Synthesis of Ferroalloys via Mill Scale-Dross-Graphite Interaction: Implication for Industrial Wastes Upcycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Aluminum Dross
2.1.2. Mill Scale
2.1.3. Pellet Preparation
2.2. High-Temperature Interactions
2.3. Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Carbothermic Reduction Reactions
3.2. Effect of Carbon
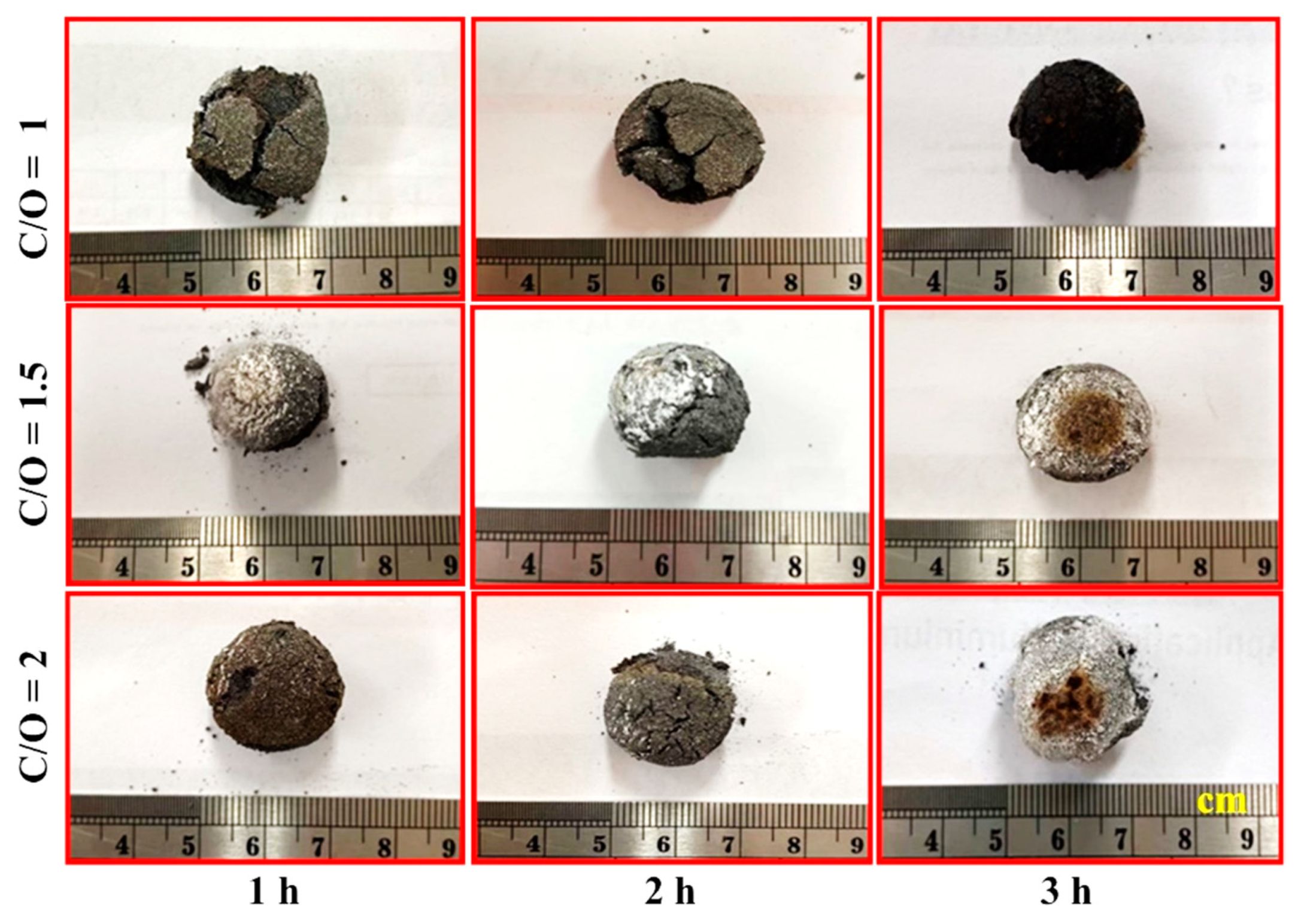
