Effect of the Surface Oxide Layer on Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of [011]-Oriented Ti-50.1Ni Single Crystals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
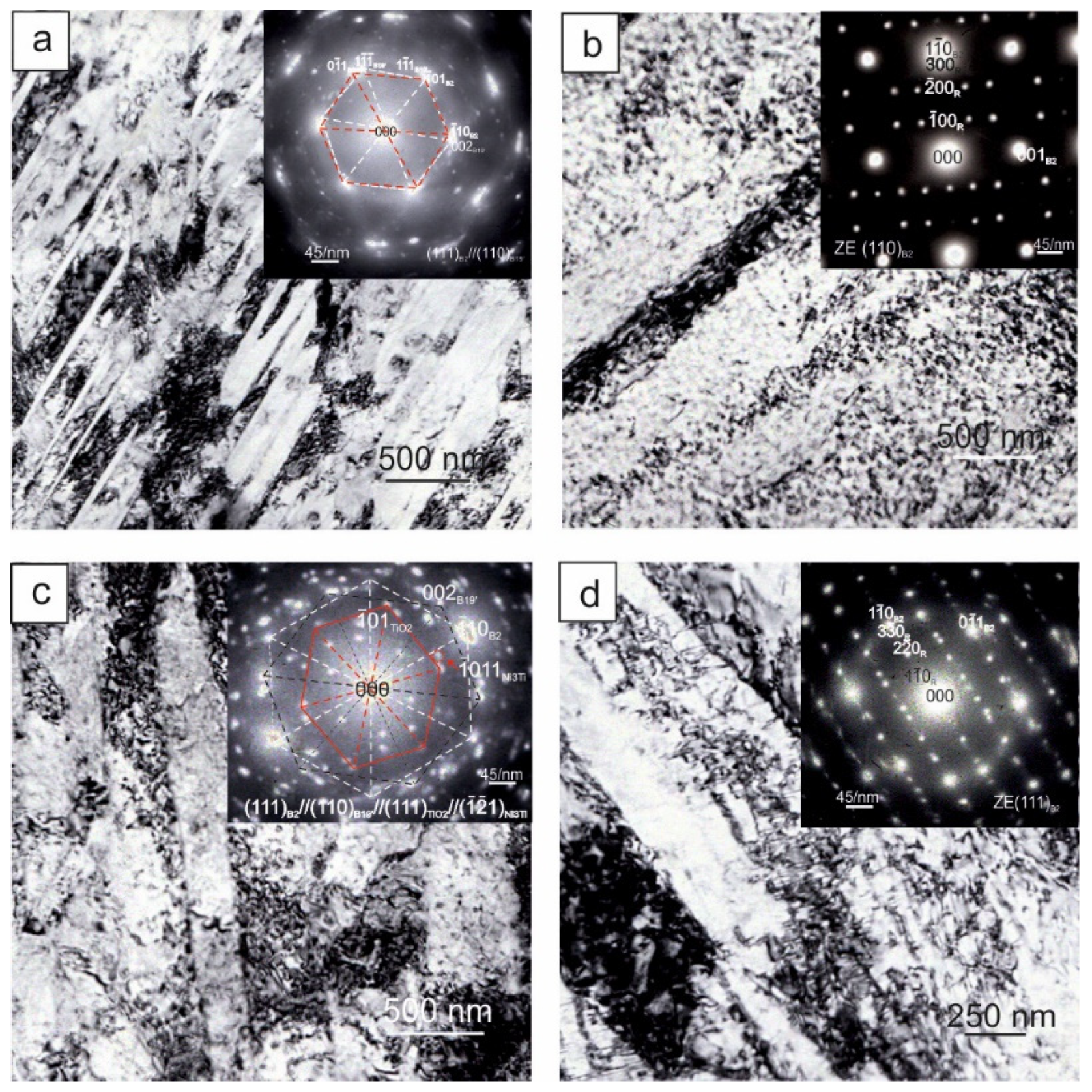
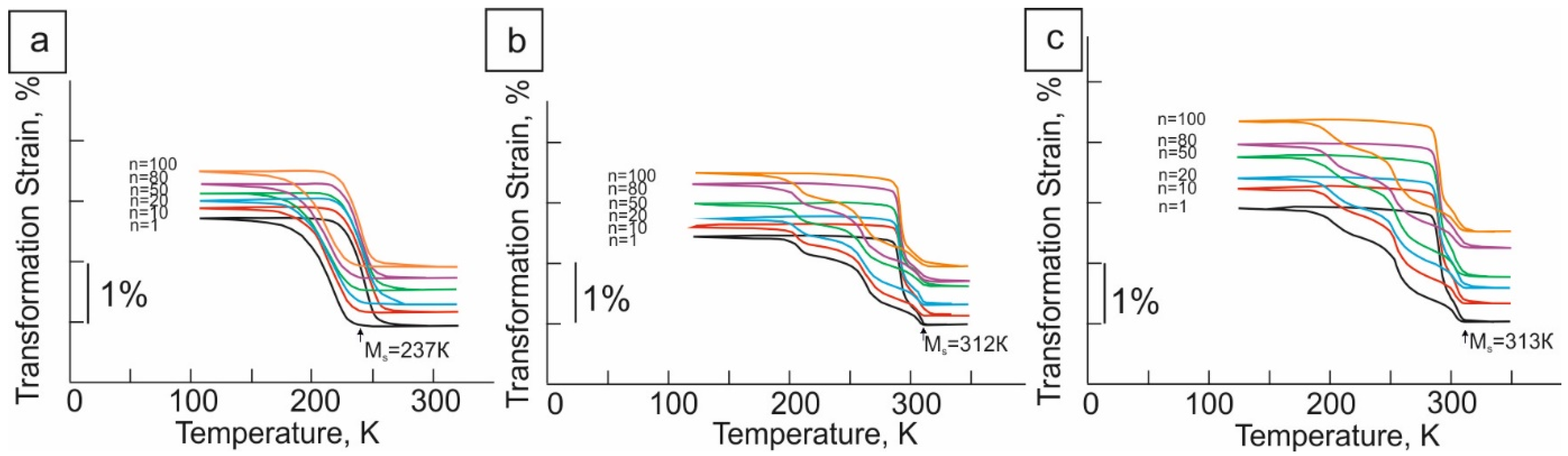
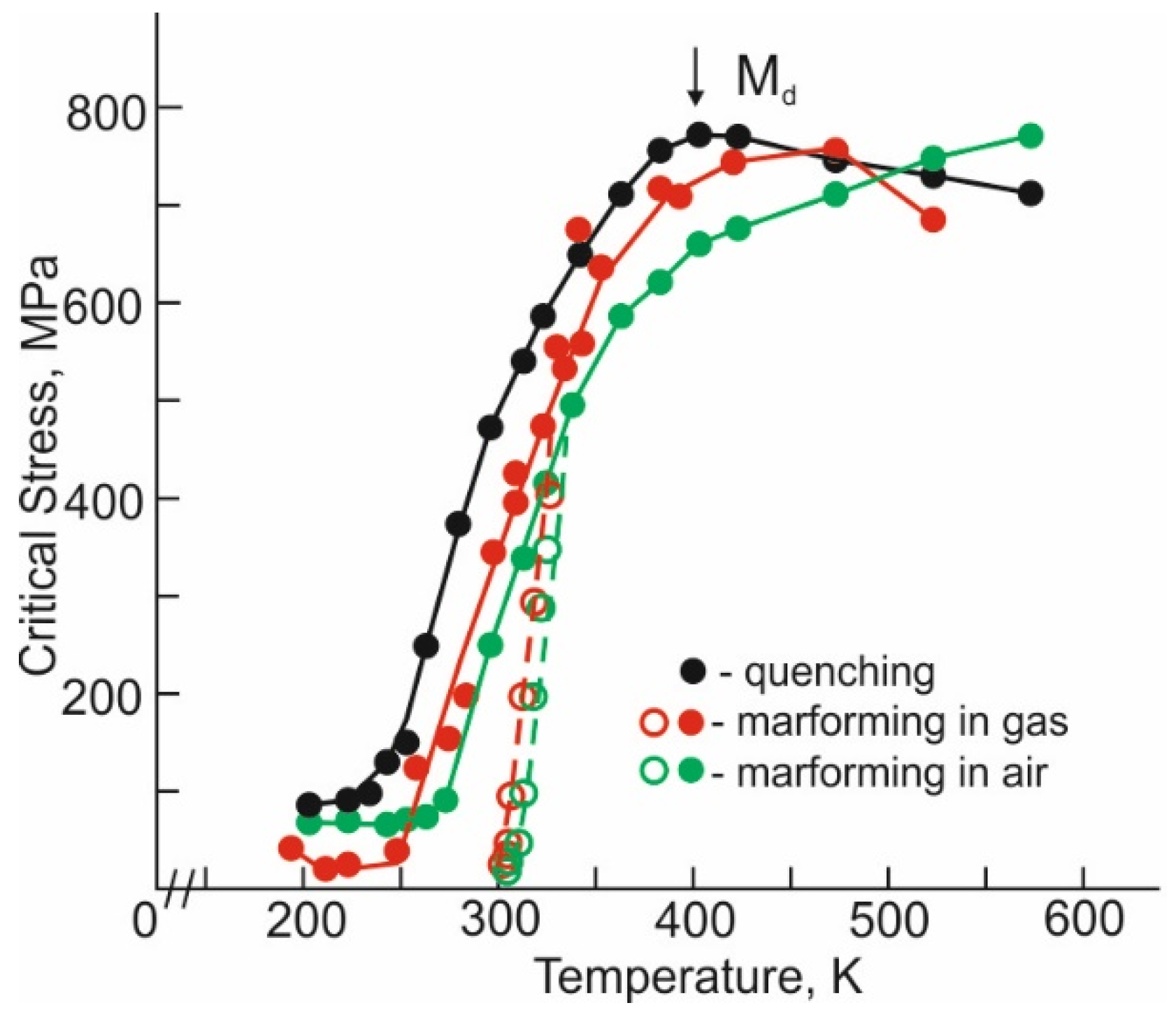
3.1. Microstructure and Martensitic Transformation Temperatures after Marforming
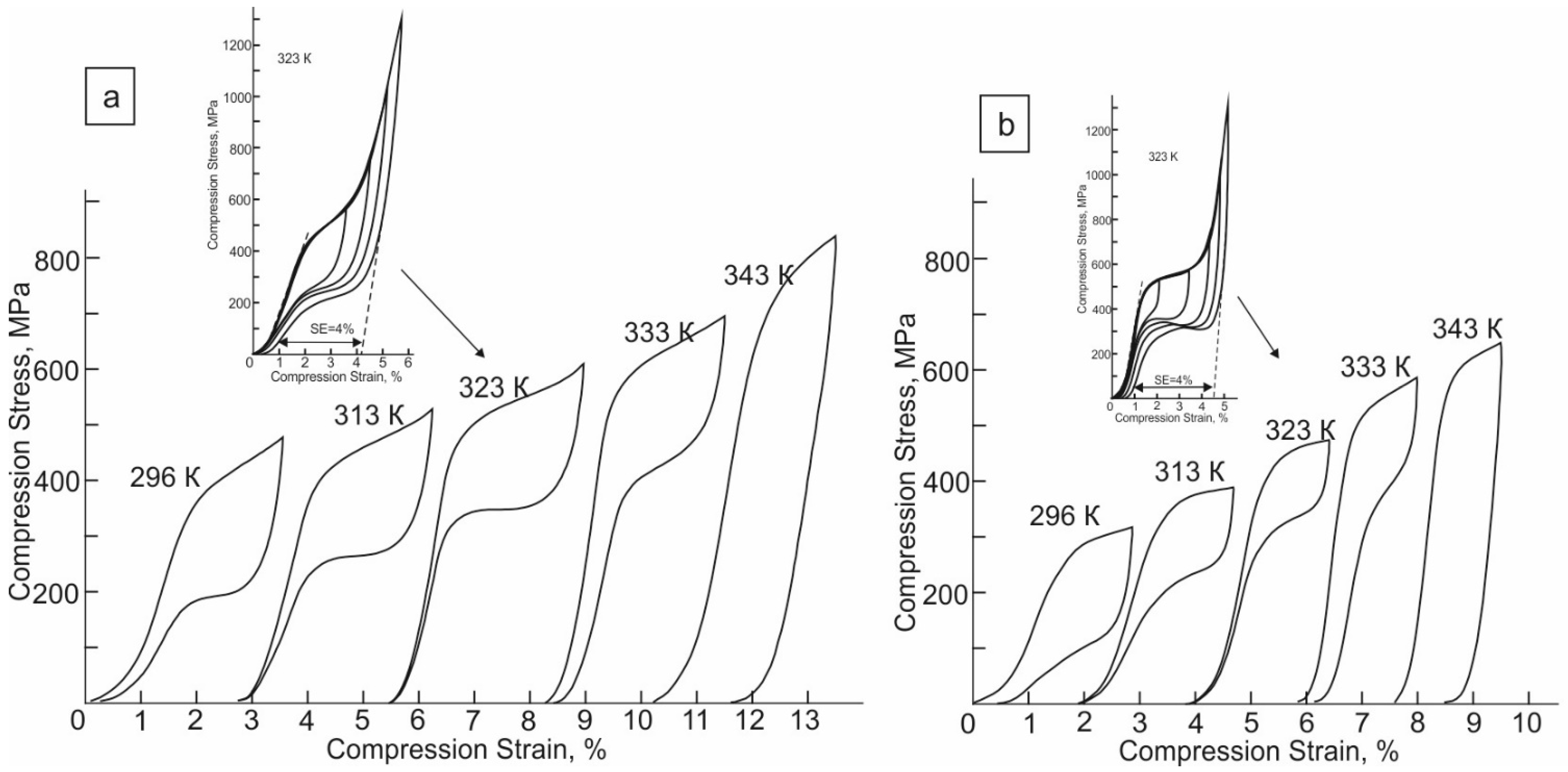
