Effect of Pre-Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of As-Extruded AZ91-CaO Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Material Preparation
2.2. Microstructural Characterization
2.3. Mechanical Performance Test
2.4. Corrosion Resistance Test
3. Results and Discussion
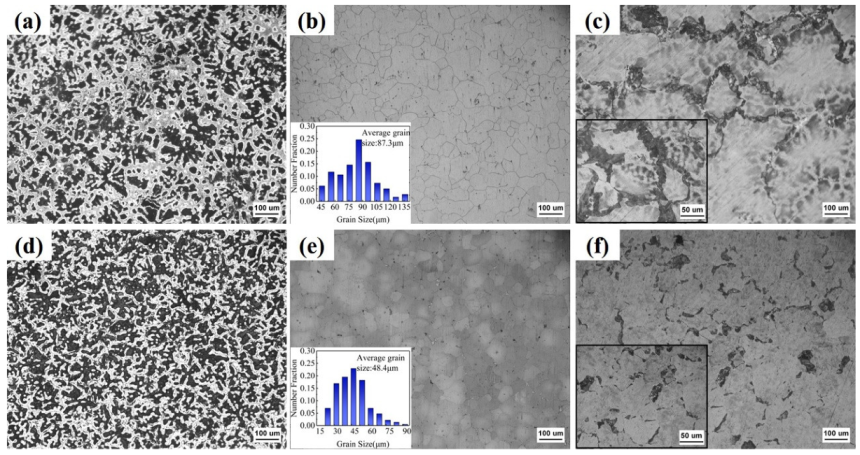
3.1. Microstructure of the Heat-Treated Alloys
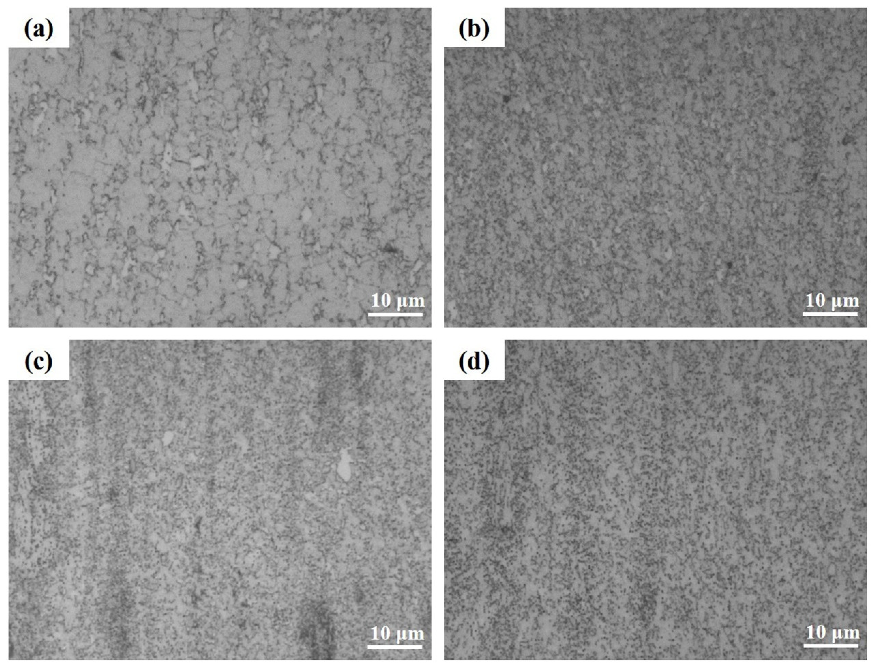
3.2. Microstructure of the Extruded Alloys with Pre-Heat Treatment
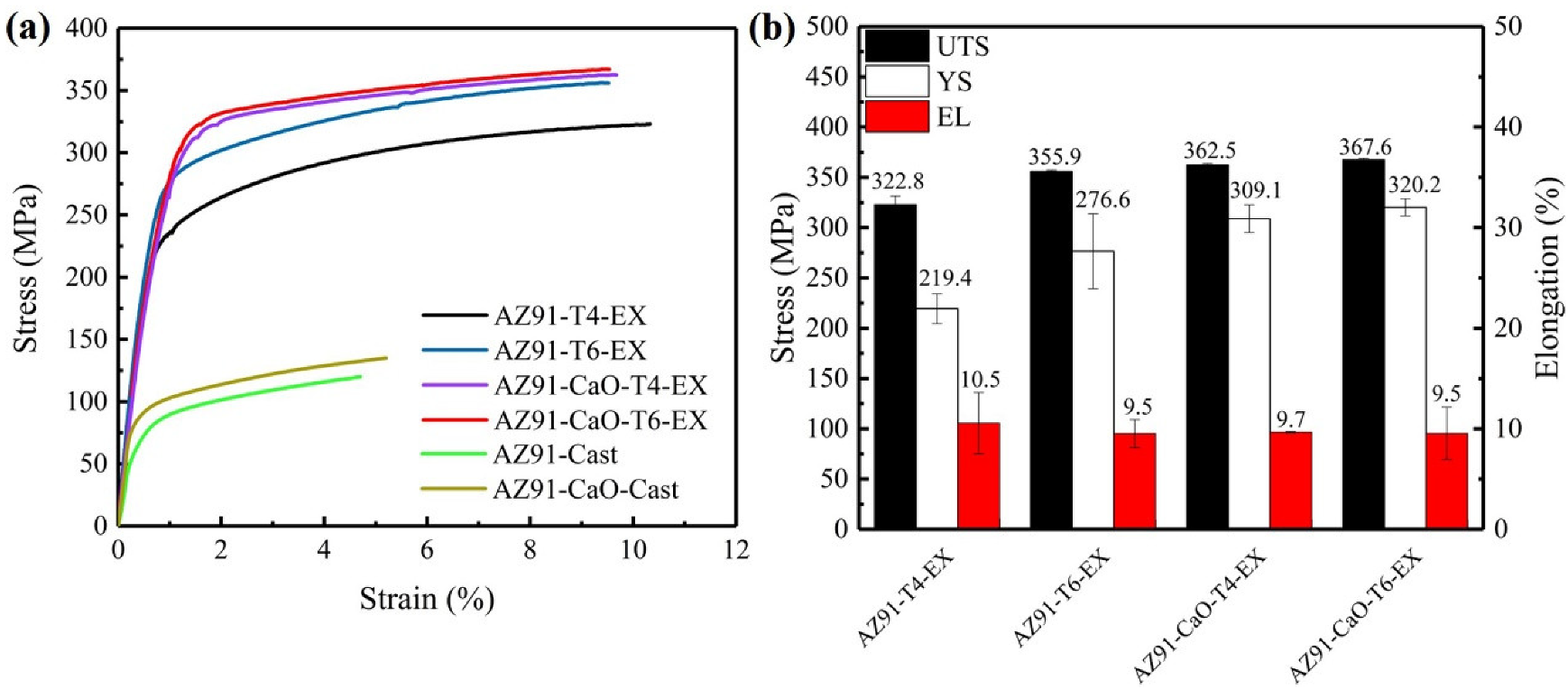
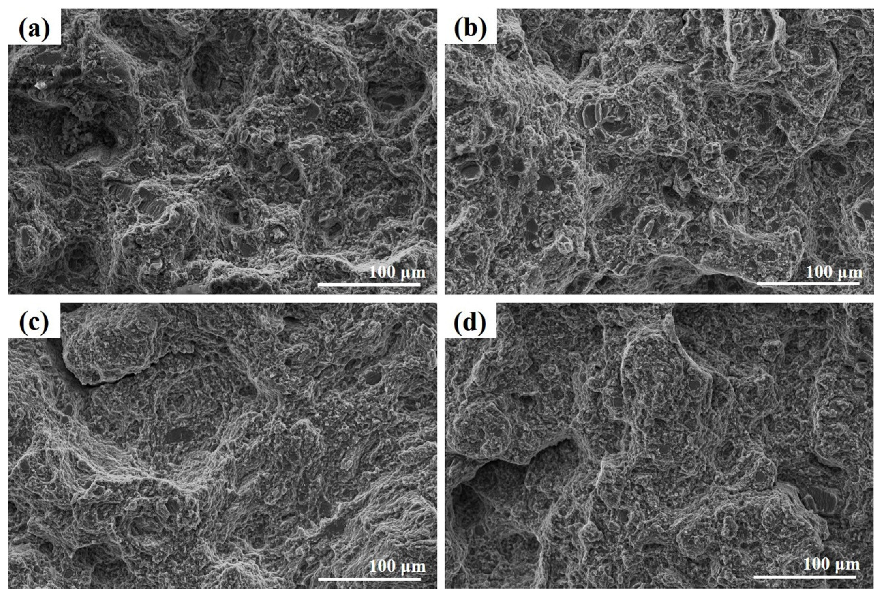
3.3. Mechanical Properties of the Pre-Heat Treated and Extruded Alloys
3.4. Corrosion Resistance Analysis of the Pre-Heat Treated and Extruded Alloys
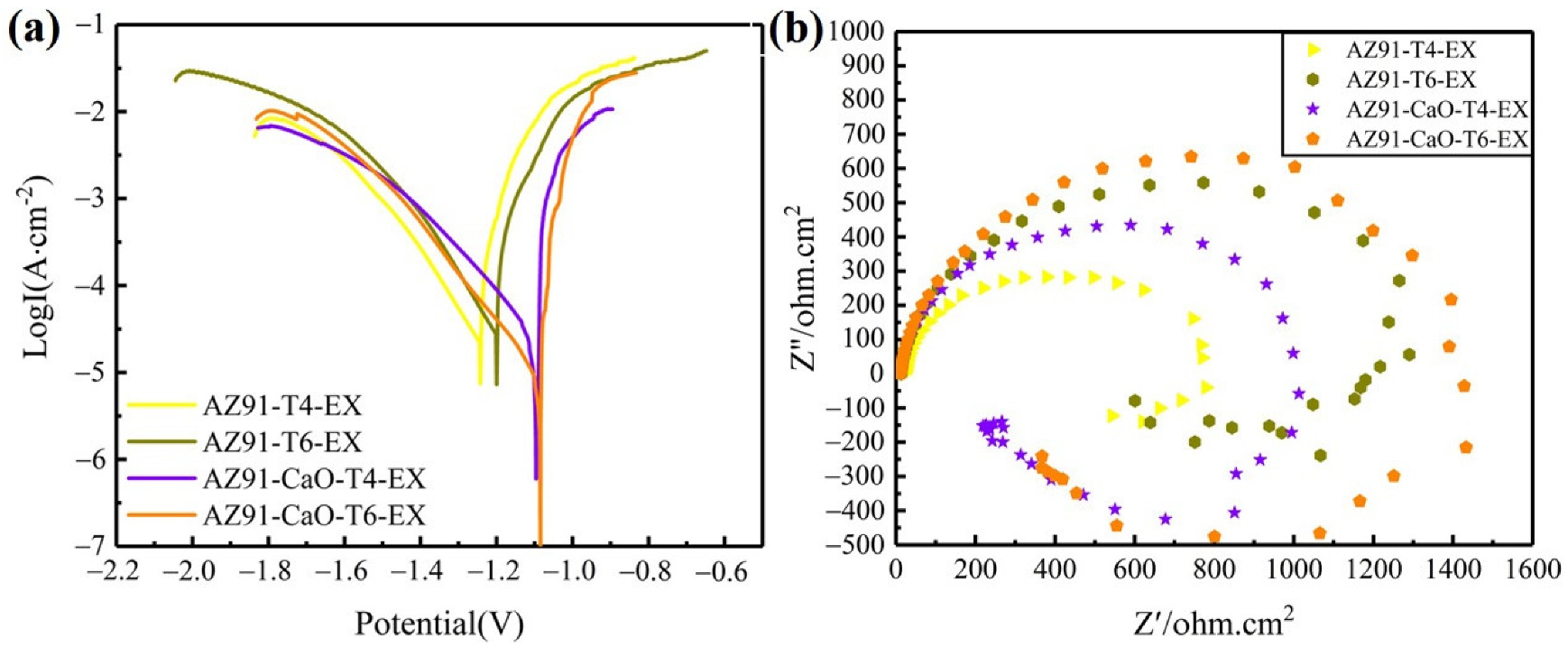
3.4.1. Electrochemical Performance
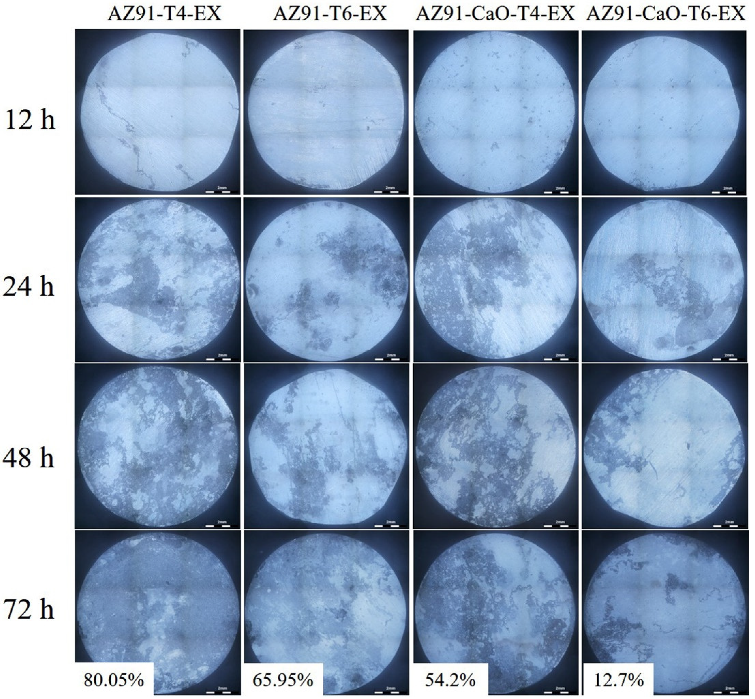
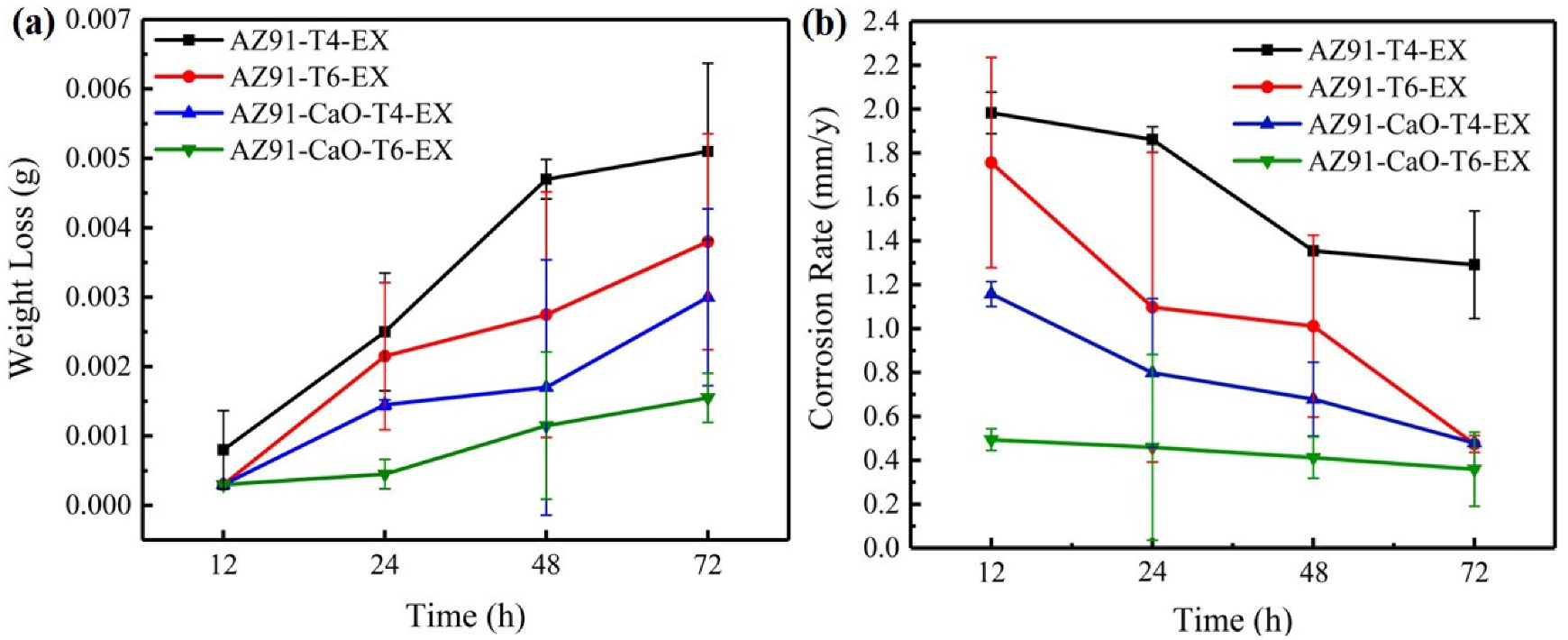
3.4.2. Corrosion Performance Analysis of Salt Spray
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The microstructure of AZ91 alloy was clearly refined after adding CaO. The addition of CaO consumed Al element in the matrix and generated Al2Ca phase. The distribution of coarse second phase changed from the continuous network structure in AZ91-Cast to the discontinuous state and size of them was clearly refined. After solution treatment, most of the Mg17Al12 were dissolved into the matrix, but there was still fishbone Mg17Al12 phase in AZ91-CaO-T4. After aging treatment, fine Mg17Al12 phase was precipitated at grain boundaries, and the Mg17Al12 in AZ91-CaO-T6 was even finer.
- (2)
- After extrusion, all the two alloys in different conditions underwent dynamic recrystallization, but the microstructures were different due to the different pretreatment processes. The size of grain and second phase of CaO-added alloys were smaller than that of extruded AZ91 alloy, while the T6-treated extruded alloy has a more fine and uniform microstructure compared with T4-treated extruded alloy.
- (3)
