Influence of Electron Beam Welding Parameters on the Microstructure Formation and Mechanical Behaviors of the Ti and Ni Dissimilar Metals Welded Joints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
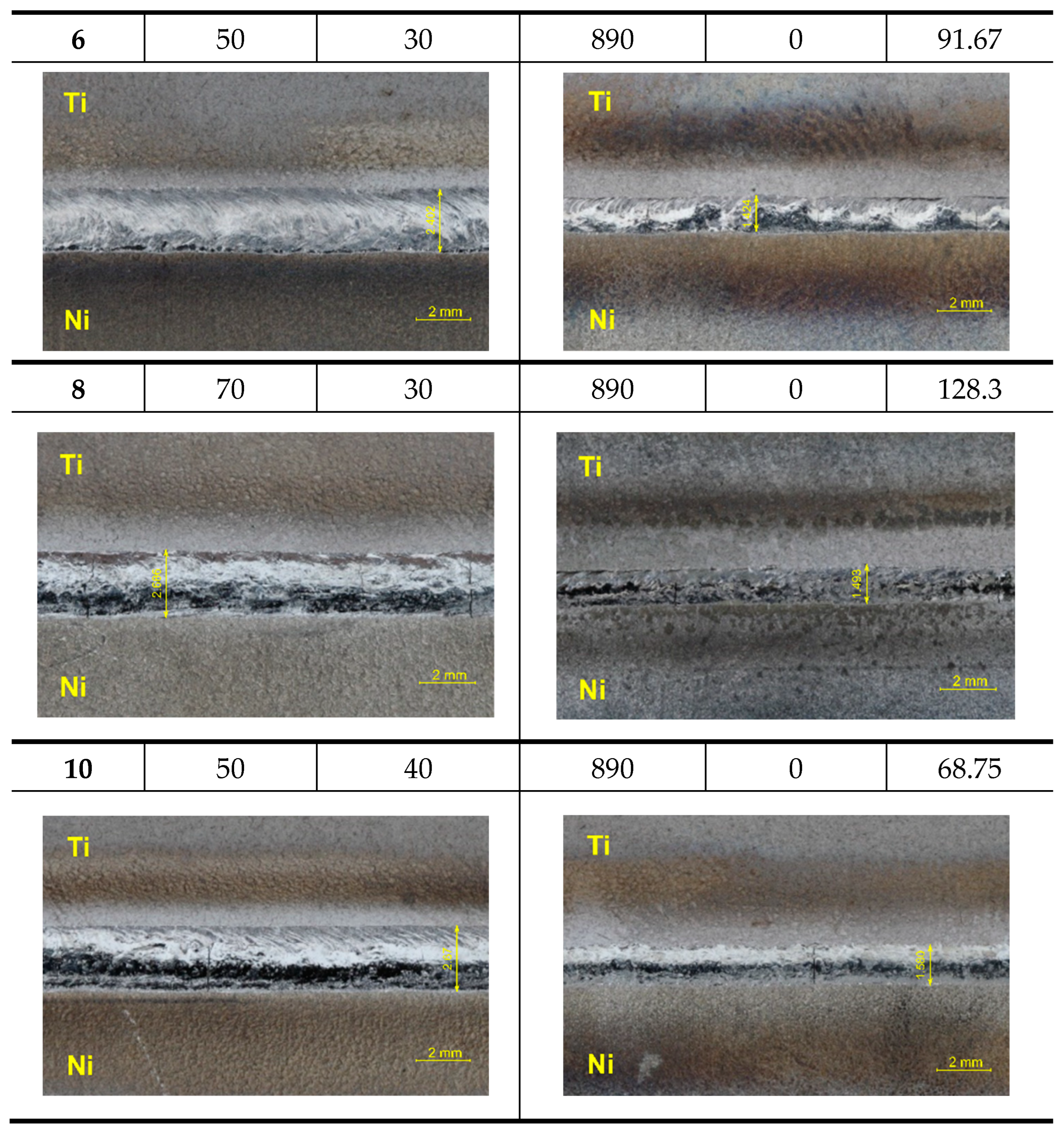
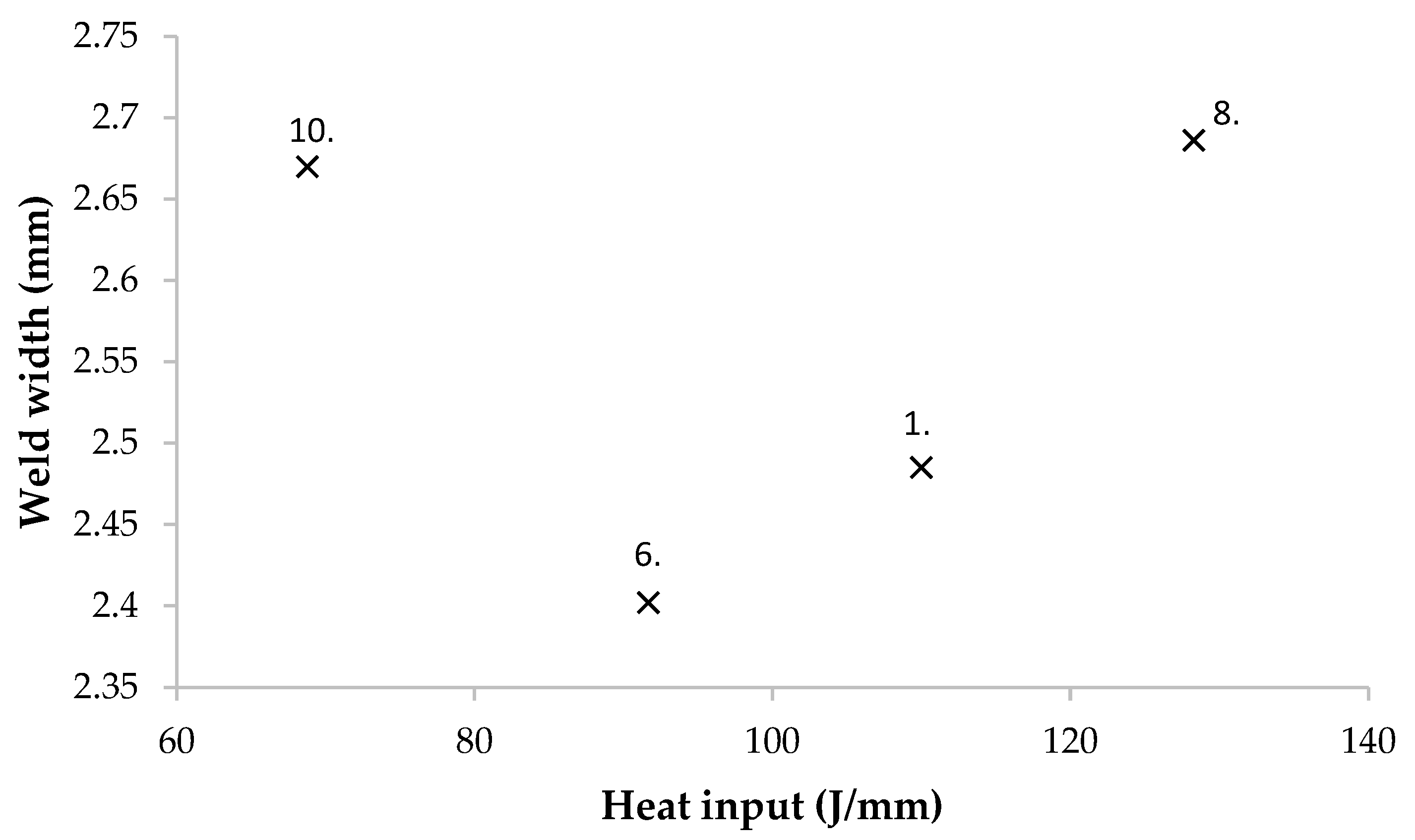
3.1. Weld Bead and Root Appearance
3.2. Analysis of Weld Cross-Sections
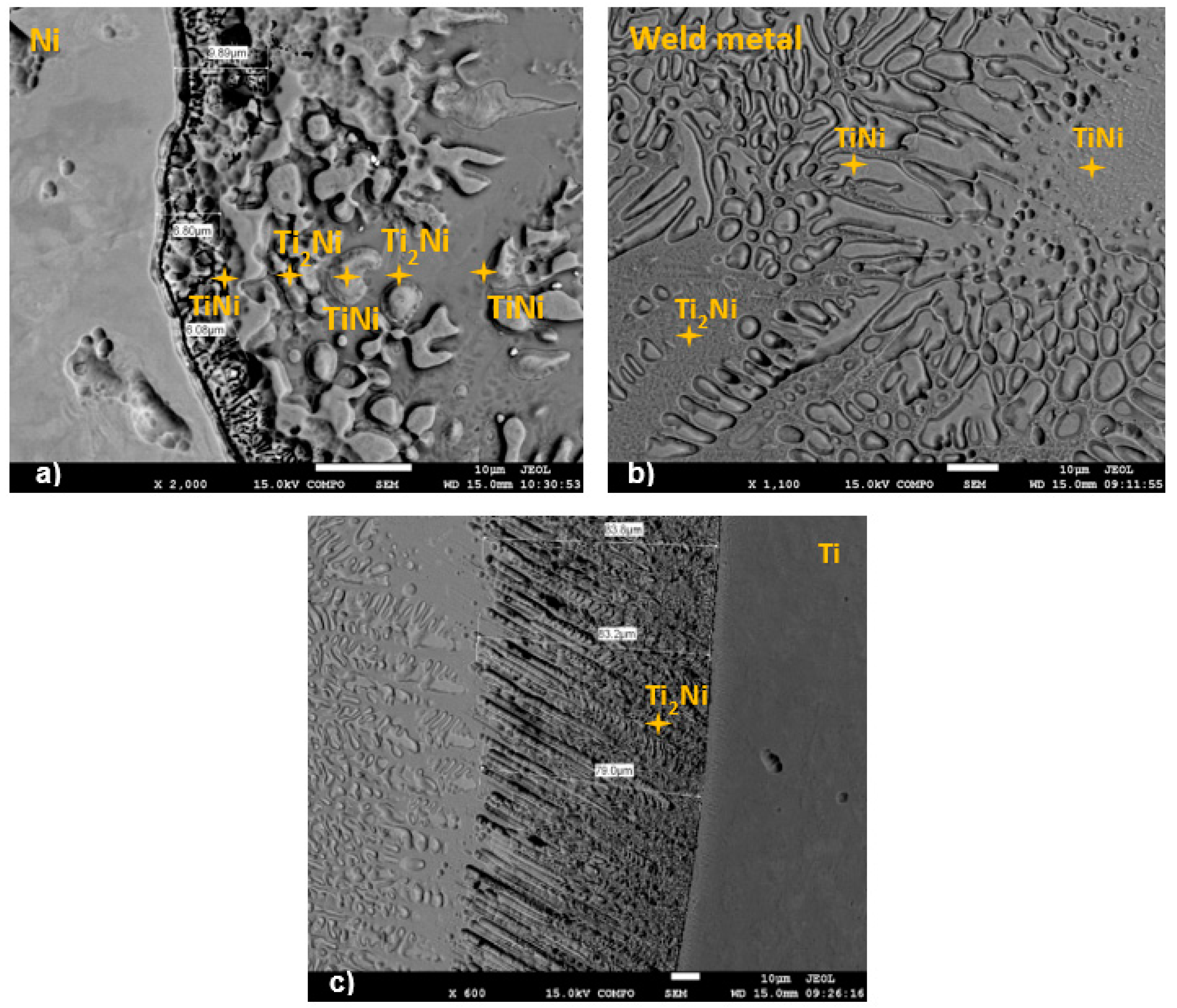
