Design and Multidimensional Screening of Flash-PEO Coatings for Mg in Comparison to Commercial Chromium(VI) Conversion Coating
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PEO Coatings Fabrication
2.2. Coating Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Electrical Response of Flash-PEO
3.2. FPEO and CCC Performance under Corrosive Media
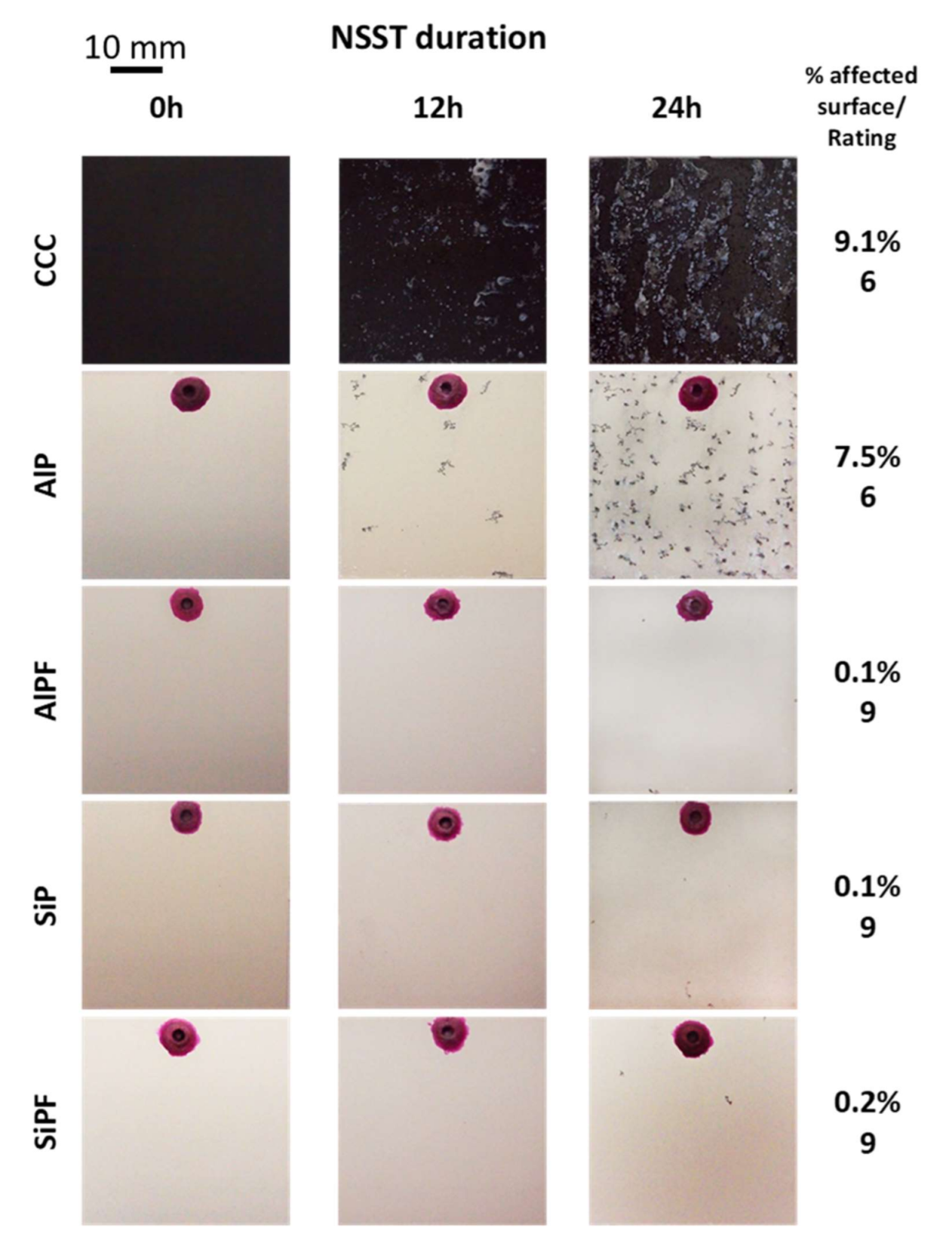
3.3. NSST of Unpainted and Painted Scratched Coatings
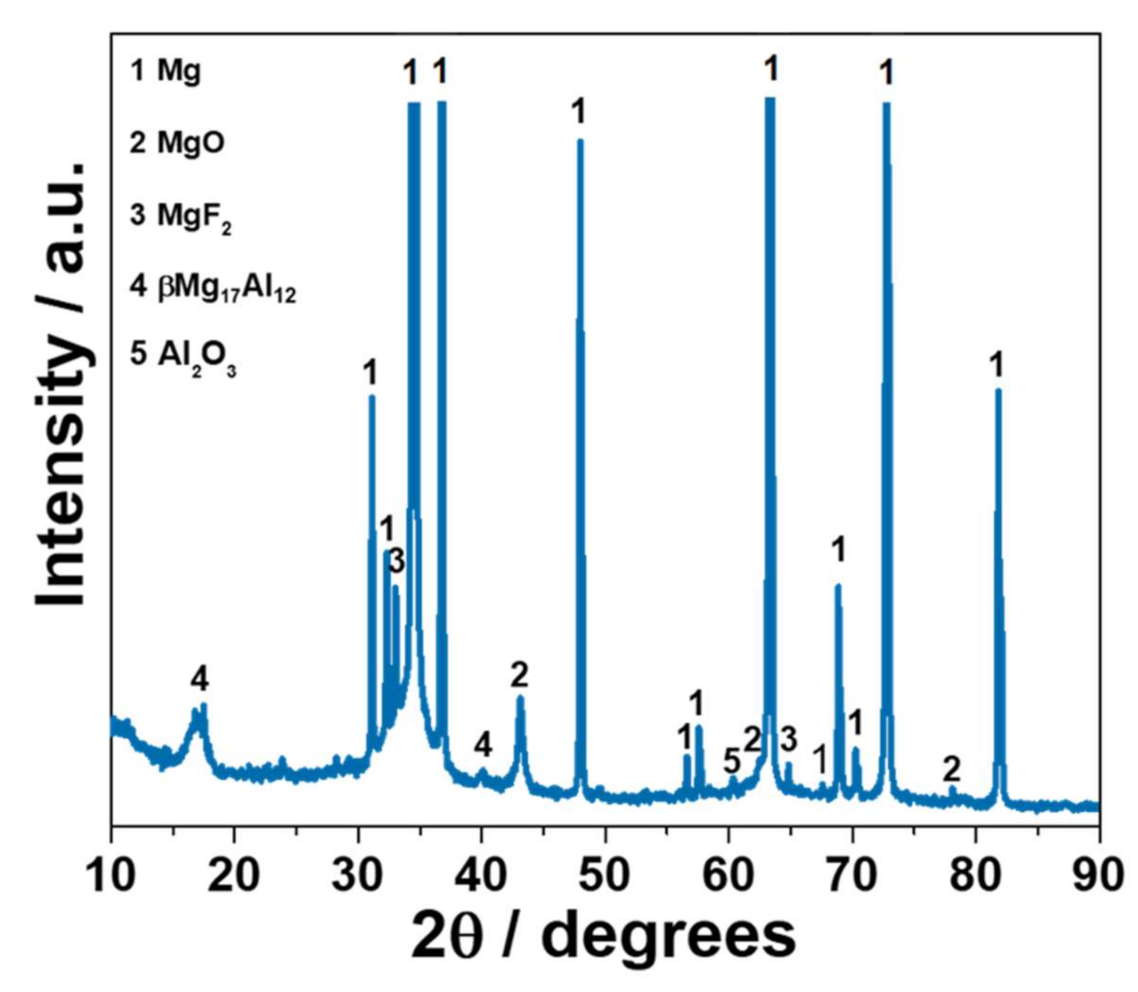
3.4. AlPF Coating Composition
