En-Garde! A Review of Fencing Blade Material Development
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Basic Characteristics of Fencing Sword
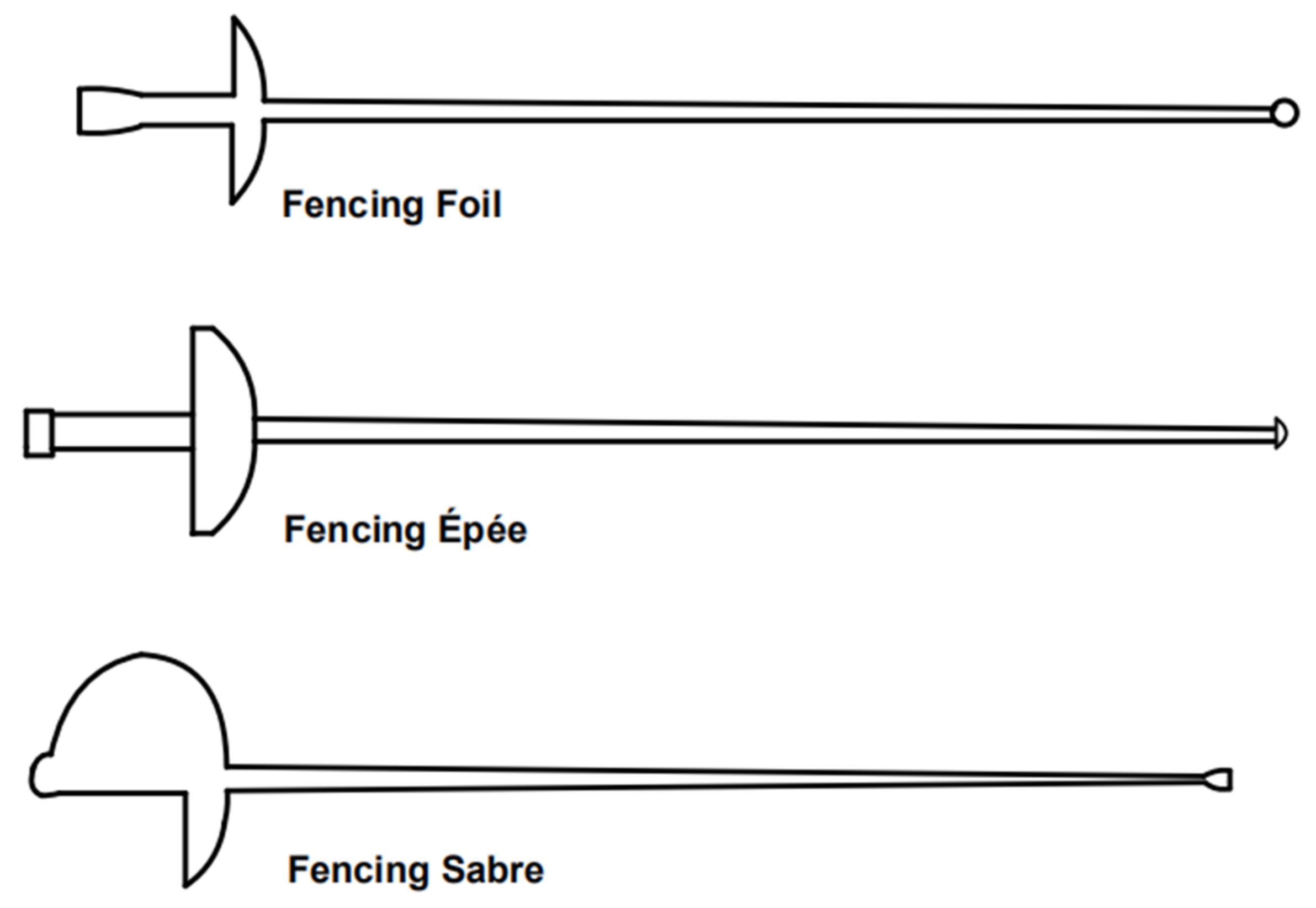
2.1. Sword Types
2.2. Manufacturing Process
2.3. Performance Requirements of Blades
3. Development of Blade Materials
3.1. Exploring the Material of the Blade
3.2. Spring Steels
3.2.1. Chemical Composition
3.2.2. Heat Treatment
3.3. Maraging Steels
3.3.1. Chemical Composition
| Type of Steels | Fe | C | Ni | Co | Mo | Ti | Al | Mn | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ni (250) [53] | Bal. | ≤0.03 | 17–19 | 7.0–8.5 | 4.6–5.1 | 0.3–0.5 | 0.05–0.15 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 |
| 18Ni (300) [53] | Bal. | ≤0.03 | 18–19 | 8.0–9.5 | 4.6–5.2 | 0.5–0.8 | 0.05–0.15 | ≤0.12 | ≤0.12 |
| 18Ni (350) [53] | Bal. | ≤0.01 | 17–18 | 12.0–13.0 | 3.5–4.0 | 1.6–2.0 | 0.10–0.20 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.10 |
| GMG [11] | Bal. | ≤0.03 | 18–20 | 8–13 | 4.0–5.0 | 0.5–2.0 | 0–0.05 | ≤0.10 | ≤0.10 |
3.3.2. Heat Treatment
4. Discussion and Outlook
4.1. Discussion
4.2. Future Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- International Fencing Federation. The International Fencing Federation Official Website. Available online: https://fie.org/fie/history (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Fare, M. History of Fencing—British Academy of Fencing. Available online: https://baf-fencing.com/history-of-fencing/ (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Hermann, R.; Dolfini, A.; Crellin, R.J.; Wang, Q.; Uckelmann, M. Bronze Age Swordsmanship: New Insights from Experiments and Wear Analysis. J. Archaeol. Method Theory 2020, 27, 1040–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, A. Sword-Wielding Scientists Show How Ancient Fighting Techniques Spread across Bronze Age Europe. Science, 2020. Available online: https://www.science.org/content/article/sword-wielding-scientists-show-how-ancient-fighting-techniques-spread-across-bronze-age (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Vass, I. Epee Fencing: A Complete System; SKA Swordplay Books: Staten Island, NY, USA, 2011; p. 303. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, N. The Inner Game of Fencing: Excellence in Form, Technique, Strategy, and Spirit; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
- Evangelista, N. The Art and Science of Fencing; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
- McInnis, E.; Root, W. The Secret History of the War. Am. Hist. Rev. 1945, 51, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberger, J.C. The Secret History of the Sword: Adventures in Ancient Martial Arts; Multi-Media Books: Burbank, CA, USA, 1999; ISBN 9781892515049. [Google Scholar]
- Roi, G.S.; Bianchedi, D. The Science of Fencing: Implications for Performance and Injury Prevention. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rules for Competitions. Book 3. Materials Rules. 2018. Available online: https://fie.org/fie/documents/rules (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Vivaldi, F.; Cortese, L.; Coppola, T.; Mazzarano, A.; Nalli, F. A Study on the Dynamic Structural Behavior of Olympic Sabres. Proc. Struct. Integr. 2018, 8, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AZO Materials. Advanced Materials in the Sport of Fencing. Available online: https://www.azom.