Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules and Advances in Extraction Technology of Valuable Elements from Manganese Nodules
Abstract
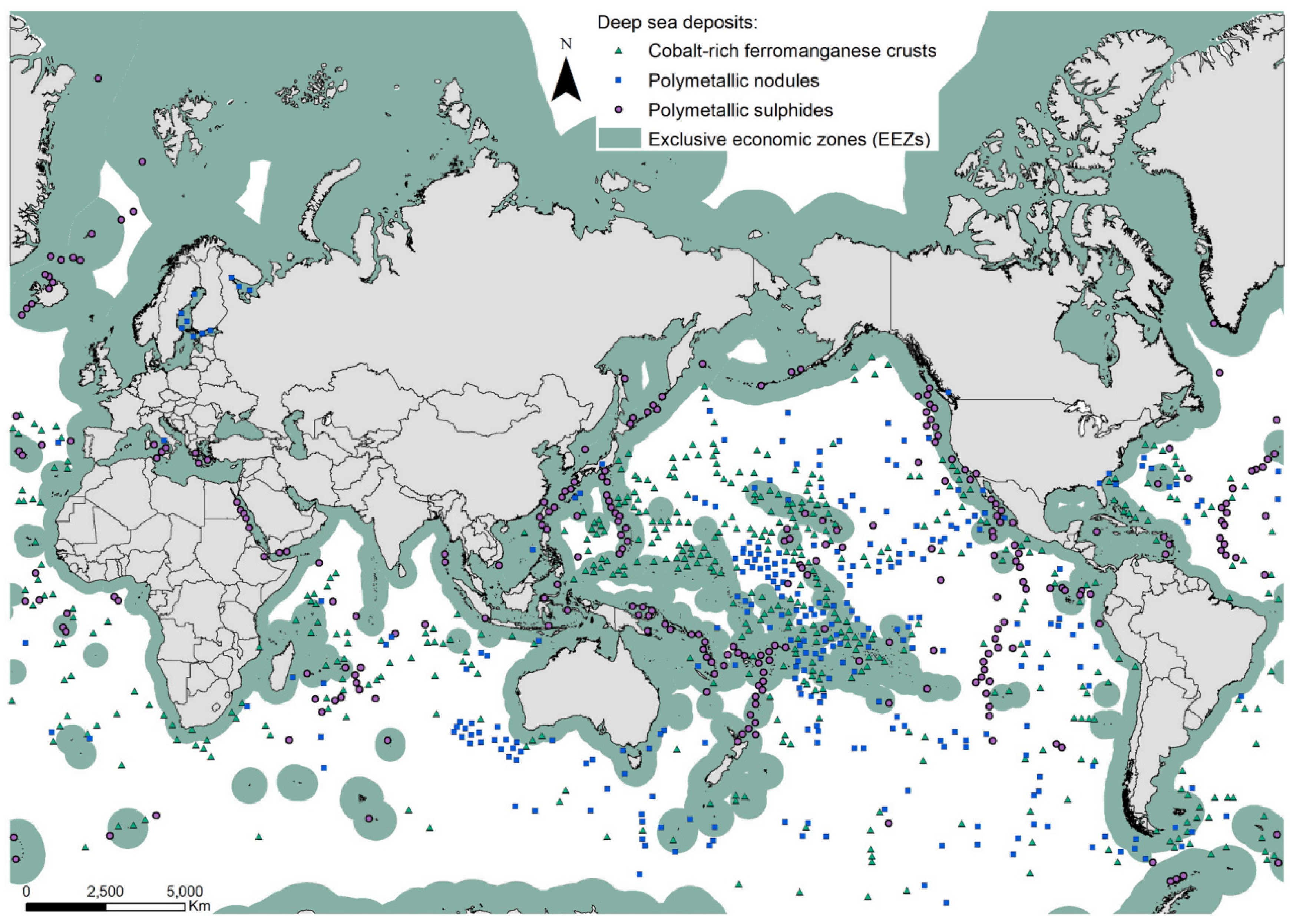
:1. Introduction
2. Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules
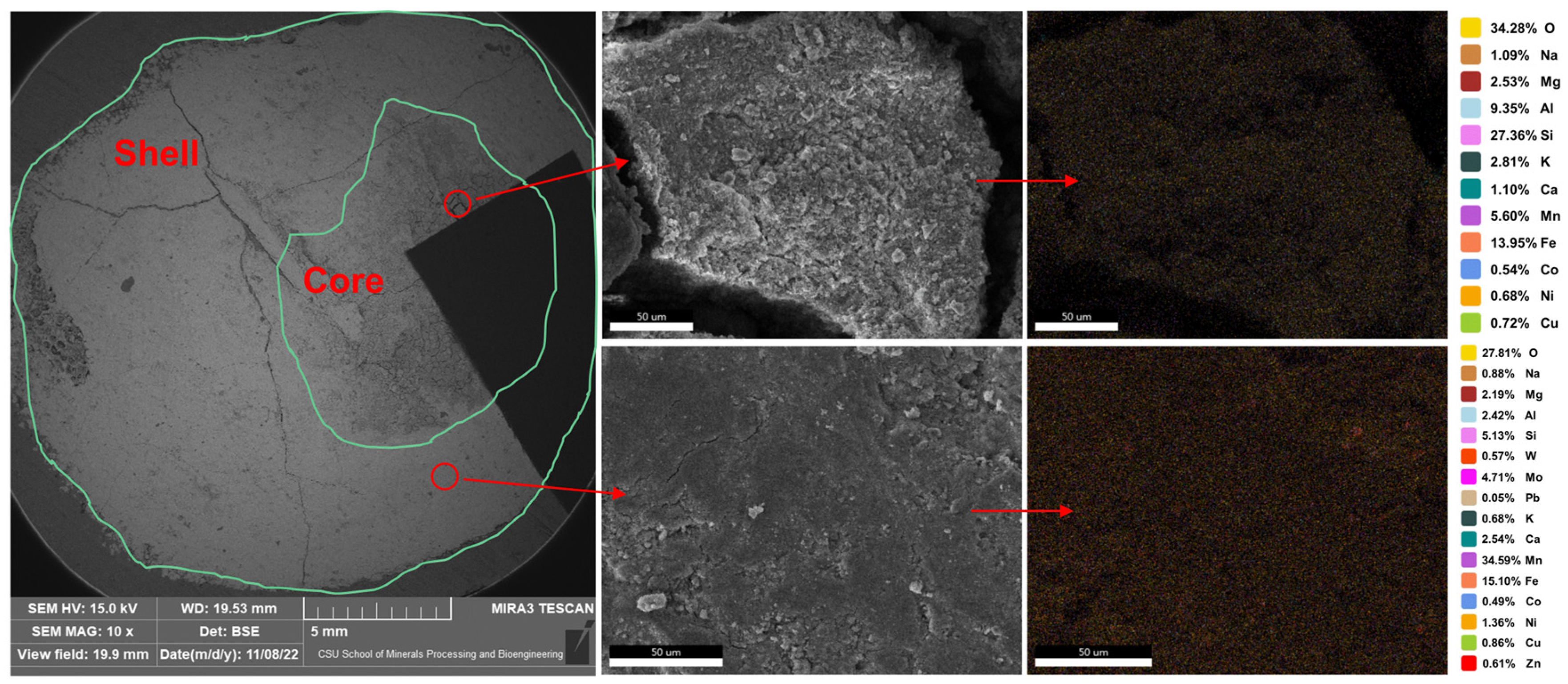
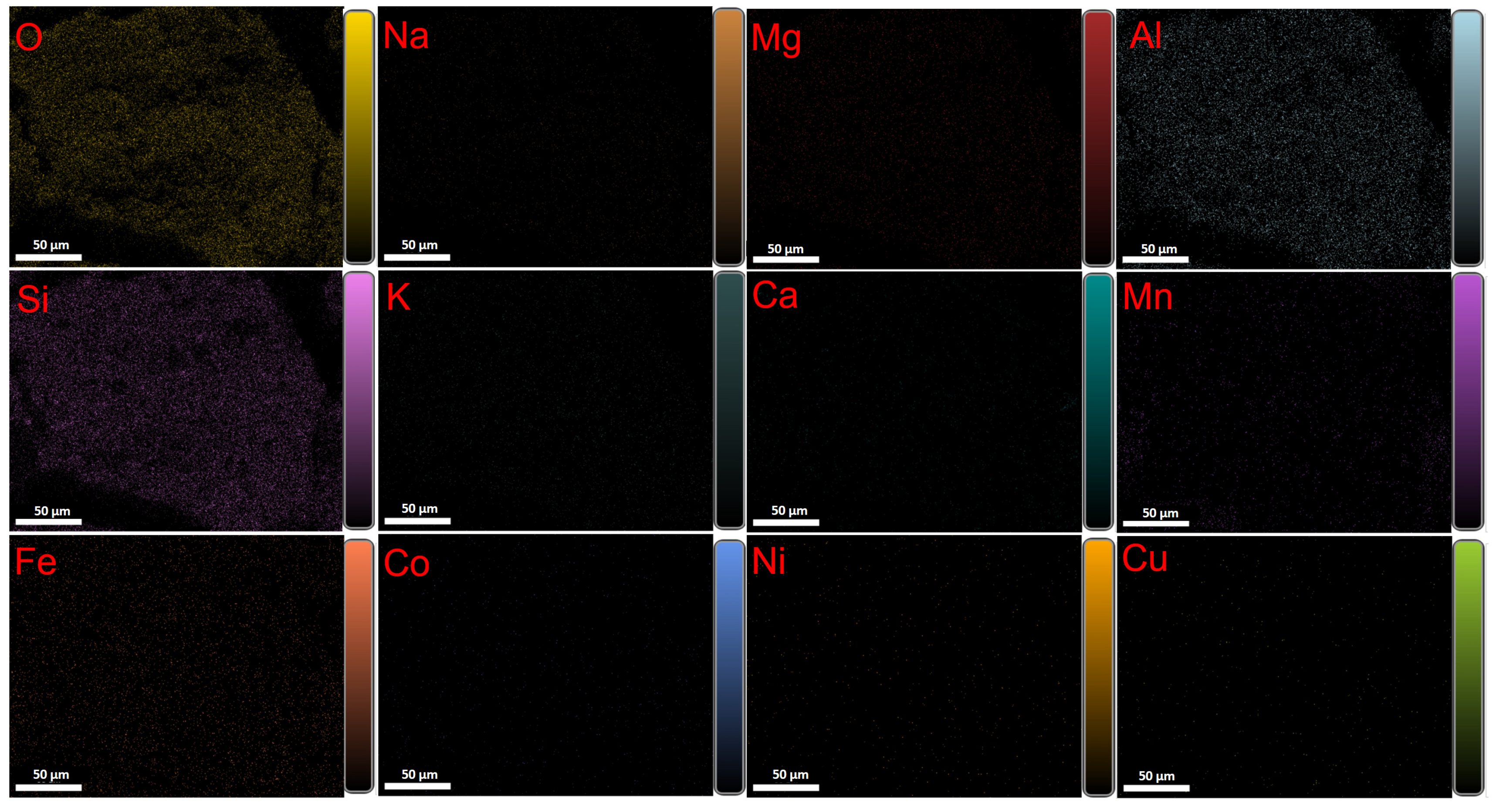
2.1. Composition and Content of Manganese Nodules
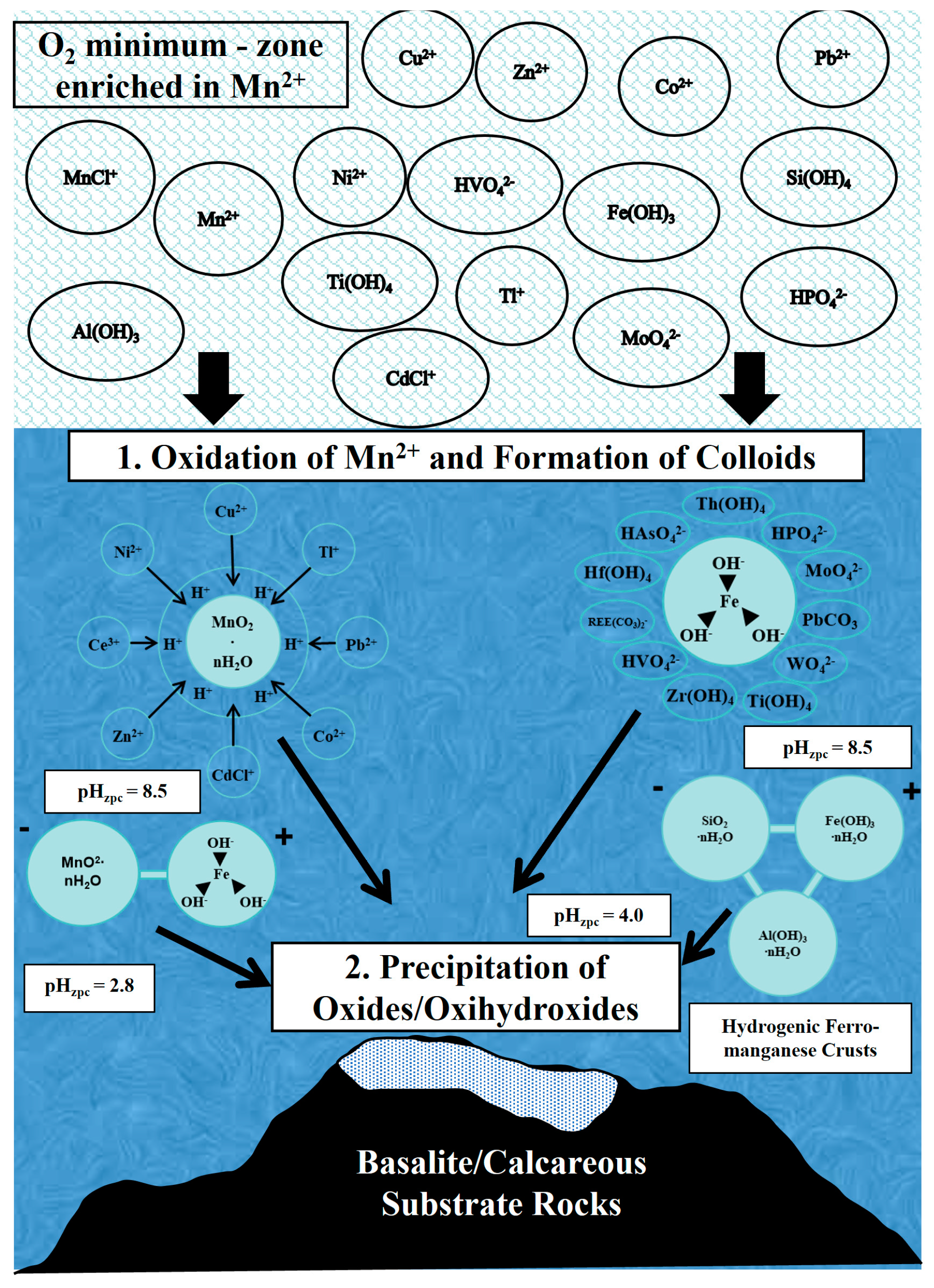
2.2. Occurrence of Main Elements of Manganese Nodules
3. Extraction of Main Valuable Elements from Manganese Nodules
3.1. Pyrometallurgical–Hydrometallurgical Process
3.1.1. Reduction Roasting–Acid Leaching Process
3.1.2. Reduction Roasting–Ammonia Leaching Process
3.2. Hydrometallurgical Process
3.2.1. Ammonia Leaching
3.2.2. Hydrochloric Acid Leaching
3.2.3. Sulfuric Acid Leaching
3.3. Other Extraction Process
4. Other Utilization Potentials of Manganese Nodules
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The mineralogy study results indicate that the manganese nodules off the coast of China in the Western Pacific are composed of a shell of dense ferromanganese phase and a core of loose silicate phase. The primary valuable metal elements mainly include Cu, Co, Ni, Mn, Fe, etc. Among them, Co and Ni are mainly distributed in the manganese oxide phase, and Cu mainly exists in the form of free copper oxide. To extract valuable metals, the key is to reduce Mn(IV) to Mn(II), which disrupts the crystal structure of the nodules and releases the valuable metal elements. During the recovery process of the primary valuable metals, the recovery of a small amount of associated non-ferrous metals and rare earth elements can also be considered to enhance the recovery and utilization value of manganese nodules.
- (2)
- The extraction processes for the main valuable metal elements of manganese nodules are mainly divided into two categories: pyrometallurgical–hydrometallurgical and sole hydrometallurgical. The pyrometallurgical–hydrometallurgical process combines the high reduction efficiency of pyrometallurgy with the high recovery rates of hydrometallurgy, but it is associated with high energy consumption and carbon emissions. By introducing hydrogen metallurgy, partially replacing carbon with hydrogen can reduce carbon emissions and improve reduction efficiency. Additionally, utilizing residual heat from the pyrometallurgical process to support the hydrometallurgical stage can further reduce energy consumption. The hydrometallurgical process avoids high-temperature operations but faces challenges such as high acid consumption, complex wastewater treatment, difficulties in handling leaching residues, and complicated downstream separation processes. These issues can be addressed by developing highly selective leaching reagents, optimizing wastewater treatment technologies, and achieving resource utilization of leaching residues to enhance economic and environmental performance.
- (3)
- Bioleaching, co-extraction technology, short-process extraction technology, etc. have attracted widespread attention due to their environmentally friendly and efficient characteristics. In the future, manganese nodule extraction technology should focus on integrated development, promote the application of technologies such as the comprehensive recovery of associated resources and tailings-free utilization, improve process stability and efficiency through intelligent control systems, increase the utilization value of manganese nodules, reduce development costs, and accelerate its commercialization process, thereby achieving more efficient and sustainable resource development.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sparenberg, O. A historical perspective on deep-sea mining for manganese nodules, 1965–2019. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2019, 6, 842–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinova, E.; Evans, C.; Lèbre, É.; Stringer, M.; Azadi, M.; Valenta, R.K. Will global cobalt supply meet demand? The geological, mineral processing, production and geographic risk profile of cobalt. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petterson, M.G.; Tawake, A. The Cook Islands (South Pacific) experience in governance of seabed manganese nodule mining. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2019, 167, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Gálvez, E.; Saldaña, M.; Jeldres, R.I. Submarine mineral resources: A potential solution to political conflicts and global warming. Miner. Eng. 2022, 179, 107441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hein, J.R.; Koschinsky, A.; Kuhn, T. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnik, V.; Chernyi, S. Future Development of the World Ocean Mining for the Industry. Procedia Eng. 2016, 150, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, L.; Koschinsky, A.; Markus, T.; Singh, P. Quantifying the fuel consumption, greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution of a potential commercial manganese nodule mining operation. Mar. Policy 2020, 114, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulikas, D.; Katona, S.; Ilves, E.; Ali, S.H. Life cycle climate change impacts of producing battery metals from land ores versus deep-sea polymetallic nodules. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 275, 123822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, R.A.F.; Préat, N.; Duhayon, C.; Dewulf, J. Prospective life cycle assessment of metal commodities obtained from deep-sea polymetallic nodules. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 330, 129884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beolchini, F.; Becci, A.; Barone, G.; Amato, A.; Hekeu, M.; Danovaro, R.; Dell’Anno, A. High fungal-mediated leaching efficiency of valuable metals from deep-sea polymetallic nodules. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 20, 101037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlaan, P.A.; Cronan, D.S. Origin and variability of resource-grade marine ferromanganese nodules and crusts in the Pacific Ocean: A review of biogeochemical and physical controls. Geochemistry 2022, 82, 125741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, H.; Siapno, B. Manganese nodules. Further resources of nickel and copper on the deep ocean floor. Geoforum 1974, 5, 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, B.; Heidak, P.; Vasters, J.; Kuhn, T.; Franken, G.; Schmidt, M. Life cycle impact on climate change caused by metal production from deep sea manganese nodules versus land-based deposits, Resources. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 193, 106976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, S.J. ‘Exploiting—Land, sea and space: Mineral superpower’ In the name of peace: A critical race to protect the depths and heights. Resour. Policy 2022, 79, 103066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heijlen, W.; Franceschi, G.; Duhayon, C.; Van Nijen, K. Assessing the adequacy of the global land-based mine development pipeline in the light of future high-demand scenarios: The case of the battery-metals nickel (Ni) and cobalt (Co). Resour. Policy 2021, 73, 102202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, A.; Svobodova, K.; Lèbre, E.; Valenta, R.; Kemp, D.; Owen, J.R. Governing deep sea mining in the face of uncertainty. