Evaluation of the Effect of Minor Additions in the Crystallization Path of [(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.2Si0.05]100-xMx Metallic Glasses by Means of Mössbauer Spectroscopy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zarazúa-Villalobos, L.; Mary, N.; Soo-Hyun, J.; Ogawa, K.; Kato, H.; Ichikawa, Y. Microstructure and corrosion study of Fe-based bulk metallic glass obtained by spark plasma sintering. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 880, 160399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüce, E.; Sarac, B.; Ketov, S.; Reissner, M.; Eckert, J. Effects of Ni and Co alloying on thermal, magnetic and structural properties of Fe-(Ni,Co)-P-C metallic glass ribbons. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 872, 159620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, C. Fe-based amorphous coatings: Structures and properties. Thin Solid Films 2014, 561, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.B.; Jiang, C.; Xu, S.; Gao, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Lu, Y. Reliability of tensile fracture strength of Co-based metallic glass microwires by Weibull statistics. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 106565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Law, J.; Huang, Y.; Franco, V.; Shen, H.; Jiang, S.; Bao, Y.; Sun, J. Design of Fe-containing GdTbCoAl high-entropy-metallic-glass composite microwires with tunable Curie temperatures and enhanced cooling efficiency. Mater. Des. 2021, 206, 109824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.X.; Lu, Z.C.; Wang, S.L.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Z.P. Fe-based bulk metallic glasses: Glass formation, fabrication, properties and applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 103, 235–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Yang, C.; Bian, X.; Zhao, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Guo, T. Application of Fe78Si9B13 amorphous particles in magnetorheological fluids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22511–22518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Iron-based bulk metallic glasses. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 131–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, K.I.; Jeong, H.; Hong, S.A.; Kim, M.; Lee, K.; Kim, K.T. Nano-crystallization behavior and magnetic domain evolution in commercial Fe–Si–B metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 157565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.C.; Sun, C.; Sun, C. Functional Applications of Metallic Glasses in Electrocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 2401–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.F.; Zheng, Y.F. Recent advances in bulk metallic glasses for biomedical applications. Acta Biomater. 