Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters of Recycled AA 6063 for Enhanced Surface Microhardness and Tribological Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
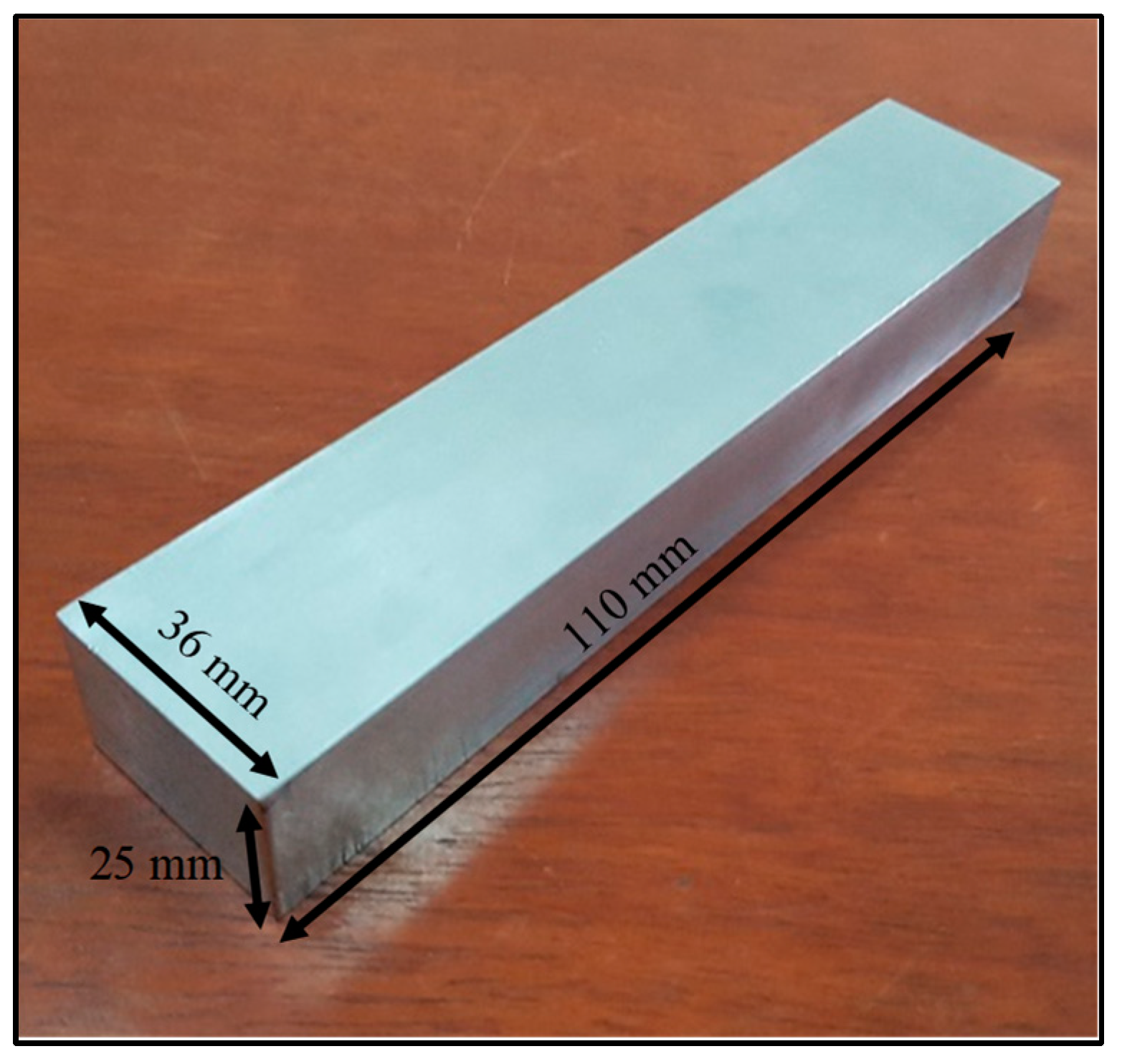
2.1. Substrate Material
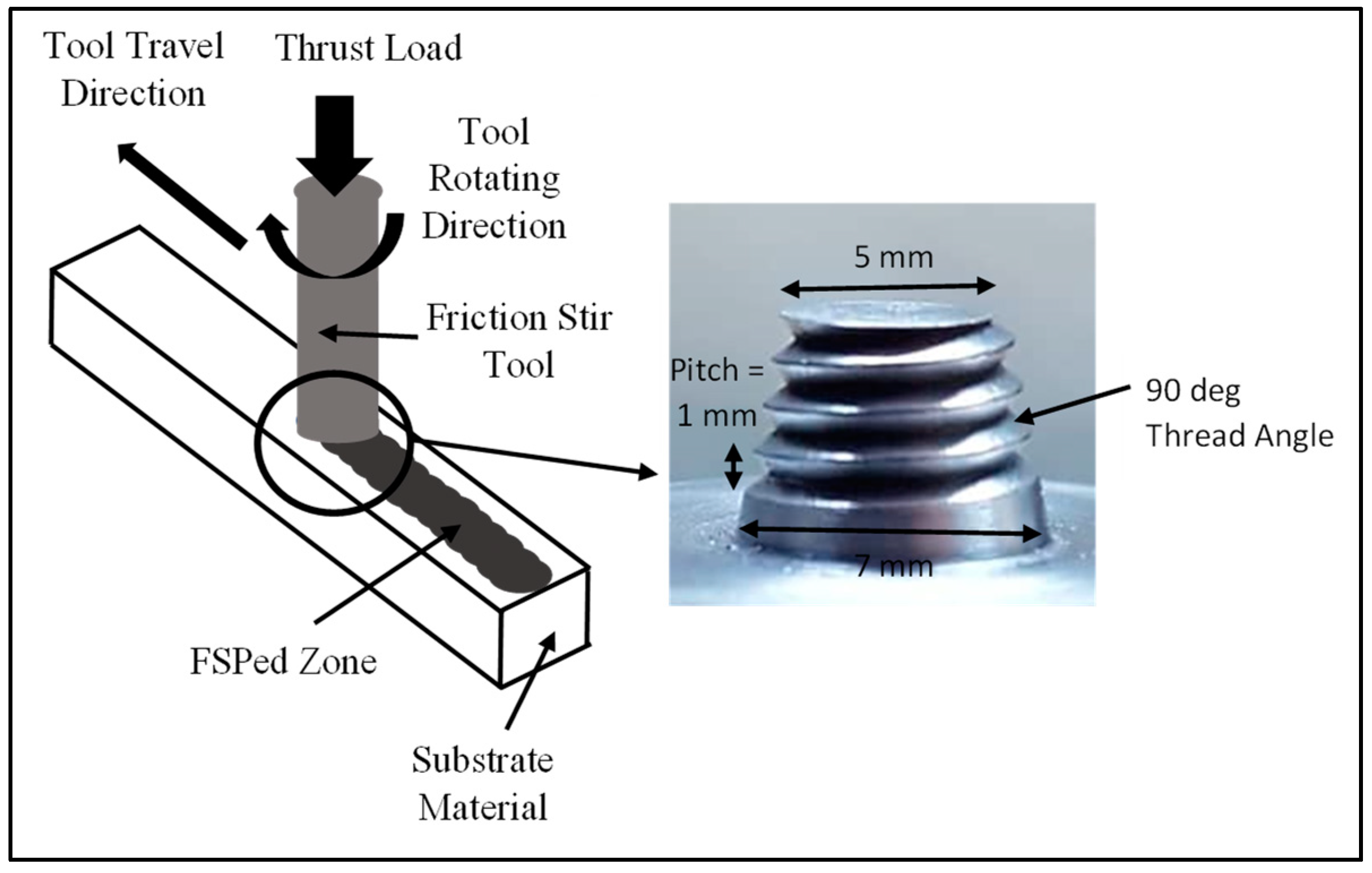
