Residence Time Distribution (RTD) Applications in Continuous Casting Tundish: A Review and New Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Residence Time Distribution Function
3. Model of Flow Characteristics in the Tundish
3.1. Single-Strand Tundish RTD Analysis Modes
3.2. Multi-Strand Tundish RTD Analysis Modes
3.3. Application for Multi-Strand Tundish RTD Analysis Models
4. F-Curve as an Analysis Model for Multi-Flow Tundish Flow Characteristics
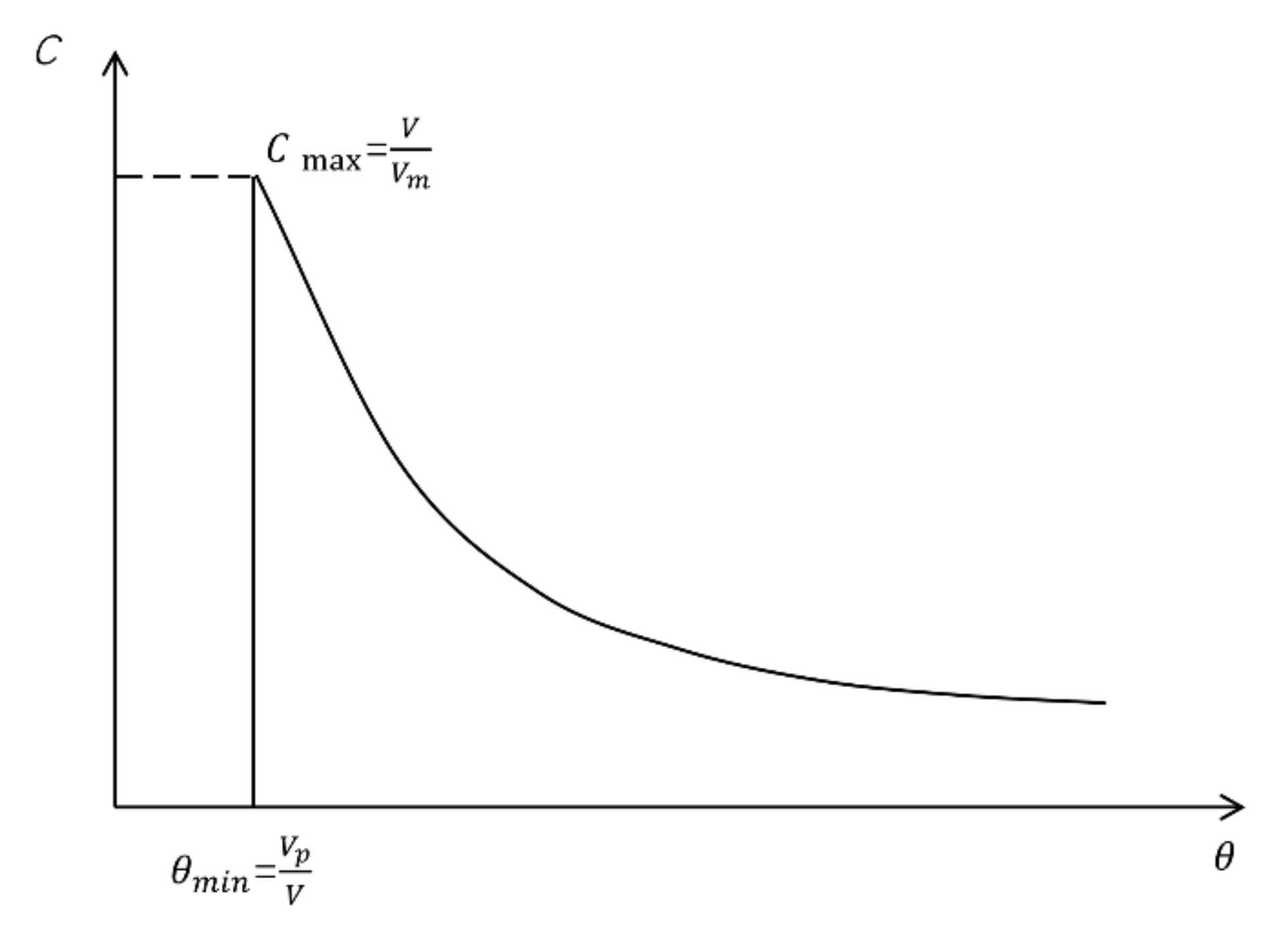
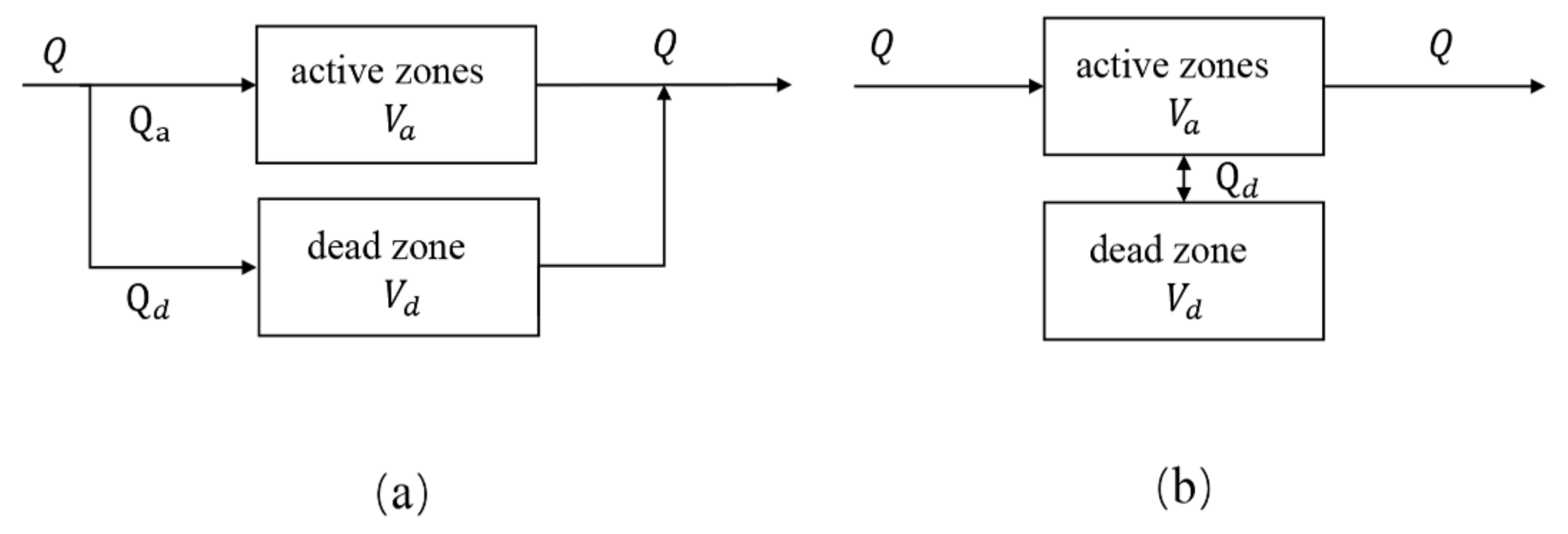
4.1. Modification of Dead Zone Calculation Method
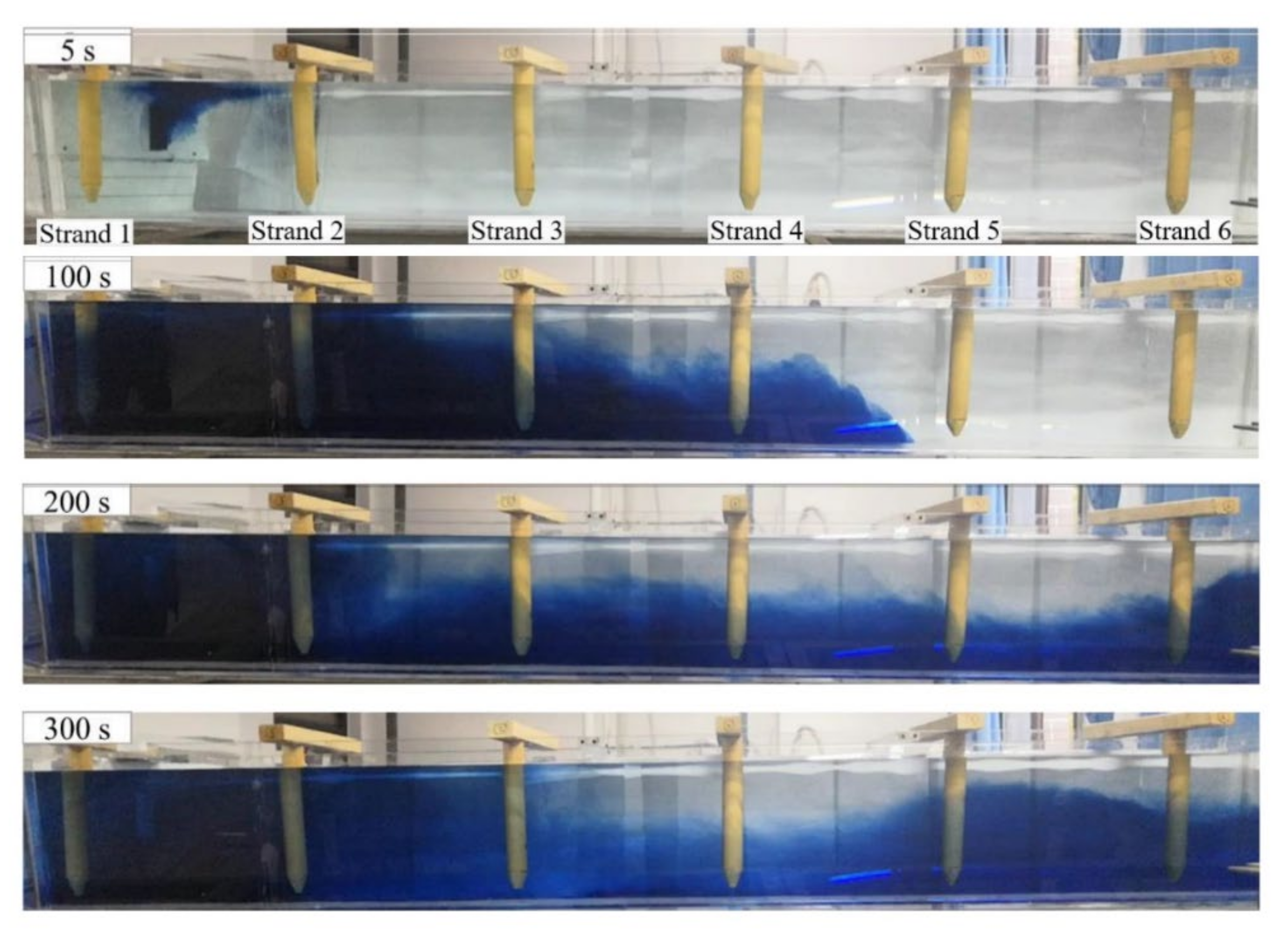
4.2. Model Application
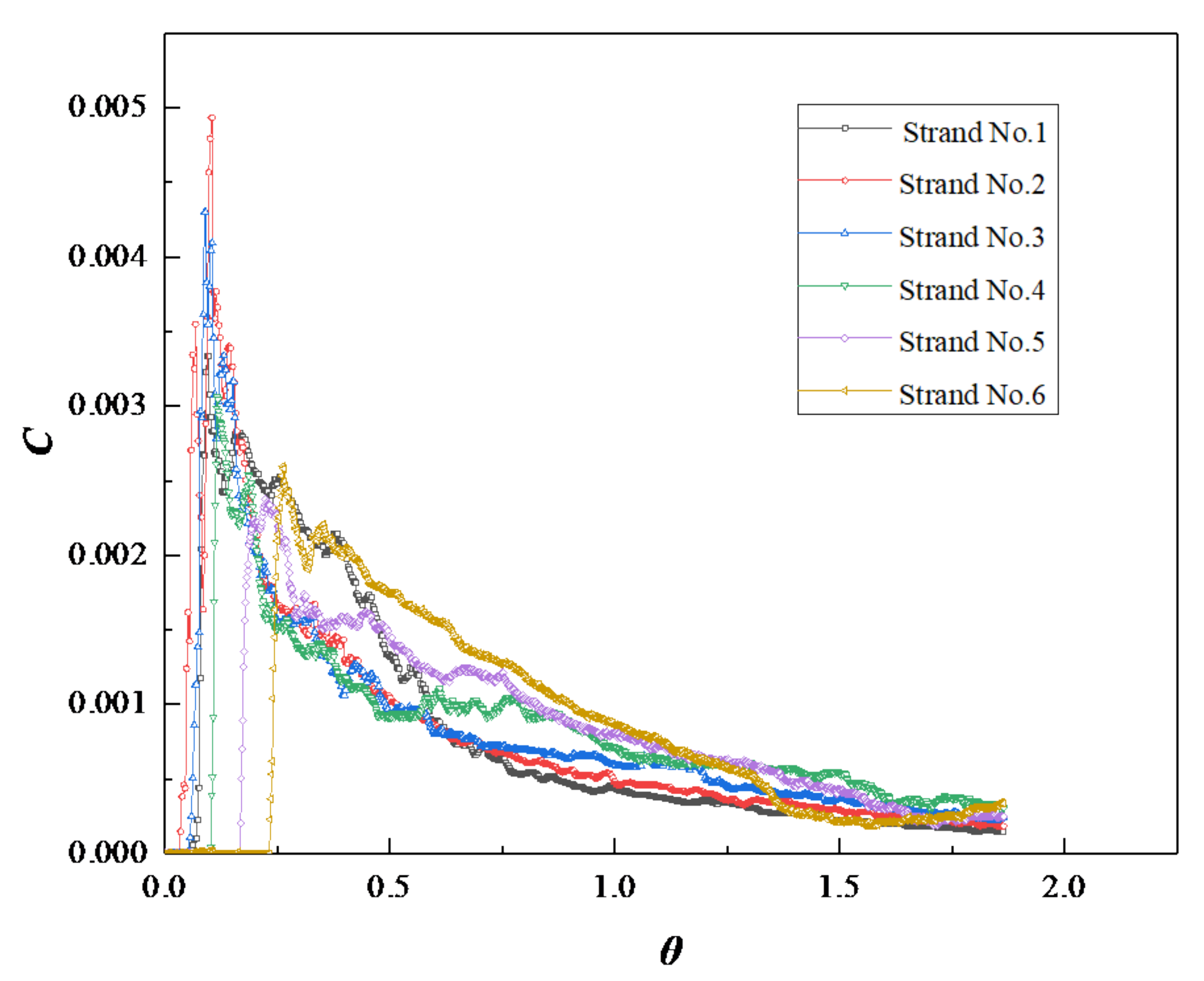
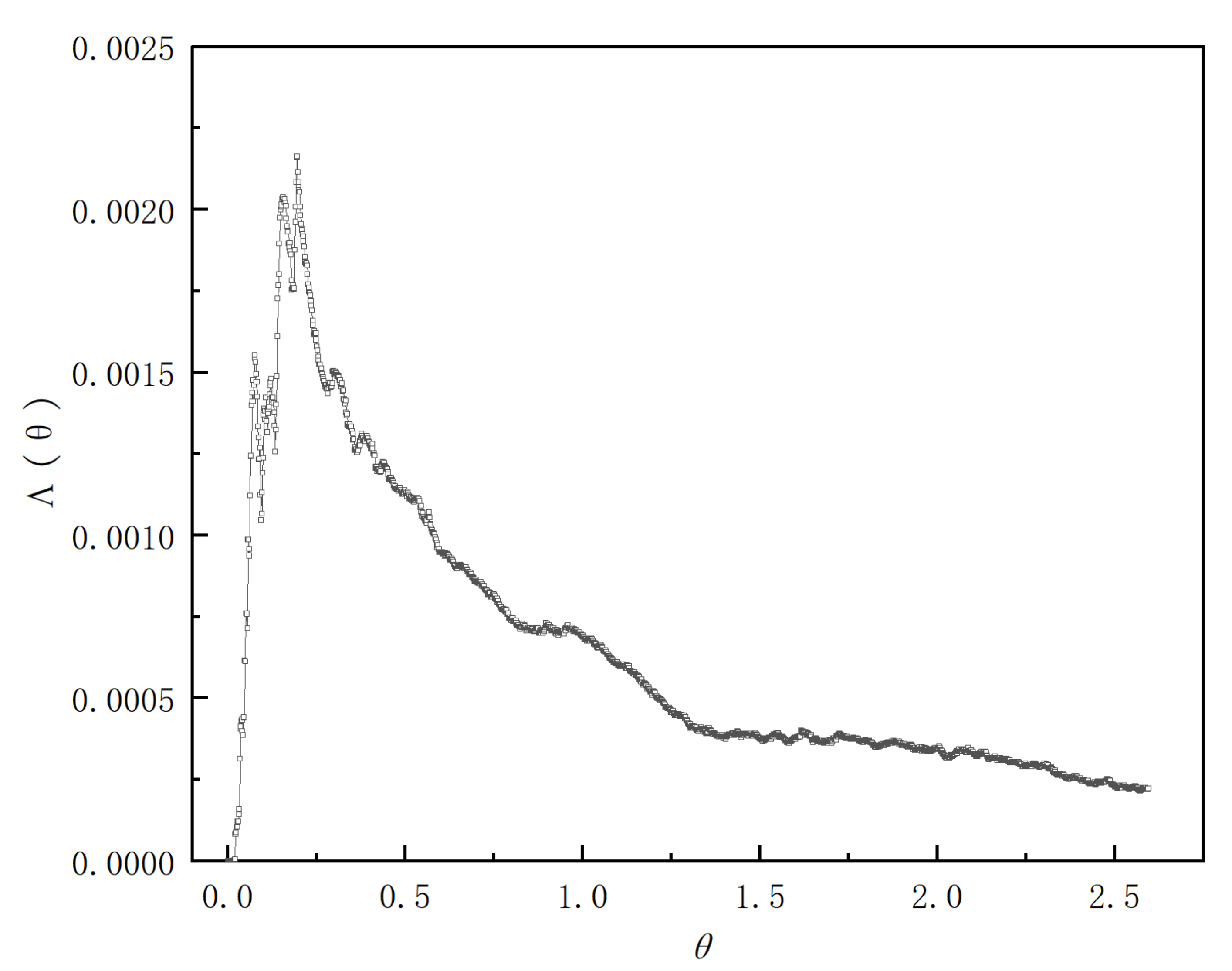
4.2.1. F-Curve and Overall Intensity Curve
4.2.2. The Dead Volume Fraction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rückert, A.; Warzecha, M.; Koitzsch, R.; Pawlik, M.; Pfeifer, H. Particle Distribution and Separation in Continuous Casting Tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2009, 80, 568–574. [Google Scholar]
- Vakhrushev, A.; Wu, M.; Ludwig, A.; Nitzl, G.; Tang, Y.; Hackl, G.; Wincor, R. A Water Experiment Benchmark to Evaluate Numerical Models for the Motion of Particles in Continuous Casting Tundish. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 88, 1600276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.-Y. Mean Age Theory in Continuous Casting Tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2022, 53, 2735–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, Y.; Emi, T. Recent, Emerging, and Novel Technologies. In Tundish Technology for Clean Steel Production; Institute of Research of Iron & Steel, Jiangsu/Sha-Steel: Zhangjiagang, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jha, P.K.; Dash, S.K.; Flow, F. Employment of different turbulence models to the design of optimum steel flows in a tundish. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2004, 14, 953–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, D.; Guthrie, R.I.L. A Comparison of three mathematical modeling procedures for simulating fluid flow phenomena in bubble-stirred ladles. