Abstract
In the iron-ore-sintering process, the use of biomass charcoal instead of coke breeze can reduce the emission of flue gas pollutants and alleviate the energy crisis of fossil fuels. However, the direct application of biomass charcoal to iron ore sintering is bound to affect the sinter properties. The effects of biomass charcoal addition on the sintering ore properties and flue gas pollutants emission were studied through sintering cup and related performance test experiments. Meanwhile, the influence mechanism of biomass charcoal instead of coke breeze on iron ore sintering was expounded. The experimental results show that with an increase in biomass charcoal, the vertical sintering rate increased, the internal pore structure developed rapidly, and the pollutant emission decreased gradually. When the biomass charcoal content was less than 40%, the sinter strength and yield were stable and slightly improved with the increase in biomass charcoal. When the biomass charcoal content was higher than 40%, the metallurgical properties of sinter degraded sharply, making it difficult to meet the production requirements. The comprehensive effect of biomass charcoal on the sinter suggests that the suitable biomass charcoal addition was 40%; under this condition, the reduction in SO2 and NOx was 28.2% and 25.7%, respectively.
1. Introduction
Most of the atmospheric pollutants released are from the iron and steel industry, and more than 42% of dust, 65% of SO2, and 55% of NOx are emitted as exhaust gas pollutants during the sintering process in the iron and steel industry [1,2]. The contents of S and N in fossil fuels is high, and a large amount of SO2 and NOx is released during iron ore sintering. To protect the environment and efficiently utilize the natural resources, novel types of environmentally friendly sintering fuels that can replace traditional fuels must be developed. Such an approach would be a direct and effective way to control the emission of pollutants during the sintering process [3,4,5].
Biomass charcoal is a type of renewable clean energy, and its S and N contents are lower than those of fossil fuels. Application of biomass charcoal in the iron-ore-sintering process can reduce the sintering flue gas pollutants. However, the reactivity of biomass charcoal is better than that of coke, which leads to a mismatch of their combustion rates, so that the heat of the combustion layer is not concentrated, and the temperature of the layer is reduced, which directly affects the sinter properties [6,7]. Liu et al. [8,9,10,11] used a fluent software to simulate the sintering process of biomass charcoal, and an evaluation system of sinter properties was constructed to determine the most suitable amount of biomass charcoal to be used in iron ore sintering. Zhao et al. [12] used a newly developed combustion model and a 2D sintering model to appropriately describe the combustion behavior in sintering based on fuel properties, as well as defined the optimum thickness and porosity of the adhering layer. Guilherme et al. [13] used charcoal as a supplementary fuel in the iron-ore-sintering process, and an extensive analysis of the environmental impact was performed regarding the characterization of the atmospheric pollutants (such as dust, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane, total hydrocarbons, and dioxins and furans). However, there is little research on the synergistic effect of biomass charcoal on sinter properties, the internal pore structure, emission reduction of flue gas pollutants and its mechanism. In this study, the vertical sintering rate, yield, drum strength, FeO content, three-dimensional (3D) pore structure of sinter, and SO2 and NOx content of the flue gas are investigated by sintering cup experiments with different proportions of biomass charcoal. The influence mechanism of biomass charcoal sintering on sinter properties and pollutant emissions are analyzed, thereby providing a theoretical basis for the rational application of biomass charcoal in iron ore sintering.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