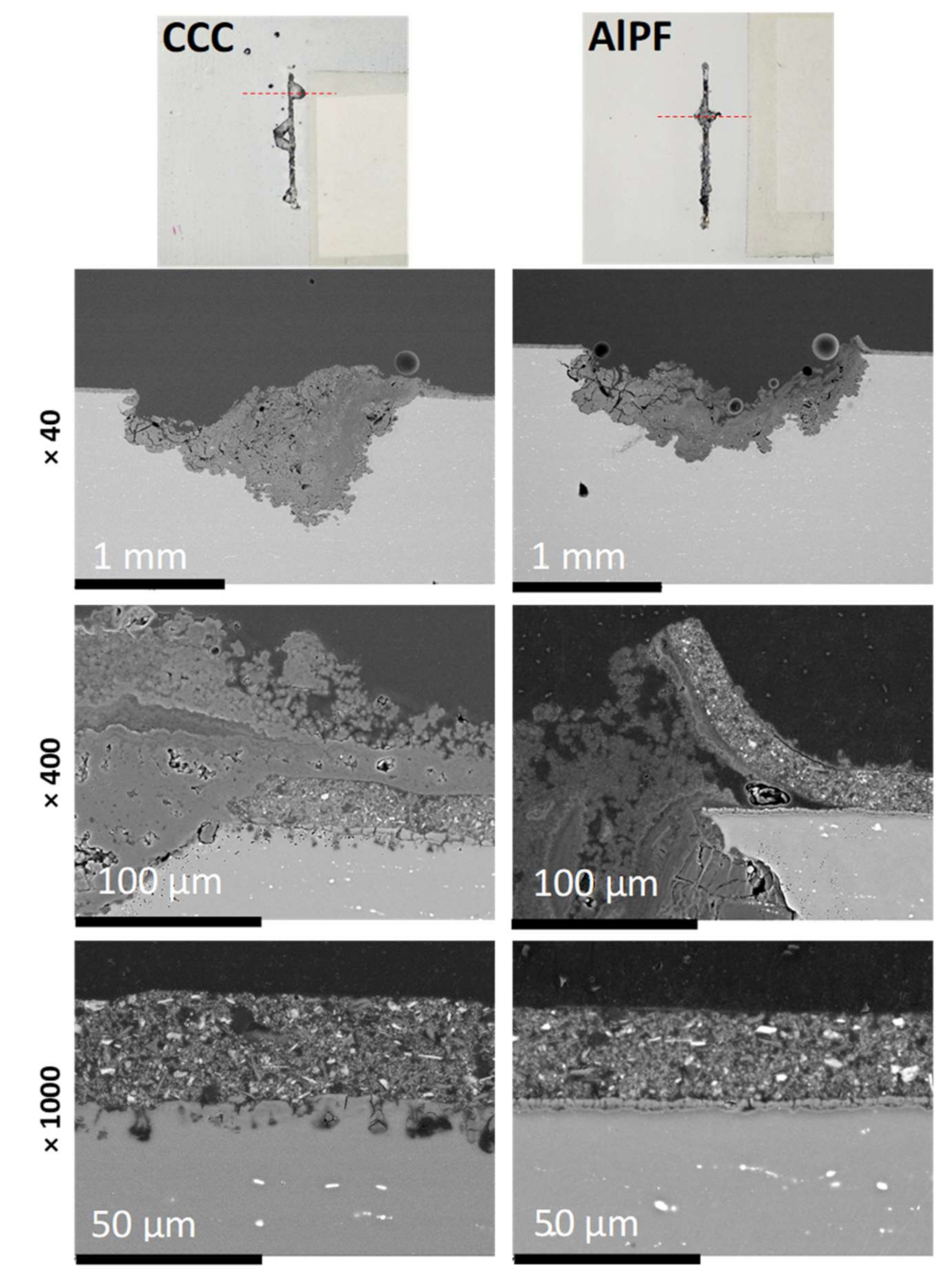
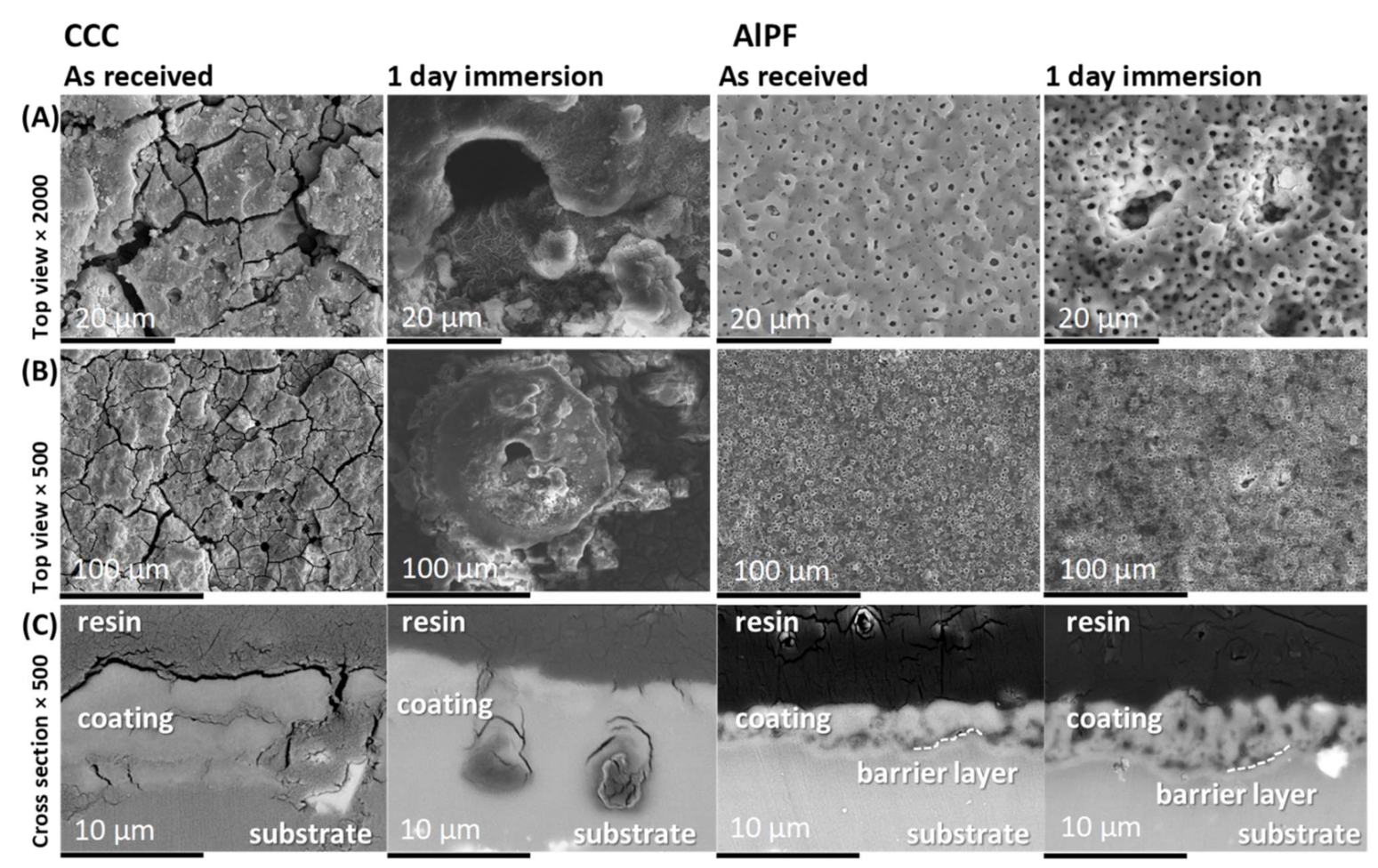
3.5. Corrosion Damage Morphology
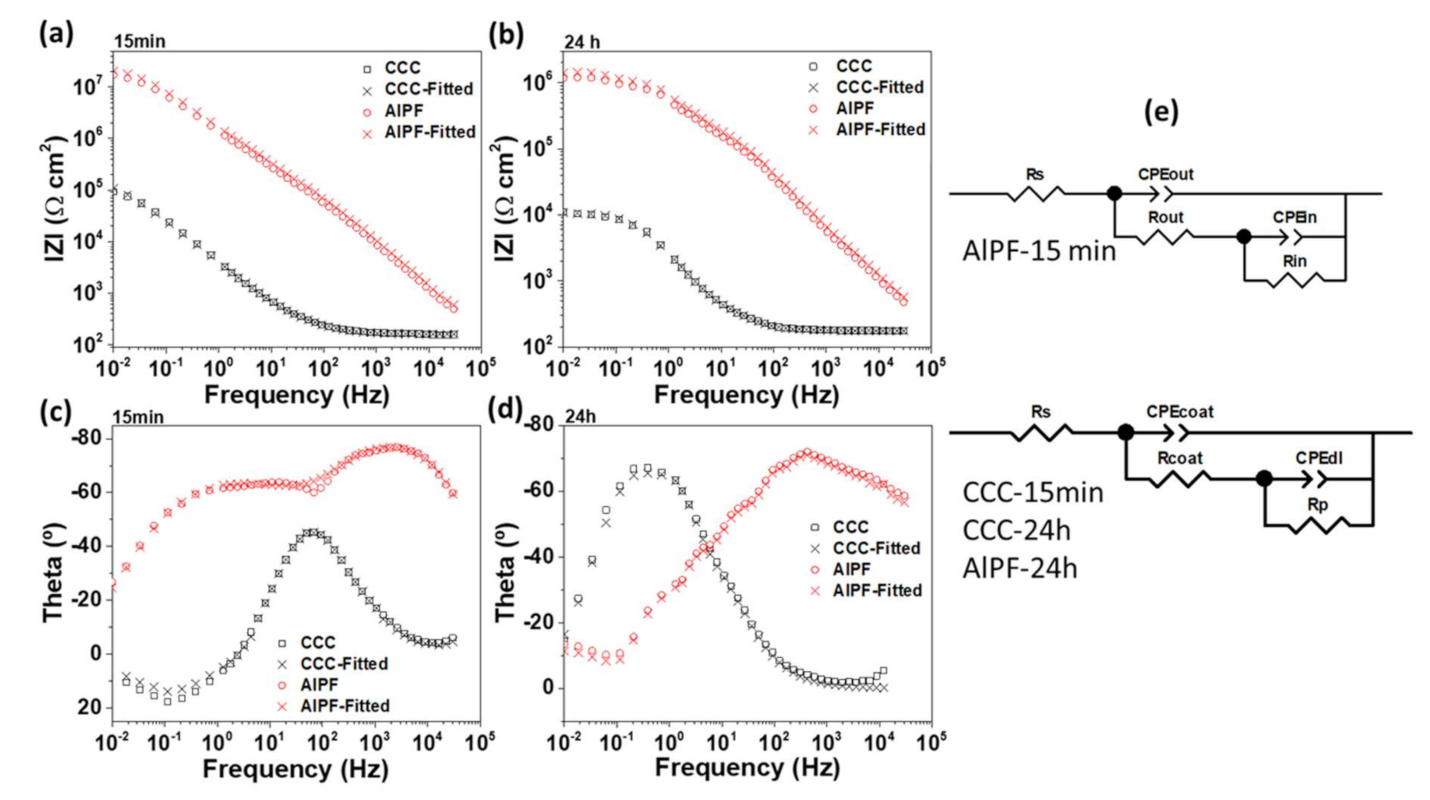
3.6. Electrochemical Impedance Response of Selected Coatings
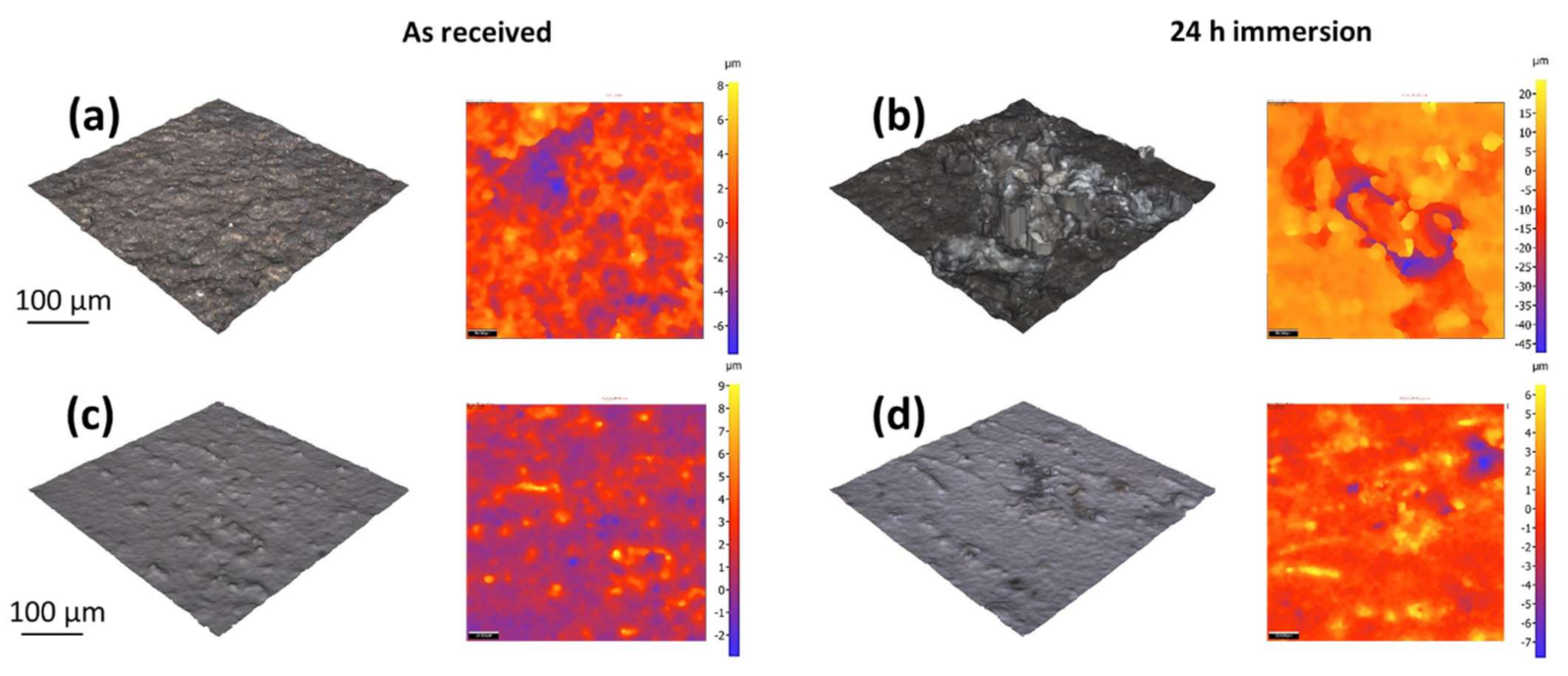