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 1994, 25, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ramirez, S.; Palafox-Ramos, J.; Morales, R.D.; Barreto, J.; Zacharias, D. Modeling study of the influence of turbulence inhibitors on the molten steel flow, tracer dispersion, and inclusion trajectories in tundishes. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2001, 32, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, G.; Song, J. Water Modeling of Turbulence Inhibitor in Four Strand Rectanglar Tundish. Iron Steel 2004, 5, 23–25. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Hong, L.; Wang, W. Water modeling study on optimization of flow control device in T type tundish of six-strand caster. Iron Steel 1998, 5, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Q. Numerical simulation of the coupled fluid flow and heat transfer and optimization of flow control devices in a six-strand tundish. Acta Metall. Sin. 1999, 11, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar]
- Kemeny, F.; Harris, D.; McLean, A.; Meadowcroft, T.; Young, J. Fluid flow studies in the tundish of a slab caster. Continuous Casting of Steel. In Proceedings of the Second Process Technology Conference, Chicago, MI, USA, 23–25 February 1981; Volume 2, pp. 232–245. [Google Scholar]
- Sahai, Y.; Ahuja, R.J.I. Steel Flow and Mixing of Melt in Steelmaking Tundishes. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1986, 13, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Sahai, Y.; Emi, T. Melt flow characterization in continuous casting tundishes. Isij Int. 1996, 36, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, D.; Yamanoglu, G.; Guthrie, R.I. Hydrodynamic performance of steelmaking tundish systems: A comparative study of three different tundish designs. Steel Res. 1997, 68, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Zamora, A.; Palafox-Ramos, J.; Morales, R.D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.; Barreto-Sandoval, J.D.J. Inertial and Buoyancy Driven Water Flows under Gas Bubbling and Thermal Stratification Conditions in a Tundish Model. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2004, 35, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.G.; Zhu, M.Y. Analysis model for flow characteristics in multi-strand continuous casting tundish. Acta Metall. Sin. 2005, 41, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar]