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=179 (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Ritchie, R.O.; Knott, J.F. Mechanisms of Fatigue Crack Growth in Low Alloy Steel. Acta Metall. 1973, 21, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Tragic Death of Olympic Fencer Vladimir Smirnov. Available online: https://www.grunge.com/285751/the-tragic-death-of-olympic-fencer-vladimir-smirnov (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Worldsteel. Maraging Steel Delivers World’s Finest Fencing Blades. Available online: https://stories.worldsteel.org/innovation/maraging-steel-olympic-fencing-blades/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Fencing Safety: The Maraging Blade. Fencing.Net. Available online: https://www.fencing.net/428/fencing-safety-the-maraging-blade/ (accessed on 1 March 2021).
- Ritchie, R.O. Near-Threshold Fatigue-Crack Propagation in Steels. Int. Met. Rev. 1979, 24, 205–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fencing Dimensions & Drawings. Available online: https://www.dimensions.com/collection/fencing (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- HowStuffWorks. How Fencing Equipment Works. Available online: https://entertainment.howstuffworks.com/fencing-equipment.htm (accessed on 16 August 2021).
- Kibaroglu, D.; Baydogan, M.; Cimenoglu, H.; Bas, B.; Yagsi, C.; Aliyeva, N. Failure Analysis of Fencing Blades. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 843, 012009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, R.O. The Conflicts between Strength and Toughness. Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sword Buyers Guide. Sword Steels 101. Available online: https://www.sword-buyers-guide.com/sword-steels.html (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Decker, R.F.; Floreen, S.; Wilson, R.K. Maraging Steel: Recent Developments and Applications. In Proceedings of the Symposium of TMS Annual Meeting, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 January 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Chen, Y.L.; Yu, W.; Su, L.; Wang, X.; Tang, D. Study on Corrosion Resistance of High-Strength Medium-Carbon Spring Steel and Its Hydrogen-Induced Delayed Fracture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 239, 117815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrão, A.M.; Denkena, B.; Köhler, J.; Breidenstein, B.; Mörke, T. The Influence of Deep Rolling on the Surface Integrity of AISI 1060 High Carbon Steel. Proc. CIRP 2014, 13, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarmiento, G.S.; Castro, M.; Totten, G.E.; Jarvis, L.M.; Webster, G.; Cabré, M.F. Modeling Residual Stresses in Spring Steel Quenching Computer Simulations with Program. Jinshu Rechuli Heat Treat. Met. 2003, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.; Tan, Y. Metallography and Heat Treatment; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2007; ISBN 9787111017967. [Google Scholar]
- Suzhou Ritong Metal Materials Co., Ltd. 60Si2MnA Spring Steel. Available online: http://www.szrtjs.com/en_product_detail.asp?id=422 (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Types of Spring Steels. Available online: http://www.xinshentex.com/news/18880.html,%202020-07-02 (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- WixSteel Industrial. 60Si2MnA Spring Steel Wire. Available online: https://www.wixsteel.com/products/alloy-steel-bar/spring-steel-wire/60si2mna (accessed on 14 August 2021).