3.7. Optical Profilometry Micrographs and Surface Roughness
3.8. Dry and Wet Paint Adhesion
4. Conclusions
- DC flash-PEO coatings were successfully developed for AZ31B Mg alloy employing design of the electrolyte composition and implementing current density and voltage limits.
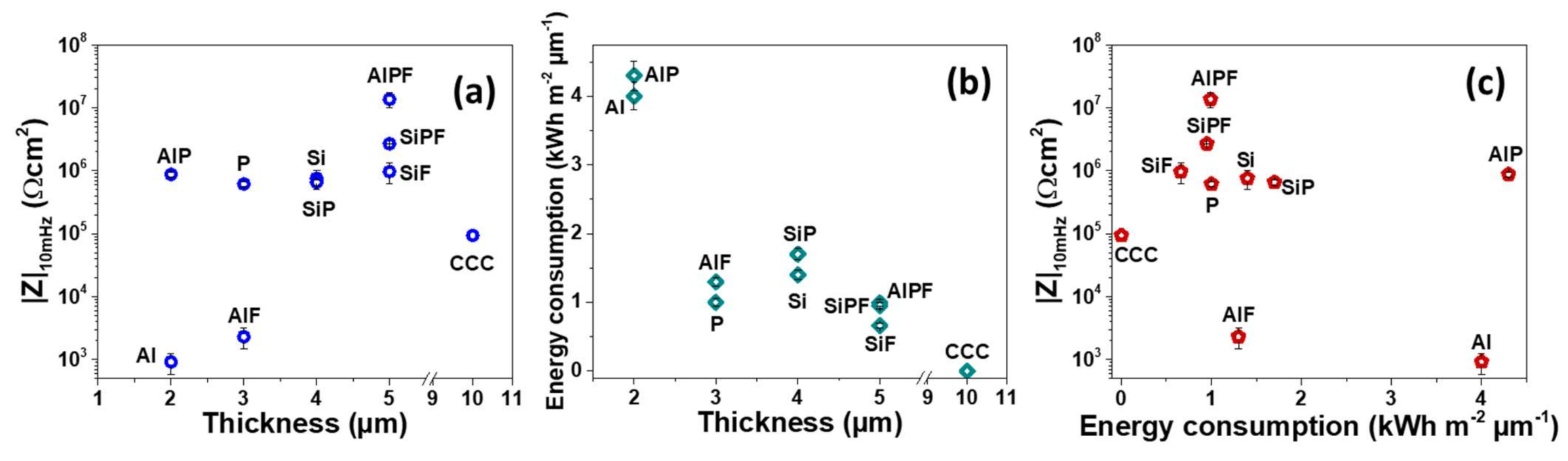
- The energy consumption of the PEO processes remained relatively low, ~1 kW h m−2 µm−1 for SiPF and AlPF, which makes only 5 kW h m−2 of energy required to produce the overall 5 µm-thick coatings.