2016, 36, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Hu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Inoue, A. Novel bioactive Fe-based metallic glasses with excellent apatite-forming ability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 69, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, S.T.; Arockiarajan, A. Thin film metallic glasses for bioimplants and surgical tools: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 876, 159939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, P.C.; Song, S.M.; Nien, Y.Y.; Wang, W.R.; Tsai, P.H.; Wu, J.L.; Jang, J.S.C. Mechanical properties enhanced by the dispersion of porous Mo particles in the biodegradable solid and bi-phase core–shell structure of Mg-based bulk metallic glass composites for applications in orthopedic implants. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 877, 160233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, M.; Greer, A. Metallic glasses as structural materials. Scr. Mater. 2006, 54, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Liang, X.; Huang, J.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J.; Shen, J. Insight into efficient degradation of 3,5-dichlorosalicylic acid by Fe-Si-B amorphous ribbon under neutral condition. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 294, 120258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, B.; Olarinoye, I.O.; Mutuwong, C.; Sriwunkum, C.; Yakout, H.A.; Tekin, H.O.; Al-Buriahi, M.S. Amorphous alloys with high Fe content for radiation shielding applications. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2021, 183, 109386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Bulk Metallic Glasses, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Shen, B.L.; Chang, C.T. Super-high strength of over 4000 MPa for Fe-based bulk glassy alloys in [(Fe1-xCox)0.75B0.2Si 0.05]96Nb4 system. Acta Mater. 2004, 52, 4093–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Inoue, A.; Chang, C. Superhigh strength and good soft-magnetic properties of (Fe,Co) -B-Si-Nb bulk glassy alloys with high glass-forming ability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 4911–4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, M.; Yin, K.; Zeng, Q.; Sun, L.; Shen, B. Enhancement of plasticity for FeCoBSiNb bulk metallic glass with superhigh strength through cryogenic thermal cycling. Scr. Mater. 2020, 187, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, J.; González, S.; Rossinyol, E.; Suriñach, S.; Baró, M.D.; Louzguine-Luzgin, D.V.; Perepezko, J.H.; Sort, J.; Inoue, A. Enhanced mechanical properties due to structural changes induced by devitrification in Fe-Co-B-Si-Nb bulk metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 6256–6266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesz, S.; Babilas, R.; Nabiałek, M.; Szota, M.; Dośpiał, M.; Nowosielski, R. The characterization of structure, thermal stability and magnetic properties of Fe-Co-B-Si-Nb bulk amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509 (Suppl. 