The experimental material was supplied by a Steel Corp sintering plant in Tangshan; the charcoal was prepared by the modification of sawdust carbon [9,10,11], and the chemical composition of the sintering material is presented in Table 1, and the Fuel performance analysis is presented in Table 2.

Table 1.
Sintering raw material composition (mass fraction/%).

Table 2.
Fuel performance analysis.
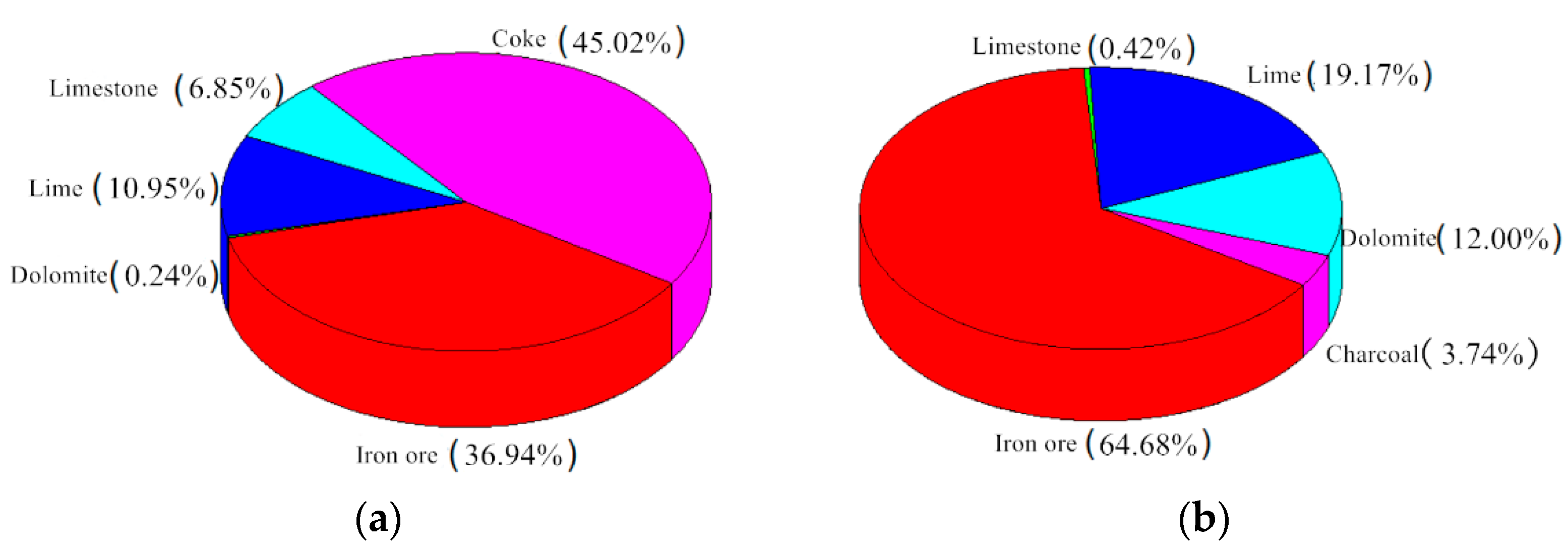
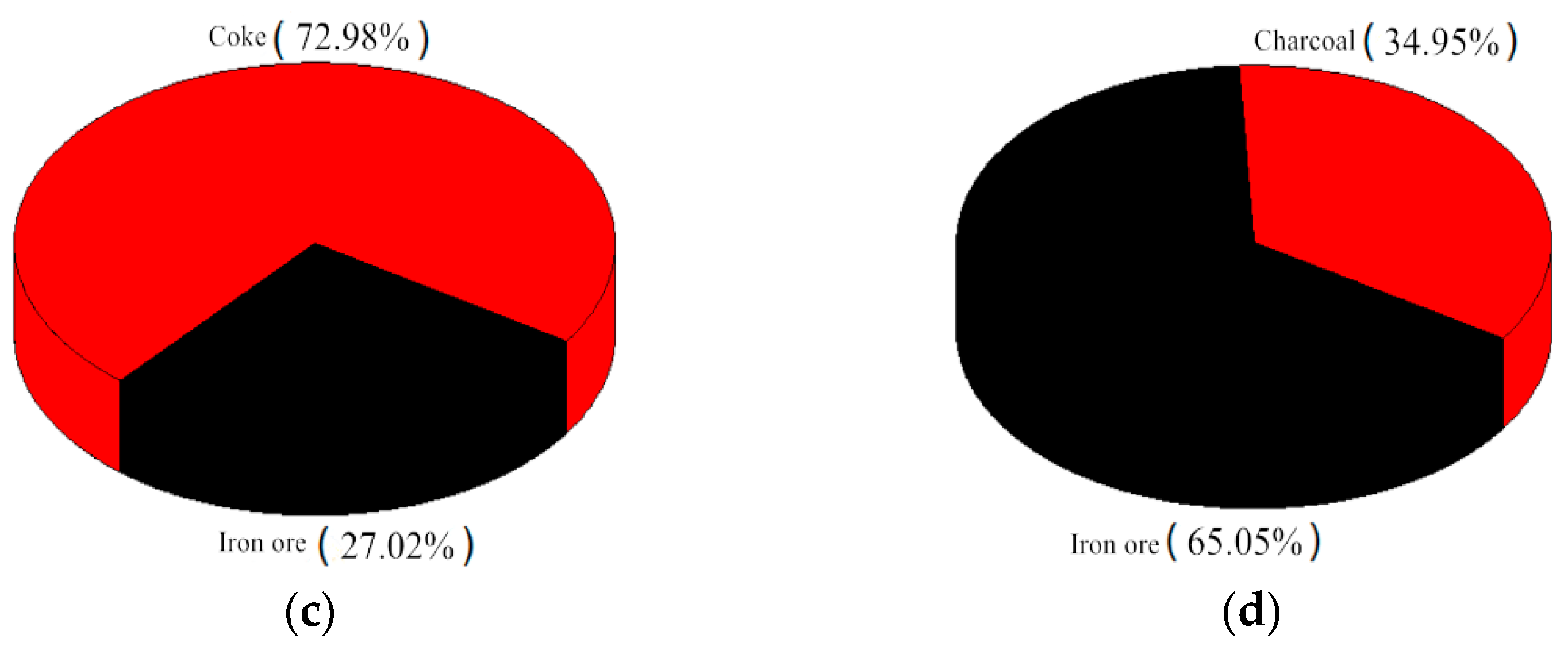
According to the sulfur and nitrogen contents in different raw materials, a distribution map of sulfur and nitrogen in the sintered mixture was drawn, and the main sources of SO2 and NOx in flue gas were clarified. The sulfur and nitrogen distribution maps in raw materials are shown in Figure 1a,c when coke was used as the sintering fuel, while Figure 1b,d show charcoal as the sintering fuel.
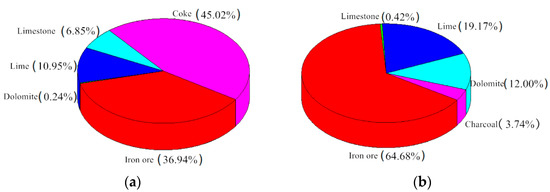
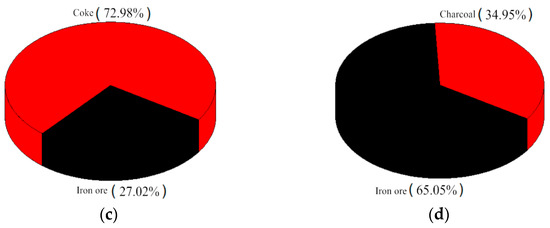
Figure 1.
S and N content in sintering raw materials. (a) S content of coke in sintering raw materials. (b) S content of charcoal in sintering raw materials. (c) N content of coke in sintering raw materials (d) N content of charcoal in sintering raw materials.
According to Figure 1a,c when coke breeze was used as the sintering fuel, the sulfur content in the sintered mixture was 0.0632%, and the sulfur was mainly concentrated in iron ore and coke breeze, accounting for 39.94% and 45.02%, respectively. The total amount of nitrogen in the sintered mixture was 0.0496%, which was mainly concentrated in coke breeze and iron ore. The nitrogen content in coke breeze was 72.98%, which was clearly higher than that in iron ore. According to the distribution map of sulfur and nitrogen in Figure 1b,d, it could be seen that the sulfur content in the sintered mixture was 0.0361% when using biomass charcoal instead of coke breeze, in which 64.68% sulfur was concentrated in iron ore; the total nitrogen content with biomass charcoal as sintering fuel was significantly reduced to 0.0206%, which was 58.5% lower than that in conventional sintering; the nitrogen content in iron ore was 65.05%, and the nitrogen content in biomass charcoal was only 34.95%. After replacing coke breeze with biomass charcoal, sulfur and nitrogen in the mixture were mainly concentrated in iron ore, and the content of sulfur and nitrogen was greatly reduced, which was beneficial to the pollutants’ source control from the sintering process.
2.2. Sintering Cup and Metallurgical Properties Experiments
The sintering experiment with biomass charcoal instead of coke breeze was performed using a laboratory sintering cup (φ 200 mm × h 600 mm), and the SO2 and NOx in the sintered flue gas were monitored in real time by a flue gas analyzer (testo 350, produced by Testo in Baden-Württemberg, Land, Germany). The effects of the biomass charcoal content instead of coke breeze on the vertical sintering rate, yield, drum strength, load-softening properties, low-temperature-breakdown properties, reduction properties (RI), and SO2/NOx content in the flue gas were studied in these experiments. Due to the calorific values of both solid fuels being relatively similar, the experimental scheme of the sintering cup keeps constant the total mass of solid fuels in the mix, which is presented in Table 3.

Table 3.
The sintering experiment scheme (mass fraction/%).
2.3. X-ray Computed Tomography Experiments
The X-ray computed tomography is a versatile high-resolution system for 2D X-ray inspection, 3D CT (micro-CT and nano-CT) and 3D metrology. The sinters obtained by different biomass charcoals were tested by X-ray CT experiments, and the influence mechanism of biomass charcoal addition on the sinter internal pore structure was studied.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Biomass Charcoal Content on Sintering Technical Indexes
The sintering cup experiments were performed according to the experimental scheme in Table 2, and the sinter’s chemical composition and sintering technical indexes were obtained, which are presented in Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 4.
