CaO–CaZrO3 Mixed Oxides Prepared by Auto–Combustion for High Temperature CO2 Capture: The Effect of CaO Content on Cycle Stability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sorbent Characterization
3.1.1. X–Ray Diffraction Characterization of the As–Prepared Sorbents
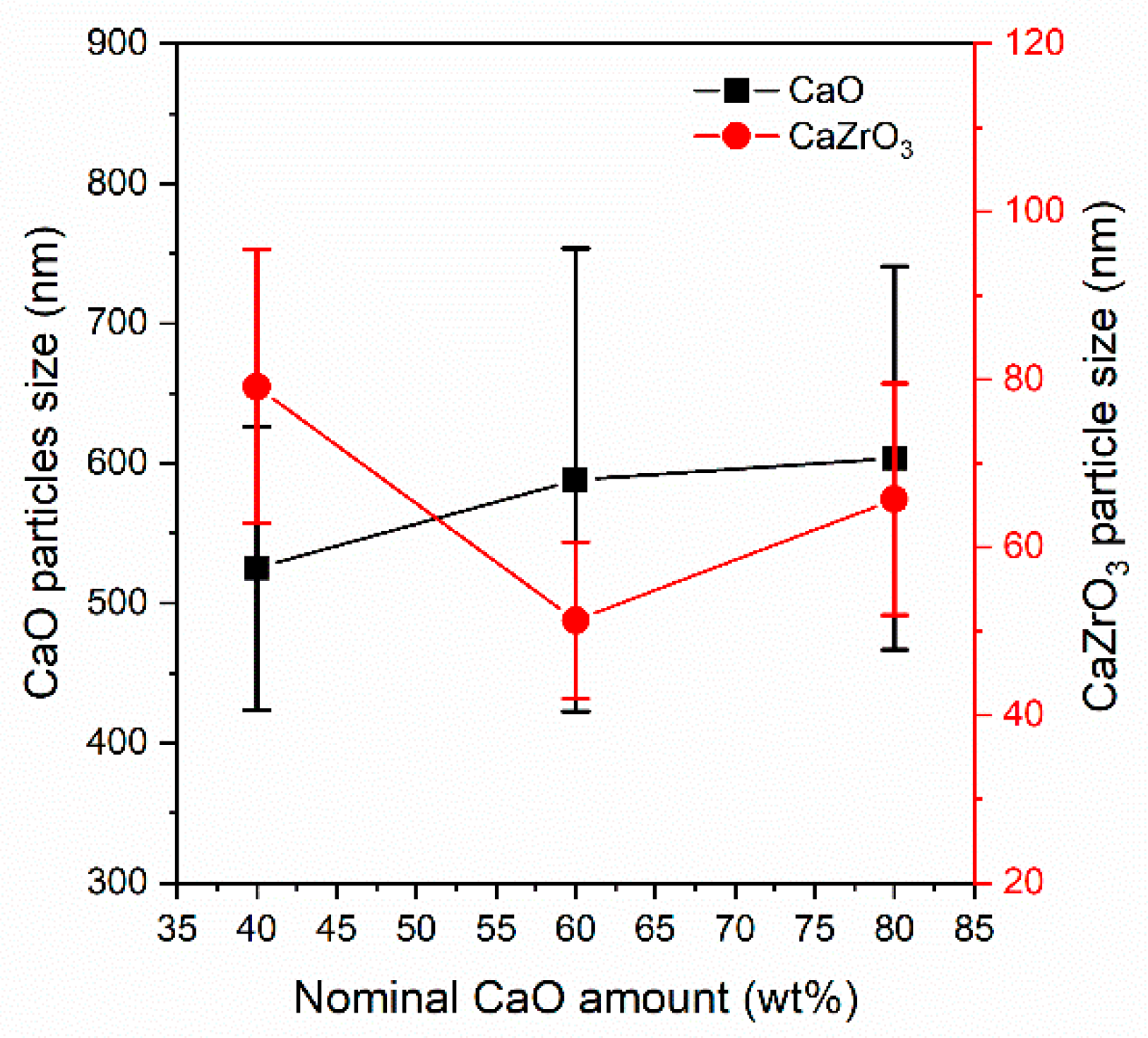
3.1.2. Textural Characterization of the As–Prepared Sorbents
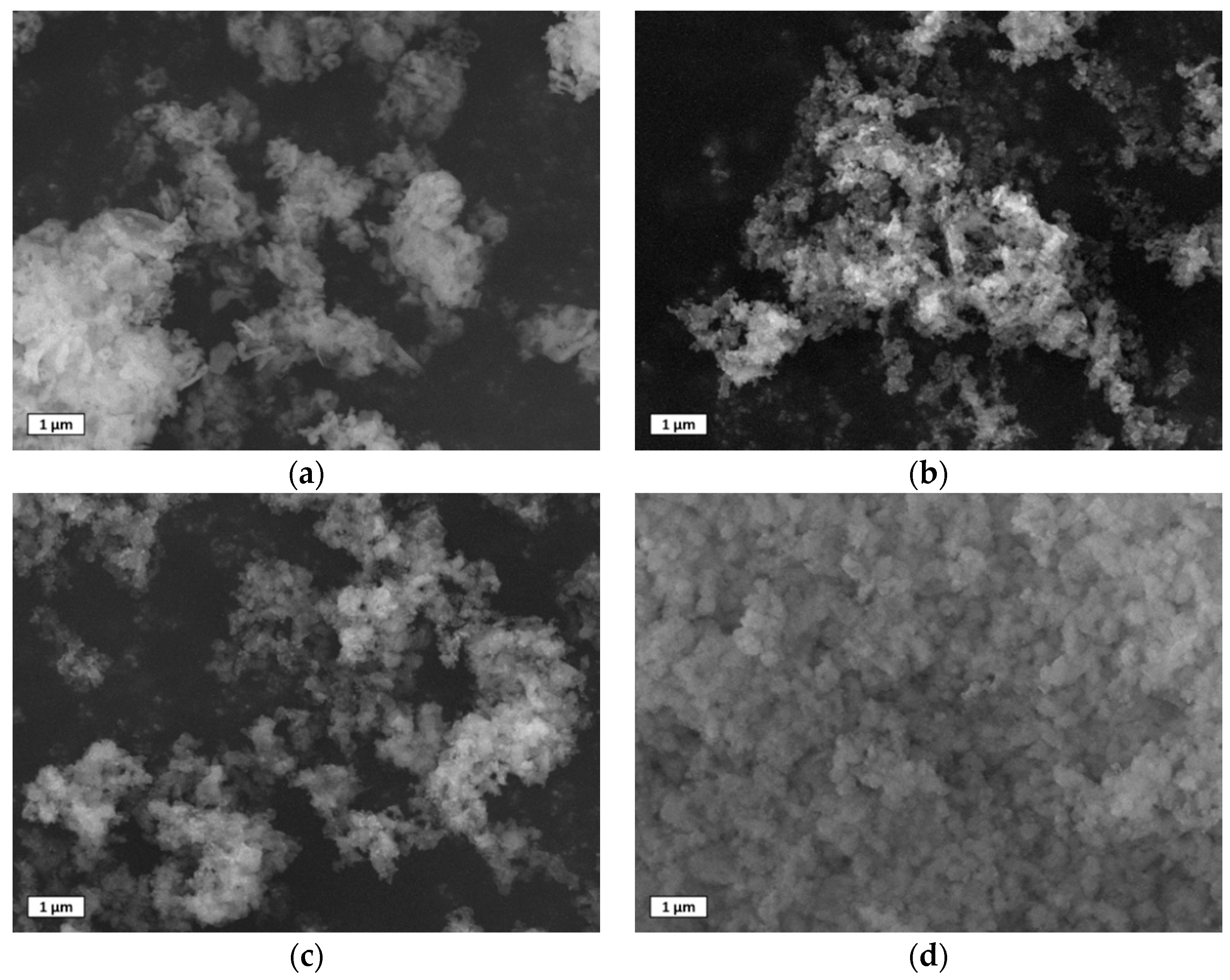
3.1.3. SEM Images of the As–Prepared Sorbents
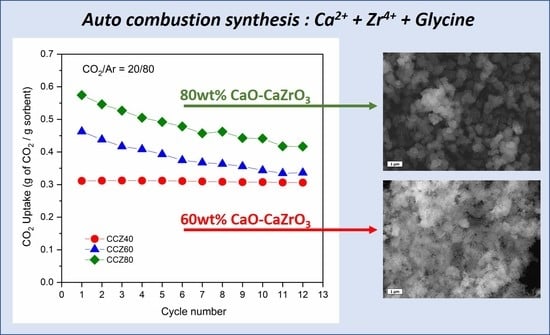
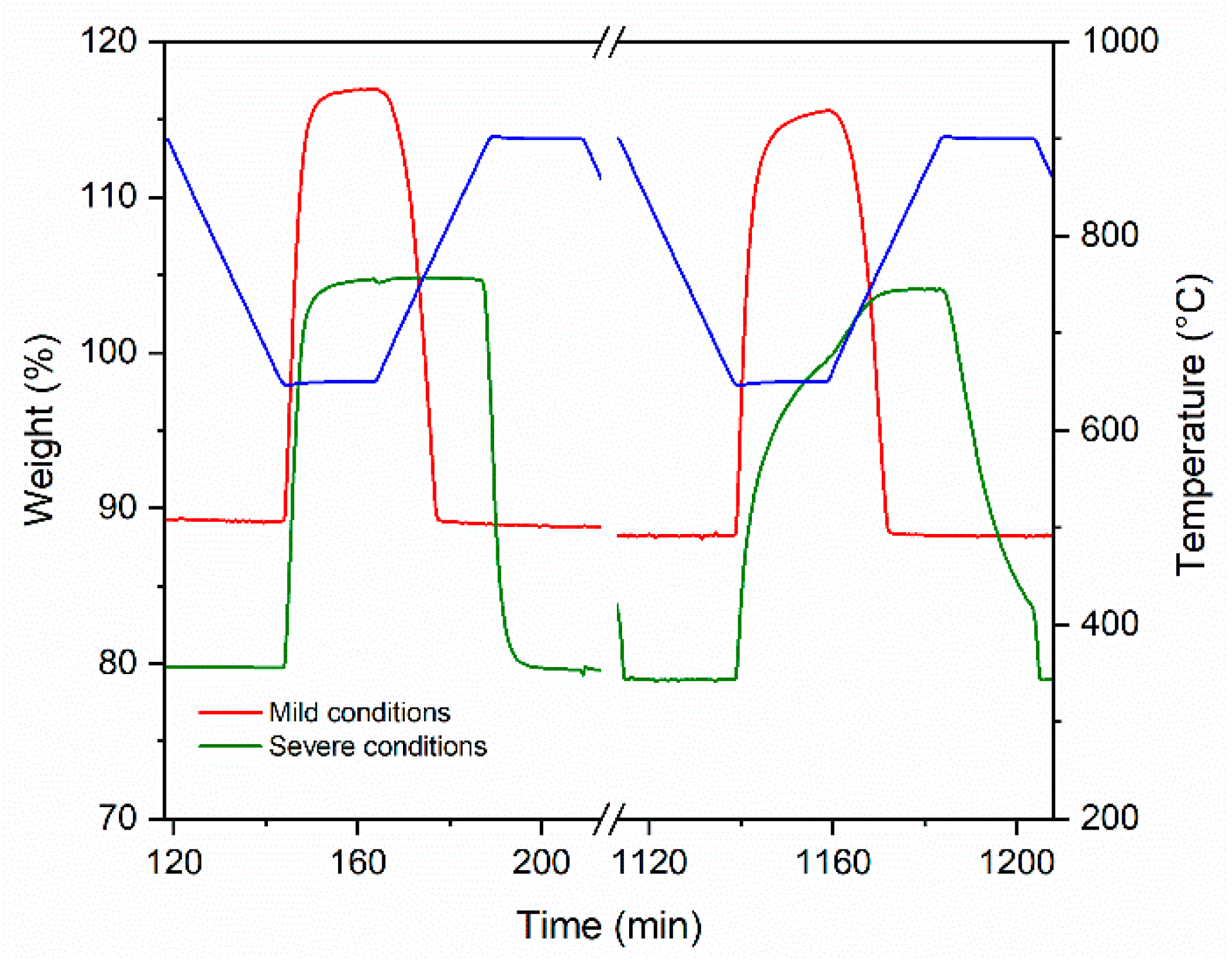
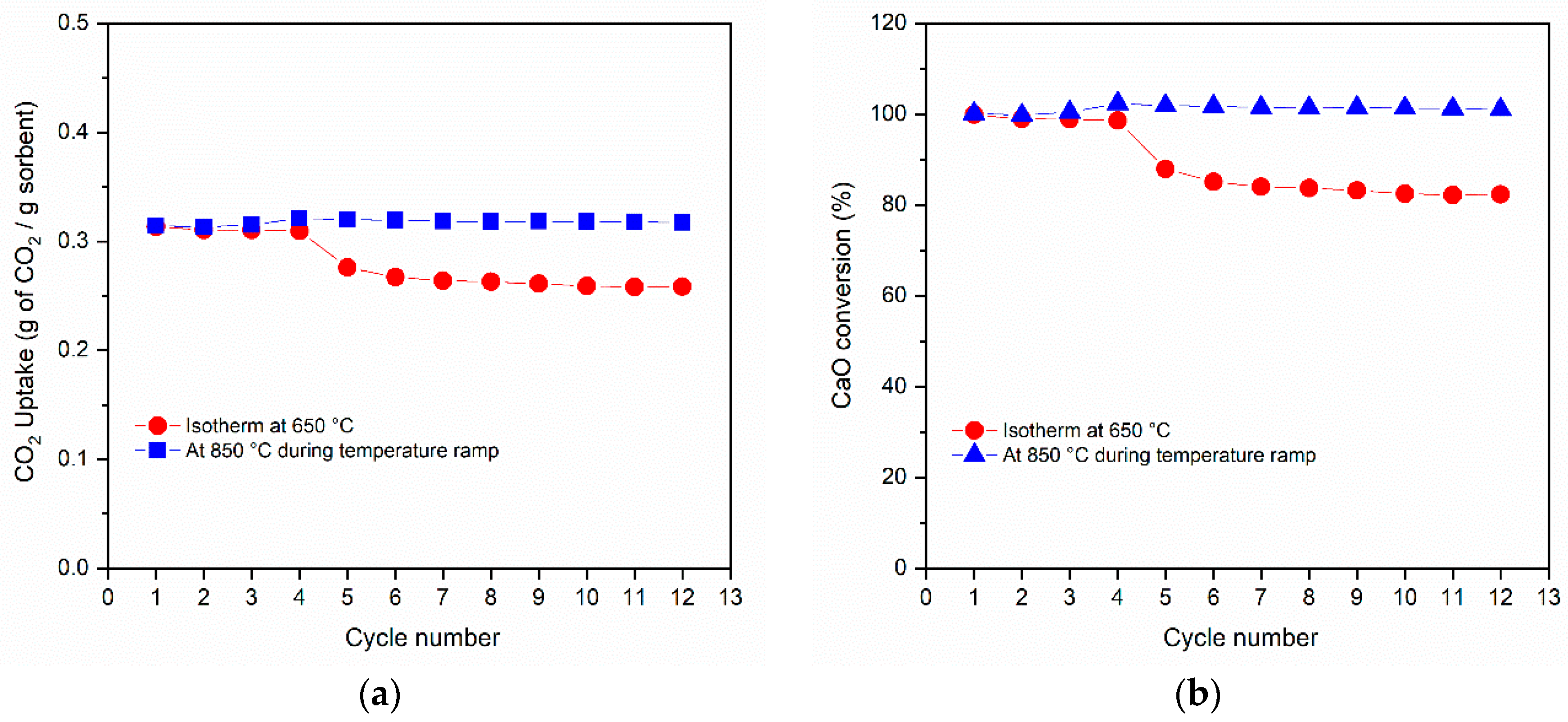
3.2. CO2 Capture Performance
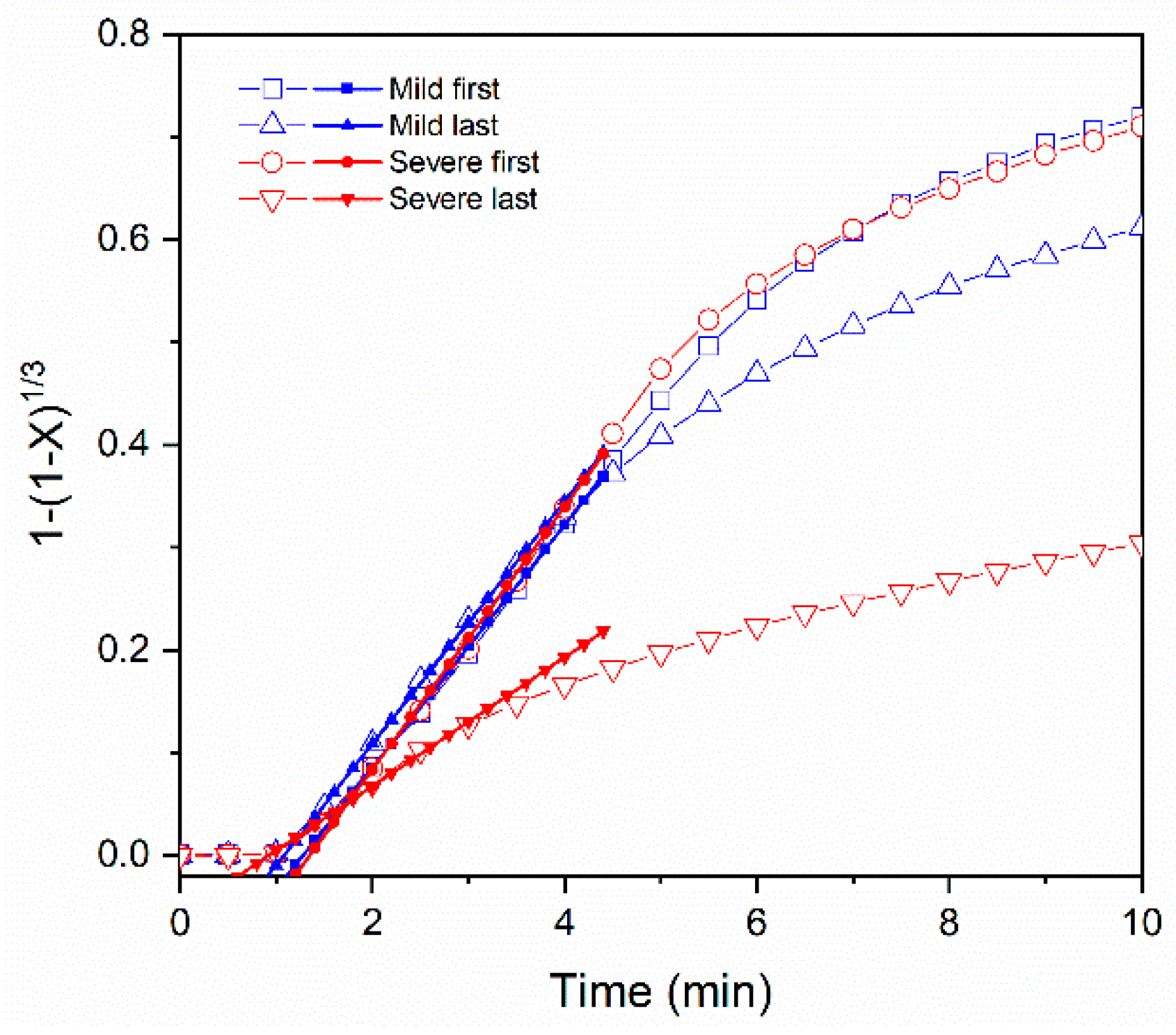
3.3. Shrinking Core Model
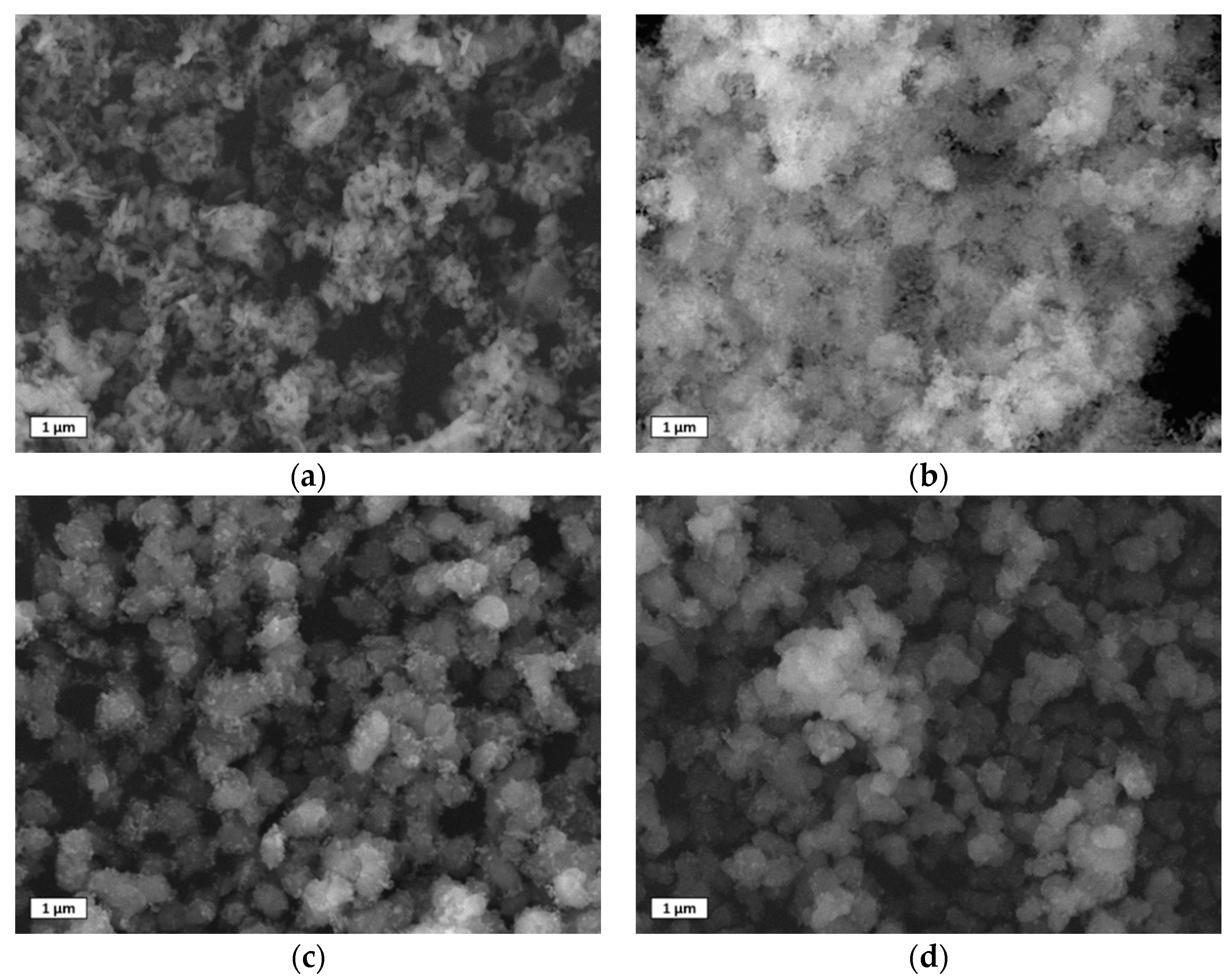
3.4. SEM Images of Used Sorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abanades, J.C.; Anthony, E.J.; Lu, D.Y.; Salvador, C.; Alvarez, D. Capture of CO2 from combustion gases in a fluidized bed of CaO. AIChE J. 2004, 50, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S.K.; Perlmutter, D.D. Effect of the product layer on the kinetics of the CO2–lime reaction. AIChE J. 1983, 29, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendardo, S.; Di Felice, L.; Gallucci, K.; Foscolo, P.U. CO2 capture with calcined dolomite: The effect of sorbent particle size. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2011, 1, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, J.C.; Anthony, E.J.; Wang, J.; Oakey, J.E. Fluidized Bed Combustion Systems Integrating CO2 Capture with CaO. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 2861–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; He, X.; Ji, G.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X. Zirconia incorporated calcium looping absorbents with superior sintering resistance for carbon dioxide capture from in situ or ex situ processes. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2018, 2, 2733–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herce, C.; Cortés, C.; Stendardo, S. Computationally efficient CFD model for scale–up of bubbling fluidized bed reactors applied to sorption–enhanced steam methane reforming. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 167, 747–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Xie, X.; Sun, R. Effect of the presence of HCl on cyclic CO2 capture of calcium–based sorbent in calcium looping process. Appl. Energy 2014, 125, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendardo, S.; Foscolo, P.U. Carbon dioxide capture with dolomite: A model for gas–solid reaction within the grains of a particulate sorbent. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2009, 64, 2343–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendardo, S.; Andersen, L.K.; Herce, C. Self–activation and effect of regeneration conditions in CO2–carbonate looping with CaO–Ca12Al14O33 sorbent. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 220, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, E.E. Effect of Steam on the Decomposition of Limestone1,1. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1927, 19, 594–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lin, S.; Suzuki, Y. Limestone Calcination with CO2 Capture (II): Decomposition in CO2/Steam and CO2/N2 Atmospheres. Energy Fuels 2008, 22, 2326–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abanades, J.C.; Rubin, E.S.; Anthony, E.J. Sorbent Cost and Performance in CO2 Capture Systems. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 3462–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallucci, K.; Stendardo, S.; Foscolo, P.U. CO2 capture by means of dolomite in hydrogen production from syn gas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 3049–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, P.S.; Pacciani, R.; Dennis, J.S.; Davidson, J.F.; Hayhurst, A.N. The Effects of Repeated Cycles of Calcination and Carbonation on a Variety of Different Limestones, as Measured in a Hot Fluidized Bed of Sand. Energy Fuels 2007, 21, 2072–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Grace, J.R.; Lim, C.J.; Anthony, E.J. The effect of CaO sintering on cyclic CO2 capture in energy systems. AIChE J. 2007, 53, 2432–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Li, Z.-S.; Cai, N.-S. Experiment and Modeling of CO2 Capture from Flue Gases at High Temperature in a Fluidized Bed Reactor with Ca–Based Sorbents. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manovic, V.; Anthony, E.J. Thermal Activation of CaO–Based Sorbent and Self–Reactivation during CO2 Capture Looping Cycles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4170–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Song, H.S.; Portillo, M.; Lim, C.J.; Grace, J.R.; Anthony, E.J. Long–Term Calcination/Carbonation Cycling and Thermal Pretreatment for CO2 Capture by Limestone and Dolomite. Energy Fuels 2009, 23, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lysikov, A.I.; Salanov, A.N.; Okunev, A.G. Change of CO2 Carrying Capacity of CaO in Isothermal Recarbonation−Decomposition Cycles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 4633–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.W.; Lu, D.; Anthony, E.J.; Wu, Y. Improved Long–Term Conversion of Limestone–Derived Sorbents for In Situ Capture of CO2 in a Fluidized Bed Combustor. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2004, 43, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, N.; Alonso, M.; Abanades, J.C. Experimental investigation of a circulating fluidized–bed reactor to capture CO2 with CaO. AIChE J. 2011, 57, 1356–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arias, B.; Grasa, G.S.; Abanades, J.C. Effect of sorbent hydration on the average activity of CaO in a Ca–looping system. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgwardt, R.H. Calcium oxide sintering in atmospheres containing water and carbon dioxide. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1989, 28, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beruto, D.; Barco, L.; Searcy, A.W. CO2–Catalyzed Surface Area and Porosity Changes in High–Surface–Area CaO Aggregates. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1984, 67, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ewing, J.; Beruto, D.; Searcy, A.W. The Nature of CaO Produced by Calcite Powder Decomposition in Vacuum and in CO2. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1979, 62, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, F. Effect of steam hydration on performance of lime sorbent for CO2 capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2008, 2, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Guo, X.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, C. CO2 capture of limestone modified by hydration–dehydration technology for carbonation/calcination looping. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, N.N.A.H.; Bitter, J.H.; de Jong, K.P. Support and Size Effects of Activated Hydrotalcites for Precombustion CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reijers, H.T.J.; Valster–Schiermeier, S.E.A.; Cobden, P.D.; van den Brink, R.W. Hydrotalcite as CO2 Sorbent for Sorption–Enhanced Steam Reforming of Methane. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 2522–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herce, C.; Stendardo, S.; Cortés, C. Increasing CO2 carrying capacity of dolomite by means of thermal stabilization by triggered calcination. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, H.; Fan, L.-S. Carbonation−Calcination Cycle Using High Reactivity Calcium Oxide for Carbon Dioxide Separation from Flue Gas. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2002, 41, 4035–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Smirniotis, P.G. Calcium Oxide Doped Sorbents for CO2 Uptake in the Presence of SO2 at High Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 5454–5459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Khan, A.; Smirniotis, P.G. Relationship between Structural Properties and CO2 Capture Performance of CaO−Based Sorbents Obtained from Different Organometallic Precursors. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2008, 47, 6216–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesch, A.; Reddy, E.P.; Smirniotis, P.G. Parametric Study of Cs/CaO Sorbents with Respect to Simulated Flue Gas at High Temperatures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2005, 44, 6485–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, C.; Duan, L.; Liang, C.; Liu, D.; Chen, X. Enhancement of reactivity in surfactant–modified sorbent for CO2 capture in pressurized carbonation. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, C.; Lu, D.; Anthony, E.J.; Abanades, J.C. Enhancement of CaO for CO2 capture in an FBC environment. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 96, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-S.; Cai, N.-S.; Huang, Y.