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Chou, K. Effect of Cerium on the Cleanliness of Spring Steel Used in Fastener of High-Speed Railway. J. Rare Earths 2014, 32, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, J.H.; Zhao, T.C.; Gao, H.J.; Hu, Y.H.; Xie, X.S. Effect of Controlled Rolling and Cooling on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 60Si2MnA Spring Steel Rod. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2005, 160, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, Y.Z.; Huang, X.Q. Heat Treatment Optimization of High-Quality 60Si2MnA Spring Steel. Jinshu Rechuli Heat Treat. Met. 2008, 33, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.M.; Ji, L.K.; Bao, D.J.; Feng, Y.R.; Li, S.X.; Weng, Y.Q. Gigacycle Fatigue Behavior of 1800 MPa Grade High Strength Spring Steel for Automobile Lightweight. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2014, 21, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Tan, W. Influence of Heat Treatment Process on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 60Si2CrVA Spring Steel. Jinshu Rechuli Heat Treat. Met. 2014, 39, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial Board. Chinese Aeronautical Materials Handbook: Structural Steel and Stainless Steel; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Floreen, S. The Physical Metallurgy of Maraging Steels. Metall. Rev. 1968, 13, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrison, W.M.; Banerjee, M.K. Martensitic Non-Stainless Steels: High Strength and High Alloy; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128035818. [Google Scholar]
- Viswanathan, U.K.; Dey, G.K.; Asundi, M.K. Precipitation Hardening in 350 Grade Maraging Steel. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 2429–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Swam, L.F.; Pelloux, R.M.; Grant, N.J. Fatigue Behavior of Maraging Steel 300. Metall. Trans. A 1975, 6, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, K.; Terasaki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Fischer, F.D.; Antretter, T.; Cailletaud, G.; Azzouz, F. Mechanical