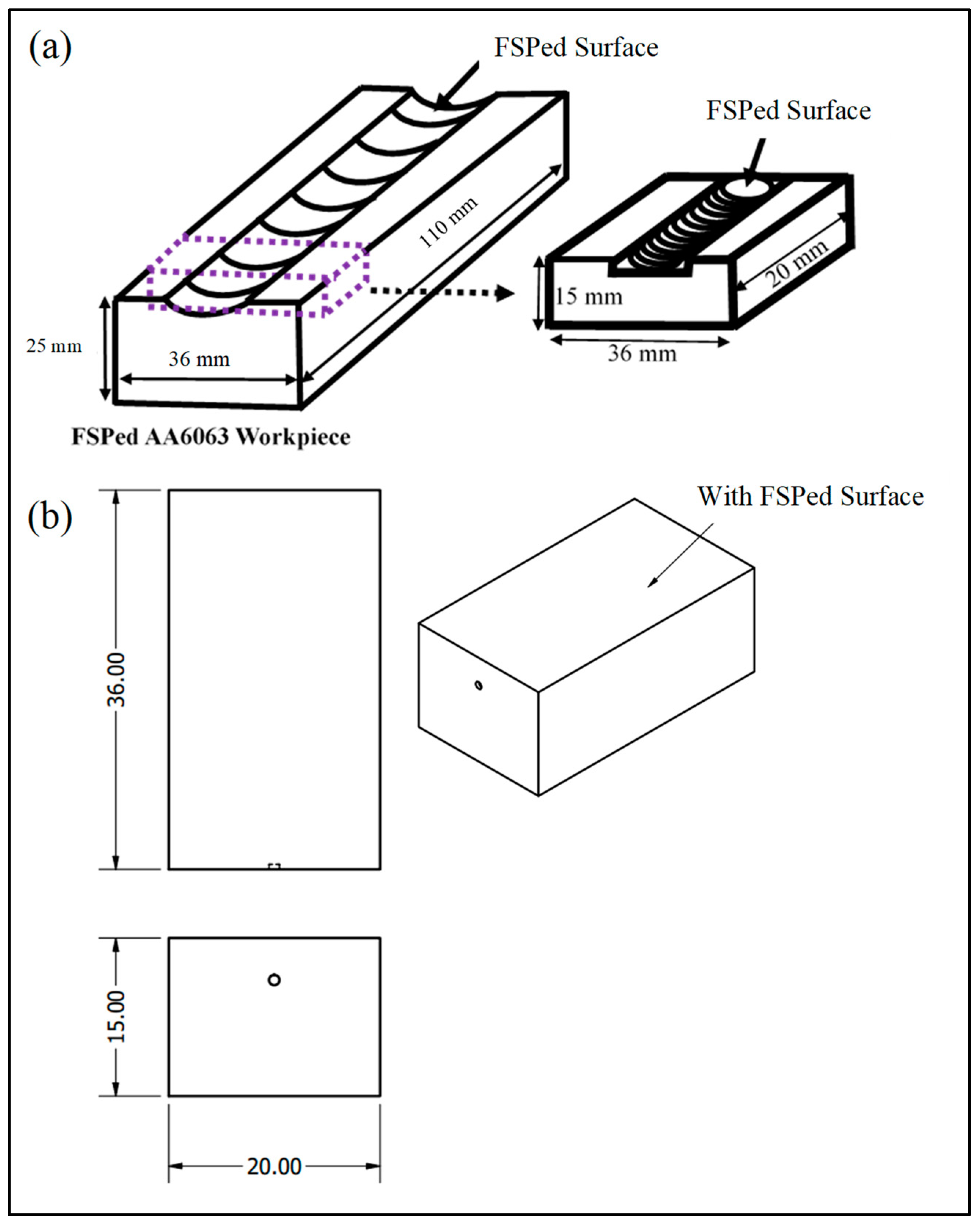
2.2. Friction Stir Processing (FSP)
2.3. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.4. Microstructure Analysis
2.5. Microhardness Measurement
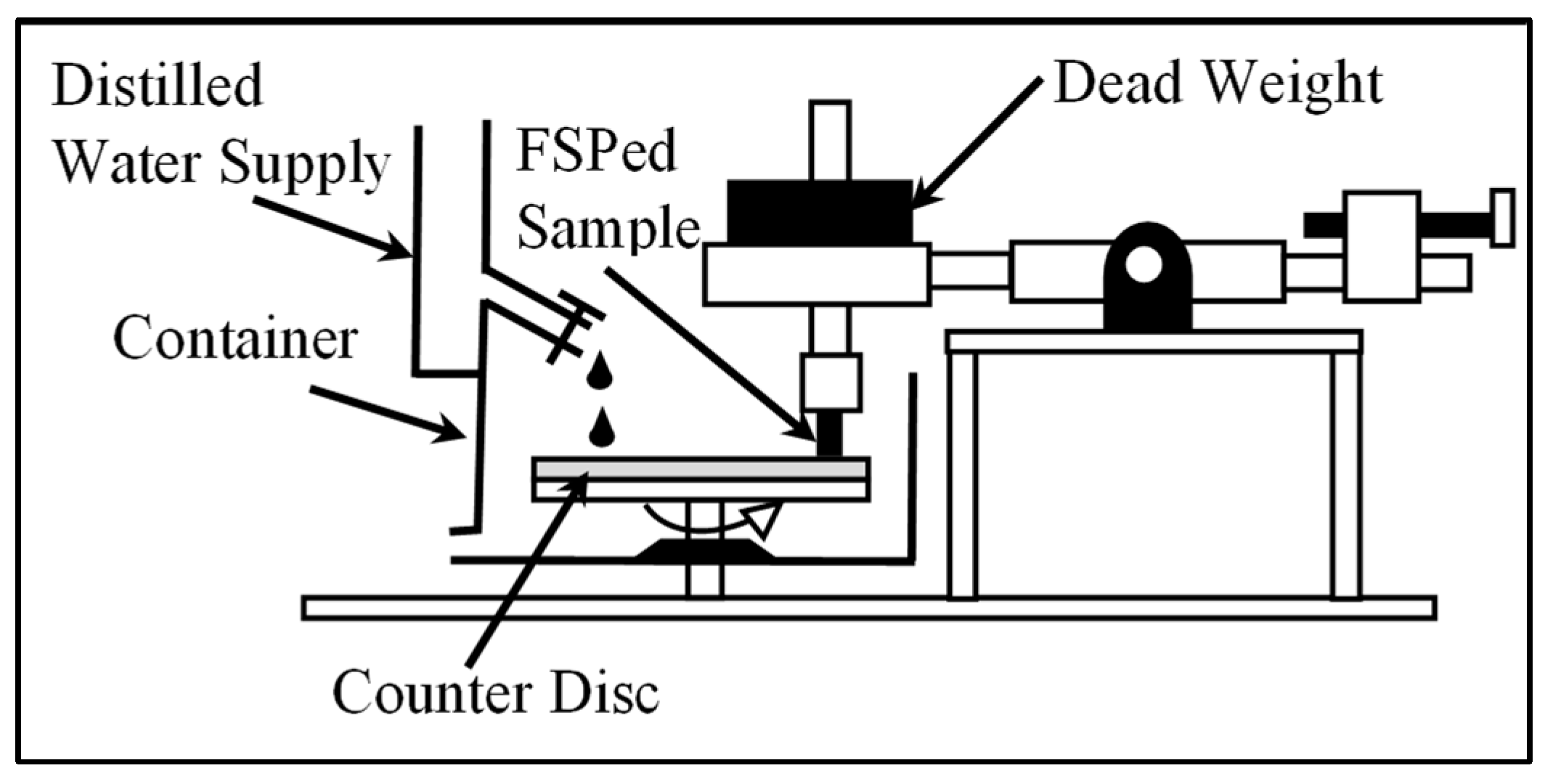
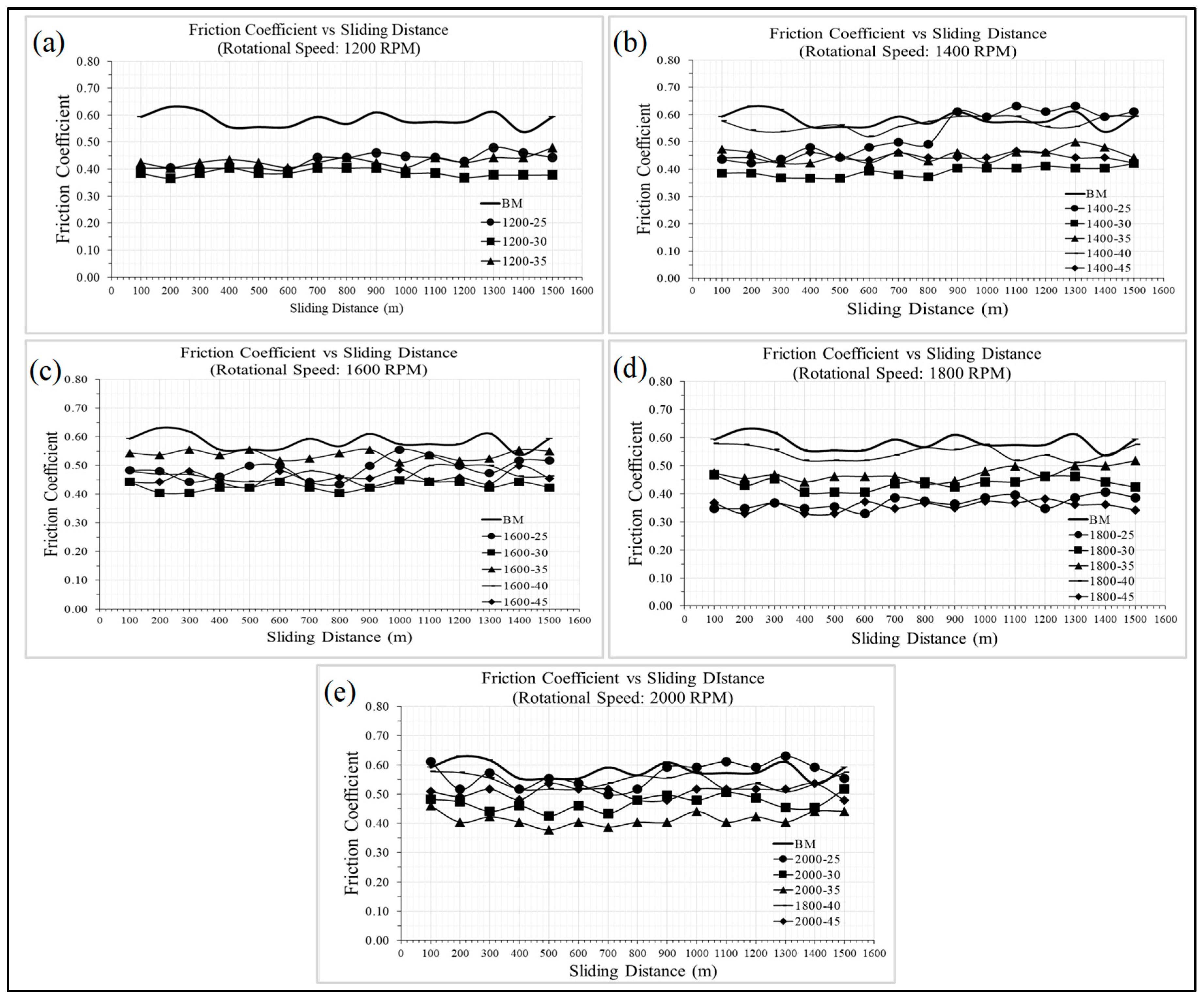
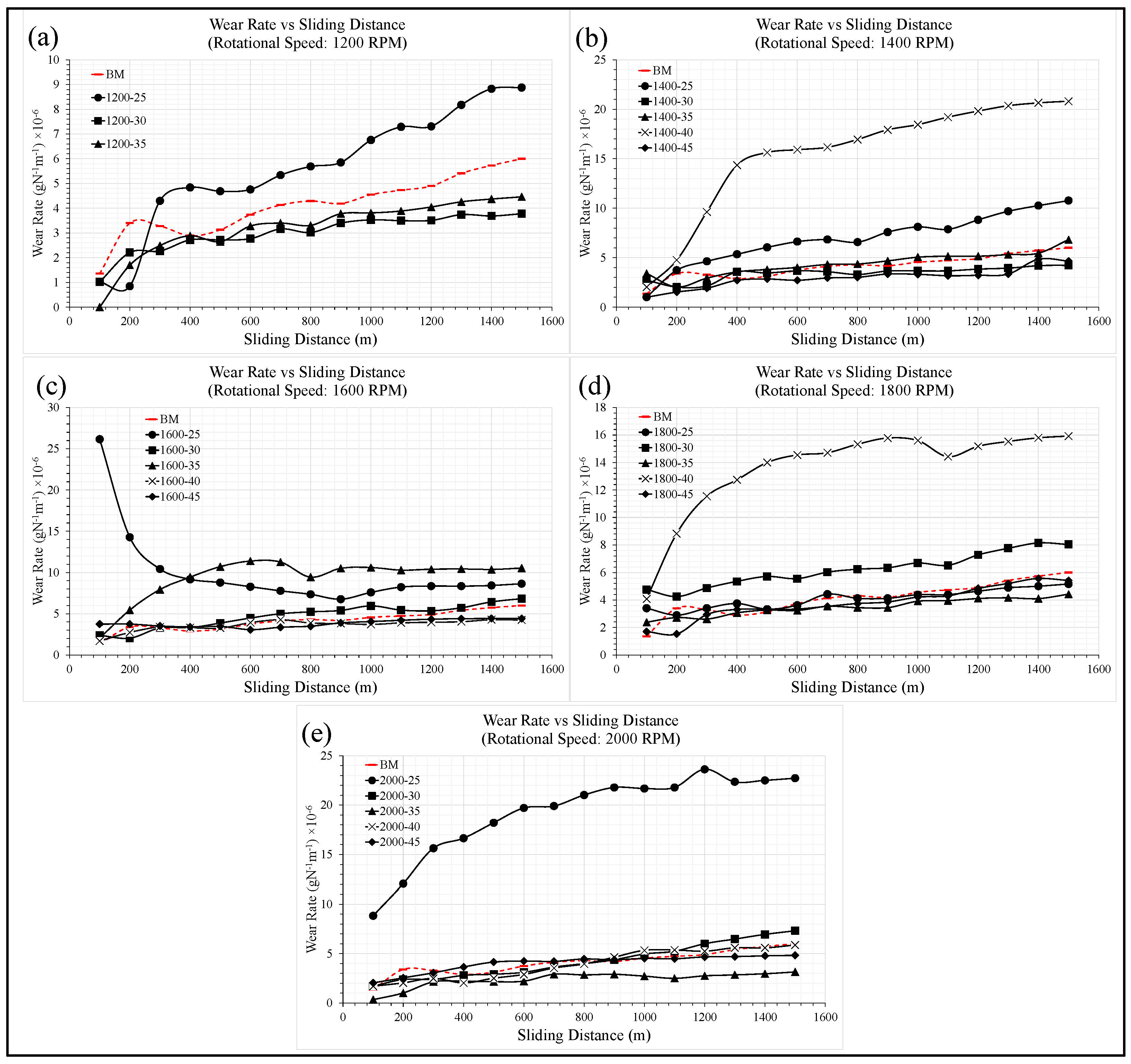