- A correlation between the energy consumption of the FPEO process and corrosion resistance was found, demonstrating that the lower the energy consumption of the respective FPEO process, the better corrosion resistance of the resulted coating.
- The preliminary EIS screening of anticorrosion properties of the FPEO coatings had an adequate and reliable correlation with NSST results for both painted and non-painted samples.
- The overall evaluation of the coatings’ corrosion protection (EIS, NSST, paintability) confirmed that two FPEO coatings (SiPF and AlPF) can be an adequate substitute for CCC.
- Implementation of PEO coatings’ protection is still pending the economic justification of the use of a current-consuming process instead of an electroless one. It is necessary to draw attention to the fact that a green solution may never be as cheap as current harmful technologies but can offer competitive advantages in terms of corrosion protection.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A.; Dowey, S.J. Plasma electrolysis for surface engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, R.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Li, D.; Guo, C.; Jiang, G.; Yu, S.; et al. Evolution processes of the corrosion behavior and structural characteristics of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on AZ31 magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 434, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankara Narayanan, T.S.N.; Park, I.S.; Lee, M.H. Strategies to improve the corrosion resistance of microarc oxidation (MAO) coated magnesium alloys for degradable implants: Prospects and challenges. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 60, 1–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Ghali, E.; Song, G. Anodizing treatments for magnesium alloys and their effect on corrosion resistance in various environments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.W. A Review of Magnesium/Magnesium Alloys Corrosion and its Protection. Recent Patents Corros. Sci. 2010, 2, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati Darband, G.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Hamghalam, P.; Valizade, N. Plasma electrolytic oxidation of magnesium and its alloys: Mechanism, properties and applications. J. Magnes. Alloy. 2017, 5, 74–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, G.H.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.Q.; Pang, H.; Zhang, G.L.; Zou, B.; Lee, H.J.; Yang, S.Z. Effect of additives on structure and corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloy in phosphate based electrolyte. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, S36–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Nie, X.; Northwood, D.O.; Hu, H. Systematic study of the electrolytic plasma oxidation process on a Mg alloy for corrosion protection. Thin Solid Films 2006, 494, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Ahn, B.H.; Jeong, Y.S.; Song, J.I.; Koo, B.H. The influence of various additives on the properties of PEO coatings formed on AZ31 Mg Alloy. Surf. Rev. Lett. 2016, 23, 1650006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.F.; An, M.Z. Growth of ceramic coatings on AZ91D magnesium alloys by micro-arc oxidation in aluminate-fluoride solutions and evaluation of corrosion resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2005, 246, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Peng, J. Effect of potassium fluoride on structure and corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation films formed on AZ31 magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 480, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazanski, B.; Kossenko, A.; Zinigrad, M.; Lugovskoy, A. Fluoride ions as modifiers of the oxide layer produced by plasma electrolytic oxidation on AZ91D magnesium alloy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 287, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, W.; Han, Y. Characterization and properties of the MgF2/ZrO2 composite coatings on magnesium prepared by micro-arc oxidation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 4278–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sah, S.P.; Aoki, Y.; Habazaki, H. Influence of phosphate concentration on plasma electrolytic oxidation of AZ80 magnesium alloy in alkaline aluminate solution. Mater. Trans. 2010, 51, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Raja, V.S.; Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K.U. The role of anions in the formation and corrosion resistance of the plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Huang, Z.; He, D.; Yan, Q.; Liu, P.; Nash, P.; Shen, D. An investigation of (NaPO3)6 effects and mechanisms during micro-arc oxidation of AZ31 magnesium alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 266, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Cai, Q.; Wei, B.; Yu, B.; Li, D.; He, J.; Liu, Z. Effect of (NaPO3)6 concentrations on corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings formed on AZ91D magnesium alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 464, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzima, B.; Kajánek, D.; Jambor, M.; Drábiková, J.; Březina, M.; Buhagiar, J.; Pastorková, J.; Jacková, M. Peo of az31 mg alloy: Effect of electrolyte phosphate content and current density. Metals 2020, 10, 1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Koshi, A.; Liao, J.; Asoh, H.; Ono, S. Characteristics and corrosion resistance of plasma electrolytic oxidation coatings on AZ31B Mg alloy formed in phosphate—Silicate mixture electrolytes. Corros. Sci. 2014, 88, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Prasad, S.; Scharnagl, N.; Störmer, M.; Starykevich, M.; Mohedano, M.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ulrich, K. Degradation behavior of PEO coating on AM50 magnesium alloy produced from electrolytes with clay particle addition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 269, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Vranescu, D.; Sinico, M.; Gennari, C.; Settimi, A.G.; Pranovi, P.; Brunelli, K.; Dabalà, M. Tribocorrosion properties of PEO Coatings produced on AZ91 magnesium alloy with silicate- or phosphate-based electrolytes. Coatings 2018, 8, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulabifard, A.; Rahmati, M.; Raeissi, K.; Hakimizad, A.; Santamaria, M. The effect of electrolytic solution composition on the structure, corrosion, and wear resistance of peo coatings on az31 magnesium alloy. Coatings 2020, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Pillado, B.; Mohedano, M.; Arrabal, R.; Matykina, E. Calcium doped flash-peo coatings for corrosion protection of Mg alloy. Metals 2020, 10, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicka, E.; Vaghefinazari, B.; Lamaka, S.V.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Mohedano, M. Flash-PEO as an alternative to chromate conversion coatings for corrosion protection of Mg alloy. Corros. Sci. 2021, 180, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
