Selective Laser Melting of Free-Assembled Stainless Steel 316L Hinges: Optimization of Volumetric Laser Energy Density and Joint Clearance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
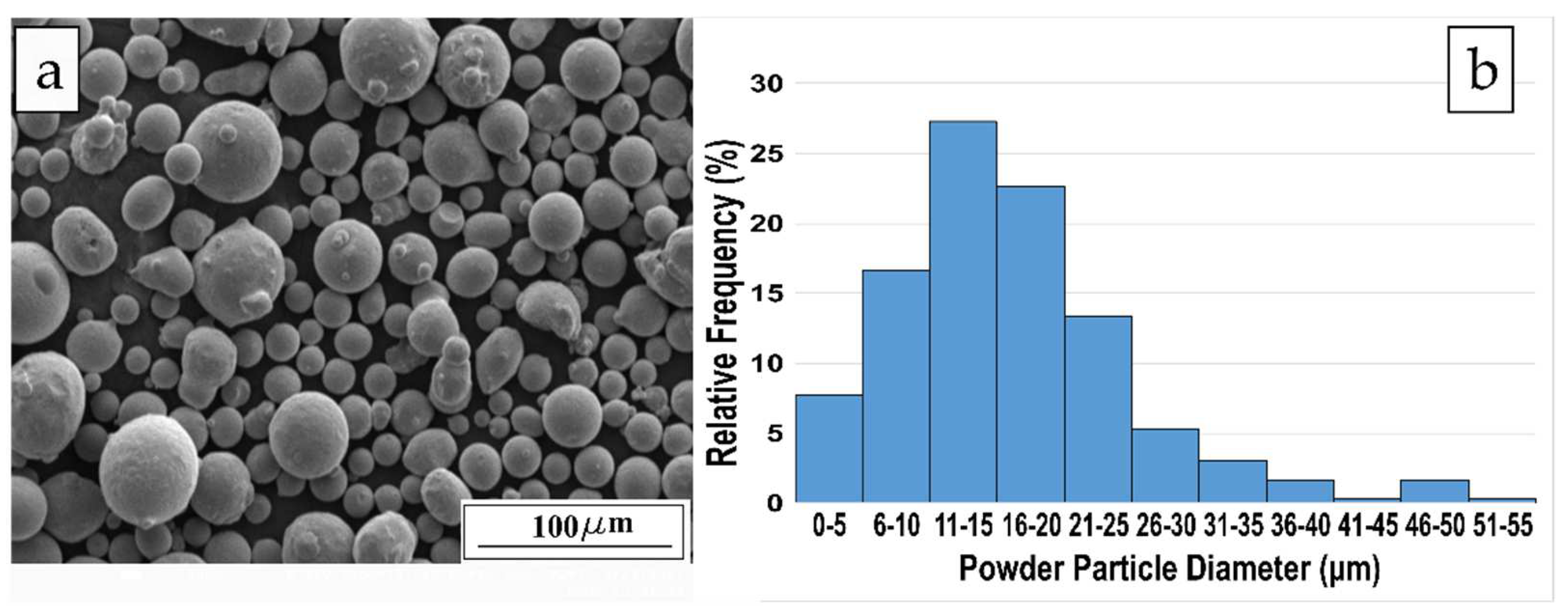
2.1. Material
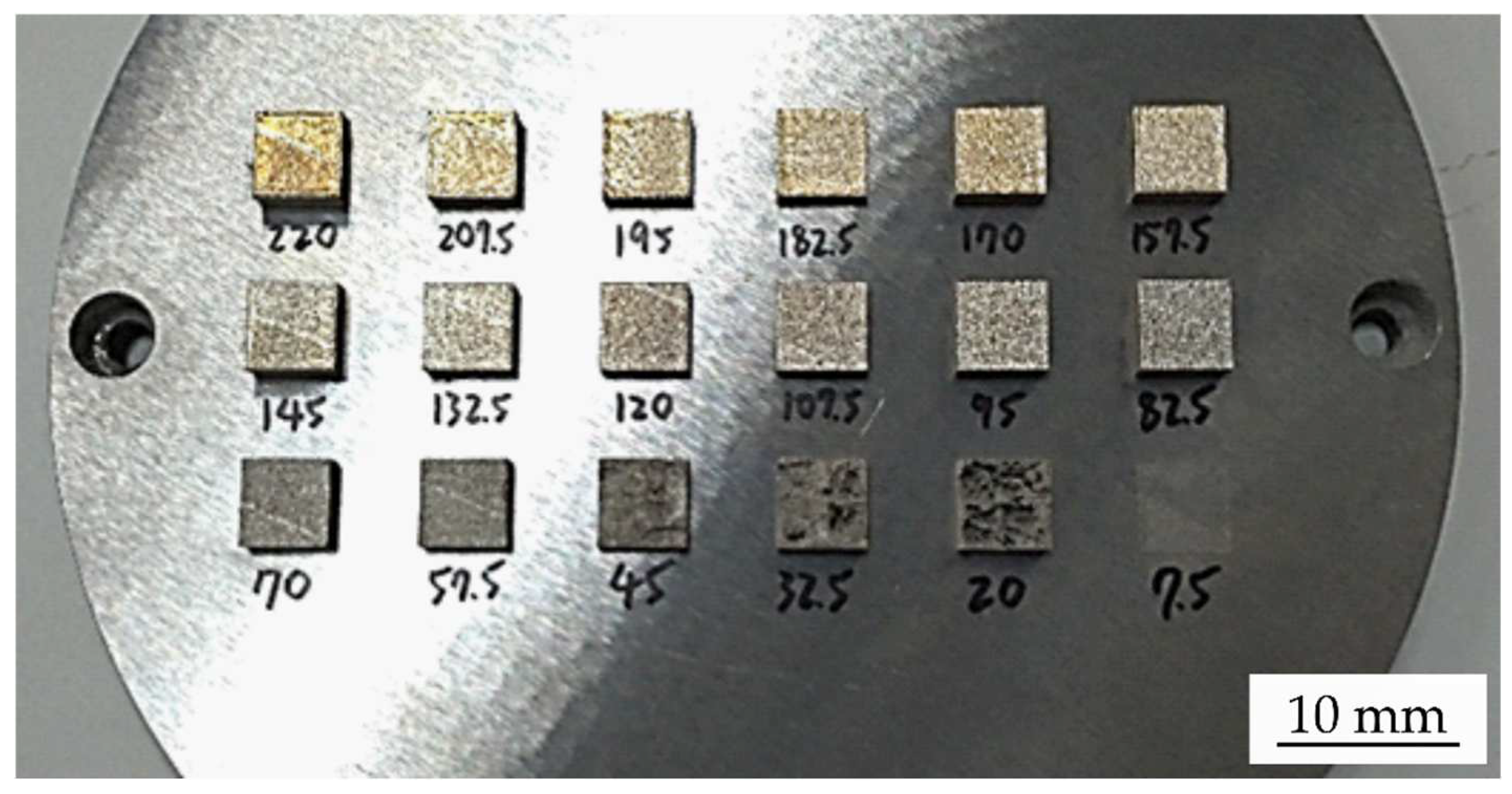
2.2. Optimization of Laser Energy Density
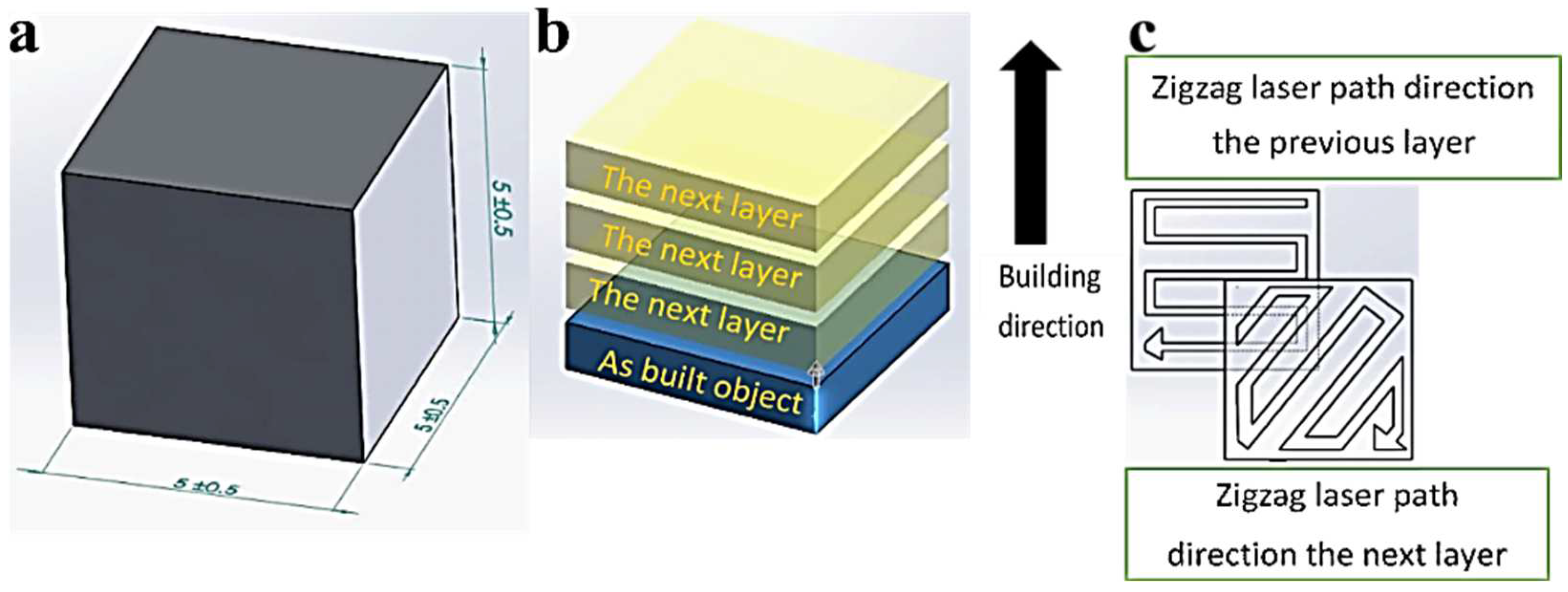