2.6. Friction and Wear Test
3. Results and Discussion
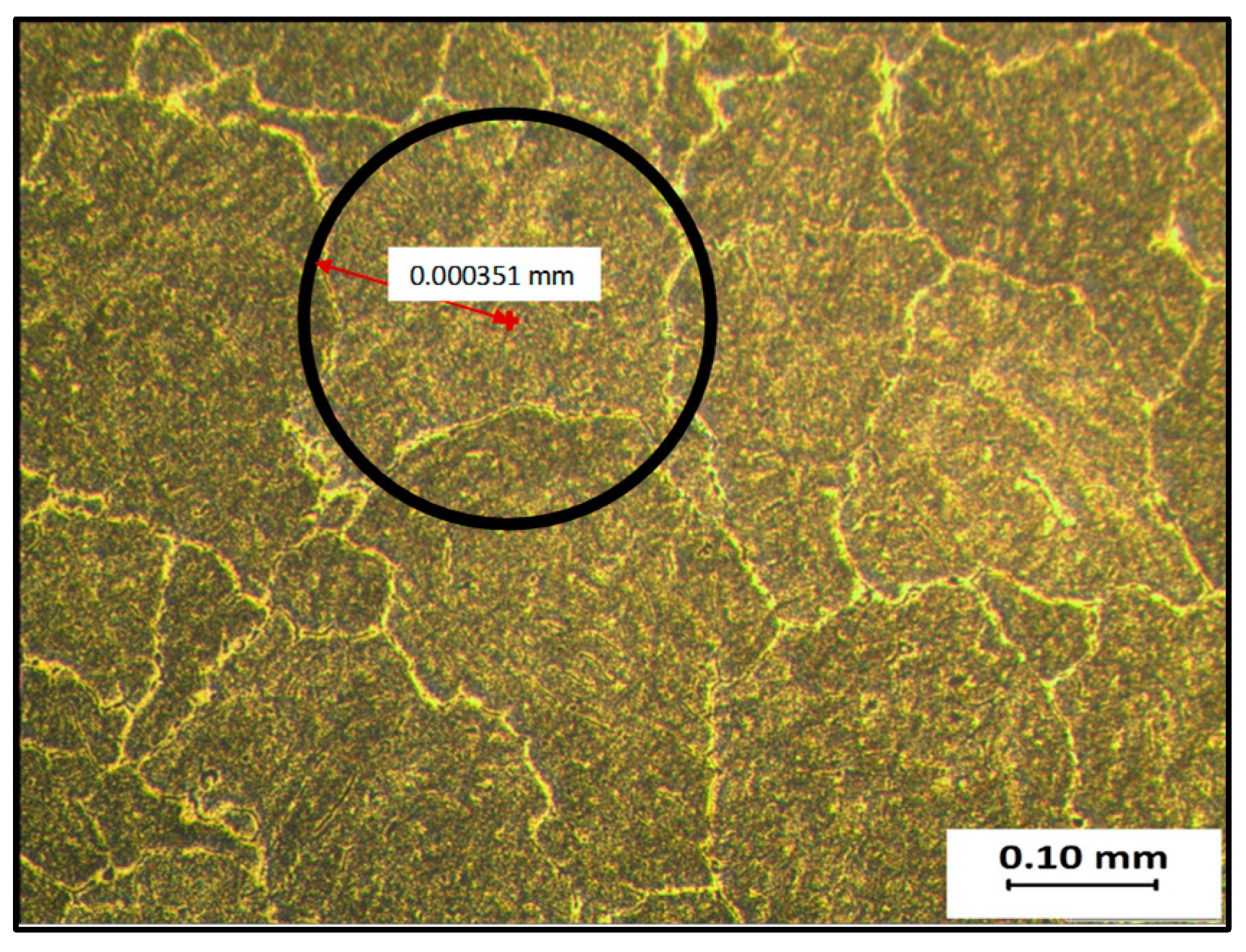
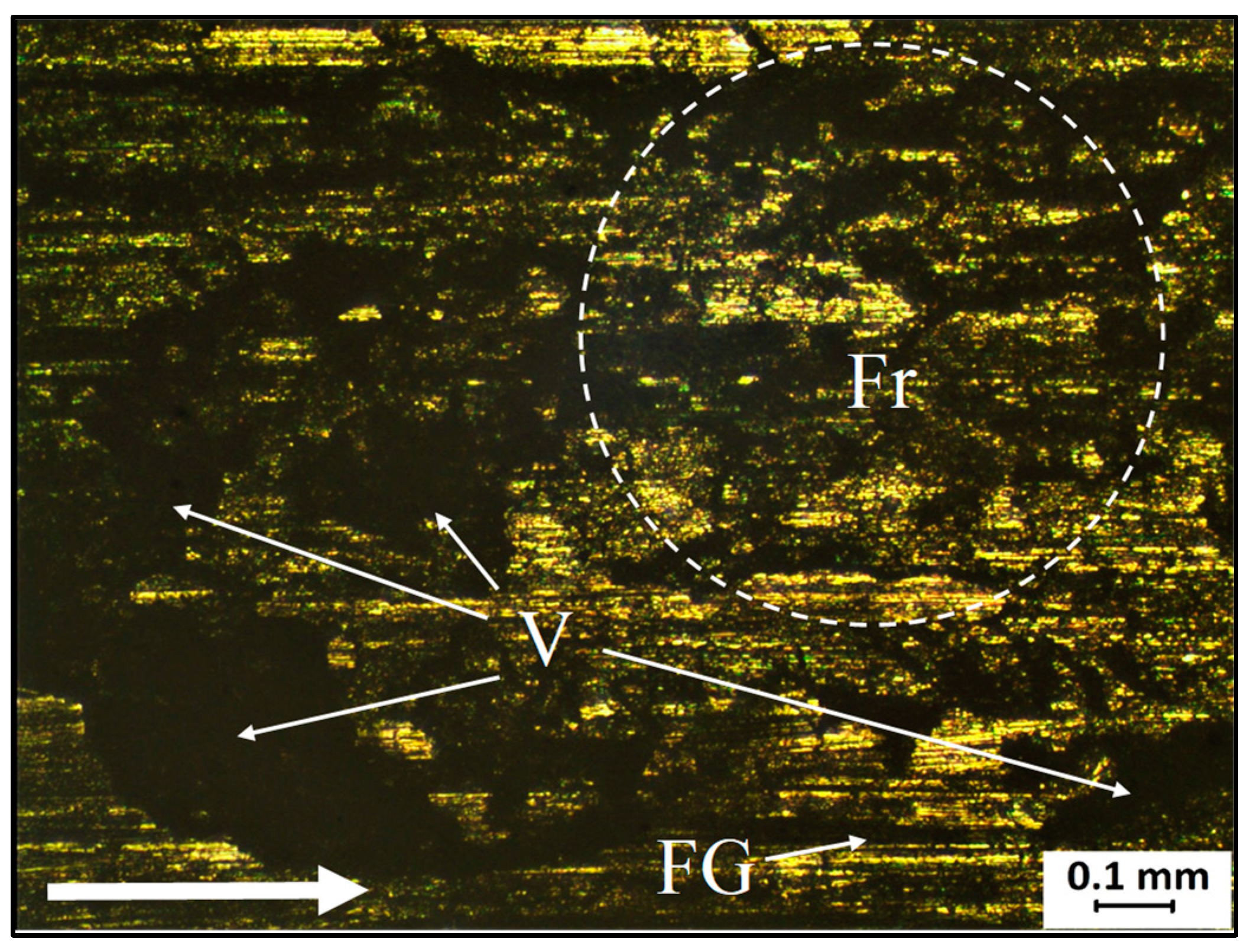
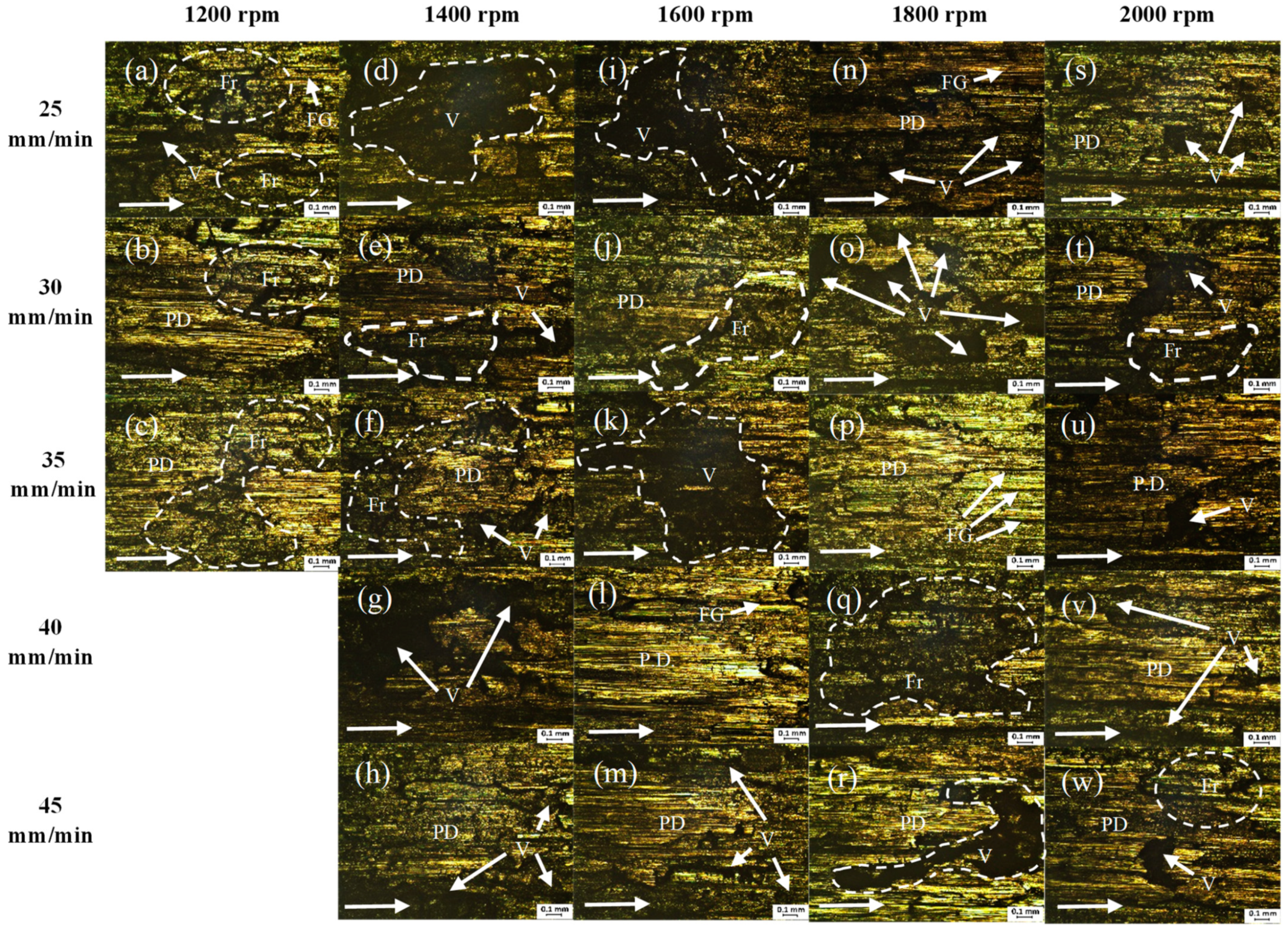
3.1. Microstructure Analysis
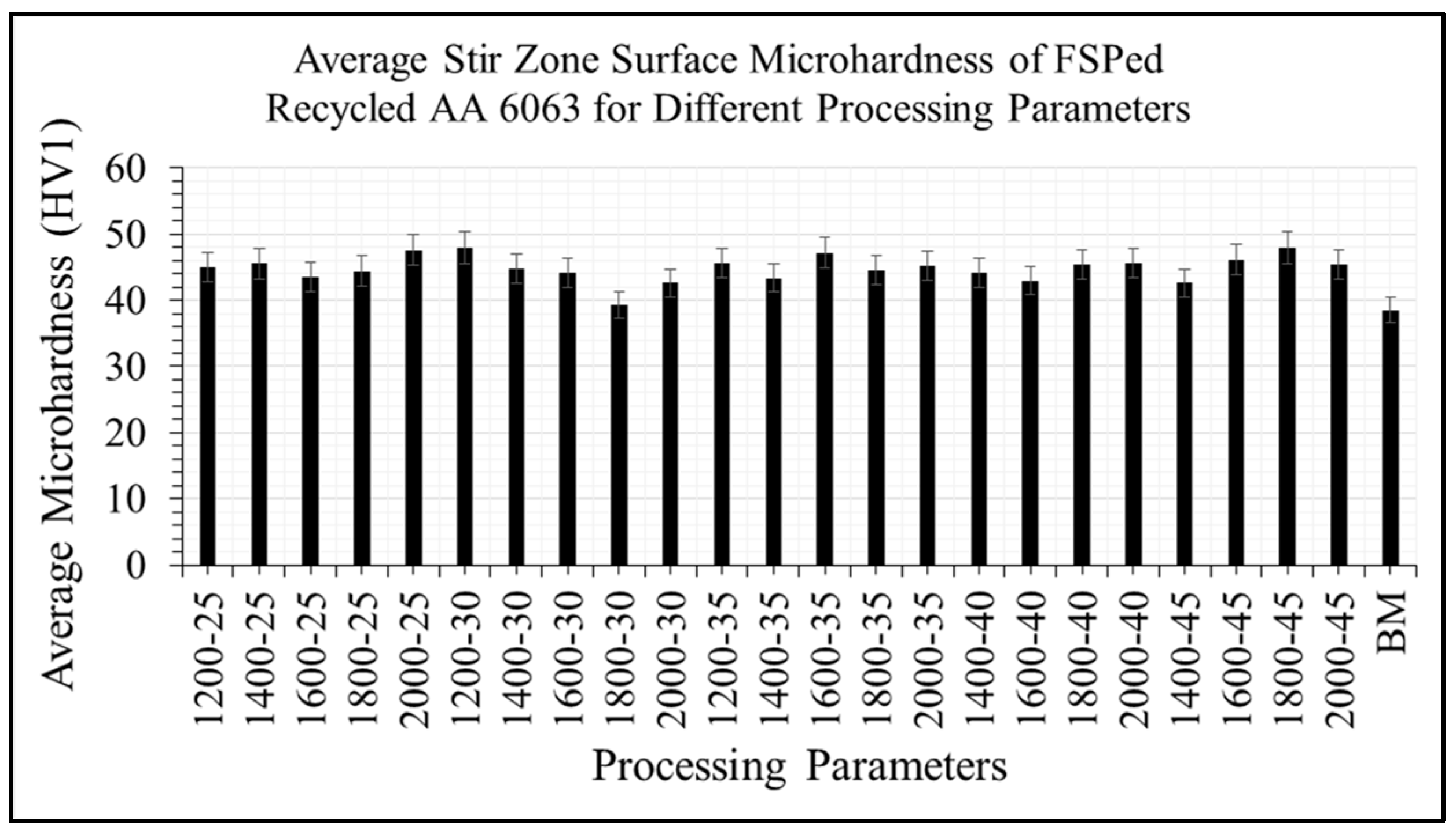
3.2. Microhardness Measurement
