Fabrication of Strong and Ductile AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Using High Strain Rate Multiple Forging in a Wide Temperature Range
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
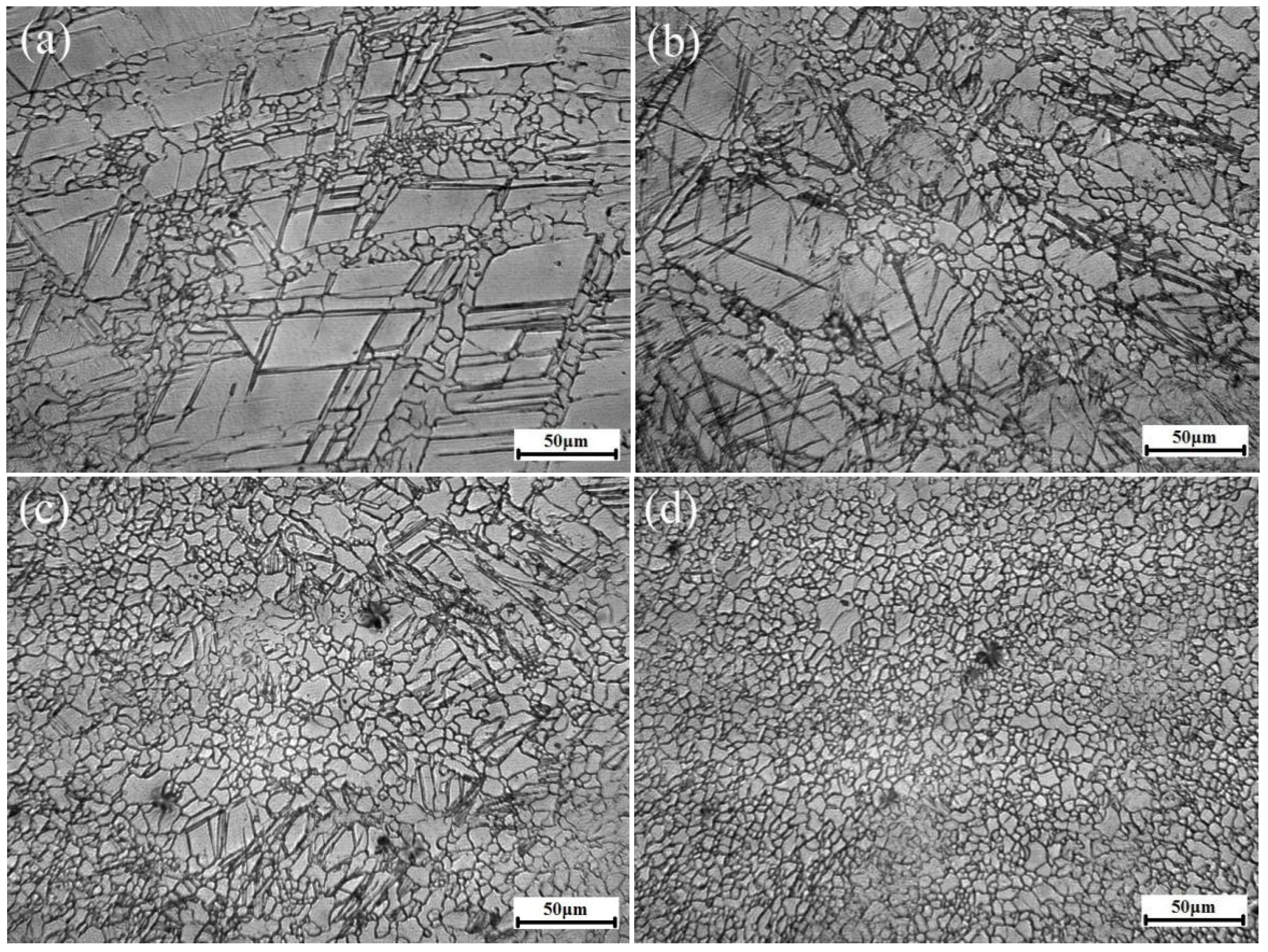
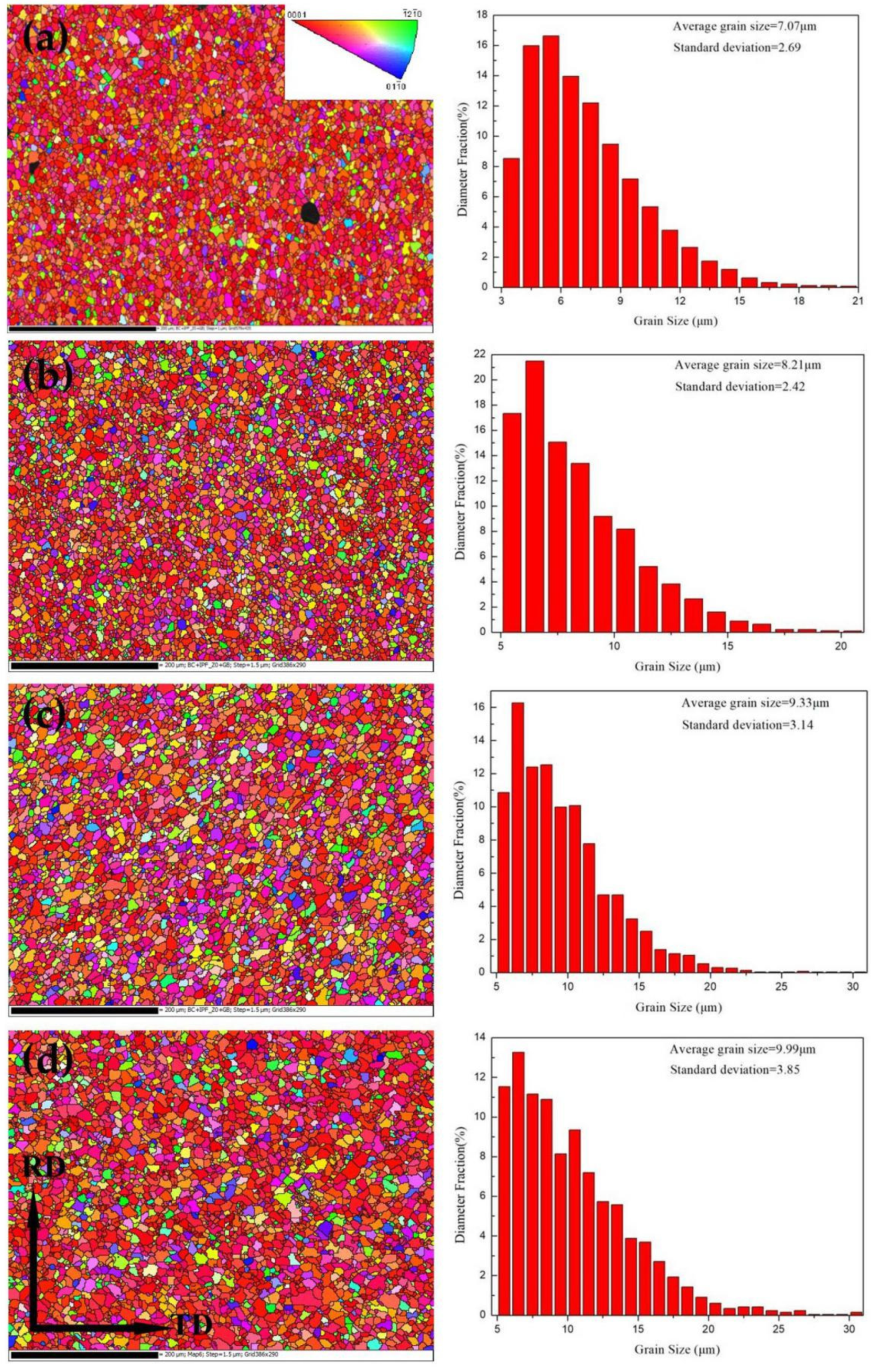
3.1. Microstructure
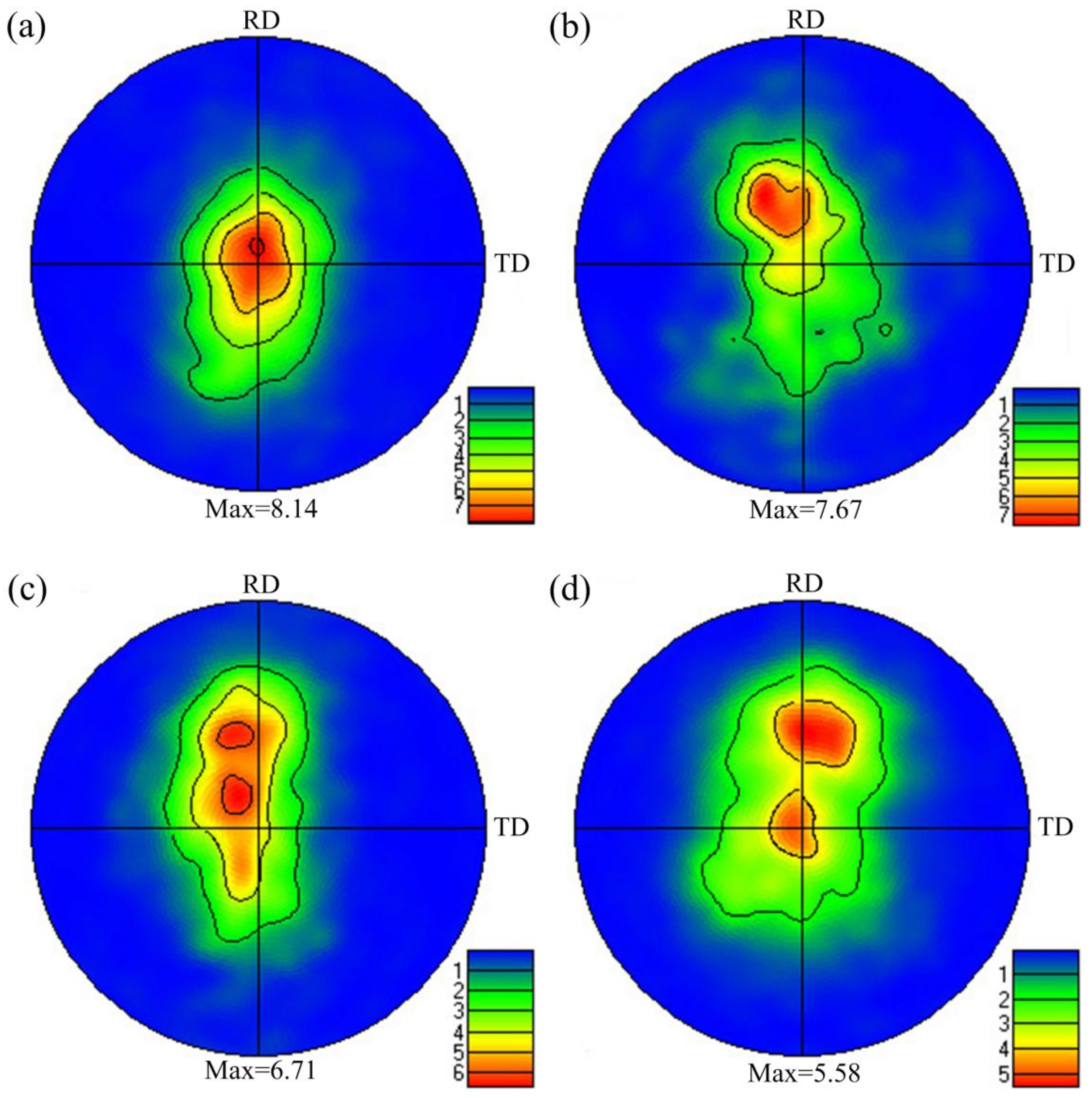