2.3. Testing of Laser Parameter Processing Performances
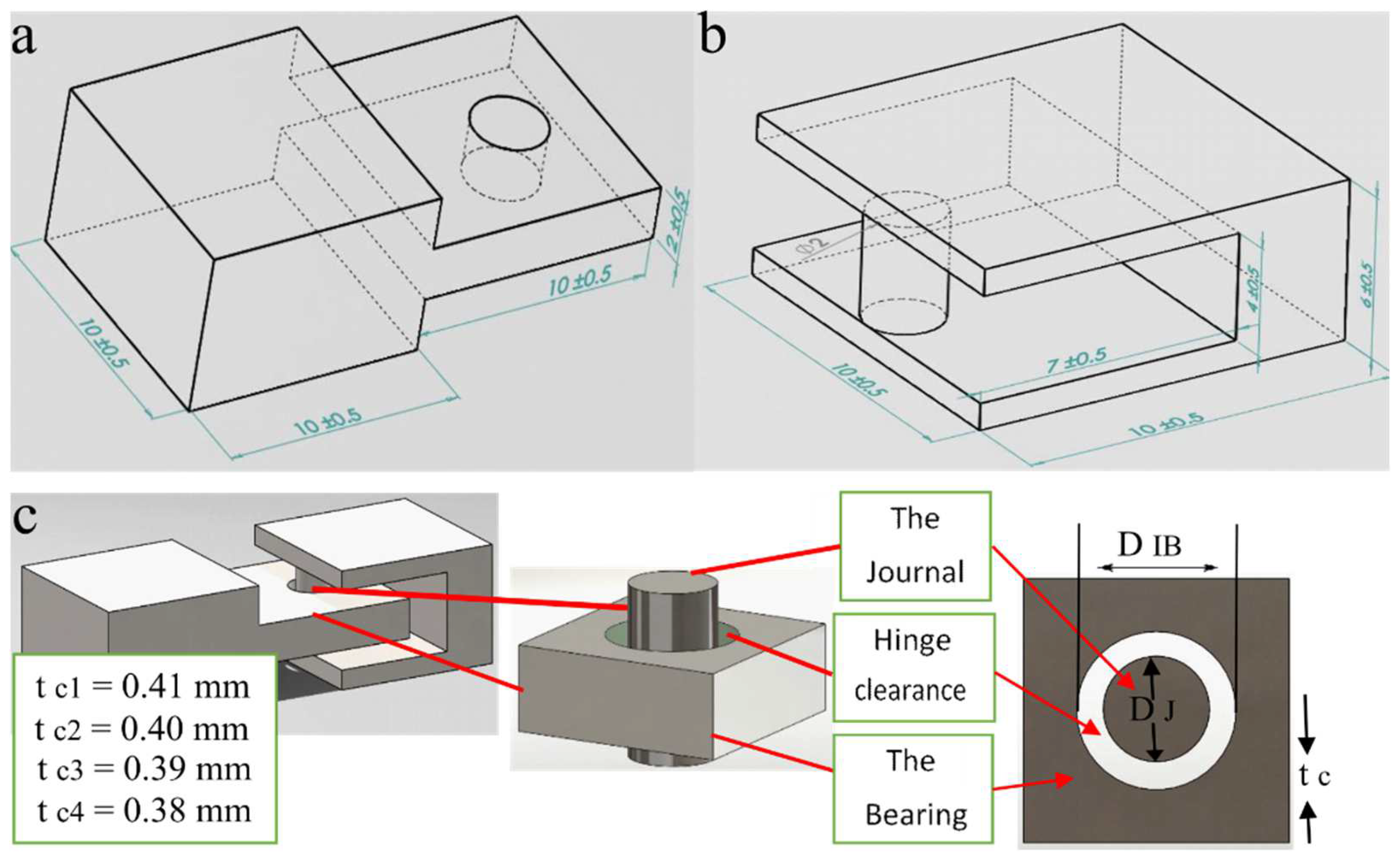
2.4. Design of Hinges
2.5. SLM Process for the Hinge and Test
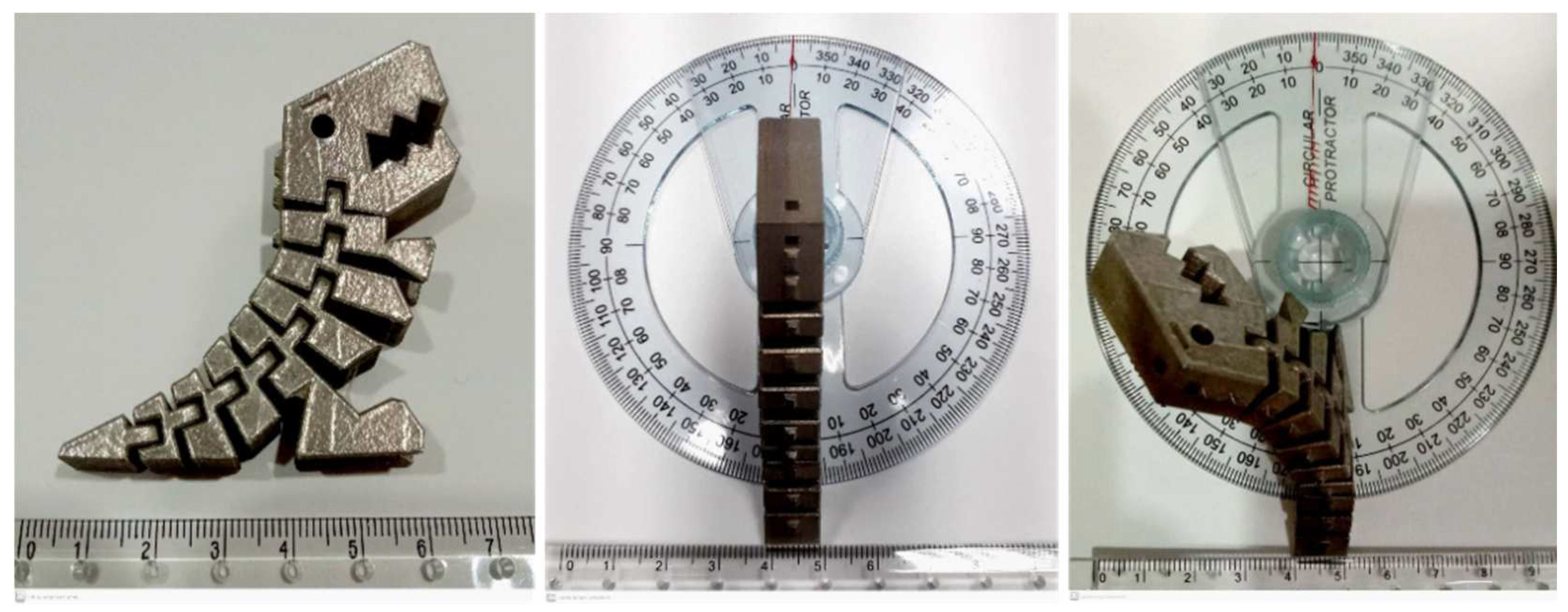
2.6. Case Implementation of Free-Assembled Hinges in Dinosaur Model
3. Results and Discussion
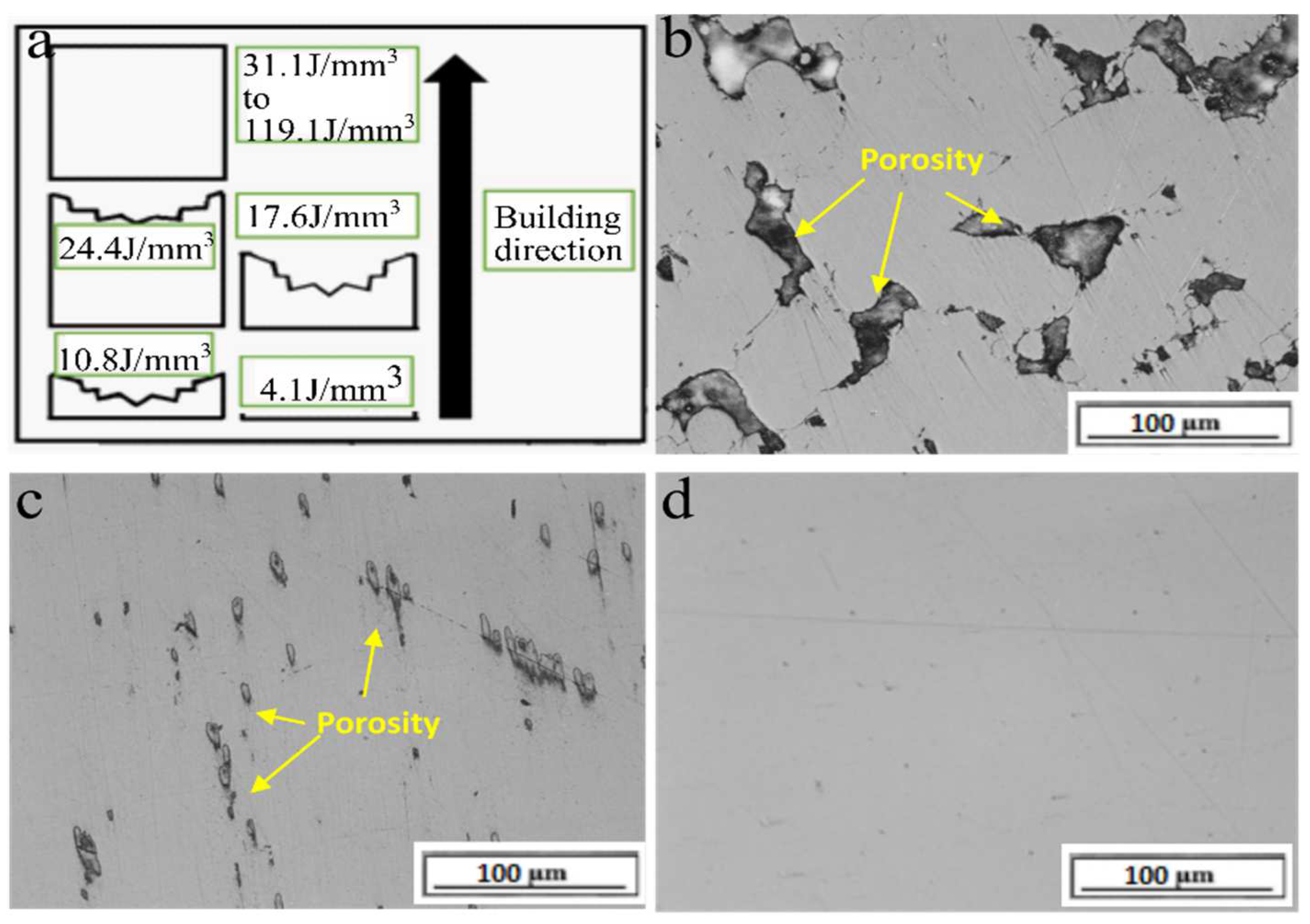
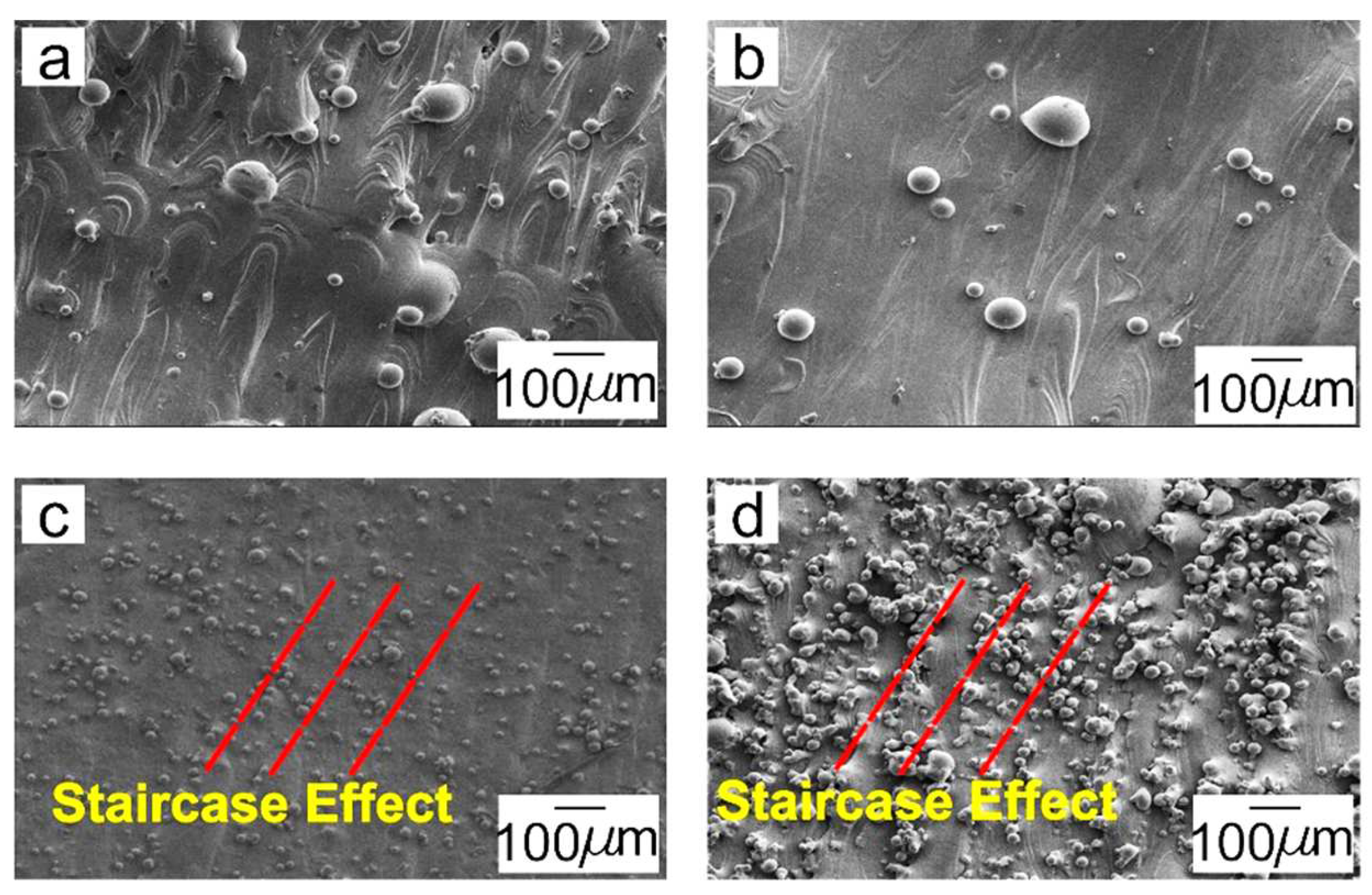
3.1. The Effect of Laser Energy Density on Porosity of Fabricated Specimens
3.2. The Effect of Laser Power and Energy Density on Hardness in Fabricated Specimens
3.3. The Fabricated Hinges
3.4. Case Implementation
4. Conclusions
- The enhancement of volumetric laser energy density ranging from 31.1 J/mm3 to 119.1 J/mm3, controlled by increasing the laser power from 57.5 W to 220 W with the constant scanning speed of 700 mm/s, layer thickness of 30 μm, and hatch space of 88.8 μm, results in the decrease in the porosity and increase in the densification of 316L. The volumetric laser energy densities from 71.7 J/mm3 to 119.1 J/mm3 generated the 3D 316L object with less than 1% porosity and densification of more than 99%.
