Comparison of Microstructures of Magnetite Reduced by H2 and CO under Microwave Field
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Work
2.1. Experimental Equipment
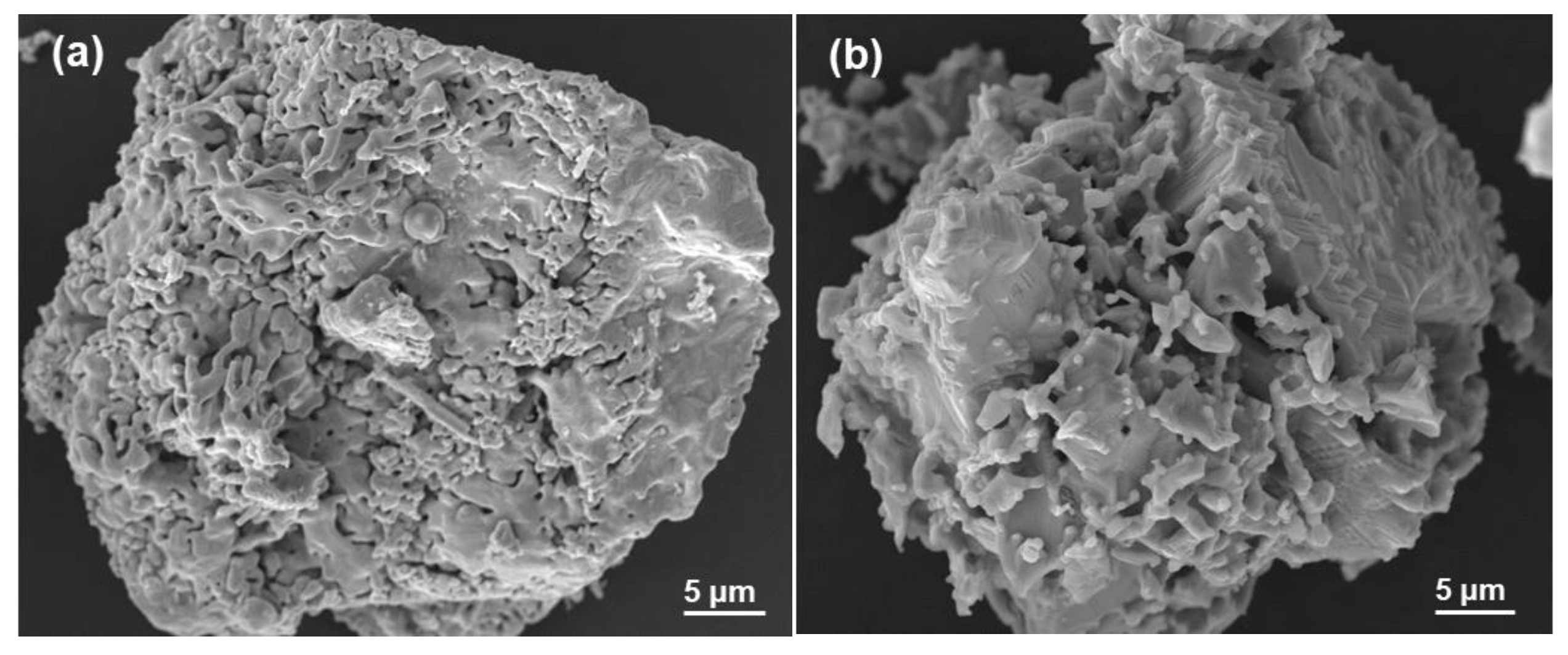
2.2. Experimental Raw Materials
3. Comparison of H2/CO Reduction Effects under a Microwave Field
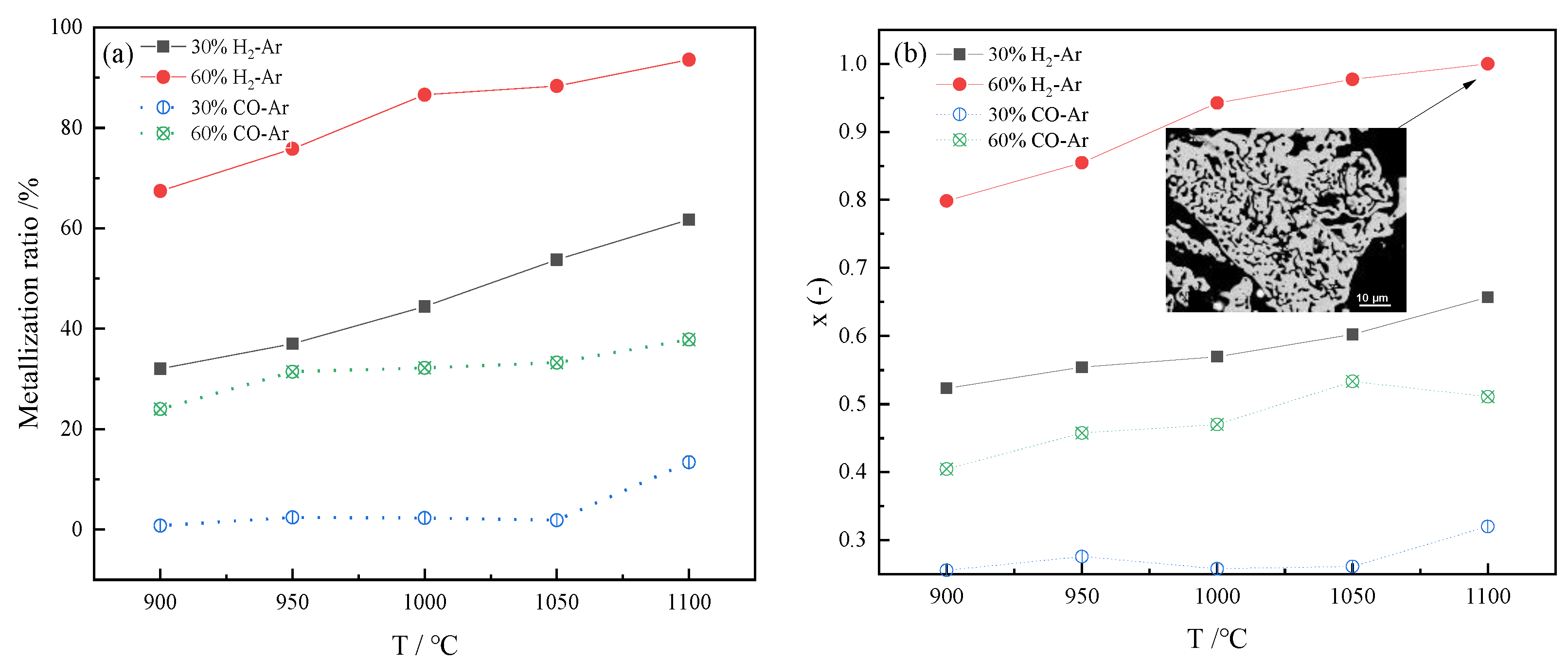
3.1. Calculation of Metallization Rate and Reduction Degree
3.2. Reduction Effect Analysis
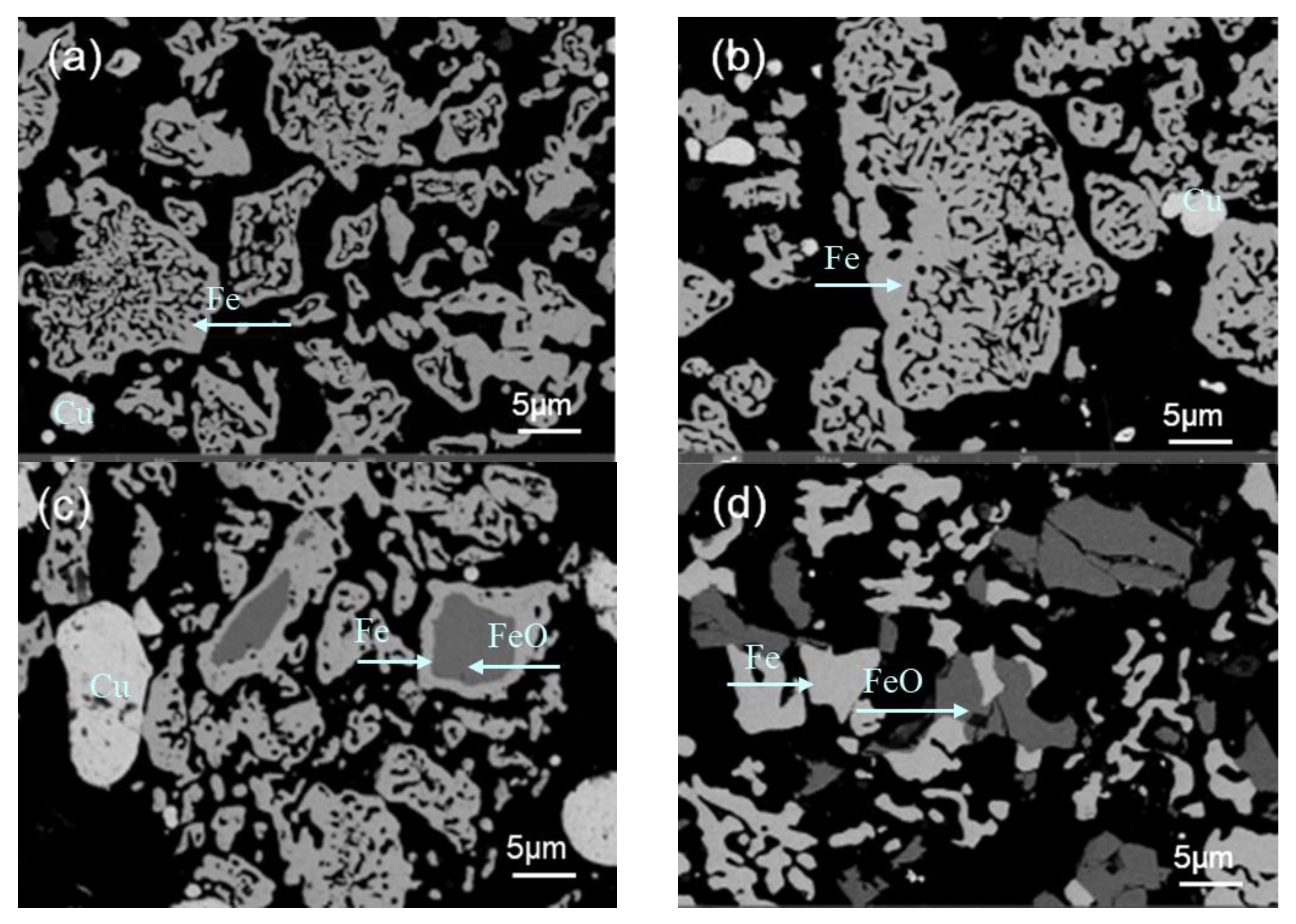
3.3. Microstructural Analysis
3.3.1. Magnetite Particle Morphology
3.3.2. The Effect of Different Temperatures
4. Reduction of Magnetite by H2 + CO Mixed Gas in Microwave Field
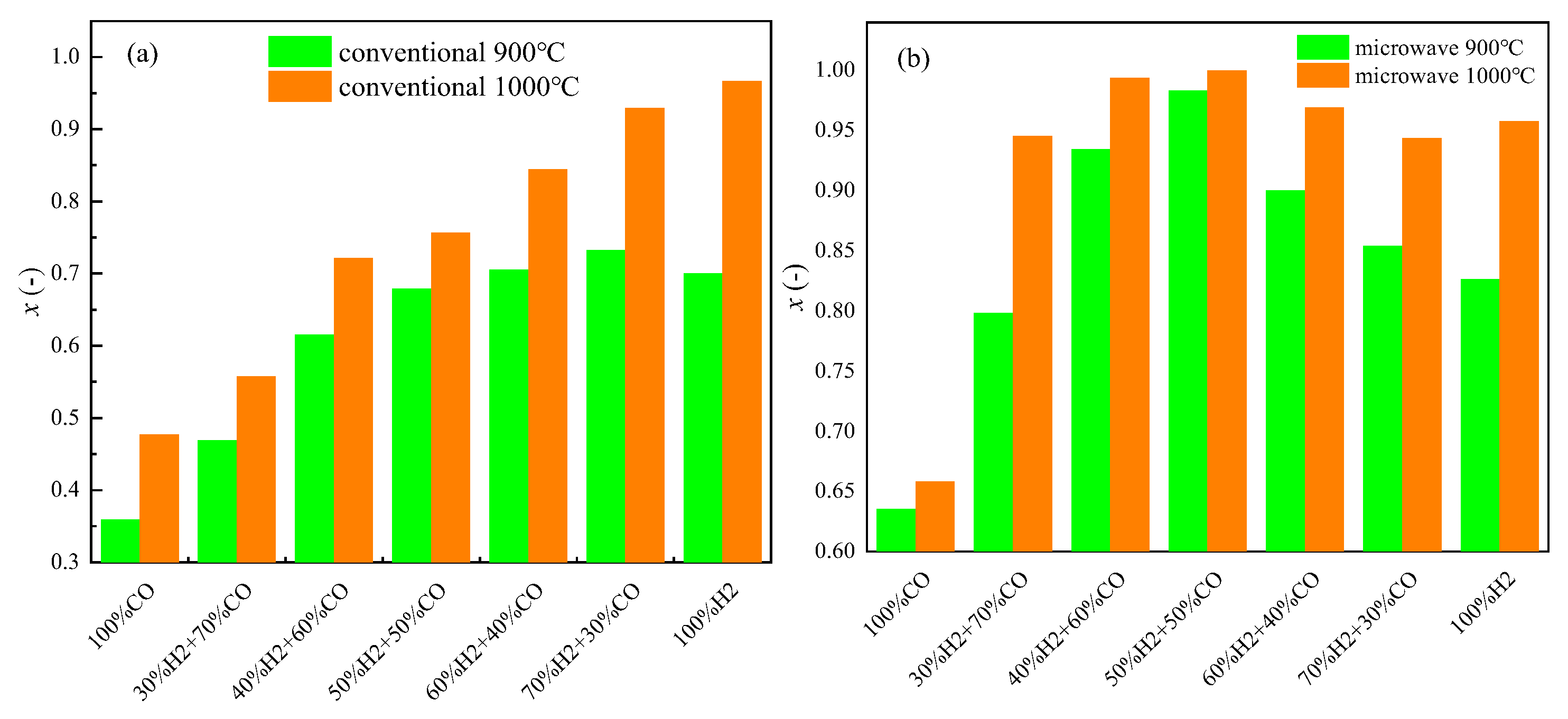
4.1. Reduction Effect Analysis
4.2. Microstructural Observation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Castro, J.A.; de Medeiros, G.A.; da Silva, L.M.; Ferreira, I.L.; de Campos, M.F.; de Oliveira, E.M. A Numerical Study of Scenarios for the Substitution of Pulverized Coal Injection by Blast Furnace Gas Enriched by Hydrogen and Oxygen Aiming at a Reduction in CO2 Emissions in the Blast Furnace Process. Metals 2023, 13, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z.; Jiao, K.; Liu, X.; Wang, R. Study on the controlling steps and reduction kinetics of iron oxide briquettes with CO-H2mixtures. Met. Res. Technol. 2017, 114, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, N.; Liang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiao, H.; Huang, Z. Coal ash induced ring formation in a pilot scale rotary kiln for low-grade iron ore direct reduction process: Characterization and mechanism. Fuel 2022, 310, 122342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahidoost, H.; Sheibani, S.; Raygan, S.; Hosseini, L.; Esmaeili, N. Mechanism of magnetite iron ore concentrate morphology affecting the pellet induration process. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, K.; Date, P.; Srivatsan, T.S. Influence of Material and Process Parameters on Reduction-Swelling Characteristics of Sintered Iron Pellets. Metals 2023, 13, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, S.; Yin, B.H.; Zhang, A.; Bumby, C.W. Pelletization and sintering of New Zealand titanomagnetite ironsand. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Wen, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, H.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z. The competitive adsorption behavior of CO and H2 molecules on FeO surface in the reduction pro-cess-ScienceDirect. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 2019, 44, 6427–6436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoy, D.; Sukhomlinov, D.; Tangstad, M. Pre-reduction Behaviour of Manganese Ores in H2 and CO Containing Gases. ISIJ Int. 2020, 60, 2325–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharm, C.; Küster, F.; Laabs, M.; Huang, Q.; Volkova, O.; Reinmöller, M.; Guhl, S.; Meyer, B. Direct reduction of iron ore pellets by H2 and CO: In-situ investigation of the structural transformation and reduction progression caused by atmosphere and temperature. Miner. Eng. 2022, 180, 107459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spreitzer, D.; Schenk, J. Iron Ore Reduction by Hydrogen Using a Laboratory Scale Fluidized Bed Reactor: Kinetic Investigation—Experimental Setup and Method for Determination. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2019, 50, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farjas, J.; Roura, P. Modification of the Kolmogorov–Johnson–Mehl–Avrami rate equation for non-isothermal experiments and its analytical solution. Acta Mater. 2006, 54, 5573–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, A.; Hunt, J.; Lita, A.; Ashleyl, B.; Stiegmanl, A.E. Microwave-Specific Effects on the Equilibrium Constants and Thermo-dynamics of the Steam−Carbon and Related Reactions. Indian J. Chem. A 2014, 118, 9346–9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Hosseini, M.; Zaferani, S.H.; Hall, M.; Vashaee, D. Enhancement of Diffusion, Densification and Solid-State Reactions in Dielectric Materials Due to Interfacial Interaction of Microwave Radiation: Theory and Experiment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50941–50952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, W.; You, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Gao, L.; Yin, C.; Peng, R.; Lan, L. A New Type of Power energy for Accelerating Chemical Reactions: The Nature of a Microwave-driving Force for Accelerating Chemical Reactions. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arshad, F.; Munir, A.; Tahir, A.; Hussain, S.Z.; Jilani, A.; Hussain, A.; Ullah, N.; Sher, F.; Hussain, I. Microwave-assisted growth of spherical core-shell NiFe LDH@CuxO nanostructures for electrocatalytic water oxidation reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energ. 2023, 48, 4719–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.-L.; Zhuang, C.