Erosion–Corrosion of AISI 304L Stainless Steel Affected by Industrial Copper Tailings
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Measurements
2.3. Characterization and Surface Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of AISI 304L
3.2. Characterization of Tailing Particles
3.3. Polarization Curves and Corrosion Rate
3.4. Wear Behavior and Synergism
3.5. Morphological Observations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hakiki, N.E.; Montemor, M.F.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; da Cunha Belo, M. Semiconducting properties of thermally grown oxide films on AISI 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, C.M.; Cristóbal, M.J.; Losada, R.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Pena, G.; Pérez, M.C. Long-term behaviour of AISI 304L passive layer in chloride containing medium. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 1881–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.; Sun, W.; Jiang, J.; Song, D.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D. Passivation characteristics of alloy corrosion-resistant steel Cr10Mo1 in simulating concrete pore solutions: Combination effects of pH and chloride. Materials 2016, 9, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Domene, R.M.; Sánchez-Tovar, R.S.; García-Antón, J. Passive behavior and passivity breakdown of AISI 304 in LiBr solutions through scanning electrochemical microscopy. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, C565–C572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wharton, J.A.; Wood, R.J.K. Influence of flow conditions on the corrosion of AISI 304L stainless steel. Wear 2004, 256, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klapper, H.S.; Goellner, J.; Burkert, A.; Heyn, A. Environmental factors affecting pitting corrosion of type 304 stainless steel investigated by electrochemical noise measurements under potentiostatic control. Corr. Sci. 2013, 75, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaey, S.A.M.; Taha, F.; Abd El-Malak, A.M. Corrosion and inhibition of stainless steel pitting corrosion in alkaline medium and the effect of Cl− and Br− anions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 242, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.M.B.; Moreira, J.L.; Martins, J.I. Corrosion in water supply pipe stainless steel 304 and a supply line of helium in stainless steel 316. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2014, 39, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghuy, A.A.; Zakeri, M.; Moayed, M.H.; Mazinani, M. Effect of grain size on pitting corrosion of 304L austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2015, 94, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, P.H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Skeldon, P. Pitting corrosion behaviour of large area laser surface treated 304L stainless–steel. Thin Solid Films 2004, 453–454, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, J.; Hoche, H.; Oechsner, M. Corrosion properties of polished and shot-peened austenitic stainless steel 304L and 316L with and without plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 313, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.T.; Mao, L.C.; Luo, J.L. Hydrodynamic effects on erosion-enhanced corrosion of stainless steel in aqueous slurries. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 56, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.J.K.; Walker, J.C.; Harvey, T.J.; Wang, S.; Rajahram, S.S. Influence of microstructure on the erosion and erosion–corrosion characteristics of 316 stainless steel. Wear 2013, 306, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Tan, M.Y.; Huang, Y. An overview of major experimental methods and apparatus for measuring and investigating erosion-corrosion of ferrous-based steels. Metals 2020, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Yan, F. Effect of halide concentration on tribocorrosion behavior of 304 SS in artificial seawater. Corros. Sci. 2015, 99, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Ya, H.H.; Pao, W. An experimental study on the erosion-corrosion performance of AISI 1018 carbon steel and AISI 304L stainless steel 90-degree elbow pipe. Metals 2019, 9, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.B.; Zheng, Y.G. Erosion-enhanced corrosion of stainless steel and carbon steel measured electrochemically under liquid and slurry impingement. Corros. Sci. 2016, 102, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermúdez, M.D.; Carrión, F.J.; Martínez-Nicolás, G.; López, R. Erosion–corrosion of stainless steels, titanium, tantalum and zirconium. Wear 2005, 258, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saada, F.B.; Antar, Z.; Elleuch, K.; Ponthiaux, P. On the tribocorrosion behavior of 304L stainless steel in olive pomace/tap water filtrate. Wear 2015, 328–329, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, M.M.; Jana, B.D.; Abdelrahman, S.M. Models and Mechanisms of Erosion-Corrosion in Metals. In Tribocorrosion of Passive Metals and Coatings, 1st ed.; Landolt, D., Mischler, S., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Cambridge, UK, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 