-Y. Effect of Preparation Temperature on Cyclic CO2 Capture and Multiple Carbonation−Calcination Cycles for a New Ca–Based CO2 Sorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2006, 45, 1911–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacciani, R.; Müller, C.R.; Davidson, J.F.; Dennis, J.S.; Hayhurst, A.N. Synthetic Ca–based solid sorbents suitable for capturing CO2 in a fluidized bed. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2008, 86, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.F.; Zhu, Y.Q. Behavior of CaTiO3/Nano–CaO as a CO2 Reactive Adsorbent. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 2701–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbard, C.R.; Snyder, R.L. RIR—Measurement and Use in Quantitative XRD. Powder Diffr. 2013, 3, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sing, K.S.W. Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


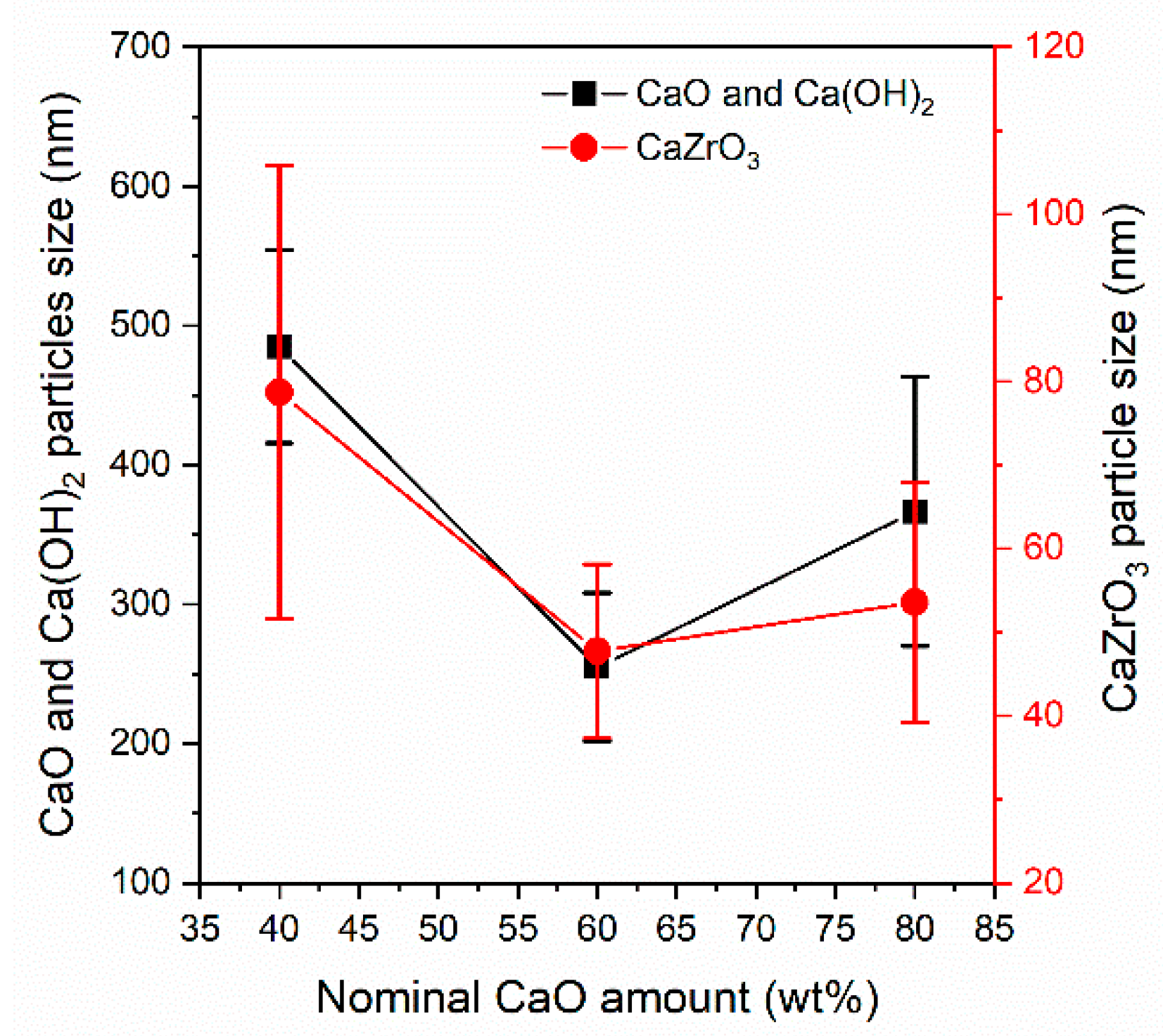

| Sample | Crystallite Size (nm) 1 | Phase Amount (%) | SSA (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CaZrO3 | CaO | Ca(OH)2 | CaZrO3 | CaO | Ca(OH)2 | CaCO3 | |||
| CZ | 63.9 | – | – | 89.12 | 6.9 | 3 | 1.0 | 11.2 | 0.043 |
| CCZ40 | 56.4 | 35.5 | 16.0 | 52.8 | 20.4 | 25.5 | 0.3 | 32.4 | 0.095 |
| CCZ60 | 30.5 | 31.2 | 12.2 | 35.8 | 44.8 | 18.9 | 0.5 | 52.7 | 0.160 |
| CCZ80 | 32.3 | – | 11.2 | 14.0 | 3.0 | 73.5 | 9.5 | 48.0 | 0.123 |
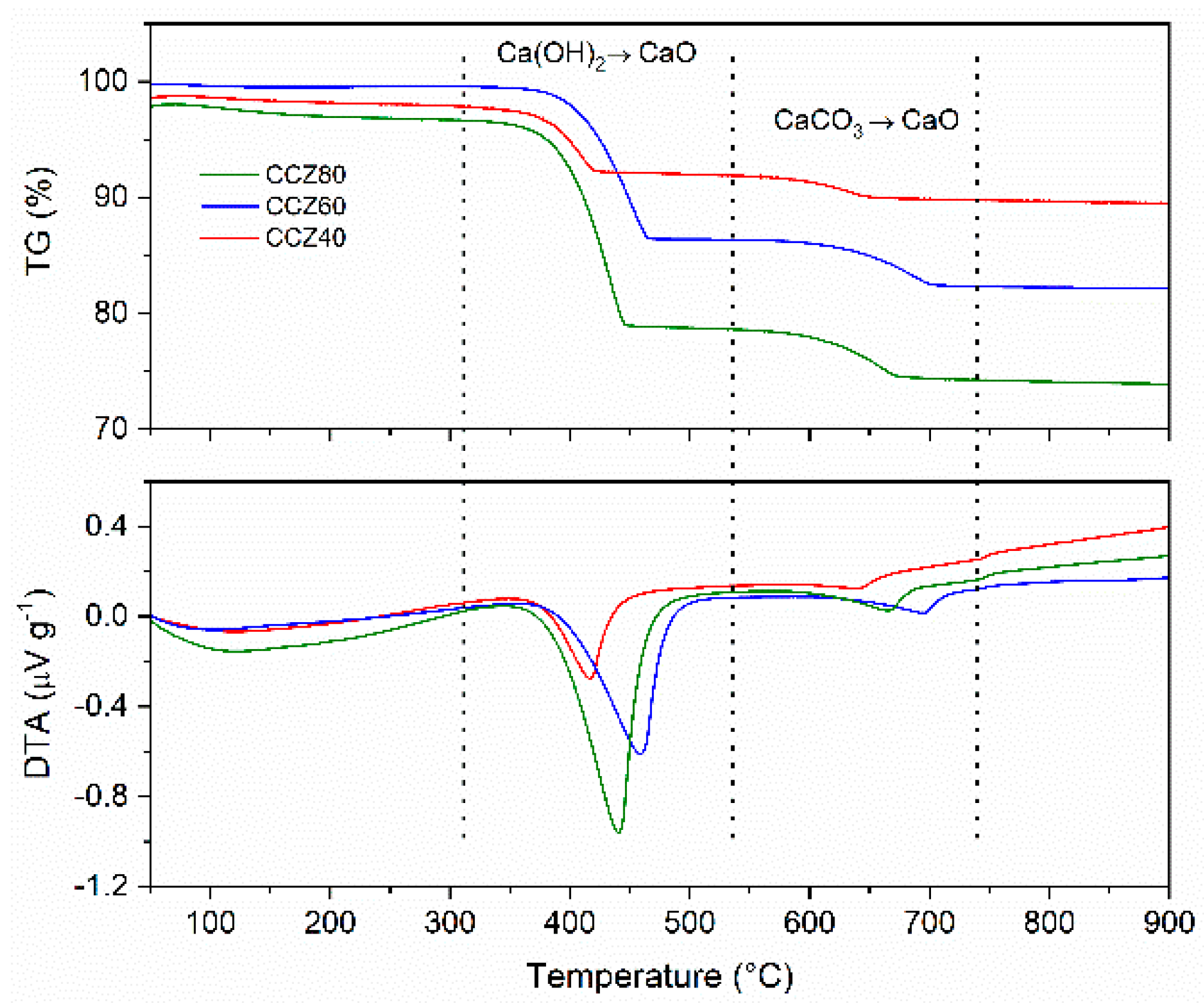
| Sample | Ca Species | Peak Temperature (°C) | Weight loss (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CZ | CaCO3 | 792.0 | 1.6 |
| CCZ40 | Ca(OH)2 | 417.0 | 5.9 |
| CaCO3 | 638.7 | 2.3 | |
