Comparative Microstructural, Mechanical and Corrosion Study between Dissimilar ATIG and Conventional TIG Weldments of 316L Stainless Steel and Mild Steel
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Welding Procedure
2.3. Design of Experiments Methodology
2.4. Weld Bead Aspect
2.5. Microstructure Assessment
2.6. Tensile Test
2.7. Hardness Test
2.8. Impact Test
2.9. Corrosion Behaviour
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Weld Bead Aspects
3.1.1. Selection of Candidate Oxides
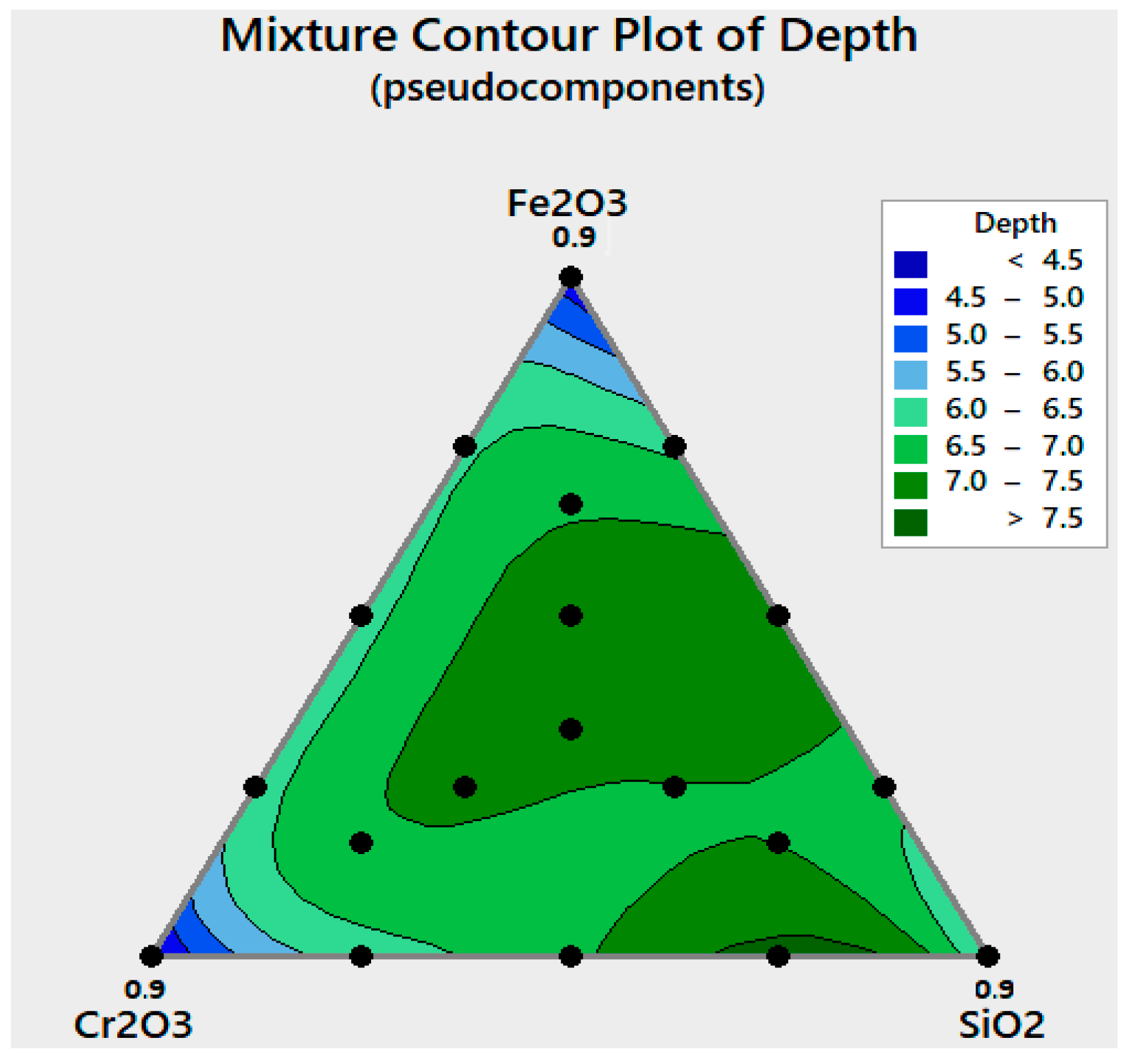
3.1.2. Mixture Contour Plot
3.1.3. Confirmation Test
3.2. Microstructure Assessment
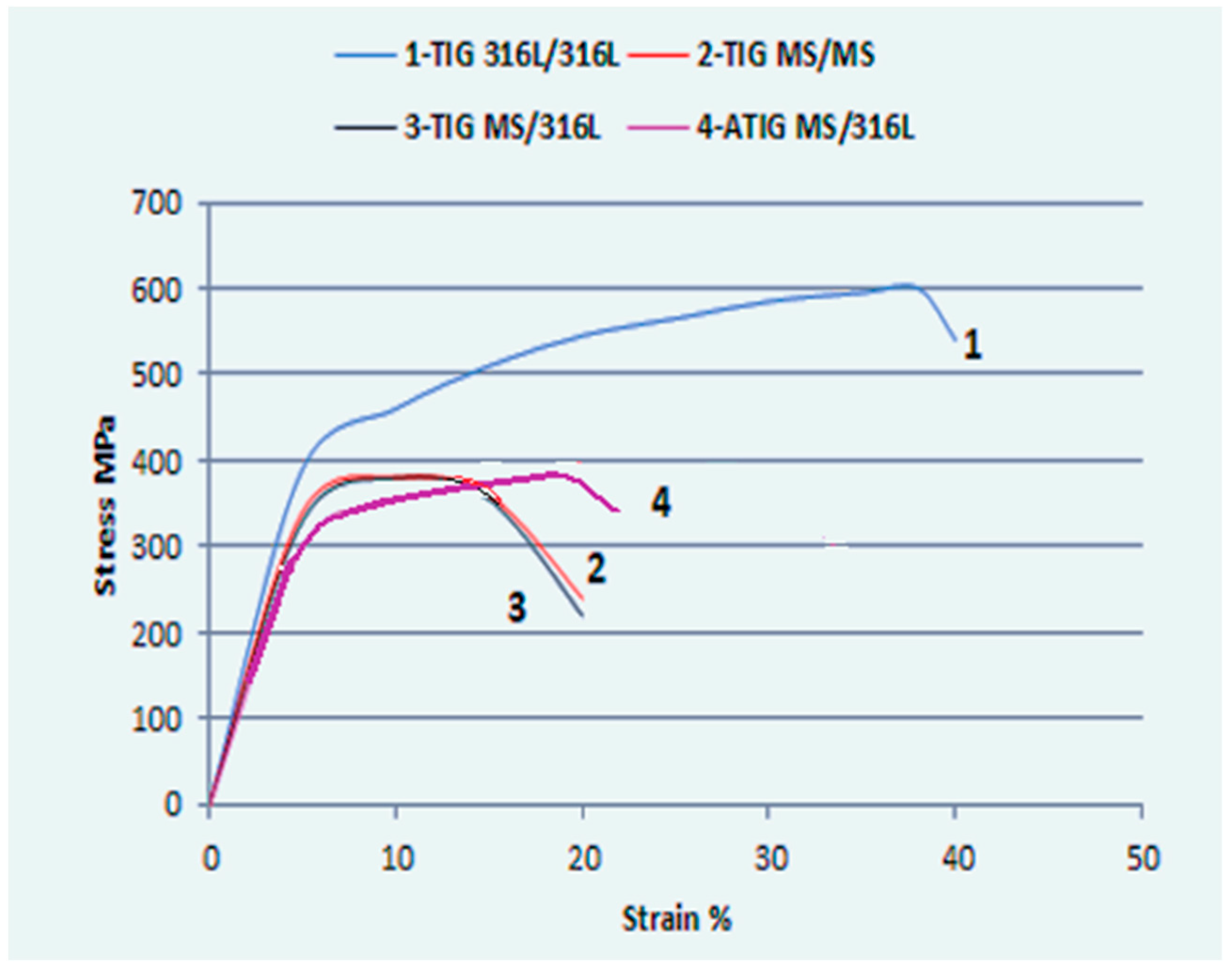
3.3. Tensile Test
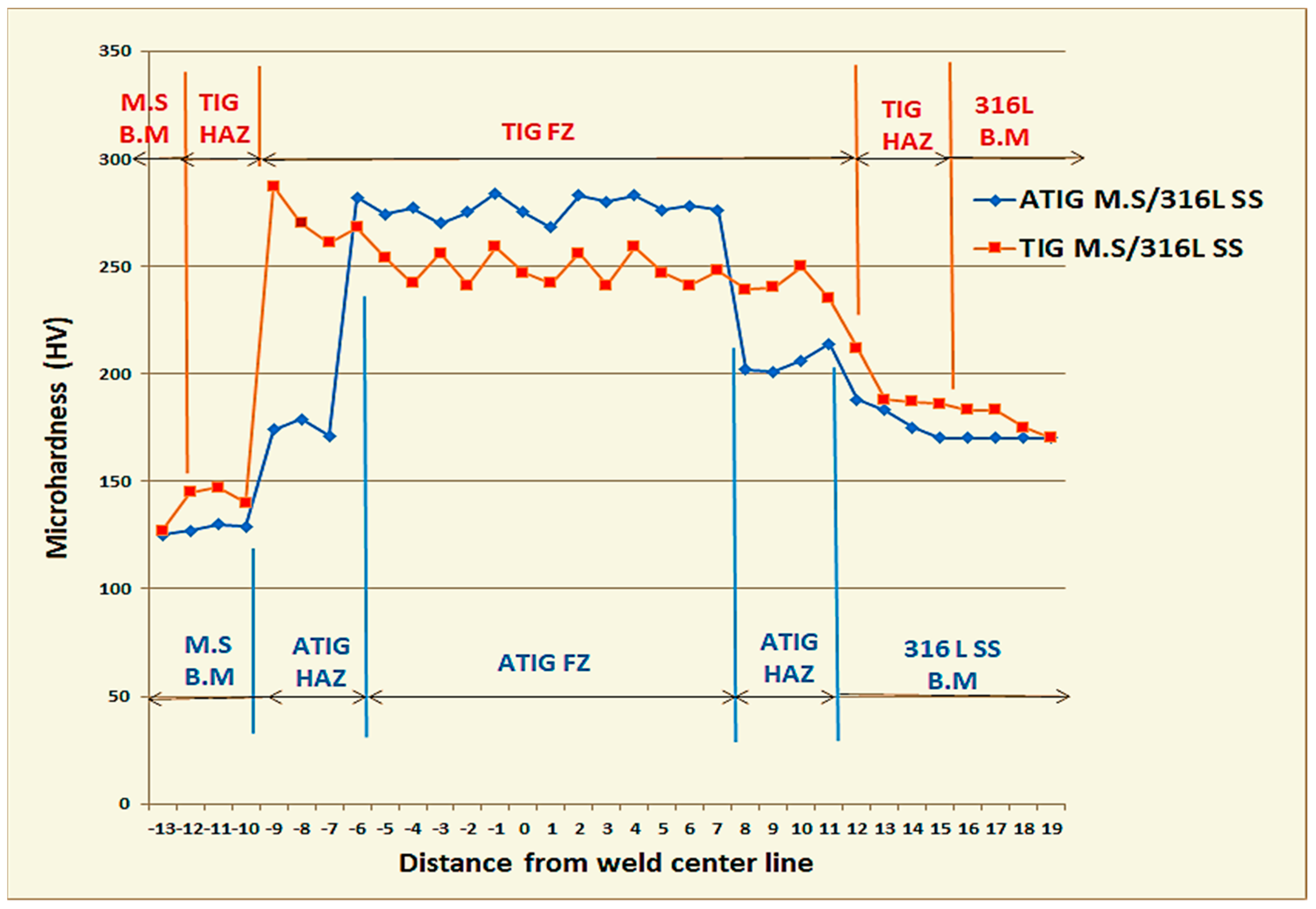
3.4. Hardness Test
3.5. Impact Test
3.6. Corrosion Behavior Investigation
4. Conclusions
- (i)
- The 316L stainless steel could be joined to mild steel using the optimal flux consisting of 74% SiO2 + 13% Cr2O3 + 3% Fe2O3 + 10% NaF;
- (ii)
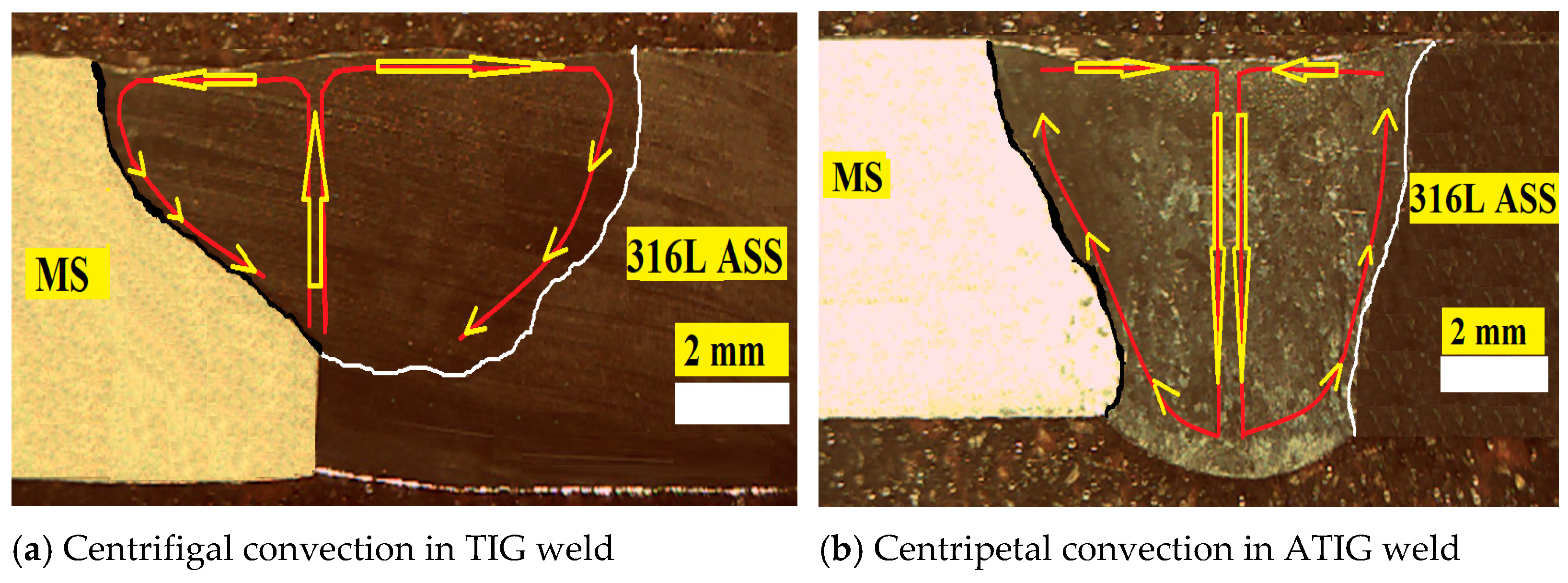
- In dissimilar ATIG welding, a fully penetrated weld bead was achieved in a single pass and without edge preparation. The obtained penetration depth (D) was 6.9 mm, the bead face width (WF) was 8.82 mm and the back face width (WB) was 5.0 mm, leading to a (D + WB)/WF aspect ratio of 1.35. The depth was increased by about 1.86 times compared to the conventional dissimilar TIG weld and the ratio was enhanced by more than 4.3 times. Hence, ATIG welding achieved significant improvements in penetration compared to conventional TIG welding. Flux was used in the constricted-arc ATIG weld owing to the presence of fluorine. Consequently, the weld bead width was reduced compared to that of the conventional TIG welding, increasing the weld penetration. Moreover, the surfactant elements such as oxygen contributed to reversal of the Marangoni convection, leading to a fully penetrated weld;
- (iii)
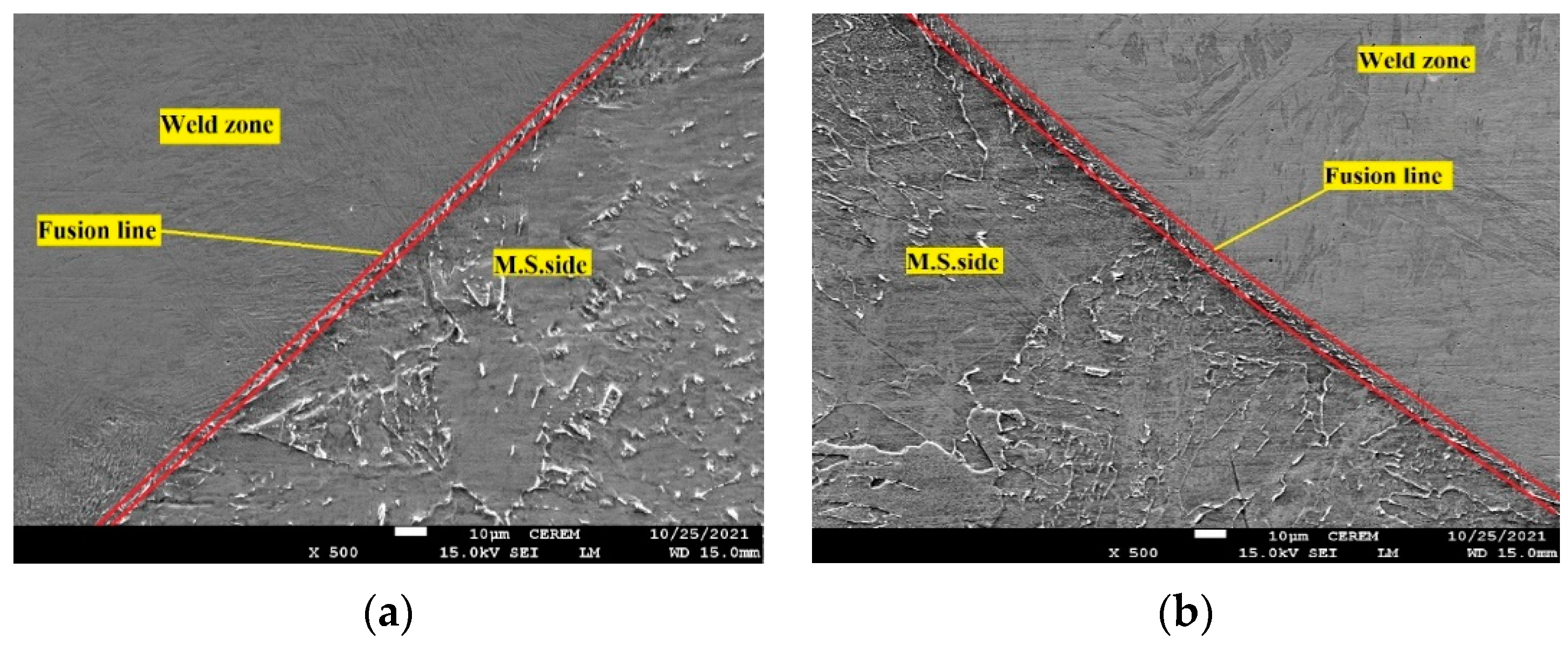
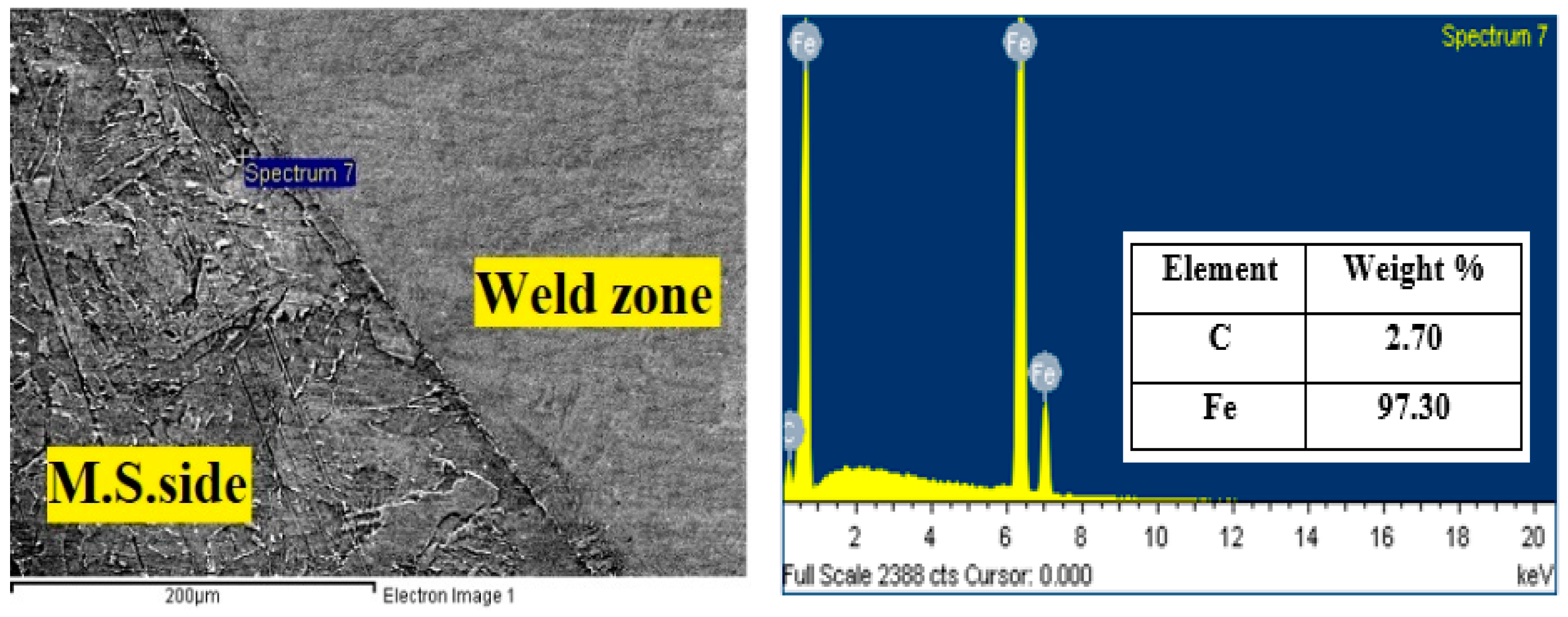
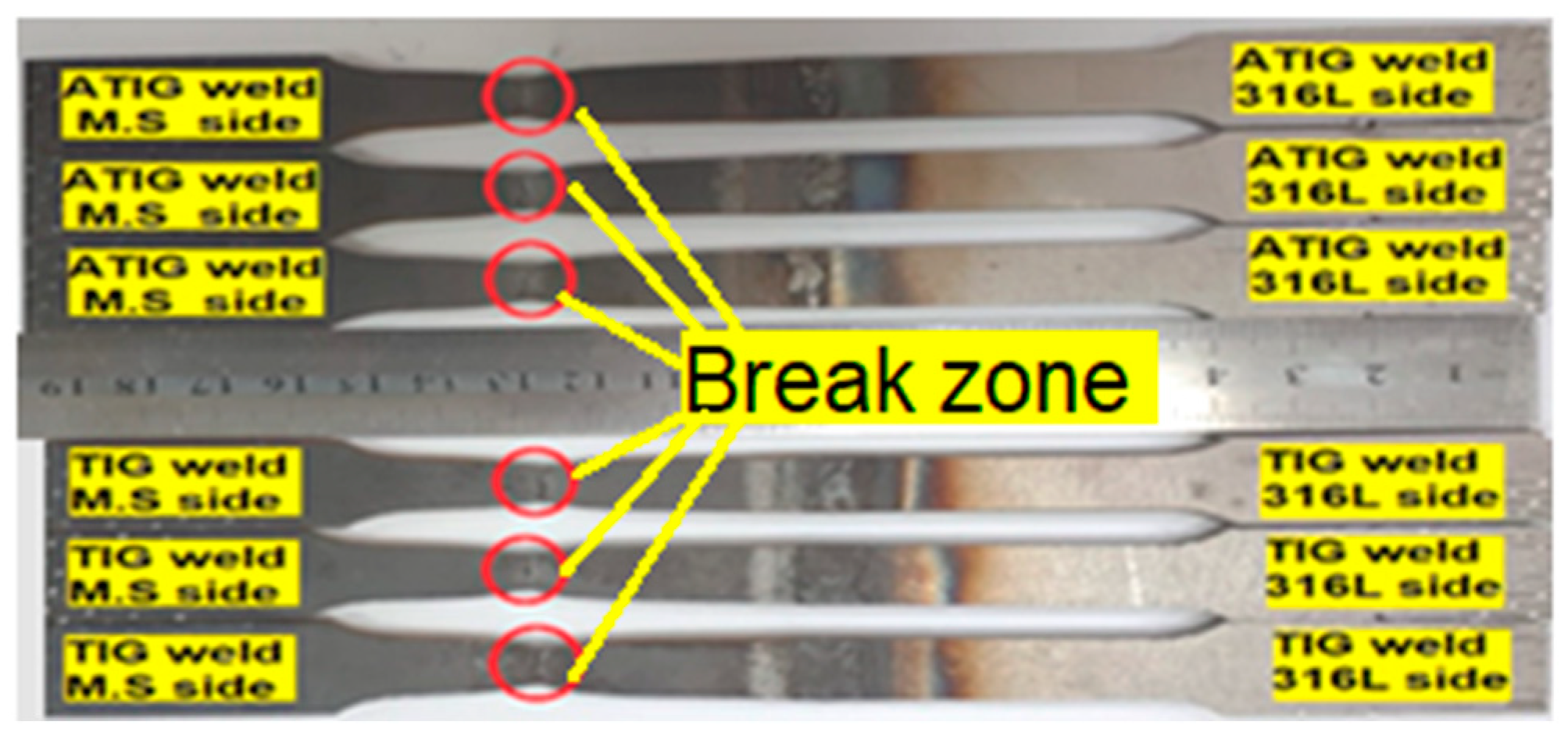
- Carbon migration from the MS to the weld zone occurred in the TIG weldment; however, SEM-EDS analysis did not show this phenomenon in the ATIG weld. The HAZ width of the ATIG weld was slightly narrower than that of the TIG weldment owing to its high cooling rate;
- (iv)