153–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, Y.F. Parametric effects on the erosion–corrosion rate and mechanism of carbon steel pipes in oil sands slurry. Wear 2012, 276–277, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, L. Research on erosion-corrosion rate of 304 stainless steel in acidic slurry via experimental design method. Materials 2019, 12, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, J.Z.; Hu, H.X.; Wang, Z.B.; Zheng, Y.G. Comparison of critical flow velocity for erosion-corrosion of six stainless steels in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution containing 2 wt% silica sand particles. Wear 2018, 416–417, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaheri, V.; Porter, D.; Kuokkala, V.T. Slurry erosion of steel—Review of tests, mechanisms and materials. Wear 2018, 408–409, 248–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafyllias, G.; Galloway, A.; Humphries, E. The effect of low pH in erosion-corrosion resistance of high chromium cast irons and stainless steels. Wear 2019, 420–421, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, J.; Walczak, M. Effect of dissolved copper ions on erosion–corrosion synergy of X65 steel in simulated copper tailing slurry. Tribol. Int. 2017, 114, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, M.; Perolainen, J. Slurry pot investigation of the influence of erodent characteristics on the erosion resistance of austenitic and duplex stainless steel grades. Wear 2014, 319, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. ASTM G119-04: Standard Guide for Determining Synergism Between Wear and Corrosion; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Soliz, A.; Cáceres, L. Corrosion of a carbon steel cylindrical band exposed to a concentrated NaCl solution flowing through an annular flow cell. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, C385–C395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCafferty, E. Introduction to Corrosion Science, 1st ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 13–31. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM International. ASTM E407-07E1: Standard Practice for Microetching Metals and Alloys; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, J.; Klemm, S.O.; Duarte, M.J.; Rossrucker, L.