- The AZ91-CaO-T6-EX alloy has the best mechanical properties due to its small grain size, fine and dispersed second phase. The ultimate tensile strength, tensile yield strength and elongation reached 367.6 MPa, 320.2 MPa and 9.5%, respectively.
- (4)
- The corrosion resistance of the extruded material was significantly improved due to its small and diffusely distributed second phase and relatively uniform structure. The electrochemical test and long-term salt spray experiments revealed that the CaO-added alloy has a higher corrosion resistance than that of AZ91 alloy, while the corrosion performance of T6-treated alloy was better than that of T4-treated alloy. The AZ91-CaO-T6-EX alloy exhibited the optimal corrosion resistance among the extruded alloys.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Z.; Ahmad, R.; Yin, B.; Sandlobes, S.; Curtin, W.A. Mechanistic origin and prediction of enhanced ductility in magnesium alloys. Science 2018, 359, 447–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, X.; Huang, G.; Liu, H.; Tang, A.; Jiang, B.; Pan, F. Enhanced strength and ductility AZ91 alloy with heterogeneous lamella structure prepared by pre-aging and low-temperature extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 812, 141094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivas, A.; Pavan, D.; Venkatesha, B.K.; Rao, R.R.; Mohith, L. Study on mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 54, 291–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, X.; Wu, K.; Gan, W.M. Effect of particle size on microstructure and mechanical properties of SiCp/AZ91 magnesium matrix composite. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 543, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, K.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Xu, L.; Wu, K.; Zheng, M. Microstructure and mechanical properties of SiC nanoparticles reinforced magnesium matrix composites fabricated by ultrasonic vibration. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 5278–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandehari Ferdowsi, M.R.; Mazinani, M.; Ebrahimi, G.R. Effects of hot rolling and inter-stage annealing on the microstructure and texture evolution in a partially homogenized AZ91 magnesium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 606, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.H.; Lee, G.M.; Park, S.H. Difference in extrusion temperature dependences of microstructure and mechanical properties between extruded AZ61 and AZ91 alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy 2022, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdary, S.; Dumpala, R.; Kondaiah, V.V. Influence of heat treatment on the machinability and corrosion behavior of AZ91 Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 6, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yan, H.; Zhou, G.; Wu, X.; Hu, Z. Effects of the second phases on corrosion resistance of AZ91-xGd alloys treated with ultrasonic vibration. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.M.; Lee, J.U.; Park, S.H. Effects of post-heat treatment on microstructure, tensile properties, and bending properties of extruded AZ80 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 12, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Park, S.H.; Yu, H.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, Y.; You, B.S. Improved mechanical properties of Mg-7.6Al-0.4Zn alloy through aging prior to extrusion. Scr. Mater. 2014, 93, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Park, S.H.; You, B.S. Effect of aging prior to extrusion on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-7Sn-1Al-1Zn alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 627, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, F.; Xin, R.; Song, B.; Liu, Q. Influence of Aging Prior to Extrusion on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of an Extruded AZ91 Alloy. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelliah, N.M.; Padaikathan, P.; Kumar, R. Evaluation of electrochemical impedance and biocorrosion characteristics of as-cast and T4 heat treated AZ91 Mg-alloys in Ringer’s solution. J. Magnes. Alloy 2019, 7, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambat, R.; Aung, N.N.; Zhou, W. Evaluation of microstructural effects on corrosion behaviour of AZ91D magnesium alloy. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 1433–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shen, T.; Aung, N.N. Effect of heat treatment on corrosion behaviour of magnesium alloy AZ91D in simulated body fluid. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.; Kim, H.J.; Jeong, H.Y.; Sohn, S.; Shin, H.; Choi, K.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.G.; Yim, C.D.; You, B.S.; et al. Effect of alloyed Ca on the microstructure and corrosion properties of extruded AZ61 Mg alloy. Corros. Sci. 2016, 112, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, G.; Atrens, A.; Ding, W. Influence of trace As content on the microstructure and corrosion behavior of the AZ91 alloy in different metallurgical conditions. J. Magnes. Alloy 2020, 8, 301–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Li, H. Effect of Rare Earth and Ca Micro-Alloying on the Microstructure and Anisotropy of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy Sheets. Metals 2022, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaily, M.; Svensson, J.E.; Fajardo, S.; Birbilis, N.; Frankel, G.S.; Virtanen, S.; Arrabal, R.; Thomas, S.; Johansson, L.G. Fundamentals and advances in magnesium alloy corrosion. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 92–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, Y.; Deng, H.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Wei, G.; Peng, X. Effect of Ca Content on the Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Behaviors of Extruded Mg–7Li–3Al Alloys. Metals 2019, 9, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Ye, R.; Liu, G. Effects of the addition of Ca and Sb on the microstructure and mechanical properties of AZ91 magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 587, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, F.; Li, M.; Hou, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Fan, L. Effect of Ca on Corrosion Resistance Behavior of as-Cast AZ91 Magnesium Alloys. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2015, 44, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Pang, S.; Wang, Y.; Ding, W. Effects of processing parameters and Ca content on microstructure and mechanical properties of squeeze casting AZ91-Ca alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 595, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Peng, G.; Song, G.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Comparative studies of grain refinement of commercial purity Mg by CaO and Ca addition. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2019, 32, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Yang, G.; Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Effect of Ca and Y additions on oxidation behavior of AZ91 alloy at elevated temperatures. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2009, 19, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.B.; Abro, M.A.; You, B.S. High-Temperature Oxidation of AZ91-0.3%Ca-0.1%Y Alloy in Air. Met. Mater. Int. 2017, 23, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.B. High temperature oxidation of AZ31 + 0.3wt.%Ca and AZ31 + 0.3wt.%CaO magnesium alloys. Corros. Sci. 2013, 70, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; You, C.; Chen, M.; Lyu, S.; Tie, D.; Liu, H. Effect of calcium oxide particle size on microstructure and properties of AZ91 Mg alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 886, 160970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Liu, W.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, M.; Pan, F. Grain refinement of Ca addition in a twin-roll-cast Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2012, 2, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Lyu, S.; Zhao, Y.; You, C.; Wang, X.; Chen, M. The first principle research of CaO and MgO particulate heterogeneous nucleation in Mg alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 593, 