Lead Electrodeposition from Triethylenetetramine Solution Containing Inhibitors
Abstract
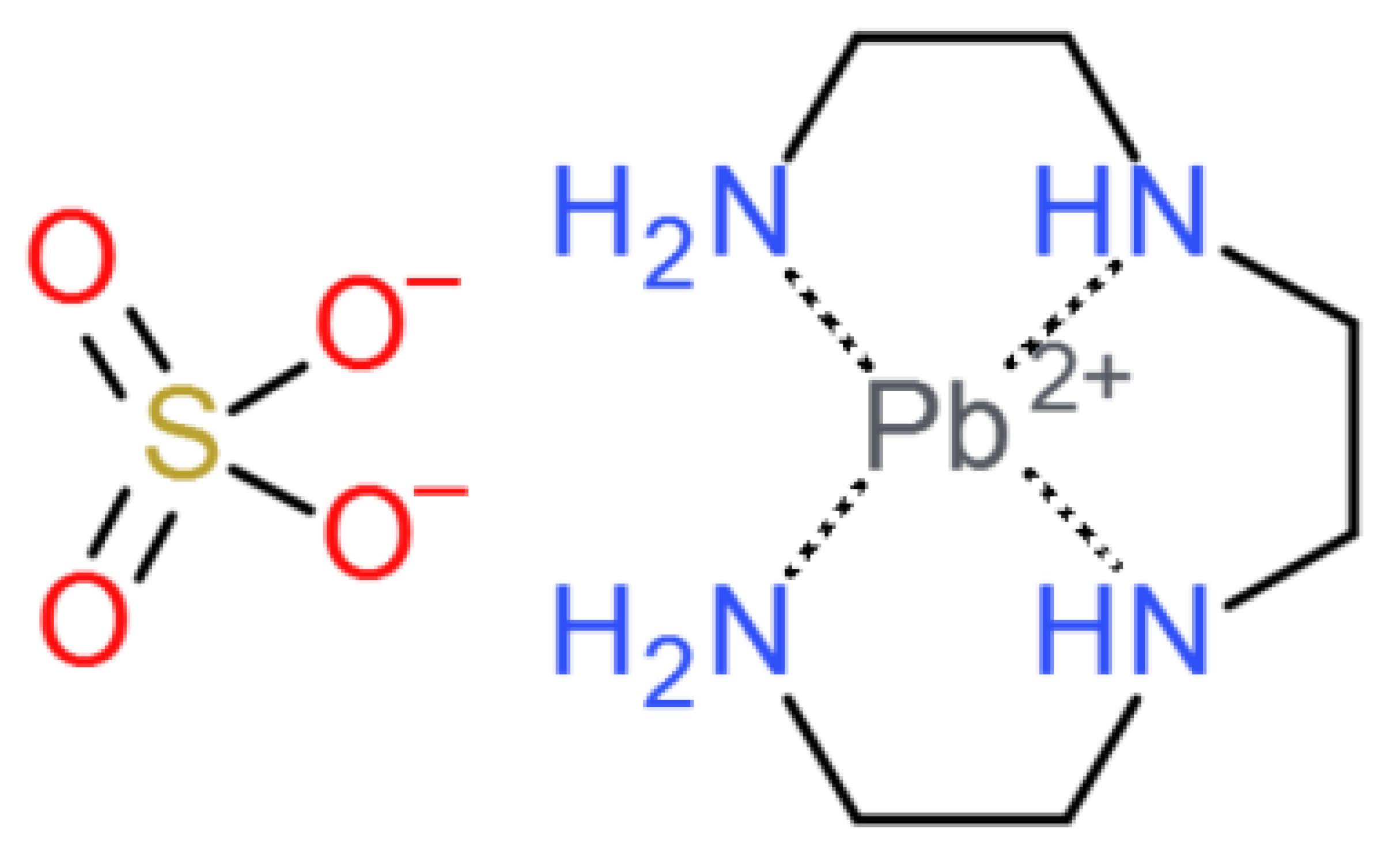
:1. Introduction
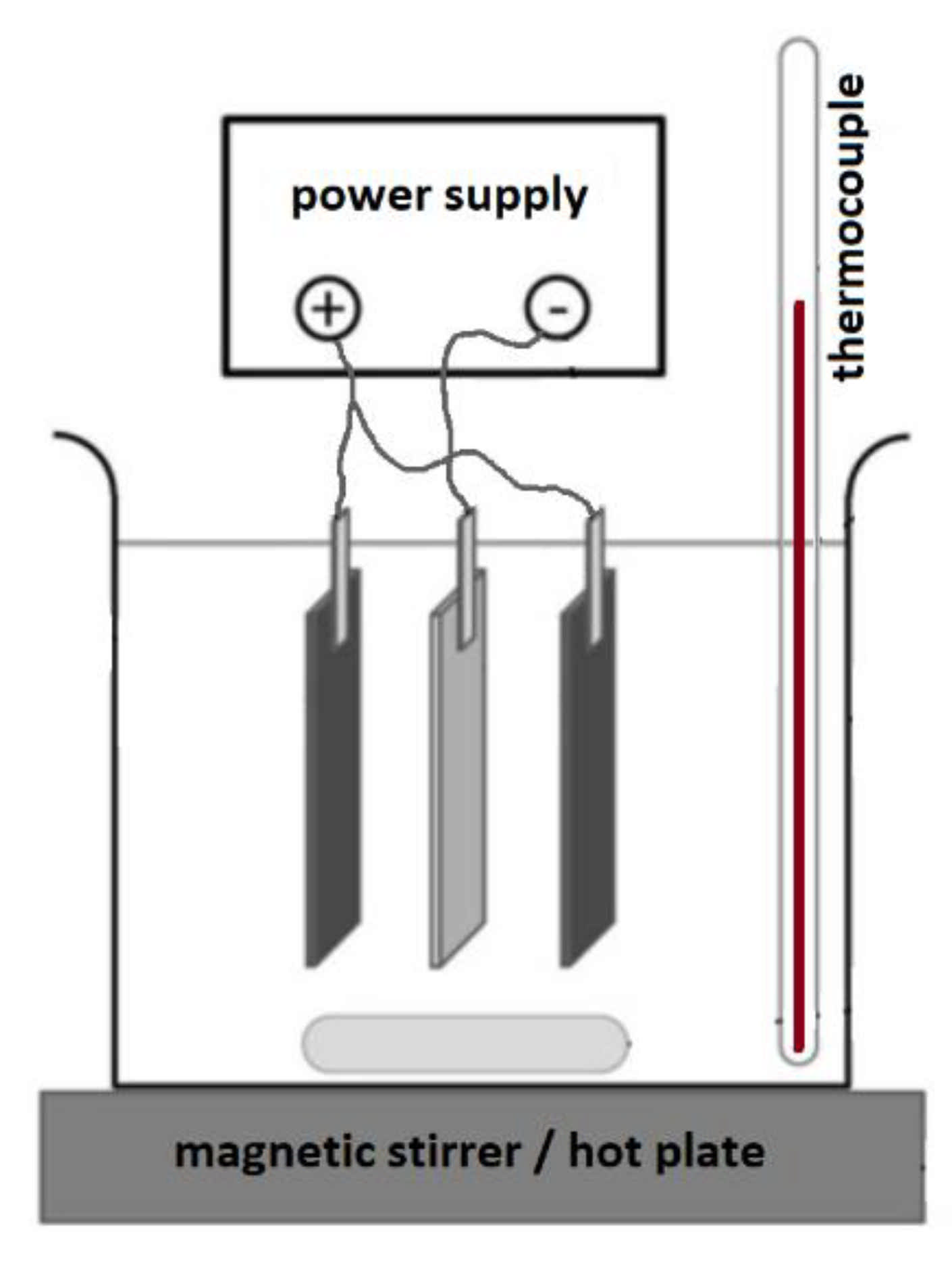
2. Materials and Methods
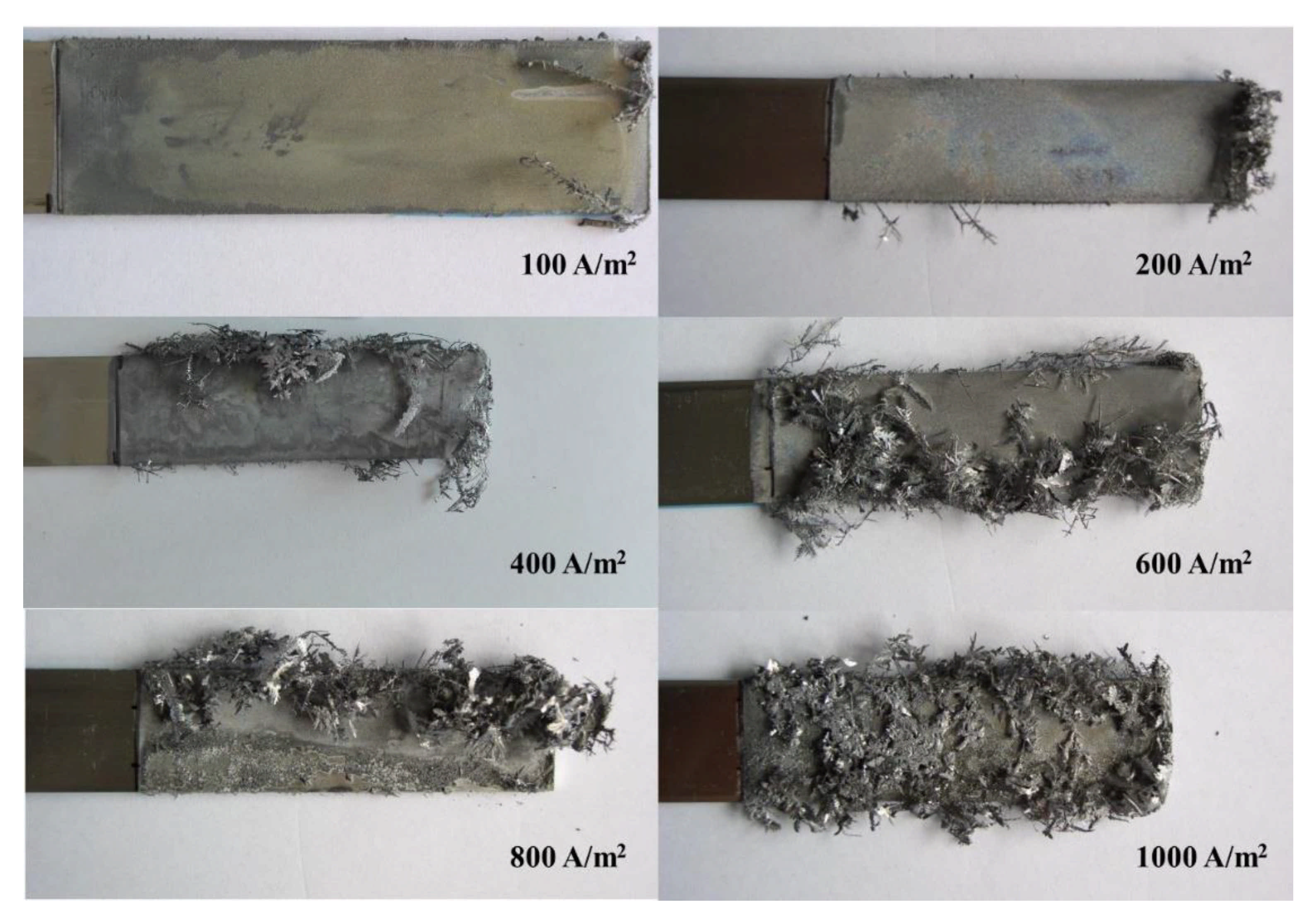
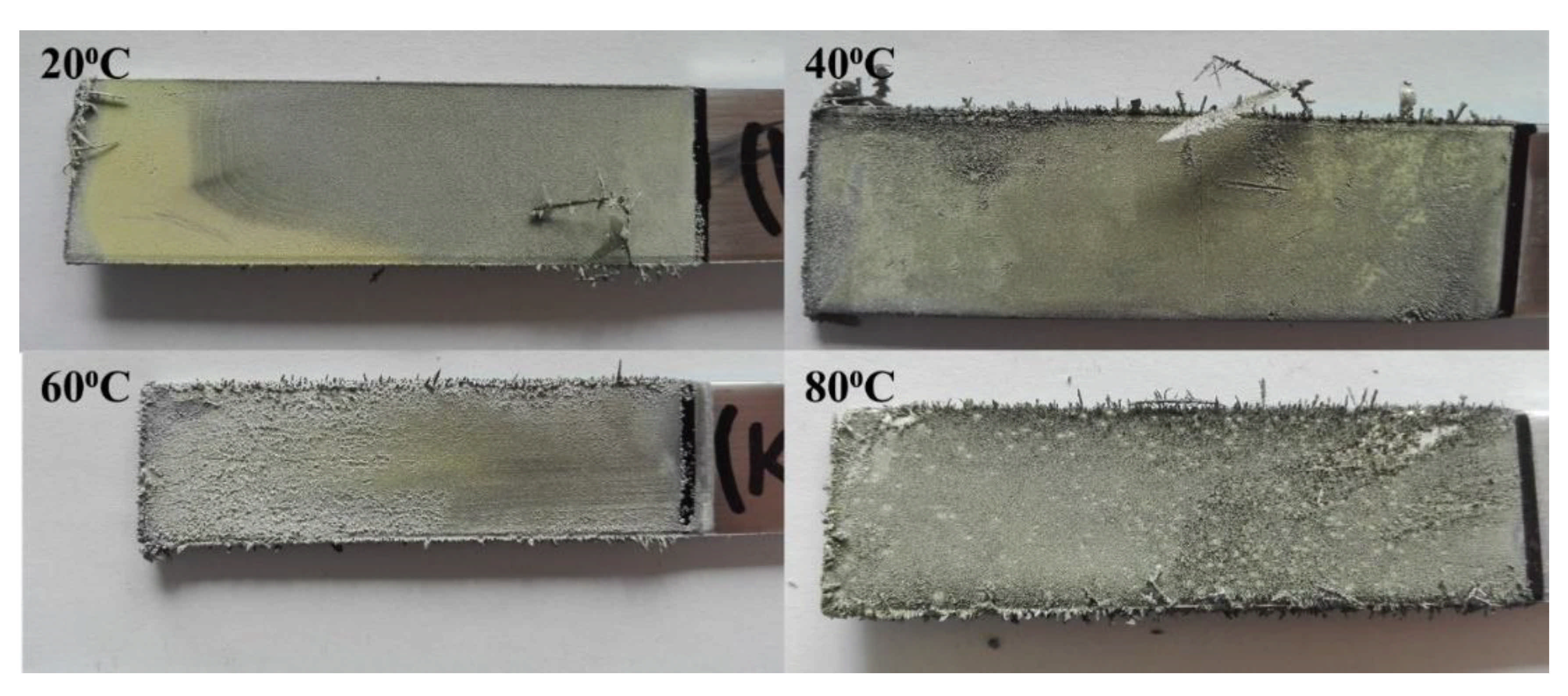
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassina, A.; Piantonea, P.; Burnola, A.; Bodénana, F.; Chateaub, L.; Lerougea, C.; Crouzeta, C.; Guyonneta, D.; Bailly, L. Reactivity of waste generated during lead recycling: An integrated study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 139, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Horckmans, L.; Spooren, J.; Vrancken, K.C.; Quaghebeur, M.; Broos, K. Selective leaching of Pb, Cu, Ni and Zn from secondary lead smelting residues. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 169, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparajith, B.; Mohanty, D.B.; Gupta, M.L. Recovery of enriched lead–silver residue from silver-rich concentrate of hydrometallurgical zinc smelter. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 105, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Mohanan, P.K.; Patnaik, S.C. Innovative processing technique to produce zinc concentrate from zinc leach residue with simultaneous recovery of lead and silver. Hydrometallurgy 1998, 48, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frıas, C.; Dıaz, G.; Ocana, N.; Lozano, J.I. Silver, gold and lead recovery from bioleaching residues using the PLINT process. Miner. Eng. 2002, 15, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, M.; Erdem, M. Cleaning of high lead-bearing zinc leaching residue by recovery of lead with alkaline leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 153, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Li, G.; Yan, P.; Zheng, L.; Sun, S.; Huang, S.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Huang, J. Production of lead concentrate from bioleached residue tailings by brine leaching followed by sulfide precipitation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 183, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, Y. Hydrometallurgical recovery of lead from spent lead-acid battery paste via leaching and electrowinning in chloride solution. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-S.; Shih, Y.-J.; Huang, Y.-H. Recovery of lead from smelting fly ash of waste lead-acid battery by leaching and electrowinning. Waste Manag. 2016, 52, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tang, C.B.; Xiao, J.; Zeng, P.; Tang, M.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z. A cleaner process for lead recovery from lead-containing hazardous solid waste and zinc leaching residue via reducing-matting smelting. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 241, 118328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielarz, A.; Szołomicki, Z.; Mrozowski, J.; Prajsnar, R.; Wolarek, J.; Skawiński, L.; Celarek, A.; Hanzel, M. Piloting amine battery paste desulphurisation process. In Proceedings of the Pb Zn 2010 Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3–6 October 2010; p. 747. [Google Scholar]