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Renner, F.U. Multi-element-resolved electrochemical corrosion analysis. Part, I. Dissolution behavior and passivity of amorphous Fe50Cr15Mo14C15B6. Corros. Sci. 2014, 89, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogle, K.; Mokaddem, M.; Volovitch, P. Atomic emission spectroelectrochemistry applied to dealloying phenomena II. Selective dissolution of iron and chromium during active–passive cycles of an austenitic stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, C.O.A.; Landolt, D. Passive films on stainless steels-chemistry, structure and growth. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.F.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Hakiki, N.E.; Da Cunha Belo, M. Chemical composition and electronic structure of the oxide films formed on 316L stainless steel and nickel based alloys in high temperature aqueous environments. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1635–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliz, A.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Cáceres, L. Influence of hydrodynamic flow patterns on the corrosion behavior of carbon steel in a neutral LiBr solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 10050–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, C.L.; Kelly, R.G.; Liu, C.; Carpenter, J.; Alshanoon, A.; Bryan, C.; Katona, R.M.; Schindelholz, E. Oxygen reduction on stainless steel in concentrated chloride media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, C869–C877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojković, S.L.J.; Zečević, S.K.; Obradović, M.D.; Dražić, D.M. Oxygen reduction on a duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 1998, 40, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babić, R.; Metikoš-Huković, M. Oxygen reduction on stainless steel. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1993, 23, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybalka, K.V.; Beketaeva, L.A.; Davydov, A.D. Effect of self-passivation on the electrochemical and corrosion behaviour of alloy C-22 in NaCl solutions. Corros. Sci. 2012, 54, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, M.M.; James, J.S.; Lu, Q. Erosion–corrosion of chromium steel in a rotating cylinder electrode system: Some comments on particle size effects. Wear 2004, 256, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, M.M.; Pungwiwat, N. Erosion–corrosion mapping of Fe in aqueous slurries: Some views on a new rationale for defining the erosion–corrosion interaction. Wear 2004, 256, 565–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourbaix, M. Atlas of Electrocemical Equilibria in Aqueous Solutions, 2nd ed.; National Association of Corrosion Engineers: Houston, TX, USA, 1974; pp. 256–271. [Google Scholar]