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, J. Geographies of deep sea mining: A critical review. Extr. Ind. Soc. 2022, 9, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, B.C. Sustainability Assessment of Deep Ocean Resources. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaddad, S.; Mehta, D.; Helmons, R. Mining of deep-seabed nodules using a Coandă-effect-based collector. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.O.B.; Ardron, J.A.; Colaço, A.; Durden, J.M. Environmental considerations for impact and preservation reference zones for deep-sea polymetallic nodule mining. Mar. Policy 2020, 118, 103312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaikkonen, L.; Venesjärvi, R.; Nygård, H.; Kuikka, S. Assessing the impacts of seabed mineral extraction in the deep sea and coastal marine environments: Current methods and recommendations for environmental risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 135, 1183–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nijen, K.; Van Passel, S.; Squires, D. A stochastic techno-economic assessment of seabed mining of polymetallic nodules in the Clarion Clipperton Fracture Zone. Mar. Policy 2018, 95, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecchetto, M.M.; Moser, A.; Smith, C.R.; van Oevelen, D.; Sweetman, A.K. Abyssal seafloor response to fresh phytodetrital input in three areas of particular environmental interest (APEIs) in the western clarion-clipperton zone (CCZ). Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2023, 195, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, J.; Stewart, R.A.; Sahin, O.; Clarke, M.; Clark, M.R. Visioning a framework for effective environmental management of deep-sea polymetallic nodule mining: Drivers, barriers, and enablers. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 337, 130487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Robles, P.; Jeldres, R.I. Seabed mineral resources, an alternative for the future of renewable energy: A critical review. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 126, 103699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błażewicz, M.; Jóźwiak, P.; Menot, L.; Pabis, K. High species richness and unique composition of the tanaidacean communities associated with five areas in the Pacific polymetallic nodule fields. Prog. Oceanogr. 2019, 176, 102141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooday, A.J.; Holzmann, M.; Caulle, C.; Goineau, A.; Kamenskaya, O.; Weber, A.A.T.; Pawlowski, J. Giant protists (xenophyophores, Foraminifera) are exceptionally diverse in parts of the abyssal eastern Pacific licensed for polymetallic nodule exploration. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 207, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirt, W.C.; Rice, D.A.; Shirts, M.B. Flotation of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crust from the Pacific Ocean. Miner. Eng. 1991, 4, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Heimendahl, M.; Hubred, G.L.; Fuerstenau, D.W.; Thomas, G. A transmission electron microscope study of deep-sea manganese nodules. Deep. Sea Res. Oceanogr. Abstr. 1976, 23, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughriet, A.; Ouddane, B.; Wartel, M.; Lalouj, C.; Cordier, C.; Gengembre, L.; Sanchez, J.P. On the oxidation states of Mn and Fe in polymetallic oxide/oxyhydroxide crusts from the Atlantic Ocean. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 1996, 43, 321–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöthe, M.; Wegorzewski, A.; Müller, C.; Simon, F.; Kuhn, T.; Schippers, A. Manganese-Cycling Microbial Communities Inside Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7692–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegorzewski, A.V.; Grangeon, S.; Webb, S.M.; Heller, C.; Kuhn, T. Mineralogical transformations in polymetallic nodules and the change of Ni, Cu and Co crystal-chemistry upon burial in sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2020, 282, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewes, K.; Mogollón, J.M.; Picard, A.; Rühlemann, C.; Kuhn, T.; Nöthen, K.; Kasten, S. Impact of depositional and biogeochemical processes on small scale variations in nodule abundance in the Clarion-Clipperton Fracture Zone. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2014, 91, 125–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplin, A.C.; Cronan, D.S. Ferromanganese oxide deposits from the Central Pacific Ocean, II. Nodules and associated sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1985, 49, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R. Deep-Sea Mining: Resource Potential, Technical and Environmental Considerations; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Senanayake, G. Acid leaching of metals from deep-sea manganese nodules—A critical review of fundamentals and applications. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 1379–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wen, H. Variabilities and enrichment mechanisms of the dispersed elements in marine Fe–Mn deposits from the Pacific Ocean. Ore Geol. Rev. 2020, 121, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koschinsky, A.; Halbach, P. Sequential leaching of marine ferromanganese precipitates: Genetic implications. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 5113–5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S.O.; Adegbie, A.T.; Akinnigbagbe, E.A.; Unyimadu, J.P. Geochemistry of ferromanganese micronodules recovered from sediment-core in the western Nigeria continental margin, Eastern Equatorial Atlantic: Implications on the genesis and depositional history. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 184, 104369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Du, Y.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, P.; Duan, X. Enrichment of REEs in polymetallic nodules and crusts and its potential for exploitation. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, N.S.; Hait, J.; Jana, R.K. A brief overview on manganese nodules processing signifying the detail. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.; Samal, A.; Das, D.; Chintalpudi, S.N. Effect of calcination temperature on Indian Ocean manganese nodules. Mössbauer, XRD, FT-IR and TG-DTA studies. Thermochim. Acta 1999, 325, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, P.; Pandey, B.D.; Abhilash. Perspective of availability and sustainable recycling prospects of metals in rechargeable batteries—A resource overview. Resour. Policy 2019, 60, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Raichur, A.M.; Natarajan, K.A.; Modak, J.M. Recent Developments in Processing Ocean Manganese Nodules—A Critical Review. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2004, 25, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.K. Metals and materials from deep sea nodules: An outlook for the future. Int. Mater. Rev. 2010, 55, 364–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Rodríguez, F.; Rojas, A.; Robles, P.; Ghorbani, Y. Leaching manganese nodules with iron-reducing agents—A critical review. Miner. Eng. 2021, 163, 106748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, V.; Verma, J.K. Extraction of copper, nickel and cobalt from the leach liquor of manganese-bearing sea nodules using LIX 984N and ACORGA M5640. Miner. Eng. 2011, 24, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.D.; Kumar, V. Extraction of copper and nickel from ammoniacal leach liquor of Indian Ocean sea