- The ATIG weld made a positive contribution to the mechanical properties, such as the hardness, tensile strength and resistance to sudden loads, as compared to the TIG weld. During the tensile test, both ATIG and TIG welded samples fractured at similar levels to the mild steel base metal, indicating that certain regions in the 316L base metal, namely the fusion zone and heat-affected zones, are stronger than in mild steel. The ATIG hardness values were homogenous and higher than those for the TIG weld;
- (v)
- The presence of optimal flux composed of 74% SiO2 + 13% Cr2O3 + 3% Fe2O3 + 10% NaF had a beneficial influence on the corrosion resistance of the ATIG weld.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.; Ma, Q.; Li, Y. Characterization of Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Dissimilar Welded Joint Between 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel and 16MnR. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulmus, M. Activated flux TIG welding of austenitic stainless steels. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2020, 9, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaijan, I.; Hedhibi, A.C.; Touileb, K.; Djoudjou, R.; Ouis, A.; Alrobei, H. Effect of Binary Oxide Flux on Weld Shape, Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel Welds. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, 5842741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakrishnan, S.; Chakravarthy, P.; Muhammed Rijas, A. Effect of Flux Gap and Particle Size on the Depth of Penetration in FBTIG Welding of Aluminium. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Vasudevan, M. Materials science & engineering a study of mechanism, microstructure and mechanical properties of activated flux TIG welded P91 steel-P22 steel dissimilar metal joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 309–323. [Google Scholar]
- Tathgir, S.; Bhattacharya, A. Activated-TIG Welding of Different Steels: Influence of Various Flux and Shielding Gas. Mater. Manuf. Process 2016, 31, 235–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klobčar, D.; Tušek, J.; Bizjak, M.; Simončič, S.; Lešer, V. Active flux tungsten inert gas welding of austenitic stainless steel aisi 304. Metalurgija 2016, 55, 617–620. [Google Scholar]