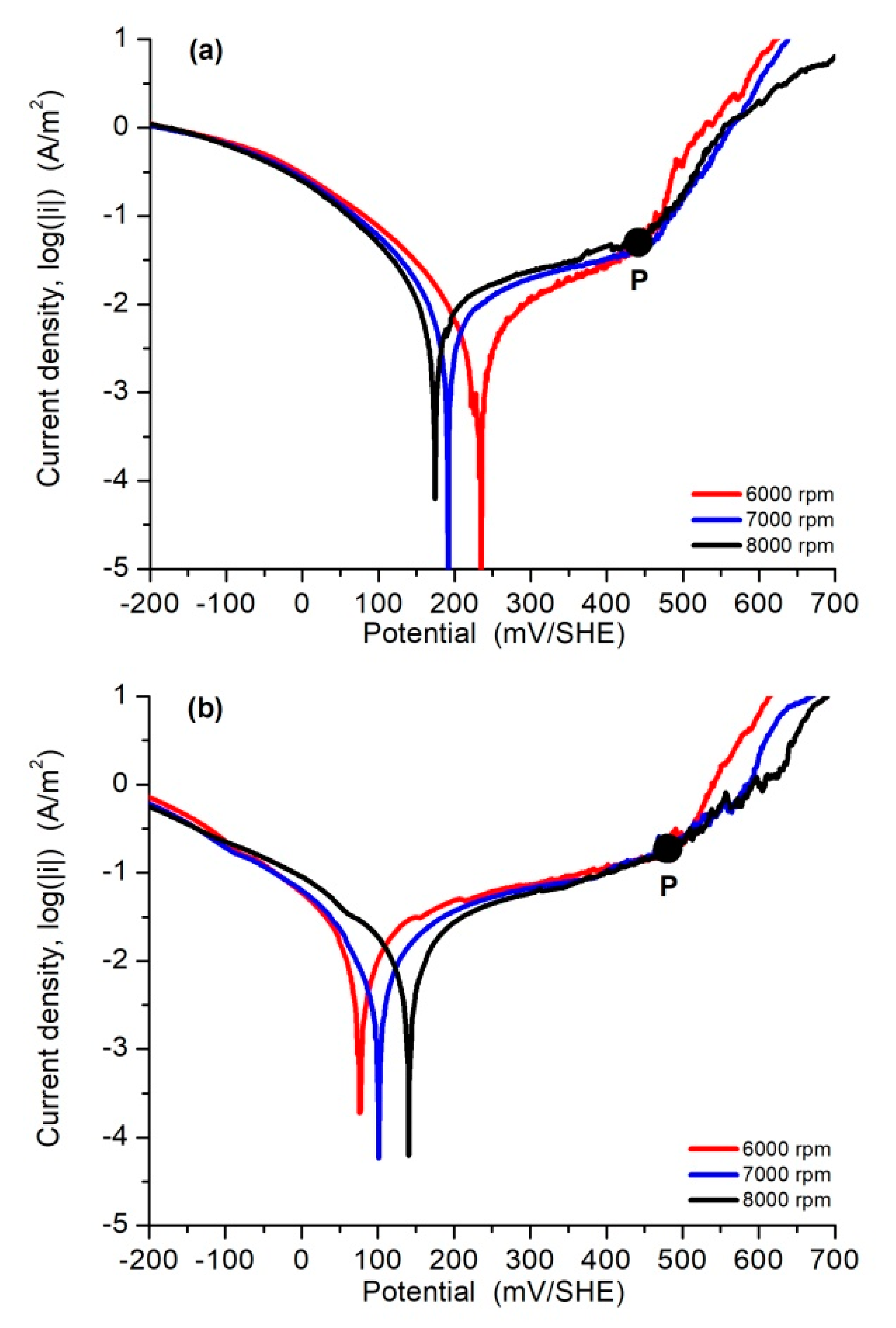

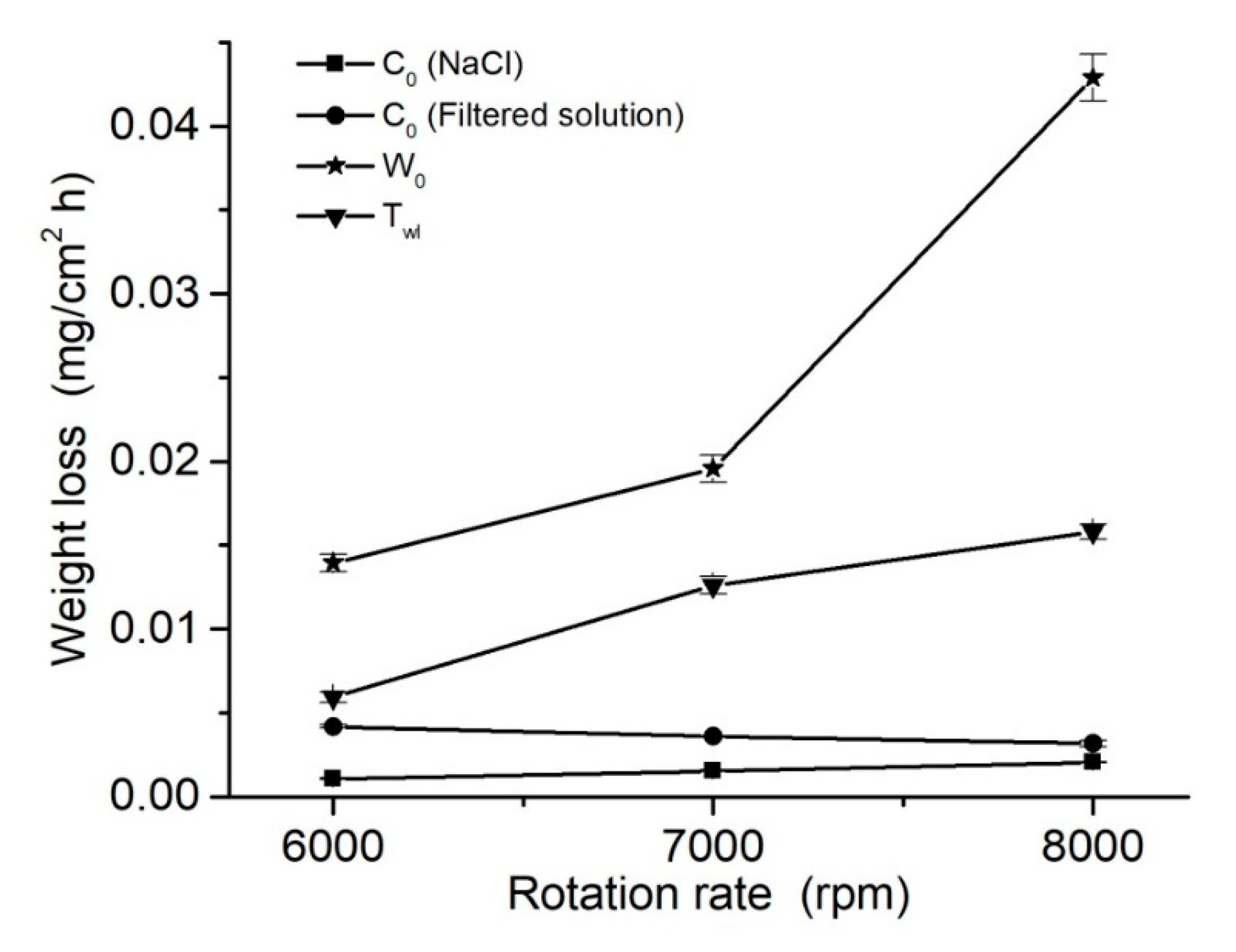



| 0.5 M NaCl | |||||||||||
| Rotation Rate | Iron Oxidation | Oxygen Reduction | Pitting Corrosion | Corrosion and Pitting Parameters | |||||||
| w, rpm | i0,Fe, A/m2 | bFe, mV/dec | i0,O2, A/m2 | bO2, mV/dec | i0,pit, A/m2 | bpit, mV/dec | Epit, mV/SHE | Ecorr, mV/SHE | Epit-Ecorr, mV/SHE | icorr, A/m2 | C0, mg/cm2∙h |
| 6000 | 5.1 × 10−5 | 372 | −8.6 × 10−7 | −146 | 2.9 × 10−20 | 59 | 437 | 227 | 210 | 0.010 | 1.07 × 10−3 |
| 7000 | 5.4 × 10−4 | 566 | −7.1 × 10−7 | −146 | 9.7 × 10−21 | 59 | 439 | 191 | 248 | 0.015 | 1.54 × 10−3 |
| 8000 | 1.4 × 10−3 | 694 | −6.8 × 10−7 | −146 | 1.7 × 10−20 | 59 | 427 | 173 | 254 | 0.020 | 2.05 × 10−3 |
| Average | 6.7 × 10−4 | 544 | −7.5 × 10−7 | −146 | 1.9 × 10−20 | 59 | 363 | 197 | 237 | 0.015 | 1.56 × 10−3 |
| Filtrate Solution | |||||||||||
| Rotation Rate | Iron Oxidation | Oxygen Reduction | Pitting Corrosion | Corrosion and Pitting Parameters | |||||||
| w, rpm | i0,Fe, A/m2 | bFe, mV/dec | i0,O2, A/m2 | bO2, mV/dec | i0,pit, A/m2 | bpit, mV/dec | Epit, mV/SHE | Ecorr, mV/SHE | Epit-Ecorr, mV/SHE | icorr, A/m2 | C0, mg/cm2∙h |
| 6000 | 2.9 × 10−3 | 614 | −4.7 × 10−5 | −224 | 6.6 × 10−19 | 64 | 479 | 75 | 404 | 0.040 | 4.19 × 10−3 |
| 7000 | 1.2 × 10−3 | 489 | −7.6 × 10−5 | −238 | 1.9 × 10−18 | 68 | 497 | 100 | 397 | 0.035 | 3.60 × 10−3 |
| 8000 | 8.3 × 10−4 | 482 | −1.7 × 10−4 | −265 | 3.4 × 10−17 | 74 | 500 | 141 | 359 | 0.030 | 3.16 × 10−3 |
| Average | 1.6 × 10−3 | 528 | −9.7 × 10−5 | −242 | 1.2 × 10−17 | 69 | 492 | 105 | 387 | 0.035 | 4.65 × 10−3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soliz, Á.; Cáceres, L.; Pineda, F.; Galleguillos, F. Erosion–Corrosion of AISI 304L Stainless Steel Affected by Industrial Copper Tailings. Metals 2020, 10, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081005
Soliz Á, Cáceres L, Pineda F, Galleguillos F. Erosion–Corrosion of AISI 304L Stainless Steel Affected by Industrial Copper Tailings. Metals. 2020; 10(8):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081005
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoliz, Álvaro, Luis Cáceres, Fabiola Pineda, and Felipe Galleguillos. 2020. "Erosion–Corrosion of AISI 304L Stainless Steel Affected by Industrial Copper Tailings" Metals 10, no. 8: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081005
APA StyleSoliz, Á., Cáceres, L., Pineda, F., & Galleguillos, F. (2020). Erosion–Corrosion of AISI 304L Stainless Steel Affected by Industrial Copper Tailings. Metals, 10(8), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/met10081005






