Atomic Simulations for Packing Changes of Nano-Sized Cu Clusters Embedded in the Febulk on Heating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
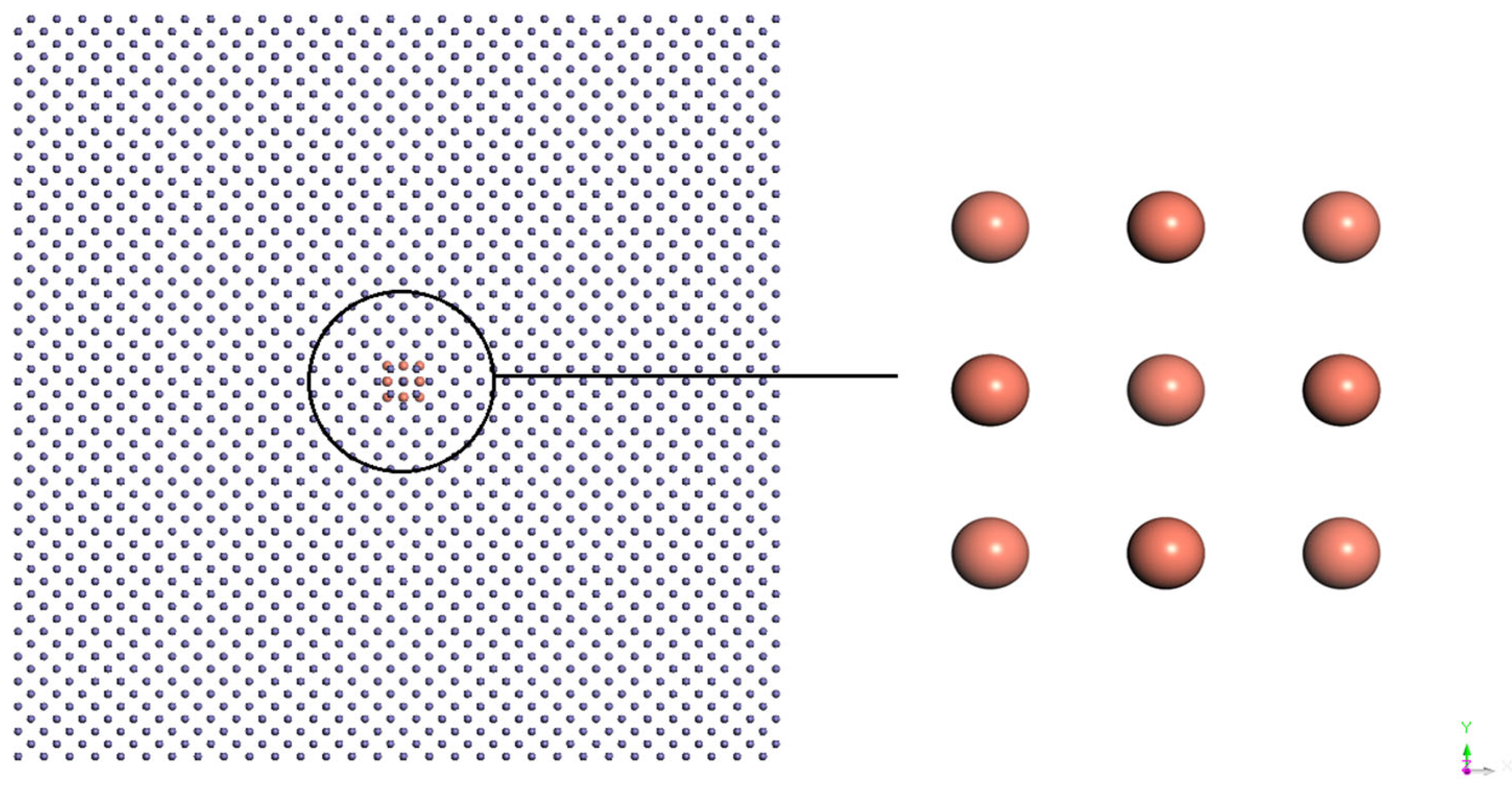
2. Model and Simulation
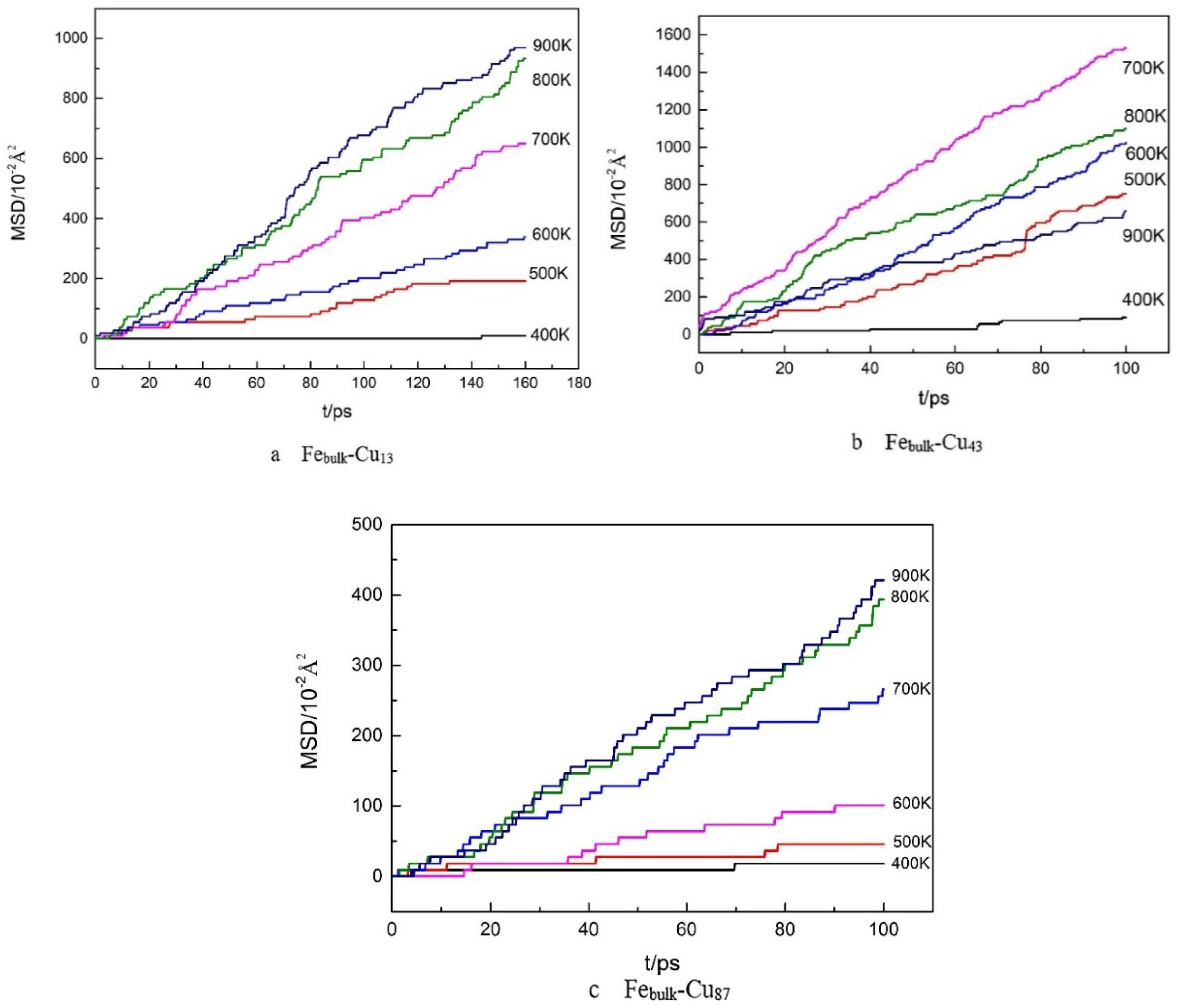
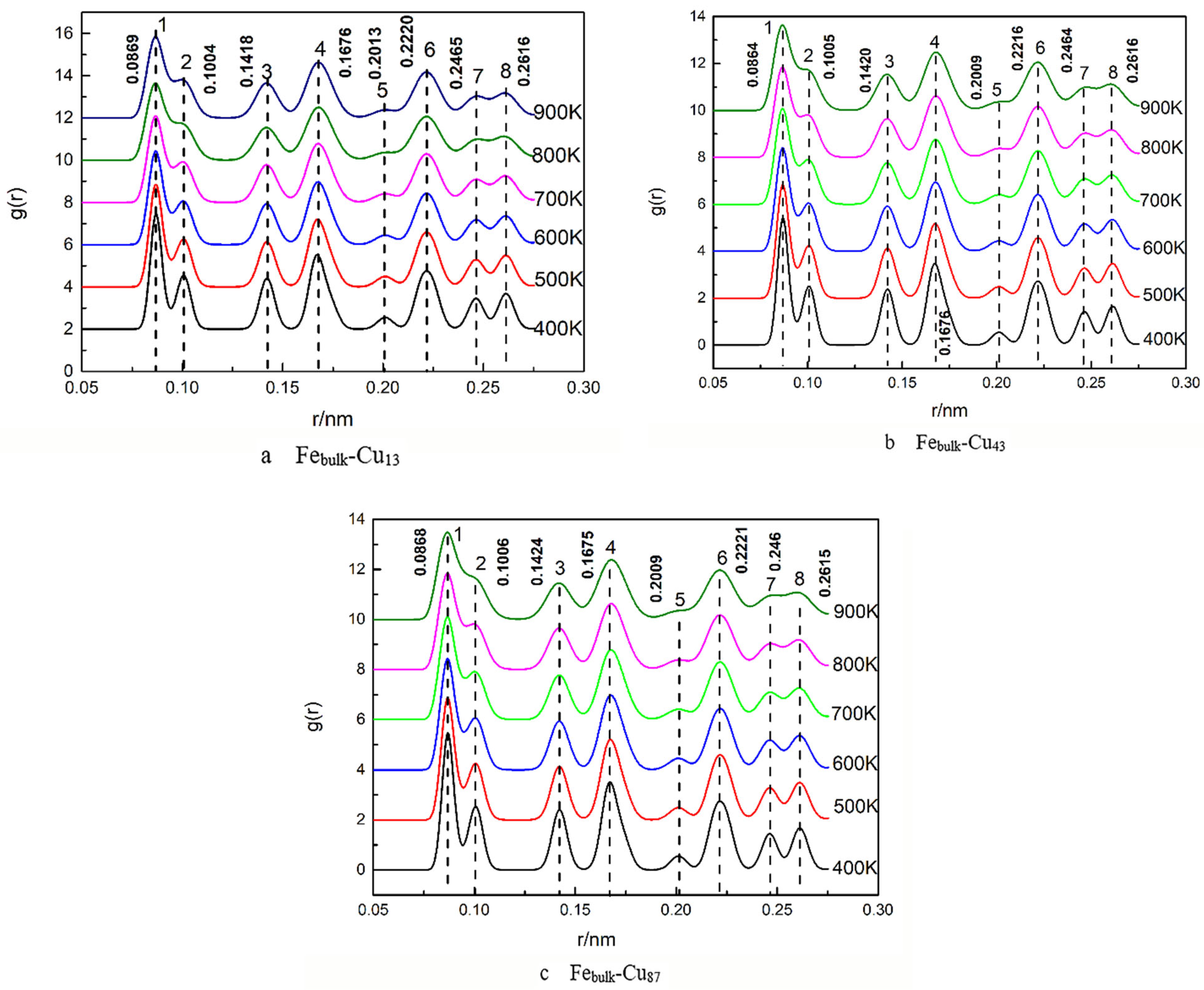
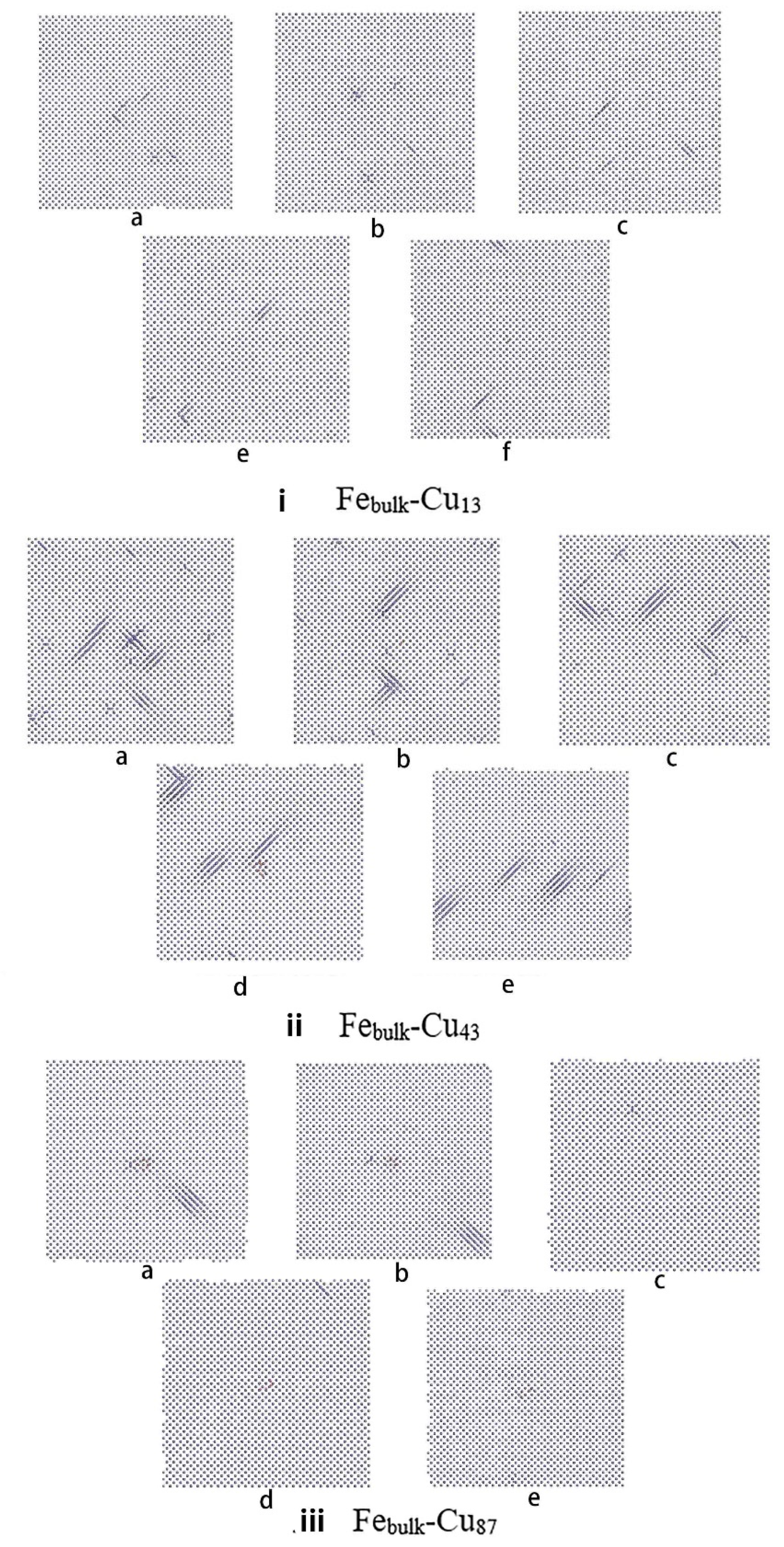
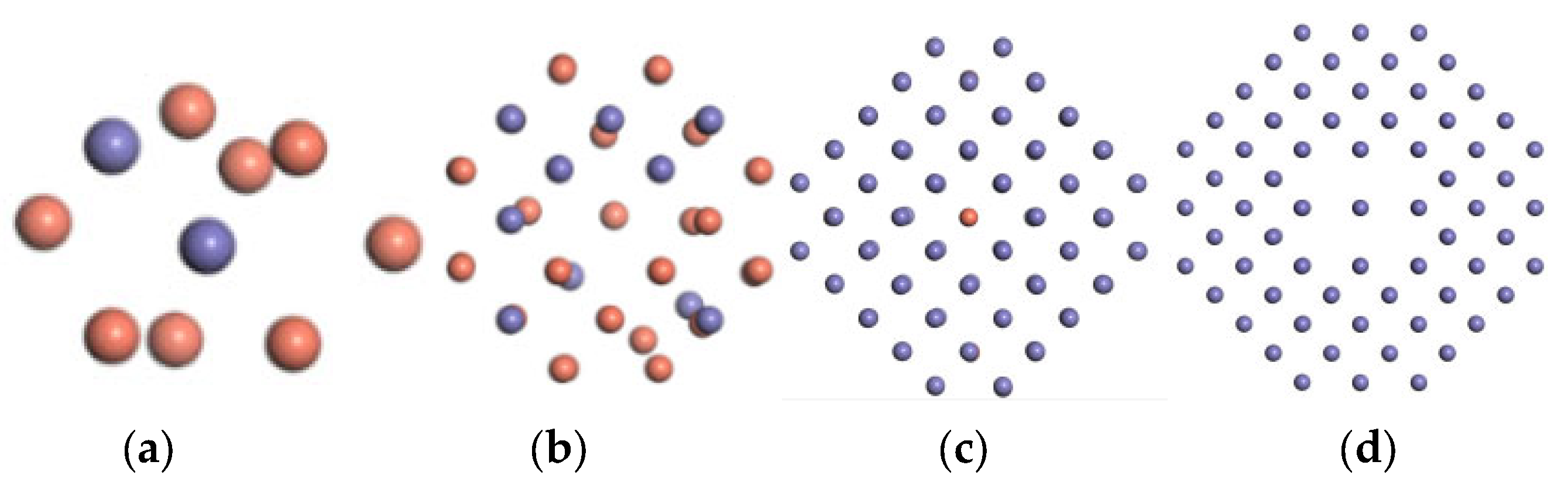
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wasserman, G.; Wincierz, P. Einfluß von Abschreckspannungen auf die Änderung der Gitterkonstanten bei der Aushärtung von Eisen-Kupfer-Legierungen. Arch. Eisenheuuenw 1958, 29, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.; Katayama, Y.; Hono, K. Microstructural Evolution in a 17-4 PH Stainless Steel after Aging at 400 °C. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.D. Reactor Materials, 2nd ed.; Atom Energy Pres: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, G.; González-Albuixech, V.F.; Niffenegger, M. Comparison of K1 calculation methods. J. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2014, 270, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.J.; Caturla, M.J. Cascade damage evolution: Rate theory versus kinetic Monte Carlo simulations. J. Comput. Aided Mater. Des. 2007, 14, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.J.; Caturla, M.J.; Fu, C.C.; Willaime, F. Nucleation and Growth of Defects in He irradiated Fe using Rate Theory and Kinetic Monte Carlo Methods. Mrs Online Proceeding