153224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Lan, Q.; Liao, Q.; Le, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Cui, J. Effect of Ca and Gd combined addition on ignition temperature and oxidation resistance of AZ80. Corros. Sci. 2019, 160, 108176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, M. Comparative study of the effects of CaO and Ce-La misch metal on the microstructure and properties of AZ91 alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 5194–5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, C.; Cai, Z.; Yang, X.; Cheng, L.; Du, Y. The effect of co-addition of Si, Ca and RE on microstructure and tensile properties of as-extruded AZ91 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 705, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, C.S.; Keshavamurthy, R.; Koppad, P.G.; Kashyap, K.T. Role of particle stimulated nucleation in recrystallization of hot extruded Al 6061/SiCp composites. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2013, 23, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Lu, L.; Feng, L.; Lu, F.; Gan, C.; Li, X. Effects of pre-aging on microstructure evolution and deformation mechanisms of hot extruded Mg-6Zn-1Gd-1Er Mg alloys. J. Magnes. Alloy 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Nie, K.; Munroe, P.; Deng, K.; Guo, Y.; Han, J. Synergistic effects of hybrid (SiC+TiC) nanoparticles and dynamic precipitates in the design of a high-strength magnesium matrix nanocomposite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2021, 259, 124048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Analyzed Locations | Alloys | Elements (at. %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Al | Ca | Mn | Zn | ||
| A | AZ91-T4 | 5.96 | 68.08 | 0.00 | 25.95 | 0.01 |
| B | AZ91-T4 | 0.75 | 67.59 | 0.00 | 31.66 | 0.00 |
| C | AZ91-T4 | 62.43 | 36.57 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.00 |
| D | AZ91-CaO-T4 | 1.03 | 62.91 | 0.04 | 36.01 | 0.00 |
| E | AZ91-CaO-T4 | 59.87 | 37.97 | 1.09 | 0.04 | 1.03 |
| Analyzed Locations | Alloys | Elements (at. %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg | Al | Ca | Mn | Zn | ||
