Abstract
In this paper, we started from the composition-dependent interdiffusion coefficients with quantified uncertainties in binary alloys by integrating the Matano-based method, distribution functions, and uncertainty propagation approach. After carefully defining the numerically stable region for the interdiffusion coefficients, the suitable pre-set functions were screened to achieve the reasonable fit to the D-c and μ-c data according to the Akaike information criterion. With the fitted D-c and μ-c curves, the impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties can be directly determined. Benchmark tests in five hypothetical binary systems with different preset D-c relations were then utilized to validate the presently effective approach, followed by practical applications in five real cases, i.e., fcc Ni-Co, fcc Cu-Al, fcc Pt-Ni, hcp Mg-Zn, and bcc Ti-V alloys. The impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties derived by the presently effective approach were found to be in excellent agreement with the data by tracer experiments, indicating that this effective approach can serve as a standard one for acquiring the high-quality impurity diffusion coefficients in binary alloys with quantified uncertainties, especially for the noble metals and the cases without suitable radioactive tracer isotopes.
1. Introduction
Accurate diffusion coefficients are necessities for understanding masses of materials preparation and service processes [1,2,3,4,5,6], such as solidification, precipitation, creep, oxidation, and so on. Among different types of diffusion coefficients, including self-, impurity, intrinsic, and chemical diffusion coefficients, the impurity diffusion coefficient, defined as the diffusion rate of a solute with an extremely low concentration in a solvent [7], might be the most important one. That is because the impurity diffusion coefficient is of both practical and theoretical interests. On one hand, the impurity diffusion coefficient serves as one of the important “building blocks” (i.e., end-members) for atomic mobility database of multi-component systems [8,9], from which various temperature-/concentration-dependent diffusion coefficients can be calculated in combination with the known thermodynamic factors. On the other hand, accurate impurity diffusion coefficients can be used to validate the theoretical calculations (e.g., first-principles calculations) [10,11], and then to help understanding the diffusion mechanisms.
Traditionally, radioactive isotope tracer diffusion experiments coupled with various sectioning techniques serve as the primary technique for measuring the impurity diffusion coefficient [12]. In principle, the impurity diffusion coefficients measured by the radioactive isotope tracer technique are regarded to be reliable. However, implementation of radioactive isotope tracer diffusion experiment is usually costly, especially for noble metals, i.e., Pt [13]. In some cases, the suitable radioactive tracer isotopes are absent, like Al [14]. Besides the experimental measurement, efforts on flourishing impurity diffusion information using density functional theory (DFT) based methods [10,11] in recent years are also extensive, but their reliability strongly depends on the known/assumed diffusion mechanisms, and always needs further experimental validation.
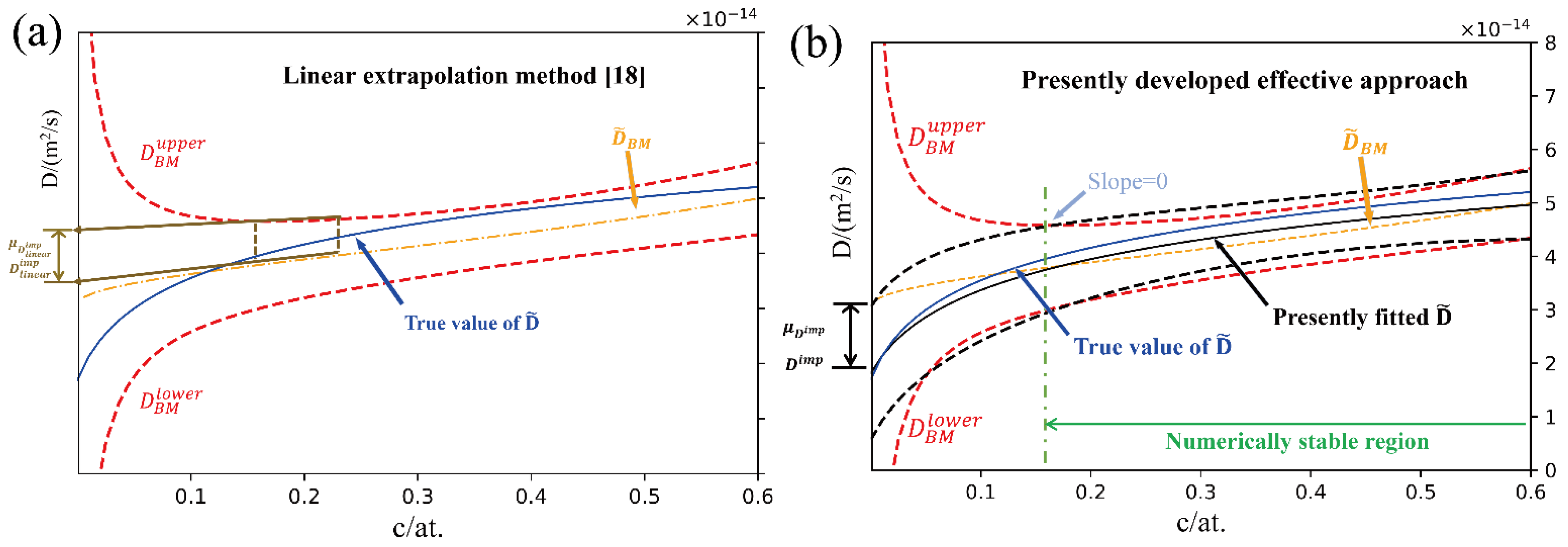
Despite of the straightforward methods mentioned above, several indirect approaches for estimation of impurity diffusion coefficients by extrapolating composition-dependent interdiffusion coefficients to the dilute region have also been proposed. Hall [15] assumed that the interdiffusion coefficients around the composition region of pure metal approach to a constant at arbitrarily defined narrow composition regions. The Hall’s method is effective when the interdiffusion coefficients at the ends of a diffusion couple are close to constant. For the systems with a strong/complex correlation between the diffusion coefficients and the compositions, the Hall’s method may lose its effectiveness. Zhao and his colleagues [16] developed a forward-simulation approach for binary alloys, in which the regression between the interdiffusion coefficients and the composition is performed, and the impurity diffusion coefficient is thus retrieved according to the regression function [17]. However, the potential options of regression functions between the interdiffusion coefficients and the composition are plentiful, which may heavily attribute reliability of the estimated impurity diffusion coefficients to expertise. Very recently, Wu et al. [18] from our research group developed a general approach to quantify the uncertainties of interdiffusion coefficients based on the Matano-based methods [19,20,21], which may result in numerically unstable regions for the evaluated interdiffusion coefficients at both ends of the diffusion couples, and thus limit the direct extrapolation to the impurity diffusion coefficients. In order to evaluate the corresponding impurity diffusion coefficients in binary system, Wu et al. [18] proposed a linear extrapolation treatment to get rid of the influence of the numerically unstable region, and determined the impurity diffusion coefficients together with quantified uncertainties in a binary fcc Co-Ni system, as schematically displayed in Figure 1a. It is quite clear that the determined impurity diffusion coefficients by means of such a linear extrapolation treatment is rather accurate when a linear correlation of D–c (at least over the investigated composition range) is roughly considered. However, the risk of obtaining the inaccurate impurity diffusion coefficients increases as the nonlinearity dominates the correlation between the interdiffusion coefficients and the composition.
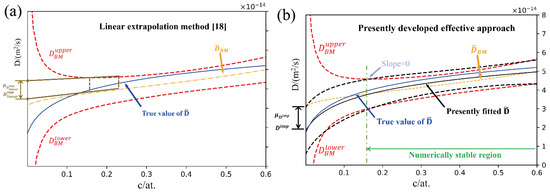
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram for acquiring the impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties in binary alloys: (a) linear extrapolation method [18]; (b) presently developed effective approach.
Consequently, such a linear extrapolation treatment is to be augmented in this paper into an effective approach for acquiring accurate impurity diffusion coefficients in binary alloys with quantified uncertainties. In this effective approach, the appropriate regression functions taking the quantified uncertainties of interdiffusion coefficients into consideration will be chosen to fit various types of interdiffusion coefficients/uncertainties of composition dependency over the numerical stable region. With the fitted regression functions of interdiffusion coefficients/uncertainties in binary alloys, the impurity diffusion coefficients with quantified uncertainties can be then determined by direct extrapolation into the end(s) of the diffusion couples.
Briefly, details of the proposed effective approach are firstly described. Benchmark tests are subsequently preformed to validate its reliability and applicable capacity, followed by its applications in several real binary alloys, including fcc Co-Ni, Cu-Al, Pt-Ni, hcp Mg-Zn, and bcc Ti-V alloys. Conclusions will be finally drawn.
2. Approach to Acquire the Impurity Diffusion Coefficients and Related Uncertainties in Binary Alloys
We start from the general relation between the interdiffusion coefficient and the impurity diffusion coefficient in a fictitious A-B binary system,
Based on above equation, the impurity diffusion coefficient can be obtained by directly taking the interdiffusion coefficient at the end of pure metal diffusion couples, i.e., the sides of pure A and/or B. However, the evaluated interdiffusion coefficients due to the Matano based methods usually have the numerical instability regions close to the ends of the diffusion couple as their uncertainties increases rapidly and tends to infinity (see Figure 1a). Thus, to acquire the reliable impurity diffusion coefficients from the interdiffusion coefficients in binary system, merely the interdiffusion coefficients and their related uncertainty over the numerical stable region can be utilized.
