Transformation Behavior and Shape Memory Effect of Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy Synthesized by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Heat Treating
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. LPBF Process
2.2. Characterization
3. Results
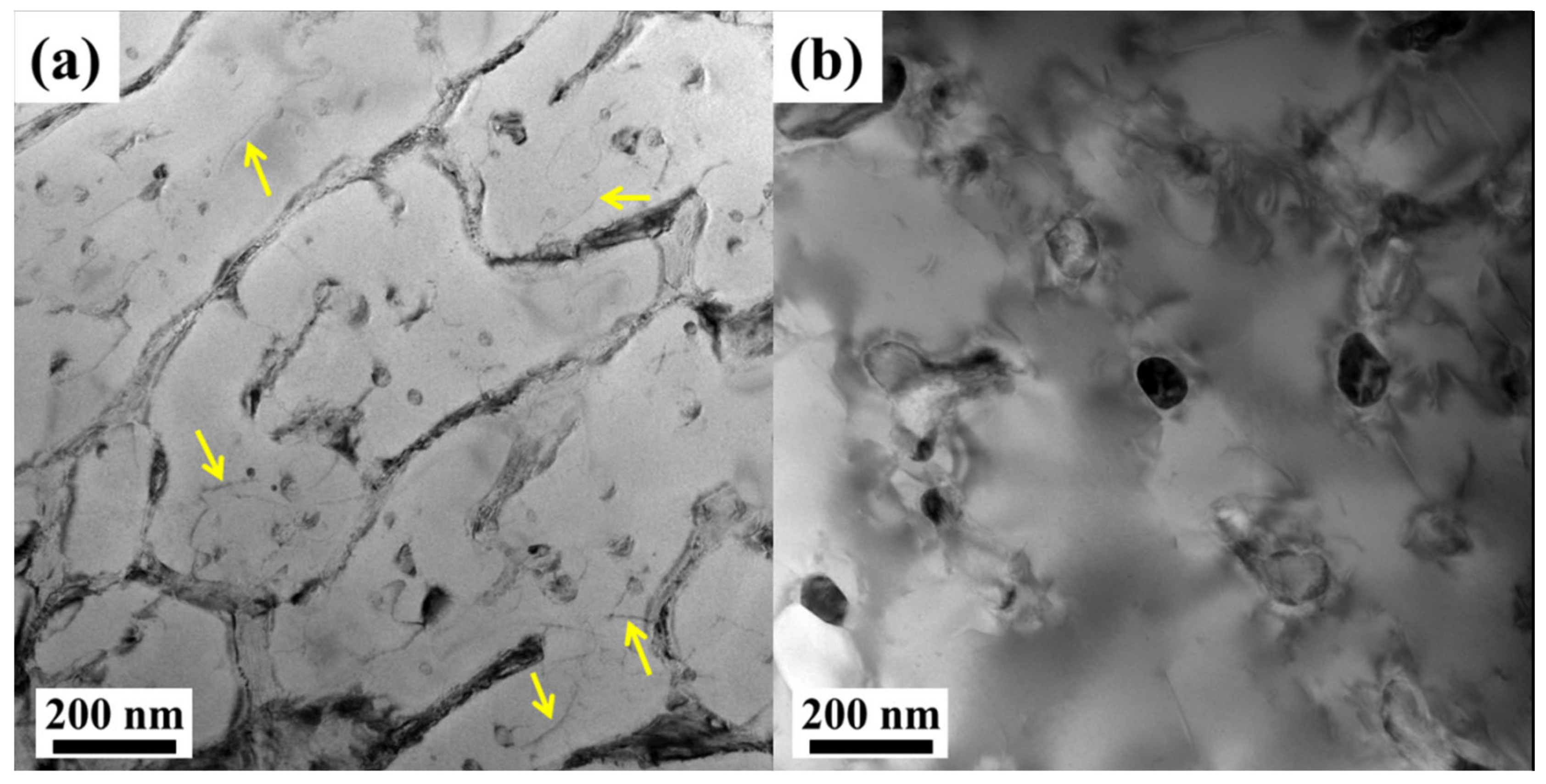
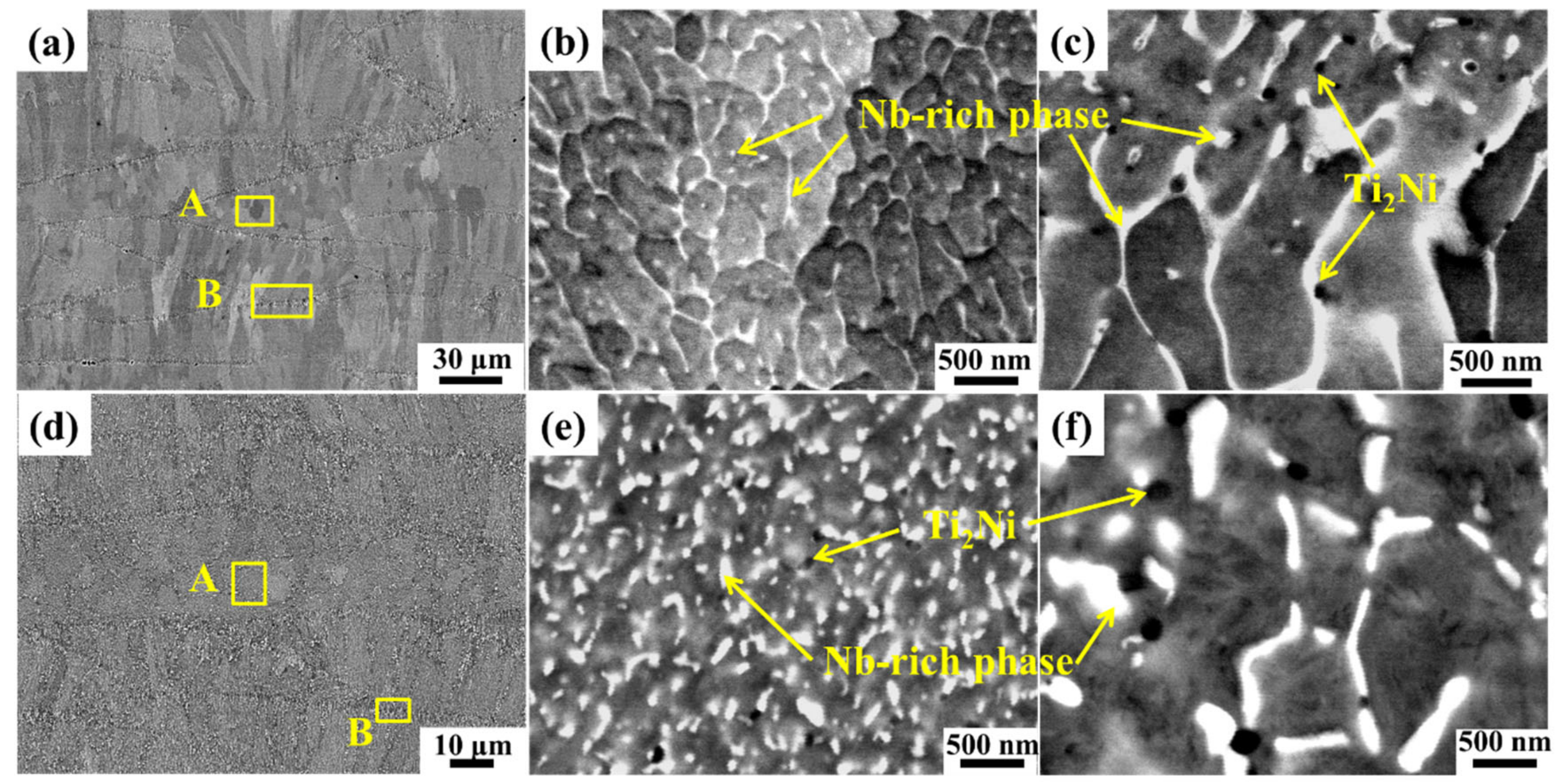