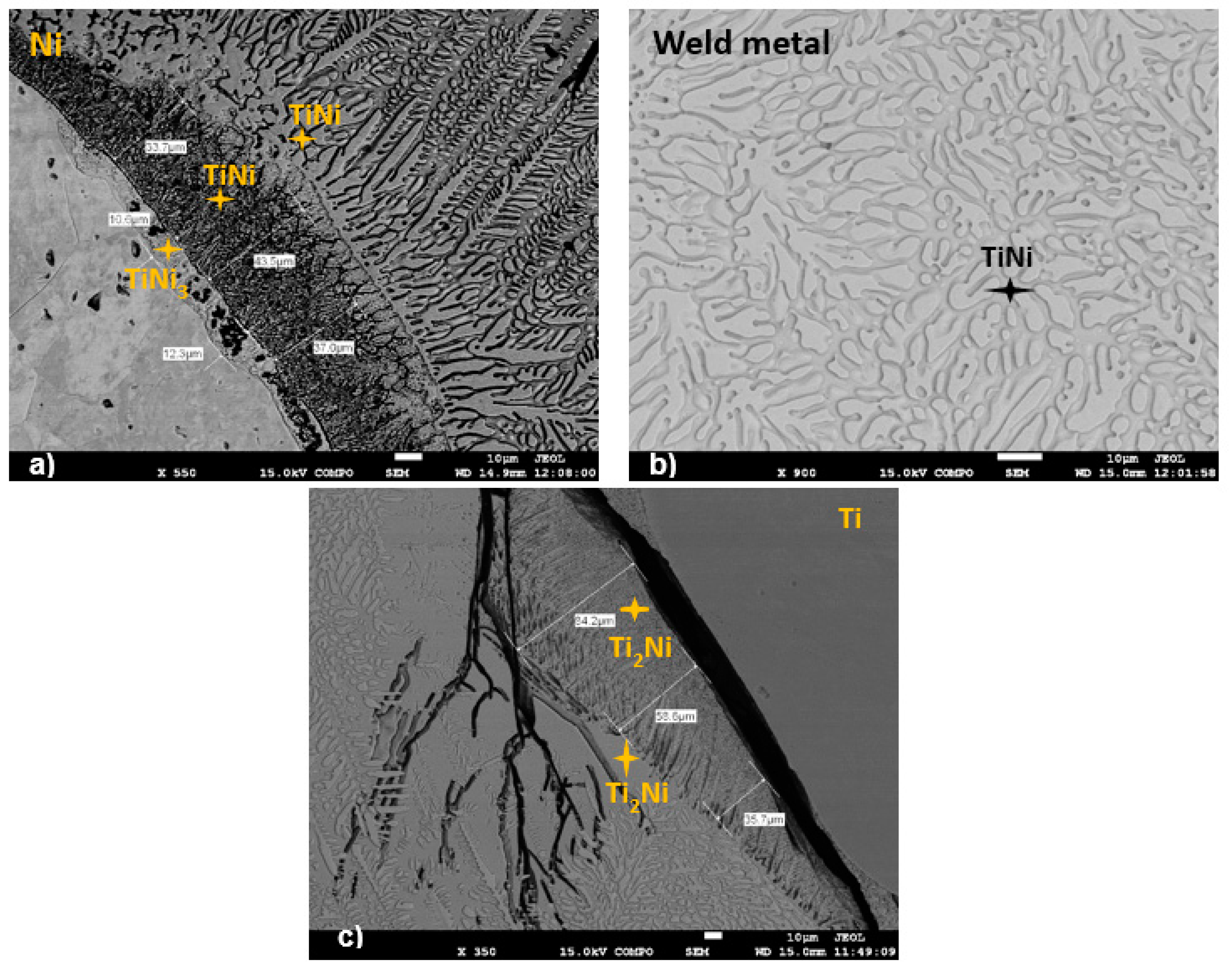
3.3. Analysis of the Microstructure
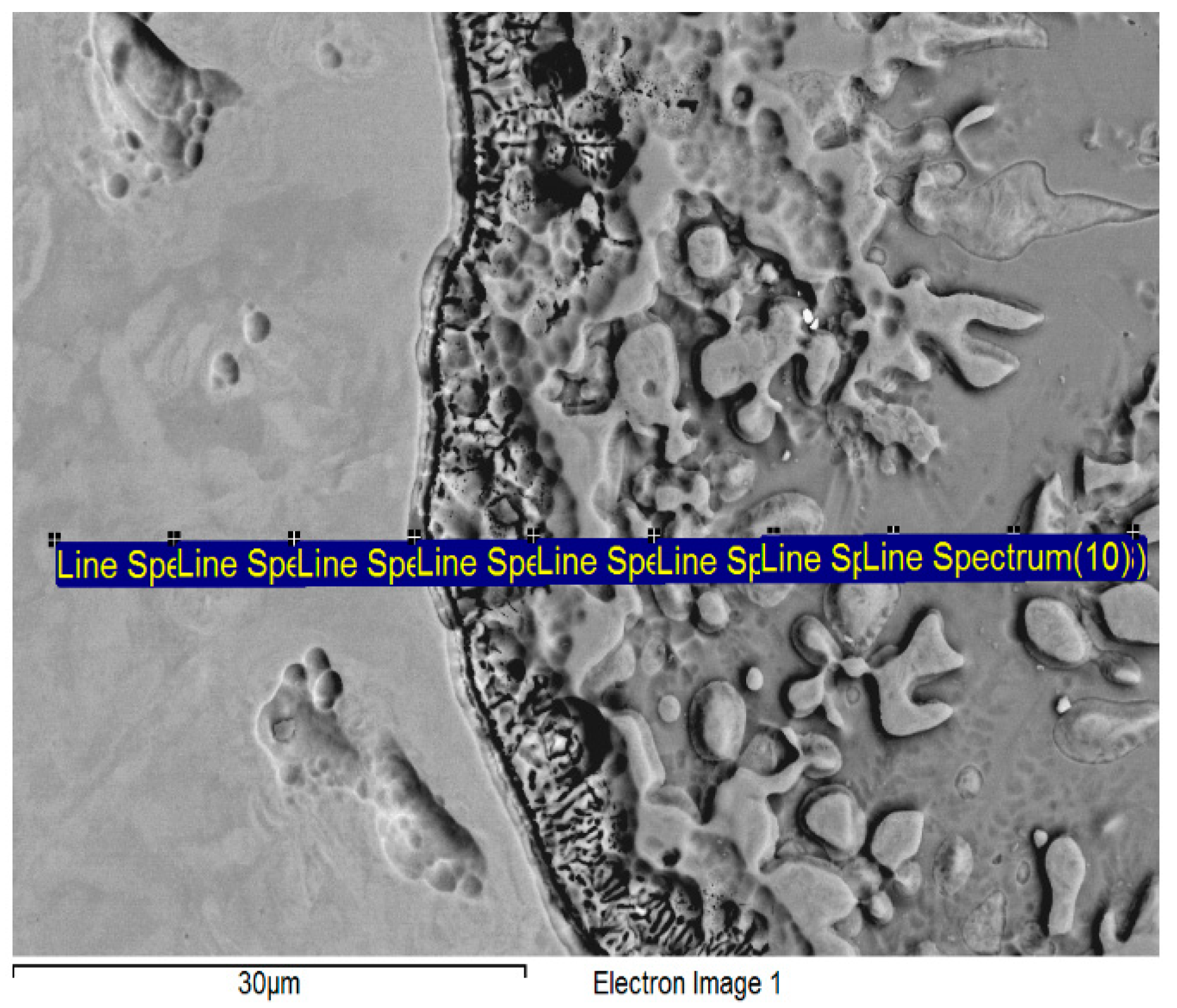
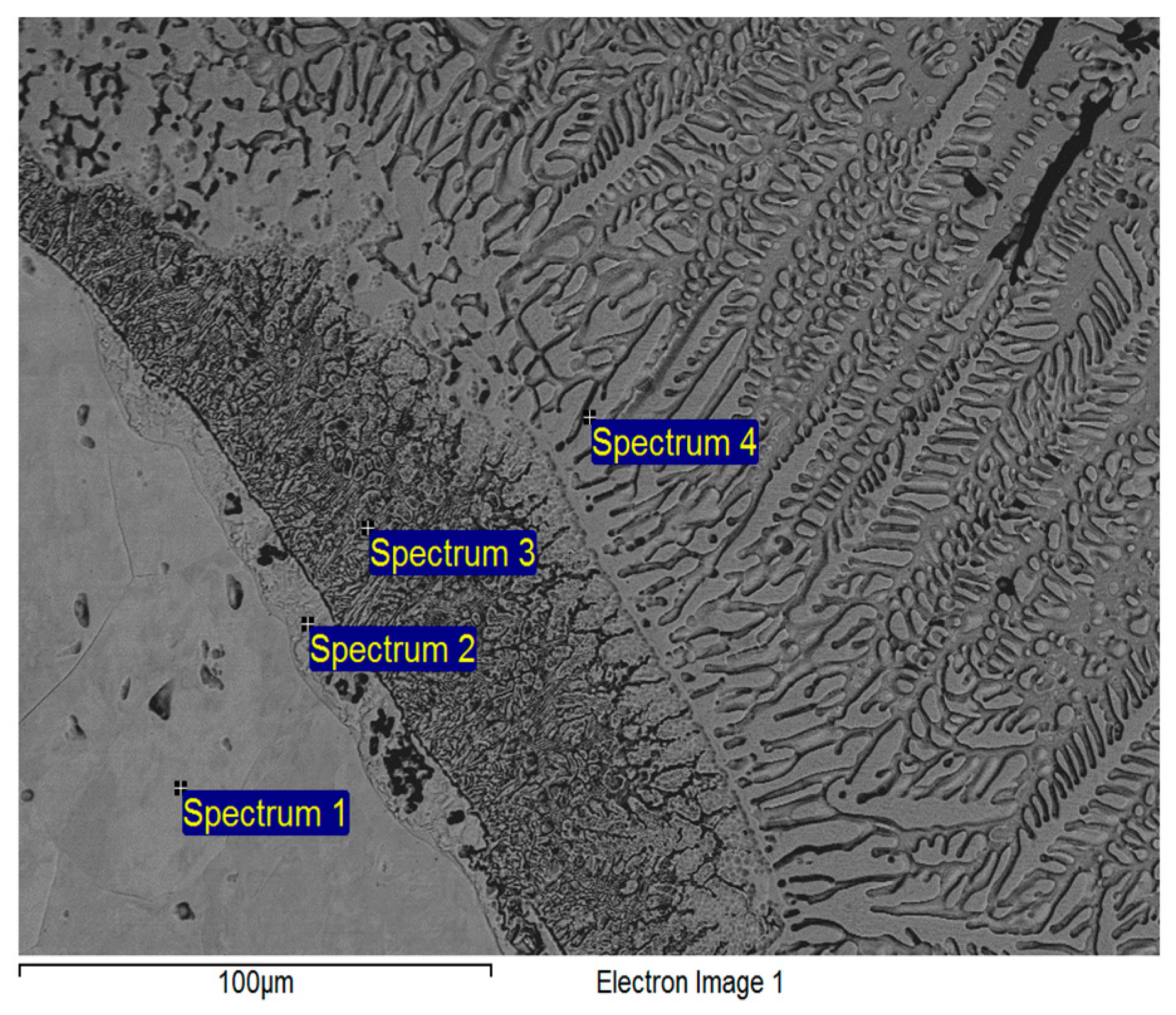
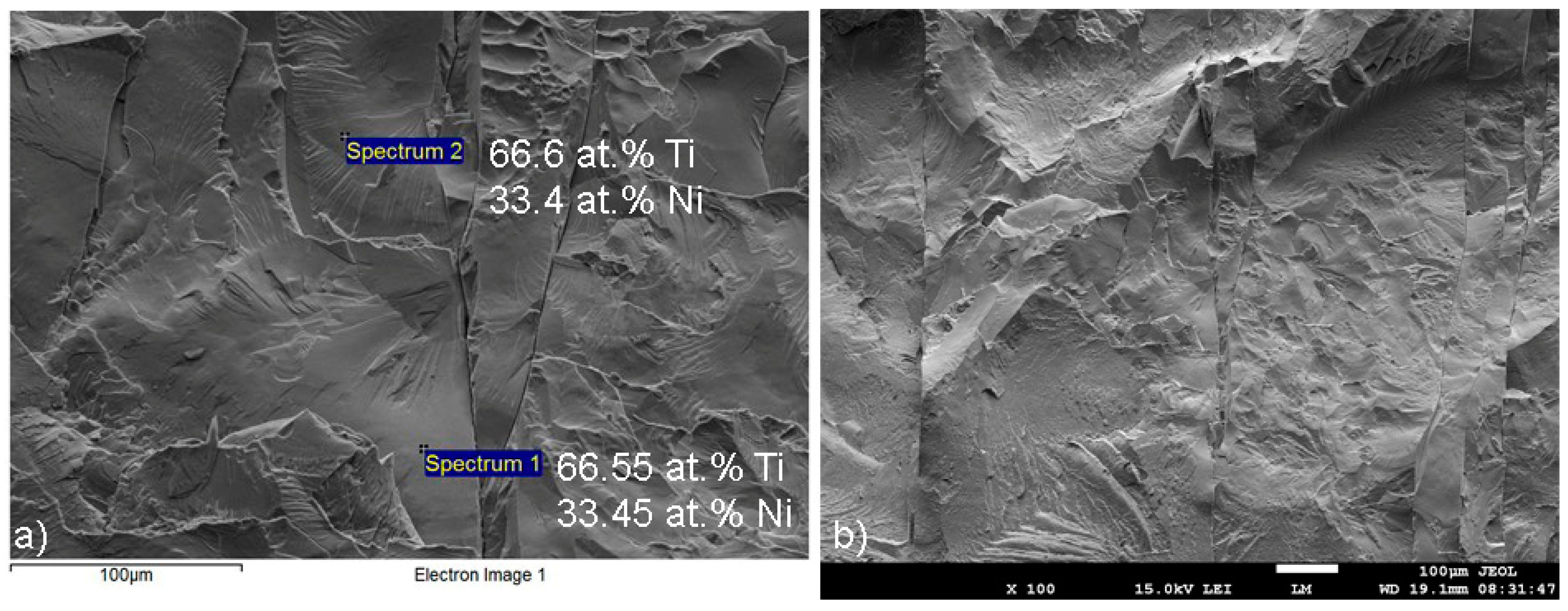