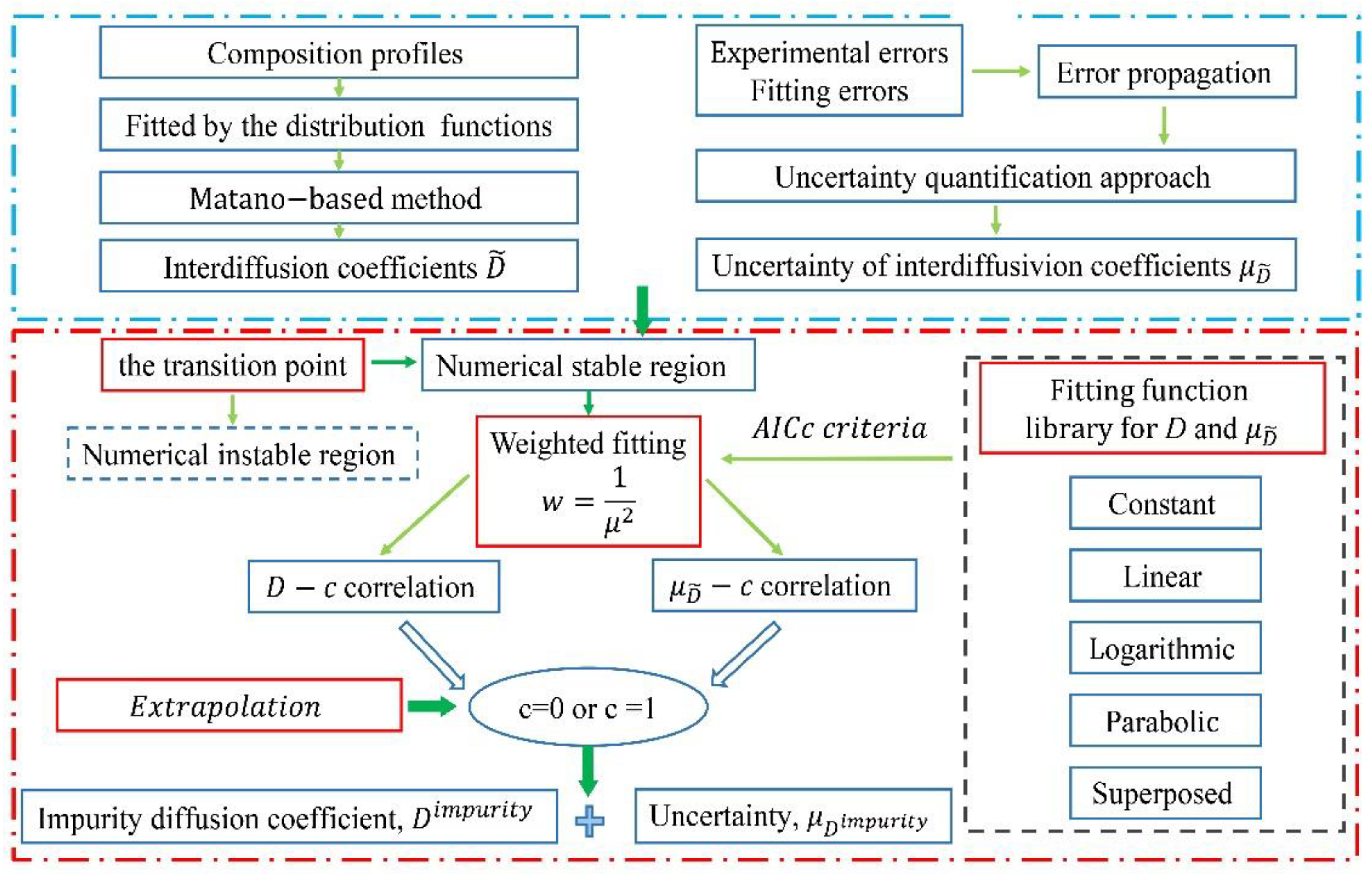
The schematic diagram of the presently proposed approach to acquire the impurity diffusion coefficients and related uncertainties in binary alloys is illustrated in Figure 1b, and its general framework is given in Figure 2.
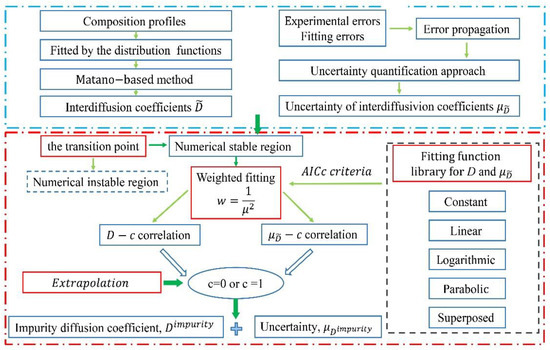
Figure 2.
Flowchart for evaluation of impurity diffusion coefficients and its uncertainty.
The first step is to evaluate the interdiffusion coefficients from the measured composition profiles fitted by the distribution function library [22]. The uncertainties, noted as μ, of the evaluated interdiffusion coefficients are then quantified following the recently developed uncertainty quantification approach [18]. The typical result is shown in Figure 1.
The second step is to determine the numerically stable region(s) for the D-c curves. Different from the previous linear extrapolation method [18], the μ-c curves are considered as a condition of priority. As can be seen in Figure 1, when the composition approaches to the end of the diffusion couple, there exists one transition point, above which the confidence interval of the interdiffusion coefficients will increase suddenly. Here, such transition point is regarded to the turning point of the upper or lower boundary of the confidence interval of the evaluated interdiffusion coefficients, for instance, the position on the upper boundary of the interdiffusion coefficient profile with zero slope, as shown in Figure 1b. This transition point actually means that, when the change in the uncertainty of interdiffusion coefficient begins to be greater than the composition correlation of the interdiffusion coefficient, that is, the physical correlation between the interdiffusion coefficient and the composition begins to weaken. Thus, the composition range between the two transition points of one diffusion couple can be treated as the numerically stable region.
The third step is to perform the fitting to both μ-c and D-c curves over the numerically stable region based on a family of pre-set fitting functions. With the fitted μ-c and D-c curves, we can directly obtain the impurity diffusion coefficients and their uncertainties based on Equation (1). Thus, the key point is to perform the high-quality fitting to the μ-c and D-c curves over the numerically stable region. Based on the idea from Kailasam et al. [23], ideal D-c relations can be classified into five types: constant, linear, logarithmic, symmetric/unsymmetric parabola ones. In this work, a family of pre-set fitting functions is constructed by including the constant, linear, parabolic, logarithmic basic functions and their combination. For a simple D-c relation, one of the basic functions should be sufficient, while, for a complex D-c relation, it is necessary to combine multiple basic functions to achieve a reasonable fitting degree. Considering that the interdiffusion coefficients with greater uncertainties suffer more risk of losing the physical relation with composition, it is necessary to take into account the uncertainty as the weight in the fitting of interdiffusion coefficients as well as the uncertainty. Moreover, during the fitting of D-c curves, the uncertainties can be used as weights [24], denoted as . The similar treatment is also applied to the μ-c curves. Furthermore, when screening for suitable fitting functions, the information criteria [25] may be employed. Here, the Akaike information criterion, as a measure of overall goodness of fit, is adopted because the fitting result with the minimum AICc value always represents the best.
3. Benchmark Test
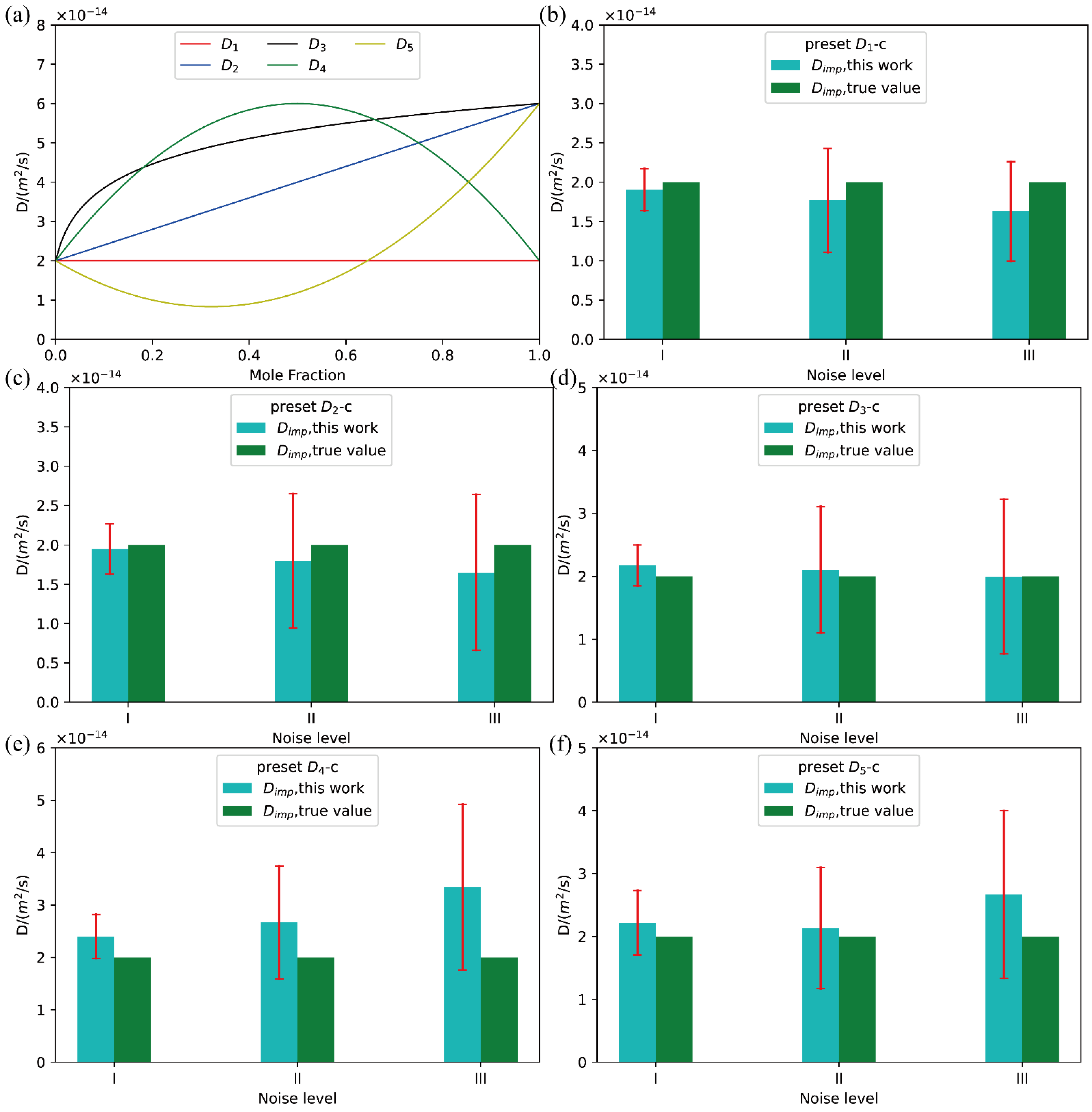
In the present benchmark tests, five different types of D-c relations in total, i.e., , , , , and , were assumed, and shown in Figure 3a refers to a constant, has a linear relation with c, presents a logarithm relationship with c, while and have parabolic relations with c:
where the unit of interdiffusion coefficients is m2/s, and that of composition is atomic fraction.
