Studies on the β → α Phase Transition Kinetics of Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V Alloy under Isothermal Conditions by X-ray Diffraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Composition of the Samples after Solution Treatment
3.2. Phase Compositions and Microstructures of the Samples after Aging Treatment
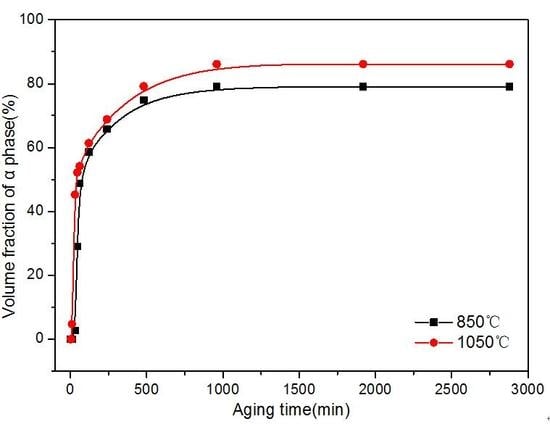
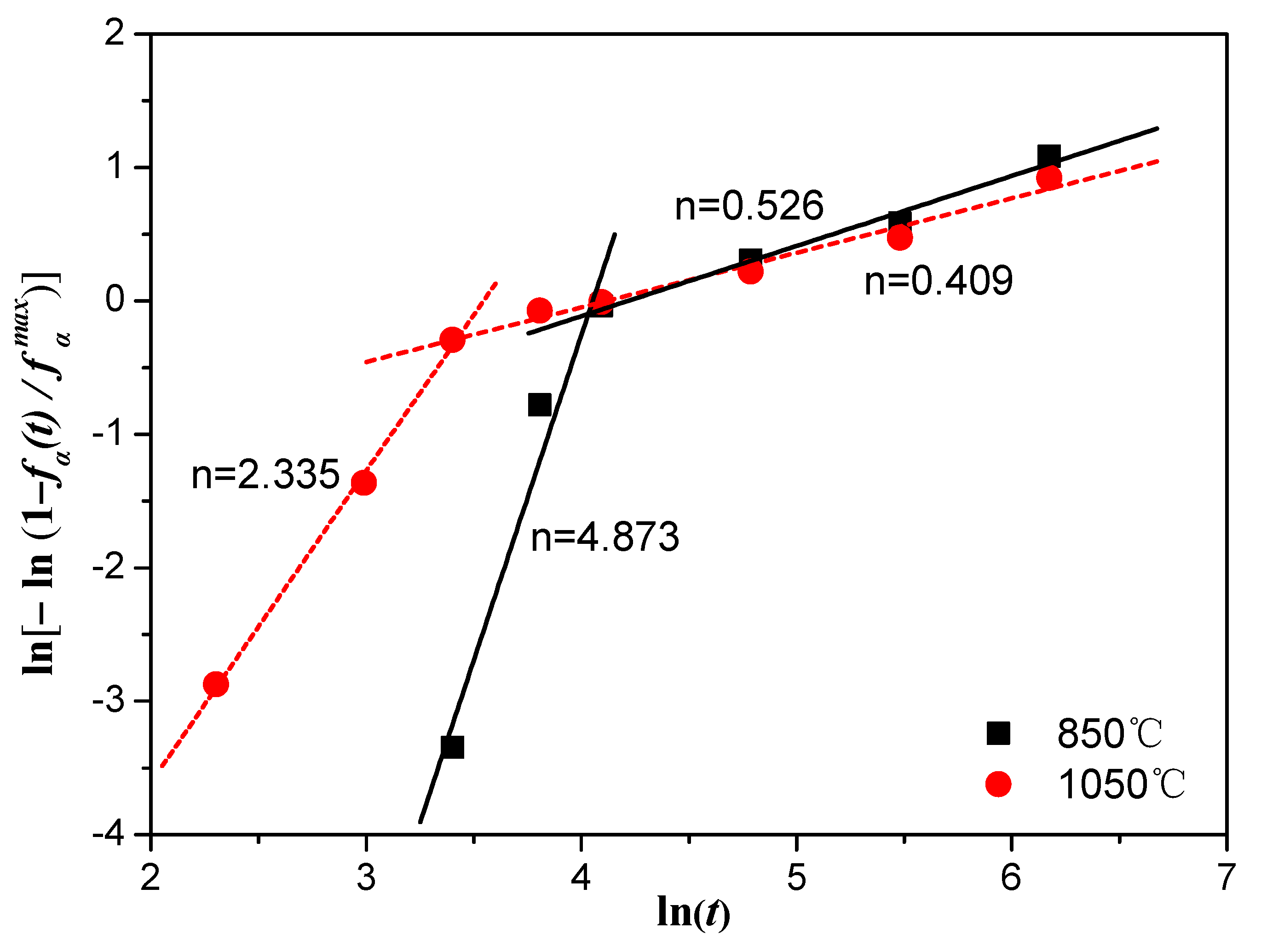
3.3. Kinetics of β → α Phase Transition
3.4. Age-Hardening Behavior
4. Conclusions
- In the early stage, the isothermally-aged α phase precipitated at the initial β grain boundaries. The value of the α precipitate fraction increased sharply at first and then increased slowly with increasing aging time, finally reaching equilibrium. The value of the α precipitate fraction was higher in the alloy aged for the same time at a higher solution temperature, while the size of the α precipitate was smaller in the alloy at a higher solution temperature.