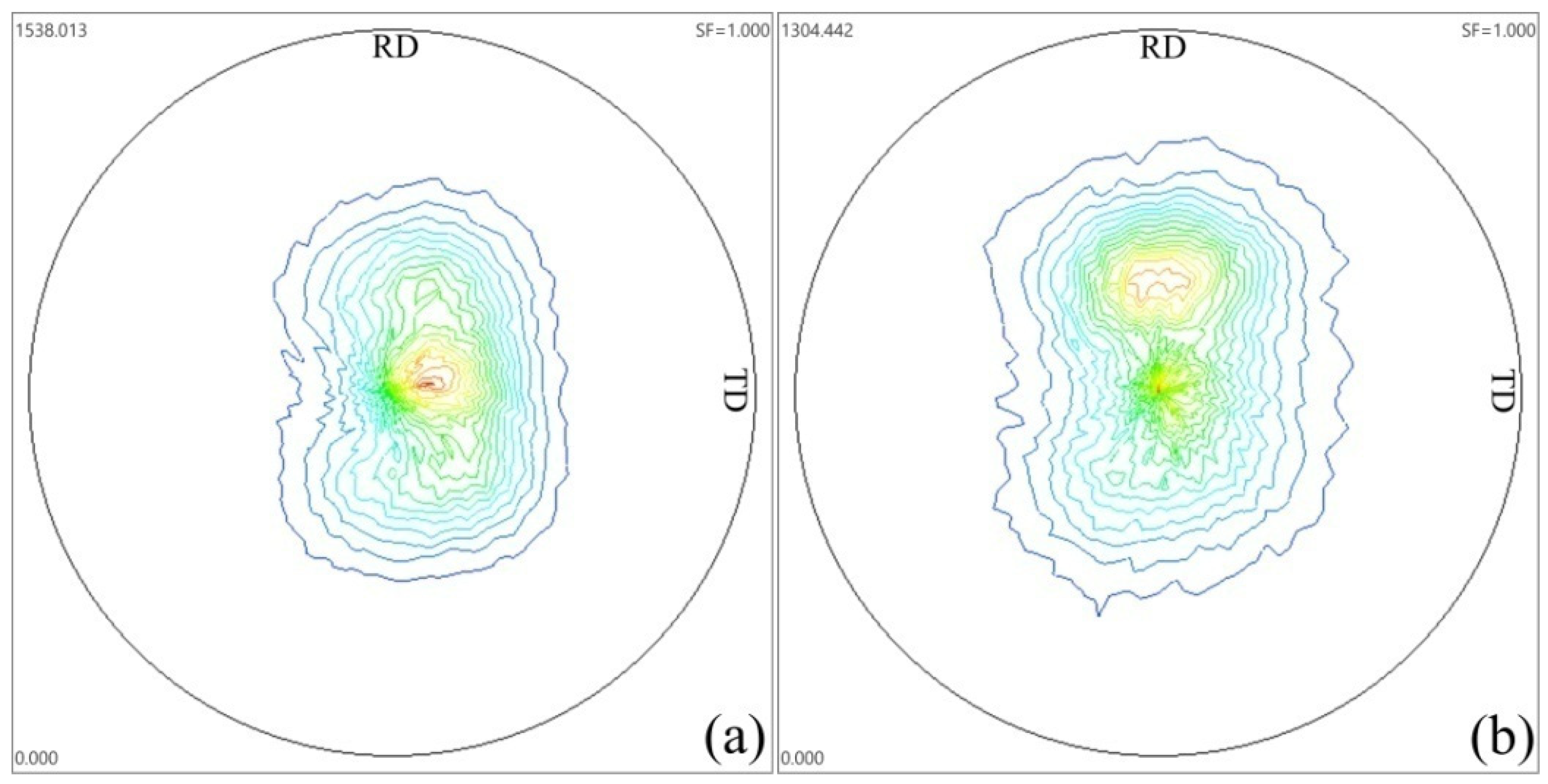
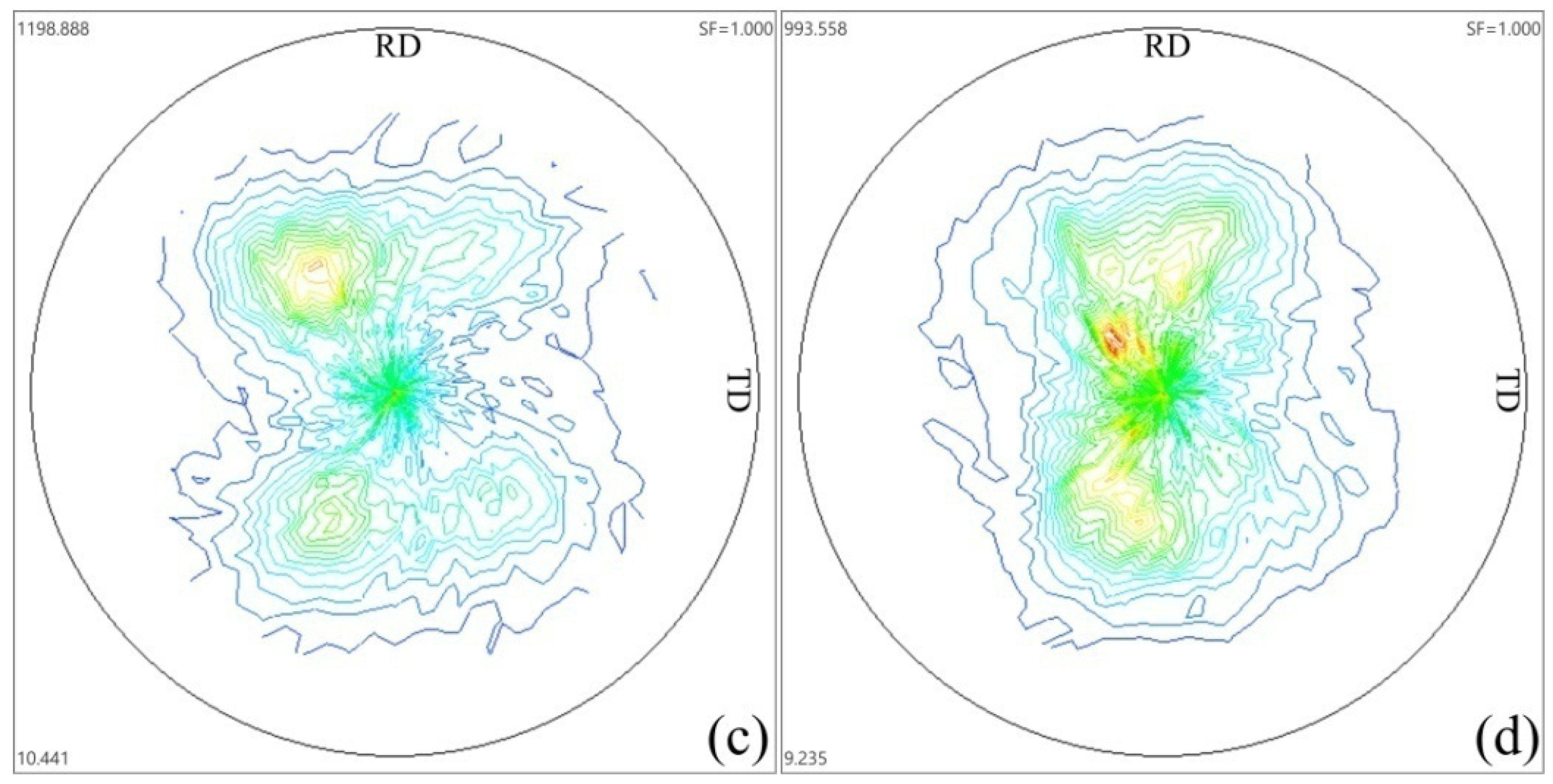
3.2. Texture
3.3. Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- The initial grain can be rapidly refined during HSRMF ascribing to the twining induced dynamic recrystallization (TDRX). The average grain sizes of the HSRMFed alloys were 7.07, 8.21, 9.33 and 9.99 μm when deformed at 250, 300, 350 and 400 °C, respectively, implying that the grain sizes of the HSRMFed alloy were less sensitive to temperature.
