Influence of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Impact Toughness in Weld Metal by High-Efficiency Submerged Arc Welding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Welding Tests
2.2. Mechanical Tests
2.3. Fracture Observation
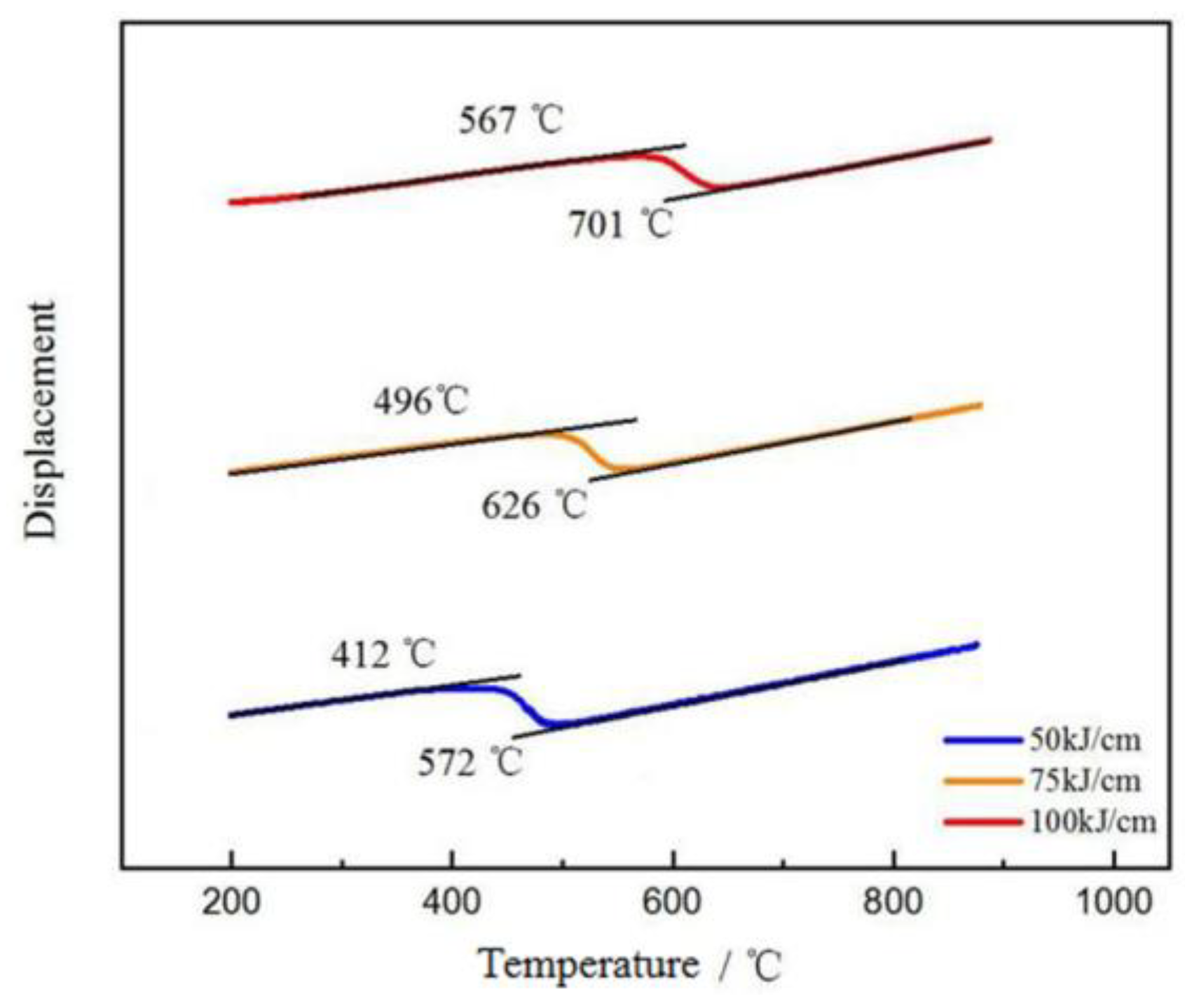
2.4. The Determination of Phase Transition Temperature
2.5. Microstructure Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Microstructure Observations of the Weld Metal
3.2. Crystallographic Characteristics of the Weld Metal
3.3. Impact Toughness and Fracture Behavior of the Weld Metal
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Ej on the Inclusions of the Weld Metal
4.2. Effect of Ej on the Microstructures of the Weld Metal
4.3. Effects of Ej on the Impact Toughness and Fracture Behaviors of the Weld Metal
5. Conclusions
- The increase in Ej from 50 kJ/cm to 100 kJ/cm led to a significant reduction in the number of inclusions in the weld metal and a significant increase in their size from 0.59 to 1.26 μm. The ability to stimulate AF nucleation of inclusions was decreased with the increase of Ej due to the increased transformation temperature from austenite to ferrite and the relaxation of stress around the interface between large-size inclusions and austenite;
- The microstructure of the weld metal welded by the high-efficiency submerged arc welding wires included GBF, FSP, PF, AF, GB, and M/A constituents. With the Ej increasing from 50 kJ/cm to 100 kJ/cm, the MEDMTA ≥ 15° of the weld metal increased from 3.1 to 5.3 μm. At the same time, AF content decreased from 84% to 65%, with an increase in PF from 5% to 13%. The average size of M/A constituents increased from 0.92 to 2.36 μm.