- Solorio-Díaz, G.; Morales, R.D.; Ramos-Banderas, A. Effect of a swirling ladle shroud on fluid flow and mass transfer in a water model of a tundish. Int. J. Heat Mass Tran. 2005, 48, 3574–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Koria, S.C.; Mazumdar, D. Basis for systematic hydrodynamic analysis of a multi-strand tundish. Isij Int. 2007, 47, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.M.; Wen, G.H.; Tang, P.; Chen, Y.Q. Analytical Method for Flow Pattern in Multi-strand Tundish. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2008, 8, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.W. Mathematical model of flow characteristic in multi-strand continuous casting tundishes. Acta Metall. Sin. 2009, 22, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Qiu, S.; Peng, S. Study on the Residence Time Distribution Characteristics of T Type Eight-strand Continuous Casting Tundish. Iron Steel Vanadium Titan. 2009, 30, 46–50. [Google Scholar]
- Bensouici, M.; Bellaouar, A.; Talbi, K. Numerical Investigation of the Fluid Flow in Continuous Casting Tundish Using Analysis of RTD Curves. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2009, 16, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhao, Y.; Bao, J.L.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, H.G.; He, J.C. Whole Analysis Approach for Residue Time Distribution Curve in Multi-Strand Continuous Casting Tundish. Acta Metall. Sin. 2010, 46, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwudzinski, A. Numerical Simulation of Liquid Steel Flow in Wedge-type One-strand Slab Tundish with a Subflux Turbulence Controller and an Argon Injection System. Steel Res. Int. 2010, 81, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y. Flow Control in Six-Strand Billet Continuous Casting Tundish with Different Configurations. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2010, 17, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, N.; Bao, Y.