- The reduction in porosity increases the hardness properties. The laser energy densities of 105.5 J/mm3, 112.3 J/mm3, and 119.1 J/mm3 are considered as the optimized laser power parameters since they produce 316L with a hardness value close to 210 HV. This hardness value is similar to the average hardness of 316L that is manufactured using other pre-existing methods.
- The minimum clearance design for hinge joints that can be fabricated using the optimized laser parameters in this work is 0.41 mm. The enhancement of laser power leads to restrictions in the hinges’ movement ability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calì, J.; Calian, D.A.; Amati, C.; Kleinberger, R.; Steed, A.; Kautz, J.; Weyrich, T. 3d-printing of non-assembly, articulated models. ACM Trans. Graph. 2012, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laurentis, K.J.; Mavroidis, C. Rapid fabrication of a non-assembly robotic hand with embedded components. Assem. Autom. 2004, 24, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneci, C.A.; Shang, J.; Darzi, A.; Yang, G.Z. Rapid manufacturing with selective laser melting for robotic surgical tools: Design and process considerations. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lu, J. Minimize joint clearance in rapid fabrication of non-assembly mechanisms. Int. J. Comput. 2011, 24, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y. Digital assembly and direct fabrication of mechanism based on selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2013, 19, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, D.; Vijayalakshmi, K. Novel synthesis of bioactive hydroxyapatite/f-multiwalled carbon nanotube composite coating on 316L SS implant for substantial corrosion resistance and antibacterial activity. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 777, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasu, A.; Czekanski, A.; Boakye, Y.S. Effect of laser powder bed fusion parameters on the microstructural evolution and hardness of 316l stainless steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. 2021, 113, 2651–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Gutzeit, K.; Hotz, H.; Kirsch, B.; Aurich, J.C. Selective laser melting (slm) of aisi 316L|impact of laser power, layer thickness, and hatch spacing on roughness, density, and microhardness at constant input energy density. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. 2020, 108, 1551–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.-P.; Wibisono, A.T.; Pasang, T. Selective laser melting of stainless steel 316l with face-centered-cubic-based lattice structures to produce rib implants. Materials 2021, 14, 5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottger, A.; Boes, J.; Theisen, W.; Thiele, M.; Esen, C.; Edelmann, A.; Hellmann, R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L austenitic stainless steel processed by different SLM devices. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. 2020, 108, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschetto, A.; Bottini, L. Manufacturability of non-assembly joints fabricated in AlSi10Mg by selective laser melting. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugwagwa, L.; Dimitrov, D.; Matope, S.; Yadroitsev, I. Influence of process parameters on residual stress related distortions in selective laser melting. Procedia Manuf. 2018, 21, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Han, G. Properties of 316l formed by a 400 w power laser selective laser melting with 250 mm layer thickness. Powder Technol. 2020, 360, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wei, H.; Liu, A.; Zhang, Y. Multi-index co-evaluation of metal laser direct deposition: An investigation of energy input effect on energy efficiency and mechanical properties of 316L parts. J. Manuf. Process. 2022, 76, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wei, P.; Lu, B.; Zhang, L.; Du, J. Thermal dynamic behavior during selective laser melting of k418 superalloy: Numerical simulation and experimental verification. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Shi, W.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J. Study on performance optimization of 316l stainless steel parts by high-efficiency selective laser melting. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 138, 106872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, M.; Elbestawi, M.; Veldhuis, S.C. On the characterization of stainless steel 316l parts produced by selective laser melting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 95, 1953–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakout, M.; Elbestawi, M.; Veldhuis, S.C. A study of thermal expansion coefficients and microstructure during selective laser melting of Invar 36 and stainless steel 316L. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 24, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Jia, X.; Gu, R.; Zhou, P.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Yan, M. 316l stainless steel manufactured by selective laser melting and its biocompatibility with or without hydroxyapatite coating. Metals 2018, 8, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayyab, K.B.; Farooq, A.; Alvi, A.A.; Nadeem, A.B.; Deen, K. Corrosion behavior of cold-rolled and post heat-treated 316L stainless steel in 0.9 wt% NaCl solution. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2021, 28, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J. Study on the influence of process parameters on the clearance feature in non-assembly mechanism manufactured by selective laser melting. J. Manuf. Processes. 2017, 27, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, Y.C.; Gwang, Y.S.; Do, S.K. Effect of laser remelting on the surface characteristics of 316L stainless steel fabricated via direct energy deposition. J. Mater. Ses. Technol. 2021, 15, 5814–5832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahshwan, M.; Gee, M.; Nunn, J.; Myant, C.W.; Reddyhoff, T. In situ observation of anisotropic tribological contact evolution in 316l steel formed by selective laser melting. Wear 2022, 490, 204193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Chen, Y.; Nien, Y. Effects of energy parameters on dimensional accuracy when joining stainless-steel powders with heterogeneous metal substrates. Materials 2021, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lussenburg, K.; Sakes, A.; Breedveld, P. Design of non-assembly mechanism: A state–of–the-art review. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 39, 101846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


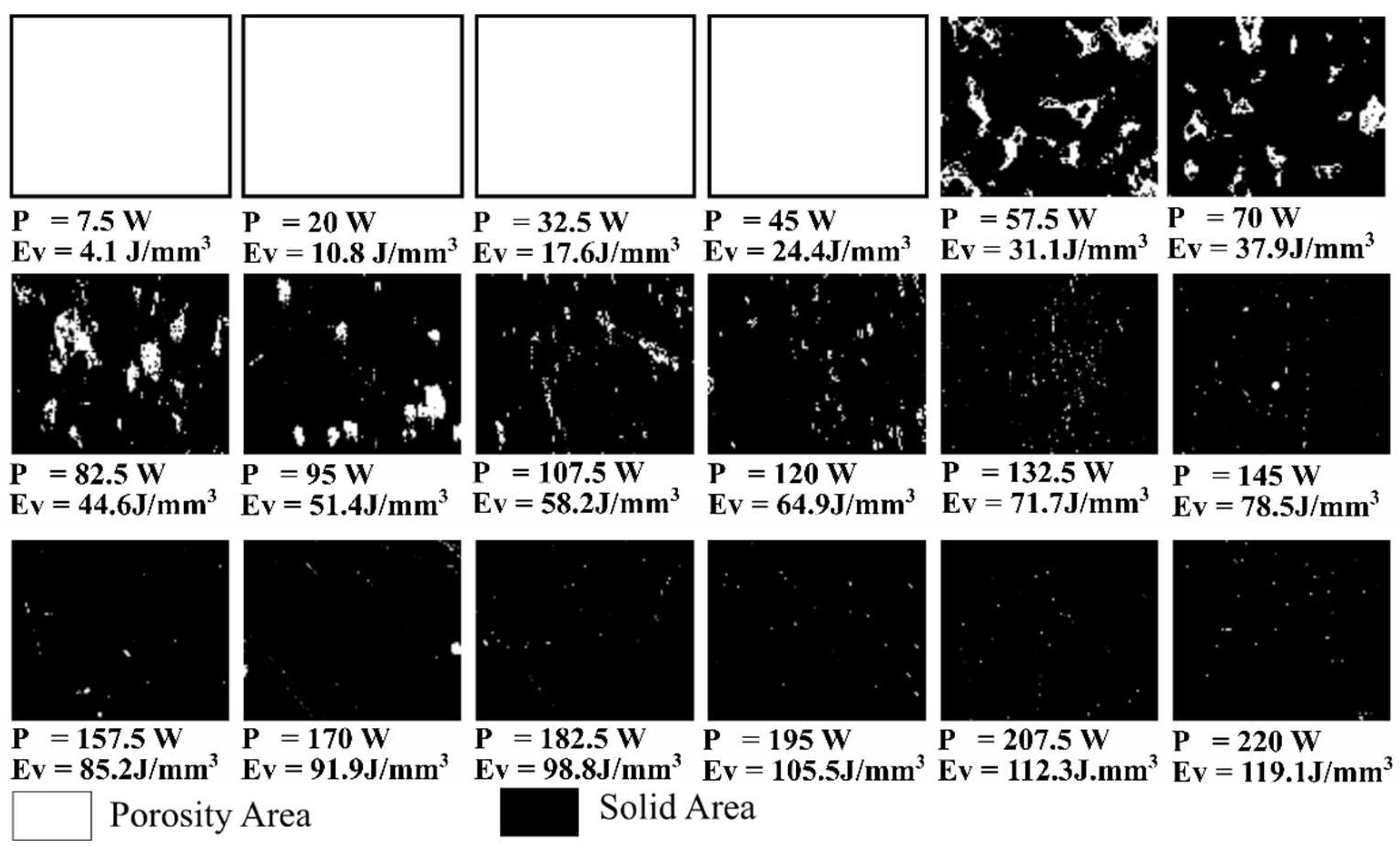

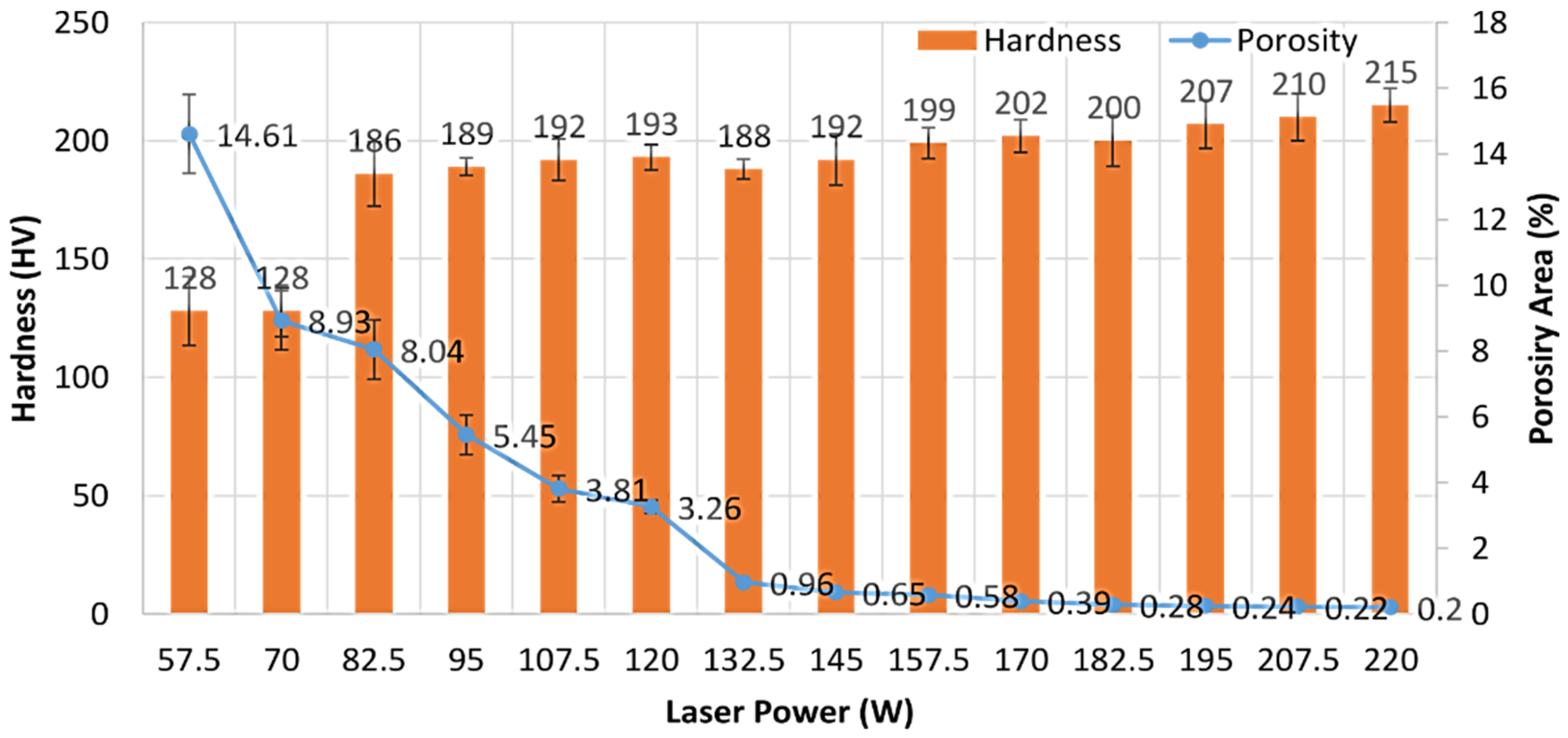
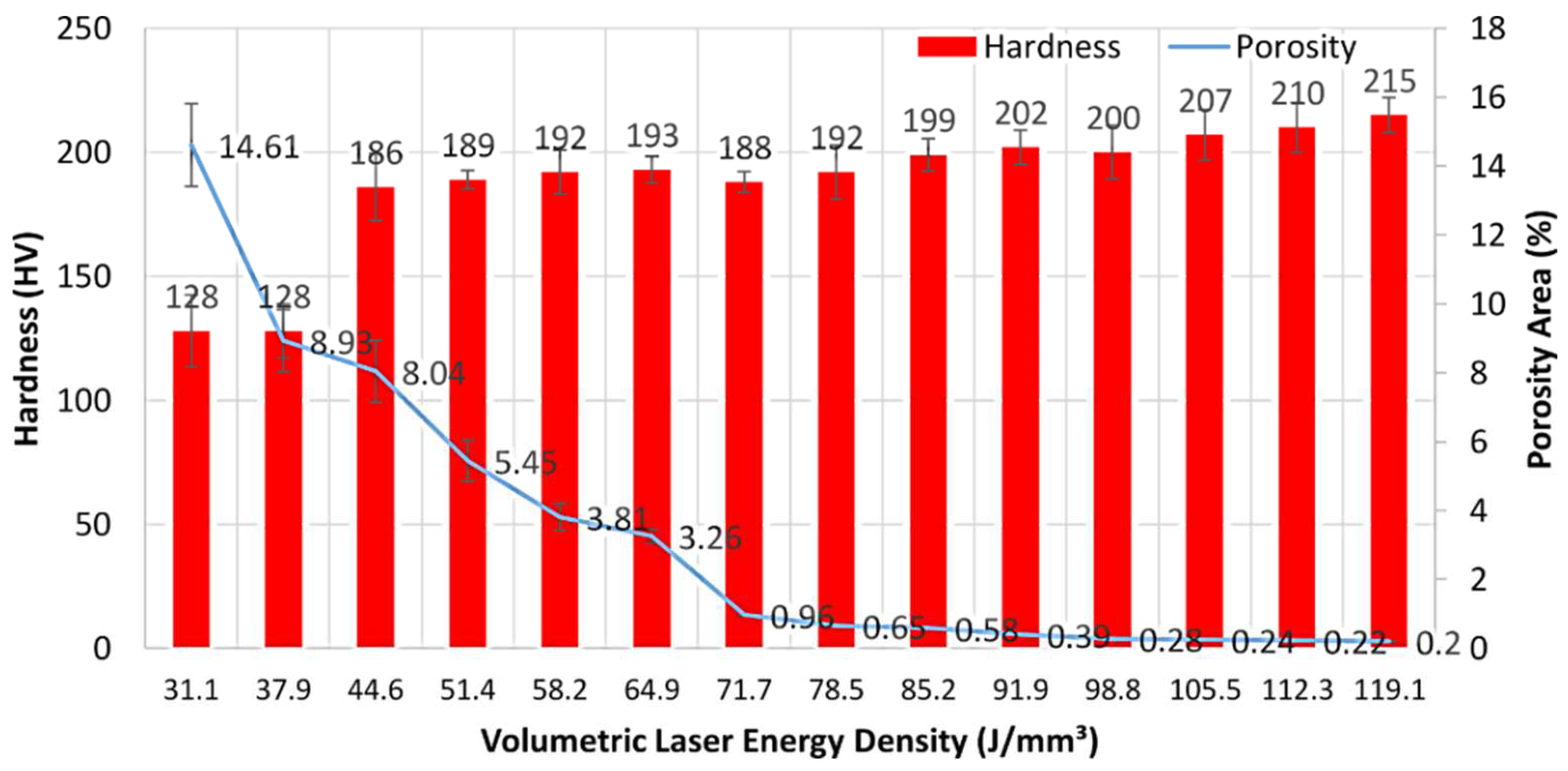
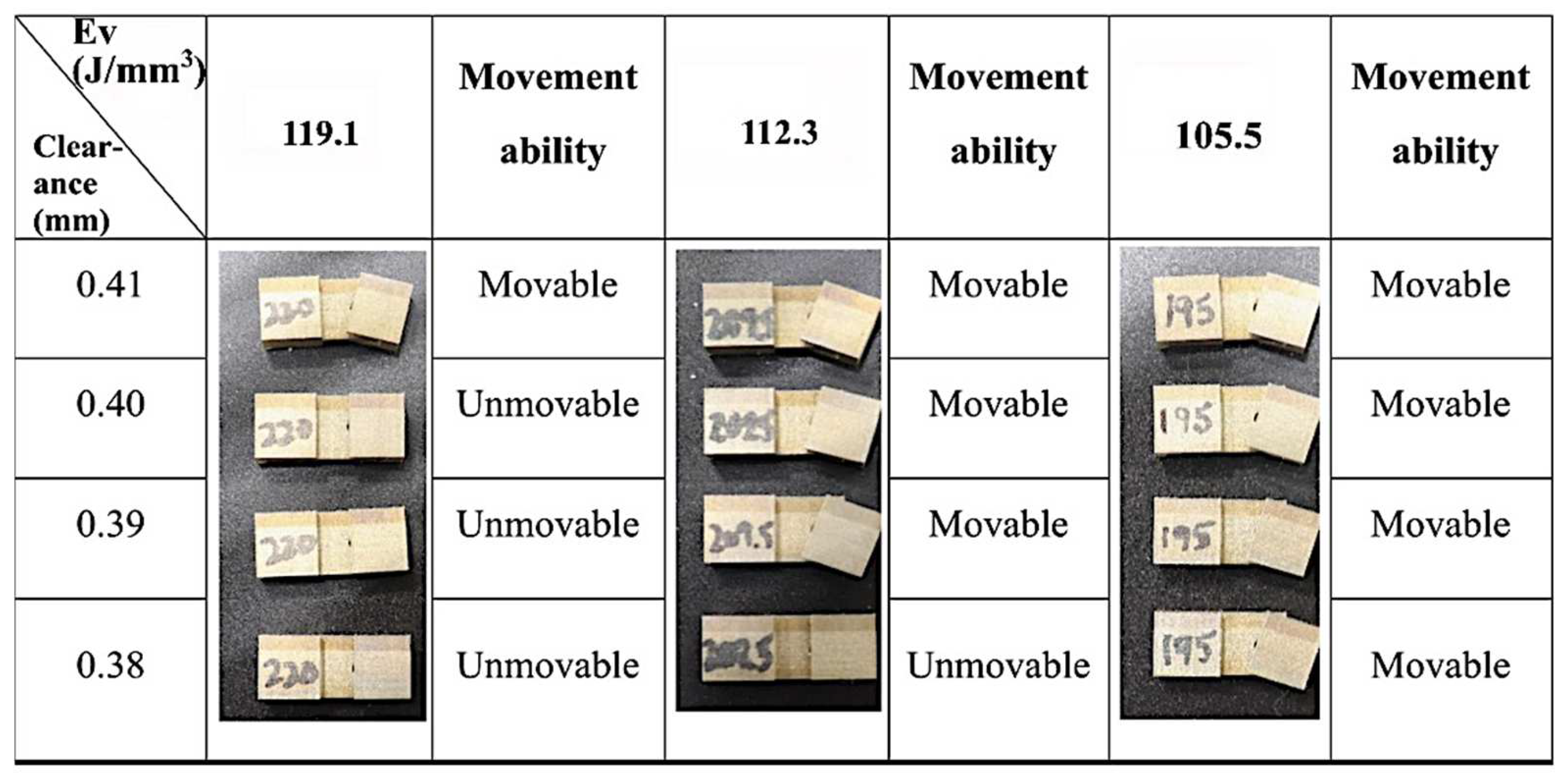
| P (W) | Ev (J/mm3) | Porosity (%) | ρcal-rel (%) | ρcal (g/cm3) | Hardness (HV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 57.5 | 31.1 | 14.61 ± 1.2 | 85.39 ± 1.2 | 6.83 ± 0.096 | 128 ± 14.5 |
| 70 | 37.9 | 8.93 ± 0.9 | 91.07 ± 0.9 | 7.29 ± 0.072 | 128 ± 10.9 |
| 82.5 | 44.6 | 8.04 ± 0.9 | 91.96 ± 0.9 | 7.36 ± 0.072 | 186 ± 13.6 |