Sinter’s chemical composition (mass fraction, %).

Table 5.
Sintering technical indexes.
Through the sintering technical indexes in Table 5, it could be seen that when the content of coke breeze replaced by charcoal increased from 0% to 40%, the vertical sintering rate increased from 23.15 mm·min−1 to 25.35 mm·min−1, the drum strength increased from 65.12% to 65.88%, and the yield was maintained at around 73%. When the charcoal content increased to 60%, the sintering technical indexes deteriorated sharply, which was not conducive to the sintering production of iron ore. The reason for this result is that the reactivity of charcoal is better than coke [9,11,12], which makes the combustion rate of charcoal and coke inconsistent, reduces the temperature of the sintering material layer, and affects the sintering technical indexes. The experimental results were consistent with the rule of sintering-layer temperature change with different charcoal contents studied by Cheng et al. [14,15]. By comparing the experimental results of conventional coke sintering and charcoal sintering, the most suitable addition amount of charcoal was 40% for compliance with the sintering technical indexes.
3.2. Effect of Biomass Charcoal Content on Sinter Metallurgical Properties
The load-softening properties (T10% was the start softening temperature, T40% was temperature of 40% shrinkage corresponding to the end of softening, and ΔT was the difference between T10% and T40%), low-temperature-breakdown properties (RDI) and reduction properties (RI) of different sinters were tested, and the test results are shown in Table 6.

Table 6.