| A | AZ91-T4-EX | 62.36 | 36.51 | - | 0.06 | 1.07 |
| B | AZ91-T4-EX | 68.34 | 30.19 | - | 0.32 | 1.15 |
| C | AZ91-T6-EX | 75.01 | 21.47 | - | 3.19 | 0.34 |
| D | AZ91-T6-EX | 70.70 | 28.15 | - | 0.00 | 1.15 |
| E | AZ91-CaO-T4-EX | 65.30 | 32.19 | 1.69 | 0.03 | 0.79 |
| F | AZ91-CaO-T4-EX | 61.58 | 34.98 | 2.20 | 0.00 | 1.24 |
| G | AZ91-CaO-T6-EX | 57.95 | 37.34 | 3.50 | 0.00 | 1.21 |
| H | AZ91-CaO-T6-EX | 58.08 | 37.24 | 3.11 | 0.46 | 1.11 |
| Sample | UTS(MPa) | YS(MPa) | EL(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AZ91-T4-EX | 322.8 ± 8.6 | 219.4 ± 14.8 | 10.5 ± 3.1 |
| AZ91-T6-EX | 355.9 ± 1.3 | 276.6 ± 37.2 | 9.5 ± 1.4 |
| AZ91-CaO-T4-EX | 362.5 ± 1.4 | 309.1 ± 13.7 | 9.7 ± 0.5 |
| AZ91-CaO-T6-EX | 367.6 ± 1.6 | 320.2 ± 8.6 | 9.5 ± 2.6 |
| Sample | Ecorr(V) | Icorr(µA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| AZ91-T4-EX | −1.243 | 21.56 |
| AZ91-T6-EX | −1.221 | 5.34 |
| AZ91-CaO-T4-EX | −1.096 | 17.79 |
| AZ91-CaO-T6-EX | −1.086 | 5.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, S.; You, C.; Tian, L.; Chen, M. Effect of Pre-Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of As-Extruded AZ91-CaO Alloy. Metals 2022, 12, 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122060
Zhang G, Zhang L, Lyu S, You C, Tian L, Chen M. Effect of Pre-Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of As-Extruded AZ91-CaO Alloy. Metals. 2022; 12(12):2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122060
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guopeng, Lu Zhang, Shaoyuan Lyu, Chen You, Limin Tian, and Minfang Chen. 2022. "Effect of Pre-Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of As-Extruded AZ91-CaO Alloy" Metals 12, no. 12: 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122060
APA StyleZhang, G., Zhang, L., Lyu, S., You, C., Tian, L., & Chen, M. (2022). Effect of Pre-Heat Treatment on Microstructure and Properties of As-Extruded AZ91-CaO Alloy. Metals, 12(12), 2060. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12122060