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Composition
3.2. Phase Transformation and Tensile Properties
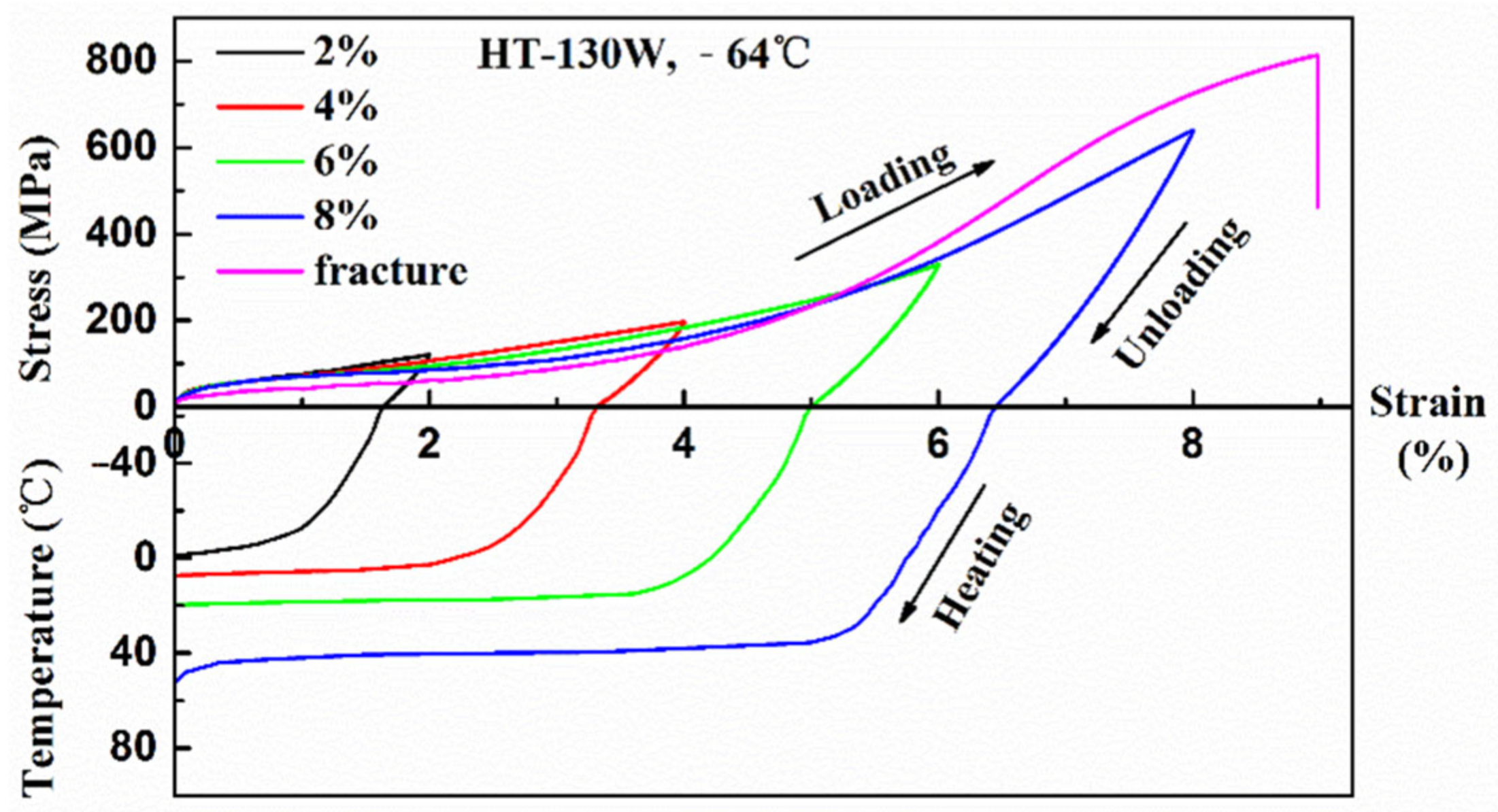
3.3. Shape Memory Response
4. Discussions
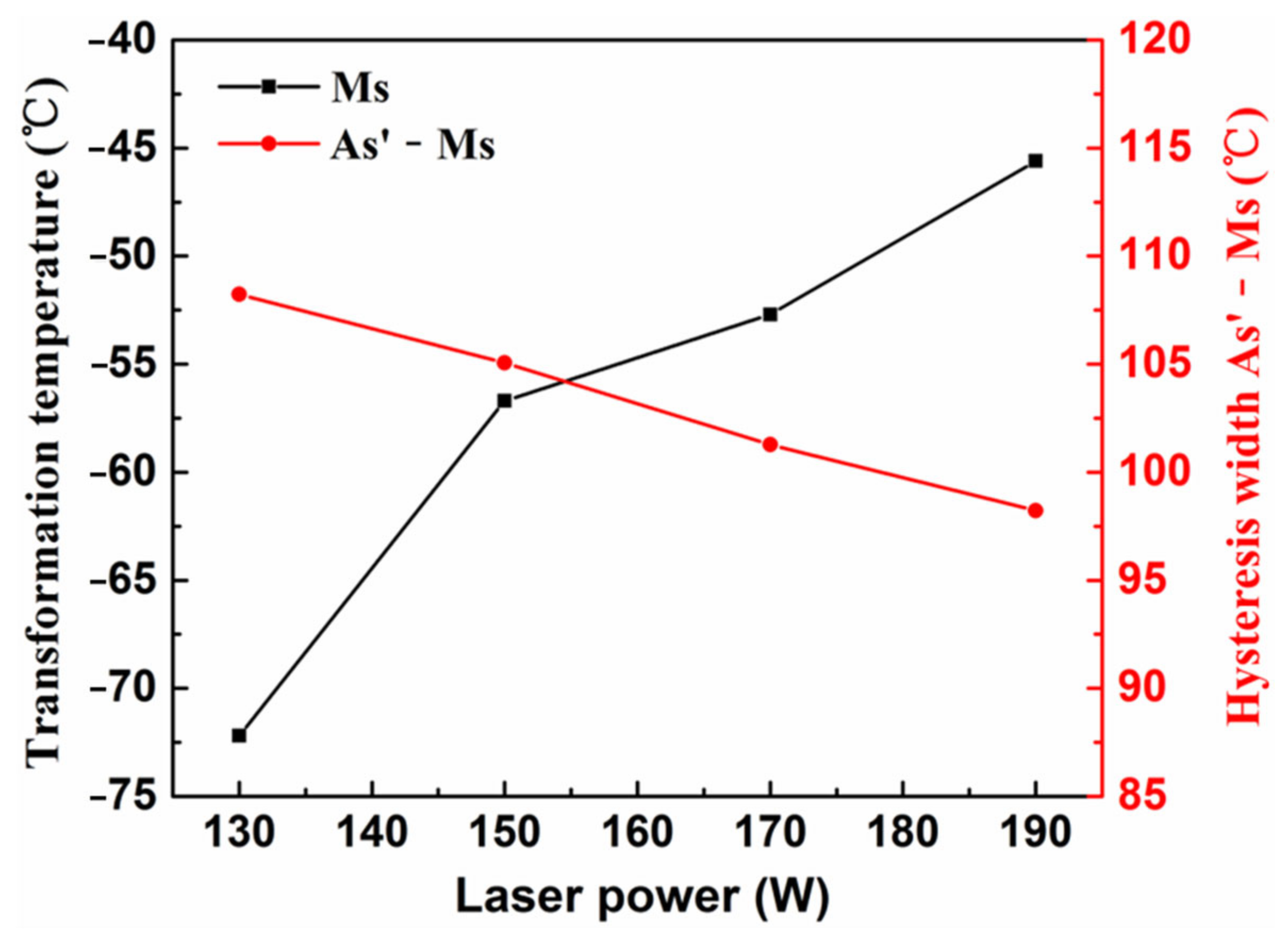
4.1. Influence of Laser Power and Heat Treatment on Phase-Transformation Behavior
4.2. Influence of Laser Power on εr and As’
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Ni47Ti44Nb9 alloys were successfully fabricated via LPBF technique with different laser powers. The as-built alloys have good shaping properties, though a few defects were discovered. The unmelted powders are owing to relatively low laser power and input energy density, while the micropores are owing to gas entrapment under high laser power.
- (2)
- There is no phase-transformation peak observed in the as-built samples, which may be due to the high dislocation density and internal stress caused by the nonequilibrium solidification process in LPBF. After heat treating, the phase-transformation peaks appear, and the phase-transformation temperatures increase with the increase in laser power, which may be due to the decrease in Ni/Ti ratio.