Load-softening properties of sinter with different charcoal content.
As could be observed from the load-softening properties in Table 6, with the increase in biomass charcoal, the initial and final softened temperature decreased gradually, but the decrease in T10% was small, and the decrease in T40% was large. This result could be attributed to the fact that the initial softening temperature mainly depends on the low-melting-point mineral-calcium ferrite phase (refer to Section 3.4). With the increase in biomass charcoal, the pore structure of the sinter developed (refer to Section 3.3), which provided better kinetic conditions for the sinter to soften, reduced the final softening temperature, reduced the softening temperature range, helped to reduce the soft melting zone of the blast furnace, and improved permeability [16].
As could be seen from the low-temperature-breakdown properties in Table 6, when the content of biomass charcoal increased from 0% to 40%, the sinter RDI−0.5 was about 8%, and the RDI+3.15 was about 70%. The reason for this result was when the biomass charcoal in the sintered fuel increased to 40%, the heat of the sintered fuel could ensure the material layer temperature, and the formation of the bonding phase was enough to ensure the low-temperature-breakdown properties (refer to Section 3.4). When biomass charcoal increased from 40% to 60%, RDI−0.5 increased from 8.63% to 11.52%, and RDI+3.15 decreased from 67.82% to 59.58%. This was because when the biomass charcoal in the sintered fuel increased to 60%, the heat of the sintered fuel was dispersed, the temperature of the material layer was low, the