Removal of Copper, Nickel, and Iron from Lead–Tin Composite by Segregation of Intermetallic Silicon Phases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
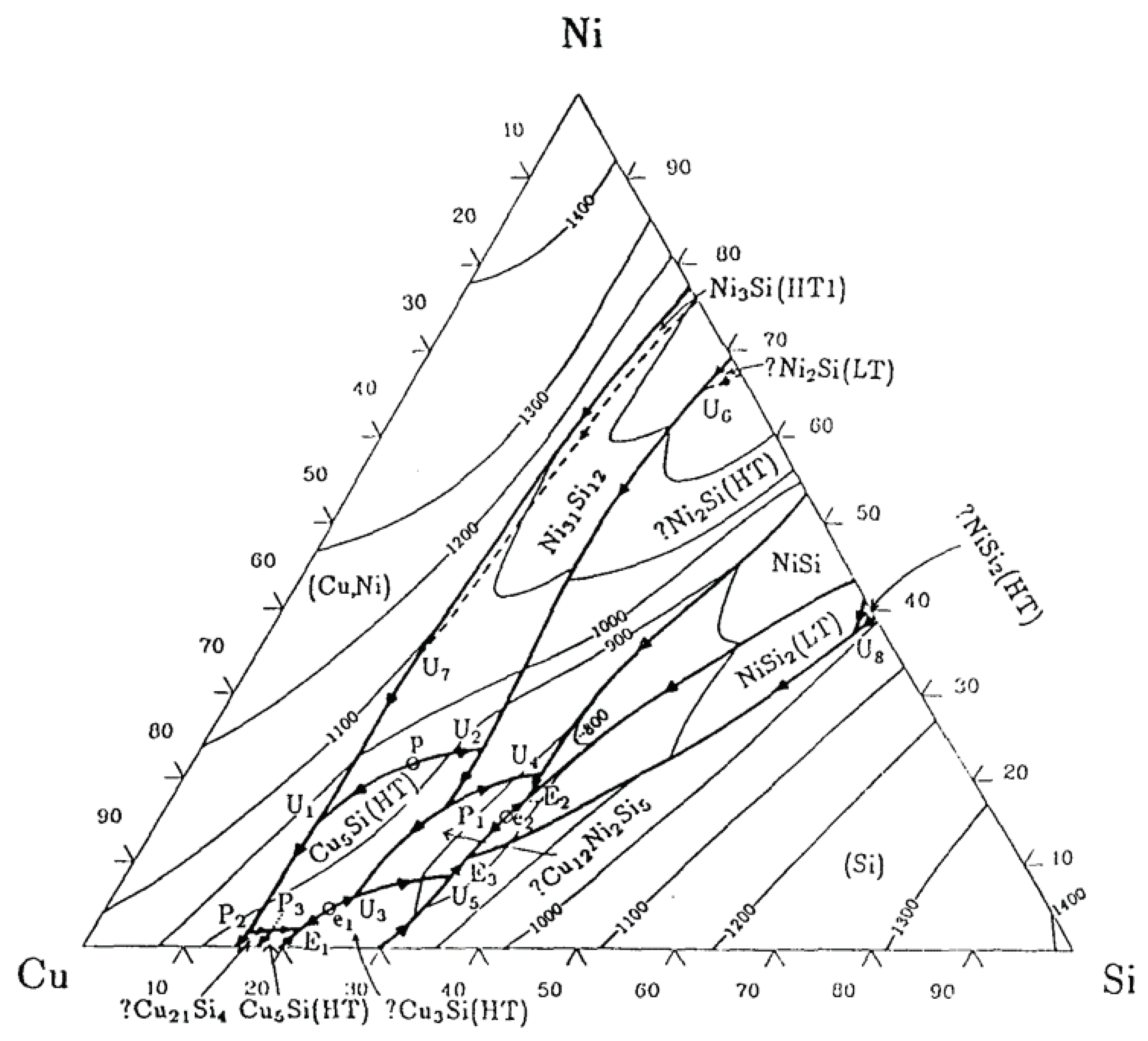
The Copper-Nickel-Silicon Three-Component System
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pilot Plant
2.2. Experimental Plan and Methodology
2.3. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Final Copper and Nickel Contents in PbSn-Composite
3.2. Quantity of Segregation and Silicide Product
3.3. Degree of Copper and Nickel Separation
3.4. Lead and Tin Losses in the Segregation Products
3.5. Experiments with Two-Stage Process Control
3.6. Metallographic Examination on the Phase Formation in the Silicide Product
- Primarily solidification of NiSi or NiSi (dark large crystals) occurs. Within NiSi copper is obviously integrated.