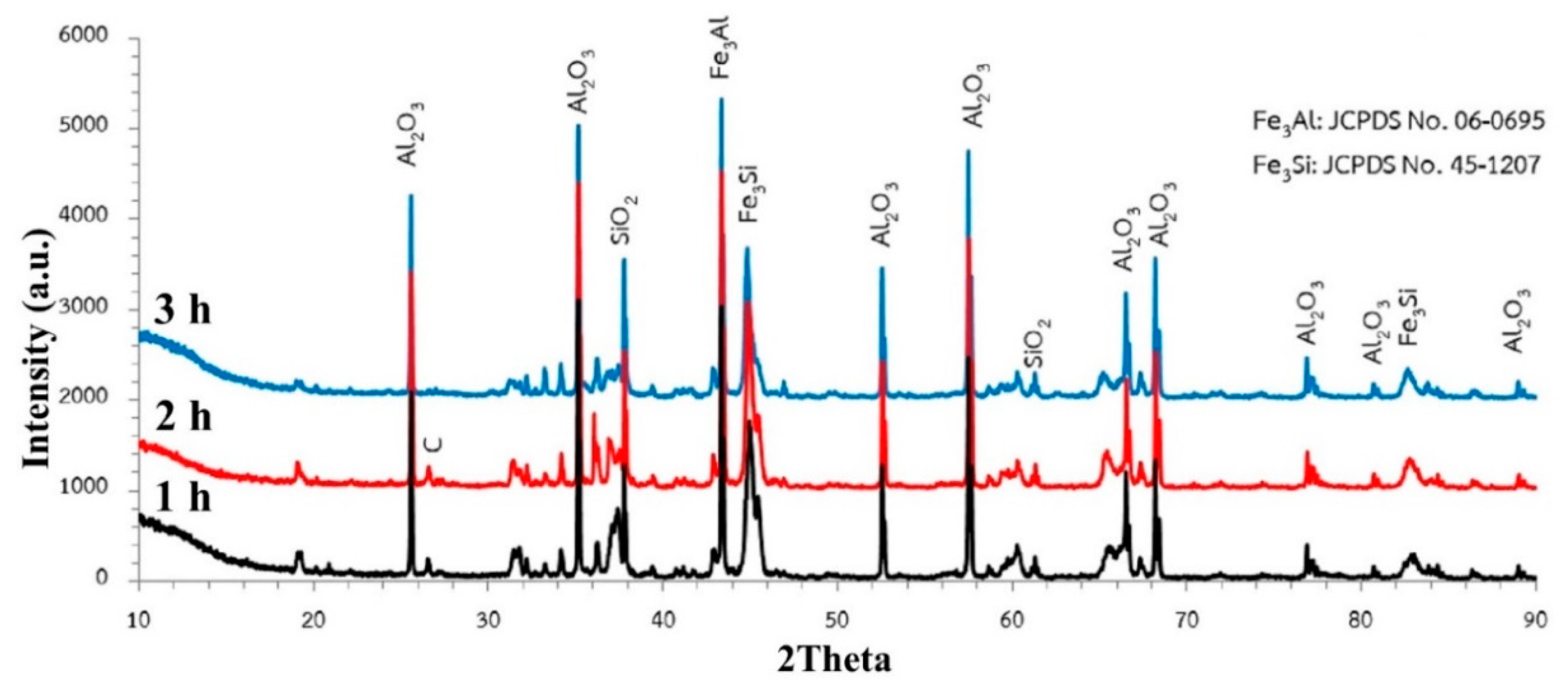
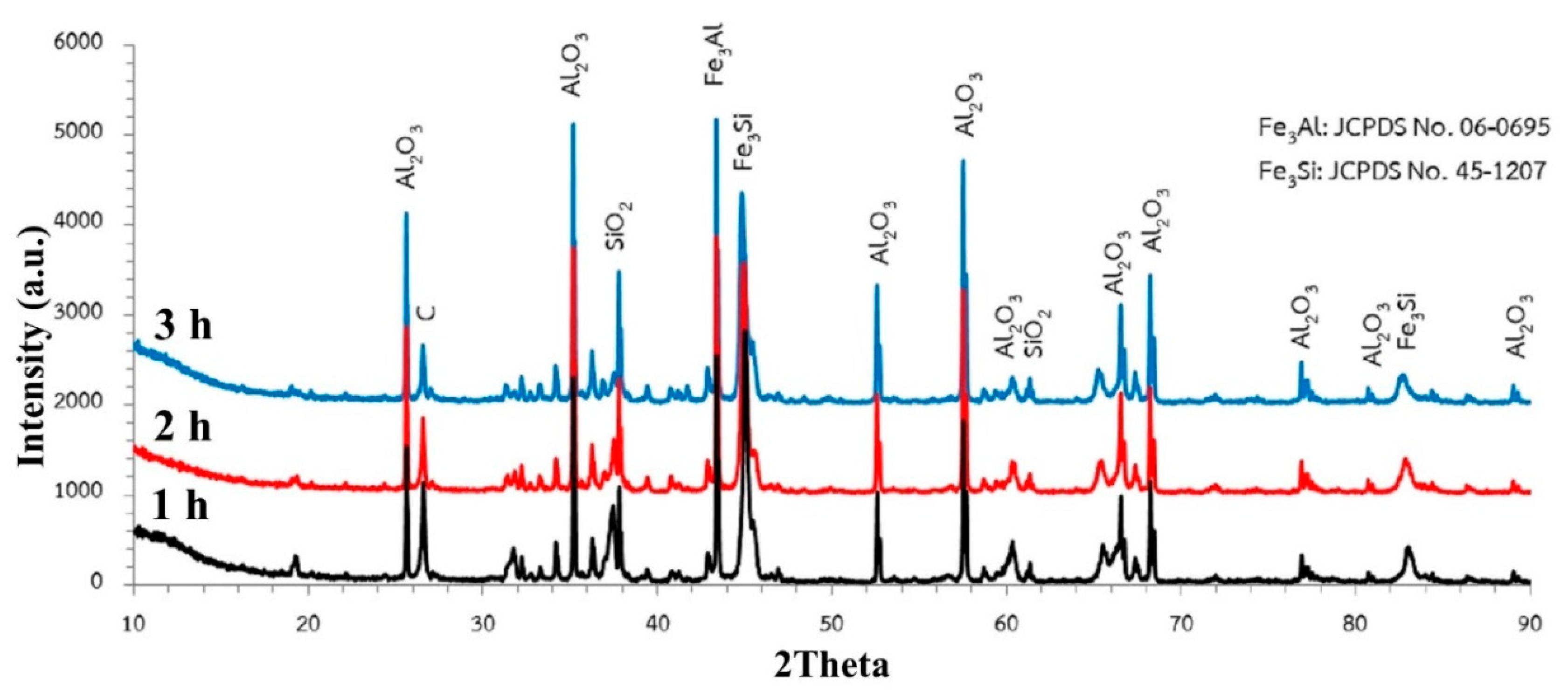
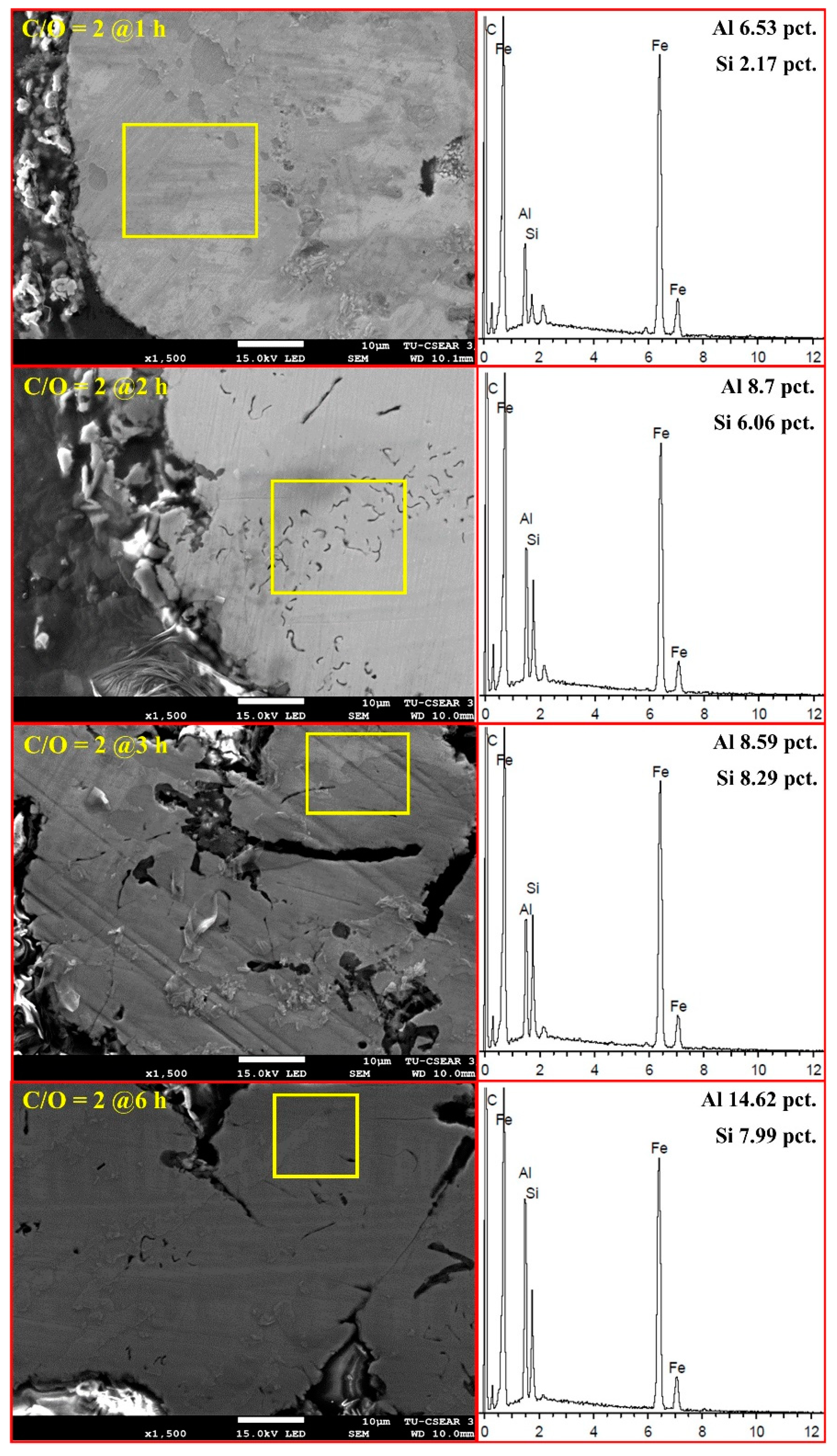
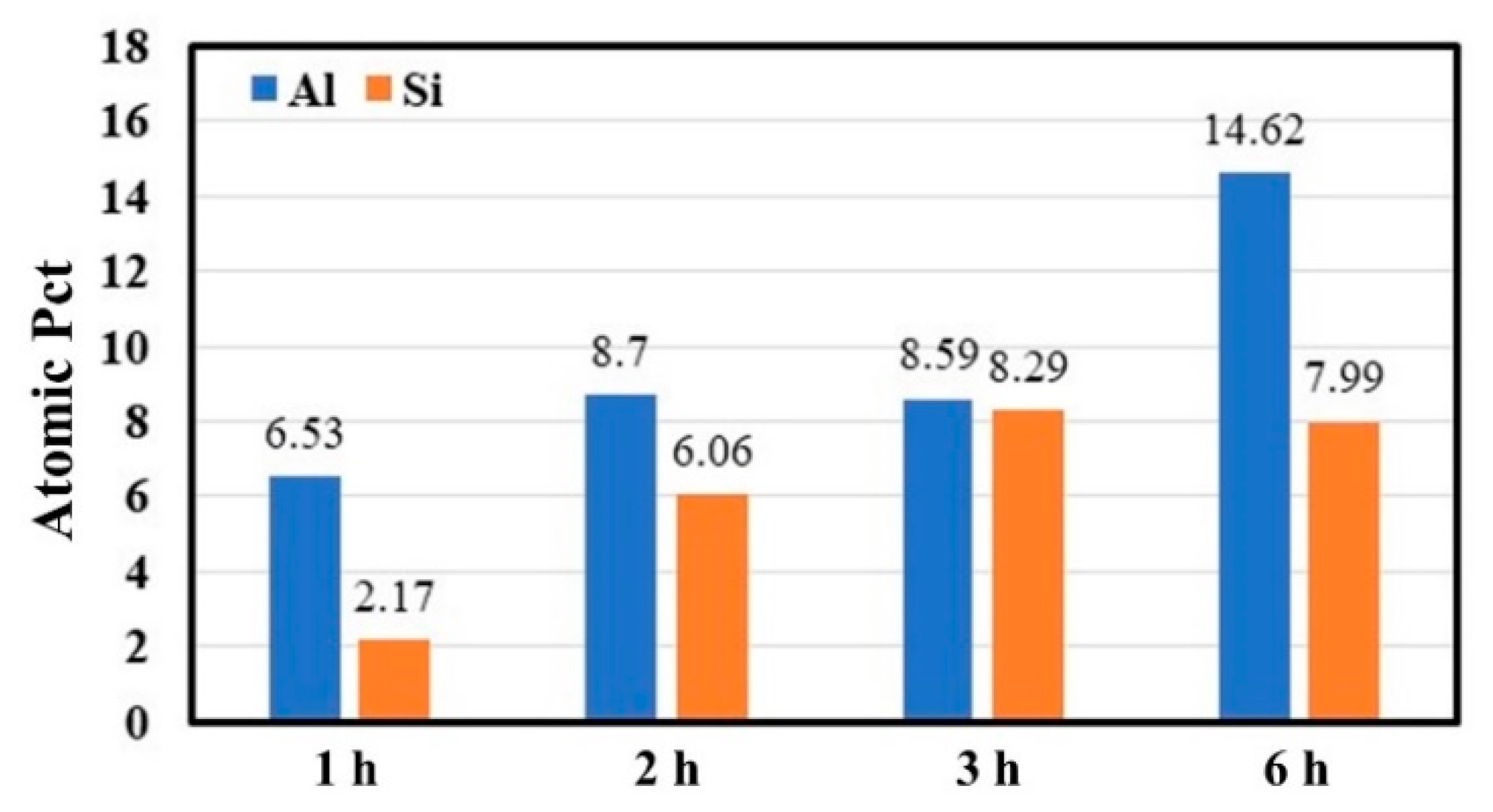
3.3. Effect of Time
4. Conclusions
- Carbothermic reduction reactions of Fe2O3 in mill scale, Al2O3, and SiO2 in aluminum dross can proceed at 1550 °C. The formation of metal droplets was observed and clearly separated from the unreacted-oxides phase. The synthesized alloys produced in the systems were Fe–Al–Si–C ferroalloys consisting of iron aluminide (Fe3Al) and iron silicide (Fe3Si) phases. Carbothermic reduction of Al2O3 in the present study can occur in the presence of liquid Fe as the metallic solvent.
- For low carbon content in the system (C/O = 1), carbon was inadequate for Al2O3 reduction because it will be consumed by Fe2O3 reduction first and then SiO2 reduction. The remaining carbon will be for Al2O3 reduction due to its lowest driving force of the reaction at 1550 °C.
- For high carbon content in the system (C/O = 2), it looked like the carbothermic reduction of Fe2O3, Al2O3, and SiO2 in this system had occurred almost concurrently, but different kinetic rates depend on the driving force for each reaction. The excess carbon in the pellet will provide adequate carbon atoms for the carbothermic reduction of each reducible oxide.
- Carbothermic reduction of SiO2 1550 °C can complete within 2–3 h, while a longer time is needed for the carbothermic reduction of Al2O3 to reach completion. However, the conditions of C/O = 2 and interaction time of 3 h were suitable for the synthesis of Fe-Al-Si-C due to the economic point of view. Further investigation is essential for the mechanical properties of the synthesized ferroalloys.