Libr. 2011, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámez, L.; Martinez, E.; Perlado, J.M.; Cepas, P.; Caturla, M.J.; Victoria, M.; Marian, J.; Arévalo, C.; Hernández, M.; Gómez, D. Kinetic Monte Carlo modelling of neutron irradiation damage in iron. Fusion Eng. Des. 2007, 82, 2666–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Meshii, M. Recovery of irradiation-induced defects in high-purity iron and iron–carbon solid solutions. Phys. Status Solidi 1974, 22, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaki, S.; Fuss, J.; Kuglers, H.; Dedek, U.; Schultz, H. The resistivity recovery of high purity and carbon doped iron following low temperature electron irradiation. Radiat. Effects 2006, 79, 87–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.K.; Russell, K.F.; Sokolov, M.A.; Nanstad, R.K. APT characterization of irradiated high nickel RPV steels. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 361, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, K.; Fukuya, K.; Nakata, N.; Hono, K.; Nagai, Y.; Hasegawa, M. Hardening and microstructural evolution in A533B steels under high-dose electron irradiation. J. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 340, 247058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.K.; Russell, K.F. Embrittlement of RPV steels: An atom probe tomography perspective. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 371, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.C.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, R.S.; Nagai, Y.; Inoue, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Toyama, T. Microstructural evolution of RPV steels under proton and ion irradiation studied by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J. Nucl. Mater. 2015, 458, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardekani, S.F.G.; Hadad, K. Monte Carlo evaluation of neutron irradiation damage to the VVER-1000 RPV. Nucl. Energy Technol. 2017, 3, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Q.; Liu, Z. Study on the irradiation effect of mechanical properties of RPV steels using crystal plasticity model. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2019, 51, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Cai, L. Study On the precipitation of cu–rich clusters in the RPV model steel by APT. Acta Metall. Sin. 2012, 48, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, B. Precipitation and Structural Evolution of Copper-Rich Nano Phases in Reactor Pressure Vessel Model Steels; School of Shanghai University: Shanghai, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.Y.; Li, Y.L.; Watanabe, K. Calculation of internal stresses around Cu precipitates in the bcc Febulk by atomic simulation. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1999, 7, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzen, R.; Jenkins, M.L.; Sutton, A.P. The bcc-to-9R martensitic transformation of Cu precipitates and the relaxation of elastic strains in an Fe-Cu alloy. Philos. Mag. A 2000, 80, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.H.; Kim, Y.O.; Kim, S.J. Crystallographic model for bcc-to-9R martensitic transformation of Cu precipitates in ferritic steel. Philos. Mag. 2007, 87, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becquart, C.S.; Domain, C. Solute–point defect interactions in bcc systems: Focus on first principles modelling in W and RPV steels. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2012, 16, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelev, M.I.; Han, A.; Srolovitz, D.J.; Ackland, G.J.; Sun, D.Y.; Asta, M. Asta.Development of new interatomic potentials appropriate for crystalline and liquid iron. Philos. Mag. A 2003, 83, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishin, Y.; Mehl, M.J.; Papaconstantopoulos, D.A.; Voter, A.F.; Kress, J.D. Structural stability and lattice defects in copper: Ab initio, tight-binding, and embedded-atom calculations. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 63, 224106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voter, A.F.; Chen, S.P. Accurate Interatomic Potentials for Ni, Al and Ni3Al.Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 1987, 82, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasianot, R.C.; Malerba, L. Interatomic potentials consistent with thermodynamics: The Fe–Cu system. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 360, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonny, G.; Pasianot, R.C.; Malerba, L. Fitting interatomic potentials consistent with thermodynamics: Fe, Cu, Ni and their alloys. J. Philos. Mag. 2009, 89, 3451–3464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonny, G.; Pasianot, R.C.; Castin, N.; Malerba, L. Ternary Fe-Cu-Ni many-body potential to model reactor pressure vessel steels: First validation by simulated thermal annealing. Philog. Mag. 2009, 89, 3531–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, G. Deformation Characterization of Nano-Scale Cu-Rich Precipitates in Reactor Pressure Vessel Model Steel. J. Shanghai Univ. 2012, 18, 311–316. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, K.; Fukuya, K. Characterization of defect clusters in ion-irradiated A533B steel. Nucl. Mater. 2005, 336, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackland, G.J.; Bacon, D.J.; Calder, A.F.; Harry, T. Computer simulation of point defect properties in dilute Fe—Cu alloy using a many-body interatomic potential. Philos. Mag. A 1997, 75, 713–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domain, C.; Becquart, C.S. Computer simulation of point defect properties in dilute Fe—Cu alloy using a many-body interatomic potential. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 65, 024103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, X.; Li, X. Fe self-diffusion and Cu and Ni diffusion in bulk and grain boundary of Fe: A molecular dynamics study. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 2013, 307, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, L.; Chiapetto, M. An object kinetic Monte Carlo model for the microstructure evolution of neutron-irradiated reactor pressure vessel steels. Phys. Status Solidi A 2016, 213, 2974–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonny, G.; Pasianot, R.C.; Malerba, L. Fe–Ni many-body potential for metallurgical applications. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2009, 17, 025010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, P.; Zhang, L.; Du, L. Atomic Simulations for Packing Changes of Nano-Sized Cu Clusters Embedded in the Febulk on Heating. Metals 2021, 11, 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060934
Yu P, Zhang L, Du L. Atomic Simulations for Packing Changes of Nano-Sized Cu Clusters Embedded in the Febulk on Heating. Metals. 2021; 11(6):934. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060934
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Peng, Lin Zhang, and Linxiu Du. 2021. "Atomic Simulations for Packing Changes of Nano-Sized Cu Clusters Embedded in the Febulk on Heating" Metals 11, no. 6: 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060934
APA StyleYu, P., Zhang, L., & Du, L. (2021). Atomic Simulations for Packing Changes of Nano-Sized Cu Clusters Embedded in the Febulk on Heating. Metals, 11(6), 934. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11060934