Properties of a Cr-Ni-Mo-Al-Ti Maraging Steel in the Process of Martensitic Transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 308, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degarmo, E.P.; Black, J.T.; Kohser, R.A. Materials and Processes in Manufacturing, 9th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Chong, X. Development of New Cobalt-Free Maraging Steel with Superior Mechanical Properties via Electro-Pulsing Technology. Metals 2019, 9, 1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Floreen, S. Cobalt Free Maraging Steel. U.S. Patent 4443254A, 17 April 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.G.; Kim, G.S.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, D.N. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of a Cobalt-Free Tungsten-Bearing Maraging Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. 1986, 79, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asayama, Y.; Okada, M.; Kawase, Y.; Mochizuki, T.; Sakashita, S. Mechanical Properties of a Cobalt-Free Maraging Steel Containing Chromium. J. Jpn. Inst. Metals 1987, 51, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Magnee, A. Cobalt-Containing High-Strength Steels: A Critical Review of the Physical Metallurgy of Cobalt-Containing High-Strength Steels, and a Survey of Their Processing, Properties and Uses; Centre D’information du Cobalt: Brussels, Belgium, 1974. [Google Scholar]
- CSBTS. Conversion of Hardness and Strength for Ferrous Metal. PTCA(PART A:PHYSICAL TEST ING) 2001, 37. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=LHJW200109014&DbName=CJFQ2001 (accessed on 23 December 2021).
- Karl, S. Nickel-Maraging Steels for Blades of Fencing Weapons. UK Patent GB2167436A, 29 May 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, R.F.; Novak, C.J.; Landig, T.W. Developments and Projected Trends in Maraging Steels. JOM 1967, 19, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limited, W.P. Steels for Aircraft Structures. In Introduction to Aerospace Materials; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2012; pp. 232–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NiDI. 18 Per Cent Nickel Maraging Steels—Engineering Properties; Nickel Development Institute: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1976; Volume 4419, p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhu, J. Development of Ultra-High Strength Maraging Steel. Spec. Steel 2004, 9, 248–253. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, V.V.; Reddy, G.M.; Raju, A.V.S. Microstructure, Hardness and Residual Stress Distribution of Dissimilar Metal Electron Beam Welds: Maraging Steel and High Strength Low Alloy Steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, G. Martensite in Steel: Strength and Structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 1999, 273–275, 40–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, R.; Mazumder, S.; Batra, I.S.; Dey, G.K.; Banerjee, S. Precipitation in 18 wt% Ni maraging steel of grade 350. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samek, L.; De Moor, E.; Penning, J.; De Cooman, B.C. Influence of Alloying Elements on the Kinetics of Strain-Induced Martensitic Nucleation in Low-Alloy, Multiphase High-Strength Steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2006, 37, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Nasim, I.; Husain, S.W. Influence of Nickel and Molybdenum on the Phase Stability and Mechanical Properties of Maraging Steels. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 1994, 3, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, J.; Su, Y. Current Situation and Development of Maraging Steel. J. Iron Steel Res. 2014, 26, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves Dos Reis, A.; Aparecida, D.; Reis, P.; Abdalla, A.J.; Otubo, J. High-Temperature Creep Resistance and Effects on the Austenite Reversion and Precipitation of 18 Ni (300) Maraging Steel. Mater. Charact. 2015, 107, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sha, W.; Cerezo, A.; Smith, G. A field-ion microscopy and atom probe study of ageing behaviour of a co-bearing maraging steel. J. Phys. Colloq. 