- The alteration of forging directions leads to the weakening of basal texture, and the basal texture is characteristic of titled texture at low temperature (<350 °C) and double peak at high temperature (≥350 °C).
- The HSRMFed alloys demonstrate both excellent strength (UTS > 300 MPa) and good ductility (δ > 20%), resulting from the combined effects of grain refinement and weakened basal texture. Therefore, HSRMF was an efficient technique to produce strong and ductile wrought AZ31 alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lian, Y.; Liao, B.; Zhou, T.; Ge, W.J.; Shi, L.X.; Hu, L.; Yang, M.B.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and mechanical property of Mg-3Al-1Zn magnesium alloy sheet processed by integrated high temperature rolling and continuous bending. Metals 2020, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Liu, X.; Xie, C.; Su, J.; Guo, P.; Tang, C.; Liu, W. Unveiling the underlying mechanism of forming edge cracks upon high strain-rate rolling of magnesium alloy. J Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Guo, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; Xu, Q.; Wu, Y.; Song, D.; Jiang, J.H.; Ma, A. High mechanical properties of AZ91 Mg alloy processed by equal channel angular pressing and rolling. Metals 2019, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Yan, H.G.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, Y.Z.; Su, B.; Du, Y.G.; Liao, X.Z. Feasibility of high strain-rate rolling of a magnesium alloy across a wide temperature range. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Yan, H.G.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, Y.Z.; Du, Y.G.; Liao, X.Z. Fabrication of Mg-Al-Zn-Mn alloy sheets with homogeneous fine-grained structures using high strain-rate rolling in a wide temperature range. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 559, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaneme, K.K.; Okotete, E.A. Enhancing Plastic deformability of Mg and its alloys-A review of traditional and nascent developments. J. Magnes. Alloys 2017, 5, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, H.; Yu, G.; Yang, X.Y. Multi-directional forging of AZ61Mg alloy under decreasing temperature conditions and improvement of its mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 6981–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.B.; Deng, K.K.; Wang, X.J.; Xu, F.J.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M.Y. Multidirectional forging of AZ91 magnesium alloy and its effects on microstructures and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 624, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.S.; Jiang, S.N.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, C.M. Increasing strength and ductility of a Mg–9Al alloy by dynamic precipitation assisted grain refinement during multi-directional forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 780, 139192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, J. Microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ31 magnesium alloy processed by multi-directional forging at different temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.S. Twinning, recrystallization and texture development during multi-directional impact forging in an AZ61 Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 650, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.S. Microstructure, texture and mechanical properties in an as-cast AZ61 Mg alloy during multi-directional impact forging and subsequent heat treatment. Mater. Des. 2015, 87, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.G.