3.4. SEM Analysis
3.5. Microhardness Measurements
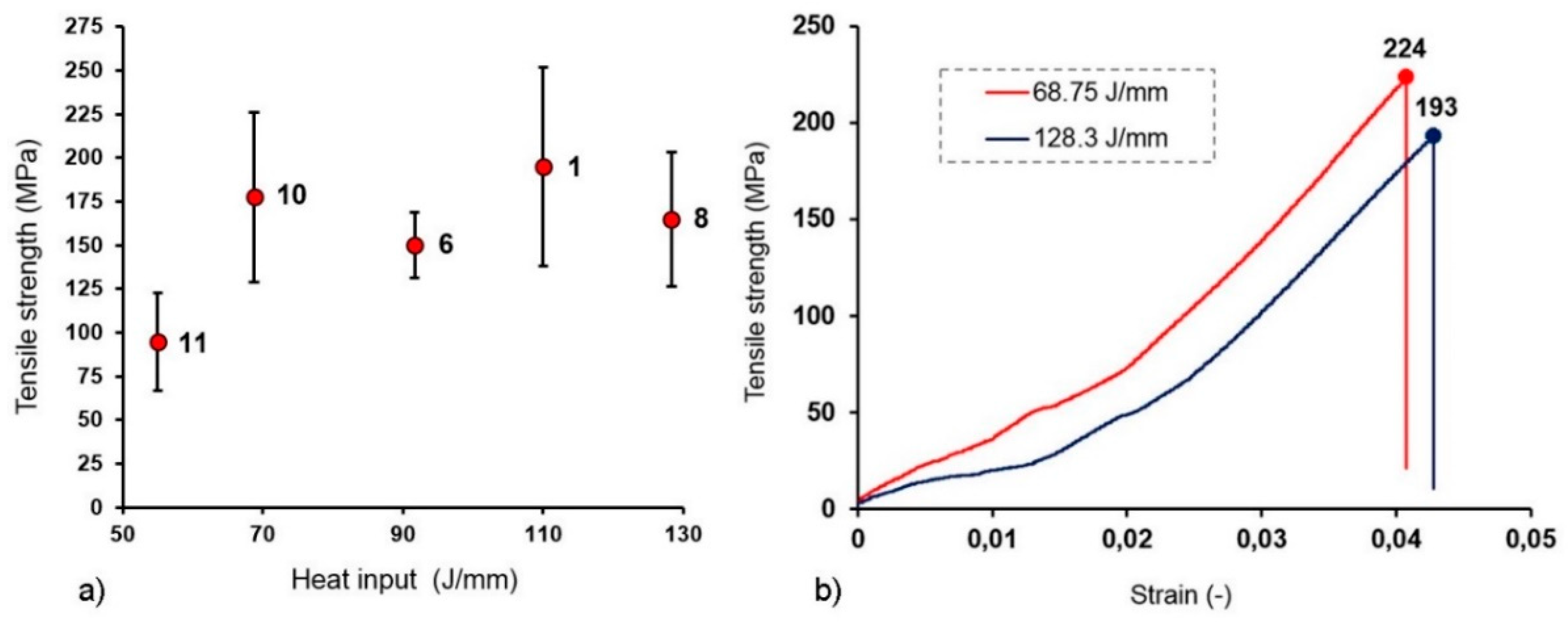
3.6. Tensile Strength Results
3.7. Fracture Surfaces
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The samples were subjected to visual testing, in which longitudinal and transverse cracks were recorded along the whole weld. Cracking in the weld after solidification led to a loss in integrity of the welded joint.