formation of the bonding phase was less, and the pore structure was developed (refer to Section 3.3), leading to the easy destruction in the reduction process and the sharp decrease in sinter RDI+3.15, which was not conducive to blast furnace smelting [17,18].
As can be seen from the RI in Table 6, with the increase in biomass charcoal, the RI increased continually. The reason for this result was that with the increase in biomass charcoal, the heat distribution was uniform, which was beneficial to low-temperature iron ore sintering. The formation of the calcium ferrite phase (refer to Section 3.4), the developed pore structure (refer to Section 3.3), and the lower content of FeO (refer to Table 4) was in turn beneficial to the indirect reduction reaction of sinter [19]. Therefore, the increase in biomass charcoal was beneficial to improving the reductivity of the sinter.
Based on the effect of biomass charcoal on the sinter metallurgical properties, it was suggested that the addition of biomass charcoal should not be more than 40% in the iron-ore-sintering process.
3.3. Effect of Biomass Charcoal Content on the Sinter Pore Structure
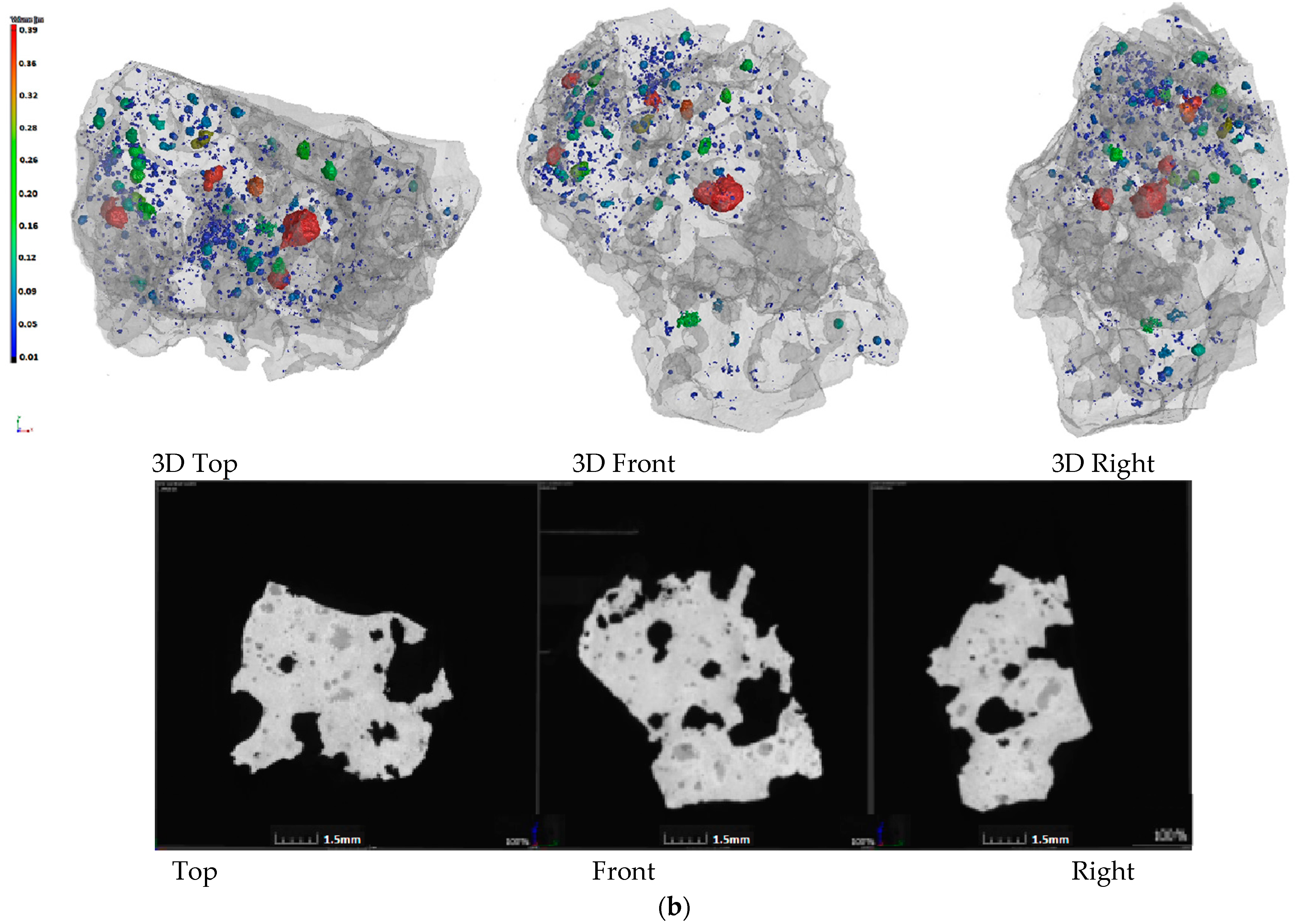
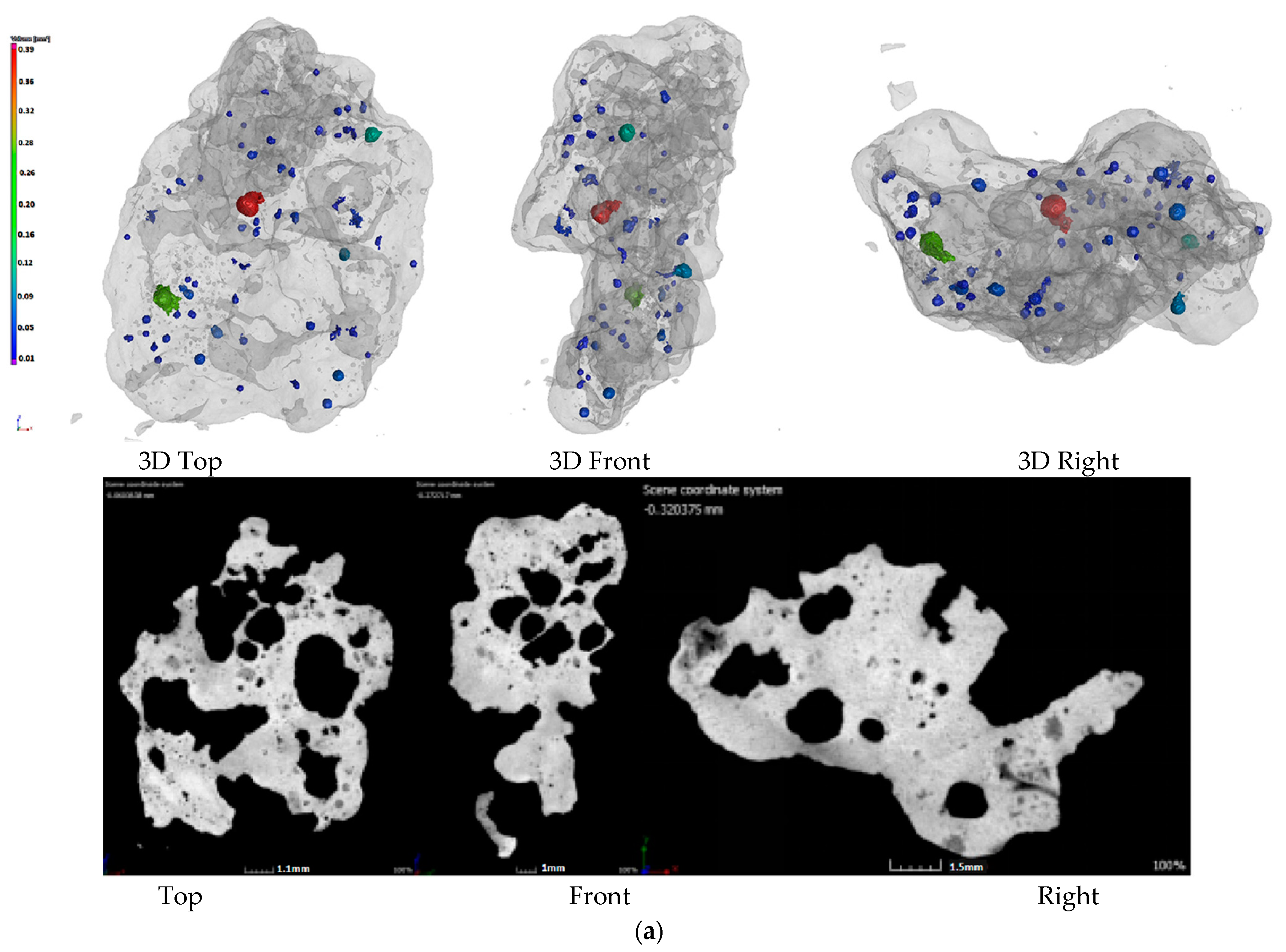
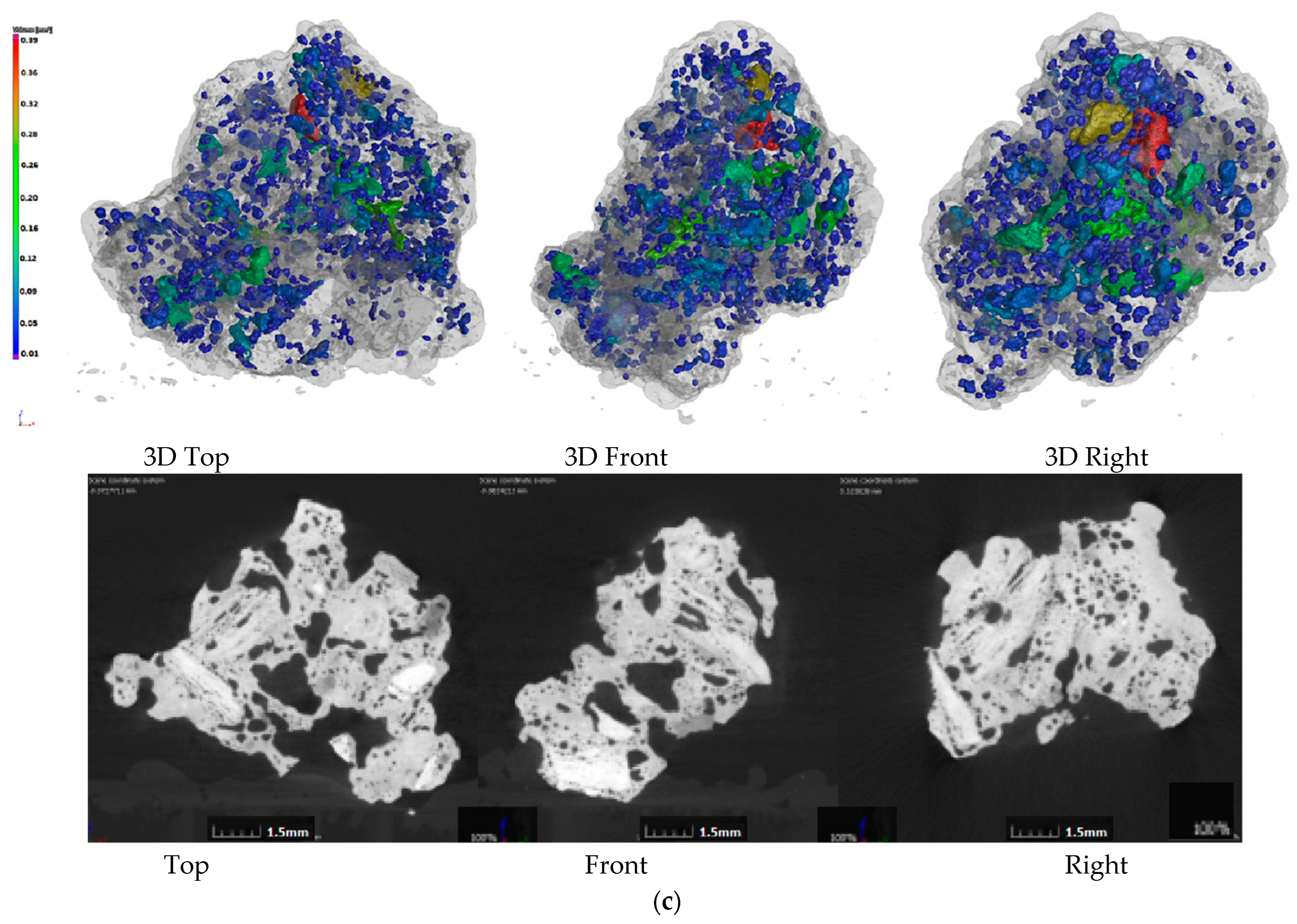
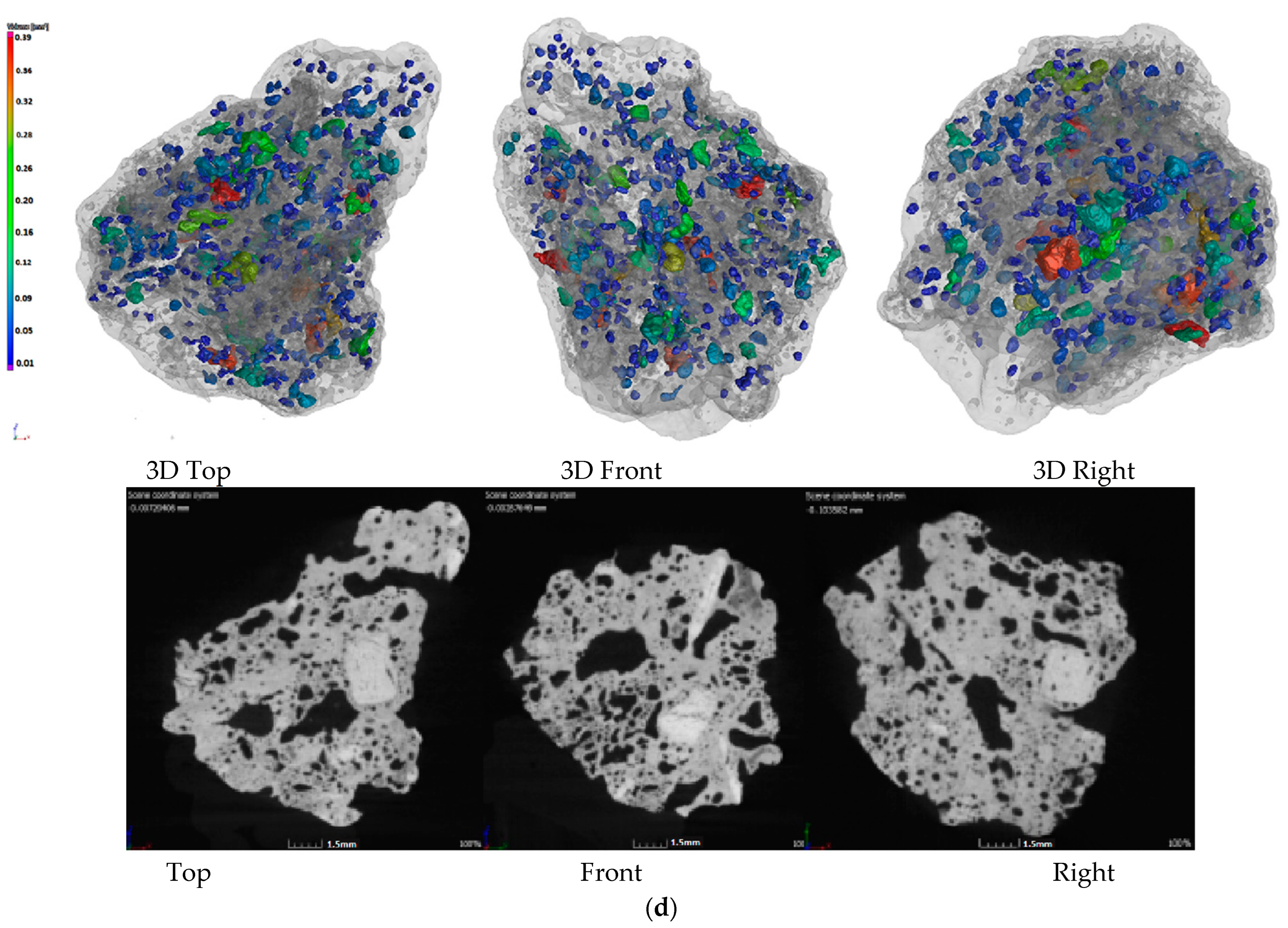
In order to further study the influence mechanism of biomass charcoal on sinter strength, yield, and reducibility, the internal sinter pore structure was obtained by X-ray CT experiments. The effect of charcoal content on the internal structure and porosity of sinter was also studied. The results are shown in Figure 2.
