Microstructure and Texture of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Additive Parts Fabricated by the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. CMT-WAAM 2205 DSS Additive Parts Microstructure Analysis
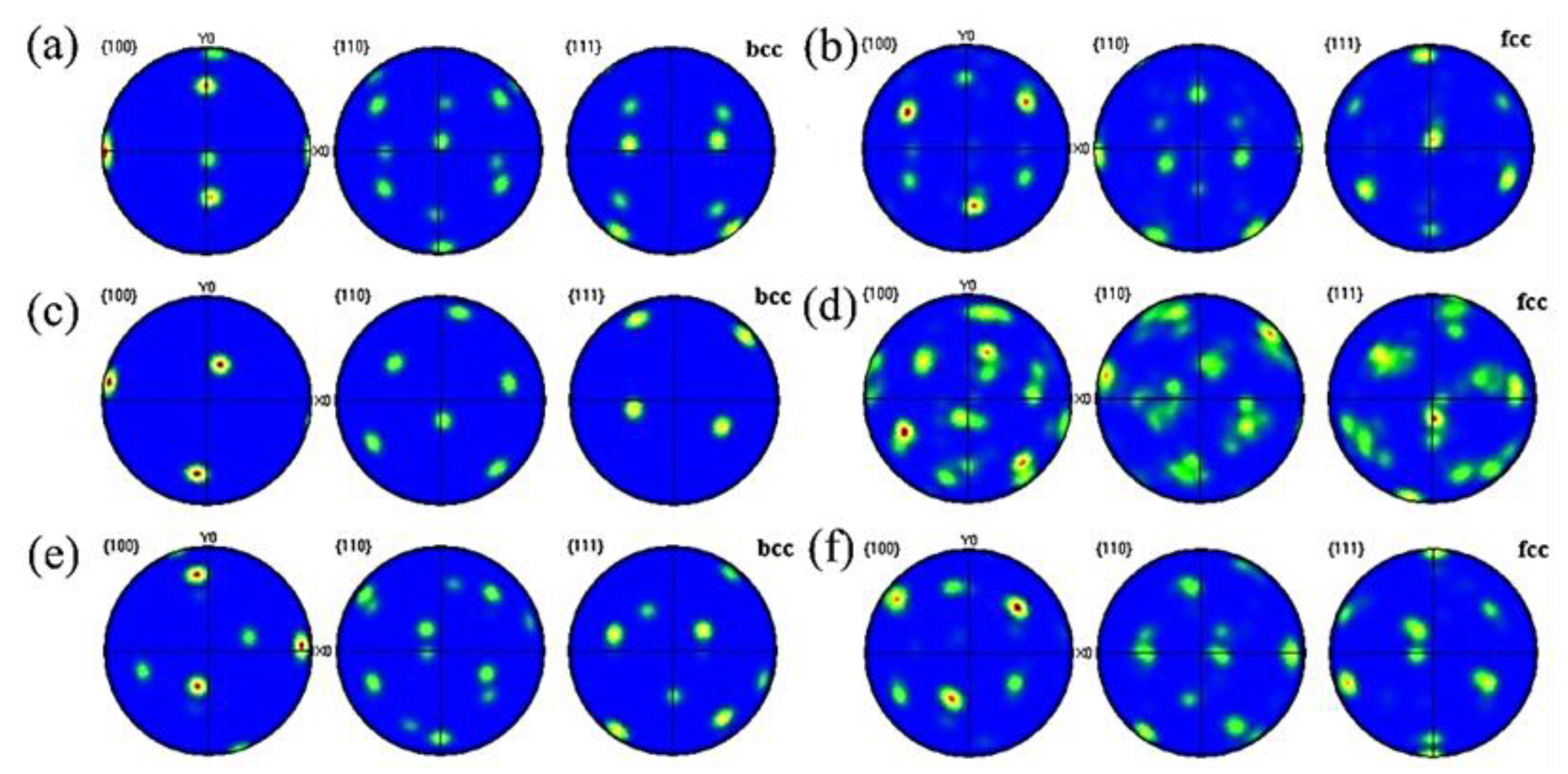
3.2. Analysis of Additive Part Textures at Different Areas