- Yanakieva, V.P.; Haralampiev, G.A.; Lyakov, N.K. Desulphurization of the damped lead battery paste with potassium carbonate. J. Power Sources 2000, 85, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyakov, N.K.; Atanasova, D.A.; Vassilev, V.S.; Haralampiev, G.A. Desulphurization of damped battery paste by sodium carbonate and sodium hydroxide. J. Power Sources 2007, 171, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yi, L.; Yang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Bian, W. A new pre-desulphurization process of damped lead battery paste with sodium carbonate based on a “surface update”concept. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 160, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, M.; Oliveri, D.; Ferrara, G.; Salvaggio, M.; Piazza, S.; Italiano, S.; Sunseri, C. Metallic lead recovery from lead-acid battery paste by urea acetate dissolution and cementation on iron. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 96, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.V.; Petrova Kotzeva, V.; Sonmez, S. Lead Recycling. US8323376B2, 4 December 2012. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US8323376B2/en (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Pan, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y. A new process of lead recovery from waste lead-acid batteries by electrolysis of alkaline lead oxide solution. Electrochem. Commun. 2012, 19, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Duan, L.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Yang, S.; Xia, Z. Facile method for preparing a nano lead powder by vacuum decomposition from spent lead-acid battery paste: Leaching and desulfuration in tartaric acid and sodium tartrate mixed lixivium. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 197, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qu, R.; Sun, C.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Ji, C.; Yin, P.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, H.; Niu, Y. Comparison of synthesis of chelating resin silica-gel-supported diethylenetriamine and its removal properties for transition metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wu, P.; Dang, Z.; Zhu, N.; Liu, Z.; Luo, H. Leaching characteristics of heavy metals in tailings and their simultaneous immobilization with triethylenetetramine functioned montmorillonite (TETA-Mt) against simulated acid rain. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gélinas, S.; Finch, J.A.; Rao, S.R. Electrowinning of Nickel and Copper from Ethylenediamine Complexes. Can. Q. 2002, 41, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Rodriguez, N.; Onghena, B.; Binnemans, K. Recovery of Lead and Silver from Zinc Leaching Residue Using Methanesulfonic Acid. ACS Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 19807–19815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szolomicki, Z.; Chmielarz, A.; Smieszek, Z.; Myczkowski, Z.; Mrozowski, J.; Wasilewski, W.; Gotfryd, L.; Prajsnar, R.; Buzek, L.; Raszka, U.; et al. Method for Desulphurization of Battery Paste. EP2333895A1, 13 June 2012. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP2333895A1/en?oq=EP2333895A1%2c+2009 (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Jordan, M. Electrodeposition of lead and lead alloys. In Modern Electroplating, 5th ed.; Schlesinger, M., Paunovic, M., Eds.; Wiley: Pennington, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 249–263. [Google Scholar]
- Exposito, E.; Gonzalez-Garcıa, J.; Bonete, P.; Montiel, V.; Aldaz, A. Lead electrowinning in a fluoborate medium. Use of hydrogen diffusion anodes. J. Power Sources 2000, 87, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
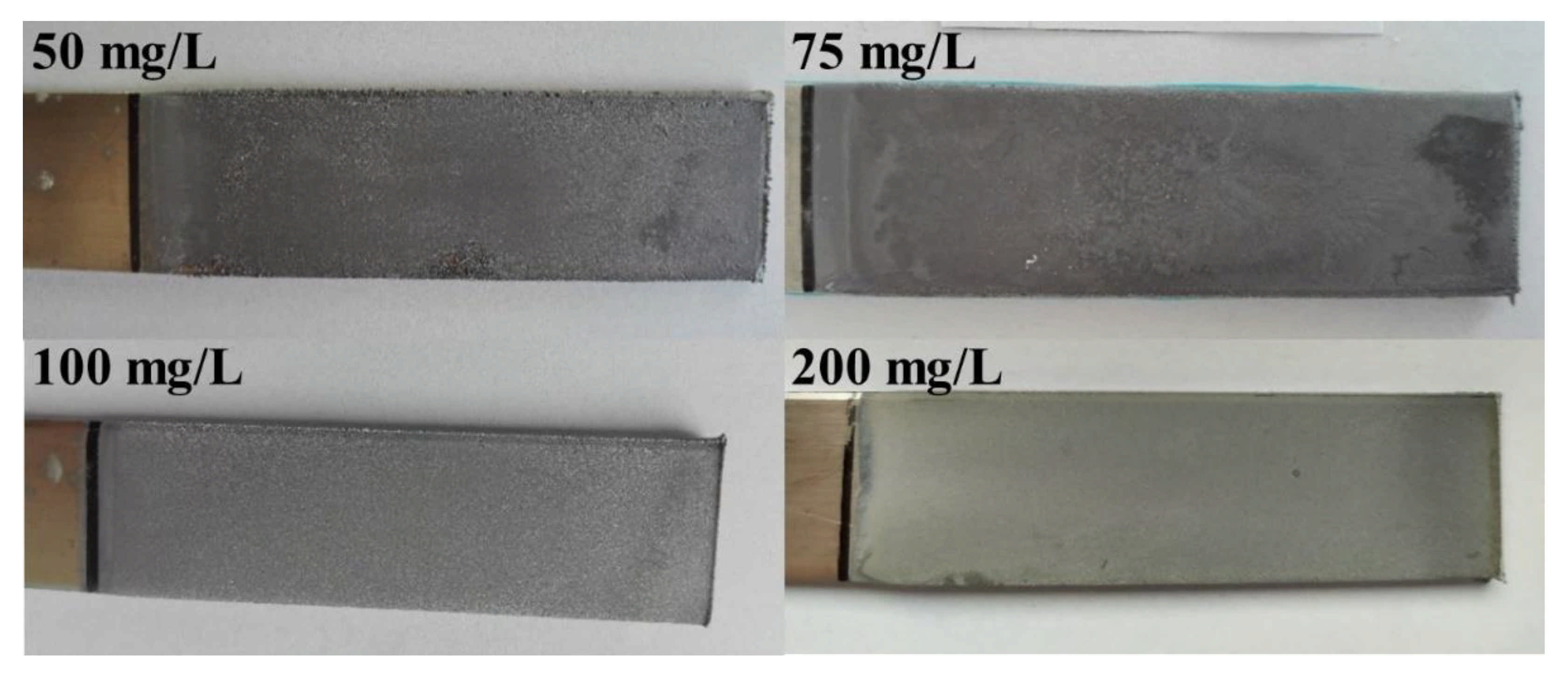
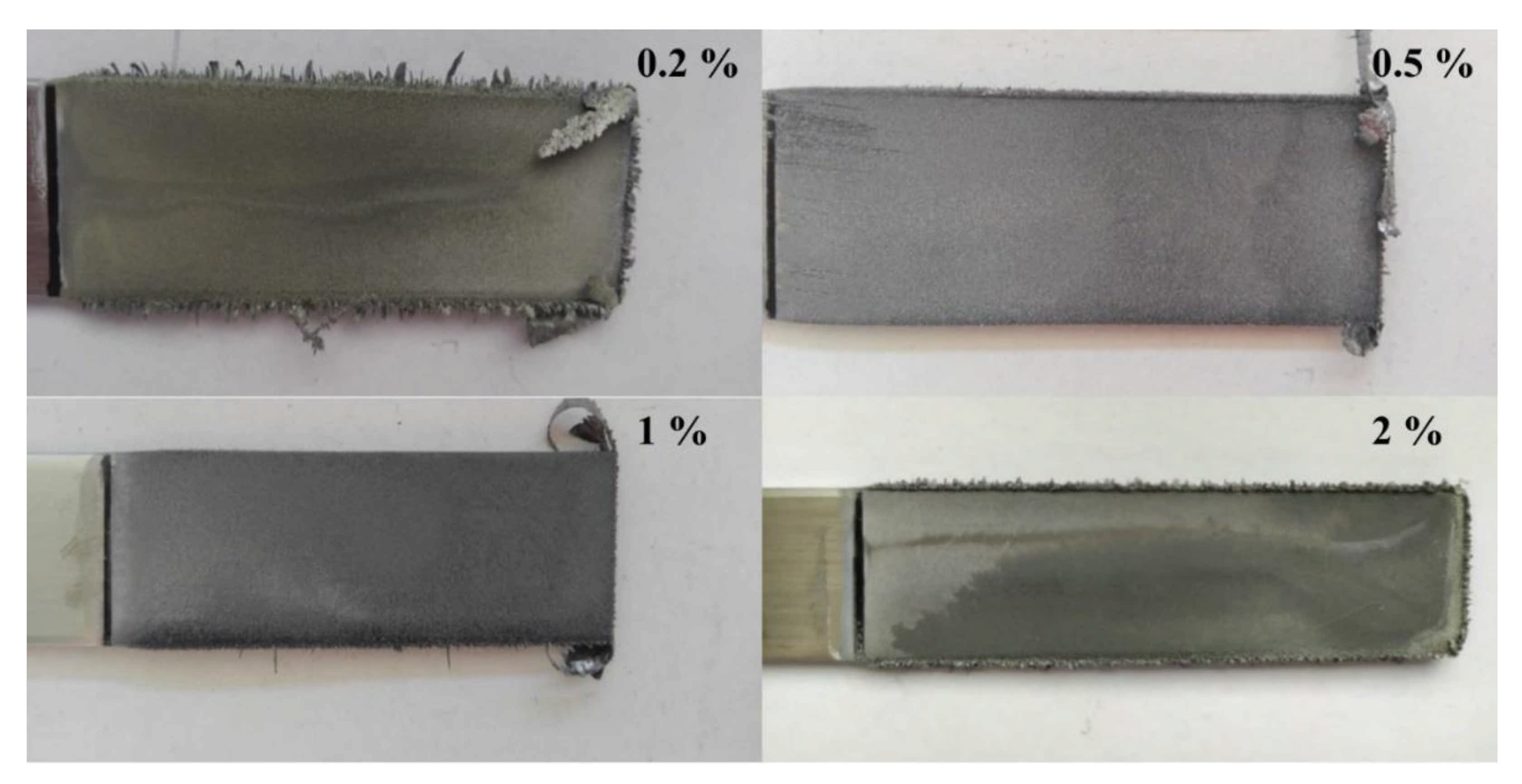

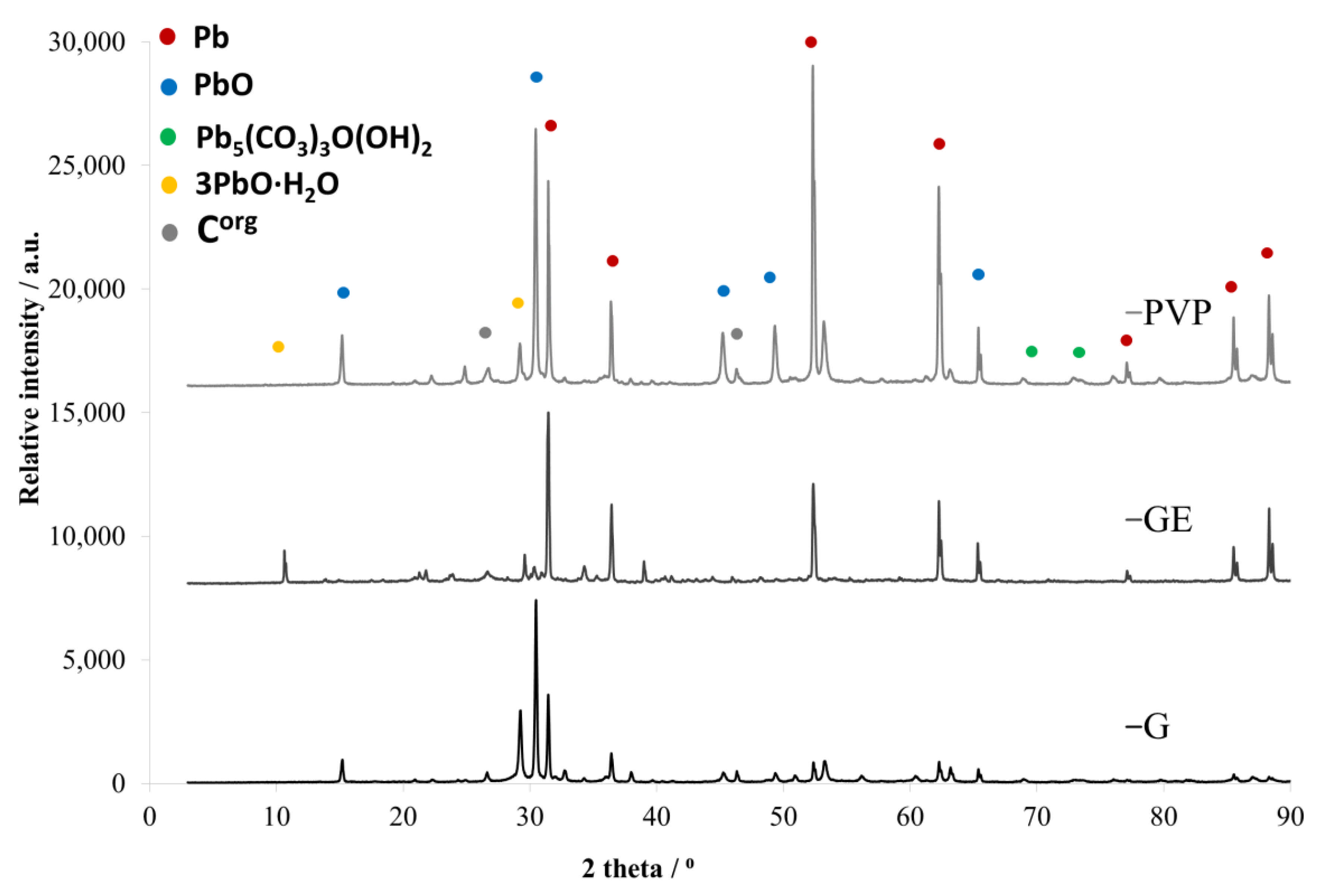


| Headings | Current Density (A/m2) | Current (A) | Voltage (V) | Cathodic Current Efficiency (%) | Energy Consumption (kWh/t Pb) | Mass of Cathodic Deposit (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | 200 | 0.56 | 2.02 | 99.20 | 527 | 4.29 |
| EG | 200 | 0.56 | 1.89 | 99.27 | 517 | 4.38 |