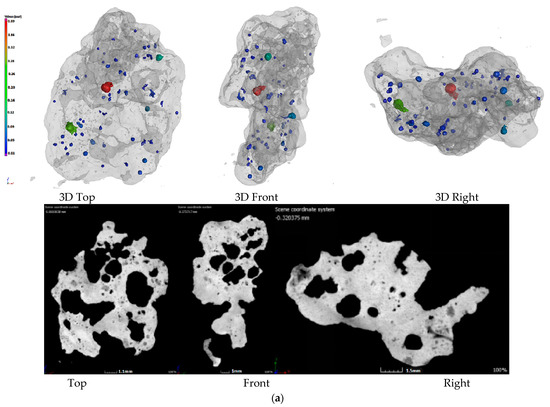

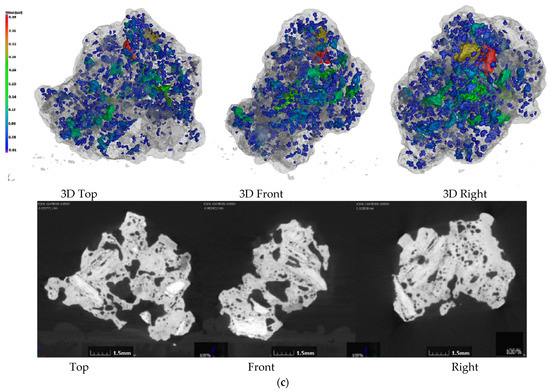
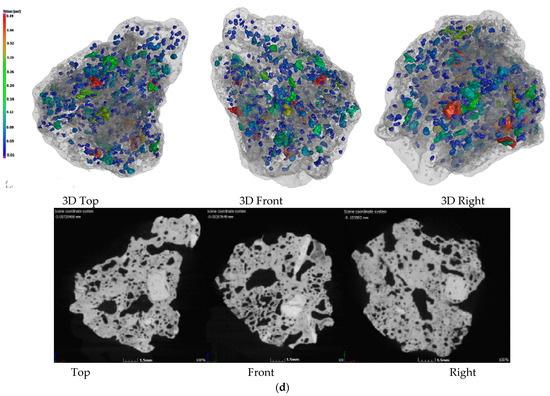
Figure 2.
Pore structure of sinter with different charcoal content. (a)100% Coke; (b) 80% Coke + 20% Charcoal; (c) 60% Coke + 40% Charcoal; (d) 40% Coke + 60% Charcoal.
Figure 2 shows the CT photos of the 3D pore structure and slices of the sinter. Figure 2a shows the CT photos of the sinter obtained by conventional coke sintering. The pore distribution shows that the energy density of the coke breeze in the conventional sintering mixture was high, the volume was small, the distribution segregation was significant, the local high temperature in the sintering mixture was caused, the number of the mesopores was small, and the pore diameter was large. Therefore, the amount of fuel and the temperature of the combustion layer should be strictly controlled in the sintering process, otherwise macroporous and thin-wall sinter could form more readily, which affects the sinter strength. Figure 2b–d are the CT photos of the sinter obtained by 20%, 40% and 60% charcoal, respectively. Compared with Figure 2a, with the increase in charcoal content in sintered mixed fuel, the macroporous amount in sinter decreased gradually, the micropore content increased gradually, the pore distribution was uniform, and the pore structure was developed. The reason for this result was that the density of charcoal was small, so with the increase in charcoal content, the volume of the sintered mixed fuel increased gradually. In the mixing process of the sintered raw materials, the distribution of mixed fuel was uniform, the energy was dispersed, and the heat distribution was uniform in the sintering process, which was beneficial to the formation of the sinter liquid phase and the formation of uniformly distributed pores in the combustion reaction process. Therefore, through the internal pore structure, it could be seen that adding an appropriate amount of charcoal in the sintering process was beneficial to forming a uniform sinter liquid phase and uniform distributed pores, which could avoid macropores and improve sinter reducibility and sinter strength (the results presented in Section 3.1 and Section 3.2). However, when the charcoal amount was too large, the pore structure in the sinter was overdeveloped, which was beneficial to the reduction reaction of sinter, but was not conducive to the improvement in sinter strength. Based on the internal structure and strength index of sinter, it was suggested that the most suitable addition of charcoal in the sintering process was 40%.
3.4. Effect of Biomass Charcoal Content on Sinter Phase Composition
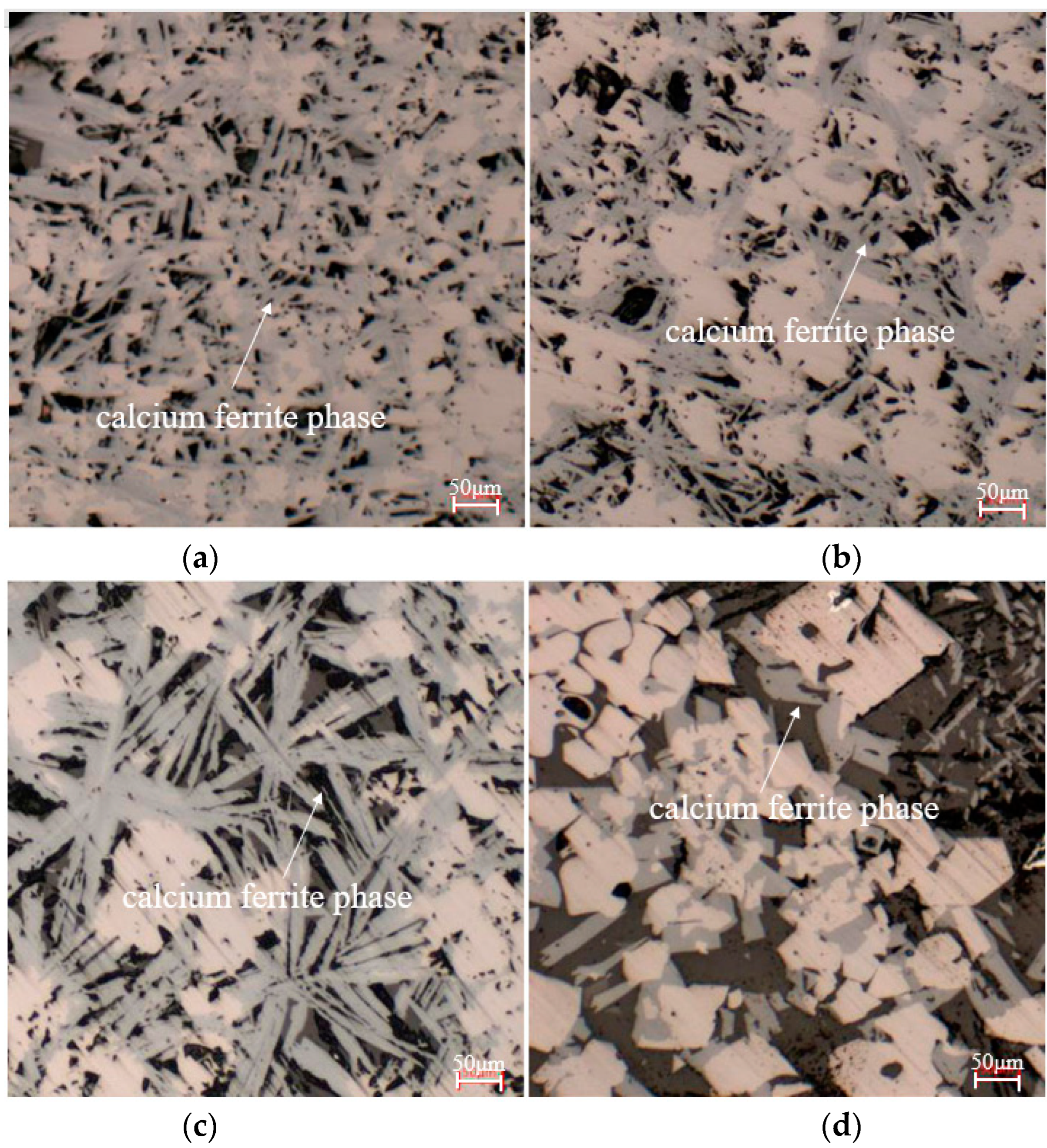
To study the effect of biomass charcoal content on sinter phase composition, the sinters with different proportions of charcoal instead of coke were sliced, and the microstructure of the sinters were detected by a Leica phase-contrast microscope which is shown in Figure 3.