- After nickel depletion, solidification of CuSi or CuNiSi (light gray phase between the dark large crystals) occurs.
- The light gray phase is not homogeneous and shows white precipitates. These consist of tin or CuSn. It is to be assumed that they will react accordingly via secondary reactions:
- Only in the contact area of PbSn composite–silicides small amounts of lead are detected in addition to tin and copper. These are PbSn composite adhesions.
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schlesinger, M.E.; King, M.J.; Sole, K.C.; Davenport, W.G. Chapter 19—Chemical Metallurgy of Copper Recycling. In Extractive Metallurgy of Copper, 5th ed.; Schlesinger, M.E., King, M.J., Sole, K.C., Davenport, W.G., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 389–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Th. Goldschmidt AG. Verfahren zur Ausscheidung Einzelner Metalle aus Metallgemischen. Patent Nr. 423245, 1 March 1921. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, A.; Toubartz, F.; Friedrich, B. Cu-Pb-Fe-S-Balances in Cu during Lead Refining; European Metallurgical Conference (EMC); GDMB Gesellschaft für Bergbau, Metallurgie, Rohstoff- und Umwelttechnik: Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, S.; Srikanth, S. The Cu-Pb-Sn (copper-lead-tin) system. J. Phase Equilibria 1994, 15, 553–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcotte, V.C.; Schroder, K. Cu-Pb-Sn Ternary System: Low Cu Additions to Pb-Sn- Binary System. MRS Online Proceedings Library Archive, Volume 19: Symposium E—Alloy Phase Diagrams; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1982; p. 403. [Google Scholar]
- Lavoie, C.; Cabral, C.; D’Heurle, F.M.; Jordan-Sweet, J.L.; Harper, J.M. Effects of alloying elements on cobalt silicide formation. J. Electron. Mater. 2002, 31, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottaviani, G. Metallic Silicides; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Geneva, Switzerland, 1999; pp. 138–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kroll, W. Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Metalltrennung. Metall Erz 1938, 35, 252–254, 282–286. [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa, A.; Itagaki, K.; Matsuda, K.; Kanazawa, K.; Hayashi, M.; Katada, K. Method for Separation Cobalt, Nickel and the Like from Alloys. U.S. Patent No. 4657585A, 14 April 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki, K.; Kanazawa, K.; Hayashi, M.; Matsuda, K.; Yazawa, A. Fundamental study on the recovery of cobalt and nickel from iron-based molten alloys by using metal solvents. In Recycle and Secondary Recovery of Metals; Taylor, H.Y., Sohn, N.J., Eds.; TMS AIME: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kubaschewski, O.; Evans, E.L.; Alcock, C. Metallurgical Thermochemistry, 5th ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK; London, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Kubaschewski, O.; Alcock, C.; Spencer, P. Materials Thermochemistry, 6th ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK; New York, NY, USA; Seoul, Korea; Tokyo, Japan, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Villars, P.; Prince, A.; Okamoto, H. Handbook of Ternary Alloy Phase Diagrams, Volume 8; ASM International; The Materials Information Society: Geauga County, OH, USA, 1995; pp. 9806–9818. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.C.H.; Kussmaul, A.; Lukas, H.L.; Effenberg, G. Cu-Ni-Si (Copper-Nickel-Silicon): Datasheet from Landolt-Börnstein—Group IV Physical Chemistry; Volume 11C2: “Non-Ferrous Metal Systems. Part 2”; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Removal of Cobalt and Nickel from a Lead-Tin Melt by Adding Silicon at 1250 C | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-Sn Ratio of the Initial Melt | Separated Fe-Si Phase | Distribution Coefficient Si Phase/Pb Phase | ||||||
| Pb [%] | Sn [%] | Fe [%] | Si [%] | Co [%] | Ni [%] | L | L | L |