3.2. Shape Memory Effect
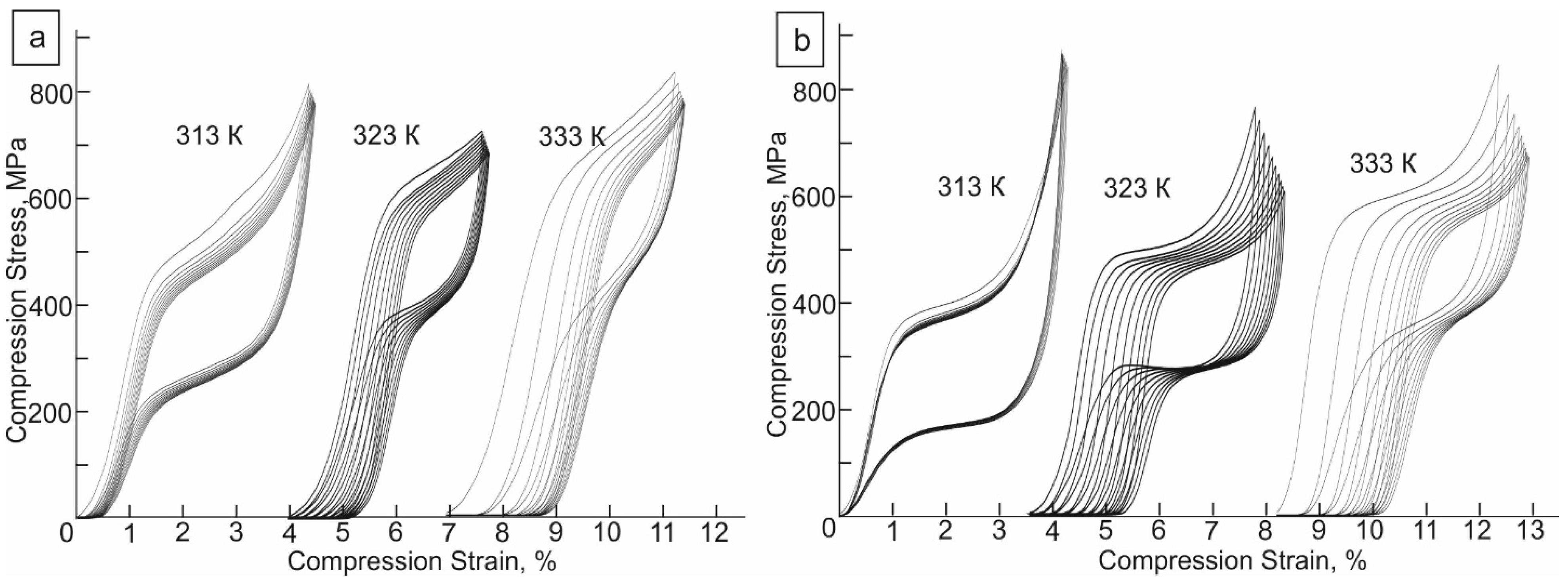
3.3. Superelasticity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- In single-phase [011]-oriented single crystals of the Ti-50.1%Ni alloy during cooling/heating in the free state and under stress, a one-stage B2-B19′ MT is observed with a low temperature hysteresis of 34 K. SME is equal to 3.1%. SE is not observed.