- Fully penetrated welds had near parallel fusion lines on both sides. The weld profile on the Ni side was straighter than on the Ti side.
- The weld metal had a predominantly dendritic morphology. Dendrites were formed by a substitution solid solution of the γ phase, which contained nickel and titanium, or a small number of alloying elements used n alloys.
- The microstructure of the weld pool was composed of various phases, which were detected by SEM composition analysis. The microstructure in the weld pool’s middle section was largely made up of NiTi and TiNi3.
- The microhardness of the base material was compared to the producer’s declared values. The values of the measured hardness of HAZ were somewhat similar to the hardness values of the base material. The hardness of weld metal was five times higher than that of the base material.
- No clear trend was found between heat input and tensile strength. Brittle fracturing was observed after tensile testing. There were several crack initiations in the traverse course. The cracks were initiated by a cleavage process due to the formation of intermetallic compounds, namely, Ti2Ni.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, X.G.; Yang, H.; Yan, S.L.; Gao, P.F.; Zhou, J.H. Mechanism and Kinetics of Static Globularization in TA15 Titanium. Alloy with Transformed Structure. J. Alloy. Compd. 2012, 533, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, G.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, W. Behavior and Modeling of Flow Softening and Ductile Damage Evolution in Hot Forming of TA15 Alloy Sheets. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezugwu, E.O.; Wang, Z.M. Titanium Alloys and Their Machinability—A Review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1997, 68, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurappa, I. Protection of Titanium Alloy Components against High Temperature Corrosion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 356, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Bi, Q.; Guo, Y.; Yan, J.; Yang, Z. Convective heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of near-critical-pressure hydrocarbon fuel in a minichannel. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 51, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ii, S.A.P.; Shyam, A.; Ritchie, R.O.; Milligan, W.W. High Frequency Fatigue Crack Propagation Behavior of a Nickel-Base Turbine Disk Alloy. Int. J. Fatigue 1999, 21, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Pinkerton, A.J.; Li, L. Fibre laser welding of dissimilar alloys of Ti-6Al-4V and Inconel 718 for aerospace applications. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 52, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z. Diffusion brazing of tungsten and steel using Ti–Ni liquid phase forming interlayer. Fusion Eng. Des. 2015, 91, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McQuillan, A.D.; McQuillan, M.K. Titanium; Butterworths Scientific Publications: London, UK, 1956; pp. 124–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Feng, J. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Electron Beam-Welded Titanium-Steel Joints with Vanadium, Nickel, Copper and Silver Filler Metals. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1498–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, K.; Ren, X. Physical metallurgy of Ti–Ni-based shape memory alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2005, 50, 511–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Miranda, R.; Braz, F. Welding and Joining of NiTi Shape Memory, Alloys—A Review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 88, 412–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahinia, M.; Hashemi, M.; Tabesh, M. Manufacturing and processing of NiTi implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 911–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Vojtěch, V.; Pecenová, Z.; Průša, F.; Pokorný, P.; Deduytsche, D.; Detavernier, C.; Bernatiková, A.; Salvetr, P.; Knaislová, A.; et al. Formation of Ni–Ti intermetallics during reactive sintering at 800–900 °C. Mater. Technol. 2017, 51, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skolakova, A.; Novak, P.; Salvetr, P. Influence of elements with high affinity to oxygen on microstructure and phase composition of Ni–Ti alloy. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 16, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Abinandanan, T.A.; Chattopadhya, K. Microstructure Development during Dissimilar Welding: Case of Laser Welding of Ti with Ni involving intermetallic Phase Formation. J. Mater. Sci. 2006, 41, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemán, B.; Gutiérrez, I.; Urcola, J.J. Interface Microstructures in the Diffusion Bonding of a Titanium Alloy Ti 6242 to an INCONEL 625. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1995, 26, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sam, S.; Kundu, S.; Chatterjee, S. Diffusion Bonding of Titanium Alloy to Micro-Duplex Stainless Steel Using a Nickel Alloy interlayer: Interface Microstructure and Strength Properties. Mater. Des. 2012, 40, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugarajan, B.; Padmanabham, G. Fusion welding studies using laser on Ti–SS dissimilar combination. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, G.; Yao, Y.L.; Qiu, C. Strength and microstructure of laser fusion-welded Ti–SS dissimilar material pair. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 66, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleiro, A.J.; Ramos, A.S.; Braz Fernandes, F.M.; Schell, N.; Vieira, M.T. In situ characterization of NiTi/Ti6Al4V joints during reaction-assisted diffusion bonding using Ni/Ti multilayers. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1625–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashchuk, I.; Sallamand, P.; Andrzejewski, H.; Grevey, D. The formation of intermetallics in dissimilar Ti6Al4V/copper/AISI 316 L electron beam and Nd:YAG laser joints. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashchuk, I.; Sallamand, P.; Belyavina, N.; Pilloz, M. Evolution of microstructures and mechanical properties during dissimilar electron beam welding of titanium alloy to stainless steel via copper interlayer. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 585, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomashchuk, I.; Grevey, D.; Sallamand, P. Dissimilar laser welding of AISI 316L stainless steel to Ti6–Al4–6V alloy via pure vanadium interlayer. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 622, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, D.; Cai, X.; Dong, P.; Gu, X. Laser welding of TiNi shape memory alloy and stainless steel using Co filler metal. Opt. Laser Technol. 2013, 45, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, D.; Gu, X.; Dong, P.; Lv, Z. Effects of the thickness of Cu filler metal on the microstructure and properties of laser-welded TiNi alloy and stainless steel joint. Mater. Des. 2013, 50, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouquet, J.; Miranda, R.M.; Quintino, L.; Williams, S. Dissimilar Laser Welding of Nitinol to Stainless Steel. Int. J. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2012, 61, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gugel, H.; Schuermann, A.; Theisen, W. Laser welding of NiTi wires. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 481–482, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannod, J.; Bornert, M.; Bidaux, J.-E.; Bataillard, L.; Karimi, A.; Drezet, J.-M.; Rappaz, M.; Hessler-Wyser, A. Mechanical and microstructural integrity of nickel–titanium and stainless steel laser joined wires. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 6538–6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretsky, J.; Ryba, E.R. Laser welding of dissimilar metals: Titanium to nickel. Weld. J. 1976, 55, 208–211. Available online: https://files.aws.org/wj/supplement/WJ_1976_07_s208.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Sun, Z.; Karppi, R. The Application of Electron Beam Welding for the Joining of Dissimilar Metals—An Overview. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1996, 59, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, P.; Feng, J.; Wu, H. Interfacial Microstructure and Strength of the Dissimilar Joint Ti3Al/TC4 Welded by the Electron Beam Process. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 425, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Mei, S.W.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, X.Y.; Zeng, X.Y. Characterisation of Laser Welded Dissimilar Ti/steel Joint Using Mg interlayer. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2012, 17, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Feng, J.; Tang, Q. Effect of a Copper Filler Metal on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Electron Beam Welded Titanium–stainless Steel Joint. Mater. Charact. 2012, 73, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, T.; Chen, G.; Feng, J. Contact Reactive Joining of TA15 and 304 Stainless Steel Via a Copper interlayer Heated by Electron Beam with a Beam Deflection. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2067–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift-Hook, D.T.; Gick, A.E.F. Penetration Welding with Lasers. Weld. J. 1973, 52, 492–499. Available online: https://files.aws.org/wj/supplement/WJ_1973_11_s492.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2022).