- (3)
- The tension test at room temperature indicates that the LPBF samples exhibit poor tensile ductility with total elongation below 1.5%, which may be related to the existence of the Ti2Ni or Ti4Ni2Ox phase or LPBF pores. However, the LPBF samples after heat treating still possess good shape memory effect (εr = 7.82–8%) and relatively high reverse transformation temperature (As’ = 36.0–52.6 °C) when deformed to 8%. In addition, the εr decreases and As’ increases with the increase in laser power.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Z.W.; Mi, X.J.; Wang, J.B.; Yuan, Z.S.; Zhou, J. Effect of annealing temperature on the transformation temperature and texture of Ni47Ti44Nb9 cold-rolled plate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 557–559, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.F.; Lanba, A.; Ozbulut, O.E.; Tittmann, B.R. Shape memory effect in cast versus deformation-processed NiTiNb alloys. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2015, 1, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhao, X.Q. Mechanical properties and transformation behavior of NiTiNb shape memory alloys. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2009, 22, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rong, L.J.; Yan, D.S.; Jiang, Z.M.; Li, Y.Y. DSC studies of the reverse martensitic transformation behavior in a shape memory alloy pipe-joint. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.M.; Rong, L.J. DSC analysis of reverse martensitic transformation in deformed Ti–Ni–Nb shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2004, 51, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.Z.; Guo, S.; Xiao, F.; Zhao, X.Q. Development of NiTiNb in-situ composite with high damping capacity and high yield strength. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Kato, H. Submicron-porous NiTi and NiTiNb shape memory alloys with high damping capacity fabricated by a new top-down process. Mater. Des. 2015, 78, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Ruan, J. Effects of Nb addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiNiNb alloys fabricated by elemental powder sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 609, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X.; Xu, H.; Jiang, H.; Rong, L. A novel TiNiNb shape memory alloy with high yield strength and high damping capacity. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6423, 64232L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zheng, Y.F.; Zhao, L.C. Electrochemical corrosion behaviour of Ti44Ni47Nb9 alloy in simulated body fluids. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 438–440, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, T.; Sutou, Y.; Kainuma, R.; Yamauchi, K.; Ishida, K. Effect of prestrain on martensitic transformation in a Ti46.4Ni47.6Nb6.0 superelastic alloy and its application to medical stents. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 76B, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jin, W.; Li, X.W. Texture development in the Ni47Ti44Nb9 shape memory alloy during successive thermomechanical processing and its effect on shape memory and mechanical properties. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44A, 978–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasz, G.; Kinga, P.; Michał, D. Structure and martensitic transformation in Ti50Ni(50-X)NbX (X=5; 10) alloy produced by powder metallurgy. Key Eng. Mater. 2016, 687, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitzer, M.; Bram, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stöver, D. Phase transformation behavior of hot isostatically pressed NiTi-X (X = Ag, Nb, W) alloys for functional engineering applications. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2535–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansiddhi, A.; Dunand, D.C. Shape-memory NiTi–Nb foams. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.X.; Mentz, J.; Bram, M.; Buchkremer, H.P.; Stöver, D. Powder metallurgical production of TiNiNb and TiNiCu shape memory alloys by combination of pre-alloyed and elemental powders. J. Alloy. Compd. 2008, 463, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saedi, S.; Turabi, A.S.; Andani, M.T.; Haberland, C.; Elahinia, M.; Karaca, H. Thermomechanical characterization of Ni-rich NiTi fabricated by selective laser melting. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 035005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahinia, M.; Moghaddam, N.S.; Andani, M.T.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Bimber, B.A.; Hamilton, R.F. Fabrication of NiTi through additive manufacturing: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 630–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadbakhsh, S.; Speirs, M.; Humbeeck, J.V.; Kruth, J.-P. Laser additive manufacturing of bulk and porous shape-memory NiTi alloys: From processes to potential biomedical applications. Mrs Bull. 2016, 41, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadbakhsh, S.; Vrancken, B.; Kruth, J.