- Hedhibi, A.; Touileb, K.; Djoudjou, R.; Ouis, A.; Bouazizi, M.L.; Chakhari, J. Effect of single oxide fluxes on morphology and mechanical properties of ATIG on 316L austenitic stainless steel welds. ETASR 2018, 8, 3064–3072. [Google Scholar]
- Touileb, K.; Hdhibi, A.; Djoudjou, R.; Ouis, A.; Bouazizi, M.L. Mixing Design for ATIG Morphology and Microstructure Study of 316L Stainless Steel. ETASR 2019, 9, 3990–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenesi, P.J.; Neto, C.P.; Apolinario, E.R.; Dias, B.K. Effect of flux density and the presence of additives in ATIG welding of austenitic stainless steel. Weld. Int. 2015, 29, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magudeeswaran, G.; Sreehari, R.N.; Sundar, L.; Harikannan, N. Optimization of process parameters of the activated tungsten inert gas welding for aspect ratio of UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel welds. Def. Technol. 2014, 10, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasantharaja, P.; Vasudevan, M. Studies on A-TIG welding of Low Activation Ferritic/Martensitic (LAFM) steel. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 421, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, K.H.; Hsu, C.Y. Performance of activated TIG process in austenitic stainless steel welds. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2011, 211, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.L.; Lin, S.B.; Liu, F.Y.; Lin, W.; Zhang, Q.T. Research on the mechanism of penetration increase by flux in ATIG welding. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2003, 19, 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Howse, D.S.; Lucas, W. An investigation in to arc construction by active flux for TIG welding. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2000, 5, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, W.; Howse, D.S. Activating flux—Increasing the performance and productivity of the TIG and plasma processes. Weld. Metal Fabr. 1996, 64, 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Aniekan, E.I.; Ikechukwu, O.; Ikpe, E.E. Effects of arc voltage and welding current on the arc length of tungsten inert gas welding (TIG). Int. J. Eng. Technol. 2017, 3, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhao, J.; Huang, J.; Yu, X.; Liu, S. Microstructure and performances of dissimilar joints between 12Cr2Mo1R steel and 06Cr18Ni11Ti austenitic stainless steel joined by AA-TIG welding. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 60, 96–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hesam, P.; Mohsen, H.; Amir, H.K.; Ali, N. Designing of CK45 Carbon Steel and AISI 304 Stainless Steel Dissimilar Welds. Mater. Res. 2014, 17, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Radha, R.M.; Visnu, K.T.; Rajesha, S. A Study of Tensile Strength of MIG and TIG Welded Dissimilar Joints of Mild Steel and Stainless Steel. Int. J. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 3, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Dixit, P.; Suketu, J. Techniques to weld similar and dissimilar materials by ATIG welding—An overview. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2021, 36, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Tayyab, I. Analysis of Dissimilar Metal Welding of 1020 Mild Steel and 304 Stainless Steel. Master’s Thesis, Department of Mechanical Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Arivarasua, M.; Kasinatha, D.R.; Natarajana, A. Effect of Continuous and Pulsed Current on the Metallurgical and Mechanical Properties of Gas Tungsten Arc Welded AISI 4340 Aeronautical and AISI 304 L Austenitic Stainless Steel Dissimilar Joints. Mater. Res. 2015, 18, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osoba, L.O.; Ekpe, I.C.; Elemuren, R.A. Analysis of dissimilar welding of austenitic stainless steel to low carbon steel by TIG welding process. Int. J. Metall. Mater. Eng. 2015, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gaffar, M.; Shankar, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Satyanarayana, V.V. Experimental Investigation on Welded Joints of Dissimilar Steels. Int. J. Cur. Eng. Technol. 2017, 7, 800–807. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarsani, S.; Anand, K.; Kumar, R. Experimental Investigation on the Welding of Stainless Steel and Mild Steel using GMAW. J. Mater. Sci. Mech. Eng. 2016, 3, 152–157. [Google Scholar]