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L. Optimization of flow control devices in a single-strand slab continuous casting tundish. Int. J. Min. Met. Mater. 2011, 18, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Jha, P.K.; Sharma, S.C.A.; Ajmani, S.K. Effect of blockage of outlet nozzle on fluid flow and heat transfer in continuously cast multistrand billet caster tundish. Can. Metall. Q. 2013, 51, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, A.; Mishra, P.; Singh, V.; Mishra, S.; Jha, P.; Ajmani, S.; Sharma, S. Physical modelling investigation of influence of strand blockage on RTD characteristics in a multistrand tundish. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 40, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Ramirez, R.; Diaz-Cruz, M.; Macias-Salinas, R. Characterisation of non-ideal flow behaviour in continuous casting tundish. Can. Metall. Q. 2013, 52, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengfu, C.; Xin, X.; Mujun, L.; Min, Z.; Leilei, Z.; Qi, L. Hydraulics and Mathematics Simulation on the Weir and Gas Curtain in Tundish of Ultrathick Slab Continuous Casting. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2014, 45, 392–398. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Zhong, L.C.; Zou, Z.S. Simulation of Flow and Heat Fields in a Seven-strand Tundish with Gas Curtain for Molten Steel Continuous-Casting. Isij Int. 2015, 55, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H. New insight into combined model and revised model for RTD curves in a multi-strand tundish. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2015, 46, 2408–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yun, M.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, G. Flow Mechanism of Molten Steel in a Single-Strand Slab Caster Tundish Based on the Residence Time Distribution Curve and Data. Isij Int. 2015, 55, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, D. Fluid Flow Characterization in Asymmetric Tundish. Isij Int. 2015, 55, 2604–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Zhang, L.Y.; Xu, Q.Y. Optimization of flow control devices for a T-type five-strand billet caster tundish: Water modeling and numerical simulation. China Foundry 2016, 13, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Cui, H.; Liu, Y.; Tian, E.H.; Du, J.X. A New Method Based on the F-curve for Characterizing Fluid Flow in Continuous Casting Tundishes. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 1237–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.-G.; Zhu, M.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Su, W. Flow characteristics and inclusion removal in a ten-strand continuous casting tundish: Physical modelling and industrial Trials. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2016, 23, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Cui, H. A method for characterizing the flow fluid in a multi-strand tundish. Chin. J. Eng. 2016, 38, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, D.; Qiu, S.; Zou, Z. Effect of Tunnel Filters on Flow Characteristics in an Eight-strand Tundish. Isij Int. 2017, 57, 1990–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, B.M.; Tavares, R.P. Description of a New Tundish Model for Treating RTD Data and Discussion of the Communication “New Insight into Combined Model and Revised Model for RTD Curves in a Multi-strand Tundish” by Lei. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2018, 49, 2128–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsihacacha, A.; Piyapaneekoon, A.; Kowitwarangkul, P. Physical water model and CFD studies of fluid flow in a single strand tundish. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 9220–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkadlečková, M.; Walek, J.; Michalek, K.; Huczala, T. Numerical Analysis of RTD Curves and Inclusions Removal in a Multi-Strand Asymmetric Tundish with Different Configuration of Impact Pad. Metals 2020, 10, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.Y.; Yue, Q. Modelling of Fluid Flow and Residence Time Distribution in a Five-strand Tundish. Metals 2020, 10, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Luo, R.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Ni, H. Optimization of flow, heat transfer and inclusion removal behaviors in an odd multistrand bloom casting tundish. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.Y.; Chen, D. Comparison of Fluid Flow and Temperature Distribution in a Single-Strand Tundish with Different Flow Control Devices. Metals 2021, 11, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.N.; Singh, N.P. Fluid Flow Characterization of Single-Strand Tundish with Flow Modifiers through Physical Water Model (PWM) and CFD Simulation. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022, 12, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Madias, J.; Martin, D.; Ferreyra, M.; Villoria, R.; Garamendy, A. Design and Plant Experience Using an Advanced Pouring Box to Receive and Distribute the Steel in a Six Strand Tundish. Isij Int. 1999, 39, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Higa, K.; Guthrie, R.; Isac, M.; Morales, R.D. Ladle Shroud as a Flow Control Device for Tundish Operations. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2013, 44, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.G.; Zhu, M.Y. Criteria on the Similarity of Melt Flow among Strands in Multi-strand Continuous Casting Tundish. Chin. J. Process Eng. 2006, 6, 522–526. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumdar, D.; Guthrie, R. On the numerical calculation and non-dimensional representation of velocity fields in bubble-stirred ladle systems. Steel Res. Int. 1993, 64, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, P.K.; Dash, S.K.; Kumar, S. Effect of outlet positions, height of advanced pouring box, and shroud immersion depth on mixing in six strand billet caster tundish. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2002, 29, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.B. Analysis model for flow characteristics of multi strand tundish. Shanghai Met. 2013, 35, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, L.; Yan, Z.; Guocheng, X.; Zhongqiang, S. Use of a Comprehensive Analytical Approach for Water Modeling of an Asymmetrical Two-Strand Tundish. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2011, 32, 537. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.F.; Ji, Y.L.; Liu, J.H.; He, Y.; Shen, S.B.; Cui, H. Analysis on Residence Time Distribution Curve of Continuous Casting Tundish by Combined Model. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1800085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