- The innovation of this study was to extract Fe, Al, and Si from metal oxides bearing industrial wastes at temperatures as low as 1550 °C in one step process. The final product was in the form of Fe–Al–Si–C alloys. This research increases the possible methods for industrial waste management, decreases the negative effect on the environment, and enhances sustainability for materials processing toward a circular economy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martin, M.I.; Lopez, F.A.; Torralba, J.M. Production of sponge iron powder by reduction of rolling mill scale. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2012, 39, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.; Dehiya, S.; Pandel, U.; Banerjee, M.K. Utilization of low grade coal for direct reduction of mill scale to obtain sponge iron: Effect of reduction time and particle size. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 11, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Zhu, H.; Peng, J.; Khannan, C.S.; Chen, J.; Dai, L.; Liu, P. Preparation of Reduce Iron Powders from Mill Scale with Microwave Heating: Optimization Using Response Surface Methodology. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44B, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaerudini, D.S.; Chanif, I.; Insiyanda, D.R.; Destyorini, F.; Alva, S.; Premono, A. Preparation and characterization of mill scale industrial waste reduced by biomass-based carbon. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, D.R.; He, Y.D.; Qi, H.B.; Wei, G. Reduction of oxide scale on hot-rolled Strip steels by carbon monoxide. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 3500–3502. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, C.; Li, J.; Tan, N.; He, Y.; Zhang, S. Reduction of oxide scale on hot-rolled steel by hydrogen at low temperature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 15116–15124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchiheub, O.; Mechachti, S.; Serrai, S.; Khalifa, M.G. Elaboration of iron powder from mill scale. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2010, 1, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Mechachti, S.; Benchiheub, O.; Serrai, S.; Shalabi, M.E.H. Preparation of iron Powders by Reduction of Rolling Mill Scale. Int. J. Sci. Eng. Res. 2013, 4, 1467–1472. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, C.; Dhokey, N.B. Study of Kinetics of Mill Scale Reduction: For PM Applications. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2015, 68, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sista, K.S.; Dwarapudi, S.; Nerune, V.P. Direct reduction recycling of mill scale through iron powder synthesis. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish Reddy, M.; Neeraja, D. Aluminium residue waste for possible utilization as a material: A review. Indian Acad. Sci. 2015, 43, 124. [Google Scholar]
- Das, B.R.; Dash, B.; Tripathy, B.C.; Bhattacharya, I.N.; Das, S.C. Production of η-alumina from waste aluminium dross. Miner. Eng. 2006, 20, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://www.basel.int/ (accessed on 11 August 2022).
