepreneurial ecosystems. J. Enterprising Communities People Places Glob. Econ. 2018, 12, 178–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauger, F.; Pfnür, A.; Strych, J.-O. Coworking spaces and Start-ups: Empirical evidence from a product market competition and life cycle perspective. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 132, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loots, E.; Neiva, M.; Carvalho, L.; Lavanga, M. The entrepreneurial ecosystem of cultural and creative industries in Porto: A sub-ecosystem approach. Growth Chang. 2021, 52, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinuzzi, C. Working alone together: Coworking as Emergent Collaborative Activity. J. Bus. Tech. Commun. 2012, 26, 399–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters-Lynch, J.; Potts, J.; Butcher, T.; Dodson, J.; Hurley, J. Coworking: A Transdisciplinary Overview. Available at SSRN 2712217. 2016. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2712217 (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Boari, C.; Riboldazzi, F. How knowledge brokers emerge and evolve: The role of actors’ behaviour. Res. Policy 2014, 43, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, R.M.; Gould, R.V. A Dilemma of State Power: Brokerage and Influence in the National Health Policy Domain. Am. J. Sociol. 1994, 99, 1455–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, K.; Bosma, N.; Sanders, M.; Schramm, M. Searching for the existence of entrepreneurial ecosystems: A regional cross-section growth regression approach. Small Bus. Econ. 2017, 49, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, B. Sustainable valley entrepreneurial ecosystems. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2006, 15, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.; Brown, R. Entrepreneurial ecosystems and growth oriented entrepreneurship. Final Rep. OECD Paris 2014, 30, 77–102. [Google Scholar]
- Spigel, B. The Relational Organization of Entrepreneurial Ecosystems. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2017, 41, 49–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebart, A.; Ibert, O. Beyond territorial conceptions of entrepreneurial ecosystems: The dynamic spatiality of knowledge brokering in seed accelerators. Z. Wirtschgeogr. 2019, 63, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, E.; Stevenson, T. The catalysts of small town economic development in a free market economy: A case study of New Zealand. Local Econ. 2014, 29, 486–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombelli, A.; Krafft, J.; Vivarelli, M. To be born is not enough: The key role of innovative start-ups. Small Bus. Econ. 2016, 47, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenberg, D.J. The entrepreneurship ecosystem strategy as a new paradigm for economic policy: Principles for cultivating entrepreneurship. In Proceedings of the Institute of International and European Affairs, Dublin, Ireland, 12 May 2011; Volume 1, pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Doherty, B.; Haugh, H.; Lyon, F. Social enterprises as hybrid organizations: A review and research agenda. Int. J. Manag. Rev. 2014, 16, 417–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huggins, R. The success and failure of policy-implanted inter-firm network initiatives: Motivations, processes and structure. Entrep. Reg. Dev. 2000, 12, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, C. A framework for the governance of social enterprise. Int. J. Soc. Econ. 2006, 33, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, P.T. Social entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial ecosystems: Complementary or disjoint phenomena? Int. J. Soc. Econ. 2017, 44, 1252–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peredo, A.M.; McLean, M. Social entrepreneurship: A critical review of the concept. J. World Bus. 2006, 41, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin, A.; Roy, M.J.; Grant, S.; Lewis, K.V. Advancing a Contextualized, Community-Centric Understanding of Social Entrepreneurial Ecosystems. Bus. Soc. 2023, 62, 1069–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, P.T.; Lyons, T.S. Where are the entrepreneurs? A call to theorize the micro-foundations and strategic organization of entrepreneurial ecosystems. Strateg. Organ. 