- The isothermal β → α phase transition kinetics under isothermal-aging treatments were modeled in the theoretical framework of the JMAK theory. The kinetic parameters of JMAK deduced different transformation mechanisms in the process of the transition. The mechanism of the first-stage phase transition was dominated by mixed transformation mechanisms (homogeneously nucleated and acicular-grown α structure, and grain boundary-nucleated and grown α precipitate), while the second stage involved the growth of fine α precipitates controlled by slow diffusion. The Avrami index () was higher for Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V alloy at a lower solution temperature, while the reaction rate constant () showed the opposite. A very good correspondence between calculated and experimentally measured values was found.
- As the aging time was prolonged, the hardness of the Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V alloy increased sharply. After the hardness of the alloy reached a plateau, it began to decline. The hardness of the alloy was always higher at a higher solution temperature.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivasishin, O.M.; Markovsky, P.E.; Semiatin, S.L.; Ward, C.H. Aging response of coarse- and fine-grained β titanium alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2005, 405, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahoma, H.K.S.; Chen, Y.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Xiao, S.L. Influence of (TiC + TiB) on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-B20 matrix alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 627, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zhou, L. Influence of solution conditions on aging response of a new metastable beta titanium alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2006, 35, 707–710. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.W.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhang, F.S.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J.S. Effect of ω-assisted precipitation on β → α transformation and tensile properties of Ti–15Mo–2.7Nb–3Al–0.2Si alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 654, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Du, Z.X.; Xiao, S.L.; Xu, L.J.; Tian, J. Effect of aging heat treatment on microstructure and tensile properties of a new β high strength titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, L. Aging characteristics of new metastable beta titanium alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. 2007, 17, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, P. Influence of solution conditions on aging response of Ti-3.5Al-5Mo-4V-2Cr-1Fe-2Zr-2Sn titanium alloy. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 146, 1815–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Li, T.; Casillas, G.; Cairney, J.M.; Wexler, D.; Pereloma, E.V. The evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–2Cr–1Fe during ageing. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 629, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.P.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zeng, W.D. Phase transformation kinetics of Ti-1300 alloy during continuous heating. Rare Met. 2015, 34, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, I.; Semiatin, S.L. Thermomechanical processing of beta titanium alloys—An overview. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1998, 243, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.; El-Chaikh, A.; Christ, H.J. Effect of duplex aging on the initiation and propagation of fatigue cracks in the solute-rich metastable β titanium alloy Ti 38-644. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2011, 42, 2652–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Mi, X.J.; Ye, W.J.; Hui, S.X.; Yu, Y.; Wang, W.Q. A study on the microstructures and tensile properties of new beta high strength titanium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 550, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Mi, X.J.; Ye, W.J.; Hui, S.X.; Lee, D.C.; Lee, Y.T. Influence of heat treatment on microstructure and tensile property of a new high strength beta alloy Ti–2Al–9.2Mo–2Fe. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan-Manshadi, A.; Dippenaar, R.J. Development of α-phase morphologies during low temperature isothermal heat treatment of a Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–3Cr alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 1833–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinov, S.; Markovsky, P.; Sha, W. Resistivity study and computer modelling of the isothermal transformation kinetics of Ti–8Al–1Mo–1V alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 333, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinov, S.; Markovsky, P.; Sha, W.; Guo, Z. Resistivity study and computer modelling of the isothermal transformation kinetics of Ti–6Al–4V and Ti–6Al–2Sn–4Zr–2Mo–0.08Si alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 314, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneseaux, F.; Aeby-Gautier, E.; Geandier, G.; Da Costa Teixeira, J.; Appolaire, B.; Weisbecker, P.; Mauro, A. In situ characterizations of phase transformations kinetics in the Ti17 titanium alloy by electrical resistivity and high temperature synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 476, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelier, C.; Bein, S.; Béchet, J. Building a continuous cooling transformation diagram of β-CEZ alloy by metallography and electrical resistivity measurements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1997, 28, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kherrouba, N.; Bouabdallah, M.; Badji, R.; Carron, D.; Amir, M. Beta to alpha transformation kinetics and microstructure of Ti-6Al-4V alloy during continuous cooling. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 181, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriobero-Vila, P.; Requena, G.; Warchomicka, F.; Stark, A.; Schell, N.; Buslaps, T. Phase transformation kinetics during continuous heating of a β-quenched Ti–10V–2Fe–3Al alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 1412–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.K.; Murdock, D.C.; Mataya, M.C.; Speer, J.G.; Matlock, D.K. Quantitative measurement of deformation-induced martensite in 304 stainless steel by X-ray diffraction. Scr. Mater. 2004, 50, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sha, W. Quantification of precipitate fraction in maraging steels by X-ray diffraction analysis. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2004, 20, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Mythili, R.; Raju, S.; Saroja, S. Effect of cooling rate on mechanism of β → α phase transformation on continuous cooling in Ti–5Ta–1.8Nb alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveen, M.; Santhosh, R.; Geetha, M.; Rao, M.N. Experimental study and computer modelling of the β → α+β phase transformation in Ti15-3 alloy under isothermal conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 616, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appolaire, B.; Héricher, L.; Aeby-Gautier, E. Modelling of phase transformation kinetics in Ti alloys–isothermal treatments. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 3001–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Settefrati, A.; Aeby-Gautier, E.; Appolaire, B.; Dehmas, M.; Geandier, G.; Khelifati, G. Low temperature transformations in β-metastable Ti 5553 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2013, 738–739, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, M.; Raju, S.; Mythili, R.; Saroja, S. Study of kinetics of α⇔β phase transformation in Ti–4.4 mass% Ta–1.9 mass% Nb alloy using differential scanning calorimetry. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, J. The Kinetics of Phase Transformation in Metals, 1st ed.; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1965; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Blázquez, J.S.; Conde, C.F.; Conde, A. Non-isothermal app;roach to isokinetic crystallization processes: Application to the nanocrystallization of HITPERM alloys. Acta Mater. 2005, 53, 2305–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Eckert, J.; Schultz, L.; Sordelet, D.J. Studies on the crystallization kinetics of Cu-reinforced partially crystalline Cu47Ti33Zr11Ni8Si1 metallic glass composite. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 434–435, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kou, H.C.; Gu, X.F.; Li, J.S.; Xing, L.Q.; Hu, R.; Zhou, L. On discussion of the applicability of local Avrami exponent: Errors and solutions. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1153–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.L.; Shen, J.; Sun, J.F.; Wang, G.; Xing, D.W.; Xian, H.Z.; Zhou, B.D. Crystallization behavior of ZrAlNiCu bulk metallic glass with wide supercooled liquid region. Mater. Lett. 2003, 57, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinov, S.; Sha, W.; Markovsky, P. Experimental study and computer modelling of the β ⇒ α + β phase transformation in β21s alloy at isothermal conditions. J. Alloys Compd. 2003, 348, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lütjering, G.; Williams, J.C. Titanium, 2nd ed.; Springer, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 288–289. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.S.; Yang, J.T.; Lai, Y.J.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J.S.; Zhou, L. Microstructural evolution and precipitation mechanism of α-phase in Ti-55531 alloy aged at high temperature. Mater. Sci. Forum. 