- Lukita, M.; Abidin, Z.; Riani, E.; Ismail, A. Utilization of hazardous waste of black dross aluminum: Processing and application-a review. J. Degrad. Min. Lands Manag. 2022, 9, 3265–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoldi, M.; Fuentes-Ordoñez, E.G.; Korili, S.A.; Gil, A. Efficient recovery of aluminum from saline slag wastes. Miner. Eng. 2019, 140, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Arrieta, E.; Vicente, M.A.; Korili, S.A. Synthesis and CO2 adsorption properties of Hydrotalcite like compounds prepared from aluminum saline slag wastes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría, L.; López-Aizpún, M.; García-Padial, M.; Vicente, M.A.; Korili, S.A.; Gil, A. Zn-Ti-Al layered double hydroxides synthesized from aluminum saline slag wastes as efficient drug adsorbents. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 187, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.T.N.; Lee, M.S. Hydrochloric acid leaching behavior of mechanically activated black dross. J. Korean Inst. Resour. Recycl. 2018, 27, 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Lee, M.S. Synthesis of magnesium aluminate spinel powder from the purified sodium hydroxide leaching solution of black dross. Processes 2019, 7, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawrah, M.F.; Taha, M.A.; Abo Mostafa, H. In situ formation of Al2O3/Al core-shell from waste material: Production of porous composite improved by graphene. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 10693–10699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, P.; Ranjit, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Gomes, S.A. Synthesis of high temperature (1150 °C) resistant materials after extraction of oxides of Al and Mg from aluminum dross. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobtham, C.; Kongkarat, S. Synthesis of hercynite from aluminum dross at 1550 °C: Implication for industrial waste recycling. Mat. Sci. Forum 2020, 977, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, A.; Soriano, L.; Monzó, J.; Moraes, J.C.B.; Borrachero, M.V.; Payá, J. Salt slag recycled by-products in high insulation alternative environmentally friendly cellular concrete manufacturing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 231, 117114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udvardi, B.; Géber, R.; Kocserha, I. Investigation of aluminum dross as a potential asphalt filler. Int. J. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2019, 4, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, E.; Jones, A.; Cooling, D.; Stockton, N. Magnetic separation of Red Sand to produce value. Miner. Eng. 2006, 19, 1603–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Niu, Z.; Li, W.; Zhao, H.; Tang, Q. A novel process for recovery of aluminum, iron, vanadium, scandium, titanium and silicon from red mud. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, U.U.; Hocheng, H. A review of recovery of metals from industrial waste. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 2012, 54, 156–167. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Kong, J.; Gao, S.; Zhou, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Xing, P. Preparation of Al–Si alloys with silicon cutting waste from diamond wire sawing process. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Konyukhov, Y.V.; Ikram-ul-hag, M.; Burmistrov, I.; Cayumil, R.; Belov, V.A.; Rogachev, O.; Leybo, D.V.; Mukherjee, P.S. An innovative route for vararising iron and aluminium oxide rich industrial wastes: Recovery of multiple metals. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 113035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongkarat, S.; Boonyaratchinda, M.; Chobtham, C. Formation of ferrosilicon alloy at 1550 °C via carbothermic reduction of SiO2 by coal and graphite: Implication for rice husk ash utilization. Solid State Phenom. 