- Zhan, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, Y.; Mao, Y. Prevention of crack formation in electron-beam welded joints of dissimilar metal compounds (TiNi_Ti6Al4V). Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2019, 61, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xue, L.; King, M.; Campbell, G. High power CW YAG laser weldability of dissimilar Ti to Ni metal plates through beam shift. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Huang, Y.J.; Shagiev, M.; Shena, J. Laser Welding ofTi40Zr25Ni3Cu12Be20 Bulk Metallic Glass. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 541, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


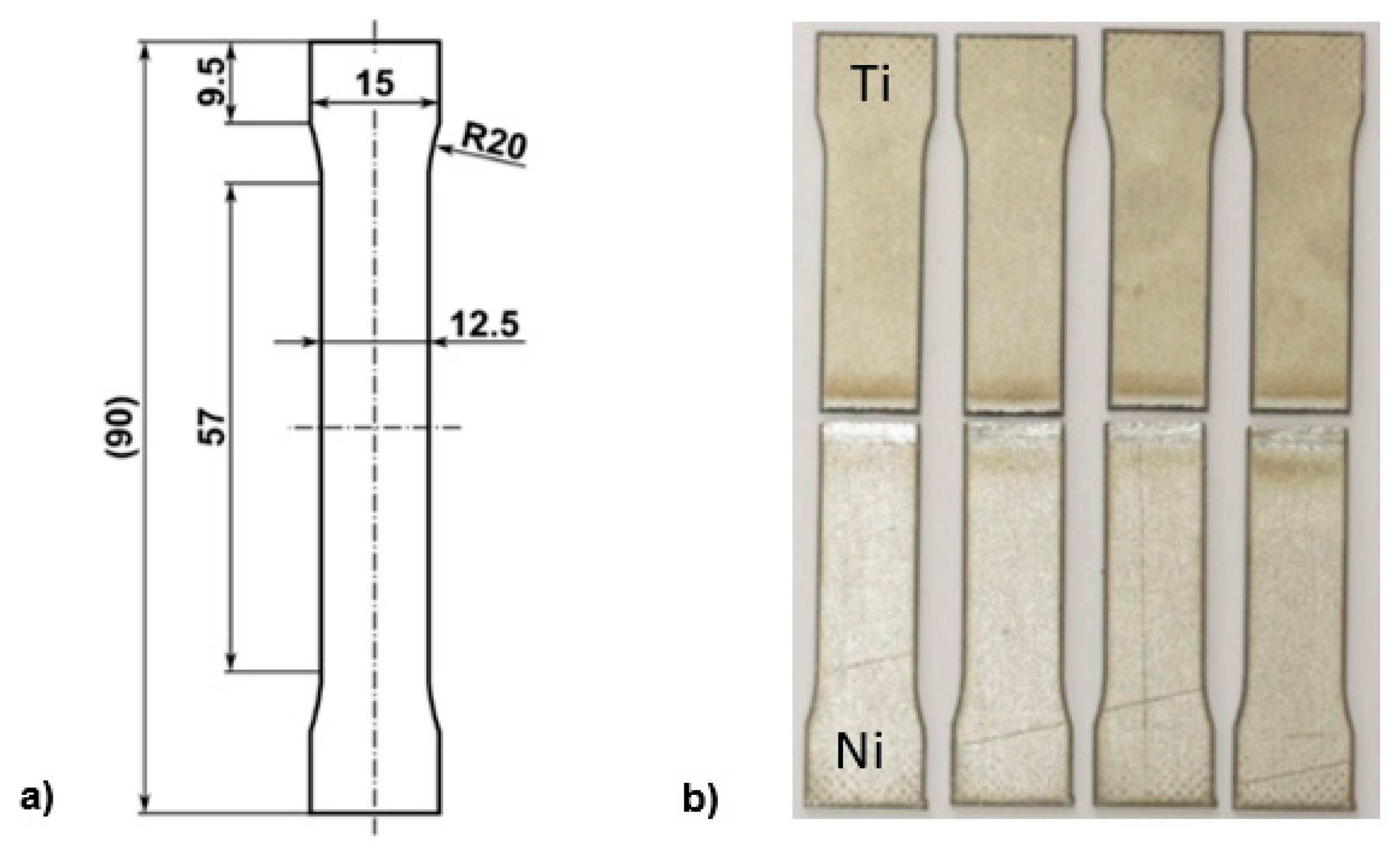








| Fe | Mn | Si | C | S | Cu | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.40 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.25 | Balance |
| Fe | C | O | H | N | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.015 | 0.03 | Balance |
| Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) | Yield Strength Rp0.2 (MPa) | Ductility (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 345 | 70 | 40 |
| Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) | Yield Strength Rp0.2 (MPa) | Ductility (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 485 | 350 | 20 |
| Welded Joint No. | Accelerating Voltage [kV] | Welding Current [mA] | Welding Speed [mm/s] | Focusing Current [mA] | Heat Input [J/mm] | Beam Offset [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 55 | 60 | 30 | 890 | 110 | 0 |
| 2 | 55 | 60 | 30 | 890 | 110 | +100 Ni |
| 3 | 55 | 60 | 30 | 890 | 110 | +200 Ni |
| 4 | 55 | 60 | 30 | 890 | 110 | +300 Ni |
| 5 | 55 | 60 | 30 | 890 | 110 | −200 Ti |
| 6 | 55 | 50 | 30 | 890 | 91.67 | 0 |
| 7 | 55 | 40 | 30 | 890 | 73.33 | 0 |
| 8 | 55 | 70 | 30 | 890 | 128.3 | 0 |
| 9 | 55 | 50 | 20 | 890 | 137.5 | 0 |
| 10 | 55 | 50 | 40 | 890 | 68.75 | 0 |
| 11 | 55 | 50 | 50 | 890 | 55 | 0 |
| 12 | 55 | 40 | 40 | 890 | 55 | 0 |
| 13 | 55 | 40 | 30 | 890 | 73.33 | 0 |
| 14 | 55 | 40 | 20 | 890 | 110 | 0 |
| 15 | 55 | 60 | 20 | 890 | 165 | 0 |
| 16 | 55 | 60 | 30 | 890 | 110 | 0 |
| Welded Joint No. | Channel Voltage A [mV] | Channel Voltage B [mV] | Frequency [Hz] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| 16 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Welded Joint No. | Width of the Weld Bead [mm] | Width of the Weld Root [mm] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.485 | 2.104 |
| 6 | 2.402 | 1.424 |
| 8 | 2.686 | 1.493 |
| 10 | 2.670 | 1.580 |
| Spectrum | Ti | Ni |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 2. | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 3. | 0.31 | 99.69 |
| 4. | 4.59 | 95.41 |
| 5. | 45.45 | 54.55 |
| 6. | 65.07 | 34.93 |
| 7. | 50.73 | 49.27 |
| 8. | 66.52 | 33.48 |
| 9. | 51.44 | 48.56 |
| 10. | 50.85 | 49.15 |
| Spectrum | Ti | Ni |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 0.00 | 100.00 |
| 2. | 21.92 | 78.08 |
| 3. | 45.91 | 54.09 |
| 4. | 49.35 | 50.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šimeková, B.; Hodúlová, E.; Kovačócy, P.; Kovaříková, I.; Sahul, M.; Sahul, M.; Pašák, M.; Pixner, F. Influence of Electron Beam Welding Parameters on the Microstructure Formation and Mechanical Behaviors of the Ti and Ni Dissimilar Metals Welded Joints. Metals 2022, 12, 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060894
Šimeková B, Hodúlová E, Kovačócy P, Kovaříková I, Sahul M, Sahul M, Pašák M, Pixner F. Influence of Electron Beam Welding Parameters on the Microstructure Formation and Mechanical Behaviors of the Ti and Ni Dissimilar Metals Welded Joints. Metals. 2022; 12(6):894. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060894
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠimeková, Beáta, Erika Hodúlová, Pavel Kovačócy, Ingrid Kovaříková, Miroslav Sahul, Martin Sahul, Matej Pašák, and Florian Pixner. 2022. "Influence of Electron Beam Welding Parameters on the Microstructure Formation and Mechanical Behaviors of the Ti and Ni Dissimilar Metals Welded Joints" Metals 12, no. 6: 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060894
APA StyleŠimeková, B., Hodúlová, E., Kovačócy, P., Kovaříková, I., Sahul, M., Sahul, M., Pašák, M., & Pixner, F. (2022). Influence of Electron Beam Welding Parameters on the Microstructure Formation and Mechanical Behaviors of the Ti and Ni Dissimilar Metals Welded Joints. Metals, 12(6), 894. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12060894