- Deformation up to 7.7% in the martensitic state at 203 K, followed by annealing at 713 K for 0.5 h in an inert helium gas and in dry air, leads to the development of a two-stage B2-R-B19′ MT and to the appearance of SE in the temperature range from 296 to 333 K. The maximum SE is 4%, and the SME is 2.4 and 2.6% in samples without and with an oxide layer, respectively.
- Annealing in dry air determines the formation of a thin oxide layer with a thickness of 170 nm, which leads to a decrease in the strength properties of the high-temperature B2-phase and the stresses in temperature range of the stress-induced MT compared to crystals without an oxide layer. These differences are associated with the formation of compressive stresses from the oxide layer.
- In experiments on the study of SE, an oxide layer of 170 nm thick reduces the transformation hardening coefficient Θ = dσ/dε from 6.5 GPa in crystals without an oxide layer to 2.0 GPa with an oxide layer; does not affect the SE value and SE temperature range ΔTSE = 37 K, but reduces the value of mechanical hysteresis Δσ. In experiments on studying the SME under stress, the oxide layer does not affect the SME value and the temperature ΔTh hysteresis.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otsuka, K.; Wayman, C.M. Shape Memory Materials; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1998; p. 284. [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 135–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahinia, M.; Moghaddam, N.S.; Andani, M.T.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Bimber, B.A.; Hamilton, R.F. Fabrication of NiTi through additive manufacturing. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 630–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moghaddam, N.S.; Saedi, S.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Hinojos, A.; Ramazani, A.; Kundin, J.; Mills, M.J.; Karaca, H.; Elahinia, M. Achieving superelasticity in additively manufactured NiTi in compression without post-process heat treatment. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gall, K.; Sehitoglu, H.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kireeva, I.V. Tension–compression asymmetry of the stress–strain response in aged single crystal and polycrystalline TiNi. Acta Mater. 1999, 47, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.S.; Pang, E.L.; Ko, W.-S.; Jun, H.; Bong, H.J.; Kirchlechner, C.; Raabe, D.; Choi, P.-P. Orientation-dependent plastic deformation mechanisms and competition with stress-induced phase transformation in microscale NiTi. Acta Mater. 2021, 208, 116731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kireeva, I.V.; Vyrodova, A.V.; Saraeva, A.A.; Pobedennaya, Z.V. Effect of marforming on superelasticity and shape memory effect of [001]-oriented Ni50.3Ti49.7 alloy single crystals under compression. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 896, 162841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbogen, E.; Mertinger, V.; Wurzel, D. Microstructure and tensile properties of two binary NiTi-alloys. Scr. Mater. 2001, 44, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kireeva, I.V.; Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Vyrodova, A.V.; Pobedennaya, Z.; Marchenko, E.S. Investigation of the orientation dependence of marforming on superelasticity and shape memory effect in equiatomic TiNi single crystals under compression. Mater. Lett. 2022, 324, 132817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Liang, C.; Zhao, T.; Wang, D.; Ding, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ren, X.; et al. Strain states and unique properties in cold-rolled TiNi shape memory alloys. Acta Mater. 