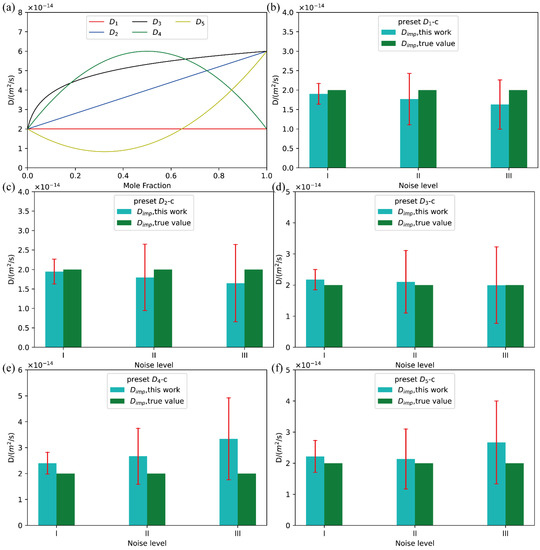
Figure 3.
(a) Five types of ideal D-c relations; (b–f) comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties and the truth values with the D-c relation from to .
With the pre-assumed interdiffusion coefficients, the imitated composition profiles were generated based on Fick’s laws. The terminal compositions (at.) at the left and right ends of the hypothetical diffusion couples were set to be 0.00 and 1.0, respectively. The length of the diffusion couples was set as 1000 μm, the position of initial interface is 500 μm, and the diffusion time 30,000 s. Moreover, different levels of normally distributed noises were also imposed on the imitated composition distance profiles as
where w is a Gaussian noise with the standard distribution N(0-1), and δ represents the level of the noise. In the present benchmark tests, three levels of noises were considered, i.e.,, ,.
Following our previous work [18], the Boltzmann–Matano method together with the distribution functions [22] were employed to retrieve the composition-dependent interdiffusion coefficients and their uncertainties. The evaluated interdiffusion coefficients and uncertainties are given in the Supporting Information in order to save the space here because some similar results have been given in our previous publication [18]. Then, the evaluated interdiffusion coefficients over the numerical stable region are fitted based on the weight due to the quantified uncertainties using the presently constructed fitting function library. The best fitting results corresponding to the minimum AICc value are selected. Similar treatment is performed for the quantified uncertainty. After that, with the constructed D-c relation and μ-c relation, the impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties can be directly obtained at c = 0.
As clearly shown in the Figure S2 of the Supporting Information, all the five different types of D-c corresponding to the composition profiles with three different noises were well fitted. The resulting interdiffusion coefficients can reproduce the pre-set correlation between interdiffusion coefficient and composition well, even over the numerical instable region. Moreover, the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficient with quantified uncertainties are compared with the true values, as displayed in Figure 3b–f. As can be seen in the plots, all the pre-set true values of impurity diffusion coefficients are well in the confidence interval of the evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients from different types of composition profiles and noise levels. A closer look at Figure 3 and further analysis indicates that, with the increase of the noise level, the uncertainty of the evaluated impurity diffusion coefficient becomes larger, and the deviation between the true values and the evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients increases. With the same noise level, the deviation of the impurity diffusion coefficient of simple D-c relations (like ) from the true value is significantly lower than that of complex D-c relations (like and ). Moreover, such difference increases as the noise level increases. All the facts infer that the higher quality the experimental composition profiles, the more accurate the impurity diffusion coefficients and the smaller the uncertainty.
4. Application in Real Binary Alloy
4.1. Co-Ni Binary Alloy
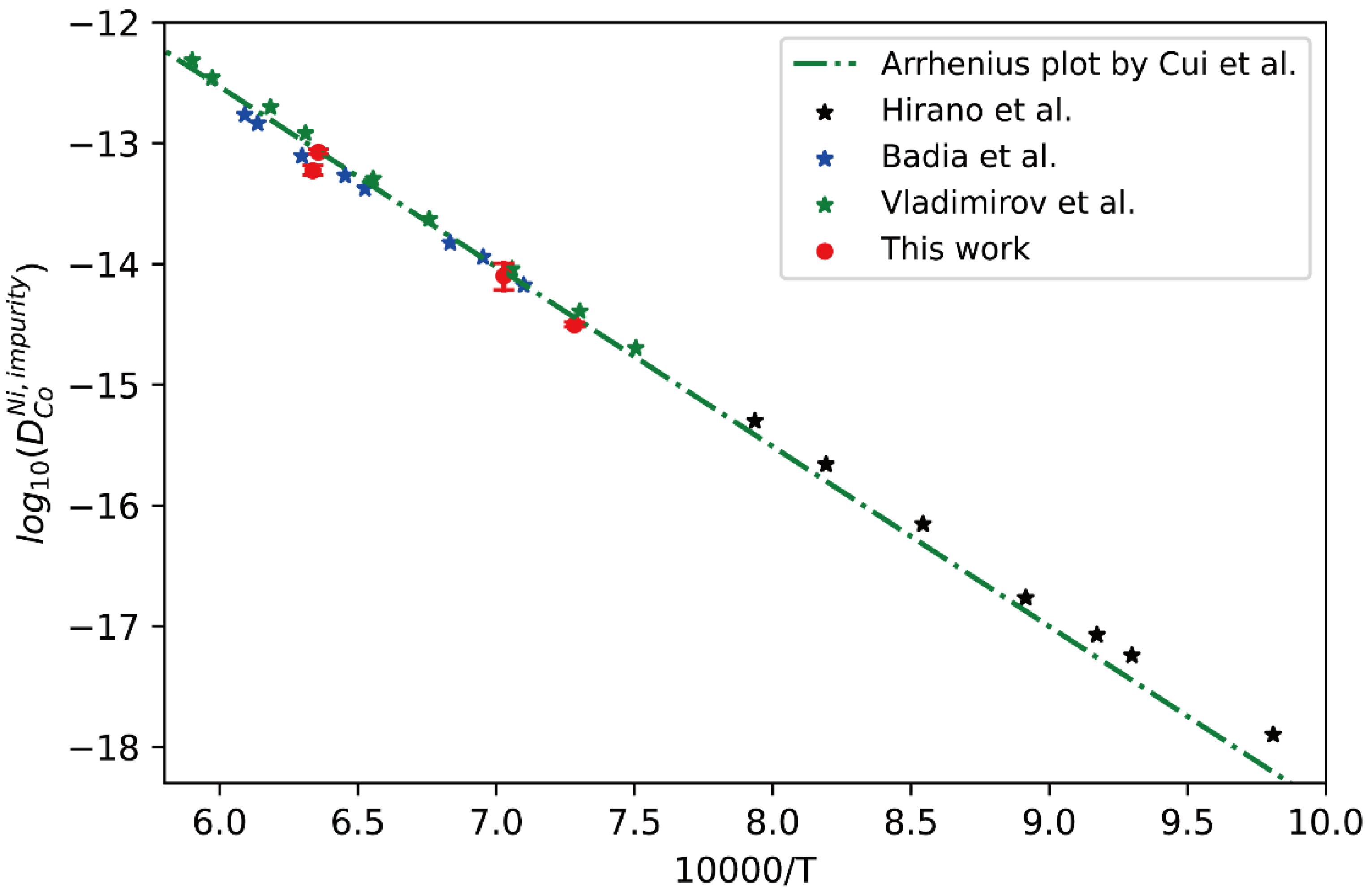
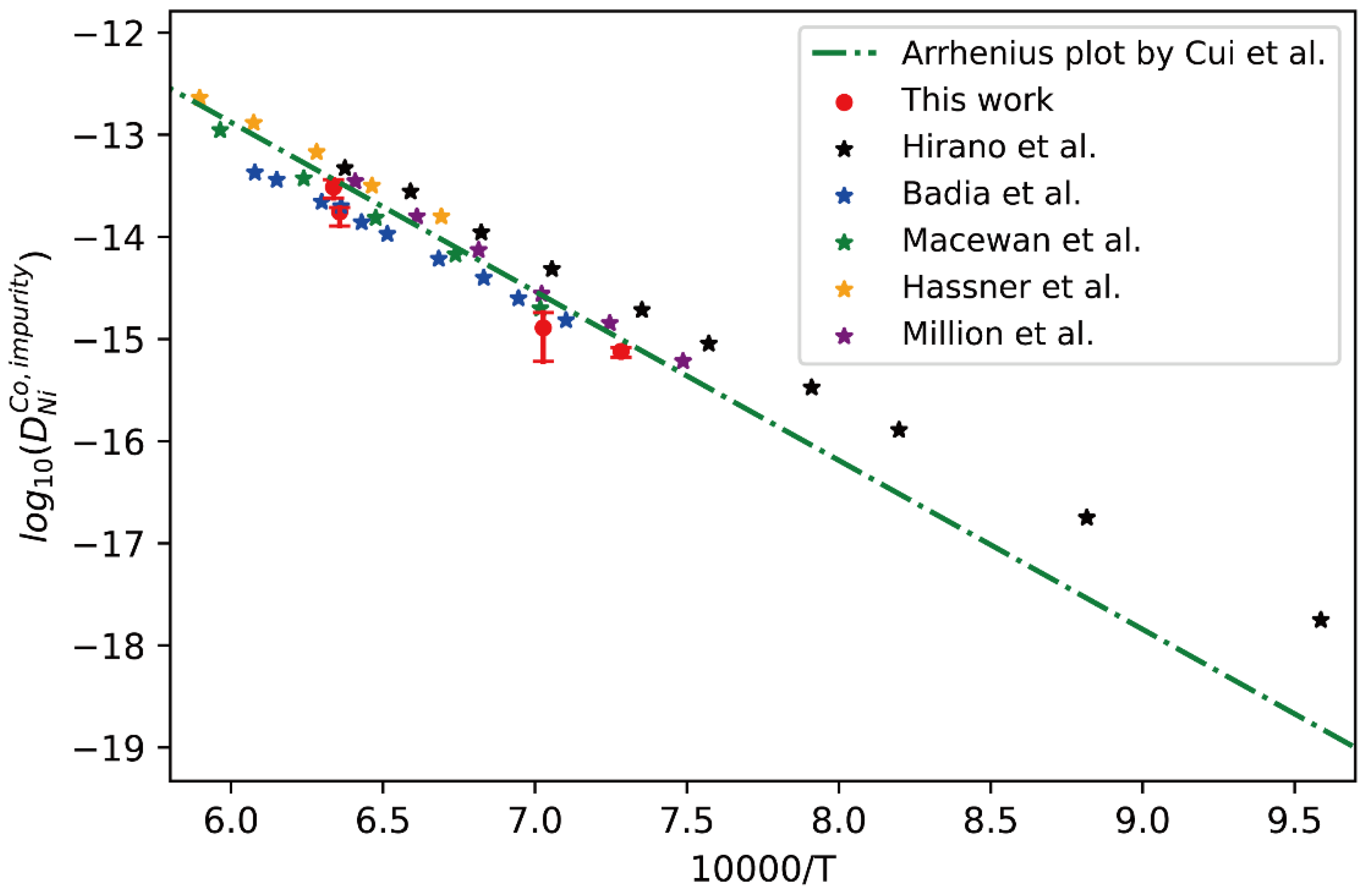
Co-Ni binary alloy is one of the most important boundary systems in Ni-/Co-based superalloys and high-entropy alloys, and thus was selected as the first example to verify the reliability of the presently effective approach. To begin with, the interdiffusion coefficients of fcc Ni-Co alloys together with their uncertainties were re-calculated based on the composition profiles of the Co/Ni diffusion couples annealed at different temperatures [26,27,28,29], following the strategy of Wu et al. [18]. The impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Co and Co in fcc Ni, as well as their corresponding uncertainties, were then determined according to the presently proposed effective approach, and given in Figure 4 and Figure 5.