- Shamsul, B.J.; Mazlee, M.N.; Shahzan, K.A.K.; Khairel, R.A. Mechanical Properties of Dissimilar Welds Between Stainless Steel and Mild Steel. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 795, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, C.-H.; Tseng, K.-H.; Chou, C.-P. Effect of activated TIG flux on performance of dissimilar welds between mild steel and stainless steel. Key Eng. Mater. 2011, 479, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayee, S.G.; Badheka, V.J. Effect of oxide-based fluxes on mechanical and metallurgical properties of Dissimilar Activating Flux Assisted-Tungsten Inert Gas Welds. J. Manuf. Process 2014, 16, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Q. Microstructure evolution and corrosion behavior of dissimilar 304/430 stainless steel welded joints. J. Manuf. Process 2020, 50, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dak, G.; Pandey, C. A critical review on dissimilar welds joint between martensitic and austenitic steel for power plant application. J. Manuf. Process 2020, 58, 377–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirohi, S.; Kumar, S.; Bhanu, V.; Pandey, C.; Gupta, A. Study on the Variation in Mechanical Properties along the Dissimilar Weldments of P22 and P91 Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 31, 2281–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leconte, S.; Paillard, P.; Chapelle, P.; Henrion, G.; Saindrenan, J. Effects of flux containing fluorides on TIG welding process. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2013, 12, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonik, A.G. The effect of contraction of the arc discharge upon the introduction of electro-negative elements. Weld. Prod. 1976, 3, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, L.Q.; Hong, W.X.; Da, Z.Z.; Jun, W. Effect of activating flux on arc shape and arc voltage in tungsten inert gas welding. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. 2007, 17, 486–490. [Google Scholar]
- Bahrami, W.J.; Aidun, D.K. Modeling of Carbon Steel Duplex Stainless Steel GTA Weld Pool. Weld. J. 2014, 93, 262–270. [Google Scholar]
- Danielewski, H.; Skrzypczyk, A.; Tofil, S.; Witkowski, G.; Rutkowski, S. Numerical Simulation of Laser Welding Dissimilar Low Carbon and Austenitic Steel Joint. De Gruyter 2020, 10, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-S.; Yang, J.; Lu, D.-H.; Bin, W.-J. Study on the microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion behaviour of S355JR/316L dissimilar welded joint prepared by gas tungsten arc welding multi-pass welding process. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2016, 21, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
