Low-Temperature CO Oxidation over CuO-CeO2/Fe2O3 Catalyst: Effect of KMnO4 Modification
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.2.1. Load Material Pretreatment
2.2.2. Modified Potassium Permanganate
2.2.3. Supported Copper Cerium
2.3. Catalyst Characterization
2.3.1. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
2.3.2. N2 Adsorption/Desorption
2.3.3. Temperature-Programmed Reduction and Desorption
2.3.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.3.5. Raman Spectroscopy (Raman)
2.4. Catalytic Activity Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Activity
3.2. Structural and Textural Properties
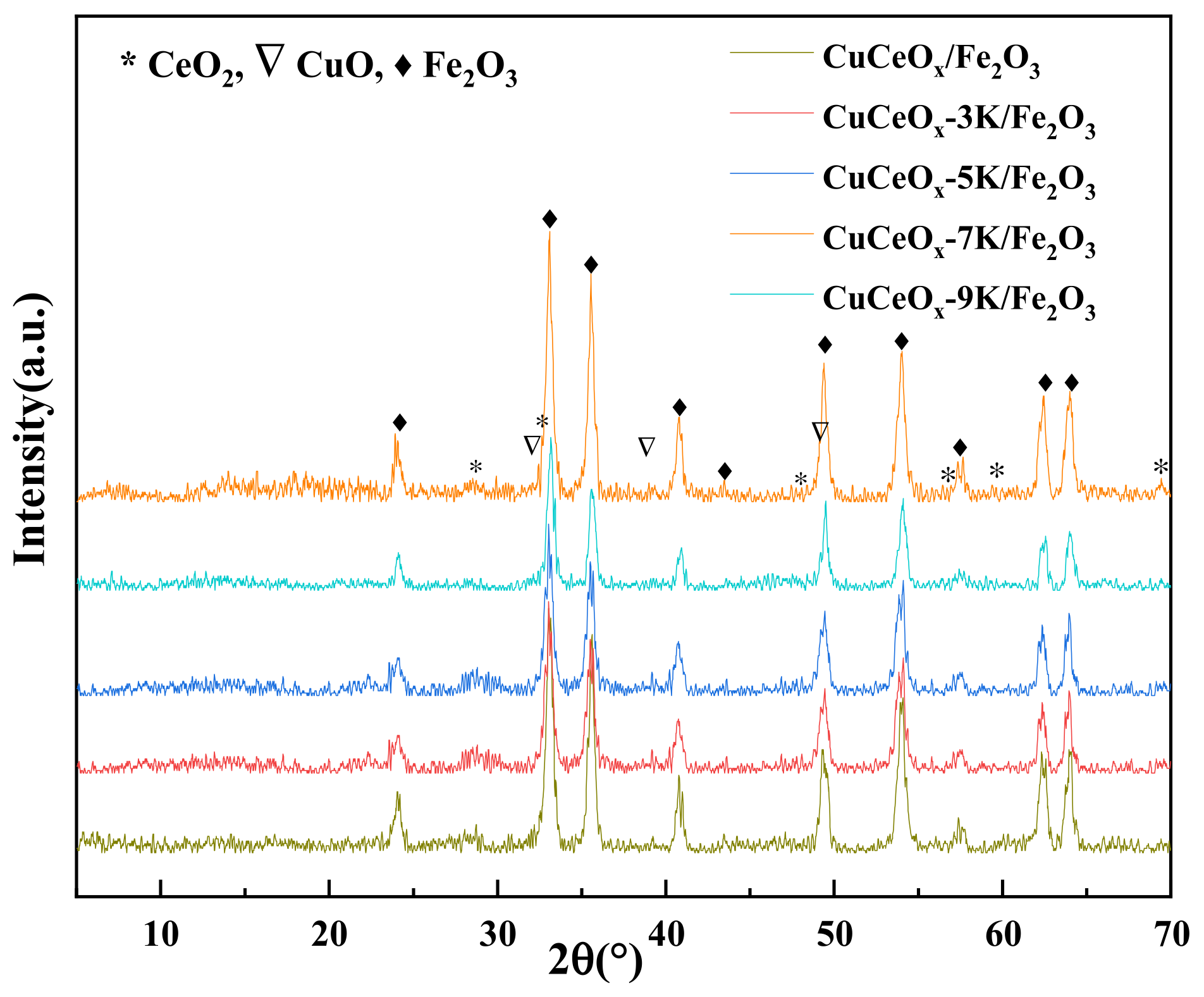
3.2.1. XRD Analysis
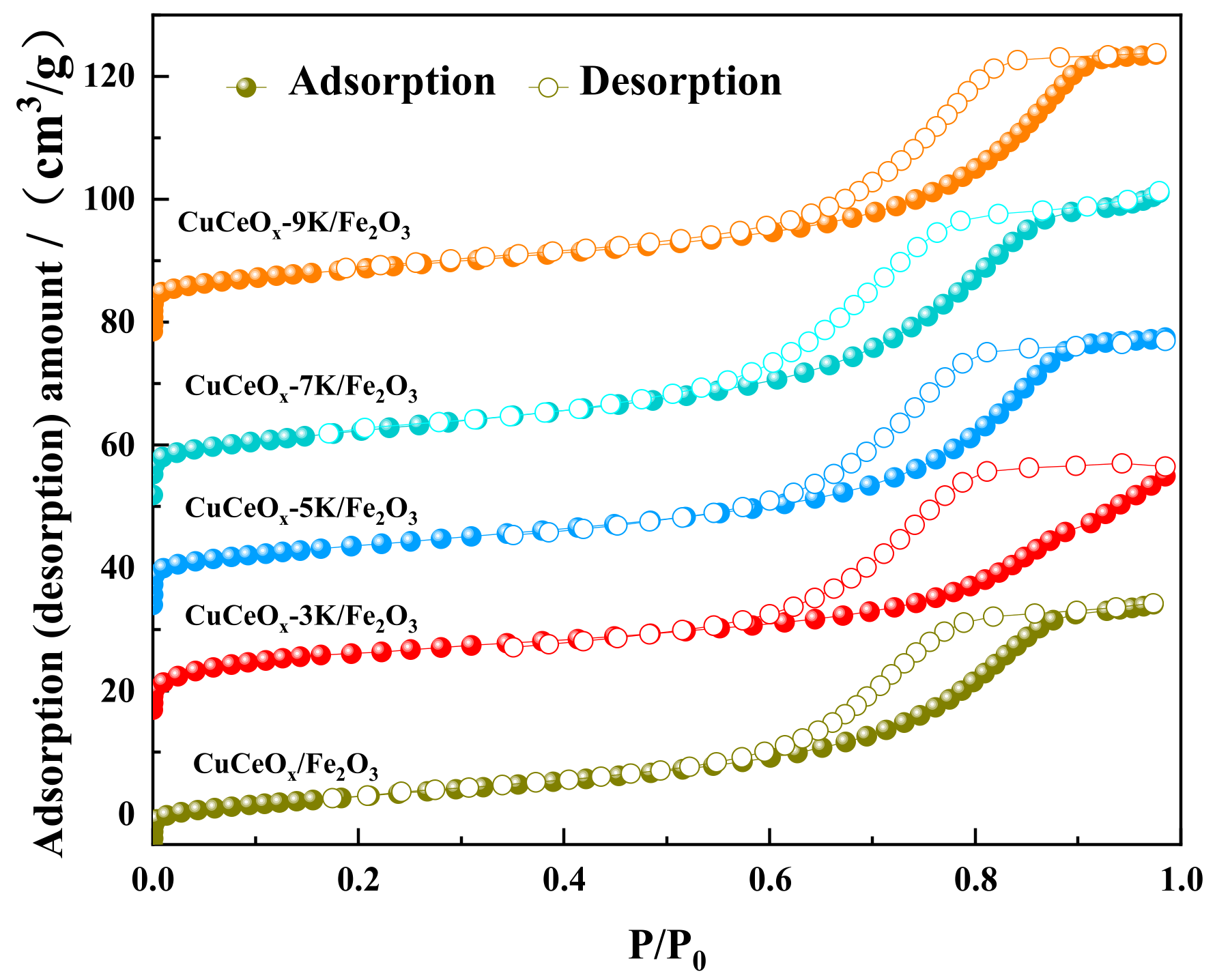
3.2.2. BET Analysis
3.2.3. SEM Analysis
3.2.4. Raman Analysis
3.3. Redox Properties