2021, 315, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyaratchinda, M.; Kongkarat, S. Fundamental investigation of ferrosilicon production using rice husk and rubber tree bark at 1550 °C: Implication for utilization of agricultural waste in steelmaking industry. Mat. Sci. Forum 2020, 977, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Kongkarat, S.; Seetharaman, S.; Sahajwalla, V. Carbothermic Reduction of Alumina at 1823K in the Presence of Molten Steel: A Sessile Drop Investigation. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dankwah, J.R.; Koshy, P.; Saha-Chaudhury, N.; O’Kane, P.; Skidmore, C.; Knights, D.; Sahajwalla, V. Reduction of FeO in EAF steelmaking slag by metallurgical coke and waste plastics blends. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, R.A.; Finn, C.W.; Elliott, J.F. Physical chemistry of the carbothermic reduction of alumina in the presence of a metallic solvent: Part II. Measurements of kinetics of reaction. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1989, 20, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.H.; Pidgeon, L.M. An investigation of the Aluminium-Oxygen-Carbon system. Can. J. Chem. 1963, 27, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinlade, O.; Singh, R.N.; Sommer, F. Thermodynamics of liquid Al–Fe alloys. J. Alloys Comp. 2000, 299, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








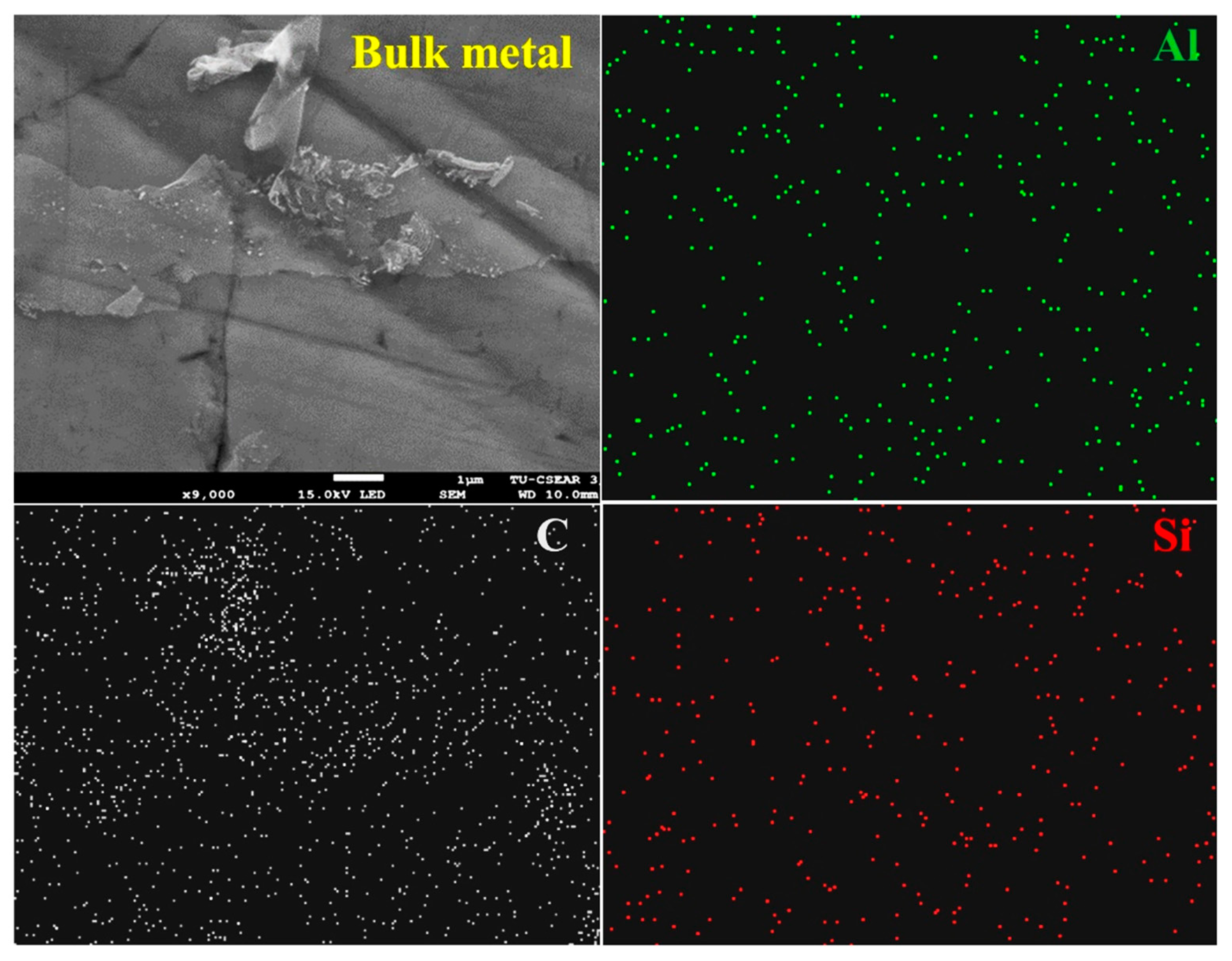
| Oxides (wt%) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al2O3 | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | CaO | K2O | MgO | MnO | Na2O | SO3 | CuO | TiO2 | ZnO | Others |
| 69.94 | 5.01 | 0.54 | 1.0 | 0.76 | 4.91 | 0.15 | 10.65 | 2.46 | 0.37 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 3.79 |
| Oxides (wt%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2O3 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | SO3 | TiO2 | K2O | P2O5 |
| 93.66 | 1.42 | 0.82 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Blend | Dross (wt%) | Scale (wt%) | Graphite (wt%) | C/O Ratios |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 41.34 | 48.44 | 10.21 | 1 |
| B | 39.37 | 46.09 | 14.57 | 1.5 |
| C | 37.52 | 43.95 | 18.53 | 2 |
| Blend | C/O Ratios | Atomic (at%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Al | Si | C | ||
| A | 1 | 69.32 | 0.69 | 4.15 | 25.84 |
| B | 1.5 | 56.08 | 7.30 | 9.94 | 26.68 |
| C | 2 | 48.19 | 8.59 | 8.29 | 34.93 |
| Heating Time (h) | Atomic (at%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Al | Si | C | |
| 1 | 55.49 | 6.53 | 2.17 | 35.81 |
| 2 | 42.11 | 8.7 | 6.06 | 43.13 |
| 3 | 48.19 | 8.59 | 8.29 | 34.93 |
| 6 | 48.02 | 14.62 | 7.99 | 29.37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wongsawan, P.; Srichaisiriwech, W.; Kongkarat, S. Synthesis of Ferroalloys via Mill Scale-Dross-Graphite Interaction: Implication for Industrial Wastes Upcycling. Metals 2022, 12, 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111909
Wongsawan P, Srichaisiriwech W, Kongkarat S. Synthesis of Ferroalloys via Mill Scale-Dross-Graphite Interaction: Implication for Industrial Wastes Upcycling. Metals. 2022; 12(11):1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111909
Chicago/Turabian StyleWongsawan, Praphaphan, Weerayut Srichaisiriwech, and Somyote Kongkarat. 2022. "Synthesis of Ferroalloys via Mill Scale-Dross-Graphite Interaction: Implication for Industrial Wastes Upcycling" Metals 12, no. 11: 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111909
APA StyleWongsawan, P., Srichaisiriwech, W., & Kongkarat, S. (2022). Synthesis of Ferroalloys via Mill Scale-Dross-Graphite Interaction: Implication for Industrial Wastes Upcycling. Metals, 12(11), 1909. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111909