1), S197–S201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, P.; Stoica, M.; Taghvaei, A.H.; Prashanth, K.G.; Kumar, R.; Eckert, J. Kinetic analysis of the non-isothermal crystallization process, magnetic and mechanical properties of FeCoBSiNb and FeCoBSiNbCu bulk metallic glasses. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 073908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Chang, C.; Inoue, A. Formation, ductile deformation behavior and soft-magnetic properties of (Fe,Co,Ni)-B-Si-Nb bulk glassy alloys. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens-Serra, J.; Bruna, P.; Stoica, M.; Roth, S.; Eckert, J. Glass forming ability, thermal stability, crystallization and magnetic properties of [(Fe,Co,Ni)0.75Si0.05B0.20] 95Nb4Zr1 metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2013, 367, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Shen, B. Soft magnetic bulk glassy Fe-B-Si-Nb alloys with high saturation magnetization above 1.5 T. Mater. Trans. 2002, 43, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, B.; Chang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Inoue, A. Enhancement of glass-forming ability of FeCoNiBSiNb bulk glassy alloys with superhigh strength and good soft-magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 102, 023515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens-Serra, J.; Bruna, P.; Stoica, M.; Eckert, J. Glass-forming ability and microstructural evolution of [(Fe0.6Co0.4)0.75Si0.05B0.20]96-xNb4Mx metallic glasses studied by Mössbauer spectroscopy. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 704, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; He, A.N.; Shen, B.L. Effect of Tb addition on the thermal stability, glass-forming ability and magnetic properties of Fe-B-Si-Nb bulk metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, S46–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Men, H.; Shen, B. Soft-ferromagnetic bulk glassy alloys with large magnetostriction and high glass-forming ability. AIP Adv. 2011, 1, 042110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, G.; Shen, B. Thermal stability and crystallization behavior of (Fe 0.75—XDyxB0.2Si0.05) 96Nb4 (x = 0–0.07) bulk metallic glasses. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2013, 365, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, P.; Stoica, M.; Bera, S.; Calin, M.; Eckert, J. Effect of replacing Nb with (Mo and Zr) on glass forming ability, magnetic and mechanical properties of FeCoBSiNb bulk metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 707, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirata, A.; Guan, P.; Fujita, T.; Hirotsu, Y.; Inoue, A.; Yavari, A.R.; Sakurai, T.; Chen, M. Direct observation of local atomic order in a metallic glass. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, A. Local structure analysis of amorphous materials by angstrom-beam electron diffraction. Microscopy 2021, 70, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrissi, H.; Ghidelli, M.; Béché, A.; Turner, S.; Gravier, S.; Blandin, J.J.; Raskin, J.P.; Schryvers, D.; Pardoen, T. Atomic-scale viscoplasticity mechanisms revealed in high ductility metallic glass films. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gemma, R.; to Baben, M.; Pundt, A.; Kapaklis, V.; Hjörvarsson, B. The impact of nanoscale compositional variation on the properties of amorphous alloys. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babilas, R.; Spilka, M.; Młynarek, K.; Łoński, W.; Łukowiec, D.; Radoń, A.; Kądziołka-Gaweł, M.; Gębara, P. Glass-forming ability and corrosion resistance of Al88Y8-xFe4+x (x = 0, 1, 2 at.%) alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolano-Burian, A.; Zackiewicz, P.; Grabias, A.; Wojcik, A.; Maziarz, W.; Szlezynger, M.; Wlodarczyk, P.; Kowalczyk, M.; Hawelek, L. Effect of Co Substitution and Thermo-Magnetic Treatment on the Structure and Induced Magnetic Anisotropy of Fe84.5−xCoxNb5B8.5P2 Nanocrystalline Alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian Baghbaderani, H.; Masood, A.; Alvarez, K.L.; Mathúna, C.; McCloskey, P.; Stamenov, P. CALPHAD-assisted development of in-situ nanocrystallised melt-spun Co-Fe-B alloy with high Bs (1.57 T). J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 877, 160194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.M.M.; López, J.E.R.; Munevar, J.; Saitovitch, E.B.; Aldana, L.C.M.; Vargas, C.A.P. Synthesis and characterization of the structural and magnetic properties of the Sm3-xGdxFe5O12(x = 0.0–1.0) garnets using solid-state reaction and citrate methods. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkov, V.I.; Martinson, K.D.; Kondrashkova, I.S.; Enikeeva, M.O.; Nevedomskiy, V.N.; Panchuk, V.V.; Semenov, V.G.; Volkov, M.P.; Pleshakov, I.V. SCS-assisted production of EuFeO3 core-shell nanoparticles: Formation process, structural features and magnetic behavior. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 859, 157812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, S.P.; Mathew, M.J. Determination of ferrimagnetic and superparamagnetic components of magnetization and the effect of particle size on structural, magnetic and hyperfine properties of Mg0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 869, 159242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, R. NORMOS-90 Mössbauer Fitting Program Package; Wissel GmbH: Starnberg, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, M.; Li, R.; Yavari, A.R.; Vaughan, G.; Eckert, J.; Van Steenberge, N.; Romera, D.R. Thermal stability and magnetic properties of FeCoBSiNb bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 504, S123–S128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea, D.; Parra, C.; Ramasamy, P.; Stoica, M.; Eckert, J.; Bolívar, F.; Echeverría, F. Structural and phase evolution upon annealing of Fe76 Si9−x B10 P5 Mox (X = 0, 1, 2 and 3) alloys. Metals 2020, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinov, V.A.; Tsurin, V.A.; Surikov, V.T. DAPO effect in Fe23B6. Phys. Met. Metallogr. 