Influence of Hot Top Height on Macrosegregation and Material Yield in a Large-Size Cast Steel Ingot Using Modeling and Experimental Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
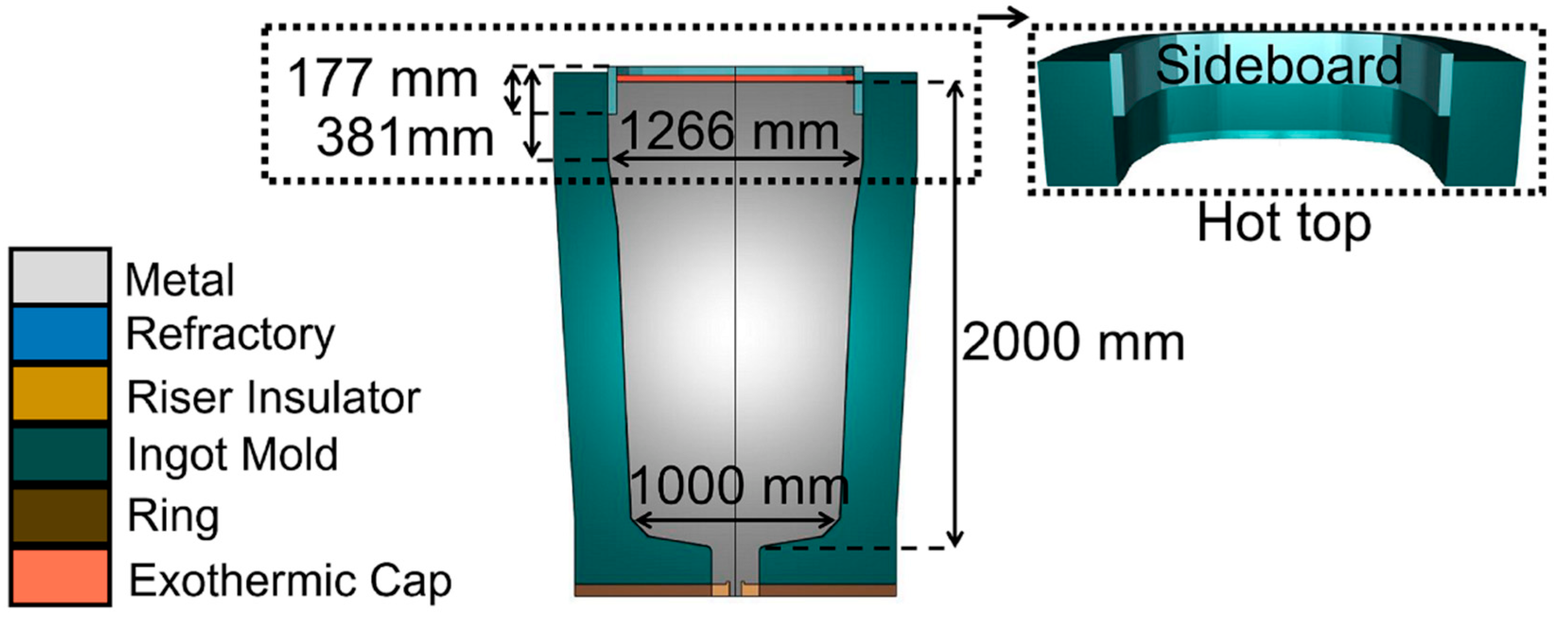
2. Experimental Procedure
3. Model Establishment
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Validation of the Model
4.2. Hot Top Characteristics and Macrosegregation
4.3. Liquid Pressure and Fluid Flow
4.4. Cooling Rate
4.5. Liquidus Temperature
5. Conclusions
- Increasing the hot top height reduced the negative and positive macrosegregation at heights of 170 mm and 1691 mm from the bottom of the ingot by up to 6.25% and 6.5%, respectively;
- Increasing the hot top height increased the solidification time by up to 8 min compared to the original design and slightly decreased the cooling rate in the mushy state;
- More liquid feeding from the hot top towards the ingot bottom and a more homogeneous distribution of solute elements in the bulk liquid were identified as the main sources of observed lower macrosegregation intensity at specified locations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.P.; Shahriari, D.; Loucif, A.; Jahazi, M.; Lapierre-Boire, L.P.; Tremblay, R. Effect of Segregated Alloying Elements on the High Strength Steel Properties: Application to the Large Size Ingot Casting Simulation. In TMS 2017 146th Annual Meeting & Exhibition Supplemental Proceedings; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 491–500. [Google Scholar]
- ElBealy, M.; Fredriksson, H. Modeling of the peritectic reaction and macro-segregation in casting of low carbon steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1996, 27, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, D.; Zabaras, N. Control of macrosegregation during the solidification of alloys using magnetic fields. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2006, 49, 4850–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.O. Modeling for Casting and Solidification Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; pp. 95–122. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Xia, M.; Li, J. Dendritic model for macrosegregation prediction of large scale castings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 227, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, E.J. Macrosegregation in Steel Ingots: The Applicability of Modelling and Characterisation Techniques. ISIJ Int. 2013, 53, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickering, E.J.; Chesman, C.; Al-Bermani, S.; Holland, M.; Davies, P.; Talamantes-Silva, J. A Comprehensive Case Study of Macrosegregation in a Steel Ingot. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 1860–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, H.; Ren, F.; Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Xia, M.; Li, J. Modelling of ingot size effects on macrosegregation in steel castings. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemings, M.C. Solidification processing. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1974, 5, 2121–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Ren, F.; Cai, D.; Hao, J.; Li, J.; Li, J. Gradual-cooling solidification approach to alleviate macrosegregation in large steel ingots. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 262, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Ren, F.; Li, J.; Han, X.; Xia, M.; Li, J. Four-phase dendritic model for the prediction of macrosegregation, shrinkage cavity, and porosity in a 55-ton ingot. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Loucif, A.; Jahazi, M.; Tremblay, R.; Lapierre, L.P. On the effect of filling rate on positive macrosegregation patterns in large size cast steel ingots. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Jahazi, M.; Tremblay, R. Simulation and experimental validation of the effect of superheat on macrosegregation in large-size steel ingots. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 107, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucif, A.; Zhang, C.; Morin, J.B.; Jahazi, M. A FEM Analysis on the Influence of Manganese on Carbon and Chromium Macrosegregation in Large Size Steel Ingot. In Materials Science Forum; Trans Tech Publ.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hurtuk, D.J. Steel ingot casting. In Casting; ASM Handbook; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 2008; Volume 15, p. 911. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Fu, P.; Liu, H.; Li, D.; Li, Y. Shrinkage porosity criteria and optimized design of a 100-ton 30Cr2Ni4MoV forging ingot. Mater. Des. 2012, 35, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tashiro, K.; Watanabe, S.; Kitagawa, I.; Tamura, I. Influence of mould design on the solidification and soundness of heavy forging ingots. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1983, 23, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, A.; Založnik, M.; Combeau, H.C. Experimental and Numerical Studies on the Influence of Hot Top Conditions on Macrosegregation in an Industrial Steel Ingot. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Ingot Casting, Rolling and Forging (IRCF), Aachen, Germany, 3–7 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kermanpur, A.; Eskandari, M.; Purmohamad, H.; Soltani, M.A.; Shateri, R. Influence of mould design on the solidification of heavy forging ingots of low alloy steels by numerical simulation. Mater. Des. 2010, 31, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scepi, M.; Andreoli, B.; Basevi, S.; Giorgetti, A.L. Thermal and metallurgical control of the efficiency of ingot moulds for forging ingots. Boll. Technol. 1981, 391, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.N. Influence of Mould Slenderness Ratio on the Solidification of Heavy Ingots by Numerical Simulation. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publ.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guide, J.U.S.; Sente Software Ltd.: Guildford, UK, 2005.
- THERCAST® NxT 2.1 USER MANUAL Ingot Casting; Transvalor, S.A.: Biot, France, 2017.
- Duan, Z.; Tu, W.; Shen, B.; Shen, H.; Liu, B. Experimental Measurements for Numerical Simulation of Macrosegregation in a 36-Ton Steel Ingot. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2016, 47, 3597–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MATLAB and Statistics Toolbox Release 2012b; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2012.
- Patil, P.; Marje, V.; Balachandran, G.; Balasubramanian, V. Theoretical study on influence of steel composition on solidification behaviour in ingot casting of low alloy steels at similar casting conditions. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2015, 28, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Puranik, A.; Balachandran, G.; Balasubramanian, V. Improvement in Quality and Yield of the Low Alloy Steel Ingot Casting Through Modified Mould Design. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2016, 70, 2001–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellet, M.; Fachinotti, V.D. ALE Method for Solidification Modelling. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2004, 193, 4355–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Shahriari, D.; Loucif, A.; Melkonyan, H.; Jahazi, M. Influence of thermomechanical shrinkage on macrosegregation during solidification of a large-sized high-strength steel ingot. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 99, 3035–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Ludwig, A.; Kharicha, A. Simulation of As-Cast Steel Ingots. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1700037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.sorelforge.com/ (accessed on 3 November 2022).