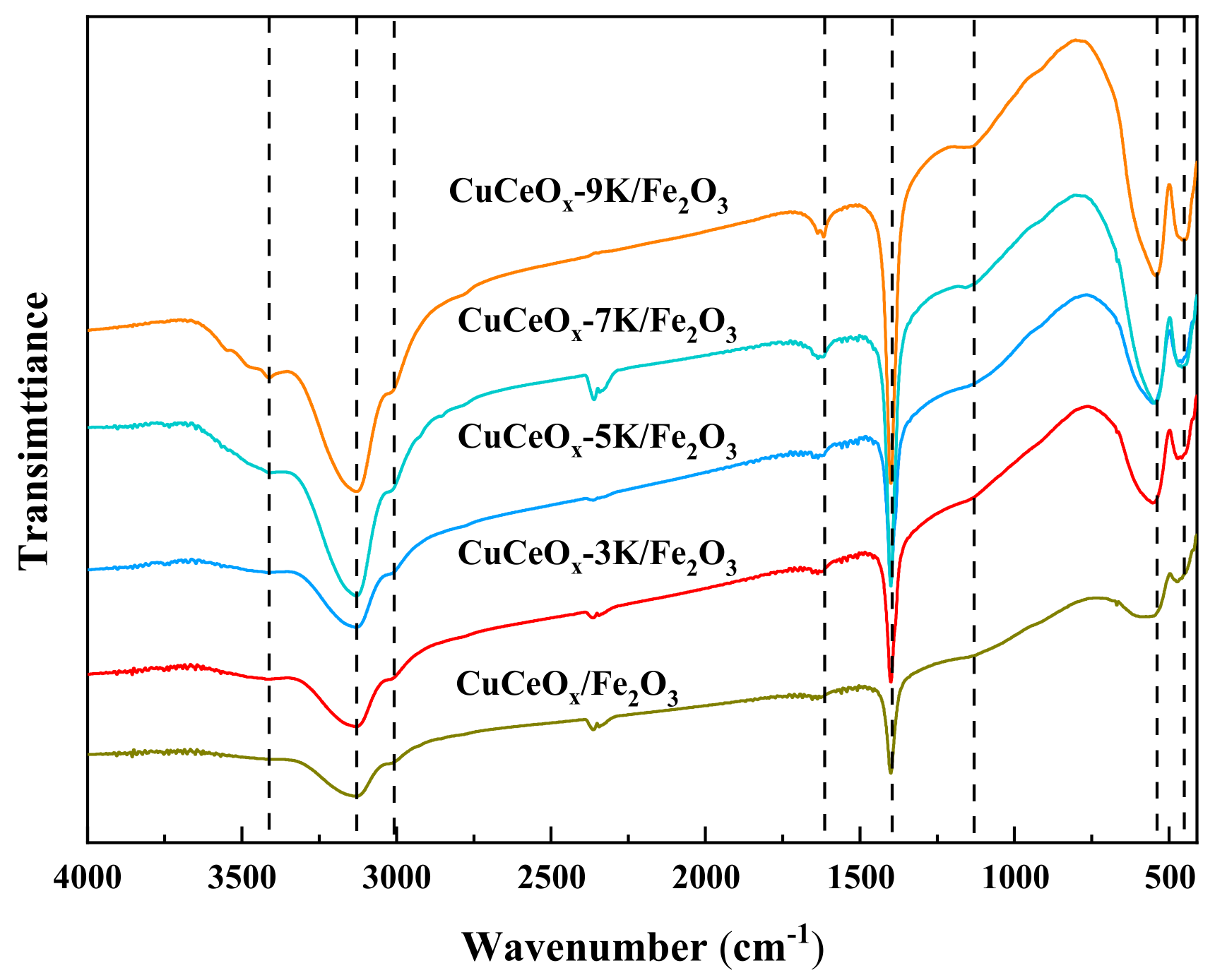
3.3.1. FT-IR Analysis
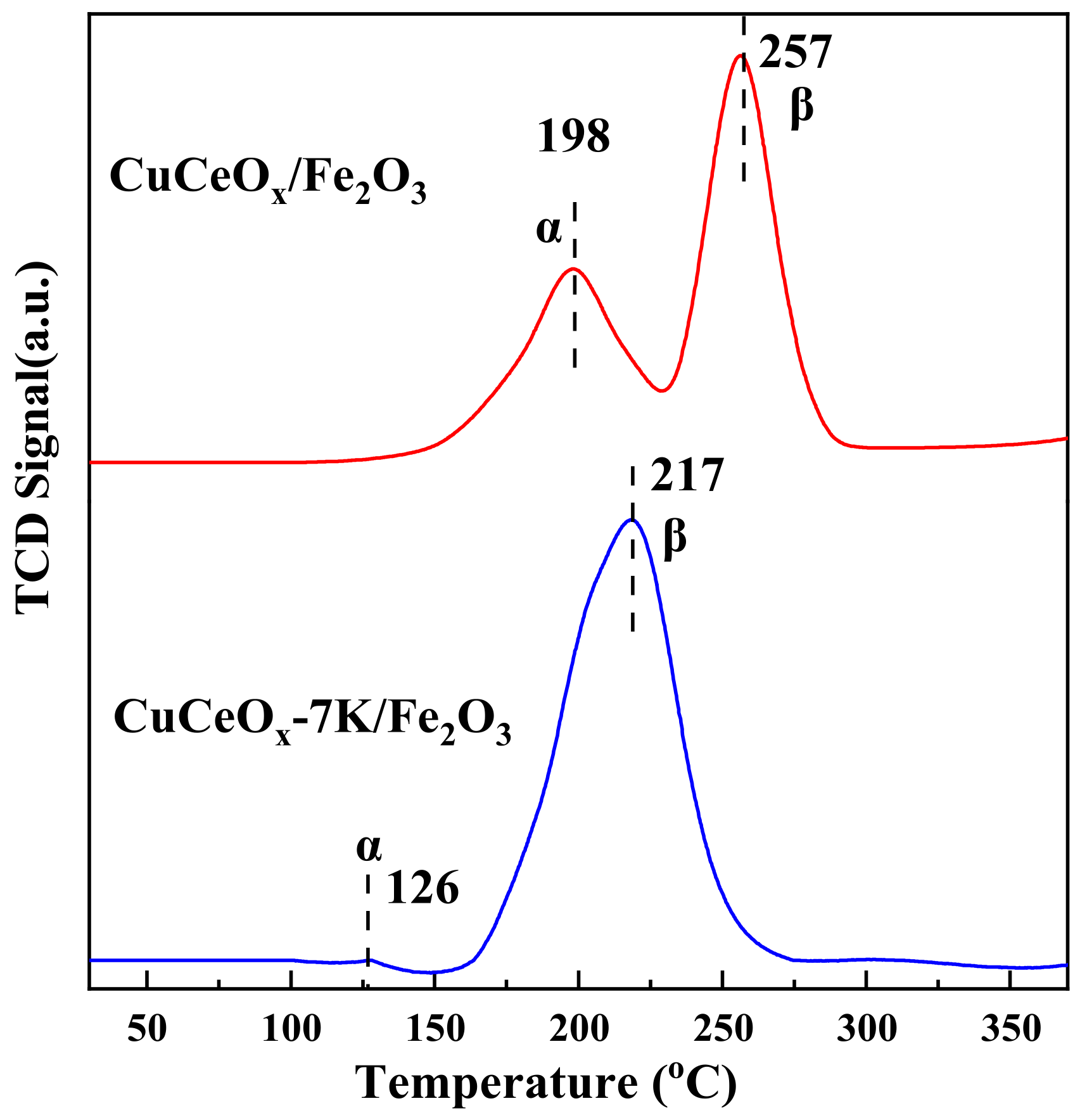
3.3.2. H2-TPR Analysis
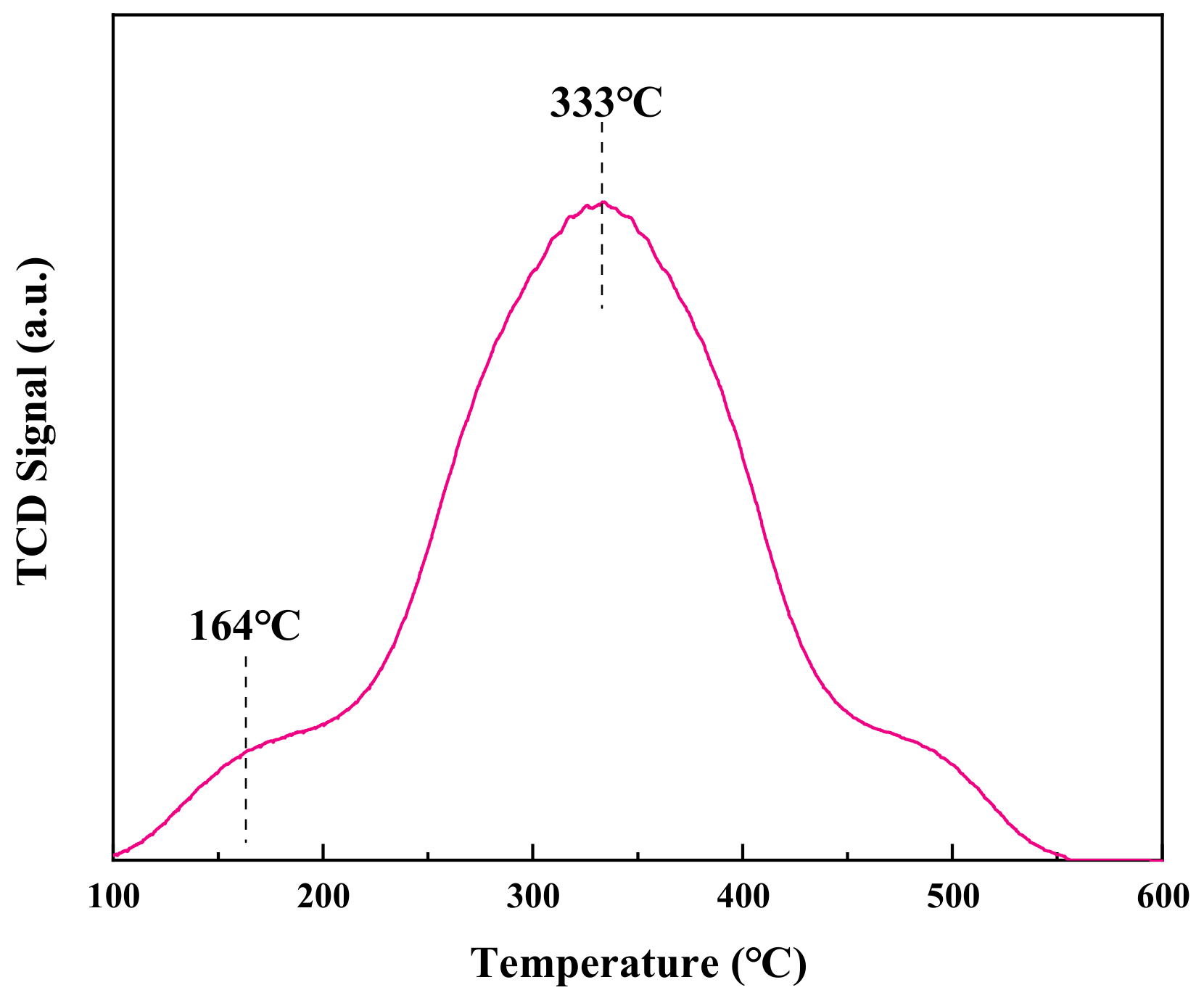
3.3.3. CO-TPD Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The modification of KMnO4 inhibited the growth of the particles and promoted the uniform dispersion of the active components.
- (2)
- The number of oxygen-containing functional groups increased after KMnO4 modification, which could provide anchoring sites for metal oxides and provide reactive oxygen species for CO oxidation as an oxygen source.