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.S. Enhanced mechanical properties due to grain refinement and texture modification in an AZ61 Mg alloy processed by small strain impact forging. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 621, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.S.A.; Wu, D.; Chen, R.S.; Song, G.S. Static recrystallization behavior of multi-directional impact forged Mg-Gd-Y-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Yan, H.G.; Chen, J.H.; Zhu, S.Q.; Su, B.; Zeng, P.L. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ZK60 alloy fabricated by high strain rate multiple forging. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, A.; Mahmudi, R. Evolution of microstructure, texture, and mechanical properties in a multi-directionally forged ZK60 Mg alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 752, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.Z.; Yan, H.G.; Chen, J.H.; Zhu, S.Q.; Bo, H.W.; Wang, L.W. Microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of AZ31 alloy fabricated by high strain rate triaxial-foring. Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2012, 24, 310–316. [Google Scholar]
- Salandari-Rabori, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Fatemi, S.M.; Ghambari, M.; Moghaddam, M. Microstructure and superior mechanical properties of a multi-axially forged WE magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salandari-Rabori, A.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Abedi, H.R.; Lecomte, J.S.; Khatami-hamedani, H. Micro and macro texture evolution during multiaxial forging of a WE43 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 739, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yan, H.G.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, H. Grain refinement in as-cast AZ80 magnesium alloy under large strain deformation. Mater. Des. 2007, 58, 162–167. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Shu, D.; Hu, C.; Zhao, Z.; Yuan, B. Grain refinement in an as-cast AZ61 magnesium alloy processed by multiaxial forging under the multi temperature processing procedure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Wu, S.; Bian, H.; Tang, N.; Liu, B.; Koizumi, Y.; Chiba, A. Grain refinement due to complex twin formation in rapid hot forging of magnesium. Scripta Mater. 2013, 68, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Yan, H.G.; Chen, J.H.; Wu, Y.Z.; Liu, J.Z.; Tian, J. Effect of twinning and dynamic recrystallization on the high strain rate rolling process. Scripta Mater. 