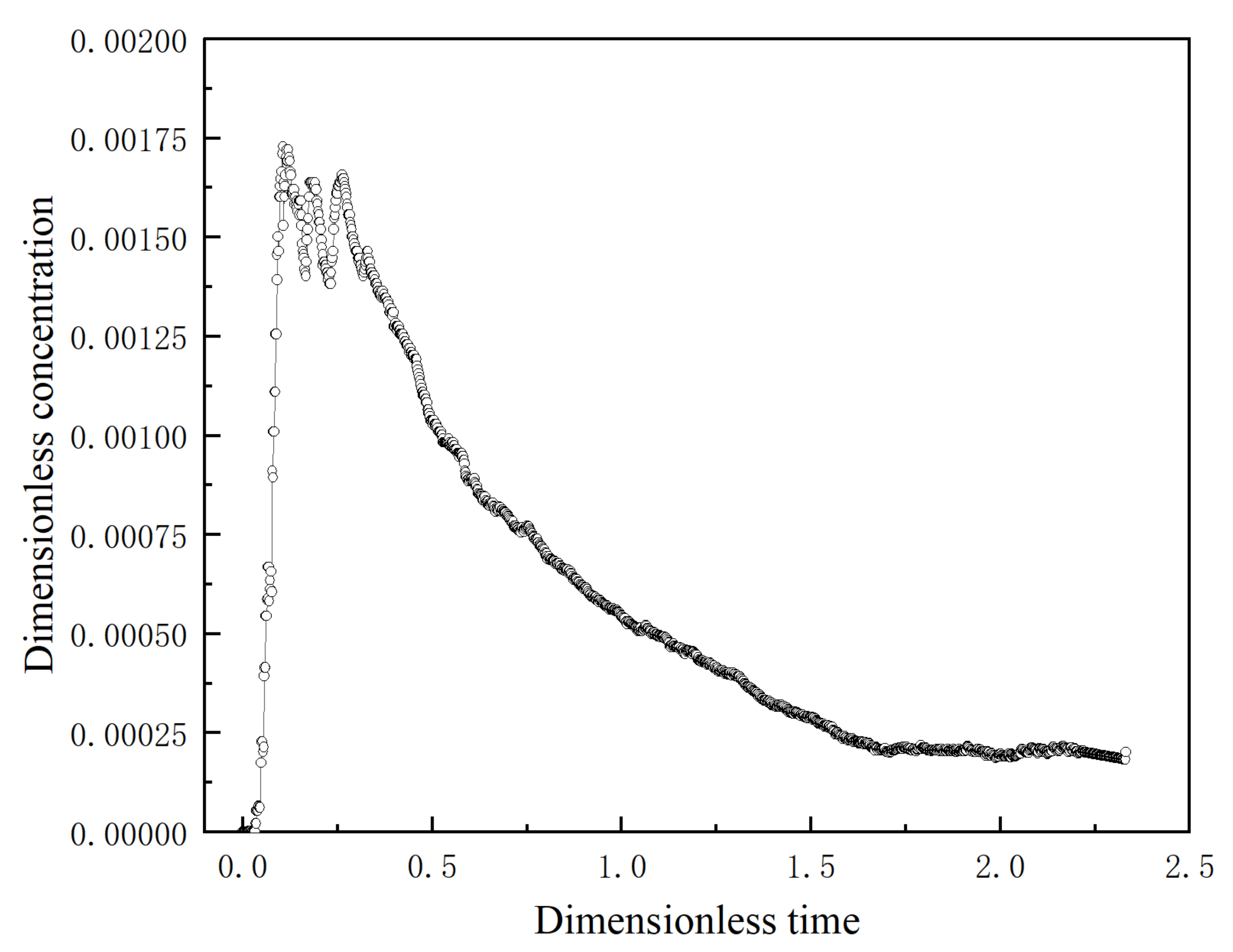
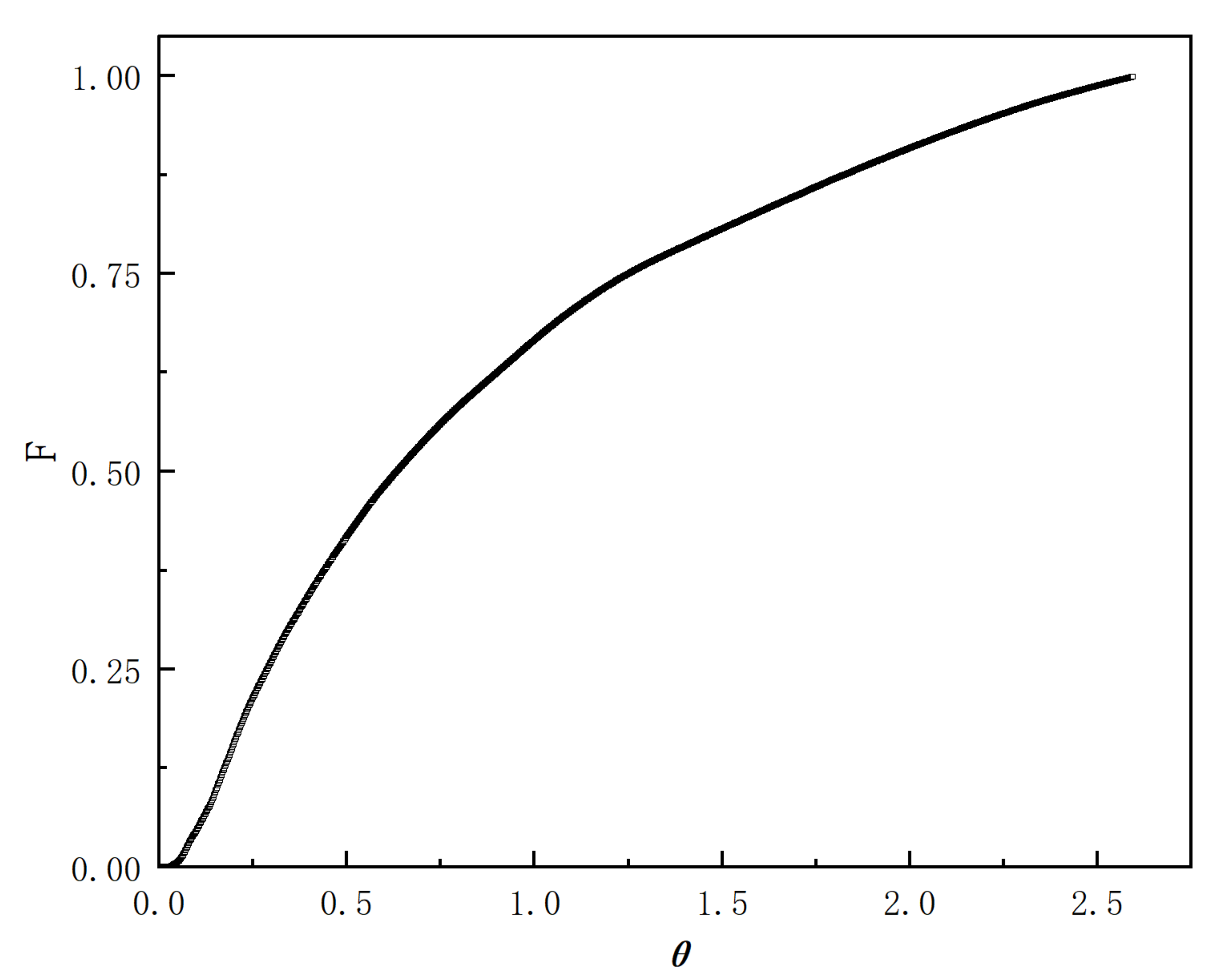

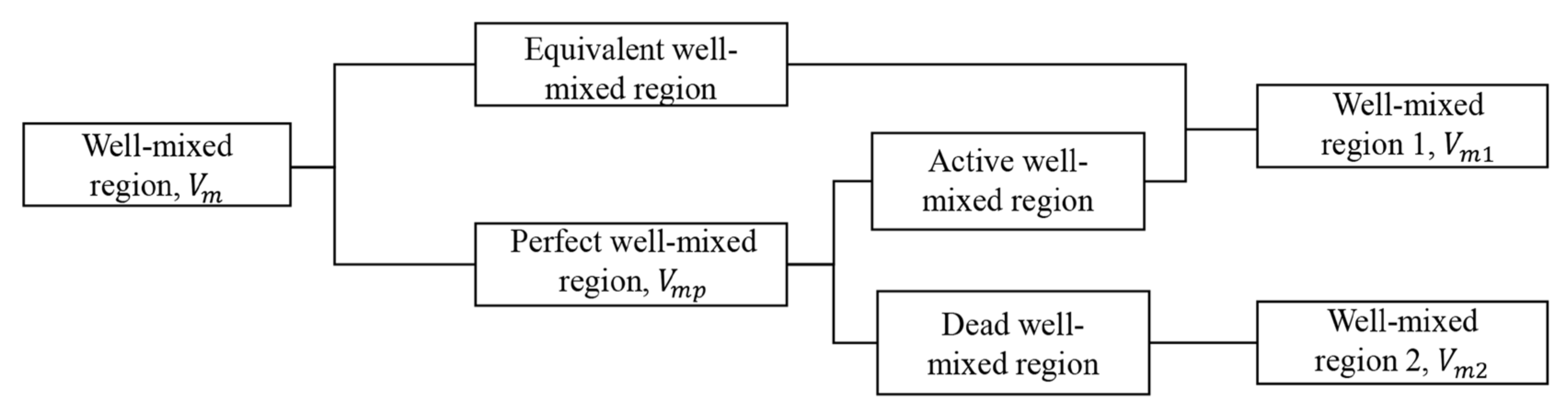
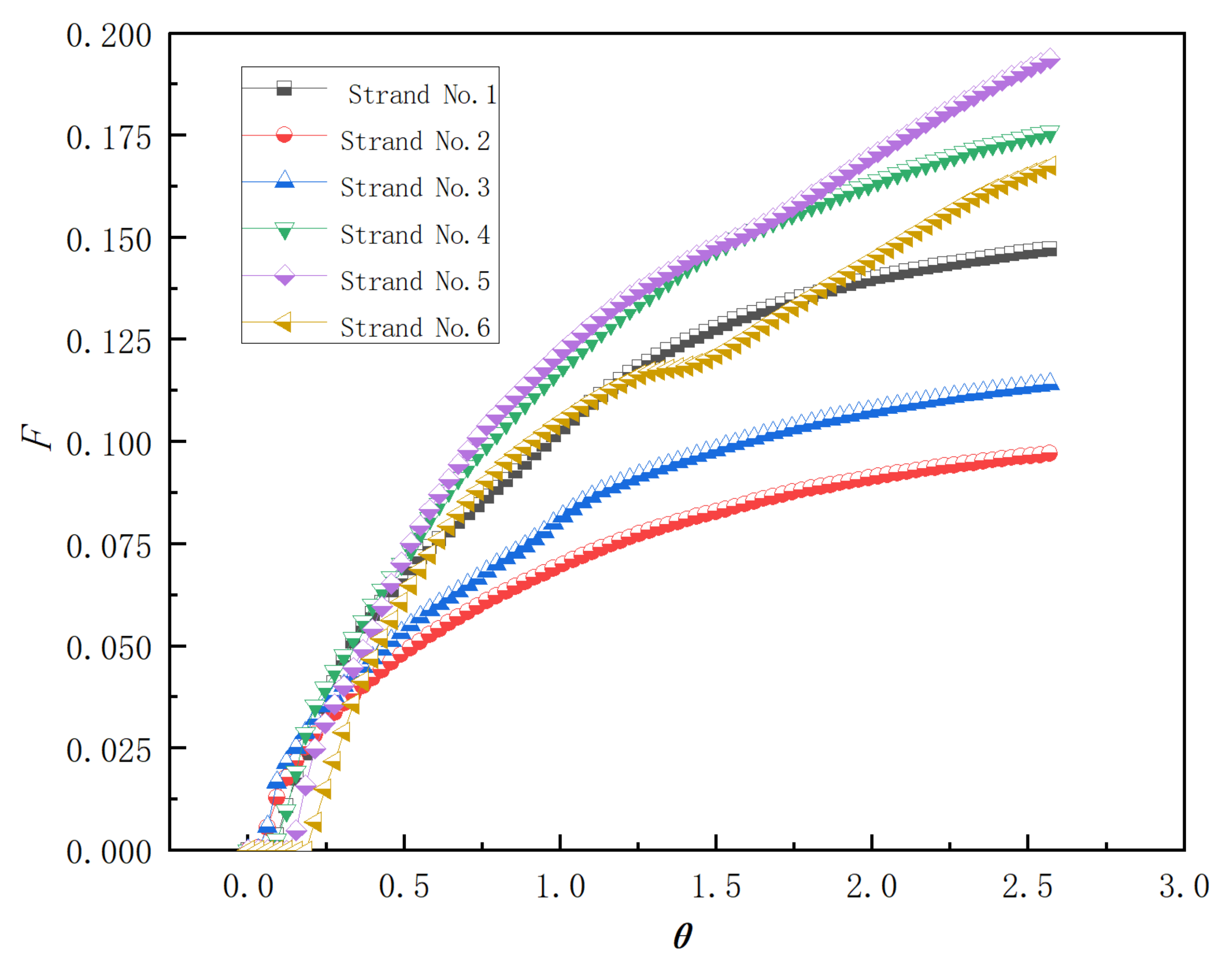
| Year | Author | Number of Strands | Dead Volume Method | Computational Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | Kemeny F. [11] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 1986 | Sahai Y. [12] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 1996 | Sahai Y. [13] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 1997 | Mazumdar Dipak [14] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2004 | Vargas -Zamora [15] | Single-Strand | F | |
| 2005 | Zheng Shuguo [16] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2005 | Solorio-Díaz G. [17] | Two-Strand | C | |
| 2007 | Kumar Anil [18] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2008 | Zhu Mingmei [19] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2009 | Pan Hongwei [20] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2009 | Chen Yuanqing [21] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2009 | Bensouici [22] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2010 | Lei Hong [23] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2010 | Cwudzinski A. [24] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2010 | Zhong Liang-cai [25] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2011 | Ning Ding [26] | Single-Strand | F | |
| 2012 | Mishra [27] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2013 | Sengupta A. [28] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2013 | Sanchez-Ramirez R. [29] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2013 | Chen D. [30] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2015 | Chang S. [31] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2015 | Lei Hong [32] | Two-Strand | C | |
| 2015 | Guocheng Wang [33] | Single-Strand | F | |
| 2015 | Cui Heng [34] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2016 | Fei He [35] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2016 | Li D. X [36] | Two-Strand | F | |