- (3)
- The KMnO4 modification improved the redox performance of the catalyst and increased the number of active sites for CO adsorption.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, B. Low-temperature and stable CO oxidation of Co3O4/TiO2 monolithic catalysts. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Kouotou, P.M.; El Kasmi, A.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.Y. Role of copper grid mesh in the catalytic oxidation of CO over one-step synthesized Cu-Fe-Co ternary oxides thin fil. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Yin, Q.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Xu, L.; Lv, B.; Zhang, G. Self-assembly of a highly stable and active Co3O4/H-TiO2 bulk heterojunction with high-energy interfacial structures for low temperature CO catalytic oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 8374–8382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegarpanah, A.; Rezaei, M.; Meshkani, F.; Dai, H. 3D ordered honeycomb-shaped CuO center dot Mn2O3: Highly active catalysts for CO oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2020, 485, 110820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, S.; Xing, X.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q. Effect of MnO2 crystal types on CeO2@MnO2 oxides catalysts for low-temperature NH3-SCR. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Teng, Z.; Kang, R.; Bin, F.; Wei, X.; Hao, Q.; Hui, K.N.; Hui, K.S.; Dou, B. Study on activity, stability limit and reaction mechanism of CO self-sustained combustion over the LaMnO3, La0.9Ce0.1MnO3 and La0.9Sr0.1MnO3 perovskite catalysts using sugar agent. Fuel 2021, 292, 120289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKetbi, M.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Jaoude, M.A.; Vasiliades, M.A.; Sebastian, V.; Hinder, S.J.; Baker, M.A.; Zedan, A.F.; Efstathiou, A.M. Cu-Ce-La-Ox as efficient CO oxidation catalysts: Effect of Cu content. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 505, 144474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Fan, L.; Liao, W.; Zhao, F.; Tang, C.; Zhang, J.; Feng, M.; Lu, J.Q. Structure sensitivity of CuO in CO oxidation over CeO2-CuO/Cu2O catalysts. J. Catal. 2022, 405, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariño, F.; Iglesias, I.; Baronetti, G.; Alemany, L.; Laborde, M. Egg-shell CuO/CeO2/Al2O3 catalysts for CO preferential oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 11235–11241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.G.; Almeida, K.A.; Silva, T.F.; Assaf, J.M. CO preferential oxidation reaction aspects in a nanocrystalline CuO/CeO2 catalys. Catal. Today 2020, 344, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Lao, J.; Ye, J.; Cheng, D.G.; Chen, F.; Zhan, X. Role of Two-Electron Defects on the CeO2 Surface in CO Preferential Oxidation over CuO/CeO2 Catalysts. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 18421–18433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Ding, T.; Gao, W.; Ma, K.; Tian, Y.; Li, X. CuO/CeO2 catalysts synthesized from Ce-UiO-66 metal-organic framework for preferential CO oxidation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 17457–17465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhang, X.; Su, D.; Wang, Z.; Chang, J.; Ma, C. NO reduction by CO over copper catalyst supported on mixed CeO2 and Fe2O3: Catalyst design and activity test. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2018, 239, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.W.; Du, P.P.; Zou, S.H.; He, H.Y.; Wang, R.X.; Jin, Z.; Shi, S.; Huang, Y.Y.; Si, R.; Song, Q.S.; et al. Highly Dispersed Copper Oxide Clusters as Active Species in Copper-Ceria Catalyst for Preferential Oxidation of Carbon Monoxide. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Han, C.; Gao, X.; Lu, J.; Wan, G.; He, D.; Chen, R.; Chen, K.; He, S.; Luo, Y. Rapid synthesis of Fe-doped CuO-Ce0.8Zr0.2O2 catalysts for CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich streams: Effect of iron source and the ratio of Fe/Cu. J. Power Sources 2017, 343, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, Z. Effects of the Fe/Ce ratio on the activity of CuO/CeO2–Fe2O3 catalysts for NO reduction by CO. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 3336–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Zou, Q.; He, D.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z.; He, S.; Luo, Y. Unravelling the Nature of the Active Species as well as the Doping Effect over Cu/Ce-Based Catalyst for Carbon Monoxide Preferential Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 2177–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Duan, Y.; Zhong, X.; Xie, W.; Luo, Y.; Huang, L. Formic Acid Modified Co3O4-CeO2 Catalysts for CO Oxidation. Catalysts 2016, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, C.; Si, Z.; Ma, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis to light olefins over iron-based catalysts supported on KMnO4 modified activated carbon by a facile method. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 541, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, X.; Ji, J.; Duan, X.; Qian, G.; Zhou, X.; Chen, D.; Yuan, W. Modified carbon nanotubes by KMnO4 supported iron Fischer–Tropsch catalyst for the direct conversion of syngas to lower olefins. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 4560–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, B. Effect of iron on physicochemical properties: Enhanced catalytic performance for novel Fe2O3 modified CuO/Ti0.5Sn0.5O2 in low temperature CO oxidation. Mol. Catal. 2018, 456, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, B.; Shan, C.; Zhang, W.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Pan, B. Roles of oxygen-containing functional groups of O-doped g-C3N4 in catalytic ozonation: Quantitative relationship and first-principles investigation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2021, 292, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Tsiakaras, P.; Song, S. In-situ electrosynthesis of hydrogen peroxide and wastewater treatment application: A novel strategy for graphite felt activation. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2018, 237, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xing, X.; Pang, Z.; Wang, S.; Du, Y.; Lv, M. Effect of Na2CO3, HF, and CO2 Treatment on the Regeneration of Exhausted Activated Carbon Used in Sintering Flue Gas. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 25762–25771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Xing, X.; Pang, Z.; Wang, S.; Lv, M.; Jiang, X. Low Temperature CO Oxidation in Sintering Flue Gas Over Cu-Ce/AC Catalysts: Effect of Pretreatment with KMnO4 on Activity. Catal. Lett. 2022, 7, 10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, D.; Jia, C.J.; Bongard, H.; Spliethoff, B.; Weidenthaler, C.; Schmidt, W.; Schüth, F. Ordered mesoporous Cu–Ce–O catalysts for CO preferential oxidation in H2-rich gases: Influence of copper content and pretreatment conditions. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2014, 152–153, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Lu, G.; Tang, Z. Controlled pore size of 3D mesoporous Cu-Ce based catalysts and influence of surface textures on the CO catalytic oxidation. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 231, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Mao, D.; Shen, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, J. Preparation and characterization of mesostructured cellular foam silica supported Cu-Ce mixed oxide catalysts for CO oxidation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 9732–9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reagent | Chemical Formula | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| Cerium nitrate Copper nitrate | Ce(NO3)3·6H2O Cu(NO3)2·3H2O | Analytical-grade reagent Analytical-grade reagent |
| Ferric nitrate | Fe(NO3)2·9H2O | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Ammonia | NH3·H2O | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Nitric acid | HNO3 | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Sulfuric acid | H2SO4 | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Potassium permanganate | KMnO4 | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Polyvinyl alcohol | C2H4On | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Potassium bromide | KBr | Analytical-grade reagent |
| Nitrogen | N2 | High-purity gas (99.9%) |
| Oxygen | O2 | High-purity gas (99.9%) |
| Sulfur dioxide | SO2 | N2-SO2 (1.05%) |
| Carbon monoxide | CO | N2-CO (1.03%) |
| Name | Model |
|---|---|
| Electronic analytical balance | AL204 |
| Electric blast-drying oven | DZF-6020A |
| Magnetic stirrer | DF101-S |
| Constant-temperature water bath | THZ-82 |
| Vacuum tube furnace | GSL-1400X |
| X-ray photoelectron spectrometer | Thermo ESCALAB 250XI |
| X-ray diffractometer | D8 ADVANCE A25 |
| Scanning electron microscope | VEGA 3 XMU/XMH |
| Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy | Nexus870 |
| Chemisorber | AutoChem II 2920 |
| Confocal laser Raman spectrometer | LabRAM HR |
| Pore size analyzer | JW-BK222 |
| Samples | Sg (m2/g) | Vp (m3/g) | Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CuCeOx/Fe2O3 | 36 | 0.076 | 8.022 |
| CuCeOx-3K/Fe2O3 | 35 | 0.070 | 7.774 |
| CuCeOx-5K/Fe2O3 | 33 | 0.067 | 7.786 |
| CuCeOx-7K/Fe2O3 | 29 | 0.064 | 7.936 |
| CuCeOx-9K/Fe2O3 | 27 | 0.061 | 8.395 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, L.; Xing, X.; Du, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Yang, L.; Lv, M. Low-Temperature CO Oxidation over CuO-CeO2/Fe2O3 Catalyst: Effect of KMnO4 Modification. Metals 2023, 13, 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020186
Feng L, Xing X, Du Y, Shen Z, Zhang H, Yang L, Lv M. Low-Temperature CO Oxidation over CuO-CeO2/Fe2O3 Catalyst: Effect of KMnO4 Modification. Metals. 2023; 13(2):186. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020186
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Lu, Xiangdong Xing, Yueli Du, Zhenghua Shen, Hui Zhang, Liu Yang, and Ming Lv. 2023. "Low-Temperature CO Oxidation over CuO-CeO2/Fe2O3 Catalyst: Effect of KMnO4 Modification" Metals 13, no. 2: 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020186
APA StyleFeng, L., Xing, X., Du, Y., Shen, Z., Zhang, H., Yang, L., & Lv, M. (2023). Low-Temperature CO Oxidation over CuO-CeO2/Fe2O3 Catalyst: Effect of KMnO4 Modification. Metals, 13(2), 186. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13020186