2012, 113, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, M.; Yao, L.; Nan, R.; Jian, Z.; Chang, F. Effect of Mo substitution for Nb on the glass-forming ability, magnetic properties, and electrical resistivity in Fe 80 (Nb 1–x Mo x) 5 B 15 (x = 0–0.75) amorphous ribbons. Vacuum 2019, 163, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, T. Effect of similar element substitution on Fe-B-Si-Mo bulk metallic glasses studied by experiment and ab initio molecular dynamics simulation. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 784, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



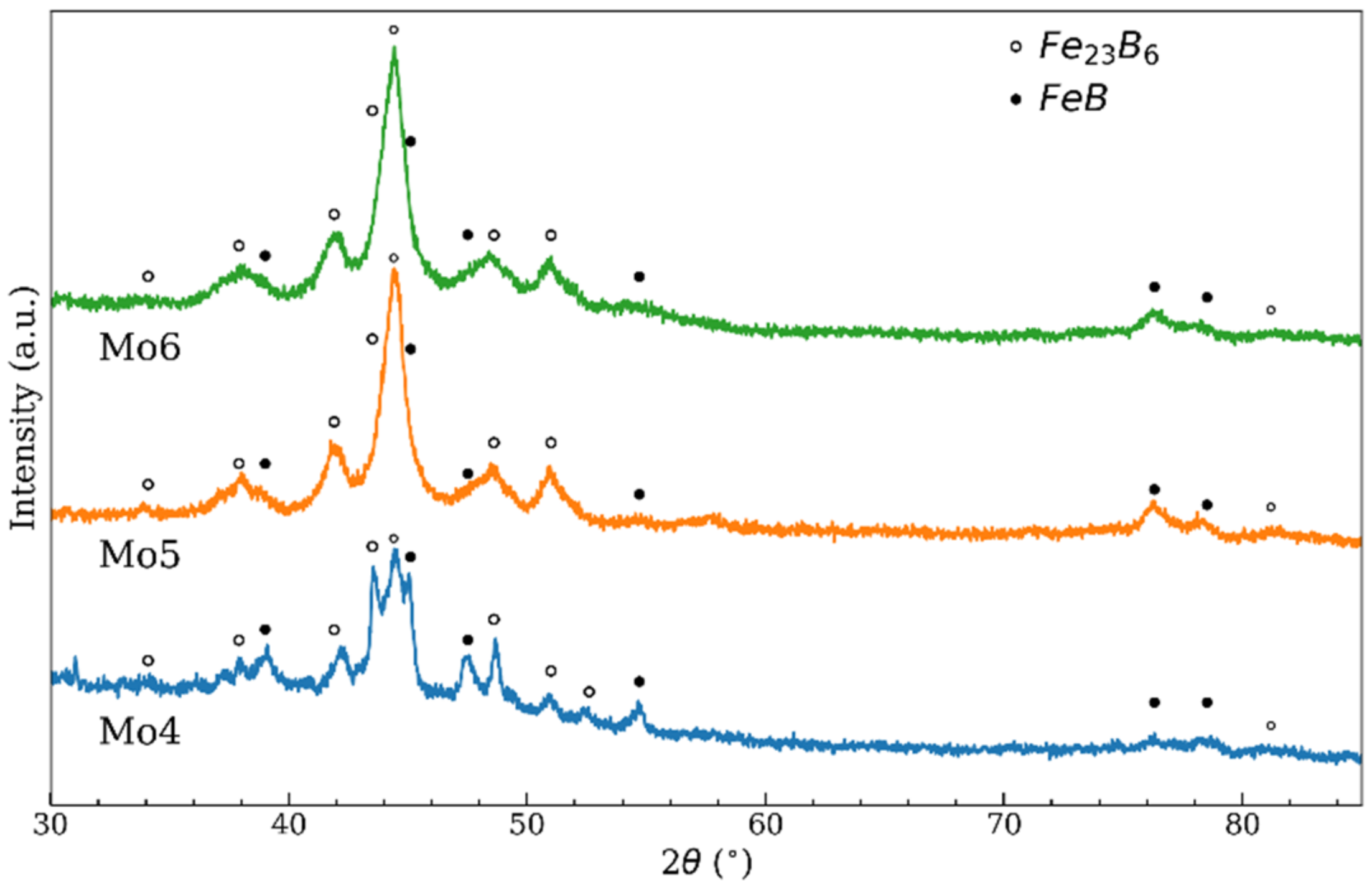
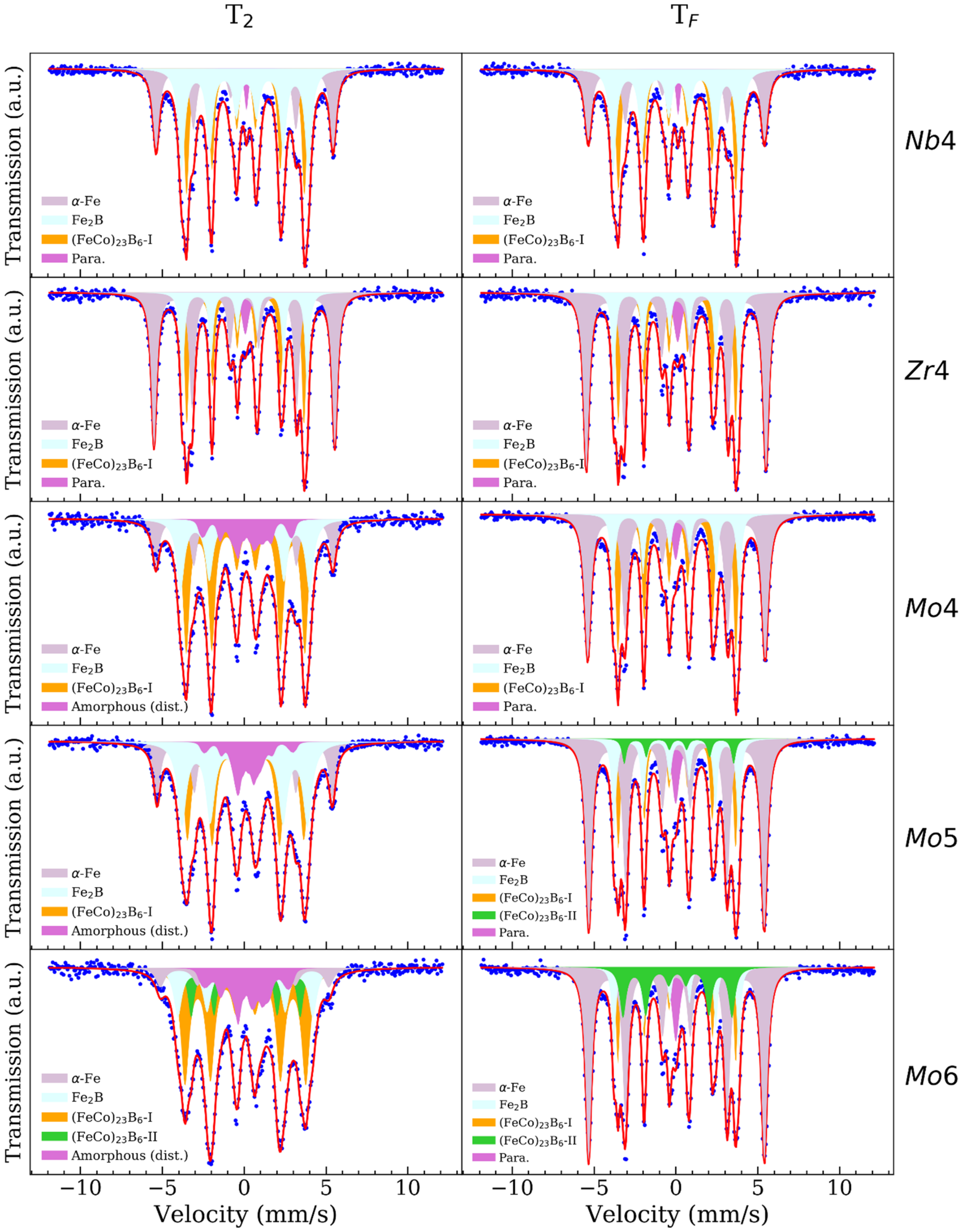

| Temperature | Zr4 | Nb4 | Mo4 | Mo5 | Mo6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | 900 | 910 | 891 | 885 | 875 |
| T2 | 1003 | 1023 | 975 | 1010 | 990 |
| T3 | - | - | 1056 | 1063 | - |
| TF | 1093 | 1118 | 1169 | 1159 | 1169 |
| Nb4 | Mo4 | Mo5 | Mo6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-Fe/Fe-borides | 0.37 | 0.23 | 0.26 | 0.1 |
| dc (mm) | 3 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panahi, S.L.; Ramasamy, P.; Masdeu, F.; Stoica, M.; Torrens-Serra, J.; Bruna, P. Evaluation of the Effect of Minor Additions in the Crystallization Path of [(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.2Si0.05]100-xMx Metallic Glasses by Means of Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Metals 2021, 11, 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081293
Panahi SL, Ramasamy P, Masdeu F, Stoica M, Torrens-Serra J, Bruna P. Evaluation of the Effect of Minor Additions in the Crystallization Path of [(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.2Si0.05]100-xMx Metallic Glasses by Means of Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Metals. 2021; 11(8):1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081293
Chicago/Turabian StylePanahi, S. Leila, Parthiban Ramasamy, Francesc Masdeu, Mihai Stoica, Joan Torrens-Serra, and Pere Bruna. 2021. "Evaluation of the Effect of Minor Additions in the Crystallization Path of [(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.2Si0.05]100-xMx Metallic Glasses by Means of Mössbauer Spectroscopy" Metals 11, no. 8: 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081293
APA StylePanahi, S. L., Ramasamy, P., Masdeu, F., Stoica, M., Torrens-Serra, J., & Bruna, P. (2021). Evaluation of the Effect of Minor Additions in the Crystallization Path of [(Fe0.5Co0.5)0.75B0.2Si0.05]100-xMx Metallic Glasses by Means of Mössbauer Spectroscopy. Metals, 11(8), 1293. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081293