-L. Carbothermal reduction characteristics of oxidized Mn ore through conventional heating and microwave heating. Int. J. Miner. Met. Mater. 2021, 28, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Liu, Y.Q.; Wang, X.N. Reaction Kinetics of Niobium Concentrate Microwave Carbothermal Reduction. Non-Ferr. Met. 2022, 7, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Binner, J.G.P.; Al-Dawery, I.A.H. Microwave melt texturing of bulk YBCO superconductors. Supercond. Sci. Technol. 1998, 11, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stir, M.; Ishizaki, K.; Vaucher, S.; Nicula, R. Mechanism and kinetics of the reduction of magnetite to iron during heating in a microwave E-field maximum. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 124901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Ohno, K.-I.; Maeda, T.; Kunitomo, K. Effect of the Ratio of Magnetite Particle Size to Microwave Penetration Depth on Reduction Reaction Behaviour by H2. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, C.; Ai, L.; Hong, L.; Li, Y. Study on solid state steelmaking from thin cast iron sheets through decarburization in H2O–H2. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2019, 47, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, A.; Kanari, N.; Gaballah, I. Kinetics of reduction of iron oxides by H2: Part I: Low temperature reduction of hematite. Thermochim. Acta 2006, 447, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Kamiya, Y.; Kodaira, T.; Kasai, E. Reduction Disintegration Behavior of Iron Ore Sinter under High H2 and H2O Conditions. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pineau, A.; Kanari, N.; Gaballah, I. Kinetics of reduction of iron oxides by H2: Part II. Low temperature reduction of magnetite. Thermochim. Acta 2007, 456, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, S.P.; Cho, T.R.; Hayes, P.C. Mechanisms of porous iron growth on wustite and magnetite during gaseous reduction. Met. Trans. B 1990, 21, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishihiro, K.; Maeda, T.; Ohno, K.-I.; Kunitomo, K. Effect of H2 Concentration on Carbon Deposition Reaction by CO–H2 Gas Mixture at 773 K to 973 K. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, Z.; Zhu, Q.; Fan, C.; Pan, F.; Li, H.; Xie, Z. Influence of reduction condition on the morphology of newly formed metallic iron during the fluid-ized bed reduction of fine iron ores and its corresponding agglomeration behavior. Steel Res. Int. 2016, 87, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Nakada, T.; Nagata, K. In-Situ Observation of Fe0.94O Reduction at High Temperature with the Use of Optical Microscopy. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2007, 38, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ei-Geassy, A.A.; Shehata, K.A.; Ezz, S.Y. Mechanism of Iron Oxide Reduction with Hydrogen/Carbon Monoxide Mixtures. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1977, 17, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, I.-J.; Rhee, C.-H.; Min, D.-J. Reduction of hematite compacts by H2-CO gas mixtures. Steel Res. 1998, 69, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, R.G.; Turkdogan, E.T. Catalytic effect of iron on decomposition of carbon monoxide: II. Effect of additions of H2, H2O, CO2, SO2 and H2S. Met. Trans. 