1989, 50, C8-407–C8-412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moura Da Fonseca, D.P.; Larissa, A.; Feitosa, M.; Gomes De Carvalho, L.; Plaut, R.L.; Fernando Padilha, A. A Short Review on Ultra-High-Strength Maraging Steels and Future Perspectives. Mater. Res. 2021, 24, 20200470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W.; Cerezo, A.; Smith, G.D.W. Phase Chemistry and Precipitation Reactions in Maraging Steels: Part IV. Discussion and Conclusions. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1993, 24, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, D.R.; Wilson, E.A. Effect of Cobalt on Impact Toughness of Steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1994, 10, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemperle, A.; Gemperlová, J.; Sha, W.; Smith, G.D.W. Aging Behaviour of Cobalt Free Chromium Containing Maraging Steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. United Kingd. 1992, 8, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, A.; Mattar, T.; El-Faramawy, H.; Bleck, W. Mechanical Properties of New Low-Nickel Cobalt-Free Maraging Steels. Steel Res. 2002, 73, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Filho, V.X.; Lima, T.N.; Griza, S.; Saraiva, B.R.C.; de Abreu, H.F.G. The Increase of Fracture Toughness with Solution Annealing Temperature in 18Ni Maraging 300 Steel. Mater. Res. 2021, 24, e20200472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Shi, Y. Effect of Multi-Level Grain Fining on Fracture Toughness of 18Ni Maraging Steel. Jinshu Rechuli Heat Treat. Met. 2014, 39, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, K.; Sha, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, K. Age Hardening and Mechanical Properties of a 2400 MPa Grade Cobalt-Free Maraging Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2006, 37, 1107–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yang, K.; Sha, W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a 2000 MPa grade co-free maraging steel. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2005, 36, 2273–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvinall, R.C.; Marshek, K.M. Fundamentals of Machine Component and Design; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; ISBN 9781118012895. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Ell, J.; Huang, M.X.; Ritchie, R.O. Making Ultrastrong Steel Tough by Grain-Boundary Delamination. Science 2020, 368, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese Fencing Association. Available online: http://fencing.sport.org.cn/ (accessed on 7 December 2021).
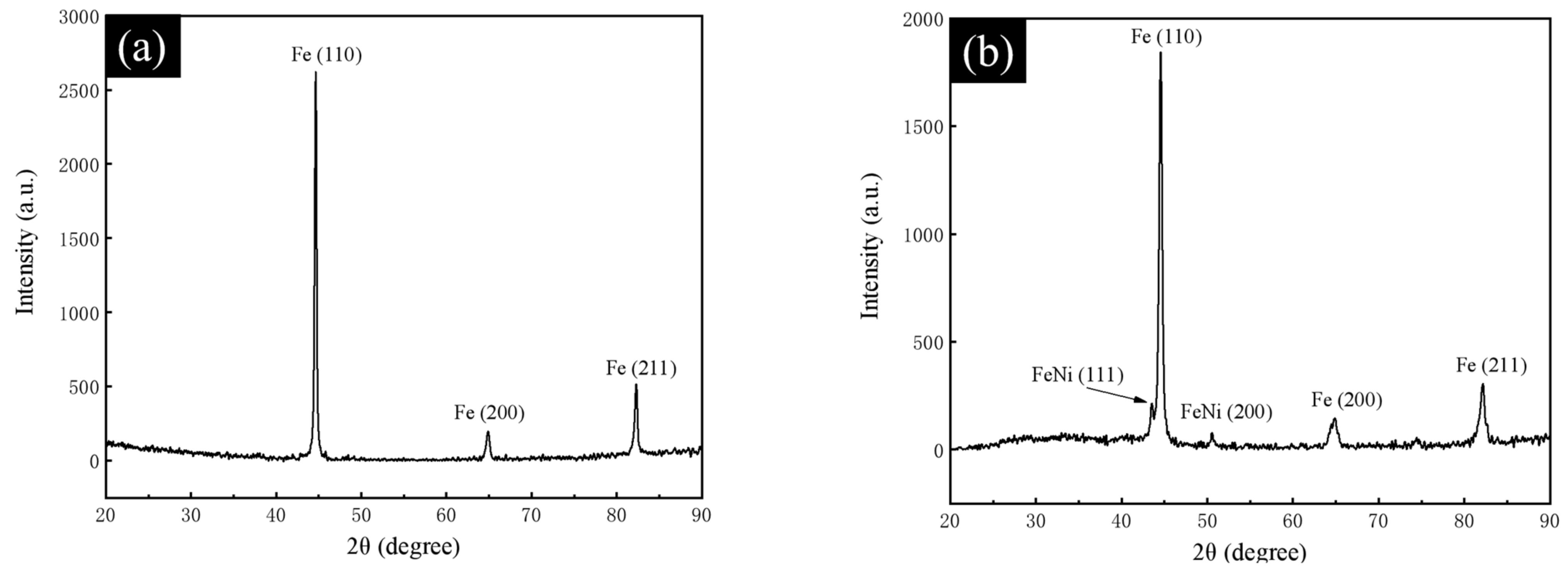
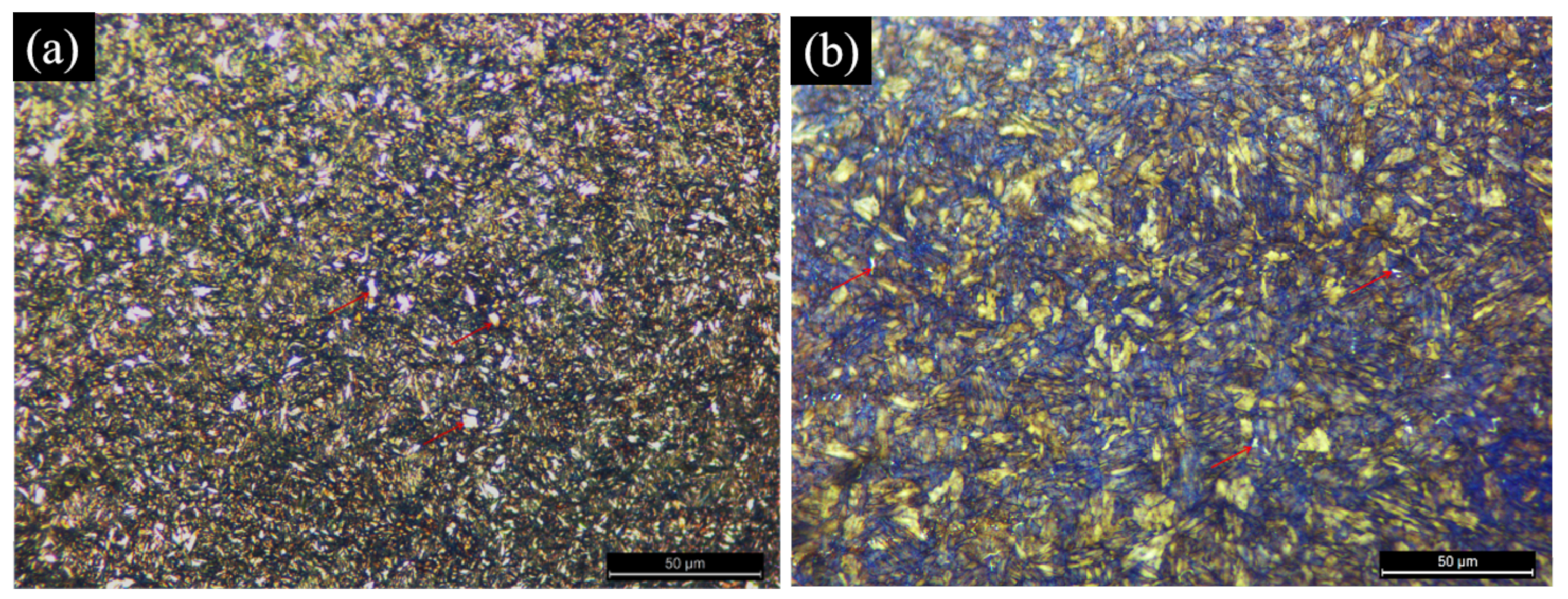



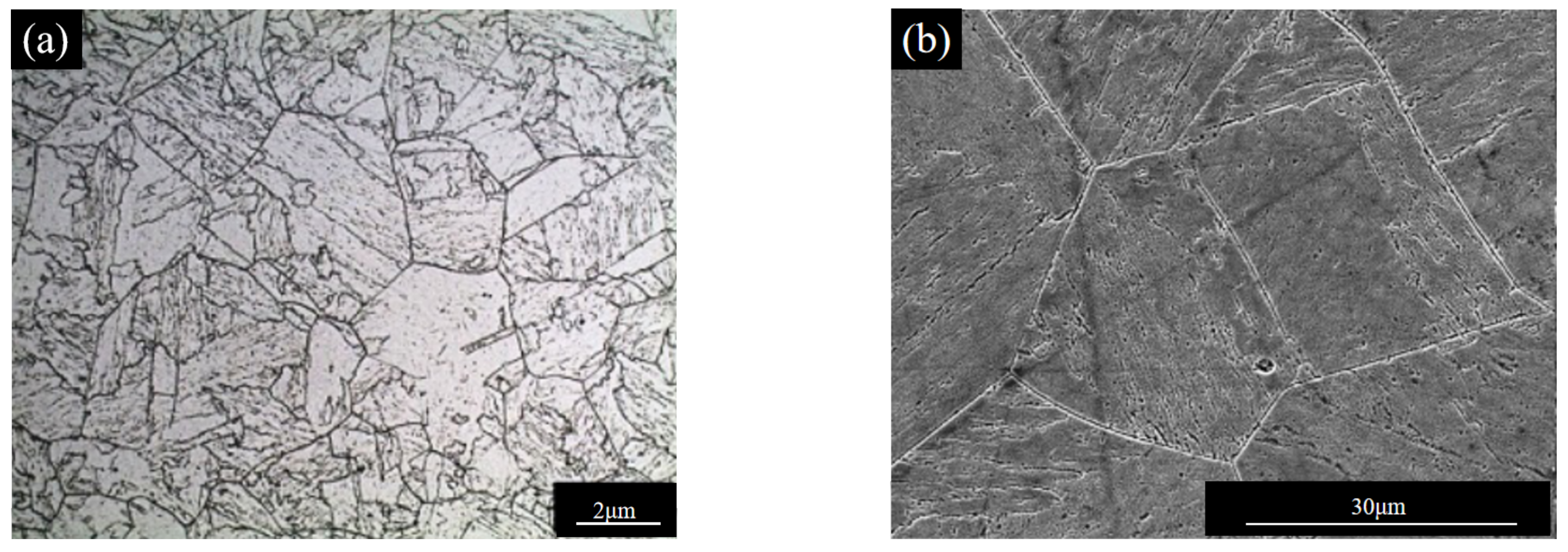

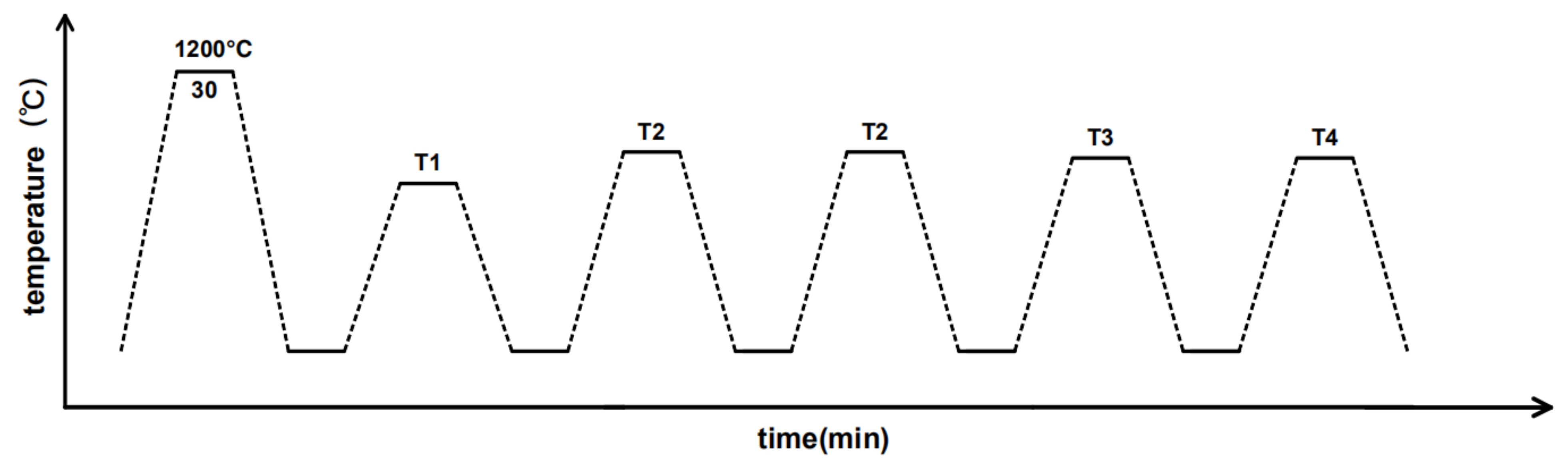
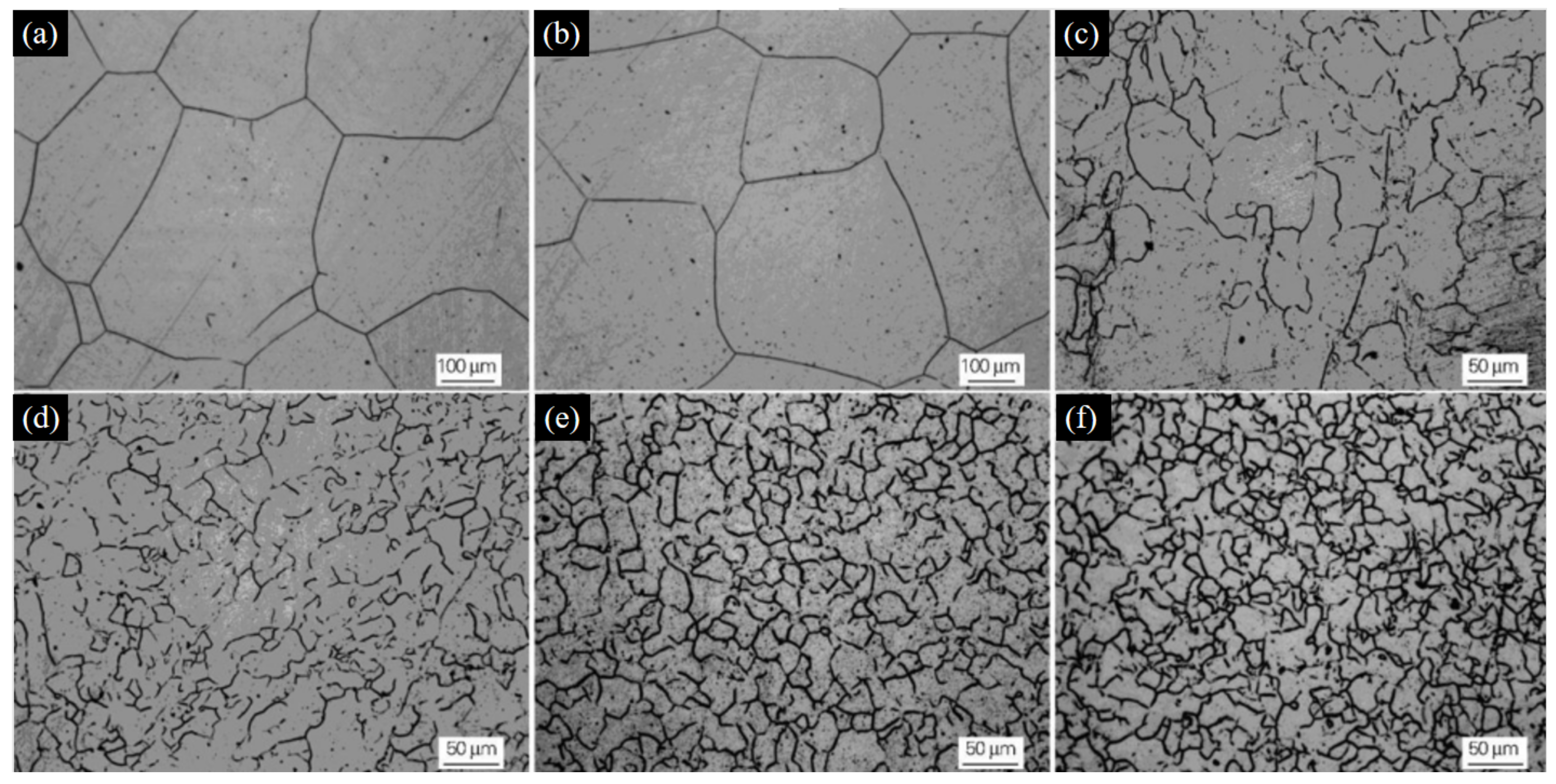

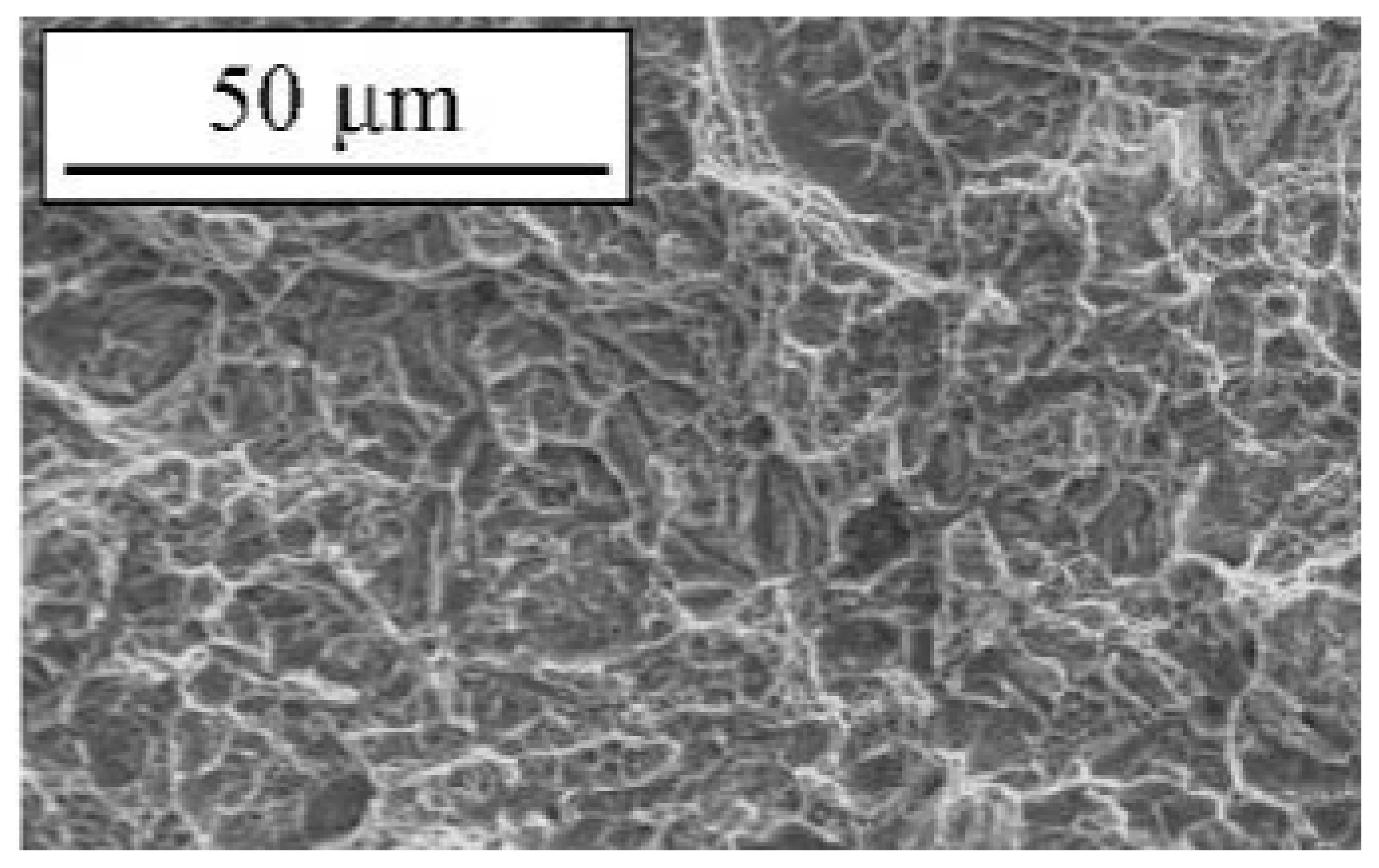
| Type of Steel | Process |
|---|---|
| GMG |
|
| Re (MPa) | Rm (MPa) | A (%) | Z (%) | KCU (J/cm2) | KIC (MPa m1/2) | HV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≥1900 | ≥2000 | ≥7 | ≥35 | ≥30 | ≥120 | ≥500 |
| Blade Types | Fe | Si | Mn | Ni | Co | Mo | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| From China | 97.17 | 1.89 | 0.94 | / | / | / | / |
| From Europe | 66.10 | / | / | 18.96 | 8.96 | 5.24 | 0.74 |
| Type of Steels (In China Grade System) | Re (MPa) | Rm (MPa) | A (%) | Z (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60Si2MnA | ≥1373 | ≥1569 | ≥5 | ≥20 |
| 60Si2CrA | ≥1569 | ≥1765 | ≥6 | ≥20 |
| 60Si2CrVA | ≥1667 | ≥1863 | ≥6 | ≥20 |
| GMG | ≥1900 | ≥2000 | ≥7 | ≥35 |
| Type of Steels | Fe | C | Si | Mn | Cr | V | S | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 60Si2MnA | balance | 0.56~0.64 | 1.60~2.00 | 0.60~0.90 | ≤0.35 | / | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 |
| 60Si2CrA | balance | 0.56~0.64 | 1.40~1.80 | 0.40~0.70 | 0.70~1.00 | / | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 |
| 60Si2CrVA | balance | 0.56~0.64 | 1.40~1.80 | 0.40~0.70 | 0.90~1.20 | 0.10~0.20 | ≤0.030 | ≤0.030 |
| Type of Steels | Re (MPa) | Rm (MPa) | A (%) | Z (%) | KIC (MPa m1/2) | HV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18Ni (250) | 1655–1825 | 1690–1860 | 6–10 | 35–60 | 99–165 | 482–512 |
| 18Ni (300) | 1790–2070 | 1825–2105 | 5–10 | 30–50 | 88–143 | 527–596 |
| 18Ni (350) | 2427 | 2468 | 8 | 43 | 40 | / |
| GMG | ≥1900 | ≥2000 | ≥7 | ≥35 | ≥120 | ≥500 |
