Improving Welding Penetration and Mechanical Properties via Activated-Flux Smearing by Tungsten Inert Gas Arc Welding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Details
2.1. Materials
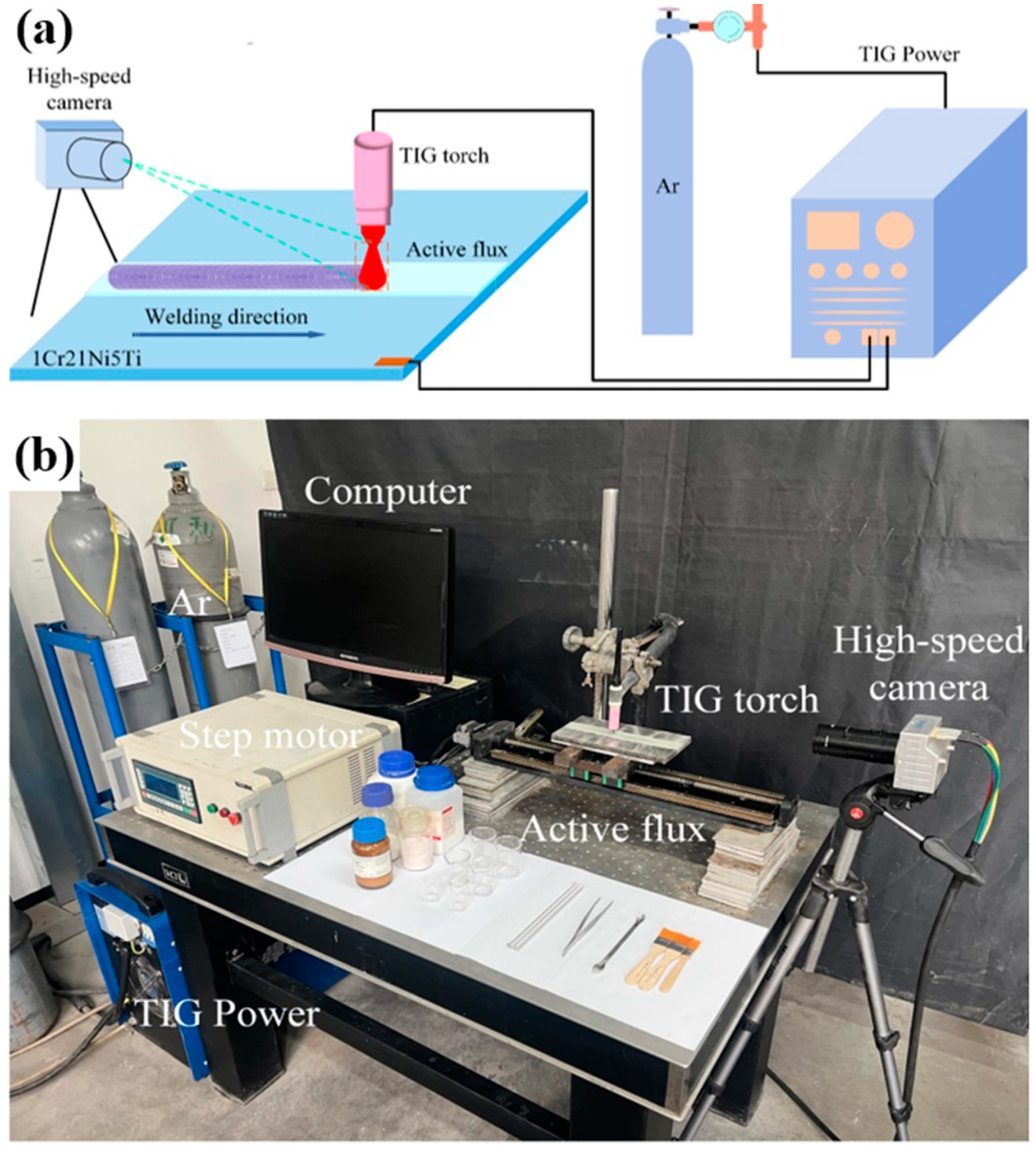
2.2. Experimental Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
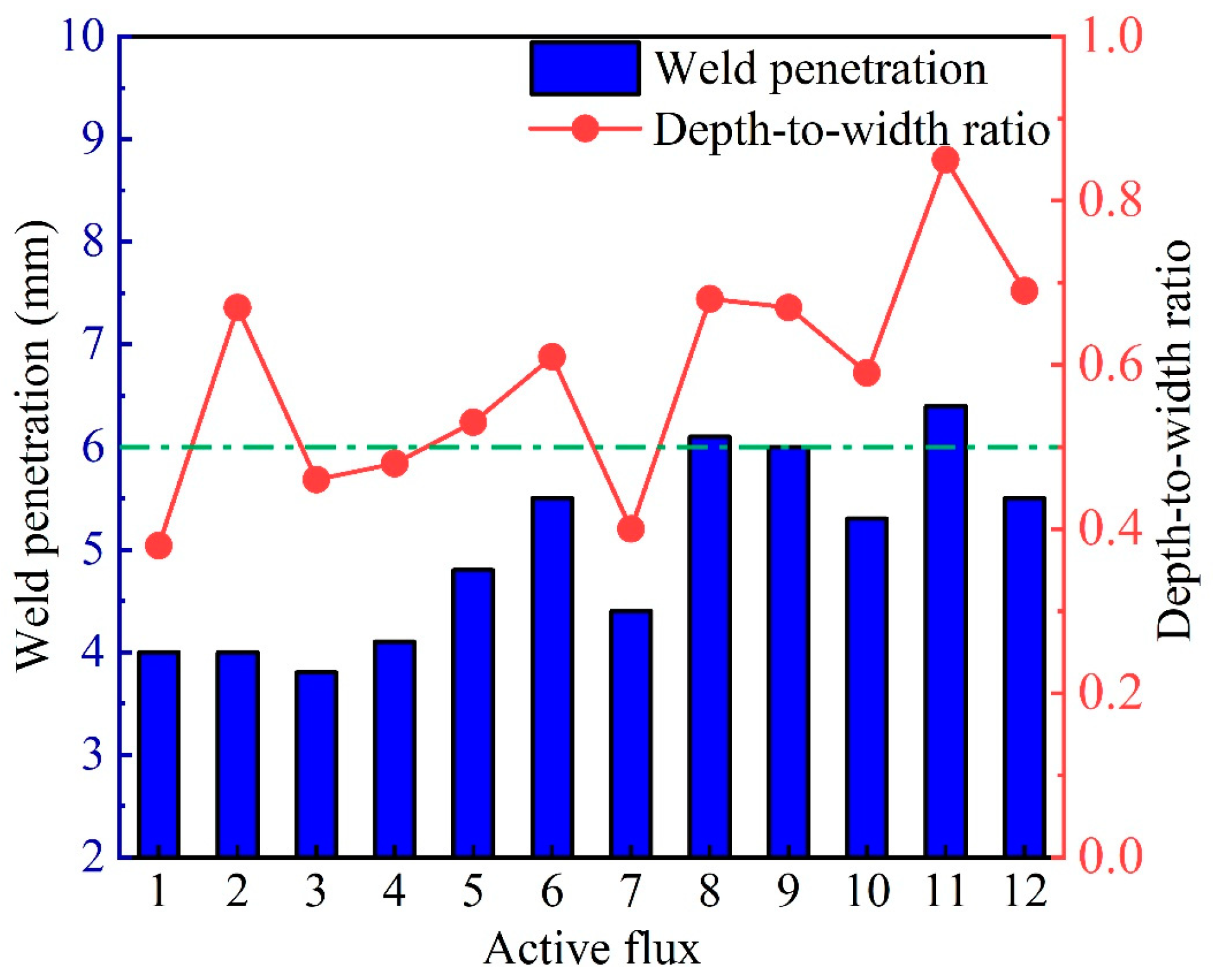
3.1. Effects of the Activated-Flux Type on the Weld Penetration
3.2. Comparison of the Welding Formation
3.3. Weld-Shift Experiment
3.4. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties
4. Conclusions
- In the A-TIG welding process of 1Cr21Ni5Ti stainless steel, the primary factor contributing to the increased penetration depth was the reversal of Marangoni convection. When employing the optimal activator ratio (0.033NiO + 0.632SiO2 + 0.037TiO2 + 0.162Cr2O3 + 0.137Al2O3) and optimal welding parameters (current I = 245A, speed V = 80 mm/min), A-TIG welding achieved a 1.67-fold increase in weld penetration depth compared with conventional TIG welding.