| 95 | 51.4 | 5.45 ± 0.6 | 94.55 ± 0.6 | 7.56 ± 0.048 | 189 ± 3.7 |
| 107.5 | 58.2 | 3.81 ± 0.4 | 96.19 ± 0.4 | 7.69 ± 0.032 | 192 ± 8.8 |
| 120 | 64.9 | 3.26 ± 0.2 | 96.74 ± 0.2 | 7.73 ± 0.016 | 193 ± 5.4 |
| 132.5 | 71.7 | 0.96 ± 0.01 | 99.04 ± 0.01 | 7.92 ± 0.008 | 188 ± 4.2 |
| 145 | 78.5 | 0.65 ± 0.01 | 99.35 ± 0.01 | 7.94 ± 0.008 | 182 ± 10.8 |
| 157.5 | 85.2 | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 99.42 ± 0.01 | 7.96 ± 0.008 | 188 ± 6.5 |
| 170 | 91.9 | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 99.61 ± 0.01 | 7.97 ± 0.008 | 202 ± 6.9 |
| 182.5 | 98.8 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 99.72 ± 0.01 | 7.97 ± 0.008 | 200 ± 10.8 |
| 195 | 105.5 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 99.76 ± 0.01 | 7.98 ± 0.008 | 207 ± 10.2 |
| 207.5 | 112.3 | 0.22 ± 0.01 | 99.78 ± 0.01 | 7.98 ± 0.008 | 210 ± 9.8 |
| 220 | 119.1 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 99.80 ± 0.01 | 7.98 ± 0.008 | 215 ± 7.1 |
| P (W) | v (mm/s) | h (mm) | t (mm) | Ev (J/mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 195 | 700 | 0.089 | 0.030 | 105.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, C.-P.; Wibisono, A.T.; Wang, S.-H.; Pasang, T.; Ramezani, M. Selective Laser Melting of Free-Assembled Stainless Steel 316L Hinges: Optimization of Volumetric Laser Energy Density and Joint Clearance. Metals 2022, 12, 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071223
Jiang C-P, Wibisono AT, Wang S-H, Pasang T, Ramezani M. Selective Laser Melting of Free-Assembled Stainless Steel 316L Hinges: Optimization of Volumetric Laser Energy Density and Joint Clearance. Metals. 2022; 12(7):1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071223
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Cho-Pei, Alvian Toto Wibisono, Shun-Hsien Wang, Tim Pasang, and Maziar Ramezani. 2022. "Selective Laser Melting of Free-Assembled Stainless Steel 316L Hinges: Optimization of Volumetric Laser Energy Density and Joint Clearance" Metals 12, no. 7: 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071223
APA StyleJiang, C.-P., Wibisono, A. T., Wang, S.-H., Pasang, T., & Ramezani, M. (2022). Selective Laser Melting of Free-Assembled Stainless Steel 316L Hinges: Optimization of Volumetric Laser Energy Density and Joint Clearance. Metals, 12(7), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12071223