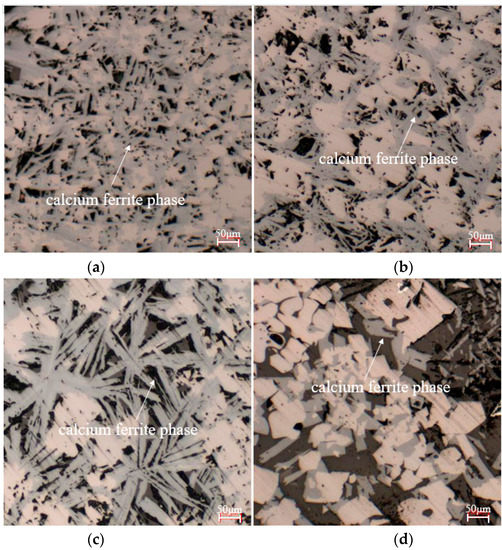
Figure 3.
Mineralogical microstructure of sinter with different charcoal content. (a) 100% coke; (b) 20% charcoal; (c) 14% coke; (d) 60% coke.
Figure 3a is the sinter mineral phase picture obtained by conventional coke sintering; many calcium ferrite phase minerals can be seen. The existence of the calcium ferrite phase could increase the content of the sinter-bonded phase. The higher the content of the calcium ferrite phase, the more favorable it was for improving the drum strength and reducibility of the sinter. Figure 3b shows the mineral phase of the sinter obtained by 20% charcoal and 80% coke, which was similar to the sinter obtained by 100% coke, so that the addition of 20% charcoal has an insignificant effect on the sinter mineral phase composition. When the charcoal content increased to 40%, as shown in Figure 3c, the content of the calcium ferrite phase in the sinter increased noticeably. The reason for this result was that the sintering layer temperature was slightly lower and could realize low-temperature sintering, which could promote the formation of the calcium ferrite phase and prevent the decomposition of the calcium ferrite phase and the over-melting of sinter. When the charcoal content further increased to 60%, as shown in Figure 3d, the amount of the calcium ferrite phase in the sinter decreased, which inevitably affected the sinter metallurgical properties. This was because the increase in charcoal content shortened the residence time at high temperature, affecting the microstructure and sintering properties of the sinter. The above results showed that the most suitable addition of charcoal instead of coke breeze was 40%.
3.5. The Effect of Biomass Charcoal Content on the Emission of SO2 and NOx in Flue Gas
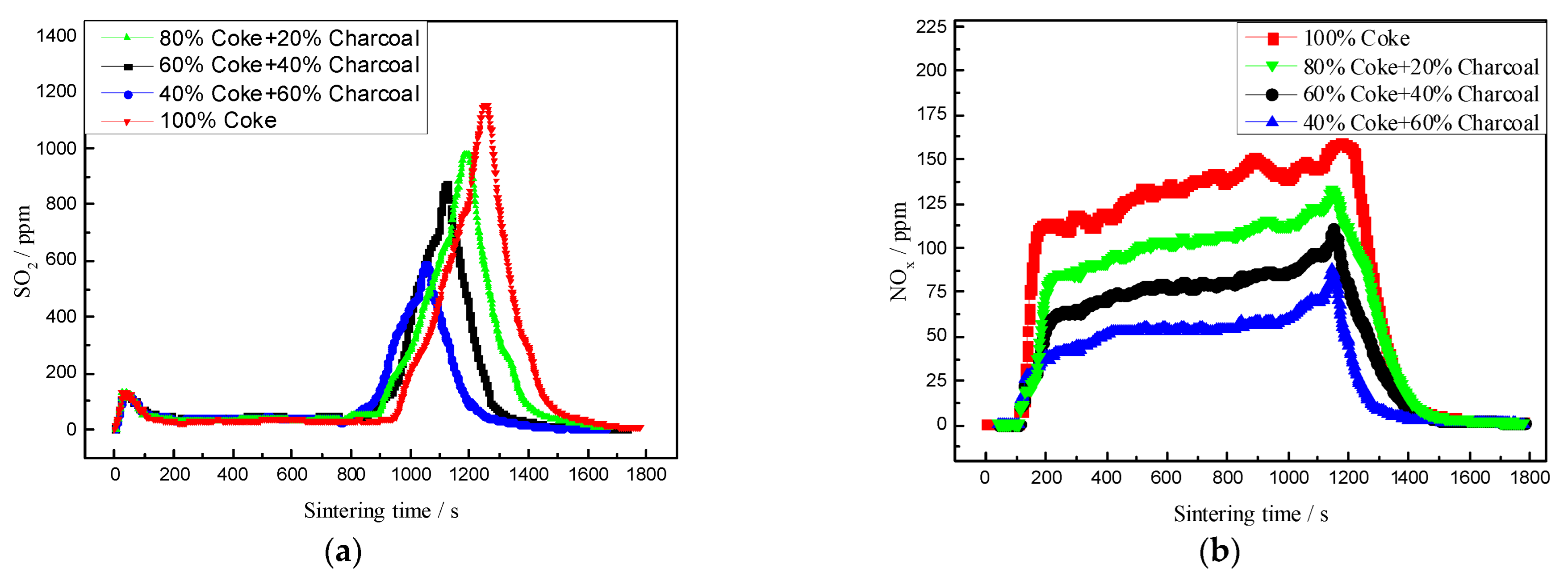
In the process of sintering cup experiments, the SO2 and NOx in sintering flue gas pollutants were detected using a smoke detection device (testo 350). The effect of charcoal content on SO2 and NOx emissions from flue gas pollutants was studied, and the detection results are shown in Figure 4.
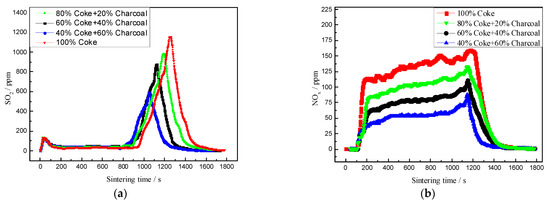
Figure 4.
Effects of charcoal on the SO2 and NOx content in flue gas. (a) SO2 emission curve; (b) NOx emission curve.