- In terms of microstructure, A-TIG welding led to a significant improvement. It reduced the overall grain size within the weld by 61.2%, with the maximum grain-size shrinking by 30.8%, leading to a more disordered grain orientation. Furthermore, the ferrite content showed a remarkable increase of 91.3%.
- In contrast to conventional TIG welding, A-TIG-welded joints demonstrate notable improvements in several aspects. These include a higher overall hardness, an increased tensile strength of 10.3%, a substantial elongation increase of 69.2%, and a noticeable enhancement in impact energy of 16.3%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rodrigues, D.G.; Maria, G.G.B.; Viana, N.A.L.; Santos, D.B. Effect of low cold-rolling strain on microstructure, texture, phase transformation, and mechanical properties of 2304 lean duplex stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2019, 150, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Q.; Ding, J.; Ganguly, S.; Marzio, G.; Yang, D.; Xu, X.; Dirisu, P.; Williams, S.W. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TOP-TIG-wire and arc additive manufactured super duplex stainless steel (ER2594). Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762, 138097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quackatz, L.; Griesche, A.; Kannengiesser, T. In situ investigation of chemical composition during TIG welding in duplex stainless steels using Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS)-ScienceDirect. Forces Mech. 2021, 6, 2666–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Das, Y.; Babu, R.P.; Wessman, S.; Jonsson, J.Y.; Odqvist, J.; King, S.M.; Hedström, P. Small-angle neutron scattering study on phase separation in a super duplex stainless steel at 300 °C—Comparing hot-rolled and TIG welded material. Mater. Charact. 2022, 190, 112044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebaraj, A.V.; Ajaykumar, L.; Deepak, C.; Aditya, K. Weldability, machinability and surfacing of commercial duplex Stainless Steel AISI2205 for marine applications –Arecent review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.W.; Cong, S.; Luo, S.B.; Fang, J.H. Effects of Energy Density and Shielding Medium on Performance of Laser Beam Welding (LBW) Joints on SAF2205 Duplex Stainless Steel. J. Miner. 2018, 70, 1554–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Odqvist, J.; Colliander, M.H.; King, S.; Thuvander, M.; Steuwer, A.; Hedström, P. Effect of cooling rate after solution treatment on subsequent phase separation during aging of Fe-Cr alloys: A small-angle neutron scattering study. Acta Mater. 2017, 134, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Westraadt, J.E.; Odqvist, J.; Youngs, T.G.; King, S.M.; Hedström, P. Effect of heat treatment above the miscibility gap on nanostructure formation due to spinodal decomposition in Fe-52.85 at. %Cr. Acta Mater. 2018, 145, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Thuvander, M.; Lindgren, K.; Oliver, J.; Folkeson, N.; Gonzalez, D.; Karlsson, L. Fe and Cr phase separation in super and hyper duplex stainless steel plates and welds after very short aging times. Mater. Des. 2021, 210, 110055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouali, N.; Khenfer, K.; Belkessa, B.; Fajoui, J.; Cheniti, B.; Idir, B.; Branchu, S. Effect of Heat Input on Microstructure, Residual Stress, and Corrosion Resistance of UNS 32101 Lean Duplex Stainless Steel Weld Joints. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2019, 28, 4252–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Cheng, X.; Wang, Y.; Dong, C.; Li, X. Effect of Mo on interaction between alpha/gamma phases of duplex stainless steel. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 267, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Odqvist, J.; Ruban, A.; Thuvander, M.; Xiong, W.; Ågren, J.; Olson, G.B.; Hedström, P. Effect of solution treatment on spinodal decomposition during aging of an Fe-46.5 at.% Cr alloy. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Lindgren, K.; Thuvander, M.; Gonzalez, D.; Oliver, J.; Karlsson, L. Nanoscale phase separations in as-fabricated thick super duplex stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 12475–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, A.; Martinez, C.; Hausbauer, M.; Kapp, M. Early Stages of Deleterious Phases in Super and Hyper Duplex Stainless Steel and Their Effect on Toughness. Berg Huettenmaenn Monatsh 2020, 165, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, V.A.; Hurtig, K.; Karlsson, L. Effect of multipass TIG welding on the corrosion resistance and microstructure of a super duplex stainless steel. Mater. Corros. 2017, 68, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhandha, K.H.; Badheka, V.J. Effect of activating fluxes on weld bead morphology of P91 steel bead-on-plate welds by flux assisted tungsten inert gas welding process. J. Manuf. Process. 2015, 17, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Luo, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zeng, Y. Effect of cerium oxide flux on active flux TIG welding of 800 MPa super steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2016, 230, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anup, K.; Dwivedi, D.K.; Vasudevan, M. Study of mechanism, microstructure and mechanical properties of activated flux TIG welded P91 Steel-P22 steel dissimilar metal joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 731, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinheiro, F.W.; de Souza, L.M.; Pereira, E.C.; Monteiro, S.N.; Azevedo, A.R. Effect of solubilization heat treatment on microstructure and corrosion resistance of joints welded with the autogenous TIG process duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Christiansen, T.L.; Somers, M.A. Influence of ferrite-austenite distribution in 2205 duplex stainless steel on high-temperature solution nitriding behaviour. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 453, 129134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L.; Lv, X.; Zhang, J. The impact of annealing temperature on improving microstructure and toughness of electron beam welded duplex stainless steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 31, 568–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wei, Y.; Yang, C. Marangoni convection and weld shape variation in A-TIG welding process. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2007, 48, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Huang, Y.; Fan, D.; Guo, Y. Investigation of heat transfer and fluid flow in activating TIG welding by numerical modeling. Appl. Therm. Eng. Des. Process. Equip. Econ. 2017, 113, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucott, L.; Dong, H.B.; Mirihanage, W.; Atwood, R.; Kidess, A.; Gao, S.A.; Wen, S.W.; Marsden, J.; Feng, S.; Tong, M.M.; et al. Revealing internal flow behavior in arc welding and additive manufacturing of metals. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modenesi, P.J.; Neto, P.C.; Apolinário, E.R.; Dias, K.B. Effect of flux density and the presence of additives in ATIG welding of austenitic stainless steel. Weld. Int. 2015, 29, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.-H.; Liu, M.-H.; Yi, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-P.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Xu, L. Activated flux tungsten inert gas welding of 8mm-thick AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. J. Cent. South Univ. 2015, 22, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippold, J.C.; Savage, W.F. Solidification of austenitic stainless steel weldments: Part 2-The effect of alloy composition on ferrite morphology. Weld. J. 1980, 59, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Vidyarthy, R.S.; Kulkarni, A.; Dwivedi, D.K. Study of microstructure and mechanical property relationships of A-TIG welded P91–316L dissimilar steel joint. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 695, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayee, S.G.; Badheka, V.J. Effect of oxide-based fluxes on mechanical and metallurgical properties of dissimilar activating flux assisted-tungsten inert gas welds. J. Manuf. Process. 2014, 16, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeid, T.; Abdollah-Zadeh, A.; Assadi, H.; Ghaini, F.M. Effect of friction stir welding speed on the microstructure and mechanical properties of a duplex stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 496, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, J.; Taiwade, R.V.; Kataria, R.; Kumar, A. Welding and electrochemical behavior of ferritic AISI 430 and austeno-ferritic UNS 32205 dissimilar welds. J. Manuf. Process. 