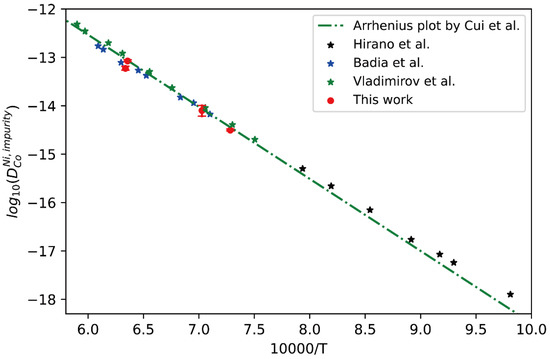
Figure 4.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of Co in fcc Ni and the impurity diffusion coefficients obtained by tracer experiment [30,31,32] and the optimized end-member of atomic mobility by Cui [33].
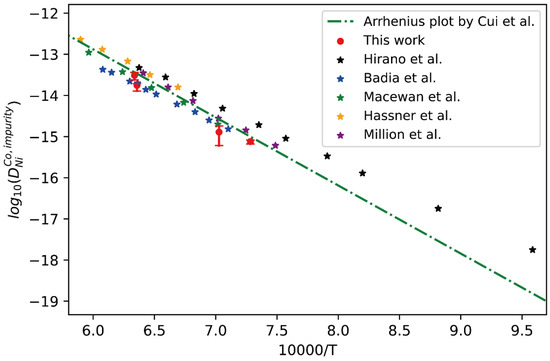
Figure 5.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of Ni in fcc Co and the impurity diffusion coefficients obtained by tracer experiment [30,31,32,34,35,36] and optimized atomic mobility result by Cui et al. [33].
In Figure 4, the presently obtained impurity diffusion coefficients of Co in fcc Ni are compared with the literature data measured by the tracer experiments [30,31,32]. Moreover, the CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagram)-type assessed result by Cui et al. [33] is also superimposed in Figure 4 for comparison. Good agreement can be seen in Figure 5 between the presently obtained impurity diffusion coefficient and the tracer experimental results at high temperature [30,31] as well as the CALPHAD-type assessed result by Cui et al. [33]. The slight deviation between the result of Hirano et al. [32] and the CALPHAD-type assessed result by Cui et al. [33] at low temperature may be due to the contribution of grain boundaries. This fact proves the reliability of presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficient and its uncertainty, and also the previously assessed result by Cui et al. [33].
Similarly, the presently obtained impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Co are compared with the literature data measured by the tracer experiments [30,32,34,35,36] and the CALPHAD-type assessed result by Cui et al. [33], as shown in Figure 5. Again, it can be seen that the presently obtained impurity diffusion coefficients are in excellent agreement with the tracer experiment data, except for very slight deviation from the results by Hirano et al. [32] at lower temperature due to the noticeable contribution of grain boundary. Generally, the short-circuit diffusion along the grain boundary in the diffusion couples prepared by polycrystalline samples may contribute to the apparent diffusion, and the obtained interdiffusion coefficients should be larger than the true values of bulk diffusion. Especially at low temperatures, such contribution may be noticeable. In general, the researchers usually subject the alloy blocks for homogenization at higher temperatures for a relatively long time before preparing the diffusion couple/multiple, making the grain size large enough in order to minimize the influence of grain boundaries. In particular, when the grain size is larger than the scale of diffusion distance, the influence of grain boundary diffusion on the interdiffusion coefficient can be reduced to zero ideally. Based on the fact, the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficient and its uncertainty, and also the previously assessed result by Cui et al. [33], should be regarded to be reliable.
4.2. Cu-Al Binary Alloy
Direct measurement of impurity diffusion of Al in different metals has always been challenging due to the absence of natural radioactive tracer isotopes of Al (Note: The only feasible radioisotope of Al, artificial 26Al, is quite expensive and very difficult to be applied for classical radiotracer methods due to its extreme low specific activity) [37,38]. The only tracer experimental data on impurity diffusion coefficient of Al in dilute Cu-Al alloys available in the literature is from Hirvonen [39], who used the resonance broadening technique to study the diffusion of 27Al+ in ion-implanted Al-Cu solid solutions at low temperature. Therefore, the presently effective approach can serve as a promising alternative for retrieving impurity diffusion coefficients of Al in fcc Cu at high temperatures.