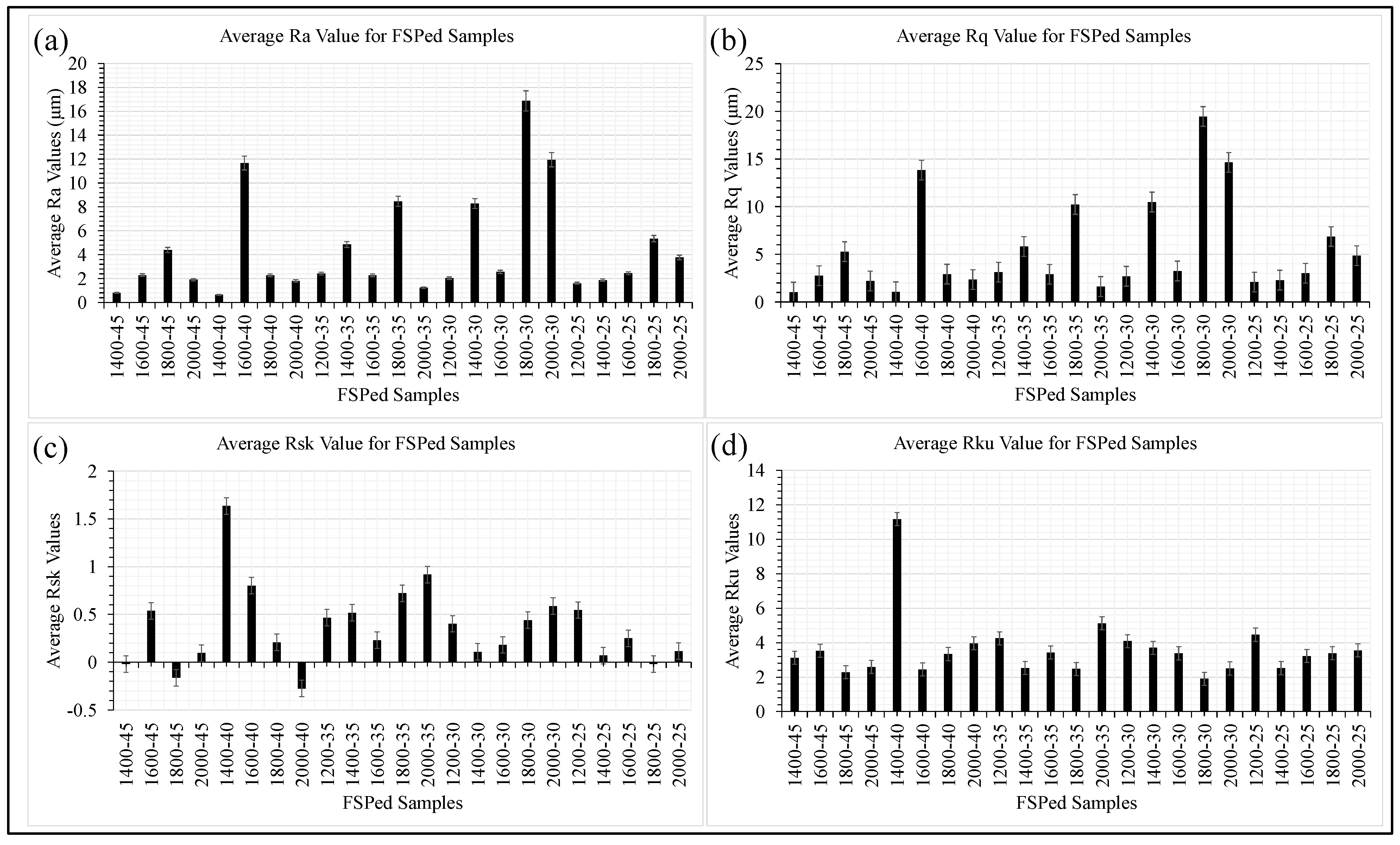
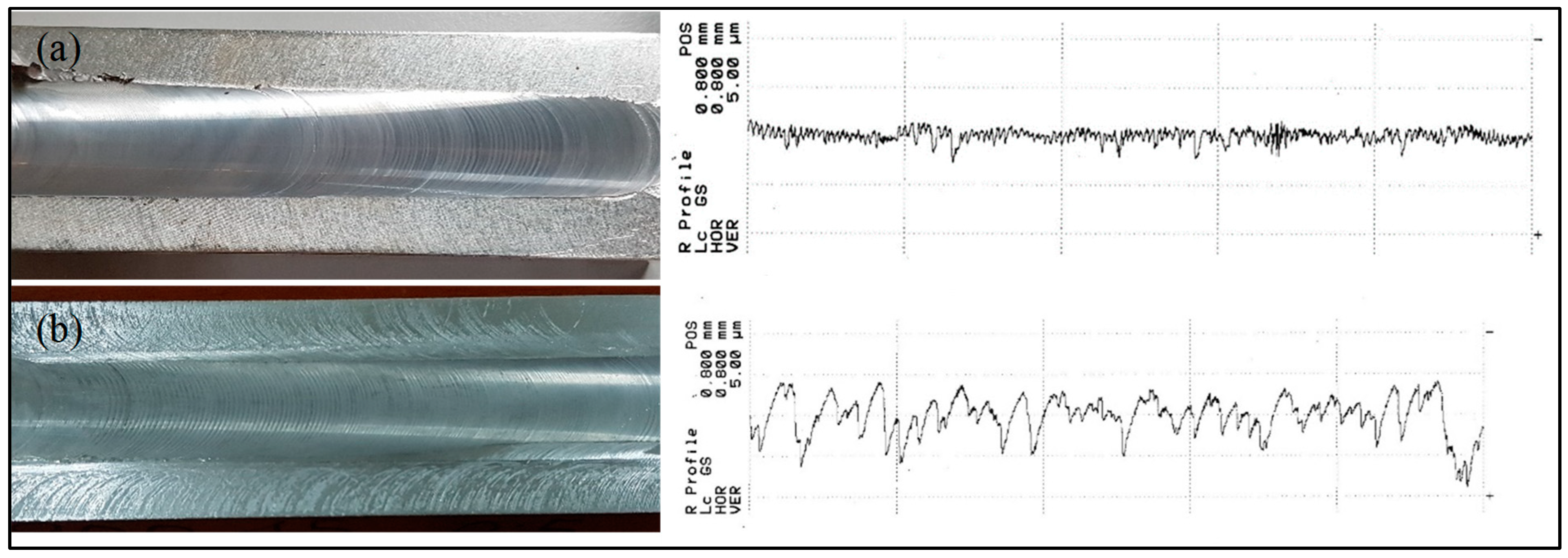
3.3. Surface Roughness Measurement
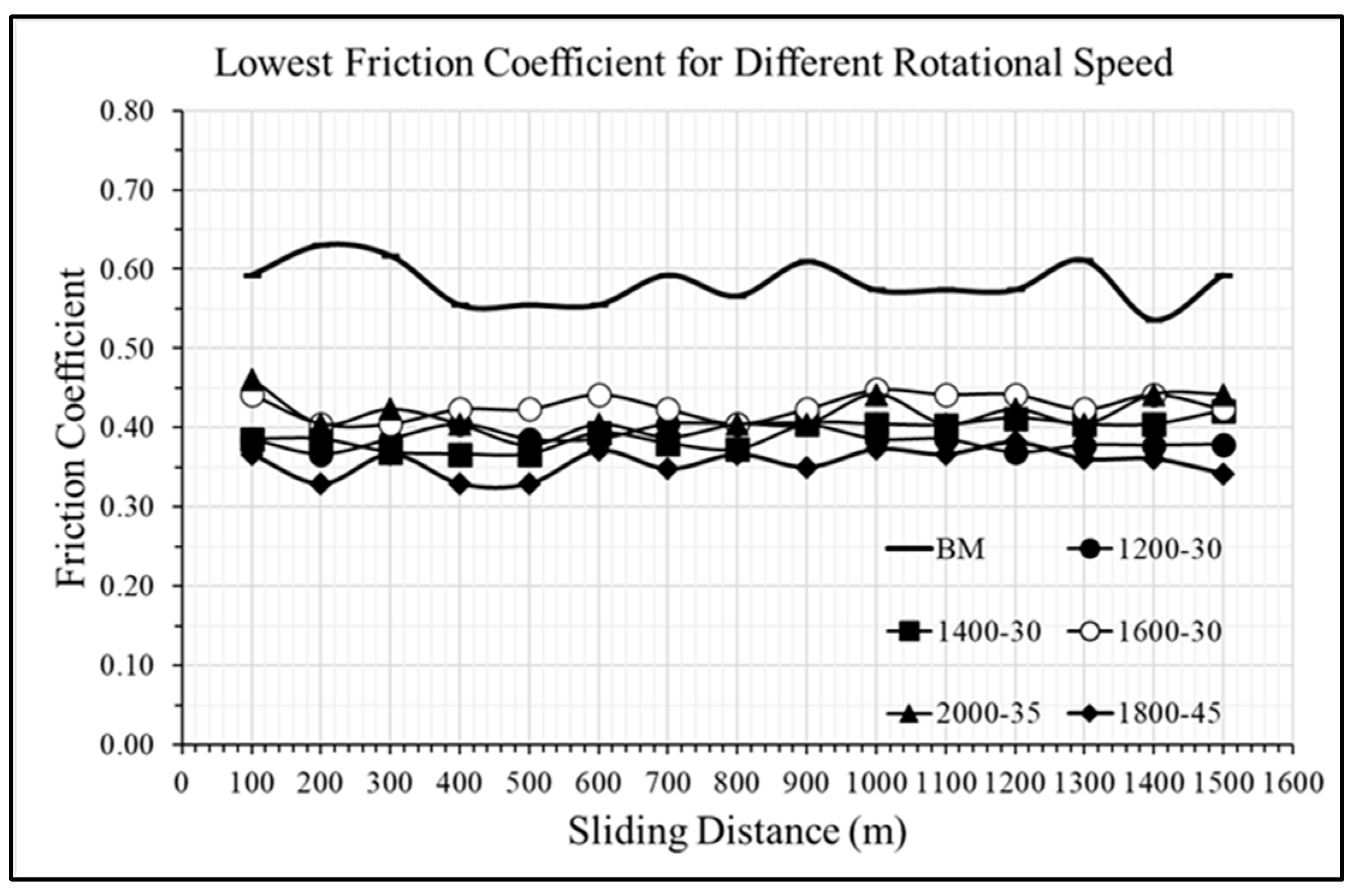
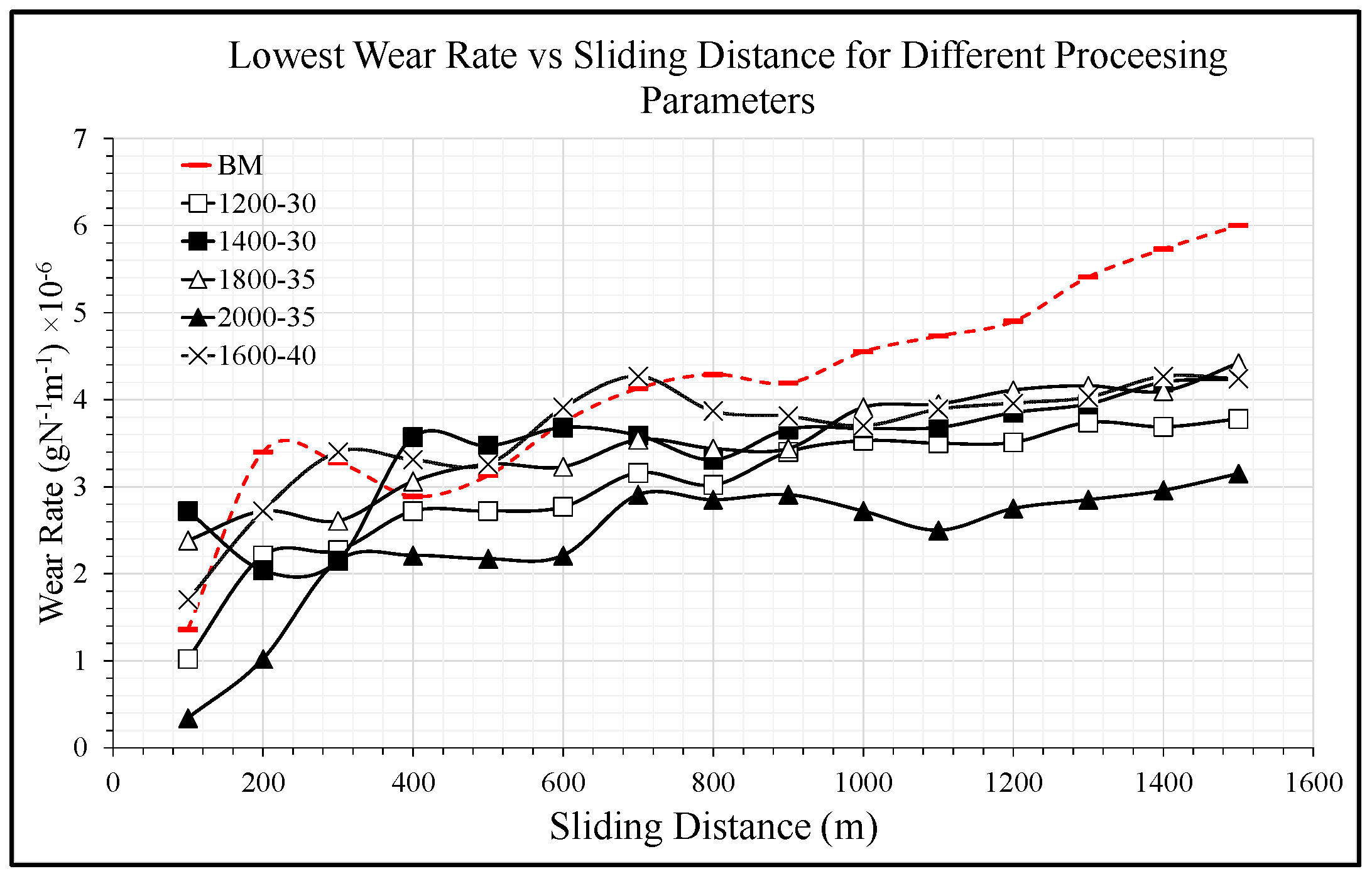
3.4. Tribological Performance
4. Conclusions
- Defect-free FSPed recycled AA 6063 was successfully produced using a CNC milling machine with the groove FSP method.
- According to the surface hardness data, Sample 2 (1200 rpm and 130 mm/min) produced the highest average hardness value of 48 HV which was enhanced by 25% over the base metal hardness, which is 38.5 HV.
- Microstructure inspection and the grain size measurement show that Sample 2 has a homogeneous grain structure and the smallest grain size that was refined by about 96%. It also has the highest hardness among the FSPed samples.
- The friction and wear rate of Sample 2 is also considerably lower than other FSPed samples. Its wear resistance was enhanced by about 37% and its friction was reduced by 33%. Wear morphology shows that Sample 2 has mostly adhesive wear and only slight fractures
- In all other samples, more fractures can be observed as the wear rate increases. Both adhesive wear and abrasive wear can be observed from the FSPed samples.