2018, 34, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokita, S.; Kokawa, H.; Sato, Y.S.; Fujii, H.T. In situ EBSD observation of grain boundary character distribution evolution during thermo mechanical process used for grain boundary engineering of 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Charact. 2017, 131, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jing, H.; Xu, L.; Han, Y.; Zhao, L. Investigation on microstructure evolution and properties of duplex stainless steel joint multi-pass welded by using different methods. Mater. Des. 2016, 109, 670–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shao, P.; Wang, X.; Fan, D. Improving weld penetration by two-TIG arc activated via mixing oxygen into shielding gas. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 125, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienert, T.; Burgardt, P.; Harada, K.; Forsyth, R.; DebRoy, T. Weld bead center line shift during laser welding of austenitic stainless steels with different sulfur content. Scr. Mater. 2014, 71, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xue, J.; Wang, Q. Correlation between arc mode, microstructure, and mechanical properties during wire arc additive manufacturing of 316L stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 751, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]























| Elements | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Ti | C | Al | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 0.49 | 0.58 | 20.42 | 5.26 | 0.55 | 0.12 | 0.09 | Bal. |
| Welding Current I/A | Welding Speed V/(mm/s) | Shielding Gas Flow Rate Q (L/min) | Arc Length L/mm | Type of Active Agent |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 260 | 1.76 | 15 | 3 | 0.033NiO + 0.632SiO2 + 0.037TiO2 + 0.162Cr2O3 + 0.137Al2O3 |
| Level | NiO/% | SiO2/% | TiO2/% | Cr2O3/% | Al2O3/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.548 | 0.103 | 0.073 | 0.057 | 0.218 |
| 2 | 0.405 | 0.008 | 0.319 | 0.123 | 0.145 |
| 3 | 0.324 | 0.188 | 0.031 | 0.323 | 0.133 |
| 4 | 0.265 | 0.032 | 0.227 | 0.456 | 0.020 |
| 5 | 0.217 | 0.264 | 0.413 | 0.013 | 0.093 |
| 6 | 0.177 | 0.062 | 0.121 | 0.240 | 0.400 |
| 7 | 0.142 | 0.349 | 0.234 | 0.172 | 0.103 |
| 8 | 0.111 | 0.097 | 0.017 | 0.679 | 0.097 |
| 9 | 0.083 | 0.459 | 0.121 | 0.014 | 0.324 |
| 10 | 0.057 | 0.139 | 0.521 | 0.083 | 0.202 |
| 11 | 0.033 | 0.632 | 0.037 | 0.162 | 0.137 |
| 12 | 0.011 | 0.183 | 0.313 | 0.391 | 0.103 |
| Elements | O | Fe | Cr | Ni | Ti | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 40.3 | 41.4 | 14.7 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| P2 | 35.2 | 49.9 | 11.8 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Elements | O | Fe | Cr | Ni | Ti | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 42.8 | 39.2 | 14.3 | 2.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| P2 | 49.5 | 33.4 | 14.6 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, S.; Huang, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ni, Y.; Fan, D. Improving Welding Penetration and Mechanical Properties via Activated-Flux Smearing by Tungsten Inert Gas Arc Welding. Metals 2023, 13, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13122017
Yue S, Huang Y, Yu X, Zhang J, Ni Y, Fan D. Improving Welding Penetration and Mechanical Properties via Activated-Flux Smearing by Tungsten Inert Gas Arc Welding. Metals. 2023; 13(12):2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13122017
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Shiqi, Yong Huang, Xiaoquan Yu, Jia Zhang, Yu Ni, and Ding Fan. 2023. "Improving Welding Penetration and Mechanical Properties via Activated-Flux Smearing by Tungsten Inert Gas Arc Welding" Metals 13, no. 12: 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13122017
APA StyleYue, S., Huang, Y., Yu, X., Zhang, J., Ni, Y., & Fan, D. (2023). Improving Welding Penetration and Mechanical Properties via Activated-Flux Smearing by Tungsten Inert Gas Arc Welding. Metals, 13(12), 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13122017







