Non-Fourier Estimate of Electron Temperature in Case of Femtosecond Laser Pulses Interaction with Metals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model
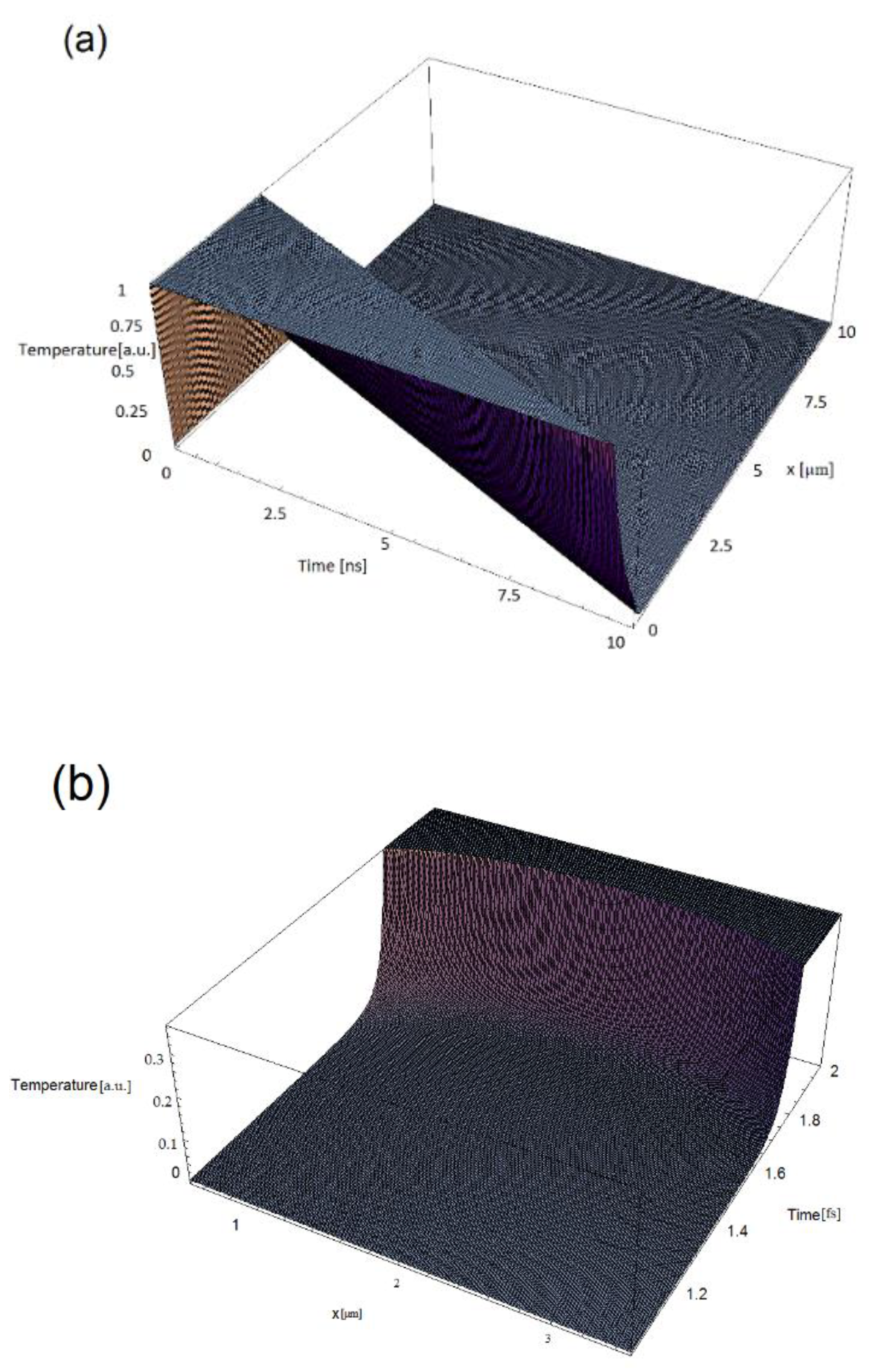
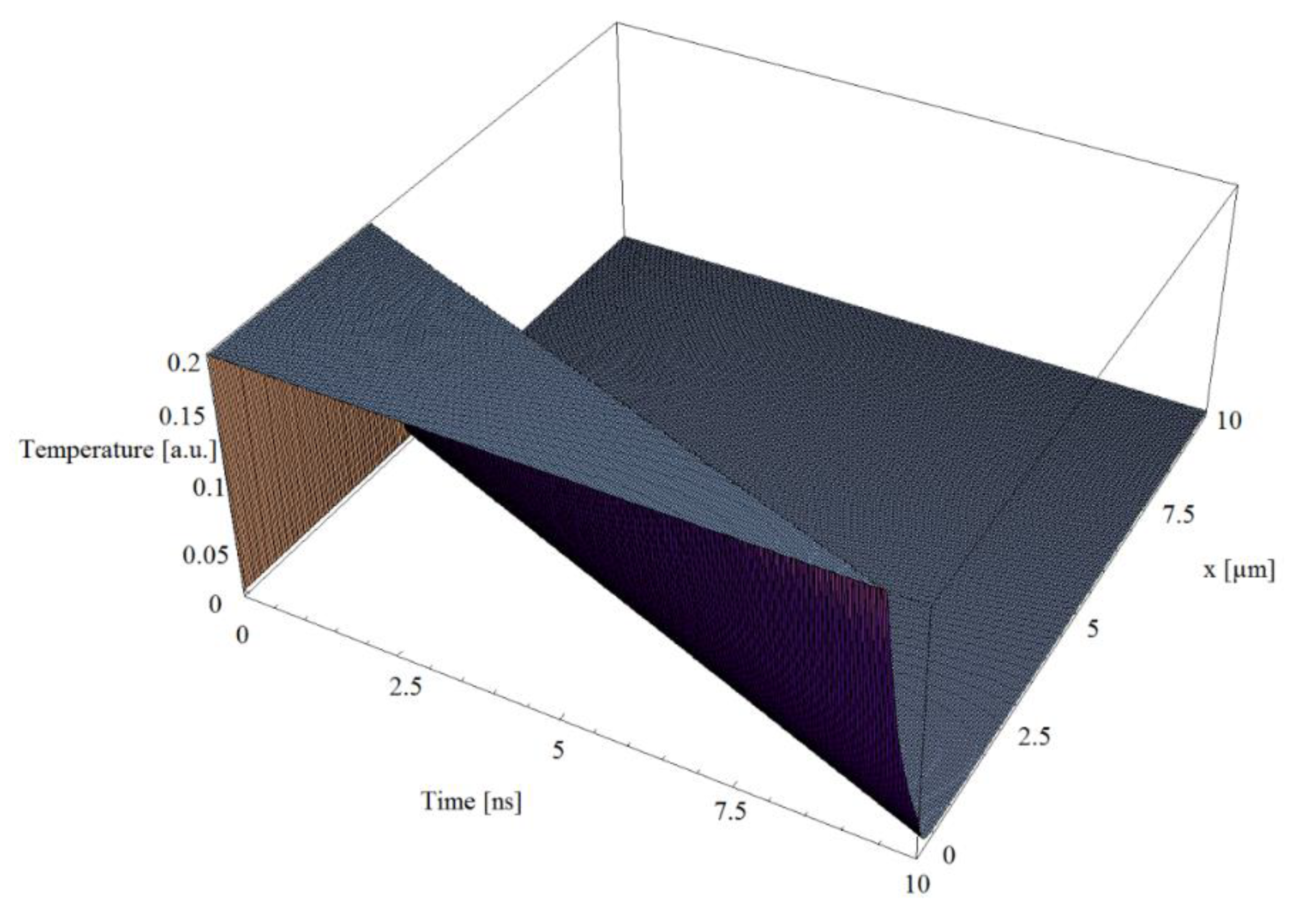
3. Simulations
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The computation time for the current model (using core i7 8th generation, 16.0 GB RAM) is equivalent to 1.5 min. This is much less than the numerical modeling of heat transfer in laser–metal interaction.
- (2)
- The lower the g/K factor, the higher the electron temperature. A lower g/K factor implies a reduced heat transfer from electrons to the lattice.
- (3)
- The lower the relaxation time, the lower the electron temperature. A lower relaxation time means a higher value of thermal speed () and a quick heat transfer between the electrons and the lattice.