| CCZ60 | Ca(OH)2 | 458.6 | 13.2 |
| CaCO3 | 694.7 | 4.1 | |
| CCZ80 | Ca(OH)2 | 440.4 | 17.6 |
| CaCO3 | 665.5 | 4.6 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luisetto, I.; Mancini, M.R.; Della Seta, L.; Chierchia, R.; Vanga, G.; Grilli, M.L.; Stendardo, S. CaO–CaZrO3 Mixed Oxides Prepared by Auto–Combustion for High Temperature CO2 Capture: The Effect of CaO Content on Cycle Stability. Metals 2020, 10, 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060750
Luisetto I, Mancini MR, Della Seta L, Chierchia R, Vanga G, Grilli ML, Stendardo S. CaO–CaZrO3 Mixed Oxides Prepared by Auto–Combustion for High Temperature CO2 Capture: The Effect of CaO Content on Cycle Stability. Metals. 2020; 10(6):750. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060750
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuisetto, Igor, Maria Rita Mancini, Livia Della Seta, Rosa Chierchia, Giuseppina Vanga, Maria Luisa Grilli, and Stefano Stendardo. 2020. "CaO–CaZrO3 Mixed Oxides Prepared by Auto–Combustion for High Temperature CO2 Capture: The Effect of CaO Content on Cycle Stability" Metals 10, no. 6: 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060750
APA StyleLuisetto, I., Mancini, M. R., Della Seta, L., Chierchia, R., Vanga, G., Grilli, M. L., & Stendardo, S. (2020). CaO–CaZrO3 Mixed Oxides Prepared by Auto–Combustion for High Temperature CO2 Capture: The Effect of CaO Content on Cycle Stability. Metals, 10(6), 750. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10060750