2010, 63, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Yan, H.G.; Liao, X.Z.; Moody, S.J.; Sha, G.; Wu, Y.Z.; Ringer, S.P. Mechanisms for enhanced plasticity in magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 82, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Q.; Ringer, S.P. On the role of twinning and stacking faults on the crystal plasticity and grain refinement in magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2018, 144, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagapuram, D.; Efe, M.; Moscoso, W.; Chandrasekar, S.; Trumble, K.P. Controlling texture in magnesium alloy sheet by shear-based deformation processing. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 6843–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Prado, M.T.; Del Valle, J.A.; Contreras, J.M.; Ruan, O.A. Microstructural evolution during large strain hot rolling of an AM60 Mg alloy. Scripta Mater. 2004, 50, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.S.; Suzuki, K.; Chino, Y.; Mabuchi, M. Influence of initial texture on rolling and annealing textures of Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy sheets processed by high temperature rolling. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 537, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, L.L.; Wu, Y.J.; Cai, X.T.; Shen, H.B. Microstructure and mechanical properties of variable-plane-Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnew, S.R.; Yoo, M.H.; Tome, C.N. Application of texture simulation to understanding mechanical behavior of Mg and solid solution alloys containing Li or Y. Acta Mater. 2001, 49, 4277–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Suwas, S. Evolution of sub-micron grain size and weak texture in magnesium alloy Mg-3Al-0.4Mn by a modified multi-axial forging process. Scripta Mater. 2012, 66, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

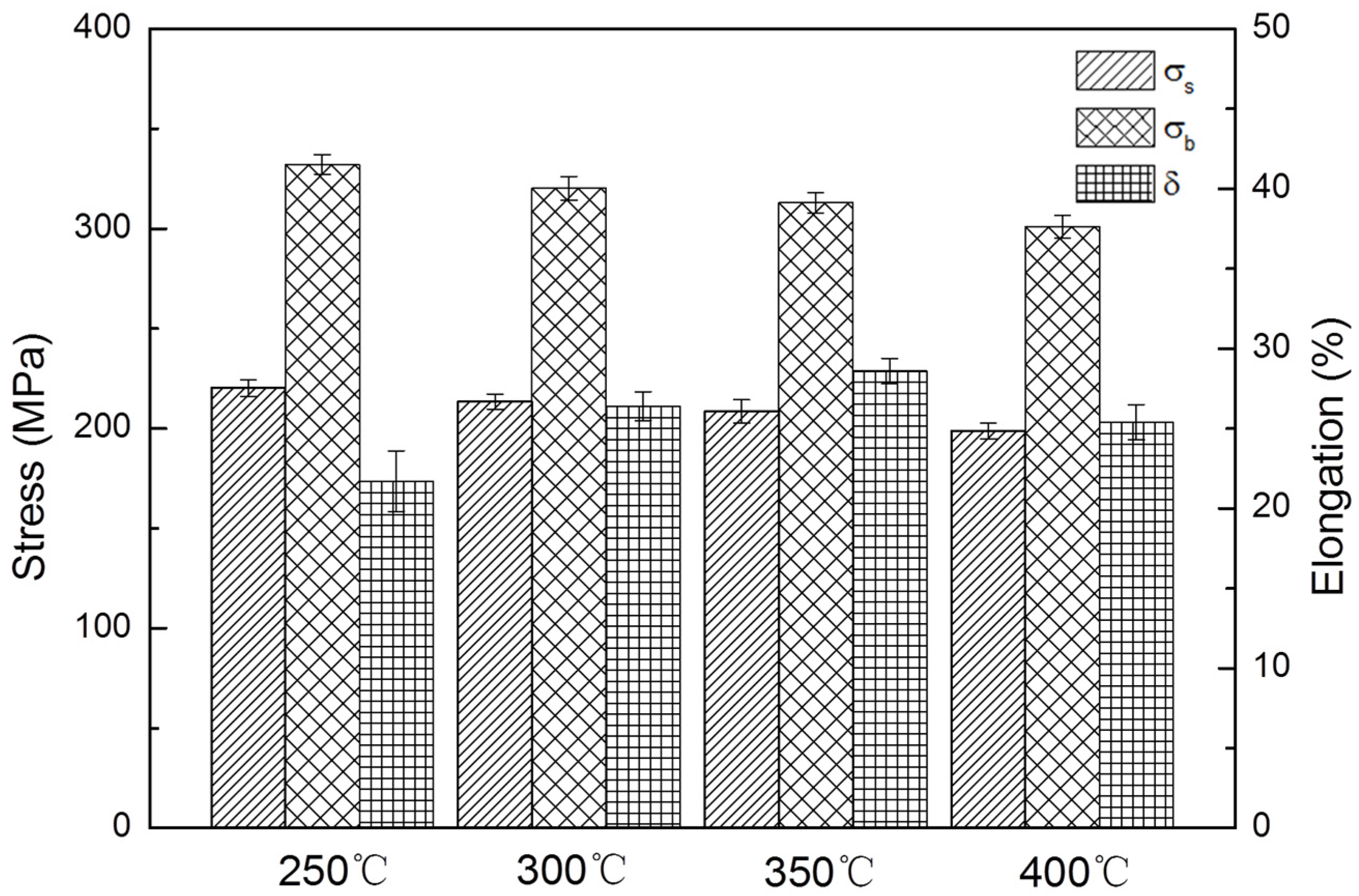
| Temperature (°C) | σs (MPa) | σb (MPa) | δ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250 | 220.3 ± 4.1 | 332.2 ± 4.8 | 21.7 ± 1.9 |
| 300 | 213.5 ± 3.8 | 320.3 ± 5.9 | 26.4 ± 0.9 |
| 350 | 208.6 ± 5.9 | 312.9 ± 5.1 | 28.6 ± 0.8 |
| 400 | 198.8 ± 3.9 | 301.1 ± 5.8 | 25.4 ± 1.1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Deng, B.; Ye, T.; Nie, Z.; Liu, X. Fabrication of Strong and Ductile AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Using High Strain Rate Multiple Forging in a Wide Temperature Range. Metals 2020, 10, 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060729
Wu Y, Deng B, Ye T, Nie Z, Liu X. Fabrication of Strong and Ductile AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Using High Strain Rate Multiple Forging in a Wide Temperature Range. Metals. 2020; 10(6):729. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060729
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yuanzhi, Bin Deng, Tuo Ye, Zhicheng Nie, and Xiao Liu. 2020. "Fabrication of Strong and Ductile AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Using High Strain Rate Multiple Forging in a Wide Temperature Range" Metals 10, no. 6: 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060729
APA StyleWu, Y., Deng, B., Ye, T., Nie, Z., & Liu, X. (2020). Fabrication of Strong and Ductile AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Using High Strain Rate Multiple Forging in a Wide Temperature Range. Metals, 10(6), 729. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060729