| 75 | 25 | 71.4 | 18.1 | 4.5 | 5.06 | 1670 | 80 | 3330 |
| 50 | 50 | 72.1 | 17.4 | 4.96 | 4.53 | 430 | 24 | 770 |
| 25 | 75 | 72.7 | 17.4 | 5.60 | 2.36 | 95 | 15 | 630 |
| Effect of Silicon Addition When Removing Nickel from a Lead or Lead-Tin Melt at 1250 C | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Pb-Sn-Phase | Ni-Si-Phase | Distribution Coefficient | |
| Ni [%] | Si [%] | L | |
| 100% Pb | 87.1 | 12.9 | 63 |
| 69.8 | 30.2 | 2700 | |
| 50.0 | 50.0 | 100,000 | |
| 50% Pb–50% Sn | 87.0 | 13.0 | 12 |
| 69.7 | 30.3 | 400 | |
| 49.4 | 50.6 | 1180 | |
| Series | Si-Content [%] | Temperature End of Segregation [C] | Cooling Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0 | 650 | ∼5 C/min |
| II | 17.5–40 | 650 | ∼5 C/min |
| III | 25 | 600, 650, 750 | ∼5 C/min |
| IV | 25 | 650 | ∼5 C/min |
| ∼5 C/min with ∼30 min holding at 800 C | |||
| ∼10 C/min | |||
| V | 25 (9/16) | 650 | ∼5 C/min |
| 25 (9/16) | 900/650 | ∼5 C/min | |
| VI | 17.5–37.5 FeSi | 650 | ∼5 C/min |
| Element | Pb | Sn | Cu | Ni | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [%] | 1.21 | 8.80 | 51.10 | 21.00 | 19.10 |
| Group | Picture/Nr. | [wt.%] | Area Percentage [%] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pb | Sn | Cu | Ni | Si | |||
| 1 | f □/1 | - | - | 9.33 | 50.89 | 39.78 | ∼45.8 |
| e /1 | - | - | 7.15 | 52.08 | 40.76 | ||
| b /1 | - | - | 6.59 | 52.66 | 40.76 | ||
| b □/2 | - | - | 8.64 | 50.30 | 41.06 | ||
| Average | - | - | 7.93 | 51.48 | 40.59 | ||
| 2 | f □/4 | - | 1.50 | 86.02 | 2.64 | 9.85 | ∼49.5 |
| b □/1 | - | - | 88.20 | 1.62 | 10.18 | ||
| a □/2 | - | 2.17 | 85.55 | 2.65 | 9.63 | ||
| a □/TF | - | - | 84.02 | 5.85 | 10.13 | ||
| Average | - | 0.92 | 85.95 | 3.19 | 9.95 | ||
| 3 | f □/3 | - | - | 73.09 | 14.52 | 12.38 | |
| b □/TF | - | 1.16 | 73.46 | 13.69 | 11.69 | ||
| Average | - | 0.58 | 73.28 | 14.11 | 12.04 | ||
| 4 | b /2 | - | 98.82 | 1.18 | - | - | ∼4.4 |
| a □/4 | - | 98.49 | 1.51 | - | - | ||
| Average | - | 98.66 | 1.35 | - | - | ||
| 5 | f □/5 | - | 61.25 | 37.88 | 0.87 | - | <0.1 |
| a □/3 | - | 61.27 | 38.73 | - | - | ||
| Average | - | 61.26 | 38.31 | 0.44 | - | ||
| 6 | a □/1 | - | - | - | 70.62 | 29.38 | <0.1 |
| 7 | f □/2 | 3.48 | 94.15 | 2.37 | - | - | <0.1 |
| Group | Pb | Sn | Cu | Ni | Si | Known Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | 1 | 7 | 12 | NiSi |
| 2 | - | - | 25 | 1 | 7 | CuSi |
| 3 | - | - | 5 | 1 | 2 | CuNiSi |
| 4 | - | 39 | 1 | - | - | Sn |
| 5 | - | 1 | 1 | - | - | SnCu (h-Phase) |
| 6 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 | NiSi |
| 7 | 1 | 47 | 2 | - | - | Sn |
| Pb [%] | Sn [%] | Cu [%] | Ni [%] | Fe [%] | Si [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw PbSn composite | 63–68 | 34–36 | ∼11 | ∼2.5 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PbSn composite | 62–66 | 30–33 | 3.5–6 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| Silicide product | <2 | 6–7 | 50–60 | 20–25 | <7 | 15–18 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jessen, S.; C. Curtolo, D.; Friedrich, B. Removal of Copper, Nickel, and Iron from Lead–Tin Composite by Segregation of Intermetallic Silicon Phases. Metals 2021, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010081
Jessen S, C. Curtolo D, Friedrich B. Removal of Copper, Nickel, and Iron from Lead–Tin Composite by Segregation of Intermetallic Silicon Phases. Metals. 2021; 11(1):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010081
Chicago/Turabian StyleJessen, Stefan, Danilo C. Curtolo, and Bernd Friedrich. 2021. "Removal of Copper, Nickel, and Iron from Lead–Tin Composite by Segregation of Intermetallic Silicon Phases" Metals 11, no. 1: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010081
APA StyleJessen, S., C. Curtolo, D., & Friedrich, B. (2021). Removal of Copper, Nickel, and Iron from Lead–Tin Composite by Segregation of Intermetallic Silicon Phases. Metals, 11(1), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11010081