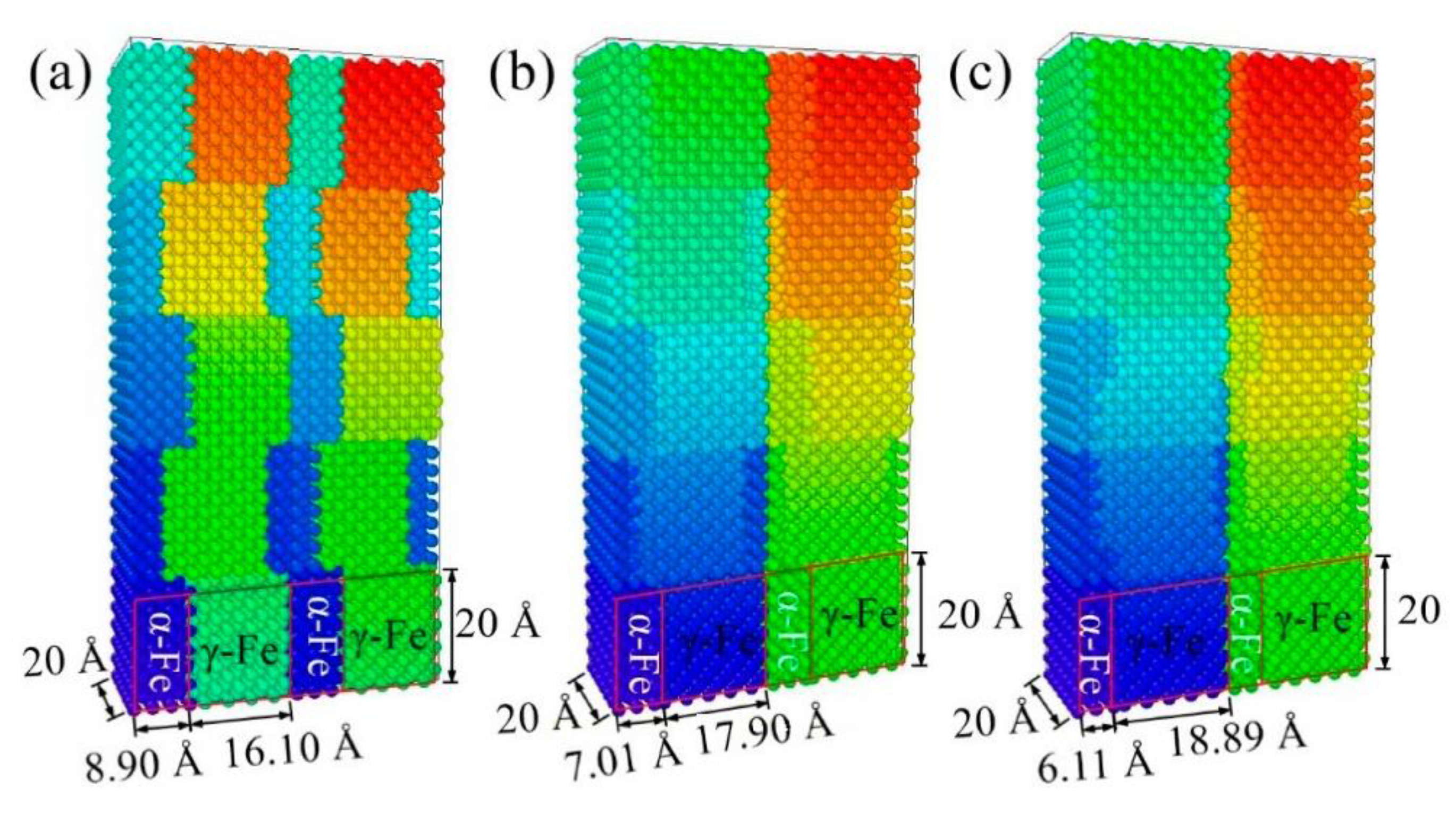
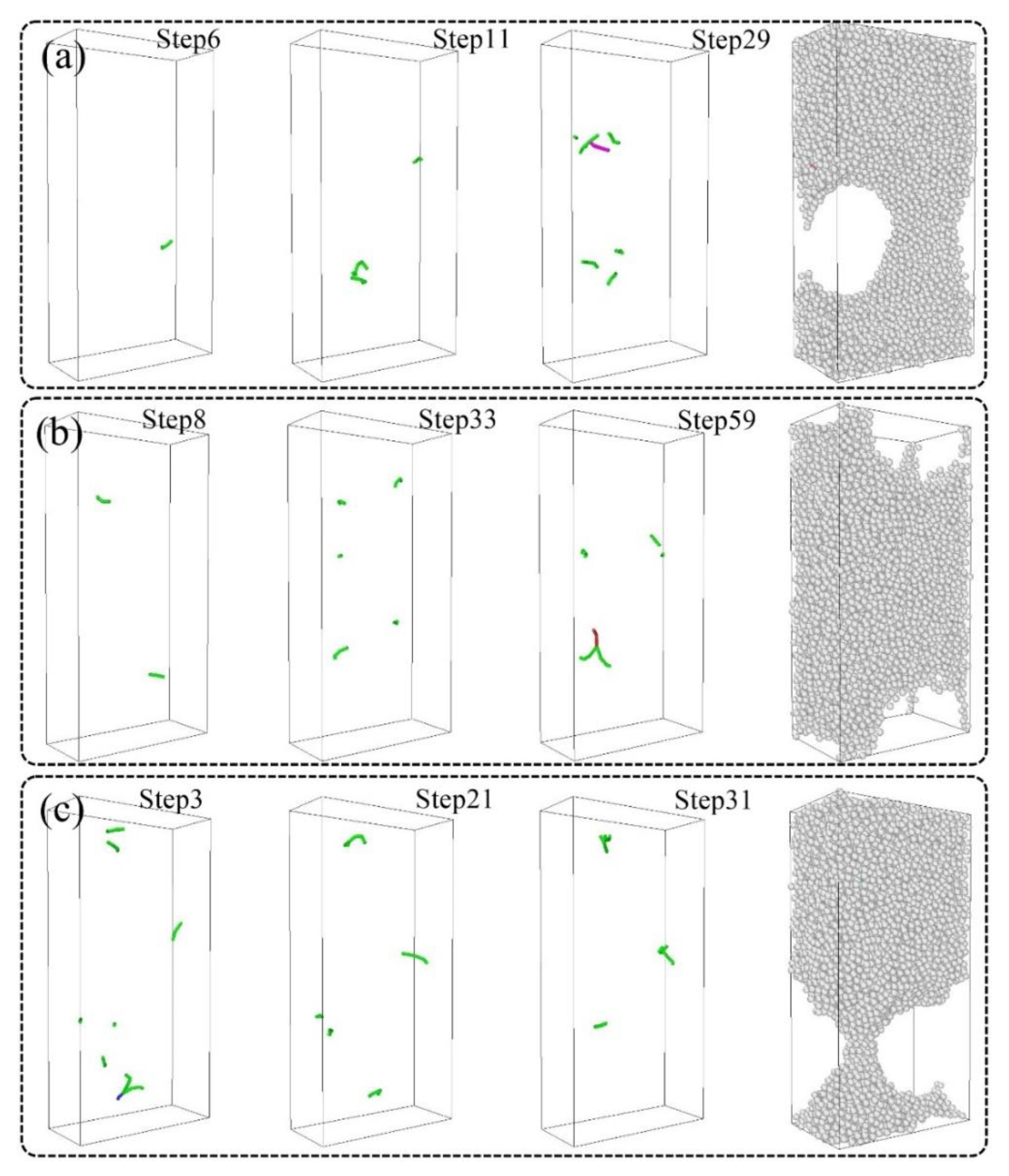
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Ferrite and Austenite with Different Volume Ratios
4. Conclusions
- (1)
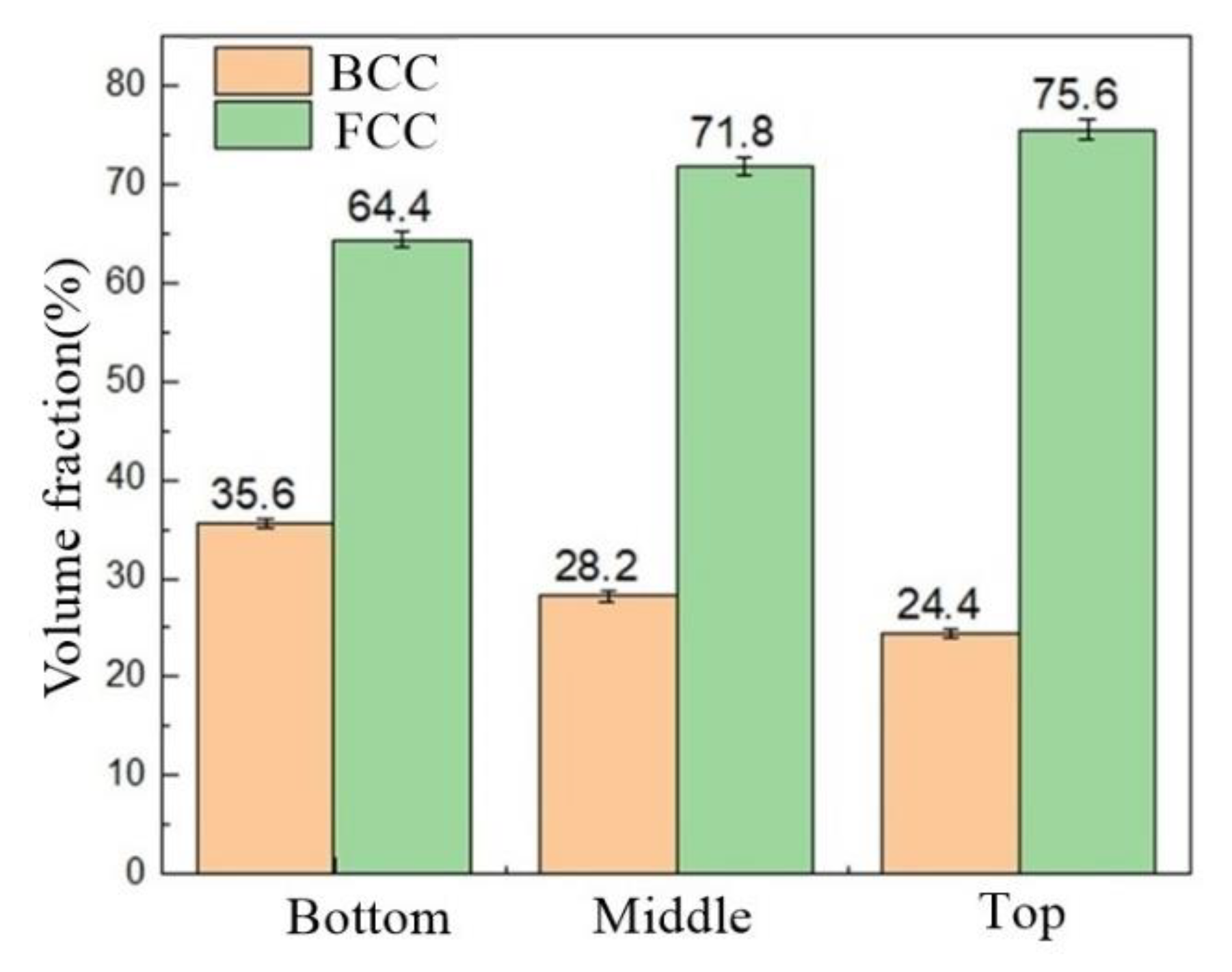
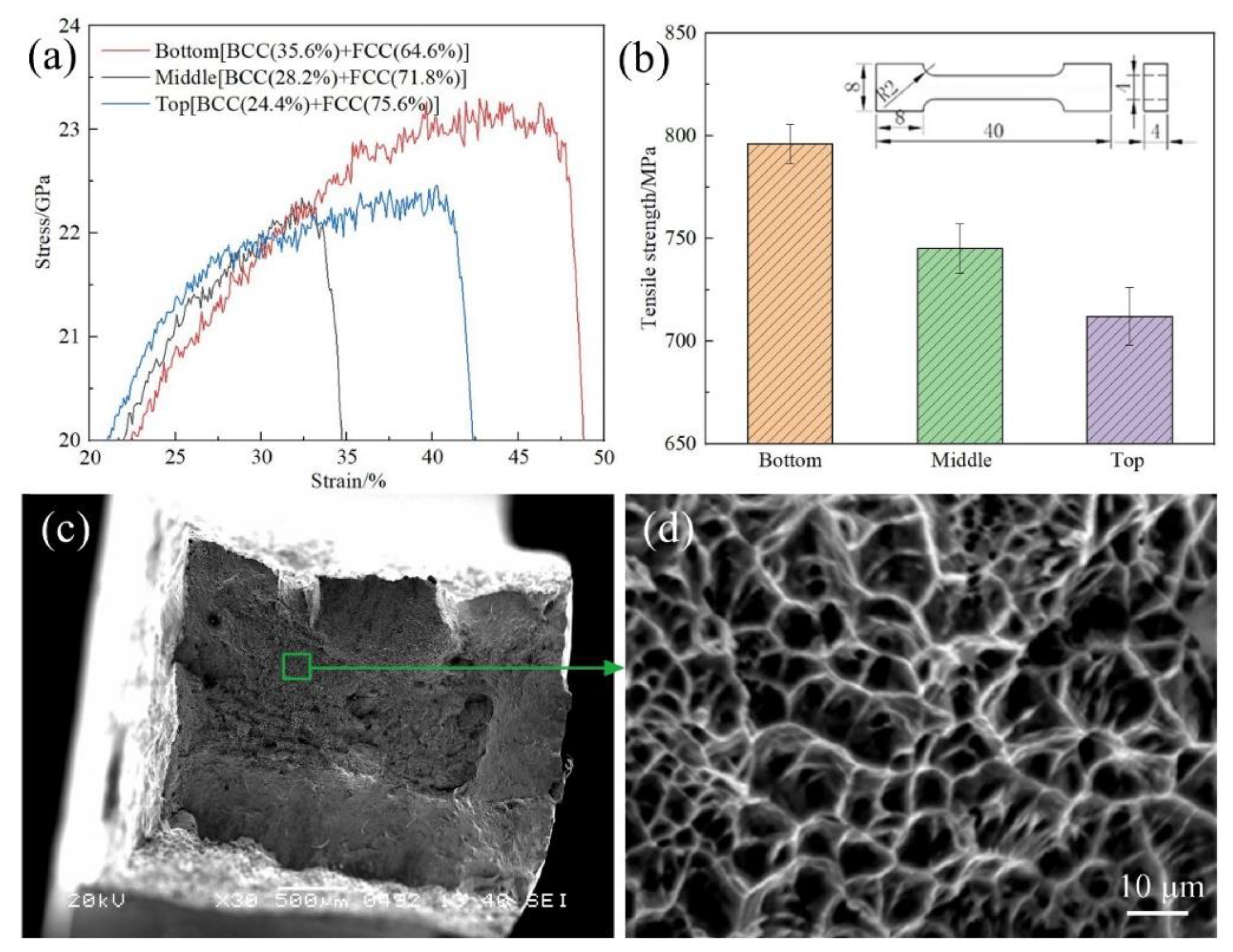
- The residual stress was the smallest at the top of the additive