- TherCast 2.1®; Transvalor, S.A.: Biot, France, 2017.
- Baghani, A. Modeling of Macrosegregation and Shrinkage Cavity during Solidification of a Multi-Components Steel Ingot. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Li, Q. Gravity- and Solidification-Shrinkage-Induced Liquid Flow in a Horizontally Solidified Alloy Ingot. Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 1991, 20, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J. Complete Casting Handbook—Metal Casting Processes, Metallurgy, Techniques and Design; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hultgren, A. A and V segregation in killed steel ingots. Scand. J. Metall. 1973, 2, 217–227. [Google Scholar]
- Loucif, A.; Ben Fredj, E.; Harris, N.; Shahriari, D.; Jahazi, M.; Lapierre-Boire, L.P. Evolution of A-Type Macrosegregation in Large Size Steel Ingot After Multistep Forging and Heat Treatment. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 1046–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| C | Mn | P | S | Si | Ni | Cr | Mo | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.32 | 0.57 | 0.015 | 0.001 | 0.27 | 0.23 | 1.08 | 0.34 | 0.16 | Balance |
| Property | Unit | Value | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steel | Reference density | Kg/m3 | 6.93 × 10–6 | [22,32] |
| Melting temperature of pure iron | °C | 1540 | [32] | |
| Reference temperature (liquidus) | °C | 1502 | [22] | |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | 1/K | 8.853 × 10–5 | [32] | |
| Latent heat of fusion | kJ/kg | 265 | [32] | |
| Emissivity | - | 0.8 | [29,32] | |
| Cast iron | Density | kg/m3 | 7000 | [32] |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m/K | 30 | [32] | |
| Refractory | Density | kg/m3 | 2353 | [29,32] |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m/K | 1.2 | [29,32] | |
| Riser insulator | Density | kg/m3 | 868 | [32] |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m/K | 0.45 | [32] | |
| Exothermic cap | Density | kg/m3 | 500 | [31] |
| Thermal conductivity | W/m/K | 0.2 | [32] | |
| Initial condition | Filling time | min | 26 | [31] |
| Initial temperature of mold and mold components | °C | 60 | [31] | |
| Exterior environmental temperature | °C | 20 | [31] | |
| Pouring temperature | °C | 1580 | [31] | |
| Superheat temperature | °C | 78 | [22,31] | |
| Liquidus temperature | °C | 1502 | [22] | |
| Flow rate for 90° symmetry model | mm3/s | 265,385 | [31] | |
| Energy of ignition of two exothermic caps | MJ | 72 | [31] | |
| Number of the mesh of the ingot and the components of the mold | - | 746,196 | - | |
| Mesh size | mm | 30 | - | |
| Mesh refinement | mm | 15 and 8 | - |
| Type | Symbol | Hot Top Height | Mass Ratio | Slenderness Ratio (H/D) | Sideboard Height |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original Design | OD | 381 mm | 21.35% | 1.3 | 203 mm |
| New Design | ND | 546 mm | 31.25% | 1.16 | 203 mm |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghodrati, N.; Baiteche, M.; Loucif, A.; Gallego, P.I.; Jean-Benoit, M.; Jahazi, M. Influence of Hot Top Height on Macrosegregation and Material Yield in a Large-Size Cast Steel Ingot Using Modeling and Experimental Validation. Metals 2022, 12, 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111906
Ghodrati N, Baiteche M, Loucif A, Gallego PI, Jean-Benoit M, Jahazi M. Influence of Hot Top Height on Macrosegregation and Material Yield in a Large-Size Cast Steel Ingot Using Modeling and Experimental Validation. Metals. 2022; 12(11):1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111906
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhodrati, Neda, Mounir Baiteche, Abdelhalim Loucif, Paloma Isabel Gallego, Morin Jean-Benoit, and Mohammad Jahazi. 2022. "Influence of Hot Top Height on Macrosegregation and Material Yield in a Large-Size Cast Steel Ingot Using Modeling and Experimental Validation" Metals 12, no. 11: 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111906
APA StyleGhodrati, N., Baiteche, M., Loucif, A., Gallego, P. I., Jean-Benoit, M., & Jahazi, M. (2022). Influence of Hot Top Height on Macrosegregation and Material Yield in a Large-Size Cast Steel Ingot Using Modeling and Experimental Validation. Metals, 12(11), 1906. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111906