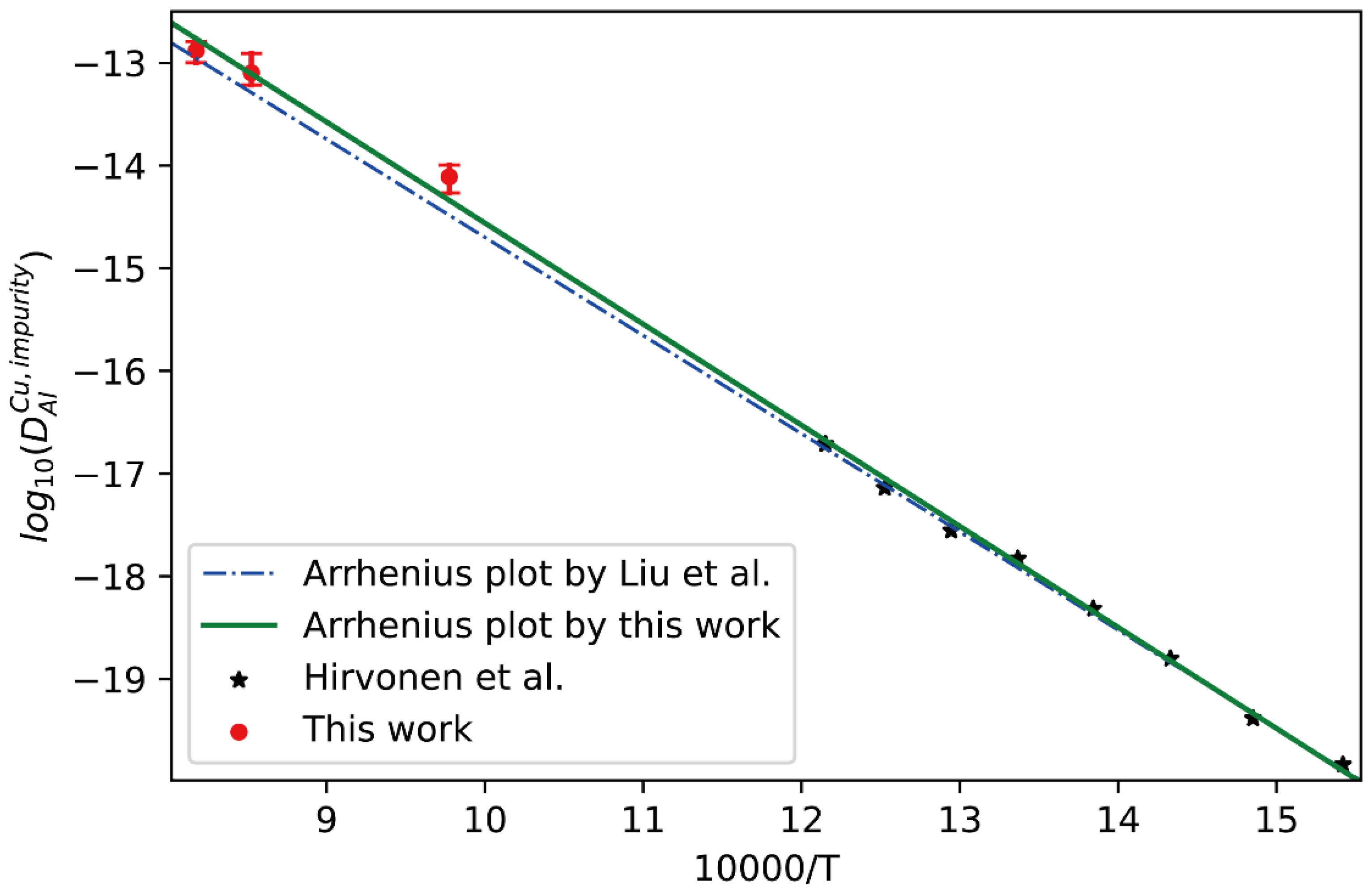
Here, following the above strategy, the interdiffusion coefficients in fcc Cu-Al alloys at 1023 K, 1173 K and 1223 K together with the corresponding uncertainties were first calculated from the composition profiles of the Cu/Al diffusion couples reported in the literature [40,41,42]. Then, the presently developed approach was utilized to evaluate the impurity diffusion coefficients of Al in fcc Cu with quantified uncertainties, as displayed in Figure 6. In the figure, the experimental data at low temperatures by Hirvonen et al. [39] and the CALPHAD assessed result by Liu et al. [40] (shown in dot-dashed line) are also appended for direct comparison. As can be seen that the Arrhenius plot reported by Liu et al. [40] can reproduce the experimental data at low temperatures by Hirvonen et al. [39] well, but show noticeable deviation from the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients at high temperatures. Thus, the Arrhenius description of impurity diffusion coefficient of Al in fcc Cu needs to be updated by fully considering the experimental data over the wider temperature range. The newly updated Arrhenius description of impurity diffusion coefficients of Al in fcc Cu is given as
and the corresponding result is presented as the solid line in Figure 6. It can be clearly seen in Figure 6 that the new Arrhenius plot obtained in the present work shows better agreement with both the experimental data of Hirvonen et al. [39] and the presently evaluated data than the previous plot by Liu et al. [40].
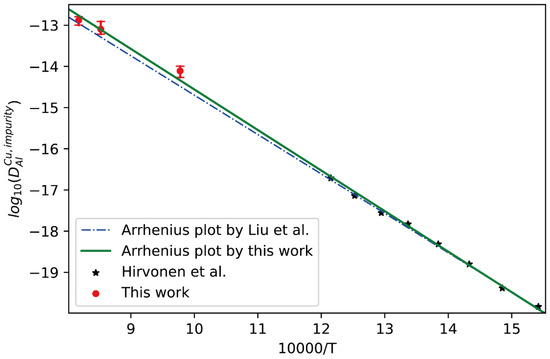
Figure 6.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of Al in fcc Cu and the impurity diffusion coefficients obtained by tracer experiment [39] and optimized atomic mobility result by Liu et al. [40].
4.3. Pt-Ni Binary Alloy
Platinum-group metals, such as Pt, Ru, and Ir, have been added to yield the creep resistance of the Ni-based superalloys [13]. The micro mechanisms of creep deformation in superalloys are the subject of much debate; a better understanding of their creep behavior and structural stability requires diffusion information of the noble elements in Ni-based superalloys. However, there is very limited experimental information in the literature.
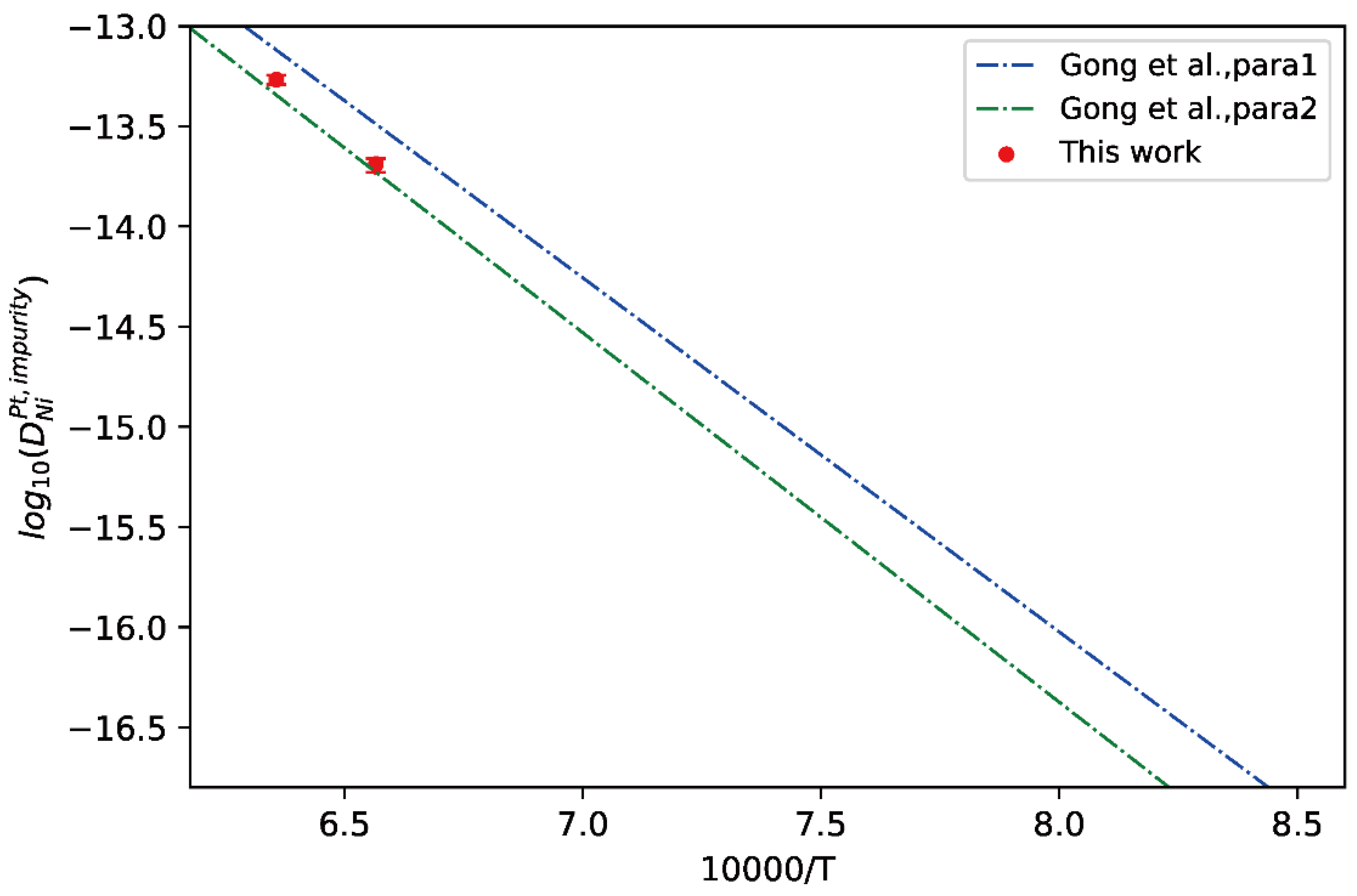
Here, fcc Pt-Ni binary alloys were chosen as the application case. The measured composition profiles of fcc Pt/Ni diffusion couples annealed at 1523 K and 1573 K by Gong et al. [13] were adopted for the calculation of impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Pt and Pt in fcc Ni together with uncertainties, following the presently effective approach. The comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Pt and the calculated temperature-dependent impurity diffusion coefficients by Gong et al. [13] were presented in Figure 7. In the figure, the CALPHAD assessed result by Gong et al. [13] based on different thermodynamic parameters were denoted as “Para 1” and “Para 2”. It can be seen from Figure 7 that the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients at 1423 K and 1573 K agree very well with “Para 2” from Gong et al. [13], indicating that the “Para 2” of Gong et al. [13] is more reasonable than “Para 1”, and also validate the reliability of the impurity diffusion coefficients evaluated using the presently developed approach.
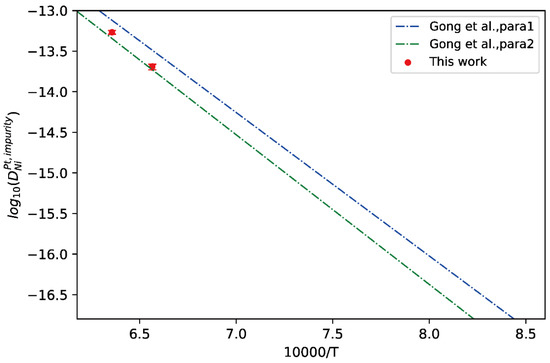
Figure 7.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of Ni in fcc Pt and the optimized mobility results by Gong et al. [13].