part, followed by the bottom, while the residual stress was the largest at the middle of the additive part. With an increase in the distance from the base plate, austenite gradually increased and ferrite gradually decreased.
- (2)
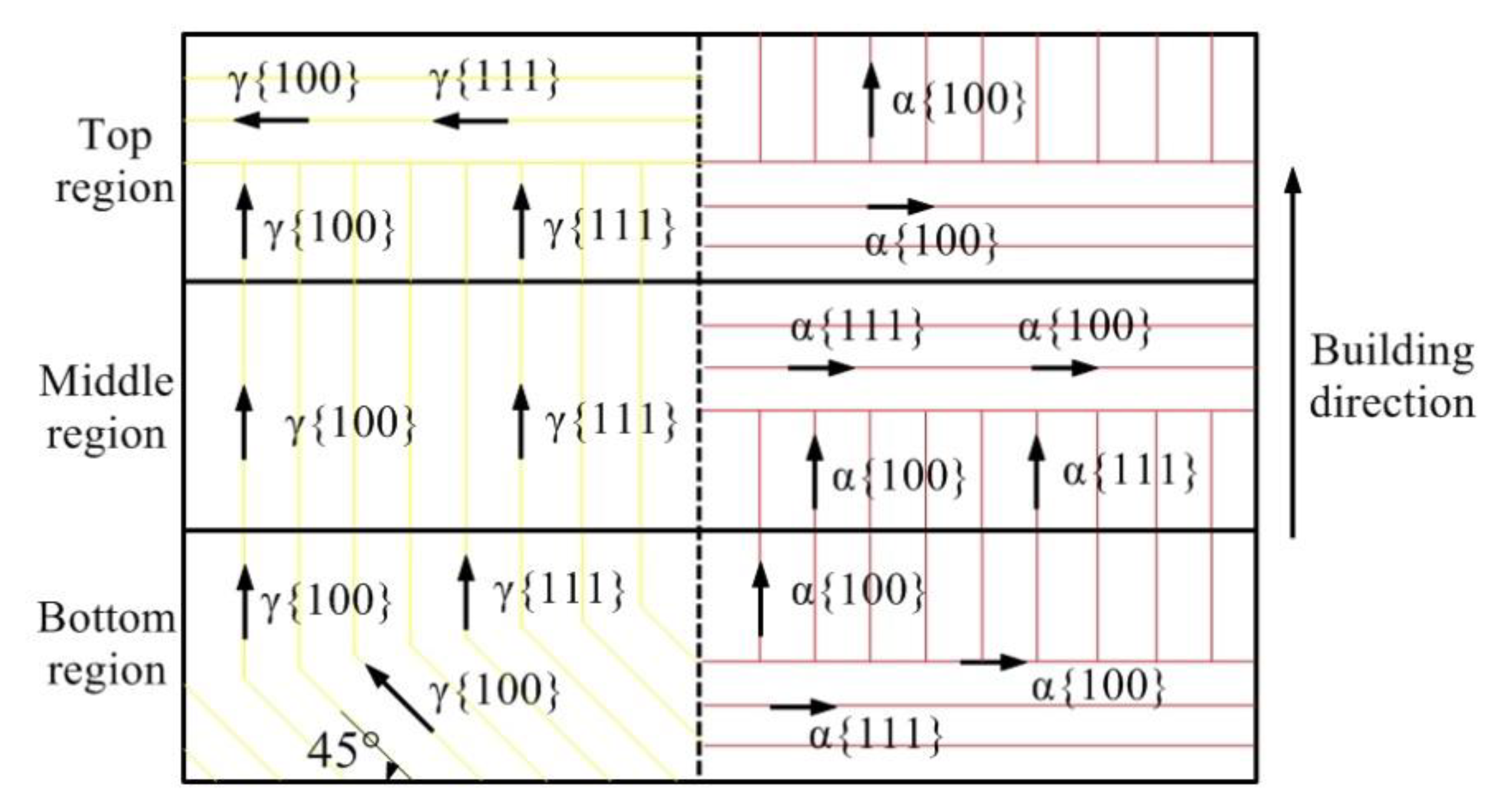
- The microstructure had no obvious orientation distribution at the bottom of the additive part. Obvious orientation distributions were detected at the bottom and top of the additive part. The ferrite grains mainly grew along (101) at the middle of the additive part, and along (102) and (001) at the top. The austenite grains mainly grew along (111) and (112) at the middle and top of the additive part.