1974, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelyushin, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jeong, S.; Ostrovski, O. Effects of Temperature and Gas Composition on Reduction and Swelling of Magnetite Concentrates. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2016, 47, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamser, D.J.; Johnson, D.L. Simulation of Hybrid Heating. MRS Proc. 1994, 347, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

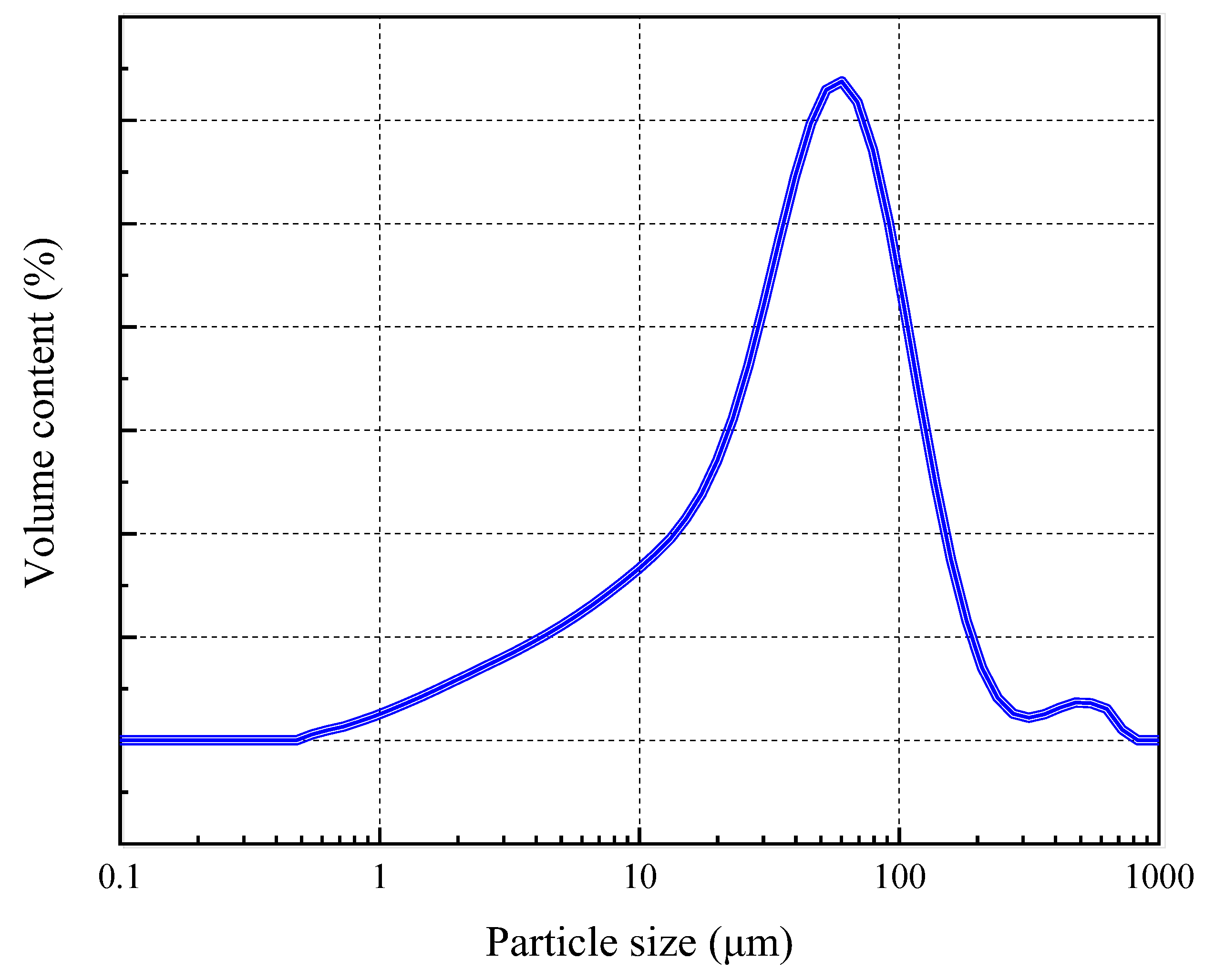





| Component | Magnetite | Mica | Quartz | Amphibole |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight percent | 95.7% | 1% | 0.4% | 2.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Ai, L.; Hong, L.; Sun, C.; Yuan, Y.; Tong, S. Comparison of Microstructures of Magnetite Reduced by H2 and CO under Microwave Field. Metals 2023, 13, 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13081367
Zhou M, Ai L, Hong L, Sun C, Yuan Y, Tong S. Comparison of Microstructures of Magnetite Reduced by H2 and CO under Microwave Field. Metals. 2023; 13(8):1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13081367
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Meijie, Liqun Ai, Lukuo Hong, Caijiao Sun, Yipang Yuan, and Shuai Tong. 2023. "Comparison of Microstructures of Magnetite Reduced by H2 and CO under Microwave Field" Metals 13, no. 8: 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13081367
APA StyleZhou, M., Ai, L., Hong, L., Sun, C., Yuan, Y., & Tong, S. (2023). Comparison of Microstructures of Magnetite Reduced by H2 and CO under Microwave Field. Metals, 13(8), 1367. https://doi.org/10.3390/met13081367