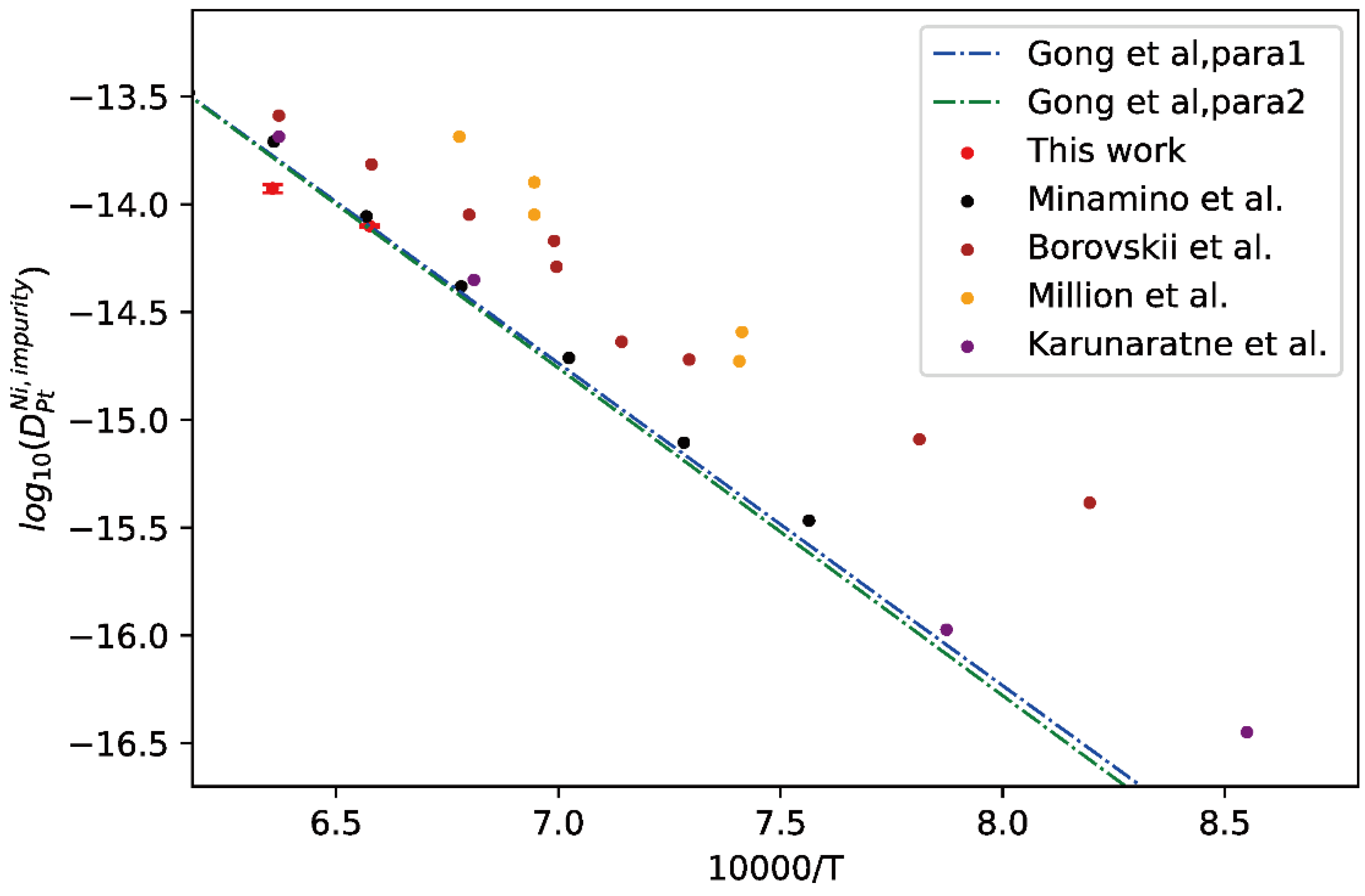
Moreover, the comparison between presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Pt and the calculated temperature-dependent impurity diffusion coefficients by Gong et al. [13] as well as the experimental results [43,44,45,46] was given in Figure 8. As can be seen in figure, the experimental results are quite scattering. The presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Pt are close to the tracer experiment data by Minamino et al. [43] and those at high temperatures by Borovskii et al. [43] but show noticeable deviation from the others [44,45,46]. In addition, the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients of Ni in fcc Pt are also in very good agreement with the two sets of mobility parameters, i.e., “Para 1” and “Para 2”, by Gong et al. [13].
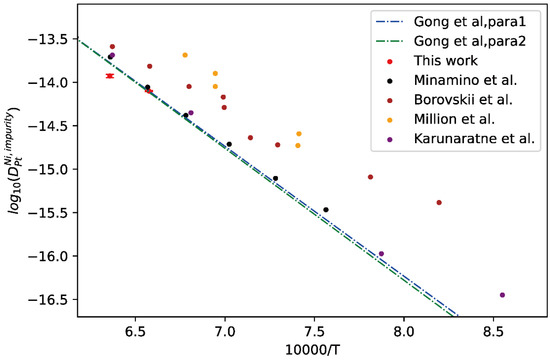
Figure 8.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of Ni in fcc Pt and the optimized mobility results by Gong et al. [13] as well as the experimental results [43,44,45,46].
4.4. Mg-Zn Binary Alloy
Mg-Zn alloy is one of the most important sub binary for the Mg-based alloys. Thus, hcp Mg-Zn binary alloys were chosen here for the validation of universality of the presently developed approach in the evaluation of impurity diffusion coefficients in hcp phase.
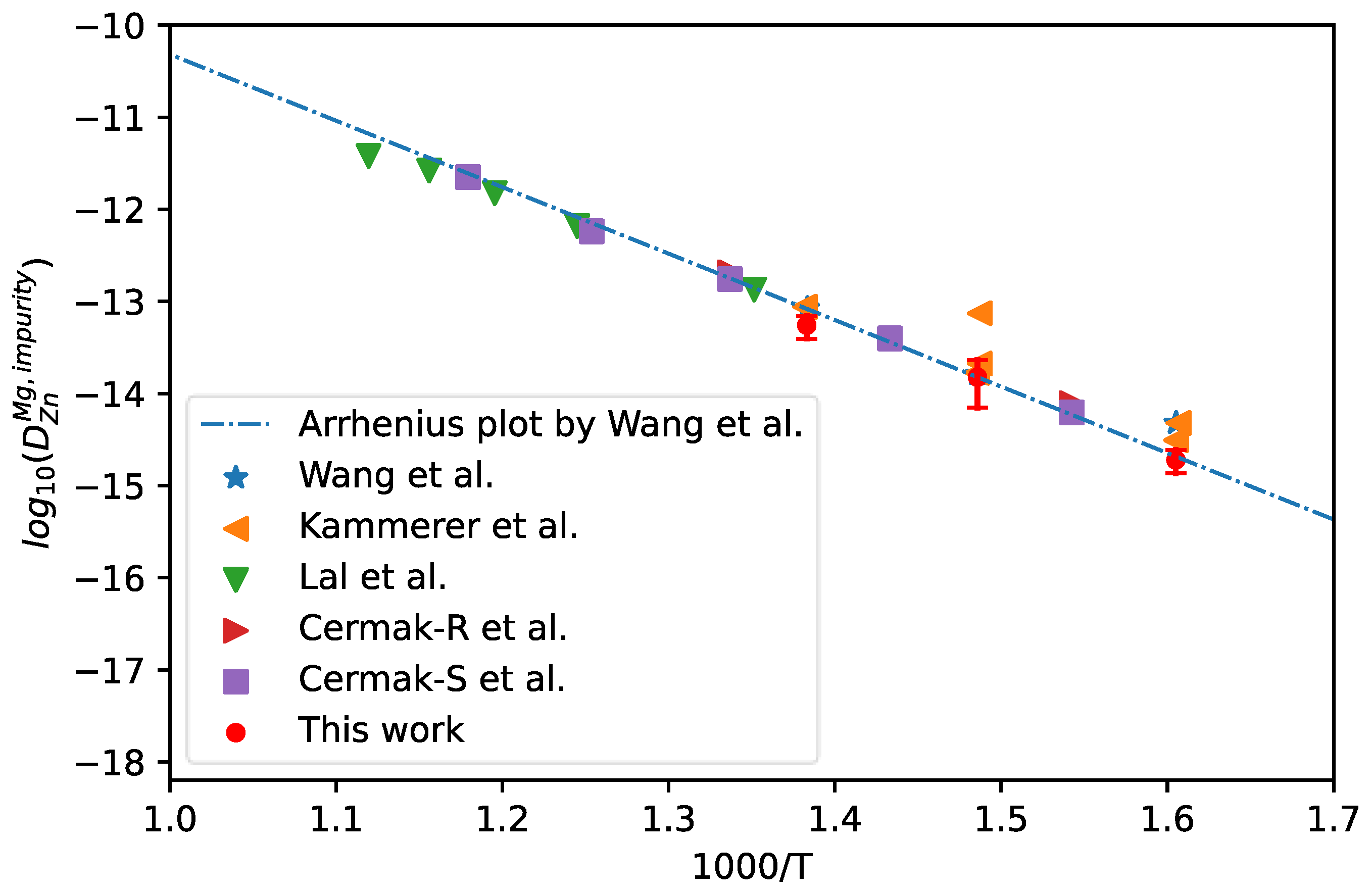
The measured composition profiles of hcp Mg/Zn diffusion couple at 623 K, 673 K, and 723 K by Kammerer et al. [47] were adopted for the calculation of impurity diffusion coefficients of Zn in hcp Mg together with uncertainties, following the presently effective approach. The corresponding results are shown in Figure 9. In the figure, the results calculated using the Hall method by Kammerer et al. [47,48], the intrinsic experimental results by Lal [49] and Cermak [50], and the CALPHAD assessed results by Wang et al. [51] (shown in dot-dashed line) are also appended for direct comparison. It can be clearly seen in Figure 9 that presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients at the three temperatures are in good agreement with the Arrhenius plot obtained by Wang et al. [51] and the other experimental results, especially the results due to the intrinsic experiments.