- (3)
- The ferrite and austenite grains preferred orientation along the heat dissipation direction with the largest temperature gradient. Ferrite grew along the {100} and {111} planes and austenite grew along the {100} and {111} planes at the middle of the additive part.
- (4)
- A simulation was performed in this study using the LAMMPS software to study the effect of ferrite and austenite content on the performance of the additive parts. The dislocations were found to move mainly along the 1/6<112> crystallographic direction families.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, W.; Li, R.; Chen, Z.; Gu, J.; Tian, Y. A comparative study on microstructure and properties of traditional laser cladding and high-speed laser cladding of Ni45 alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Li, R.; He, P.; Yue, H.; Gu, J. Investigation on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of CNTs-AlSi10Mg Composites Fabricated by Selective Laser Melting. Materials 2021, 14, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, R.; Wu, M.; Yue, H.; Li, T.; Chen, Y. Effect of c-BN on the microstructure and high temperature wear resistance of laser cladded Ni-based composite coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 421, 127466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yuan, W.; Yue, H.; Zhu, Y. Study on microstructure and properties of Fe-based amorphous composite coating by high-speed laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 146, 107574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, R.; Chang, T.; Ye, X.; Wang, F. Texture evolution and properties analysis of R60702 pure zirconium joint by fiber laser welding. Mater. Charact. 2021, 182, 111581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Long, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, H.; Zheng, K.; Qiao, Y. Corrosion and impact–abrasion–corrosion behaviors of quenching–tempering martensitic Fe–Cr alloy steels. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2022, 21, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Ma, A.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y. Crystallographic anisotropy of corrosion rate and surface faceting of polycrystalline 90Cu-10Ni in acidic NaCl solution. Mater. Des. 2022, 215, 110429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, L. Welding duplex stainless steels: A review of current recommendations. Zavar. Zavarene Konstr. 2018, 63, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, W.E. Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papula, S.; Song, M.; Pateras, A.; Chen, X.; Brandt, M.; Easton, M.; Yagodzinskyy, Y.; Virkkunen, I.; Hänninen, H. Selective laser melting of duplex stainless steel 2205: Effect of post-processing heat treatment on microstructure, mechanical properties, and corrosion resistance. Materials 2019, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhang, L.; Ning, J.; Xue, F.; Lei, X.; Zhang, J.; Na, S. Laser additively manufactured intensive dual-phase steels and their microstructures, properties and corrosion resistance. Mater. Des. 2020, 192, 108710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Kong, J.; Peng, Y.; Ding, J.; Diao, C.; Yang, D.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, T. Element partitioning and electron backscatter diffraction analysis from feeding wire to as-deposited microstructure of wire and arc additive manufacturing with super duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 773, 138856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, A.R.; Shanmugam, N.S.; Rajkumar, V.; Vishnukumar, M. Insight into the microstructural features and corrosion properties of wire arc additive manufactured super duplex stainless steel (ER2594). Mater. Lett. 2020, 270, 127680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejripour, F.; Binesh, F.; Hebel, M.; Aidun, D.K. Thermal modeling and characterization of wire arc additive manufactured duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 272, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Duarte, V.; Avila, J.A.; Santos, T.G.; Miranda, R.M.; Oliveira, J.P. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of HSLA steel: Effect of thermal cycles on microstructure and mechanical properties. Addit. Manuf. 2019, 27, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stützer, J.; Totzauer, T.; Wittig, B.; Zinke, M.; Jüttner, S. GMAW cold wire technology for adjusting the ferrite–austenite ratio of wire and arc additive manufactured duplex stainless steel components. Metals-Basel 2019, 9, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Lin, X.; Zhang, F. Geometric limitation and tensile properties of wire and arc additive manufacturing 5A06 aluminum alloy parts. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, M.; Fiebig, S.; Hensel, J.; Dilger, K. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of aluminum components. Metals 2019, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, R.; Shi, Y. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of aluminum alloy lattice structure. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 50, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Sasahara, H.; Abe, T.; Sannomiya, H.; Nishiyama, S.; Ohta, S.; Nakamura, K. Material-property evaluation of magnesium alloys fabricated using wire-and-arc-based additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Lin, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, W.; Liang, E. Microstructure and mechanical