Aluminium Recycling in Single- and Multiple-Capillary Laboratory Electrolysis Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- □
- oxide layers having high permittivity and insulation properties can be obtained through surface treatment;
- □
- high-purity aluminium contains only a small number of impurity elements, precipitates, and inclusions;
- □
- it exhibits high electrical and thermal conductivities.
- □
- extremely high hygroscopicity of AlCl3;
- □
- significant volatility of AlCl3.
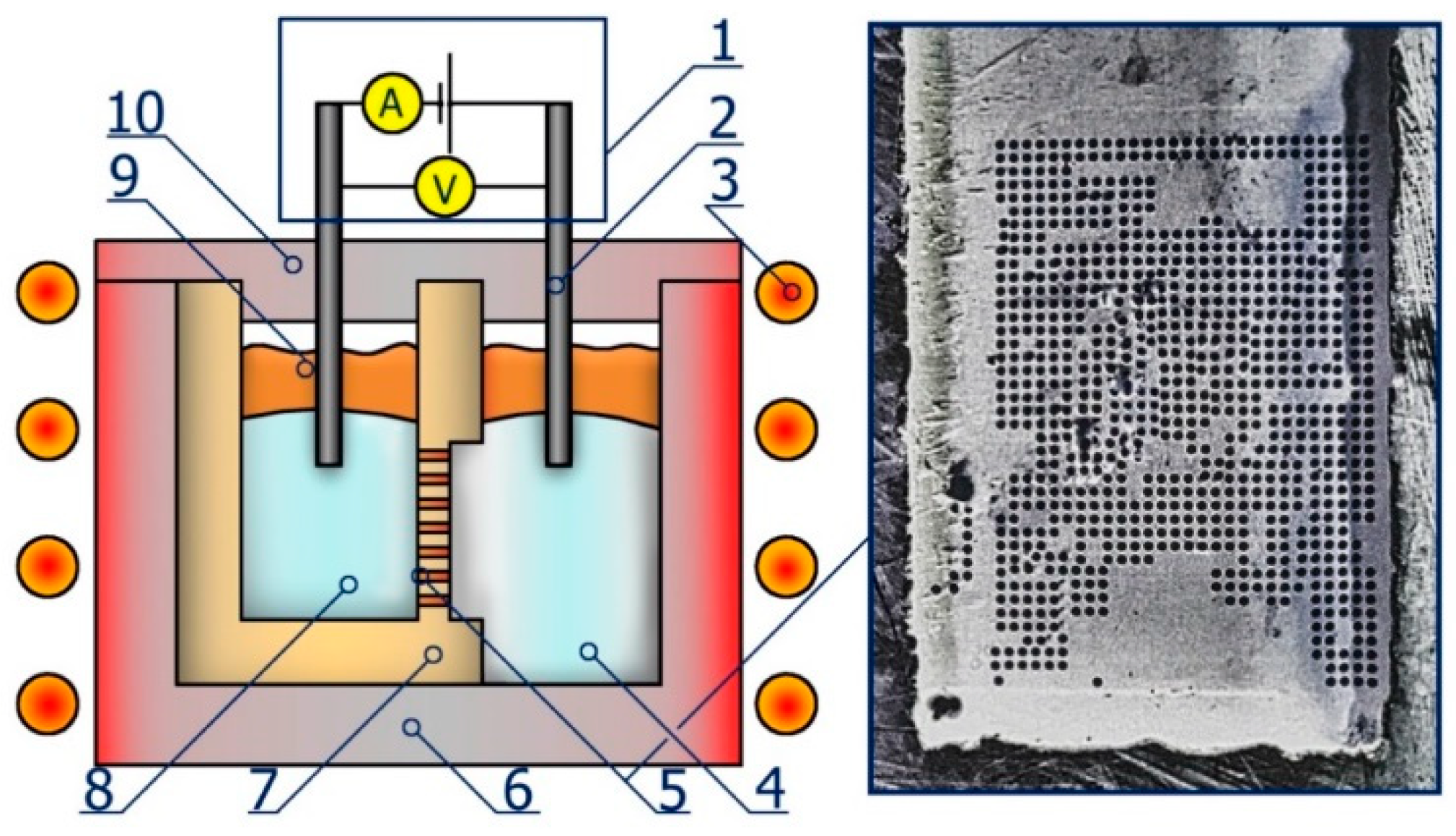
2. Experiment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Single-Capillary Electrolysis
3.2. Multiple-Capillary Electrolysis
4. Conclusions
- □
- the cathodic process on a vertical liquid-aluminium electrode in the NaCl–KCl (+10 wt.% AlF3) in the 2.5 mm length capillary had mixed kinetics with signs of both diffusion and chemical reaction control;
- □
- the apparent mass transport coefficient changed from 5.6 × 10−3 cm.s−1 to 13.1 × 10−3 cm.s−1, which is at least 10 times higher than usually observed in traditional molten salt cells;
- □
- the dependence between the mass transport coefficient and the temperature follows an Arrhenius-type behaviour with the activation energy being 60.5 kJ.mol−1;
- □
- the presence of sodium or potassium in the electrolyte leads to the co-reduction of these metals with aluminium at relatively low current densities. For the refinery process, it is reasonable to keep the current density below 1 A.cm−2 or consider revising the electrolyte (the LiF-AlF3 was tested as a promising candidate);
- □
- the galvanostatic electrolysis in the multiple-capillary cell with the 64LiF–36AlF3 melt showed that the electrochemical refinery can be performed at a current density of 1 A.cm−2, or higher, with the total voltage around 2.0 V and the specific energy consumption about 6–7 kWh.kg−1;