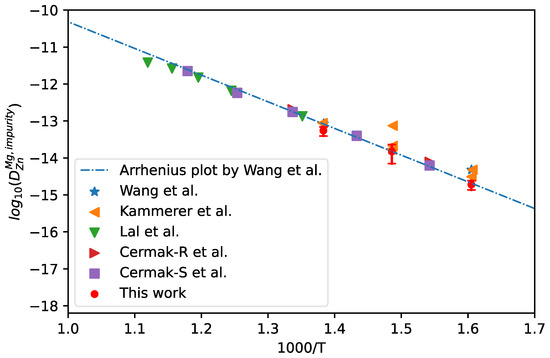
Figure 9.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of Zn in hcp Mg and the CALPHAD mobility results by Wang et al. [51] as well as the experimental results [47,48,49,50].
4.5. Ti-V Binary Alloy
Ti-Al-V alloys, especially most notably the long-established Ti-6AI-4V alloy, have been widely applied in aerospace engineering. Thus, bcc Ti-V alloys were also chosen for the validation of presently developed approach in the bcc alloy system.
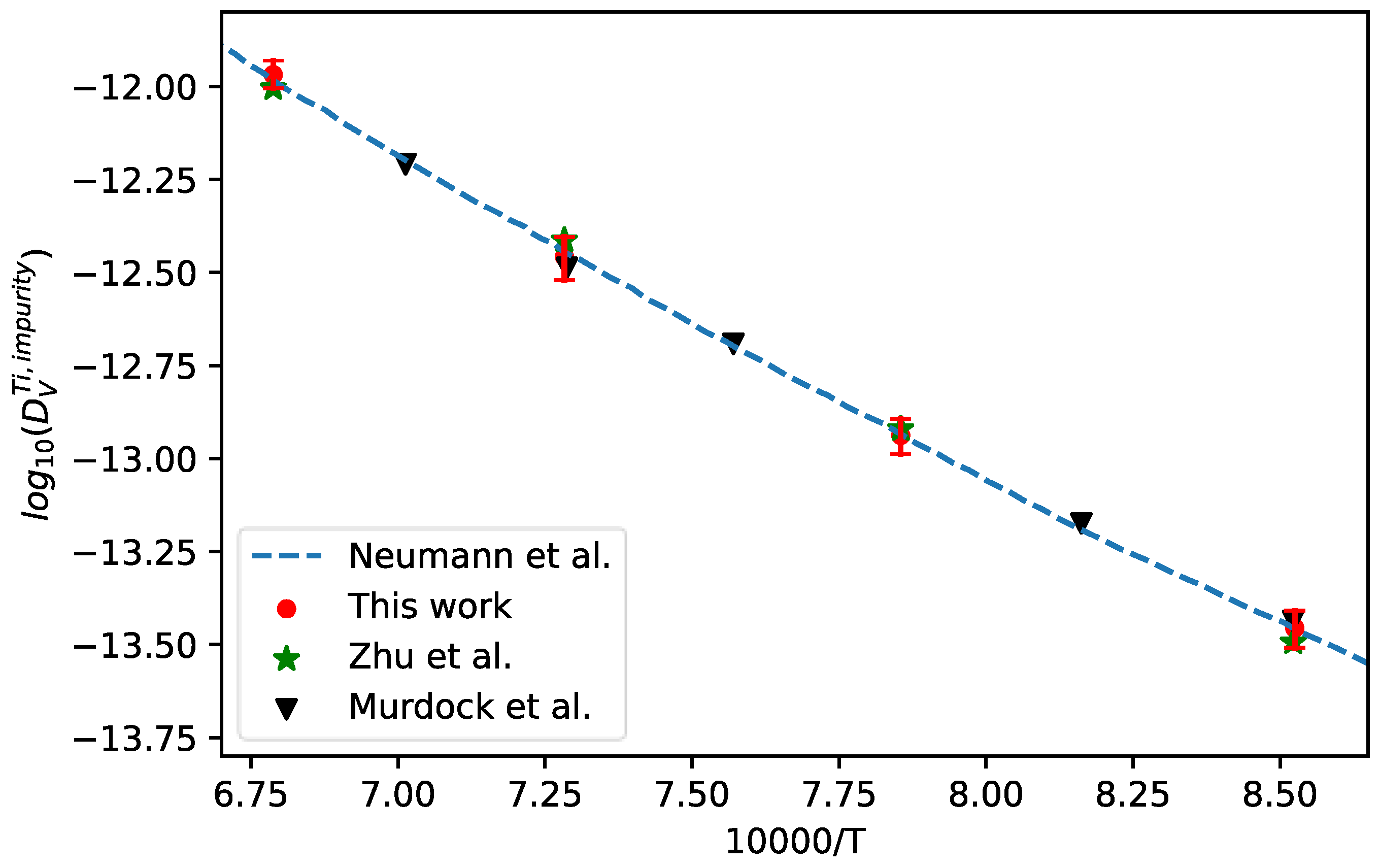
The interdiffusion coefficients in bcc Ti-V alloys at 1173 K, 1273 K, 1373 K, and 1473 K together with the corresponding uncertainties were first calculated from the composition profiles of the Ti/V diffusion couples reported in the literature [52]. Then, the presently developed approach was utilized to evaluate the impurity diffusion coefficients of V in bcc Ti with quantified uncertainties, as displayed in Figure 10. In the figure, the experimental data reported in the literature [52,53], and the assessed results by Neumann et al. [7] (shown in dashed line) are also appended for direct comparison. As can be seen in figure, the presently evaluated data show very nice agreement with the result assessed by Neumann et al. [7] as well as the intrinsic experimental results [53] and the results of Zhu et al. evaluated using the forward-simulation method [52].
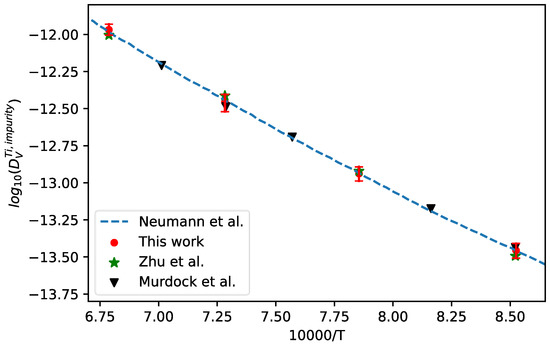
Figure 10.
Comparison between the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients with uncertainties of V in bcc Ti and the data assessed by Neumann et al. [7] as well as the experimental results [52,53].
5. Conclusions
- A general but effective approach to acquire the impurity diffusion coefficients with quantified uncertainties in binary alloys was developed in this work from the well-determined composition-dependent interdiffusion coefficients. Benchmark tests in five types of D-c relations with different noises were performed to validate the presently proposed approach, and the resulting impurity diffusion coefficients with quantified uncertainties reproduce the true values very well. Moreover, the presently effective approach was also demonstrated to be superior to the previous linear extrapolation method.
- The presently developed effective approach was then applied in the real fcc Ni-Co, Cu-Al, Pt-Ni systems. The evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients, including Ni in fcc Co, Co in fcc Ni, Al in fcc Cu, Al in fcc Cu, Pt in fcc Ni, Ni in fcc Pt, Zn in hcp Mg and V in bcc Ti, were compared with the direct experimental data measured by the tracer experiments, and also utilized to verify the previously assessed mobility descriptions. It was found that: (i) the presently evaluated impurity diffusion coefficients are in good agreement with most tracer experimental data, and (ii) the previously assessed mobility descriptions for Zn in hcp Mg, V in bcc Ti, Ni in fcc Co, Co in fcc Ni, Pt in fcc Ni and Ni in fcc Pt are reliable, while that for Al in fcc Cu needs updating.
- It is highly anticipated that the presently effective approach can serve as a standard one for acquiring the high-quality impurity diffusion coefficients in binary alloys with quantified uncertainties, especially for the noble metals and the cases without suitable radioactive tracer isotopes.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/met11050809/s1, Figure S1: Composition profiles fitted by distribution functions compared with the data due to the pre-set , , , , with different noise levels. (a–e) noise level I; (f–j) noise level II; (k–o) noise level III. Figure S2. Fitted interdiffusion coefficients together with uncertainties compared with the interdiffusion coefficient evaluated using the Boltzmann–Matano method from the data due to the pre-set , , , , with noise and uncertainties evaluated using the uncertainty quantification approach. (a–e) noise level I; (f–j) noise level II; (k–o) noise level III. Figure S3. (a–d) Composition profiles fitted by distribution functions compared with the experimental data of the Co/Ni diffusion couples annealed at different temperatures [1,2,3,4]; (c–h) presently fitted interdiffusion coefficients and uncertainties compared with the interdiffusion coefficients evaluated using the Boltzmann–Matano method and the uncertainties quantified using the uncertainty quantification approach. Figure S4. (a–c) Composition profiles fitted by distribution functions compared with the experimental data of the Al-Cu/Cu diffusion couples annealed at different temperatures [5,6,7]; (c–h) presently fitted interdiffusion coefficients and uncertainties compared with the interdiffusion coefficients evaluated using the Boltzmann–Matano method and the uncertainties quantified using the uncertainty quantification approach. Figure S5. (a–b) Composition profiles fitted by distribution functions compared with the experimental data of the Ni/Pt diffusion couples annealed at different temperatures [8]; (c–d) presently fitted interdiffusion coefficients and uncertainties compared with the interdiffusion coefficients evaluated using the Boltzmann–Matano method and the uncertainties quantified using the uncertainty quantification approach. Figure S6. (a,b) Composition profiles fitted by distribution functions compared with the experimental data of the hcp Mg/Zn diffusion couples annealed at different temperatures [9]; (c,d) presently fitted interdiffusion coefficients and uncertainties compared with the interdiffusion coefficients evaluated using the Boltzmann–Matano method and the uncertainties quantified using the uncertainty quantification approach. Figure S7. (a–b) Composition profiles fitted by distribution functions compared with the experimental data of the bcc Ti/V diffusion couples annealed at different temperatures [10]; (c,d) presently fitted interdiffusion coefficients and uncertainties compared with the interdiffusion coefficients evaluated using the Boltzmann–Matano method and the uncertainties quantified using the uncertainty quantification approach.