properties of wire and arc additive manufactured AZ31 magnesium alloy using cold metal transfer process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 774, 138942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Sasahara, H. Dissimilar metal deposition with a stainless steel and nickel-based alloy using wire and arc-based additive manufacturing. Precis. Eng. 2016, 45, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, F.; Wu, S. Improvement of pitting corrosion resistance of wire arc additive manufactured duplex stainless steel through post-manufacturing heat-treatment. Mater. Charact. 2021, 171, 110743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Gao, H.; Yao, Z. Location-Dependent Microstructure and Properties for Plasma Arc Additively Manufactured Duplex Stainless Steel ER2209 Wire. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 6788–6800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvi, S.; Vishvaksenan, A.; Rajasekar, E. Cold metal transfer (CMT) technology—An overview. Def. Technol. 2018, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xizhang, C.; Su, C.; Wang, Y.; Siddiquee, A.N.; Sergey, K.; Jayalakshmi, S.; Singh, R.A. Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Based Wire and Arc Additive Manufacture (WAAM) System. J. Surf. Investig. X-ray Synchrotron Neutron Tech. 2018, 12, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lervåg, M.; Sørensen, C.; Robertstad, A.; Brønstad, B.M.; Nyhus, B.; Eriksson, M.; Aune, R.; Ren, X.; Akselsen, O.M.; Bunaziv, I. Additive manufacturing with superduplex stainless steel wire by cmt process. Metals 2020, 10, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramkumar, K.D.; Bajpai, A.; Raghuvanshi, S.; Singh, A.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Arivarasu, M.; Arivazhagan, N. Investigations on structure-property relationships of activated flux TIG weldments of super-duplex/austenitic stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 638, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, W.N.; Mahajan, S.; Chhibber, R. Investigations on reformed austenite in the microstructure of dissimilar super duplex/pipeline steel weld. Mater. Lett. 2021, 285, 129109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhdoom, M.A.; Ahmad, A.; Kamran, M.; Abid, K.; Haider, W. Microstructural and electrochemical behavior of 2205 duplex stainless steel weldments. Surf. Interfaces 2017, 9, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, G.N.; Raza, M.S.; Singh, N.K.; Kumar, H. Experimental investigation on Ytterbium fiber laser butt welding of Inconel 625 and Duplex stainless steel 2205 thin sheets. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.; Wu, W. Overview of Intermetallic Sigma (σ) Phase Precipitation in Stainless Steels. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2012, 2012, 732471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badji, R.; Bacroix, B.; Bouabdallah, M. Texture, microstructure and anisotropic properties in annealed 2205 duplex stainless steel welds. Mater. Charact. 2011, 62, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigon, G.N.; Isgor, O.B.; Pasebani, S. The effect of annealing on the selective laser melting of 2205 duplex stainless steel: Microstructure, grain orientation, and manufacturing challenges. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdadi, N.; Ledermueller, C.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Rohrer, G.; Liao, X.; Ringer, S.; Primig, S. Evolution of microstructure and mechanical properties in 2205 duplex stainless steels during additive manufacturing and heat treatment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 835, 142695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calliari, I.; Straffelini, G.; Ramous, E. Investigation of secondary phase effect on 2205 DSS fracture toughness. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
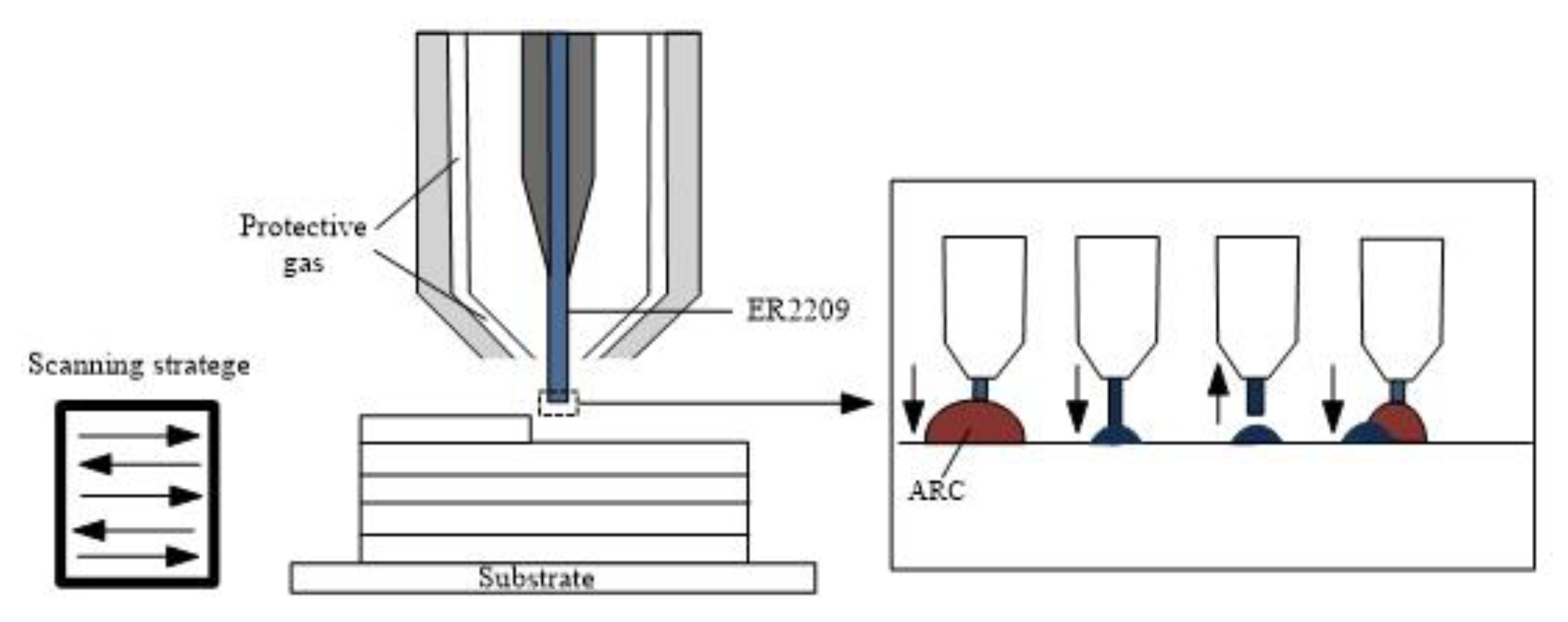
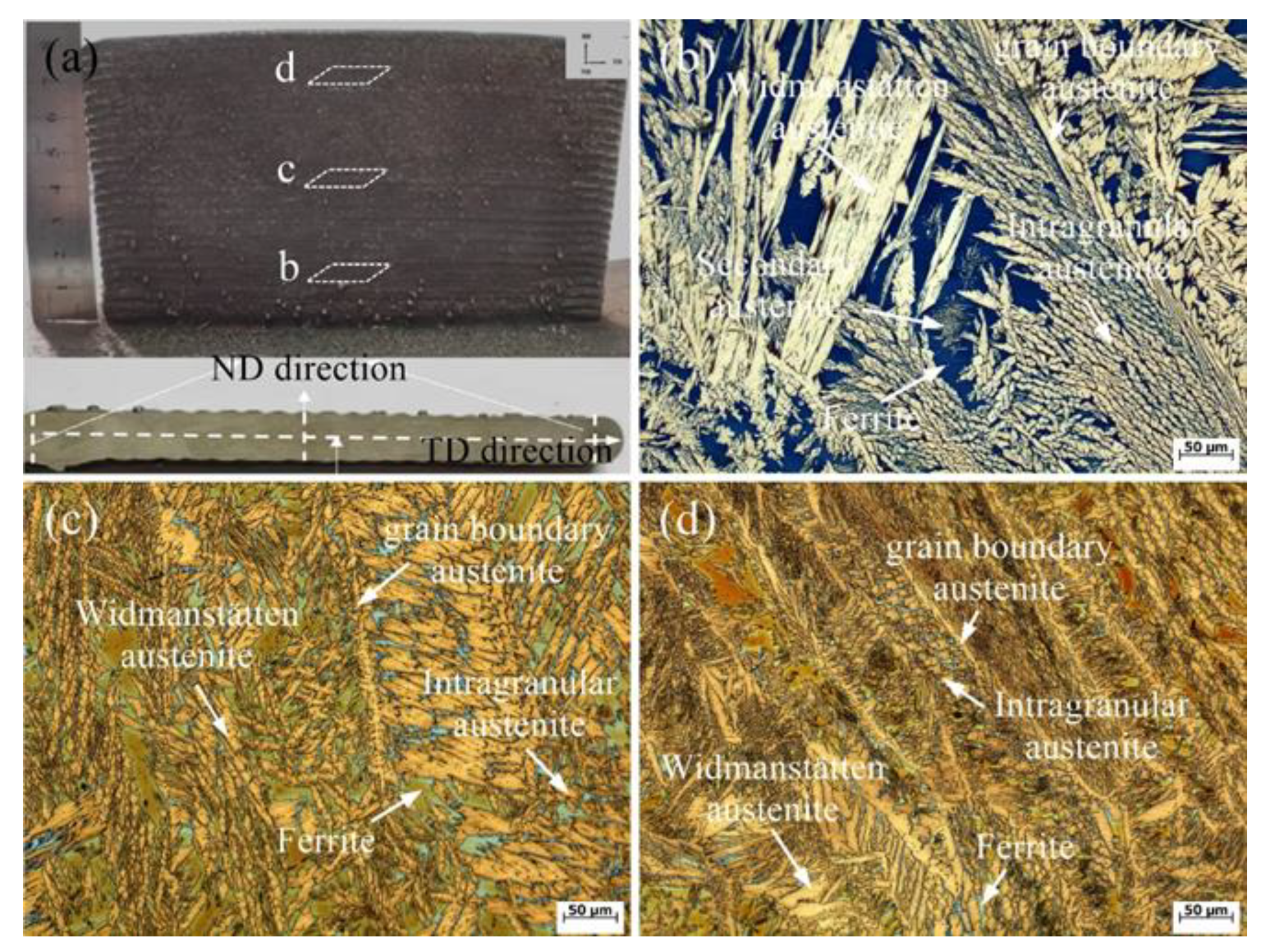
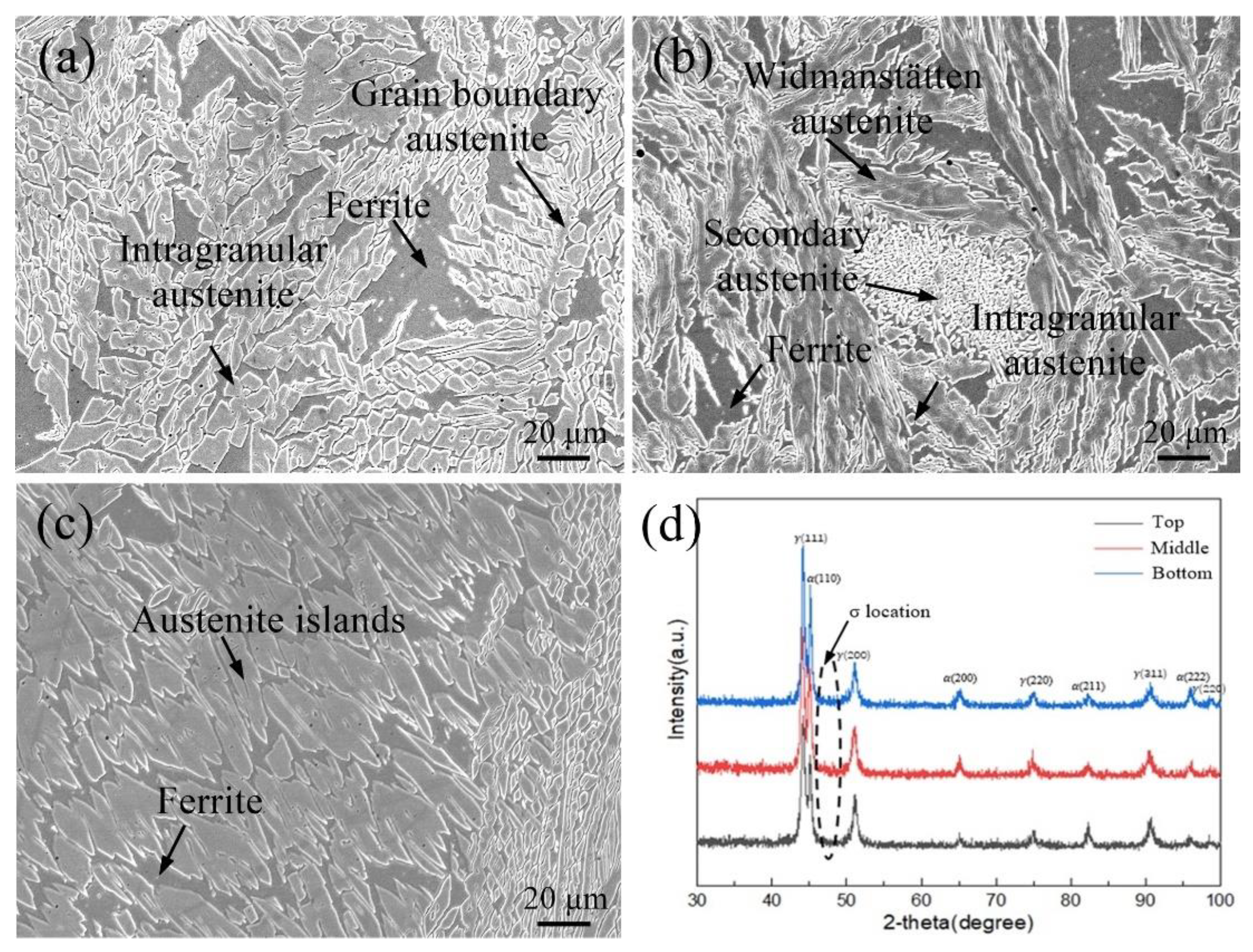
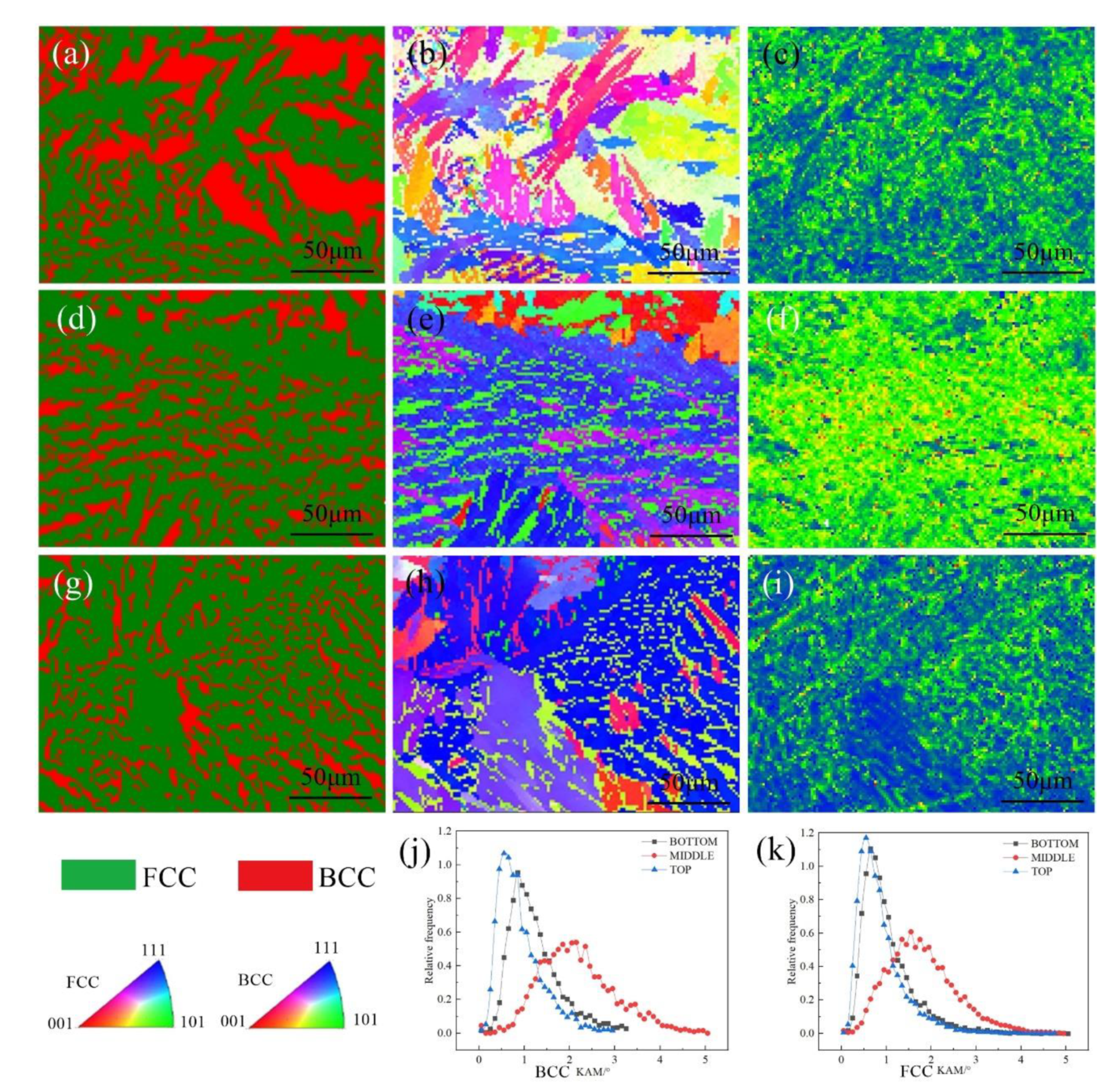
| Material | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ER2209 | 0.013 | 0.49 | 1.54 | 0.018 | 0.007 | 22.92 | 8.6 | 3.2 | 0.17 | Bal. |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bi, X.; Li, R.; Hu, Z.; Gu, J.; Jiao, C. Microstructure and Texture of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Additive Parts Fabricated by the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). Metals 2022, 12, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12101655
Bi X, Li R, Hu Z, Gu J, Jiao C. Microstructure and Texture of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Additive Parts Fabricated by the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). Metals. 2022; 12(10):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12101655
Chicago/Turabian StyleBi, Xiaolin, Ruifeng Li, Zhenxing Hu, Jiayang Gu, and Chen Jiao. 2022. "Microstructure and Texture of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Additive Parts Fabricated by the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM)" Metals 12, no. 10: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12101655
APA StyleBi, X., Li, R., Hu, Z., Gu, J., & Jiao, C. (2022). Microstructure and Texture of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Additive Parts Fabricated by the Cold Metal Transfer (CMT) Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). Metals, 12(10), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12101655