- □
- the resistance fluctuated between 0.9 and 1.4 Ω during the electrolysis depending on the current density.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Soo, V.K.; Peeters, J.; Paraskevas, D.; Compston, P.; Doolan, M.; Duflou, J.R. Sustainable aluminium recycling of end-of-life products: A joining techniques perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 178, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bureau of International Recycling (BIR). Annual Report 2019. Available online: https://www.bir.org/publications/annual-reports/download/648/1000000235/36?method=view (accessed on 5 May 2021).
- Eggen, S.; Sandaunet, K.; Kolbeinsen, L.; Kvithyld, A. Recycling of Aluminium from Mixed Household Waste, Light Metals; Tomsett, A., Ed.; TMS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; p. 1091. [Google Scholar]
- Huan, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, K.; Peng, J.; Di, Y. Impurity Behavior in Aluminum Extraction by Low-Temperature Molten Salt Electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 103503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, S.; Eskin, D.; Jacot, A. Fractional Solidification for Purification of Recycled Aluminium Alloys, Light Metals; Tomsett, A., Ed.; TMS: San Diego, CA, USA, 2020; p. 1110. [Google Scholar]
- Mikubo, S. The Latest Refining Technologies of Segregation Process to Produce High Purity Aluminum. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, Yokohama, Japan, 5–9 September 2010; p. 224. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshikawa, H.; Tanaka, I.; Megumi, T. Refining Technology and Low Temperature Properties for High Purity Aluminium, Translated from R&D Report, “SUMITOMO KAGAKU”, vol. 2013. Available online: https://www.sumitomo-chem.co.jp/english/rd/report/files/docs/2013E_2.pdf (accessed on 14 May 2021).