- (4)
- Last, but not least, this model is based on the solution given by heat operators and therefore, is highly performing. On the other hand, it can be easily used by the researcher as the laser–metal interaction is treated in a classical way.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dyukin, R.V.; Martsinovskiy, G.A.; Sergaeva, O.N.; Shandybina, G.D.; Svirina, V.V.; Yakovlev, E.B. Interaction of femtosecond laser pulses with solids: Electron/phonon/plasmon dynamics. In Laser Pulses-Theory, Technology, and Applications; Peshko, I., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, T.; Teitelbaum, S.; Wolfson, J.; Kandyla, M.; Nelson, K.A. Extended two-temperature model for ultrafast thermal response of band gap materials upon impulsive optical excitation. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 143, 194705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Tsai, H.-L. Improved two-temperature model and its application in ultrashort laser heating of metal films. J. Heat Trans. 2005, 127, 1167–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihăilescu, I.N.; Oane, M.; Ticoş, C.M.; Ristoscu, C.; Bădiceanu, M. Linear Fourier Model Predictions in Case of Solids under IR FS Laser Irradiation. J. Las. Opt. Photonics 2019, 6, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, S.I.; Kapeliovich, B.L.; Perel’man, T.L. Electron emission from metal surfaces exposed to ultrashort laser pulses. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1974, 66, 776–781. [Google Scholar]
- Zhukovsky, K. Operational Approach and Solutions of Hyperbolic Heat Conduction Equations. Axioms 2016, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovsky, K. Operational solution for some types of second order differential equations and for relevant physical problems. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 2017, 446, 628–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovsky, K. Operational solution of differential equations with derivatives of non-integer order, Black-Scholes type and heat conduction. Mosc. Univ. Phys. Bull. 2016, 71, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukovsky, K.; Oskolkov, D.; Gubina, N. Some Exact Solutions to Non-Fourier Heat Equations with Substantial Derivative. Axioms 2018, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokhorov, A.M.; Konov, V.I.; Ursu, I.; Mihailescu, I.N. Laser Heating of Metals; Institute of Physics Publishing: London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Lorin, E.; Chelkowski, S.; Bandrauk, A. A numerical Maxwell–Schrödinger model for intense laser–matter interaction and propagation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2007, 177, 908–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hu, M.; Chen, X. An improved three-dimensional two-temperature model for multi-pulse femtosecond laser ablation aluminum. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 063104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.D.; Preziosi, L. Heat wave. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1989, 61, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oane, M.; Taca, M.; Tsao, S.L. Two Temperature Models for Metals: A New “Radical” Approach. Lasers Eng. (LIE) 2012, 24, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.L.; Huang, Z.P.; Ye, Y.K.; Wang, H.L. Femtosecond laser inscribed cladding waveguide lasers in Nd: LiYF4 crystals. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 102, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bucă, A.M.; Oane, M.; Mahmood, M.A.; Mihăilescu, I.N.; Popescu, A.C.; Sava, B.A.; Ristoscu, C. Non-Fourier Estimate of Electron Temperature in Case of Femtosecond Laser Pulses Interaction with Metals. Metals 2020, 10, 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050606
Bucă AM, Oane M, Mahmood MA, Mihăilescu IN, Popescu AC, Sava BA, Ristoscu C. Non-Fourier Estimate of Electron Temperature in Case of Femtosecond Laser Pulses Interaction with Metals. Metals. 2020; 10(5):606. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050606
Chicago/Turabian StyleBucă, Anca M., Mihai Oane, Muhammad Arif Mahmood, Ion N. Mihăilescu, Andrei C. Popescu, Bogdan A. Sava, and Carmen Ristoscu. 2020. "Non-Fourier Estimate of Electron Temperature in Case of Femtosecond Laser Pulses Interaction with Metals" Metals 10, no. 5: 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050606
APA StyleBucă, A. M., Oane, M., Mahmood, M. A., Mihăilescu, I. N., Popescu, A. C., Sava, B. A., & Ristoscu, C. (2020). Non-Fourier Estimate of Electron Temperature in Case of Femtosecond Laser Pulses Interaction with Metals. Metals, 10(5), 606. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10050606