2023, 21, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzaga, C.; Galera, G.; Franchini, B.; Chiomento, S.; Nogales, R.; Carini, C. Social Enterprises and Their Ecosystems in Europe; Comparative Synthesis Report; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020; Available online: https://www.bollettinoadapt.it/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/KE0220042ENN.en_.pdf (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Roundy, P.T.; Lyons, T.S. Humility in social entrepreneurs and its implications for social impact entrepreneurial ecosystems. J. Bus. Ventur. Insights 2022, 17, e00296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, T.A.; Purdy, J.M.; Ventresca, M.J. How entrepreneurial ecosystems take form: Evidence from social impact initiatives in Seattle. Strateg. Entrep. J. 2018, 12, 96–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukier, D.; Kon, F.; Lyons, T.S. Software Startup Ecosystems Evolution: The New York City Case Study. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation/IEEE International Technology Management Conference (ICE/ITMC), Trondheim, Norway, 13–15 June 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, K. Is your entrepreneurial ecosystem scaling? An approach to inventorying and measuring a region’s innovation momentum. Innov. Technol. Gov. Glob. 2016, 11, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S. In the making: Open Creative Labs as an emerging topic in economic geography? Geogr. Comp. 2019, 13, e12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, B.; Bürkner, H.-J. Open workshops as sites of innovative socio-economic practices: Approaching urban post-growth by assemblage theory. Local Environ. 2018, 23, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R. Role of proximity in interaction and performance: Conceptual and empirical challenges. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Steyaert, C. The politics of narrating social entrepreneurship. J. Enterprising Communities People Places Glob. Econ. 2010, 4, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, A.W.; Dacin, P.A.; Dacin, M.T. Collective Social Entrepreneurship: Collaboratively Shaping Social Good. J. Bus. Ethics 2012, 111, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, P.T.; Bonnal, M. The Singularity of Social Entrepreneurship: Untangling its Uniqueness and Market Function. J. Entrep. 2017, 26, 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, C.; Lounsbury, M.; Greenwood, R. Introduction: Community as an Institutional Order and a Type of Organizing. In Communities and Organizations; Marquis, C., Lounsbury, M., Greenwood, R., Eds.; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2011; Volume 33, pp. ix–xxvii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, P.H.; Ocasio, W.; Lounsbury, M. The Institutional Logics Perspective: A New Approach to Culture, Structure and Process; OUP: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Avdikos, V.; Pettas, D. The new topologies of collaborative workspace assemblages between the market and the commons. Geoforum 2021, 121, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Mason, C. Looking inside the spiky bits: A critical review and conceptualisation of entrepreneurial ecosystems. Small Bus. Econ. 2017, 49, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbasari, R.; Wijaya, C.; Rahayu, N. Most Roles Actors Play in Entrepreneurial Ecosystem: A Network Theory Perspective. J. Entrep. Educ. 2020, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, B.; Schmidt, S. Entrepreneurial ecosystems as a bridging concept? A conceptual contribution to the debate on entrepreneurship and regional development. Growth Change 2021, 52, 790–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednář, P.; Danko, L.; Smékalová, L. Coworking spaces and creative communities: Making resilient coworking spaces through knowledge sharing and collective learning. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2023, 31, 490–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.; Ressia, S. Neither office nor home: Coworking as an emerging workplace choice. Employ. Relat. Rec. 2015, 15, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gandini, A.; Cossu, A. The third wave of coworking: ‘Neo-corporate’ model versus ‘resilient’ practice. Eur. J. Cult. Stud. 2019, 14, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.; Brinks, V.; Brinkhoff, S. Innovation and creativity labs in Berlin. Z. Wirtschgeogr. 2014, 58, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebart, A. Open creative labs as functional infrastructure for entrepreneurial ecosystems: Using sequence analysis to explore tempo-spatial trajectories of startups in Berlin. Res. Policy 2022, 51, 104444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orel, M.; Mayerhoffer, M.; Fratricova, J.; Pilkova, A.; Starnawska, M.; Horvath, D. Coworking spaces as talent hubs: The imperative for community building in the changing context of new work. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2022, 16, 1503–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnossen, B.; Bencherki, N. The role of space in the emergence and endurance of organizing: How independent workers and material assemblages constitute organizations. Hum. Relat. 