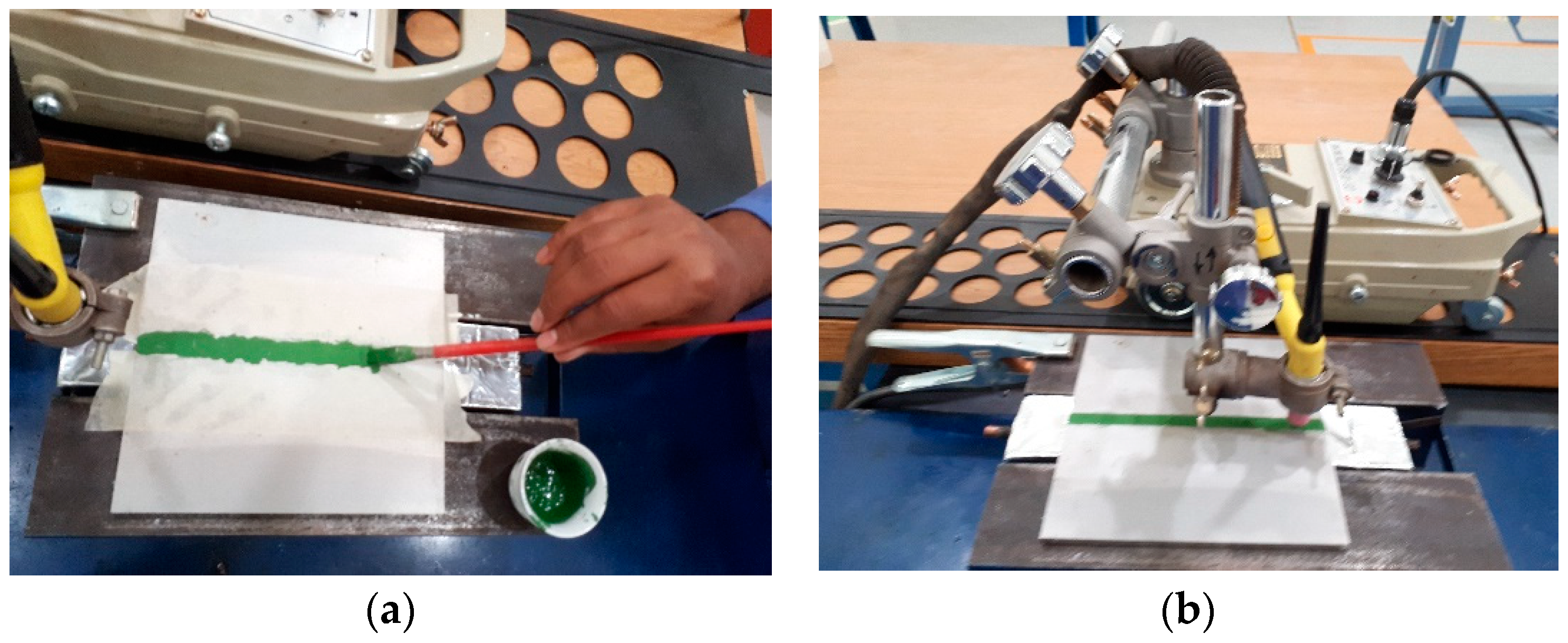

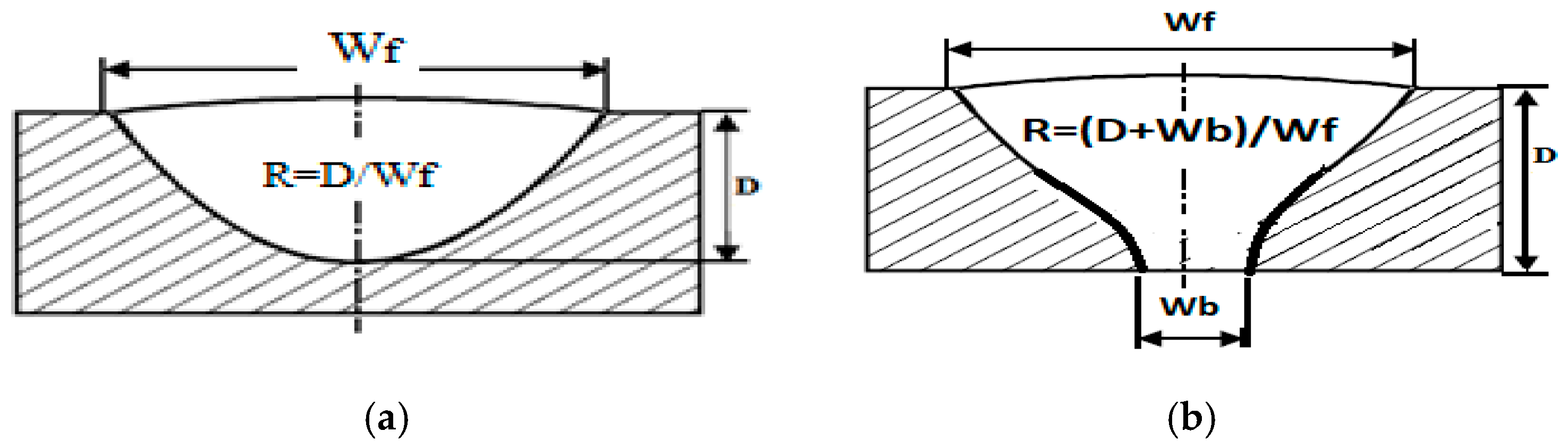
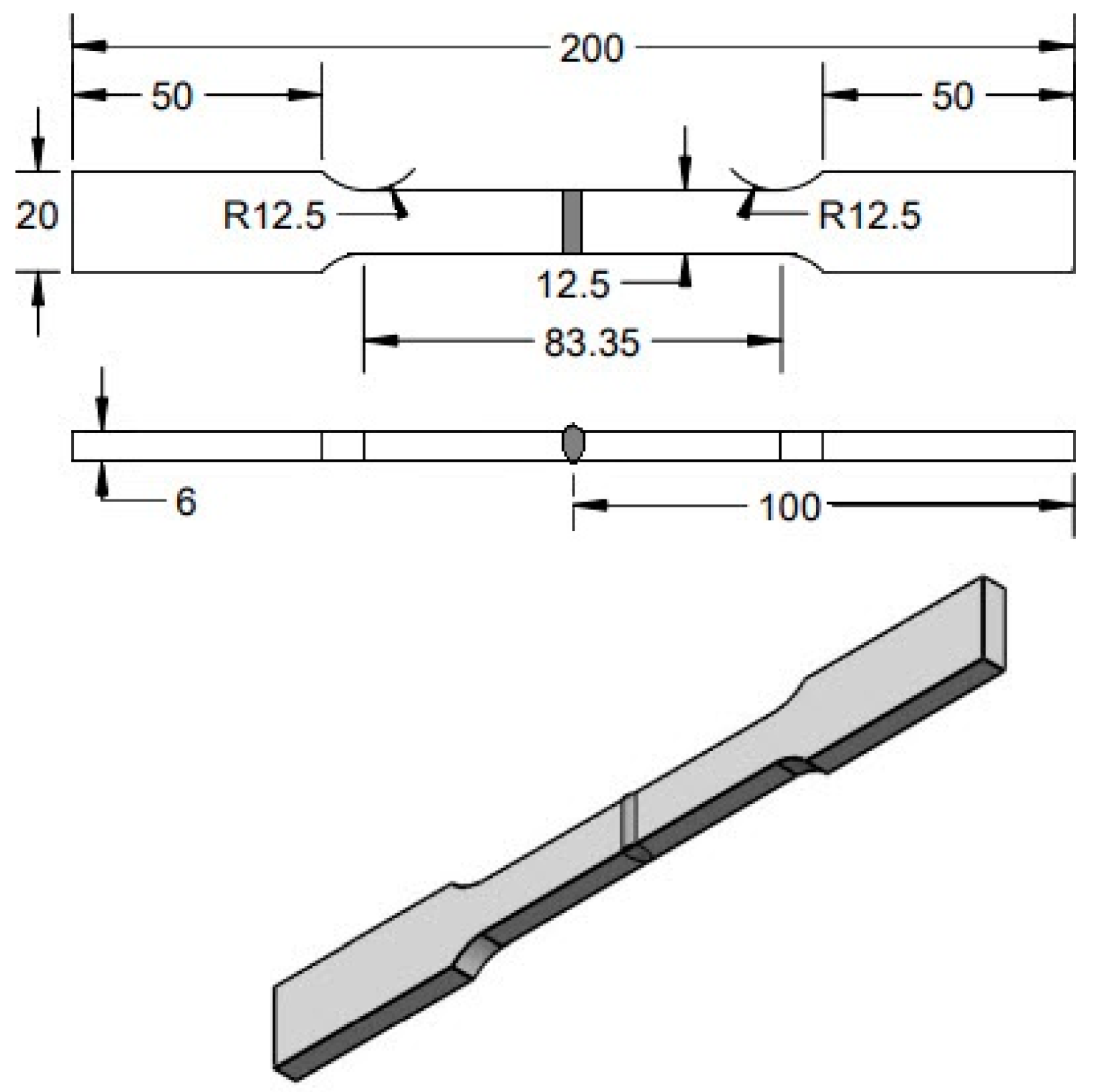
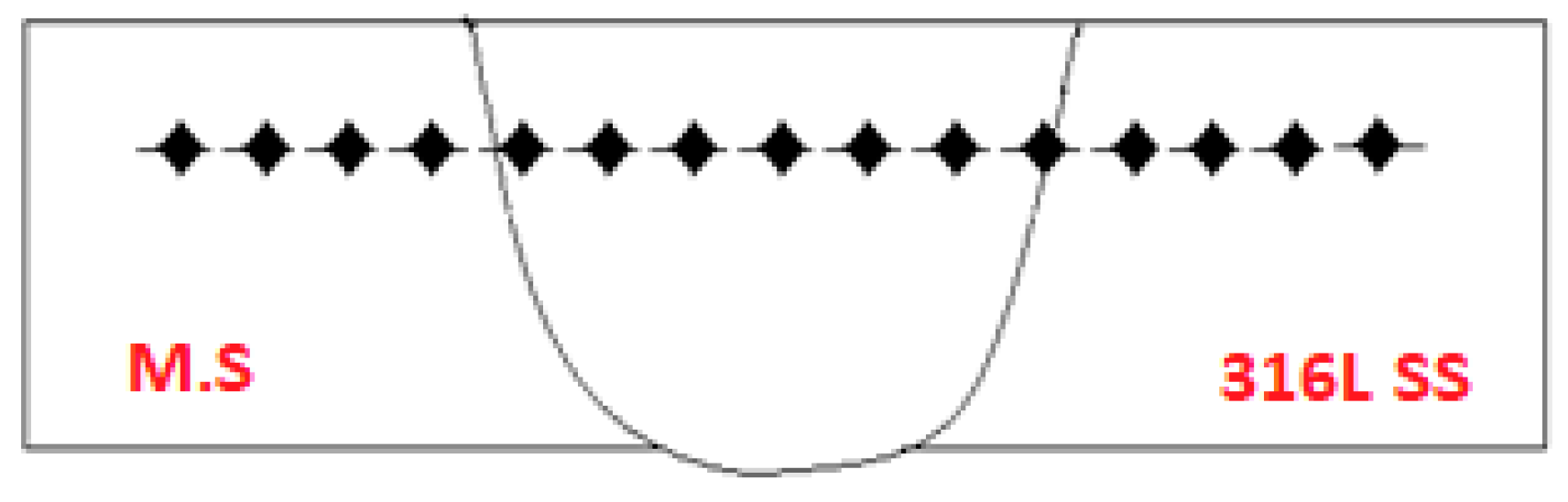







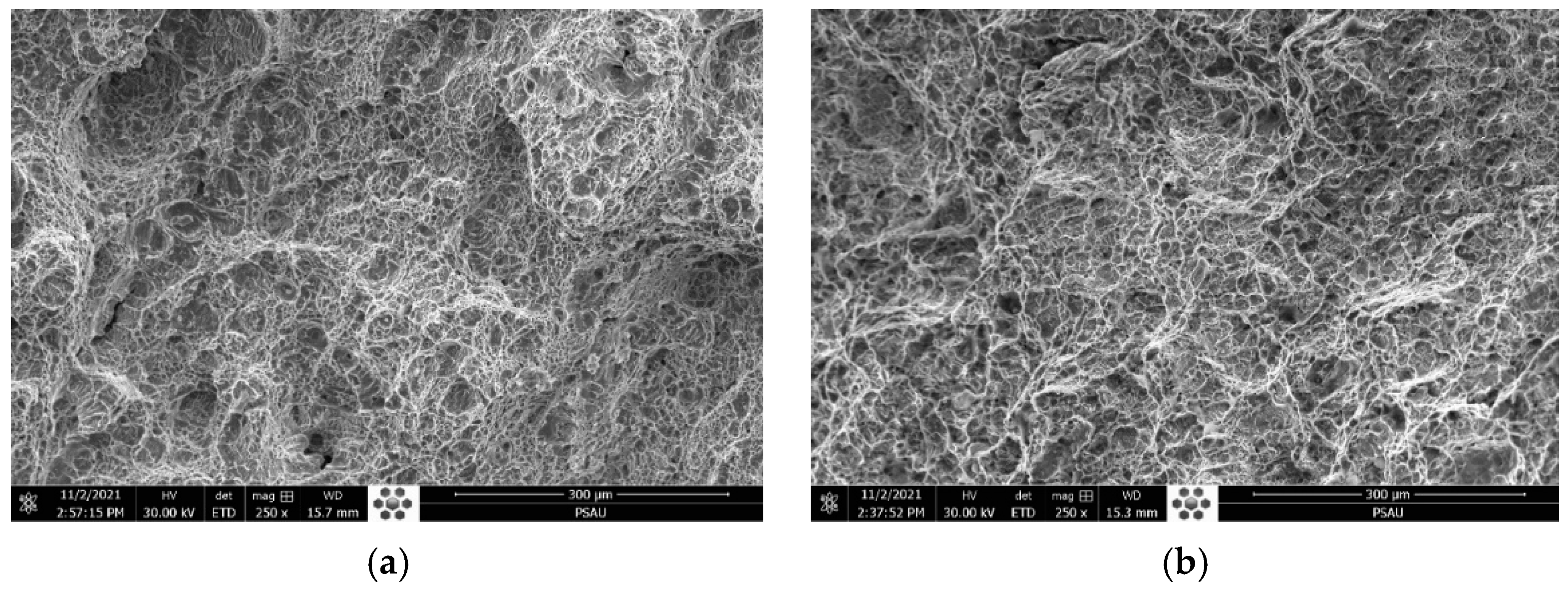
| Elements | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight % | 0.026 | 1.47 | 0.42 | 0.034 | 0.0016 | 16.60 | 10.08 | 2.14 | 0.044 | 0.50 | Balance |
| Elements | C | Mn | Si | P | S | Cr | Ni | Mo | N | Cu | Al | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight % | 0.0521 | 0.165 | 0.009 | 0.0098 | 0.0137 | 0.0234 | 0.0277 | 0.00647 | 0.0053 | 0.0985 | 0.0245 | Balance |
| Parameters | Range |
|---|---|
| Welding speed | 13 cm/min |
| Welding current | 150 Amp |
| Arc Length | 2 mm |
| Electrode tip angle | 45° |
| Shielding gas on the workpiece | Argon with flow rate 10 L/min |
| Shielding gas on the backside | Argon with flow rate 5 L/min |
| Welding mode | Negative direct current electrode |
| Elements | SiO2 | TiO2 | Fe2O3 | Cr2O3 | Mn2O3 | V2O5 | MoO3 | Co2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth (mm) | 5.96 | 3.28 | 4.59 | 4.33 | 3.01 | 3.26 | 3.95 | 3.29 |
| Width (mm) | 12.22 | 11.28 | 11.40 | 11.08 | 10.6 | 11.54 | 11.16 | 11.12 |
| Ratio | 0.49 | 0.29 | 0.40 | 0.39 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.29 |
| Input Data | Output | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Combinations | Fe2O3 % | Cr2O3 % | SiO2 % | NaF % | Depth D (mm) | Ratio R: (D + Wb)/Wf |
| 1 | 67.5 | 22.5 | 0 | 10 | 6.46 | 1.09 |
| 2 | 67.5 | 0 | 22.5 | 10 | 6.46 | 1.13 |
| 3 | 0 | 67.5 | 22.5 | 10 | 6.29 | 0.96 |
| 4 | 22.5 | 67.5 | 0 | 10 | 6.24 | 1.01 |
| 5 | 22.5 | 0 | 67.5 | 10 | 6.77 | 1.21 |
| 6 | 0 | 22.5 | 67.5 | 10 | 7.18 | 1.42 |
| 7 | 0 | 45 | 45 | 10 | 6.79 | 1.21 |
| 8 | 45 | 0 | 45 | 10 | 6.82 | 1.30 |
| 9 | 45 | 45 | 0 | 10 | 6.13 | 0.89 |
| 10 | 45 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 10 | 6.65 | 1.25 |
| 11 | 22.5 | 45 | 22.5 | 10 | 6.46 | 1.31 |
| 12 | 22.5 | 22.5 | 45 | 10 | 7.14 | 1.52 |
| 13 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 10 | 6.41 | 1.14 |
| 14 | 60 | 15 | 15 | 10 | 6.70 | 1.14 |