| Type of Steels | Re (MPa) | Rm (MPa) | A (%) | Z (%) | KCU (J/cm2) | KIC (MPa m1/2) | HV | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 18Ni (250) | 1655–1825 | 1690–1860 | 6–10 | 35–60 | / | 99–165 | 482–512 | [39,48] |
| 2 | 18Ni (250) | 1853 | 1906 | 14.46 | 52.1 | / | 128.69 | / | [69] |
| 3 | 18Ni (300) | 1790–2070 | 1825–2105 | 5–10 | 30–50 | / | 88–143 | 527–596 | [39,48] |
| 4 | 18Ni (300) | 1912 | 1928 | 10.4 | 17.5 | / | 76 | 600 | [68] |
| 5 | 18Ni (350) | 2427 | 2468 | 8 | 43 | / | 40 | / | [39,48] |
| 6 | Fe-18Ni-4Mo-2.5Ti | 2330 | 2370 | 6.7 | 24 | / | 18.4 | / | [70] |
| 7 | Fe-18.9Ni-4.1Mo-1.9Ti | 1957 | 2017 | 8.0 | 50 | / | 64 | / | [71] |
| 8 | 60Si2MnA | 1640 | 1810 | 6.9 | 29.1 | 24 | / | 587 | [31] |
| 9 | 60Si2CrA | 1756 | 1569 | 6 | 20 | / | / | / | [28] |
| 10 | 60Si2CrVA | 1804 | 2142 | 11.57 | 42.17 | 53.75 | / | 615 | [36] |
| 11 | 40CrMnSiMoVA | 1662 | 1981 | 10.4 | 42.6 | 65 | 71.2 | 578 | [37] |
| 12 | Fe-9.95Mn-0.44C-1.87Al-0.67V | 1978 | 2144 | 19.0 | / | / | 101.5 (Crack initiation toughness) | / | [73] |
| 13 | GMG (meeting FIE standard) | ≥1900 | ≥2000 | ≥7 | ≥35 | ≥30 | ≥120 | ≥500 | [11] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, H.; Shen, J.; Yao, X.; Van Horne, C.; Lu, X.; Xiong, Y.; Cha, L. En-Garde! A Review of Fencing Blade Material Development. Metals 2022, 12, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020236
Jiang H, Shen J, Yao X, Van Horne C, Lu X, Xiong Y, Cha L. En-Garde! A Review of Fencing Blade Material Development. Metals. 2022; 12(2):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020236
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Haocheng, Jingfang Shen, Xingyu Yao, Constance Van Horne, Xianhui Lu, Yong Xiong, and Limei Cha. 2022. "En-Garde! A Review of Fencing Blade Material Development" Metals 12, no. 2: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020236
APA StyleJiang, H., Shen, J., Yao, X., Van Horne, C., Lu, X., Xiong, Y., & Cha, L. (2022). En-Garde! A Review of Fencing Blade Material Development. Metals, 12(2), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020236