2022, 231, 117890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Gui, X.; Liu, E.; Feng, X.; Dong, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, G. Influence of microstructure on phase transformation behavior and mechanical properties of plasma arc deposited shape memory alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinskiy, S.; Prokoshkin, S.; Sheremetyev, V.; Konopatsky, A.; Korotitskiy, A.; Tabachkova, N.; Blinova, E.; Glezer, A.; Brailovski, V. The mechanisms of stress-induced transformation in ultimately fine-grained titanium nickelide, and critical grain size for this transformation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2021, 858, 157733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenko, M.; Godec, M.; Kocijan, A.; Rudolf, R.; Dolinar, D.; Ovsenik, M.; Gorenšek, M.; Zaplotnik, R.; Mozetic, M. A new route to biocompatible Nitinol based on a rapid treatment with H2/O2 gaseous plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabalovskaya, S.; Anderegg, J.; Humbeeck, J.V. Critical overview of Nitinol surfaces and their modifications for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2008, 4, 447–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barison, S.; Cattarin, S.; Daolio, S.; Musiani, M.; Tuissi, A. Characterisation of surface oxidation of nickel–titanium alloy by ion-beam and electrochemical techniques. Electrochim. Acta 2004, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firstov, G.S.; Vitchev, R.G.; Kumar, H.; Blanpain, B.; Van Humbeeck, J. Surface oxidation of NiTi shape memory alloy. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 4863–4871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.L.; Wu, S.K.; Yen, Y.C. Oxidation behavior of equiatomic TiNi alloy in high temperature air environment. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1996, 216, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelakantan, L.; Swaminathan, S.; Spiegel, M.; Eggeler, G.; Hassel, A.W. Selective surface oxidation and nitridation of NiTi shape memory alloys by reduction annealing. Corros. Sci. 2009, 51, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, T.-H.; Chung, D.-W.; Lee, H.-W.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, M.-S. Effect of the surface oxide layer on transformation behavior and shape memory characteristics of Ti-Ni and Ti-Ni-Mo alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.; Mahmud, A.S.; Ahmad, M.N.; Razali, M.F.; Liu, Y. Estimation of titanium oxide layer thickness on thermally oxidized NiTi alloy based on color variations. Mater. Werkst. 2022, 53, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, T.E.; Wert, J.A. Modeling the effects of stress state and crystal orientation on the stress-induced transformation of NiTi single crystals. Met. Mater. Trans. A 1994, 25, 2383–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, I.; Karaca, H.; Souri, M.; Chumlyakov, Y.; Kurkcu, H. Effects of orientation on the shape memory behavior of Ni 51 Ti 49 single crystals. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 686, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayman, C.M.; Tong, H. On the equilibrium temperature in thermoelastic martensitic transformations. Scr. Met. 1977, 11, 3341–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.; Wayman, C.M. Thermodynamics of thermoelastic martensitiC transformations. Acta Met. 1975, 23, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakubo, H. Shape Memory Alloys; Gordon and Breach Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1987; 276p, [translated from the Japanese by J.B. Kennedy]. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chumlyakov, Y.I.; Kireeva, I.V.; Saraeva, A.A.; Pobedennaya, Z.V.; Vyrodova, A.V. Effect of the Surface Oxide Layer on Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of [011]-Oriented Ti-50.1Ni Single Crystals. Metals 2022, 12, 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111932
Chumlyakov YI, Kireeva IV, Saraeva AA, Pobedennaya ZV, Vyrodova AV. Effect of the Surface Oxide Layer on Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of [011]-Oriented Ti-50.1Ni Single Crystals. Metals. 2022; 12(11):1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111932
Chicago/Turabian StyleChumlyakov, Yuriy I., Irina V. Kireeva, Anastasia A. Saraeva, Zinaida V. Pobedennaya, and Anna V. Vyrodova. 2022. "Effect of the Surface Oxide Layer on Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of [011]-Oriented Ti-50.1Ni Single Crystals" Metals 12, no. 11: 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111932
APA StyleChumlyakov, Y. I., Kireeva, I. V., Saraeva, A. A., Pobedennaya, Z. V., & Vyrodova, A. V. (2022). Effect of the Surface Oxide Layer on Shape Memory Effect and Superelasticity of [011]-Oriented Ti-50.1Ni Single Crystals. Metals, 12(11), 1932. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12111932