| 15 | 15 | 60 | 15 | 10 | 6.66 | 1.27 |
| 16 | 15 | 15 | 60 | 10 | 6.69 | 1.09 |
| 17 | 90 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 4.59 | 0.40 |
| 18 | 0 | 90 | 0 | 10 | 4.33 | 0.39 |
| 19 | 0 | 0 | 90 | 10 | 5.96 | 1.11 |
| TIG | ATIG | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D | WF | WB | (D + WB)/WF | D | WF | WB | (D + WB)/WF |
| 3.7 | 11.78 | 0 | 0.31 | 6.9 | 8.8 | 5.0 | 1.35 |
| Sample | Zones | Area (mm2) |
|---|---|---|
| TIG M.S/316L | M.S Side | 12.02 |
| 316L SS Side | 25.38 | |
| ATIG M.S/316L | M.S Side | 22.1 |
| 316L SS Side | 24.5 |
Horizontal Point Scan from MS Side to 316L SS Side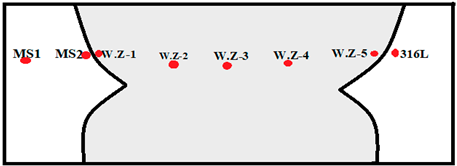 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elements Weight % | M.S-1 | M.S-2 Carbon Depletion Zone | W.Z-1 | W.Z-2 | W.Z-3 | W.Z-4 | W.Z-5 | 316L |
| C | 5.03 | 0 | 3.58 | 2.45 | 2.34 | 2.23 | 0.58 | 0 |
| Cr | 0 | 0 | 4.86 | 11.25 | 11.17 | 12.51 | 15.86 | 18.82 |
| Fe | 94.97 | 100 | 84.20 | 81.82 | 80.85 | 80.33 | 75.03 | 70.82 |
| Ni | 0 | 0 | 2.06 | 4.48 | 4.76 | 4.82 | 6.75 | 8.29 |
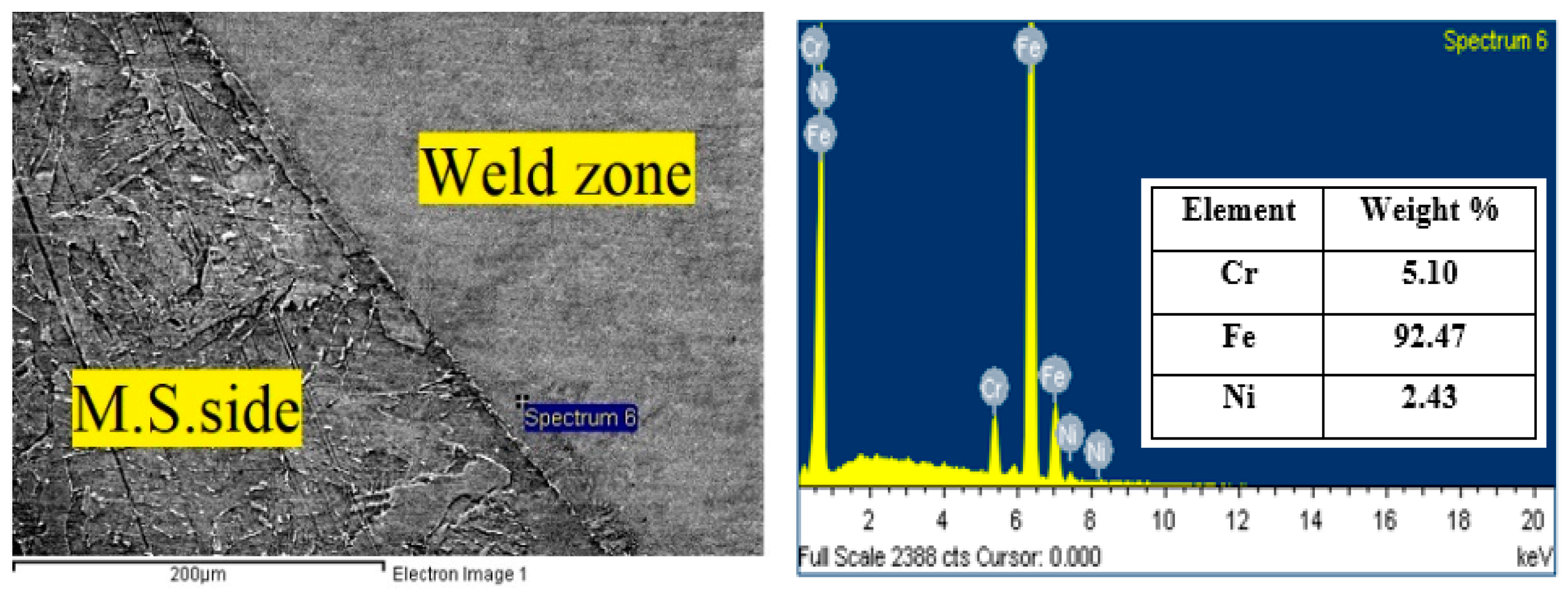
Horizontal Point Scan from MS Side to 316L Side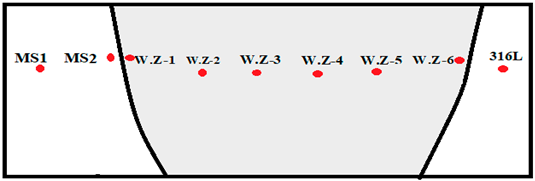 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elements Weight % | M.S-1 | M.S-2 | W.Z-1 | W.Z-2 | W.Z-3 | W.Z-4 | W.Z-5 | W.Z-6 | 316L |
| C | 2.95 | 2.70 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cr | 0 | 0 | 5.10 | 5.91 | 9.67 | 10.42 | 10.56 | 14.98 | 18.75 |
| Fe | 97.05 | 97.30 | 92.47 | 92.02 | 85.81 | 83.77 | 83.4 | 76.77 | 71.54 |
| Ni | 0 | 0 | 2.43 | 2.07 | 3.48 | 4.58 | 4.92 | 4.00 | 7.47 |
| Sample | Number of Tests | UTS Max. (MPa) | UTS Min. (MPa) | UTS Average (MPa) | Standard Deviation σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIG MS/M.S | 3 | 379 | 370 | 375 | 3.36 |
| TIG 316L/316L | 3 | 598 | 594 | 596 | 2.08 |
| TIG MS/316L | 3 | 380 | 372 | 376 | 4.00 |
| ATIG MS/316L | 3 | 379 | 376 | 378 | 1.53 |
| Sample | Zone of Tests | HV Max. | HV Min. | HV Average | Standard Deviation σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIG | FZ | 287 | 235 | 252 | 12.75 |
| ATIG | FZ | 284 | 270 | 277 | 4.84 |
| Sample | Zone of Tests | HV Max. | HV Min. | HV Average | Standard Deviation σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIG | HAZ FZ/MS | 147 | 140 | 144 | 3.61 |