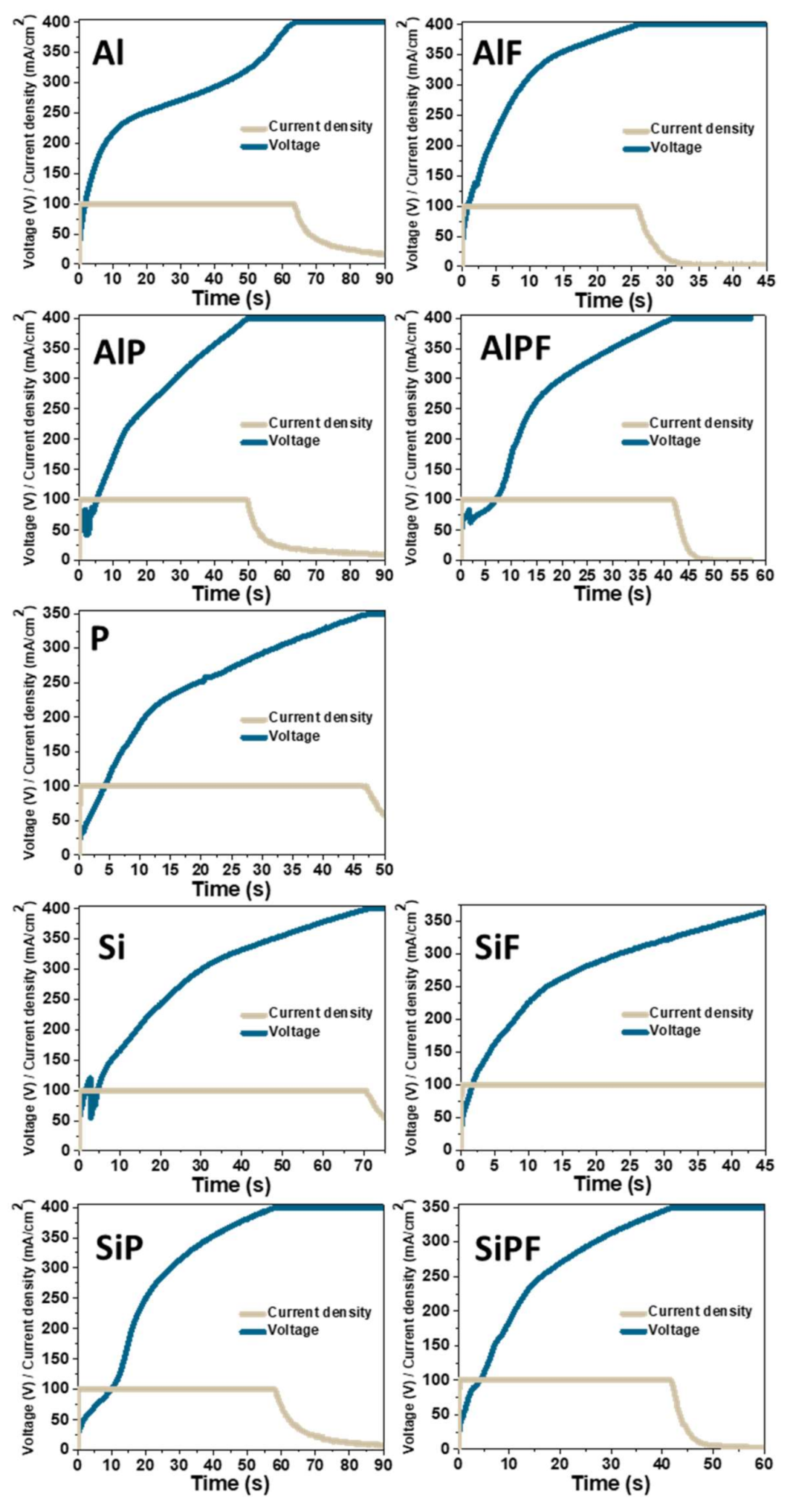

| Coating | Electrolyte | PEO Process Parameters | Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | 7.5 g/L NaAlO2 + 1 g/L KOH | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 400 V, 90 s | 2 ± 0.82 |
| AlF | 7.5 g/L NaAlO2 + 1 g/L KOH + 3 g/L KF | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 400 V, 45 s | 3 ± 0.79 |
| AlP | 4 g/L NaAlO2 + 5 g/L Na3PO4 × 12H2O + 1.5 g/L KOH | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 400 V, 90 s | 2 ± 1.2 |
| AlPF | 4 g/L NaAlO2 + 5 g/L Na3PO4 × 12H2O + 1.5 g/L KOH + 3 g/L KF | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 400 V, 60 s | 5 ± 0.64 |
| P | 10 g/L Na3PO4 × 12 H2O + 2.8 g/L KOH | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 350 V, 50 s | 3 ± 0.97 |
| Si | 10 g/L Na2SiO3 × 5H2O + 2.8 g/L KOH | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 400 V, 75 s | 4 ± 0.98 |
| SiF | 10 g/L Na2SiO3 × 5H2O + 2.8 g/L KOH + 3 g/L KF | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 350 V, 45 s | 5 ± 1.6 |
| SiP | 5 g/L Na2SiO3 × 5H2O + 5 g/L Na3PO4 × 12H2O + 2.8 g/L KOH | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 400 V, 90 s | 4 ± 0.48 |
| SiPF | 5 g/L Na2SiO3 × 5H2O + 5 g/L Na3PO4 × 12H2O + 2.8 g/L KOH + 3 g/L KF | DC, 100 mA/cm2, Efin = 350 V, 60 s | 5 ± 0.64 |
| Coating | Rs | CPEout | CPE-n | Rout | CPEin | CPE-n | Rin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AlPF-15 min | 184.2 | 4.04 × 10−8 | 0.90 | 1.11 × 105 | 1.47 × 10−7 | 0.67 | 2.61 × 107 |
| Coating | Rs | CPEcoat | CPE-n | Rcoat | CPEdl | CPE-n | Rp |
| AlPF-24 h | 139.1 | 1.61 × 10−7 | 0.79 | 2.81 × 105 | 1.54 × 10−6 | 0.59 | 9.79 × 105 |
| CCC-15 min | 163.7 | 5.77 × 10−5 | 0.78 | 2.01 × 105 | 7.22 × 10−7 | 0.98 | 12,024 |
| CCC-24 h | 176.4 | 5.93 × 10−5 | 0.85 | 1200 | 1.40 × 10−5 | 0.96 | 9987 |
| Parameter | AlPF As-received | AlPF 24 h | CCC As-received | CCC 24 h | Description |
| Sa, µm | 0.819 | 1.035 | 1.586 | 7.102 | Average height of selected area |
| Sq, µm | 1.127 | 1.473 | 1.964 | 9.45 | Root-Mean-Square height of selected area |
| Sp, µm | 7.898 | 6.452 | 8.282 | 23.259 | Maximum peak height of selected area |
| Sv, µm | 4.112 | 7.902 | 7.538 | 47.406 | Maximum valley depth of selected area |
| Sz, µm | 12.01 | 14.353 | 15.821 | 70.644 | Maximum height of selected area |
| S10z, µm | 10.47 | 13.077 | 12.060 | 67.070 | Ten-point height of selected area |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wierzbicka, E.; Mohedano, M.; Matykina, E.; Arrabal, R. Design and Multidimensional Screening of Flash-PEO Coatings for Mg in Comparison to Commercial Chromium(VI) Conversion Coating. Metals 2021, 11, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020337
Wierzbicka E, Mohedano M, Matykina E, Arrabal R. Design and Multidimensional Screening of Flash-PEO Coatings for Mg in Comparison to Commercial Chromium(VI) Conversion Coating. Metals. 2021; 11(2):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020337
Chicago/Turabian StyleWierzbicka, Ewa, Marta Mohedano, Endzhe Matykina, and Raul Arrabal. 2021. "Design and Multidimensional Screening of Flash-PEO Coatings for Mg in Comparison to Commercial Chromium(VI) Conversion Coating" Metals 11, no. 2: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020337
APA StyleWierzbicka, E., Mohedano, M., Matykina, E., & Arrabal, R. (2021). Design and Multidimensional Screening of Flash-PEO Coatings for Mg in Comparison to Commercial Chromium(VI) Conversion Coating. Metals, 11(2), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11020337