Author Contributions
L.Z., X.W. and Y.Z. conceived the prototype of the approach and designed the benchmark tests as well as the practical cases; Y.Z. performed the benchmark tests as well as studies in the practical alloys; Y.Z., X.W. and L.Z. analyzed the data; Y.Z., X.W., L.Z., J.Z. and C.D. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, grant number 2019YFB2006500, the projects of Key-Area Research and Development Programs of Guangdong Province, grant number 2019B010936001, and Guangzhou, grant number 202007020008, and the Youth Talent Project of Innovation-driven Plan at Central South University, grant number 2282019SYLB026, is acknowledged.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhong, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. High-throughput determination of high-quality interdiffusion coefficients in metallic solids: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 10303–10338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L. Automation of diffusion database development in multicomponent alloys from large number of experimental composition profiles. NPJ Comput. Mater. 2021, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Steinbach, I.; Chen, Q.; Huang, B. Diffusivities of an Al–Fe–Ni melt and their effects on the microstructure during solidification. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 3664–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.R.; Jaskari, M.; Jarvenpää, A.; Davis, T.P.; Kömi, J.; Porter, D. Precipitation Versus Partitioning Kinetics during the Quenching of Low-Carbon Martensitic Steels. Metals 2020, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedoseeva, A.; Nikitin, I.; Tkachev, E.; Mishnev, R.; Dudova, N.; Kaibyshev, R. Effect of Alloying on the Nucleation and Growth of Laves Phase in the 9–10% Cr-3% Co Martensitic Steels during Creep. Metals 2021, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, N.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Lin, Y. High-temperature oxidation of pure Al: Kinetic modeling supported by experimental characterization. Corros. Sci. 2018, 139, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Tuijn, C. Self-Diffusion and Impurity Diffusion in Pure Metals: Handbook of Experimental Data; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.E.; Boettinger, W.J.; Kattner, U.R. Development of a diffusion mobility database for Ni-base superalloys. Acta Mater. 2002, 50, 775–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Chen, Q.; Steinbach, I.; Huang, B. Atomic mobilities and diffusivities in the fcc, L12 and B2 phases of the Ni-Al system. Int. J. Mater. Res. 2010, 101, 1461–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeshan, S.; Hector, L.G.; Liu, Z.K. First-principles calculations of impurity diffusion coefficients in dilute Mg alloys using the 8-frequency model. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 3214–3228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, M.H.; Baranovskiy, A.; Natanzon, Y.; Amouyal, Y. A first-principles study of the temperature-dependent diffusion coefficients of silver in the thermoelectric compound PbTe. Acta Mater. 2021, 202, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrer, H. Diffusion in Solids: Fundamentals, Methods, Materials, Diffusion-Controlled Processes; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, L.; Yao, D.; Zhou, C. Diffusivities and atomic mobilities in fcc Ni–Pt alloys. Scr. Mater. 2009, 61, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gong, W.; Chen, J.; Du, Y. Diffusivities and atomic mobilities in fcc Pt–Al alloys. Calphad 2014, 46, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, L.D. An analytical method of calculating variable diffusion coefficients. J. Chem. Phys. 1953, 21, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.-C. Extracting interdiffusion coefficients from binary diffusion couples using traditional methods and a forward-simulation method. Intermetallics 2013, 34, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, W.; Zhao, J.-C. Accurate and efficient measurement of impurity (dilute) diffusion coefficients without isotope tracer experiments. Scr. Mater. 2017, 128, 32–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, L. A general approach to quantify the uncertainty of interdiffusion coefficients in binary, ternary and multicomponent systems evaluated using Matano-based methods. Acta Mater. 2020, 188, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, C. On the relation between the diffusion-coefficients and concentrations of solid metals. Jpn. J. Phys. 1933, 8, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Sauer, F.; Freise, V. Diffusion in binären Gemischen mit Volumenänderung, Zeitschrift für Elektrochemie. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1962, 66, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkaldy, J.S.; Brown, L. Diffusion behaviour in ternary, multiphase systems. Can. Metall. Q. 1963, 2, 89–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zhang, L. Application of distribution functions in accurate determination of interdiffusion coefficients. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kailasam, S.K.; Lacombe, J.C.; Glicksman, M.E. Evaluation of the methods for calculating the concentration-dependent diffusivity in binary systems. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 2605–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutz, T. Data Fitting and Uncertainty: A Practical Introduction to Weighted Least Squares and Beyond; Vieweg and Teubner: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura, N. Further analysts of the data by akaike’s information criterion and the finite corrections: Further analysts of the data by akaike’s. Commun. Stat. Theory Methods 1978, 7, 13–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heumann, T.; Kottmann, A. Uber den ablauf der diffusionsvorgange in substitutionsmischkristallen (English translation: On the diffusion processes in the substitutional mixed crystals). Z. Met. 1953, 44, 139–154. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, C.E. A New Technique for Evaluating Diffusion Mobility Parameters. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2005, 26, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, Y.; Hirano, K.-I. Interdiffusion in co-ni alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1971, 35, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- HŘebíček, J.; Kučera, J.; Stránský, K. Determination of interdiffusion coefficients in the Co-Ni system with the use of spline function. Czechoslov. J. Phys. B 1975, 25, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, M.; Vignes, A. Iron Nickel and Cobalt diffusion in transition metals of iron group. Acta Metall. 1969, 17, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimirov, A.; Kajgorodov, V.; Klotsman, S.; Trakhtenberg, I.S. Volume diffusion of cobalt and tungsten in nickel. Fiz. Met. I Metalloved. 1978, 46, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, K.I.; Agarwala, R.; Averbach, B.; Cohen, M. Diffusion in cobalt-nickel alloys. J. Appl. Phys. 1962, 33, 3049–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.W.; Jiang, M.; Ohnuma, I.; Oikawa, K.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Computational Study of Atomic Mobility for fcc Phase of Co-Fe and Co-Ni Binaries. J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2007, 29, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacEwan, J.; MacEwan, J.; Yaffe, L. Diffusion of Ni63 in iron, cobalt, nickel, and two iron–nickel alloys. Can. J. Chem. 1959, 37, 1629–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hässner, A.; Lange, W. Volumenselbstdiffusion in Kobalt-Nickel-Legierungen. Phys. Status Solidi 1965, 8, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Million, B.; Kučera, J. Concentration dependence of nickel diffusion in nickel-cobalt alloys. Czechoslov. J. Phys. B 1971, 21, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askill, J. Tracer Diffusion Data for Metals, Alloys, and Simple Oxides; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fielitz, P.; Borchardt, G.; Ganschow, S.; Bertram, R.; Markwitz, A. 26Al tracer diffusion in titanium doped single crystalline α-Al2O3. Solid State Ion. 2008, 179, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirvonen, J. Aluminum diffusion in ion-implanted noble metals. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 6143–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, L. Assessment of atomic mobilities of Al and Cu in fcc Al–Cu alloys. Calphad 2009, 33, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laik, A.; Bhanumurthy, K.; Kale, G. Diffusion in Cu (Al) solid solution. Defect Diffus. Forum Trans. Tech. Publ. 2008, 279, 63–69. [Google Scholar]
- Mehl, R.; Rhines, F. Rates of diffusion in the alpha solid solutions of copper. AIME Trans. 1938, 128, 185–221. [Google Scholar]
- Minamino, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Jung, S.B.; Hirao, K.; Yamane, T. Diffusion of platinum and molybdenum in Ni and Ni3Al. Defect Diffus. Forum Trans. Tech. Publ. 1997, 143–147, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borovskiy, I.; Marchukova, I.; Ugaste, Y.E. Local X-ray Spectranalysis of Mutual Diffusion in Binary Systems Forming a Continuuous Series of Solid Solutions-Systems Fe-Ni Ni-Co Ni-Pt and Co-Pt. Phys. Met. Met. 1967, 24, 436–441. [Google Scholar]
- Million, B.; Kucera, J. Diffusion of sup (193m) Pt in platinum, γ-iron, cobalt and nickel. Kov. Mater. 1973, 11, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Karunaratne, M.S.A.; Reed, R.C. Interdiffusion of the platinum-group metals in nickel at elevated temperatures. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 2905–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, C.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Warmack, R.J.; Sohn, Y.H. Interdiffusion and impurity diffusion in polycrystalline Mg solid solution with Al or Zn. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 617, 968–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kammerer, C.; Kulkarni, N.; Warmack, R.; Sohn, Y. Al and Zn impurity diffusion in binary and ternary magnesium solid-solutions. In Magnesium Technology 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 407–411. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, K. Study of the Diffusion of Some Elements in Magnesium; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Čermák, J.; Stloukal, I. Diffusion of 65Zn in Mg and in Mg–x Al solid solutions. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2006, 203, 2386–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Beltran, J.I.; Lorca, J.L.; Cui, Y. Computational study of atomic mobility in hcp Mg–Al–Zn ternary alloys. Calphad 2016, 54, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wei, C.; Cai, G.-M.; Jiang, L.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, J.-C. Measurement of interdiffusion and impurity diffusion coefficients in the bcc phase of the Ti–X (X = Cr, Hf, Mo, Nb, V, Zr) binary systems using diffusion multiples. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 3255–3268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, J.; Lundy, T.; Stansbury, E. Diffusion of Ti44 and V48 in titanium. Acta Metall. 1964, 12, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).