- Kondo, M.; Maeda, H.; Mizuguchi, M. The production of high purity aluminum in Japan. JOM 1990, 42, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Long, W.J., III; Hayden, H.W.; Green, J.A.S.; Hunt, W.H., Jr. Energy implications of the changing world of aluminum metal supply. JOM 2003, 56, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padamata, S.K.; Yasinskiy, A.S.; Polyakov, P.V. The cathodic behavior of aluminum from Pt/Al2O3 catalysts in molten LiF-AlF3-CaF2 and implications for metal recovery from spent catalysts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 013505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasinskiy, A.; Polyakov, P.; Varyukhin, D.Y.; Padamata, S.K. Liquid Bipolar Electrode for Extraction of Aluminium and PGM Concentrate from Spent Catalysts, 150th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings; TMS: Orlando, FL, USA, 2021; p. 812. [Google Scholar]
- Padamata, S.K.; Yasinskiy, A.S.; Polyakov, P.V.; Pavlov, E.A.; Varyukhin, D.Y. Recovery of noble metals from spent catalysts: A review. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2020, 51, 2413–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Z. Extracting aluminum from aluminum alloys in AlCl3-NaCl molten salts. High Temp. Mater. Proc. 2013, 32, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grjotheim, K.; Matiasovsky, K. Some Problems Concerning Aluminium Electro-plating in Molten Salts. Acta Chem. Scand. A 1980, 34, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasinskiy, A.; Polyakov, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Suzdaltsev, A.; Moiseenko, I.; Padamata, S.K. Electrochemical reduction and dissolution of liquid aluminium in thin layers of molten halides. Electrochim. Acta. 2021, 366, 137436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasinskiy, A.; Polyakov, P.; Moiseenko, I.; Padamata, S.K. Electrochemical Reduction and Dissolution of Aluminium in a Thin-Layer Refinery Process, Light Metals; TMS: Orlando, FL, USA, 2021; p. 519. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, N. Electrochemical deposition of aluminum on W electrode from AlCl3-NaCl melts. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China. 2010, 20, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, J.; Di, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, L. Recovery of aluminum from waste aluminum alloy by low-temperature molten salt electrolysis. Miner. Eng. 2020, 154, 106386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaev, A.Y.; Suzdaltsev, A.V.; Zaikov, Y.P. Cathode Process in the KF-AlF3-Al2O3 Melts. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, D784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzdaltsev, A.V.; Nikolaev, A.Y.; Zaikov, Y.P. Towards the Stability of Low-Temperature Aluminum Electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 046521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonstad, J.; Fellner, P.; Haarberg, G.M.; Híveš, J.; Kvande, H.; Sterten, Â. Aluminium Electrolysis: Fundamentals of the Hall-Hérout Process, 3rd ed.; Aluminium: Dusseldorf, Germany, 2001; p. 359. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, J.L.; McAIister, A.J. The AI-Si (Aluminum-Silicon) System. Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 1984, 5, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, T.; Morita, K.; Sano, N. Thermodynamic Properties of Aluminum, Magnesium, and Calcium in Molten Silicon. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1998, 29, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods. Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 833. [Google Scholar]




| θ, °C | OCP, V | il, A.cm−2 | Km∙103, cm.s−1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 720 | 0.001791 | −0.075 | 2.9 | 5.6 |
| 780 | 0.001753 | −0.073 | 4.7 | 9.3 |
| 800 | 0.001740 | −0.043 | 4.9 | 9.7 |
| 850 | 0.001709 | −0.031 | 6.5 | 13.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yasinskiy, A.; Padamata, S.K.; Moiseenko, I.; Stopic, S.; Feldhaus, D.; Friedrich, B.; Polyakov, P. Aluminium Recycling in Single- and Multiple-Capillary Laboratory Electrolysis Cells. Metals 2021, 11, 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071053
Yasinskiy A, Padamata SK, Moiseenko I, Stopic S, Feldhaus D, Friedrich B, Polyakov P. Aluminium Recycling in Single- and Multiple-Capillary Laboratory Electrolysis Cells. Metals. 2021; 11(7):1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071053
Chicago/Turabian StyleYasinskiy, Andrey, Sai Krishna Padamata, Ilya Moiseenko, Srecko Stopic, Dominic Feldhaus, Bernd Friedrich, and Peter Polyakov. 2021. "Aluminium Recycling in Single- and Multiple-Capillary Laboratory Electrolysis Cells" Metals 11, no. 7: 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071053
APA StyleYasinskiy, A., Padamata, S. K., Moiseenko, I., Stopic, S., Feldhaus, D., Friedrich, B., & Polyakov, P. (2021). Aluminium Recycling in Single- and Multiple-Capillary Laboratory Electrolysis Cells. Metals, 11(7), 1053. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11071053