2013, 747, 912–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.W.; Kou, H.C.; Li, J.S.; Zhang, F.S.; Feng, Y. Effect of phase transformation conditions on the microstructure and tensile properties of Ti-3Al-15Mo-3Nb-0.2Si alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2015, 24, 3018–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prima, F.; Vermaut, P.; Gloriant TDebuigne, J.; Ansel, D. Experimental evidence of elastic interaction between ω nanoparticles embedded in a metastable β titanium alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 2002, 21, 1935–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. I General Theory. J. Chem. Phys. 1939, 7, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Kinetics of phase change. II Transformation-Time relations for random distribution of nuclei. J. Chem. Phys. 1940, 8, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avrami, M. Granulation, phase change, and microstructure kinetics of phase change. III. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G. General equation of the kinetics of phase transformation with nucleation and growth mechanism. Phil. Mag. Lett. 1997, 75, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Malinov, S. Titanium Alloys: Modelling of Microstructure, Properties and Applications; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; pp. 125–140. [Google Scholar]
- Margolin, H.; Farrar, P. The physical metallurgy of titanium alloys. Ocean. Eng. 1969, 1, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, D.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Dargusch, M.S. Influence of ageing temperature and heating rate on the properties and microstructure of β Ti alloy, Ti–6Cr–5Mo–5V–4Al. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 531, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.B.; Tian, C.; Liu, W.C.; Xiang, S.; Zhao, F.; Liang, Y.L. Effect of rolling temperature on the microstructure and tensile properties of 47Zr–45Ti–5Al–3V alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2018, 27, 1803–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Mi, X.J.; Ye, W.J.; Hui, S.X.; Lee, D.G.; Lee, Y.T. Microstructural evolution and age hardening behavior of a new metastable beta Ti–2Al–9.2Mo–2Fe alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 645, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| Element | Al | Mo | V | Cr | Sn | Zr | Fe | C | N | O | H | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass percent/% | 3.62 | 4.83 | 3.86 | 2.09 | 1.98 | 2.02 | 1.01 | 0.032 | 0.019 | 0.007 | 0.002 | Bal. |
| Diffraction Peak | α(100) | α(002) | α(101) | α(102) | α(110) | α(103) | α(112) | α(201) | β(110) | β(200) | β(211) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | ||||||||||||
| Vi | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.15 | 35.39 | 35.39 | 35.39 | |
| 317.12 | 1194.95 | 866.33 | 226.39 | 780.50 | 521.27 | 650.01 | 160.96 | 1170.97 | 847.86 | 703.35 | ||
| 6 | 2 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 6 | 24 | ||
| 19.13 | 15.80 | 14.19 | 7.62 | 5.12 | 3.94 | 3.50 | 3.40 | 14.88 | 6.43 | 4.05 | ||
| 0.96 | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.91 | 0.87 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.82 | 0.95 | 0.89 | 0.85 | ||
| 28.15 | 28.97 | 112.56 | 15.18 | 16.94 | 16.81 | 18.29 | 4.37 | 157.77 | 23.33 | 46.19 | ||
| Solution Treatment Temperature, °C | n | k | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| 850 | 4.87286 ± 0.03922 | 2.65243 × 10−9 | 0.97801 |
| 0.52571 ± 0.04553 | 0.108961573 | 0.99258 | |
| 1050 | 2.33497 ± 0.07564 | 0.000254088 | 0.99894 |
| 0.40872 ± 0.02978 | 0.185691237 | 0.98955 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, P.; Xiang, S.; Tan, Y.; Ji, X. Studies on the β → α Phase Transition Kinetics of Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V Alloy under Isothermal Conditions by X-ray Diffraction. Metals 2020, 10, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010090
Ge P, Xiang S, Tan Y, Ji X. Studies on the β → α Phase Transition Kinetics of Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V Alloy under Isothermal Conditions by X-ray Diffraction. Metals. 2020; 10(1):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010090
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Panpan, Song Xiang, Yuanbiao Tan, and Xuanming Ji. 2020. "Studies on the β → α Phase Transition Kinetics of Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V Alloy under Isothermal Conditions by X-ray Diffraction" Metals 10, no. 1: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010090
APA StyleGe, P., Xiang, S., Tan, Y., & Ji, X. (2020). Studies on the β → α Phase Transition Kinetics of Ti–3.5Al–5Mo–4V Alloy under Isothermal Conditions by X-ray Diffraction. Metals, 10(1), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10010090