2019, 72, 1057–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Prentice, C.; Wallis, J.; Patel, A.; Waxin, M.-F. An integrative study of the implications of the rise of coworking spaces in smart cities. Entrep. Sustain. Issues 2020, 8, 467–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasov, M.; Bonnedahl, K.J.; Vincze, Z. Entrepreneurship for resilience: Embeddedness in place and in trans-local grassroots networks. J. Enterprising Communities People Places Glob. Econ. 2018, 12, 374–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motoyama, Y.; Knowlton, K. Examining the connections within the startup ecosystem: A case study of St. Louis. Entrep. Res. J. 2017, 7, 20160011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdikos, V.; Iliopoulou, E. Community-Led Coworking Spaces: From Co-location to Collaboration and Collectivization. In Creative Hubs in Question: Place, Space and Work in the Creative Economy; Gill, R., Pratt, A.C., Virani, T.E., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bednář, P.; Danko, L. Coworking Spaces as a Driver of the Post-Fordist City: A Tool for Building a Creative Ecosystem. Eur. Spat. Res. Policy 2020, 27, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barley, S.R. Technicians in the workplace: Ethnographic evidence for bringing workinto organizational studies. Adm. Sci. Q. 1996, 41, 404–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.; Mingo, S.; Chen, D. Collaborative brokerage, generative creativity, and creative success. Adm. Sci. Q. 2007, 52, 443–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S.; Soda, G. Network Capabilities: Brokerage as a Bridge Between Network Theory and the Resource-Based View of the Firm. J. Manag. 2021, 47, 1698–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. The Network Structure of Social Capital. Res. Organ. Behav. 2000, 22, 345–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. Structural Holes and Good Ideas. Am. J. Sociol. 2004, 110, 349–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Tsui, A.S. When brokers may not work: The cultural contingency of social capital in Chinese high-tech firms. Adm. Sci. Q. 2007, 52, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obstfeld, D. Social Networks, the Tertius Iungens Orientation, and Involvement in Innovation. Adm. Sci. Q. 2005, 50, 100–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.; Nelson, R.E. Creating Something from Nothing: Resource Construction through Entrepreneurial Bricolage. Adm. Sci. Q. 2005, 50, 329–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. Structural Holes: The Social Structure of Competition; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, S.-W.; Rondi, E.; Levin, D.Z.; De Massis, A.; Brass, D.J. Network Brokerage: An Integrative Review and Future Research Agenda. J. Manag. 2020, 46, 1092–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, R.S. Brokerage and Closure: An Introduction to Social Capital; OUP: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, A.J.; Ferreira, J.J. Entrepreneurial ecosystems and networks: A literature review and research agenda. Rev. Manag. Sci. 2022, 16, 189–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombelli, A.; Paolucci, E.; Ughetto, E. Hierarchical and relational governance and the life cycle of entrepreneurial ecosystems. Small Bus. Econ. 2019, 52, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.K. Case Study Research; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Azungah, T. Qualitative research: Deductive and inductive approaches to data analysis. Qual. Res. J. 2018, 18, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mik-Meyer, N. Multimethod qualitative research. In Qualitative Research; Silverman, D., Ed.; SAGE: London, UK, 2020; pp. 357–374. [Google Scholar]
- Ibert, O.; Müller, F.C. Network dynamics in constellations of cultural differences: Relational distance in innovation processes in legal services and biotechnology. Res. Policy 2015, 44, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, M. Qualitative content analysis in practice. In Qualitative Content Analysis in Practice; Schreier, M., Ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 1–280. [Google Scholar]
- DeLanda, M. Deleuzian social ontology and assemblage theory. In Deleuze and the Social; Fuglsang, M., Ed.; Edinburgh University Press: Edinburgh, UK, 2006; pp. 250–266. [Google Scholar]
- DeLanda, M. A New Philosophy of Society: Assemblage Theory and Social Complexity; Bloomsbury Publishing: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Karaman, O. Book Review, Manuel DeLanda, A New Philosophy of Society: Assemblage Theory and Social Complexity. Antipode 2008, 40, 935–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).