| 2016 | Zheng Shu-guo [37] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2016 | Li Dongxia [38] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2017 | Xiao-ying Wang [39] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2018 | Braga B.M. [40] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2018 | Harnsihacacha Anawat [41] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2020 | Tkadleckova Marketa [42] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2020 | Sheng D.Y. [43] | Multi-Strand | F | |
| 2020 | Fang Qing [44] | Multi-Strand | C | |
| 2021 | Sheng D.Y. [45] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2022 | Yadav J.N. [46] | Single-Strand | C | |
| 2022 | Yadav J.N. [46] | Single-Strand | C |
| Area | Analysis of Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 | Model 4 | Model 5 | Model 6 | Model 7 | Model 8 | |
| 0.364 | 0.351 | 0.350 | 0.450 | 0.325 | 0.214 | 0.334 | 0.190 | |
| 0.099 | 0.111 | 0.116 | 0.049 | 0.103 | 0.070 | 0.115 | 0.103 | |
| 0.537 | 0.538 | 0.534 | 0.502 | 0.572 | 0.716 | 0.534 | 0.707 | |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.817 | |
| 0.012 | |
| 0.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yue, Q.; Xia, Z.; Xiao, H. Residence Time Distribution (RTD) Applications in Continuous Casting Tundish: A Review and New Perspectives. Metals 2022, 12, 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081366
Wang Z, Yang Z, Wang X, Yue Q, Xia Z, Xiao H. Residence Time Distribution (RTD) Applications in Continuous Casting Tundish: A Review and New Perspectives. Metals. 2022; 12(8):1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081366
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ziming, Zexi Yang, Xiuzhen Wang, Qiang Yue, Zhendong Xia, and Hong Xiao. 2022. "Residence Time Distribution (RTD) Applications in Continuous Casting Tundish: A Review and New Perspectives" Metals 12, no. 8: 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081366
APA StyleWang, Z., Yang, Z., Wang, X., Yue, Q., Xia, Z., & Xiao, H. (2022). Residence Time Distribution (RTD) Applications in Continuous Casting Tundish: A Review and New Perspectives. Metals, 12(8), 1366. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12081366