- In a nutshell, the optimized processing parameters for FSPed recycled AA 6063 are a rotational speed of 1200 rpm and a feed rate of 30 mm/min.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozer, G.; Burgucu, S.; Marsoglu, M. A Study on the Recycling of Aluminum Alloy 7075 Scrap. Mater. Test. 2012, 54, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, G. Production of secondary auminium. In Fundamentals of Aluminium Metallurgy: Production, Processing and Applications, 1st ed.; Roger, L., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing Limited: Sawston, UK, 2010; pp. 70–82. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami, S.; Emadoddin, E.; Tajally, M.; Borhani, E. Friction stir processing of 7075 Al alloy and subsequent aging treatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, J.K. The Handbook of Advanced Materials: Enabling New Design; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Amirafshar, A.; Pouraliakbar, H. Effect of Tool Pin Design on the Microstructural Evolutions and Tribological Characteristics of Friction Stir Processed Structural Steel. Meas. J. Int. Meas. Confed. 2015, 68, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, L.; Senthil Kumar, V.S. Relationship between Process Parameters and Mechanical Properties of Friction Stir Processed AA6063-T6 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 3085–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fadhalah, K.J.; Almazrouee, A.I.; Aloraier, A.S. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Pass Friction Stir Processed Aluminum Alloy 6063. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wȩglowski, M.S.; Hamilton, C.B. An Experimental Investigation and Modelling of Friction Stir Processing. Eng. Trans. 2013, 61, 65–80. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.B.; Harington, J.; Kouch, T. Friction Stir Processing for Efficient Manufacturing; Friction Stir LInk, Inc.: Milwaukee, WI, USA, 2012; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo-Martin, C.; Ajayi, O.; Smith, C.; Krol, S. Energy Efficient Surface Hardening of 4140 Steel by Friction Stir Processing for Tribological Applications. In Proceedings of the ASME/STLE 2011 International Joint Tribology Conference. ASME/STLE 2011 Joint Tribology Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 24–26 October 2011; pp. 63–65. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Prakash, U.; Kumar, B.V. Surface Composites by Friction Stir Processing: A Review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 224, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.T.; Lammlein, D.H.; Prater, T.J.; Longhurst, W.R.; Allun, M.C.; Dharmaraj, K.J.; Cook, G.E.; Strauss, A.M. Friction Stir Welding: Process, Automation, and Control. J. Manuf. Process. 2014, 16, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, G.S.; Liew, K.W.; Kok, C.K. Enhancement of Microhardness and Tribological Properties of Recycled AA 6063 Using Energy-Efficient and Environment-Friendly Friction Stir Processing. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Sapporo, Japan, 26–28 August 2021; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 1874. [Google Scholar]
- Węglowski, M.S. Friction Stir Processing—State of the Art. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2018, 18, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. Ultrasonic Assisted Friction Stir Processing of 6063 Aluminum Alloy. Arch. Civ. Mech. 2016, 16, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Santhanam, V. Single Point Incremental Forming of Friction Stir Processed Al 6063-O Alloy. In Proceedings of the ASME 2015 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. Volume 2A: Advanced Manufacturing, Houston, TX, USA, 13–19 November 2015; pp. 2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Pan, Q.; Qin, Q.; Wu, Y.; Su, X. Effect of the Processing Parameters of Friction Stir Processing on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 6063 Aluminum Alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 751, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, T.S. Effect of Friction Stir Processing on Electrical Conductivity and Corrosion Resistance of AA6063-T6 Al Alloy. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2008, 222, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, J.; Anjaiah, M.; Mathew, A. Experimental Studies on Friction Stir Processing of AZ31 Magnesium Alloy. Mater. Todays 2018, 5, 4515–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, K.; Murty, B.S.; Prasad Rao, K. Comparison of Corrosion Behaviour of Friction Stir Processed and Laser Melted AA 2219 Aluminium Alloy. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4502–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surekha, K.; Murty, B.S.; Prasad Rao, K. Effect of Processing Parameters on the Corrosion Behaviour of Friction Stir Processed AA 2219 Aluminum Alloy. Solid State Sci. 2009, 11, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugasundaram, A.; Arul, S.; Sellamuthu, R. Investigating the Effect of WC on the Hardness and Wear Behavior of Surface Modified AA 6063. Mater. Todays 2018, 5, 6579–6587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathee, S.; Maheshwari, S.; Siddiquee, A.N.; Srivastava, M. Analysis of Microstructural Changes in Enhancement of Surface Properties in Sheet Forming of Al alloys via Friction Stir Processing. Mater. Today Proc. 2017, 4, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Rathee, S.; Maheshwari, S.; Siddiquee, A.N. Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters to Fabricate AA6063/SiC Surface Composites Using Taguchi Technique. Int. J. Mater. Prod. Technol. 2019, 58, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murali, S.; Chockalingam, A.; Suresh Kumar, S.; Remanan, M. Production, Characterization and Friction Stir Processing of AA6063-T6 / Al3Tip in-situ Composites. Int. J. Mech. Prod. 2018, 2018, 399–406. [Google Scholar]
- Liew, K.W.; Chung, Y.Z.; Teo, G.S.; Kok, C.K. Effect of Tool Pin Geometry on the Microhardness and Surface Roughness of Friction Stir Processed Recycled AA 6063. Metals 2021, 11, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaliere, P.; Squillace, A. High Temperature Deformation of Friction Stir Processed 7075 Aluminium Alloy. Mater. Charact. 2005, 66, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasavol, N.; Ramalho, A. Wear Properties of Friction Stir Processed AISI D2 Tool Steel. Tribol. Int. 2015, 97, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K.; Rao, A.G.; Balasundar, I.B.; Kashyap, P.; Prabhu, N. On the Microstructure Evolution in Friction Stir Processed 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel and Its Effect on Tensile Behaviour at Ambient and Elevated Temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 719, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chainarong, S.; Muangjunburee, P.; Suthummanon, S. Friction Stir Processing of SSM356 Aluminium Alloy. Procedia Eng. 2014, 97, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behnagh, R.A.; Shen, N.; Abdollahi, M.; Ding, H. Ultrafine-Grained Surface Layer Formation of Aluminum Alloy 5083 by Friction Stir Processing. Procedia CIRP 2016, 45, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zuo, X.; Li, Y. Influence of Surface Roughness on the Friction Property of Textured Surface. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2015, 7, 1687814014568500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivkovic, B.; Djukdjanovi, M.; Stamenkovic, D. The Influence of the Contact Surface Roughness on the Static Frictio Coefficient. Tribol. Ind. 2000, 22, 41–44. [Google Scholar]
- Stamenkovic, D.; Sundaresan, R. Effect of Hardness and Surface Roughness on Slip Resistance of Rubber Effect of Hardness and Surface Roughness on Slip Resistance of Rubber. J. Test. Eval. 2015, 43, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar]




| Element | Zn | Mg | Cu | Si | Fe | Mn | Cr | Ni | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt % | 0.0331 | 0.581 | 0.0338 | 0.43 | 0.309 | 0.0252 | 0.0335 | 0.0333 | 0.0269 | Balance |
| Samples | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotational Speed (×103 RPM) | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| Traverse Speed (mm/min) | 25 | 30 | 35 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 |
| Zones | Average Radius (μm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base Metal | 1200-30 (Sample 2) | 1400-40 (Sample 7) | 1400-45 (Sample 8) | 1800-30 (Sample 15) | |
| BM | 134.6 | 113.0 | 109.3 | 116.0 | 125.8 |
| HAZ | - | 88.8 | 83.01 | 84.5 | 91.4 |
| TMAZ | - | 45.1 | 58.54 | 40.6 | 43.3 |
| SZ | - | 4.6 | 10.6 | 13.8 | 23.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teo, G.S.; Liew, K.W.; Kok, C.K. Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters of Recycled AA 6063 for Enhanced Surface Microhardness and Tribological Properties. Metals 2022, 12, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020310
Teo GS, Liew KW, Kok CK. Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters of Recycled AA 6063 for Enhanced Surface Microhardness and Tribological Properties. Metals. 2022; 12(2):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020310
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeo, Guo Sheng, Kia Wai Liew, and Chee Kuang Kok. 2022. "Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters of Recycled AA 6063 for Enhanced Surface Microhardness and Tribological Properties" Metals 12, no. 2: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020310
APA StyleTeo, G. S., Liew, K. W., & Kok, C. K. (2022). Optimization of Friction Stir Processing Parameters of Recycled AA 6063 for Enhanced Surface Microhardness and Tribological Properties. Metals, 12(2), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12020310