| HAZ FZ/316L SS | 212 | 186 | 193 | 12.53 | |
| ATIG | HAZ FZ/MS | 179 | 171 | 175 | 4.04 |
| HAZ FZ/316L SS | 214 | 201 | 206 | 5.09 |
| Sample | Number of Tests | Absorbed Energy (J/cm2) Min | Absorbed Energy (J/cm2) Max | Absorbed Energy (J/cm2) Average | Standard Deviation σ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIG—316L SS/MS | 3 | 215 | 238 | 216 | 15.56 |
| ATIG—316L SS/MS | 3 | 239 | 252 | 245 | 9.25 |
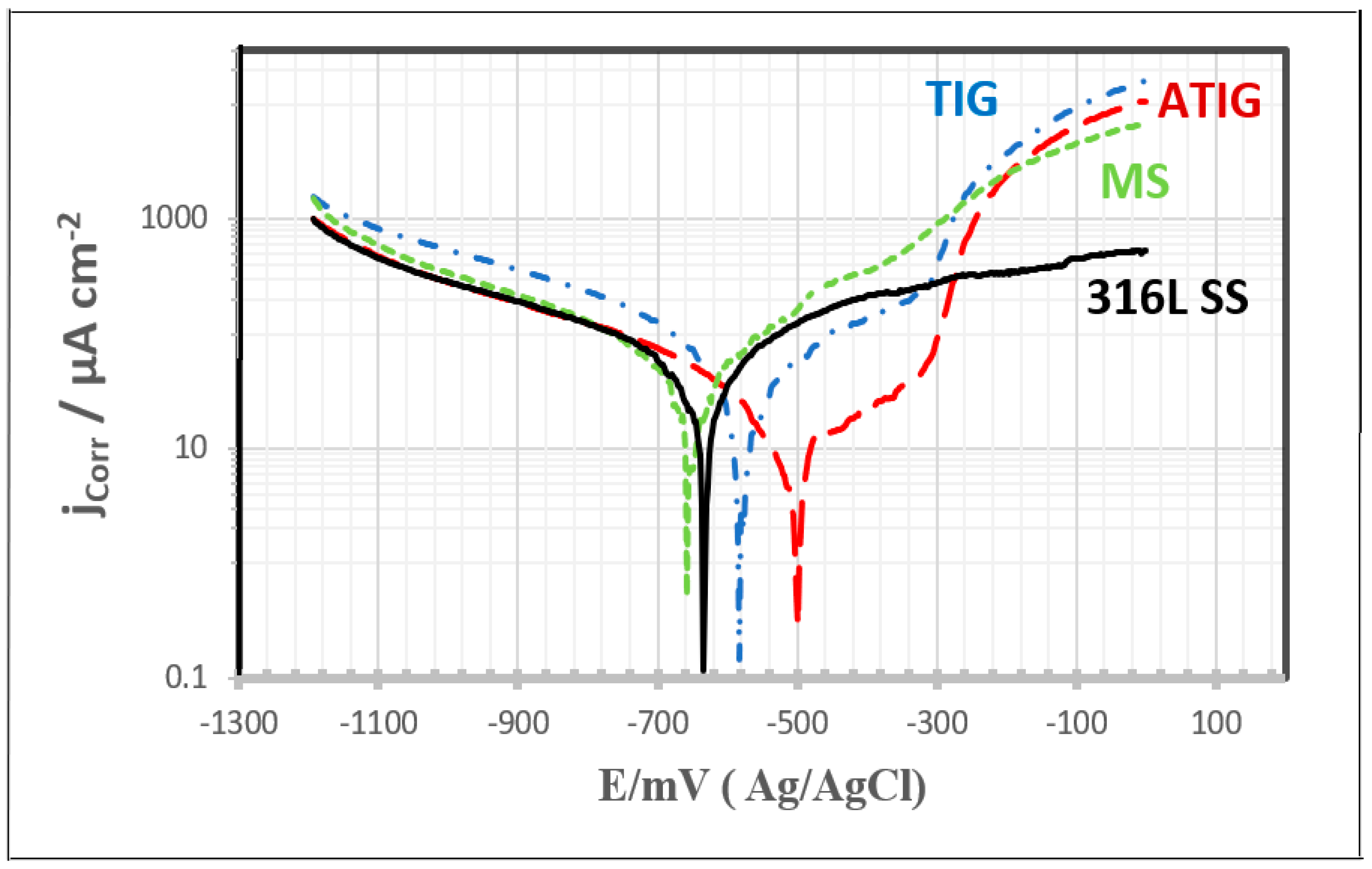
| Sample | βc/mV·dec−1 | ECorr/mV | βa/mV·dec−1 | jCorr/µA·cm−2 | RP/Ω·cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MS | 152 | –655 | 95 | 26 | 978 |
| 316 SS | 146 | –640 | 115 | 19 | 1472 |
| TIG | 163 | –570 | 90 | 17 | 1483 |
| ATIG | 130 | –515 | 125 | 10 | 2771 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Touileb, K.; Djoudjou, R.; Hedhibi, A.C.; Ouis, A.; Benselama, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Abdo, H.S.; Samad, U.A. Comparative Microstructural, Mechanical and Corrosion Study between Dissimilar ATIG and Conventional TIG Weldments of 316L Stainless Steel and Mild Steel. Metals 2022, 12, 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040635
Touileb K, Djoudjou R, Hedhibi AC, Ouis A, Benselama A, Ibrahim A, Abdo HS, Samad UA. Comparative Microstructural, Mechanical and Corrosion Study between Dissimilar ATIG and Conventional TIG Weldments of 316L Stainless Steel and Mild Steel. Metals. 2022; 12(4):635. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040635
Chicago/Turabian StyleTouileb, Kamel, Rachid Djoudjou, Abdeljlil Chihaoui Hedhibi, Abousoufiane Ouis, Abdallah Benselama, Albaijan Ibrahim, Hany S. Abdo, and Ubair Abdus Samad. 2022. "Comparative Microstructural, Mechanical and Corrosion Study between Dissimilar ATIG and Conventional TIG Weldments of 316L Stainless Steel and Mild Steel" Metals 12, no. 4: 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040635
APA StyleTouileb, K., Djoudjou, R., Hedhibi, A. C., Ouis, A., Benselama, A., Ibrahim, A., Abdo, H. S., & Samad, U. A. (2022). Comparative Microstructural, Mechanical and Corrosion Study between Dissimilar ATIG and Conventional TIG Weldments of 316L Stainless Steel and Mild Steel. Metals, 12(4), 635. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12040635