| PVP | 200 | 0.56 | 1.92 | 99.90 | 498 | 4.32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciszewski, M.; Orda, S.; Drzazga, M.; Kowalik, P.; Hawełek, Ł.; Malec, W.; Leszczyńska-Sejda, K. Lead Electrodeposition from Triethylenetetramine Solution Containing Inhibitors. Metals 2021, 11, 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081330
Ciszewski M, Orda S, Drzazga M, Kowalik P, Hawełek Ł, Malec W, Leszczyńska-Sejda K. Lead Electrodeposition from Triethylenetetramine Solution Containing Inhibitors. Metals. 2021; 11(8):1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081330
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiszewski, Mateusz, Szymon Orda, Michał Drzazga, Patrycja Kowalik, Łukasz Hawełek, Witold Malec, and Katarzyna Leszczyńska-Sejda. 2021. "Lead Electrodeposition from Triethylenetetramine Solution Containing Inhibitors" Metals 11, no. 8: 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081330
APA StyleCiszewski, M., Orda, S., Drzazga, M., Kowalik, P., Hawełek, Ł., Malec, W., & Leszczyńska-Sejda, K. (2021). Lead Electrodeposition from Triethylenetetramine Solution Containing Inhibitors. Metals, 11(8), 1330. https://doi.org/10.3390/met11081330