-P.; Luyten, J.; Humbeeck, J.V. Texture and anisotropy in selective laser melting of NiTi alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 650, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Abbara, E.M.; Jiang, D.; Azizi, A.; Poliks, M.D.; Ning, F. High-cycle fatigue properties of curved-surface AlSi10Mg parts fabricated by powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 1346–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, J.-M.; Chaves-Jacob, J.; Lopez, Q.; Sprauel, J.-M. Fatigue life optimization for 17-4Ph steel produced by selective laser melting. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.M.; Waqar, S.; Koç, E. Evolution of temperature and residual stress behavior in selective laser melting of 316L stainless steel across a cooling channel. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giganto, S.; Martínez-Pellitero, S.; Cuesta, E.; Zapico, P.; Barreiro, J. Proposal of design rules for improving the accuracy of selective laser melting (SLM) manufacturing using benchmarks parts. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorasani, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Leary, M.; Sharabian, E.; Cordova, L.; Gibson, I.; Downing, D.; Bateman, S.; Brandt, M.; Rolfe, B. The effect of absorption ratio on meltpool features in laser-based powder bed fusion of IN718. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, H.; Liang, X.; Lei, J. Titanium fabricated by selective laser melting: Microstructure, wear and corrosion behavior in different orientations. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2022, 28, 546–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yua, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Yang, Q.; Wei, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, G.; et al. Effect of process parameters on the phase transformation behavior and tensile properties of NiTi shape memory alloys fabricated by selective laser melting. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Hao, S.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Guo, W.; Yang, Y.; Ren, Y.; Cui, L.; Ren, L.; Zhang, Z. The microstructure of a selective laser melting (SLM)-fabricated NiTi shapememory alloy with superior tensile property and shape memory recoverability. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 19, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhan, J.B.; Li, B.; Lin, J.X.; Gao, J.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Ren, L.; Castany, P.; Gloriant, T. Laser beam energy dependence of martensitic transformation in SLM fabricated NiTi shape memory alloy. Materialia 2019, 6, 100305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadbakhsh, S.; Speirs, M.; Kruth, J.-P.; Schrooten, J.; Luyten, J.; Humbeeck, J.V. Effect of SLM parameters on transformation temperatures of shape memory nickel titanium parts. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2014, 16, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, T.; Schumacher, R.; Ller, B.M.; Mertmann, M.; Wild, M.d. Tailoring selective laser melting process parameters for NiTi implants. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2519–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, N.S.; Saghaian, S.E.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Ibrahim, H.; Li, P.; Toker, G.P.; Karaca, H.E.; Elahinia, M. Anisotropic tensile and actuation properties of NiTi fabricated with selective laser melting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 724, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.; Haberland, C.; Frenzel, J. Structural and functional properties of NiTi shape memory alloys produced by selective laser melting. VR@P2011 2011, 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Elahinia, M.; Moghaddama, N.S.; Amerinatanzi, A.; Saedi, S.; Toker, G.P.; Karaca, H.; Bigelow, G.S.; Benafan, O. Additive manufacturing of NiTiHf high temperature shape memory alloy. Scr. Mater. 2018, 145, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiva, S.; Palani, I.A.; Paul, C.P.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, B. Investigations on phase transformation and mechanical characteristics of laser additive manufactured TiNiCu shape memory alloy structures. J. Mater. Processing Technol. 2016, 238, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematollahi, M.; Toker, G.; Saghaian, S.E.; Salazar, J.; Mahtabi, M.; Benafan, O.; Karaca, H.; Elahinia, M. Additive manufacturing of Ni-Rich NiTiHf20: Manufacturability, composition, density, and transformation behavior. Shape Mem. Superelasticity 2019, 5, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, T.; Müller, B.; Schinhammer, M.; Kessler, A.; Thalmann, P.; Wild, M.d. Microstructure of selective laser melted nickel–titanium. Mater. Charact. 2014, 94, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.J.; Jiang, M.Y.; Liao, G.Y.; Guo, S.; Zhao, X.Q. Martensitic transformation involved mechanical behaviors and wide hysteresis of NiTiNb shape memory alloys. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuprina, V.G.; Shalya, I.M. Reactions of TiNi with oxygen. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2002, 41, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, M.; Wayman, C.M.; Honma, T. Precipitation processes in near equiatomic TiNi shape memory alloys. Metall. Trans. A 1986, 17A, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.P.; Wang, Y.B.; Dui, G.S. Constitutive modeling of rolled shape memory alloy sheets taking into account pre-texture and anisotropic hardening. Acta Mech. Solida Sin. 2014, 27, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Li, Z.; Sun, Z.; Hao, S.; Yang, Y.; Li, M.; Song, C.; Qiu, P.; Cui, L. Selective laser melting of NiTi alloy with superior tensile property and shape memory effect. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 2238–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Wu, S.K.; Chou, T.S.; Kao, H.P. The effects of cold rolling on the martensitic transformation of an equiatomic TiNi alloy. Acta Metall. Et Mater. 1991, 39, 2069–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.C.; Sun, M.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, H.B.; Sun, K.H.; Fan, X.H.; Huang, S.K.; Wen, Y.H. Influence of precipitation on phase transformation and mechanical properties of Ni-rich NiTiNb alloys. Mater. Charact. 2019, 154, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Gao, P.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, Z.; Hao, S. Study on corrosion behavior of the selective laser melted NiTi alloy with superior tensile property and shape memory effect. Corros. Sci. 2020, 175, 108891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yan, E.H.; Huang, S.K.; Wen, Y.H. Influence of Ni/Ti ratio and Nb addition on martensite transformation behavior of NiTiNb alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 790, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Fan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ge, J.; Zhang, S.; Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S. Influence of annealing temperature on microstructure and shape memory effect in austenite-martensite duplex Ni47Ti44Nb9 rolled sheets. Mater. Charact. 2021, 178, 111186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Chu, Y.S.; Famodu, O.O.; Furuya, Y.; Hattrick-Simpers, J.; James, R.D.; Ludwig, A.; Thienhaus, S.; Wuttig, M.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Combinatorial search of thermoelastic shape-memory alloys with extremely small hysteresis width. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample | Ni (wt.%) | Ti (wt.%) | Nb (wt.%) | C (wt.%) | H (wt.%) | O (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rod | 48.32 | Bal. | 14.69 | 0.0030 | <0.0010 | 0.017 |
| powder | 48.03 | Bal. | 14.91 | 0.0036 | <0.0010 | 0.028 |
| Sample | Laser Power P (W) | Scanning Velocity v (mm/s) | Hatch Spacing h (μm) | Layer Thickness t (μm) | Energy Density Eν (J/mm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB-130 W | 130 | 700 | 50 | 30 | 123.8 |
| AB-150 W | 150 | 700 | 50 | 30 | 142.9 |
| AB-170 W | 170 | 700 | 50 | 30 | 161.9 |
| AB-190 W | 190 | 700 | 50 | 30 | 181.0 |
| Sample | Ni (wt.%) | Ti (wt.%) | Nb (wt.%) | Ni (at.%) | Ti (at.%) | Nb (at.%) | Ni/Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB-130 W | 48.98 | 36.55 | 14.47 | 47.57 | 43.53 | 8.91 | 1.094 |
| AB-190 W | 48.35 | 36.81 | 14.84 | 46.99 | 43.87 | 9.14 | 1.071 |
| HT-130 W | 48.91 | 36.61 | 14.48 | 47.50 | 43.59 | 8.91 | 1.089 |
| HT-190 W | 48.49 | 37.05 | 14.46 | 47.04 | 44.07 | 8.89 | 1.068 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, M.; Chen, J.; Fan, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, G.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, S. Transformation Behavior and Shape Memory Effect of Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy Synthesized by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Heat Treating. Metals 2022, 12, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091438
Sun M, Chen J, Fan Q, Yang C, Wang G, Shen X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Huang S. Transformation Behavior and Shape Memory Effect of Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy Synthesized by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Heat Treating. Metals. 2022; 12(9):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091438
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Mingyan, Jie Chen, Qichao Fan, Chuan Yang, Guowei Wang, Xianfeng Shen, Yangyang Wang, Yonghao Zhang, and Shuke Huang. 2022. "Transformation Behavior and Shape Memory Effect of Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy Synthesized by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Heat Treating" Metals 12, no. 9: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091438
APA StyleSun, M., Chen, J., Fan, Q., Yang, C., Wang, G., Shen, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Huang, S. (2022). Transformation Behavior and Shape Memory Effect of Ni47Ti44Nb9 Alloy Synthesized by Laser Powder Bed Fusion and Heat Treating. Metals, 12(9), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/met12091438