Figure 4a shows that the distribution curve of SO2 emission in flue gas during sintering was bimodal. During ignition, the fuel combustion released a large quantity of SO2. Meanwhile, the material had not yet formed a wet layer, the permeability of the material layer was good, and the flux was too high for the material layer to absorb all the SO2 in the flue gas, so part of the SO2 was emitted, and a peak value appeared on the smoke detection curve. With the development of sintering, the production of SO2 in the flue gas decreased and most of it would be absorbed by flux through the sinter, and therefore, the SO2 emission value was extremely low in the sintering process. The SO2 absorbed by the material layer would be released intensively when approaching the sintering end point, and the second peak appeared on the SO2 emission curve simultaneously. The SO2 emission curves were consistent with Gan’s research conclusion. [20] As shown in Figure 4a, when charcoal was used instead of coke for sintering, the emission curve of SO2 changed; that is, after adding charcoal, the overall reaction performance of the sintered fuel increased and the vertical sintering rate increased, leading to the advance of the sintering end point and release of SO2 in the material layer. Because of the low S content in sawdust carbon, with the charcoal content increasing from 0 to 60%, the SO2 emission range gradually shortened, and the peak values of SO2 emission in the sintering flue gas were 1180 ppm, 996 ppm, 835 ppm and 650 ppm.
Figure 4b shows that the emission concentration of NOx in the sintering flue gas increased rapidly after ignition and remained at a stable value during the whole sintering process until the NOx emission concentration near the sintering end point dropped rapidly. The NOx emission curve obtained by replacing some of the coke with charcoal decreased gradually with the increase in charcoal content in the sintered fuel, and the emission duration was shortened. When the charcoal content increased from 0% to 60%, the emission concentration of NOx was about 158 ppm, 132 ppm, 109 ppm and 78 ppm. This was because the N content in charcoal was lower than that in coke, the responsiveness of charcoal was good, and the combustion rate of the sintered fuel increased, which led to the early termination of NOx release and resulted in a further reduction in NOx emissions. Therefore, the emission of sintered pollutant NOx could be further reduced using charcoal instead of coke in the sintering process.
4. Conclusions
The effects of the biomass charcoal contents on the sinter properties and pollutant emissions were investigated using the sintering cup, X-Ray CT, and flue gas pollutants detection experiments and the following conclusions were drawn.
With the increase in biomass charcoal content, the sintering rate increased gradually, and the load-softening, metallurgical, and sinter reduction properties were improved. When the amount of biomass charcoal was less than 40%, the sinter strength, low-temperature-breakdown property, and yield were maintained, but when the biomass charcoal reached 60%, they were greatly reduced. With the increase in biomass charcoal addition, the pores in the sinter became smaller and the number of pores increased; local over-melting of sinter was prevented, which was beneficial to the formation of the calcium ferrite phase. Excessive addition of biomass charcoal could lead to insufficient heat at the sintering layer, causing the content of the calcium ferrite phase to be reduced, the pore structure to be over-developed, and the strength of the sintered ore to be affected. The influence of comprehensive biomass charcoal on sintering was that the most suitable addition of biomass charcoal in the sintering process was 40%.
The content of SO2 and NOx in sintered flue gas decreased gradually with the addition of biomass charcoal. Based on the sintering performance of biomass charcoal, when 40% biomass charcoal was added, the reduction in SO2 and NOx in sintered flue gas was 28.2% and 25.7%, respectively.
Author Contributions
Data curation, H.X.; Funding acquisition, Y.Z.; Investigation, G.X.; Writing—original draft, C.L.; Writing—review and editing, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 51874139) and the Science and Technology Plan project of Tangshan (Grant Number 20150214C).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wu, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Gao, X.; Cen, K. Primary air pollutant emissions and future prediction of iron and steel industry in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.R.; Yan, X.M.; Qi, F.; Ye, M. Emission Characteristics of multiple pollutants from Iron- steel sintering flue gas and review of control technologies. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2014, 32, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Huang, H.; Zeng, Z.W.; Zhang, J.L.; Annanurov, S.; Zhao, Q.Z. The formation of NOx during sintering. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2017, 39, 1228–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Zhu, D.; Xue, Z.; Chun, T.; Ruan, Z. Mechanism of SO2 adsorption on mixture bed layer during iron ores sintering. Environ. Chem. 2013, 32, 1660–1667. [Google Scholar]
- Lovel, R.; Vining, K.; Amico, M. Iron ore sintering with charcoal. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2007, 116, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, M.; Ji, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, X.; Fan, Y. Insight into the high proportion application of biomass fuel in iron ore sintering through CO-containing flue gas recirculation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 232, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesler, M.; Stecko, J.; Stelmach, S.; Kwiecińska-Mydlak, A. Biochars in Iron Ores Sintering Process: Effect on Sinter Quality and Emission. Energies 2021, 13, 3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, L.; Yu-Zhu, Z.; Yan, S.; Hong-Wei, X.; Yue, K.; Jie, L. Numerical simulation of sintering based on biomass fuel. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2018, 45, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, K.; Xing, H.; Kang, Y. Effect of biomass on reaction performance of sintering fuel. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3262–3272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Xing, H.W.; Kang, Y. Research on reactive optimization of biomass fuel based on sintering. J. Northeast. Univ. 2018, 39, 654–657. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhao, K.; Xing, H.W.; Kang, Y. Modified biomass fuel instead of coke for iron ore sintering. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2020, 47, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Loo, C.E.; Yuan, J.; Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Miao, H. A Fundamental Study of the Co-Combustion of Coke and Charcoal during Iron Ore Sintering. Energy Fuel 2018, 32, 8743–8759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, G.C.; de Carvalho, J.A., Jr.; da Silva, B.E.C.; Pedrini, R.H. Operational and environmental assessment on the use of charcoal in iron ore sinter production. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 101, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Wei, S.; Guo, Z.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Optimization of gaseous fuel injection for saving energy consumption and improving imbalance of heat distribution in iron ore sintering. Appl. Energy 2017, 207, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.W. Study the replacement of coke with charcoal and methane in iron-ore sintering. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2017, 38, 188–192. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Zhu, D.; Pan, J.; Guo, Z.-Q. Overseas research advances in evaluation methods of high-temperature fundamental sintering characteristics of iron ores. Iron Steel 2022, 57, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Yufeng, G. Effect of MgO on Mineralization Mechanism of Sinter for Inhibiting the Low-Temperature Reduction Degradation. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Liang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Guan, Z. The Study on Influencing factors of low temperature reduction degradation index of sinter ore. Metall. Inf. Rev. 2021, 58, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Niu, L. Prediction research on basic properties of sintering based on chemical composition of iron ore powder. Sinter. Pelletizing 2022, 47, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, M.; Fan, X.; Ji, Z.; Jiang, T.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, G.; Yin, L. Application of biomass fuel in iron ore sintering: Influencing mechanism and emission reduction. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2014, 42, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).