- The high-efficiency submerged arc welding wires studied in this work are suitable for Ej ≤ 75 kJ/cm. With the increase in Ej from 50 kJ/cm to 100 kJ/cm, the impact absorption energy decreased significantly from 130 J to 38 J. The fracture behavior of weld metal changed from mainly ductile fracture to mainly brittle fracture. With the increase in Ej, the local stress around the large size inclusions and M/A constituents was greatly improved, while the fraction of HAGBs decreased from 46.3% to 24.1%. These two factors led to the premature cleavage fracture of weld metal, and the impact energy decreased significantly.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ribic, B.; Palmer, T.A.; DebRoy, T. Problems and Issues in Laser-Arc Hybrid Welding. Int. Mater. Rev. 2009, 54, 223–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, G.M. The Effect of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Properties of C-Mn All-Weld-Metal Deposits. Met. Constr. 1982, 61, 125S–132S. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, M.; Fan, H.; Shi, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R. Effect of Welding Heat Input on Microstructure and Impact Toughness in the Simulated CGHAZ of Low Carbon Mo-V-Ti-N-B Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xia, D.; Ma, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, C.; Gao, X.; Du, L. Study on Microstructure Characterization and Impact Toughness in the Reheated Coarse-Grained Heat Affected Zone of V-Microalloyed Steel. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stornelli, G.; Tselikova, A.; Mirabile Gattia, D.; Mortello, M.; Schmidt, R.; Sgambetterra, M.; Testani, C.; Zucca, G.; Di Schino, A. Influence of Vanadium Micro-Alloying on the Microstructure of Structural High Strength Steels Welded Joints. Materials 2023, 16, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimani, M.; Hajjari, E.; Eskandari, M.; Szpunar, J.A. Electron Backscattered Diffraction Characterization of S900 HSLA Steel Welded Joints and Evolution of Mechanical Properties. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 3985–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viano, D.M.; Ahmed, N.U.; Schumann, G.O. Influence of Heat Input and Travel Speed on Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Double Tandem Submerged Arc High Strength Low Alloy Steel Weldments. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2000, 5, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Wang, Z.; Deng, X.; Wang, G.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Low Alloy Ultra-High Strength Structural Steel Welded Joint. Steel Res. Int. 2018, 89, 1700500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, R.; Zhu, W.; Guo, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, J. Microstructure Evolution and Impact Toughness Variation for High Strength Steel Multi-Pass Weld Metals with Various Cooling Rates. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 65, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, J.R.; Wang, Z.Q.; Li, X.C.; Shang, C.J.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of Interpass Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multi-Pass Weld Metal in a 550-MPa-Grade Offshore Engineering Steel. Weld World 2017, 61, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Qiu, C.; Song, H.; Zhao, D. Correlation of Martensite–Austenite Constituent and Cleavage Crack Initiation in Welding Heat Affected Zone of Low Carbon Bainitic Steel. Mater. Lett. 2014, 125, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Cayron, C.; Cao, R.; Logé, R.; Chen, J. The Relationship between Low-Temperature Toughness and Secondary Crack in Low-Carbon Bainitic Weld Metals. Mater. Charact. 2018, 145, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluken, A.O. Grong Mechanisms of Inclusion Formation in Al−Ti−Si−Mn Deoxidized Steel Weld Metals. Metall. Trans. A 1989, 20, 1335–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, D.; Gao, X.; Du, L. Analysis of Martensite–Austenite Constituent and Its Effect on Toughness in Submerged Arc Welded Joint of Low Carbon Bainitic Steel. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 4732–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Xu, S.; Tong, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Yan, F.; Zhang, W.; Bi, Z.; Yan, C. Comparative Study of Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of X80 SAW Welds Prepared Using Different Wires and Heat Inputs. J. Mater. Eng Perform. 2020, 29, 4322–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Kong, X.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, D. Influence of Microstructural Aspects on Impact Toughness of Multi-Pass Submerged Arc Welded HSLA Steel Joints. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H.; Christian, J.W. Bainite in Steels. MTA 1990, 21, 767–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Shi, G.; Peng, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. N-Induced Microstructure Refinement and Toughness Improvement in the Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone of a Low Carbon Mo–V–Ti–B Steel Subjected to a High Heat Input Welding Thermal Cycle. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 824, 141799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. Microstructural Characteristics and Impact Fracture Behaviors of Low-Carbon Vanadium-Microalloyed Steel with Different Nitrogen Contents. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 769, 138501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, G.; Sun, R.; Guo, K.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Q. Effect of Si Content on the Microstructures and the Impact Properties in the Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone (CGHAZ) of Typical Weathering Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 762, 138082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xin, W.; Ge, Z.; Luo, G.; Peng, J. Effect of High Heat Input Welding on the Microstructures, Precipitates and Mechanical Properties in the Simulated Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of a Low Carbon Nb-V-Ti-N Microalloyed Steel. Mater. Charact. 2023, 199, 112849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, D.; Gao, X.; Du, L. Microstructural Characteristics and Toughness of the Simulated Coarse Grained Heat Affected Zone of High Strength Low Carbon Bainitic Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 529, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.; Qiu, C.; Zhao, D.; Gao, X.; Du, L. Analysis of Microstructural Variation and Mechanical Behaviors in Submerged Arc Welded Joint of High Strength Low Carbon Bainitic Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; David, S.A.; DebRoy, T. Coarsening of Oxide Inclusions in Low Alloy Steel Welds. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 1996, 1, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindborg, U.; Torssell, K. A Collision Model for the Growth and Separation of Deoxidation Products. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 1968, 242, 94–102. [Google Scholar]
- Ricks, R.A.; Howell, P.R.; Barritte, G.S. The nature of acicular ferrite in HSLA steel weld metals. J. Mater. Sci. 1982, 17, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.-K.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, B.Y.; Hwang, S.K. Effect of Inclusion Size on the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite in Welds. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarma, D.S.; Karasev, A.V.; Jönsson, P.G. On the Role of Non-Metallic Inclusions in the Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite in Steels. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 1063–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babu, S.S. The Mechanism of Acicular Ferrite in Weld Deposits. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2004, 8, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.M.; Bhadeshia, H. Solid-State Nucleation of Acicular Ferrite on Minerals Added to Molten Steel. Acta Mater. 1997, 45, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Yang, Z.G.; Bai, B.Z.; Fang, H.S. Study of thermal stress and strain energy in γ-fe matrix around inclusion caused by thermal coefficient difference. Acta Met. Sin. 2003, 39, 1037–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Tweed, J.H.; Knott, J.F. Micromechanisms of failure in C Mn weld metals. Acta Metall. 1987, 35, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, V.; Cox, T.B.; Low, J.R.; Psioda, J.S. Microstructural Aspects of Fracture by Dimpled Rupture. Int. Mater. Rev. 1985, 30, 157–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avazkonandeh-Gharavol, M.H.; Haddad-Sabzevar, M.; Haerian, A. Effect of Copper Content on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Multipass MMA, Low Alloy Steel Weld Metal Deposits. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 30, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Nan, Y.R.; Xie, Z.J.; Tsai, Y.T.; Yang, J.R.; Shang, C.J. Influence of Welding Pass on Microstructure and Toughness in the Reheated Zone of Multi-Pass Weld Metal of 550 MPa Offshore Engineering Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 702, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, G.I.; Bhadeshia, H.K.D.H. Bainite Transformation Kinetics Part 1 Modified Model. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1992, 8, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Fan, H.; Shi, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. Effect of Ferritic Morphology on Yield Strength of CGHAZ in a Low Carbon Mo-V-N-Ti-B Steel. Metals 2021, 11, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, K.; Chen, H.; Xiao, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F. Effect of Increased N Content on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of Low-C V-Microalloyed Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 651, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, M.; Tang, S.; Wang, G. Effect of Heat Input and M-A Constituent on Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of Heat Affected Zone in Low Carbon Steel. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 2017, 32, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Pan, S.; Wang, Z. Effect of Morphologies of Martensite–Austenite Constituents on Impact Toughness in Intercritically Reheated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of HSLA Steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 710, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, R.; Su, H.; Chai, F.; Wang, Q.; Yang, C. Effect of Nitrogen Content on the Second Phase Particles in V–Ti Microalloyed Shipbuilding Steel during Weld Thermal Cycling. Mater. Des. 2016, 96, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.S.; David, S.A.; Vitek, J.M.; Mundra, K.; DebRoy, T. Development of Macro- and Microstructures of Carbon–Manganese Low Alloy Steel Welds: Inclusion Formation. Mater. Sci. Technol. 1995, 11, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Kang, J.; Yuan, G.; Di, H.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of Microstructure on the Crack Propagation Behavior of Microalloyed 560MPa (X80) Strip during Ultra-Fast Cooling. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 666, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Li, J.; Liu, D.S.; Ma, J.Y.; Chen, J.H. Micromechanism of Decrease of Impact Toughness in Coarse-Grain Heat-Affected Zone of HSLA Steel with Increasing Welding Heat Input. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 2999–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Meizoso, A.; Ocaña-Arizcorreta, I.; Gil-Sevillano, J.; Fuentes-Pérez, M. Modelling Cleavage Fracture of Bainitic Steels. Acta Metall. Et Mater. 1994, 42, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert-Perlade, A.; Gourgues, A.F.; Besson, J.; Sturel, T.; Pineau, A. Mechanisms and Modeling of Cleavage Fracture in Simulated Heat-Affected Zone Microstructures of a High-Strength Low Alloy Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2004, 35, 1039–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Shang, C.; Li, X.; Misra, R.D.K. The Contribution of Intragranular Acicular Ferrite Microstructural Constituent on Impact Toughness and Impeding Crack Initiation and Propagation in the Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) of Low-Carbon Steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 636, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Sample | Welding Current (I)/A | Welding Voltage (U)/V | Welding Speed (υ)/mh−1 | Interpass Temperature (T)/°C | Heat Input (Ej)/kJ cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WM-50 kJ/cm | 680 (AW) | 30 (AW) | 24 | 150≤ | 50 |
| 630 (PW) | 32 (PW) | ||||
| WM-75 kJ/cm | 750 (AW) | 32 (AW) | 21.5 | 150≤ | 75 |
| 700 (PW) | 34 (PW) | ||||
| WM-100 kJ/cm | 800 (AW) | 34 (AW) | 21 | 150≤ | 100 |
| 750 (PW) | 36 (PW) |
| Sample | Chemical Composition/wt% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weld flux | SiO2 + TiO2 | CaO + MgO | AI2O3 + MnO | CaF2 | S | P | |||
| 25–35 | 20–30 | 15–30 | 15–25 | 0.06 | 0.08 | ||||
| Element type | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Ni | Cr | Nb + V + Ti + Al + Mo + B | |
| Base metal | 0.07 | 0.22 | 1.52 | 0.013 | 0.002 | 0.027 | 0.04 | 0.106 | |
| Weld wire | 0.06 | 0.20 | 1.55 | 0.014 | 0.003 | 0.39 | 0.03 | 0.851 | |
| WM-50 kJ/cm | 0.06 | 0.21 | 1.53 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.37 | 0.03 | 0.832 | |
| WM-75 kJ/cm | 0.05 | 0.19 | 1.49 | 0.016 | 0.004 | 0.35 | 0.03 | 0.828 | |
| WM-100 kJ/cm | 0.05 | 0.16 | 1.44 | 0.017 | 0.004 | 0.33 | 0.03 | 0.821 | |
| Heat Input /kJ·cm−1 | Microstructures | fM/A /% | dM/A /μm | fMTA ≥ 15° /% | MEDMTA ≥ 15° /μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | AF + PF + GBF + GB | 2.2 | 0.92 | 46.3 | 3.1 |
| 75 | AF + PF + GBF + GB + FSP | 4.5 | 1.59 | 37.7 | 3.9 |
| 100 | AF + PF + GBF + GB + FSP | 8.3 | 2.36 | 24.1 | 5.3 |
| Heat Input kJ/cm | CVN Impact Energy at −40 °C/J | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 | Average Value | |
| 50 | 139 | 113 | 137 | 168 |
| 75 | 87 | 75 | 69 | 119 |
| 100 | 32 | 42 | 40 | 49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Hu, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, F.; He, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R. Influence of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Impact Toughness in Weld Metal by High-Efficiency Submerged Arc Welding. Metals 2023, 13, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071217
Li J, Hu B, Zhao L, Li F, He J, Wang Q, Liu R. Influence of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Impact Toughness in Weld Metal by High-Efficiency Submerged Arc Welding. Metals. 2023; 13(7):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jinjian, Bing Hu, Liyang Zhao, Fangmin Li, Jiangli He, Qingfeng Wang, and Riping Liu. 2023. "Influence of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Impact Toughness in Weld Metal by High-Efficiency Submerged Arc Welding" Metals 13, no. 7: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071217
APA StyleLi, J., Hu, B., Zhao, L., Li, F., He, J., Wang, Q., & Liu, R. (2023). Influence of Heat Input on the Microstructure and Impact Toughness in Weld Metal by High-Efficiency Submerged Arc Welding. Metals, 13(7), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13071217