nodules. Hydrometallurgy 1991, 26, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Anand, S.; Nam, C.W.; Park, K.H.; Das, R.P. Dissolution Studies On Cu-Ni-Co-Fe Matte Obtained from Manganese Nodules. In Proceedings of the Fifth ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Tsukuba, Japan, 15–19 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rokukawa, N. Development For Hydrometallurgical Process of Cobalt Rich Crusts. In Proceedings of the First ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Tsukuba, Japan, 21–22 November 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, R.; Jones, W.E.; Warner, J.S. Extraction of copper, nickel and cobalt from sea nodules. JOM 1976, 28, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, R. Thermal upgrading of sea nodules. JOM 1974, 26, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Z.; Zequan, H.; Yujun, S.; Yongjun, M.; Shuguang, Q. The Smelting-Rusting-Solvent Extraction Process To Recover Valuable Matels From Polymetallic Nodules. In Proceedings of the Third ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Goa, India, 8–10 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kotlinski, R.; Stoyanova, V.; Hamrak, H.; Avramov, A. An Overview of the Interoceanmetal (IOM) Deep-Sea Technology Development (Mining and Processing). In Proceedings of the Workshop on Polymetallic Nodule Mining Technology-Current Status and Challenges Ahead, Chennai, India, 18–22 February 2008; pp. 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Keber, S.; Brückner, L.; Elwert, T.; Kuhn, T. Concept for a Hydrometallurgical Processing of a Copper-Cobalt-Nickel Alloy Made from Manganese Nodules. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2020, 92, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Ju, J.; Dong, L.; Bao, W.; Wang, J.; Fan, P.; Zhu, Z. Extraction of various valuable elements from oceanic manganese nodules using coal gasification slag via reduction roasting-acid leaching process. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2024, 129, 390–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Yue, L.; Zeng, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Guan, W.; Cao, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G. Recovery of critical battery metals from cobalt-rich deep-sea polymetallic nodules: Selective carbothermal reduction based on kinetics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.N.; Hoover, M.; Fuerstenau, D.W. Ammonia-ammonium leaching of deep-sea manganese nodules. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1974, 1, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kmetova, D.; Stofko, M.; Kmet, S. Ammoniacal leaching for extraction of non-ferrous metals from deep-sea nodules. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1985, 15, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.K.; Murthy, D.S.R.; Nayak, A.K.; Mahanty, M.S.; Tiwary, S.K.; Akerkar, D.D. Leaching of roast-reduced polymetallic sea nodules to optimise the recoveries of copper, nickel and cobalt. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1990, 30, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, S.; Alex, T.C.; Agrawal, A.; Premchand, P. Reduction Roasting Of Deep Sea Manganese Nodules Using Liquid And Gaseous Reductants. In Proceedings of the Second ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 24–26 November 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jana, R.K.; Pandey, B.D.; Premchand. Ammoniacal leaching of roast reduced deep-sea manganese nodules. Hydrometallurgy 1999, 53, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, D.; Srivastava, R.R.; Sahu, K.K.; Singh, T.B.; Jana, R.K. Leaching of roast-reduced manganese nodules in NH3–(NH4)2CO3 medium. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.K.; Akerkar, D.D. Studies of the metal-ammonia-carbon dioxide-water system in extraction metallurgy of polymetallic sea nodules. Hydrometallurgy 1989, 22, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwall, J.C.; Barner, H.E.; Beecher, N.; Davies, D.S.; Kust, R.N. Kennecott process for recovery of copper, nickel, cobalt and molybdenum from ocean nodules. Miner. Eng. 1979, 12, 1704–1709. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, J.; Wilder, T. Recovery of Metal Values from Manganese Nodules. U.S. Patent 3,788,841, 29 January 1974. [Google Scholar]
- Das, R.P.; Anand, S.; Das, S.C.; Jena, P.K. Leaching of manganese nodules in ammoniacal medium using glucose as reductant. Hydrometallurgy 1986, 16, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Das, R.P. Kinetics and mechanism of the reductive ammonia leaching of ocean nodules by manganous ion. Hydrometallurgy 1987, 19, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Das, S.C.; Das, R.P.; Jena, P.K. Leaching of manganese nodule in ammoniacal medium using ferrous sulfate as the reductant. Metall. Trans. B 1988, 19, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.S.; Ghosh, M.K.; Anand, S.; Das, R.P. Leaching of manganese nodules in ammoniacal medium with elemental sulphur as reductant. Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. Sec. C 1994, 103, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Das, R.P.; Anand, S. Aqueous Reduction of Polymetallic Nodule For Metal Extraction. In Proceedings of the Second ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 24–26 November 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Niinae, M.; Komatsu, N.; Nakahiro, Y.; Wakamatsu, T.; Shibata, J. Preferential leaching of cobalt, nickel and copper from cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts with ammoniacal solutions using ammonium thiosulfate and ammonium sulfite as reducing agents. Hydrometallurgy 1996, 40, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.K.; Anand, S.; Das, R.P. Minimization of Ni(II) precipitation in the Ni(II) NH3 SO2 (NH4)2SO4 MnO2 system. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1997, 50, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjay, K.; Subbaiah, T.; Anand, S.; Das, R.P. Manganese Recovery From Leach Liquors/Residues Generated During Hydrometallurgical Processing of Manganese Nodules. In Proceedings of the Third ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Goa, India, 8–10 November 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Rokukawa, N. Extraction of nickel, cobalt and copper from ocean manganese nodules with mixed solution of ammonium carbanate and ammonium sulphite. J. Min. Metall. Inst. Jpn. 1990, 106, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Das, R.P. India’s demonstration metallurgical plant to treat ocean nodule. In Proceedings of the Fourth ISOPE Ocean Mining Symposium, Szczecin, Poland, 23–27 September 2001; pp. 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, N.K.; Sen, P.K. India’s first medium scale demonstration plant for treating poly-metallic nodules. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, S.B.; Jena, P.K. Reduction leaching of manganese nodules of Indian Ocean origin in dilute hydrochloric acid. Hydrometallurgy 1988, 21, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jana, R.K.; Singh, D.D.N.; Roy, S.K. Alcohol-modified hydrochloric acid leaching of sea nodules. Hydrometallurgy 1995, 38, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Deep, A.; Singh, V.; Tandon, S.N. Recovery of cobalt, nickel, and copper from sea nodules by their extraction with alkylphosphines. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 70, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, M.P.; Aja, R.; Miyares, R.C. Optimization of the Existing Methods for Recovery of Basic Metals from Polymetallic Nodules. In Proceedings of the Tenth ISOPE Ocean Mining and Gas Hydrates Symposium, Szczecin, Poland, 22–26 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abramowski, T.; Stefanova, V.; Causse, R.; Romanchuk, A. Technologies for the processing of polymetallic nodules from Clarion Clipperton Zone in the Pacific Ocean. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2017, 52, 258–269. [Google Scholar]
- Kanungo, S.B.; Das, R.P. Extraction of metals from manganese nodules of the Indian Ocean by leaching in aqueous solution of sulphur dioxide. Hydrometallurgy 1988, 20, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Das, S.C.; Das, R.P.; Jena, P.K. Leaching of manganese nodules at elevated temperature and pressure in the presence of oxygen. Hydrometallurgy 1988, 20, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, R.; Sanjay, K.; Mishra, B.K.; Mohapatra, M. Micellar mediated selective leaching of manganese nodule in high temperature sulfuric acid medium. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 165, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.; Ayala, L.; Saldaña, M.; Cánovas, M.; Jeldres, R.I.; Nieto, S.; Castillo, J.; Robles, P.; Toro, N. Leaching Manganese Nodules in an Acid Medium and Room Temperature Comparing the Use of Different Fe Reducing Agents. Metals 2019, 9, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.; Jandová, J.; Lisá, K.; Vranka, F. Leaching of manganese deep ocean nodules in FeSO4–H2SO4–H2O solutions. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandová, J.; Lisá, K.; Vu, H.; Vranka, F. Separation of copper and cobalt–nickel sulphide concentrates during processing of manganese deep ocean nodules. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-F.; Xue, W.-Y.; Li, W.; Li, S.-D.; Liu, X.-H. Recovery of Mn2+, Co2+ and Ni2+ from manganese nodules by redox leaching and solvent extraction. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2007, 17, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, E.; Sarangi, K.; Subbaiah, T. Recovery of manganese and nickel from polymetallic manganese nodule using commercial extractants. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 126, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Sun, C. Sulfuric acid leaching of ocean manganese nodules using phenols as reducing agents. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Sun, C. Sulfuric acid leaching of ocean manganese nodules using aromatic amines as reducing agents. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariprasad, D.; Mohapatra, M.; Anand, S. Reductive Leaching of Manganese Nodule Using Saw Dust in Sulphuric Acid Medium. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2018, 71, 2971–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, L.; Wu, S.; Wang, M.; Guan, W.; Cao, Z.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G. A near-zero waste process for the full-component utilization of deep-sea polymetallic nodules based on reductive leaching with SO2 followed by separation and recovery. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 223, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, M.K.; Barik, S.P.; Anand, S. Sulphuric acid leaching of polymetallic nodules using paper as a reductant. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2008, 61, 477–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataseetharaman, A.; Mishra, G.; Ghosh, M.K.; Das, G.K. Role of Glycerol Oxidation Pathways in the Reductive Acid Leaching Kinetics of Manganese Nodules Using Glycerol. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 14903–14910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havlik, T.; Laubertova, M.; Miskufova, A.; Kondas, J.; Vranka, F. Extraction of copper, zinc, nickel and cobalt in acid oxidative leaching of chalcopyrite at the presence of deep-sea manganese nodules as oxidant. Hydrometallurgy 2005, 77, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Pérez, K.; Saldaña, M.; Jeldres, R.I.; Jeldres, M.; Cánovas, M. Dissolution of pure chalcopyrite with manganese nodules and waste water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Saldaña, M.; Gálvez, E.; Cánovas, M.; Trigueros, E.; Castillo, J.; Hernández, P.C. Optimization of Parameters for the Dissolution of Mn from Manganese Nodules with the Use of Tailings in An Acid Medium. Minerals 2019, 9, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toro, N.; Saldaña, M.; Castillo, J.; Higuera, F.; Acosta, R. Leaching of Manganese from Marine Nodules at Room Temperature with the Use of Sulfuric Acid and the Addition of Tailings. Minerals 2019, 9, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Jiang, X.; Wang, S.; Feng, L.; Li, D. The Recovery of Valuable Metals from Ocean Polymetallic Nodules Using Solid-State Metalized Reduction Technology. Minerals 2020, 10, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, S.; Qiu, J.; Chen, Z.; Du, W.; Ju, D.; Xie, K. Optimization of Gas–Solid Co-Reduction Conditions for Deep-Sea Polymetallic Nodules. JOM 2023, 75, 5718–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Velde, S.; Callebaut, I.; Gao, Y.; Meysman, F.J.R. Impact of electrogenic sulfur oxidation on trace metal cycling in a coastal sediment. Chem. Geol. 2017, 452, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaksonen, A.H.; Deng, X.; Bohu, T.; Zea, L.; Khaleque, H.N.; Gumulya, Y.; Boxall, N.J.; Morris, C.; Cheng, K.Y. Prospective directions for biohydrometallurgy. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 195, 105376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.L. Ocean manganese nodules: Biogenesis and bioleaching possibilities. Min. Metall. Explor. 2000, 17, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.Y.; Noh, S.-R.; Cho, K.-S.; Ryu, H.W. Leaching of Mn, Co, and Ni from manganese nodules using an anaerobic bioleaching method. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, K.D.; Pandey, B.D.; Mankhand, T.R. Studies on kinetics of biodissolution of metals from Indian Ocean nodules. Miner. Eng. 2003, 16, 523–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, H.; Sato, H. Bacterial leaching of cobalt-rich ferromanganese crusts. Int. J. Miner. Process. 1995, 43, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.D.; Das, C.; Pandey, B.D. Leaching of copper, nickel and cobalt from Indian Ocean manganese nodules by Aspergillus niger. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 105, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.D.; Das, C.; Kumar, R.; Pandey, B.D.; Mehrotra, S.P. Effect of mechano-chemical activation on bioleaching of Indian Ocean nodules by a fungus. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1207–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.X.; Liu, Z.G.; Jiang, Z.X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, X. The role of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans in the ocean polymetallic nodules reductive bioleaching: Electrochemical insights into interface processes. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2024, 202, 109869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Natarajan, K.A. Electroleaching of polymetallic ocean nodules to recover copper, nickel and cobalt. Miner. Eng. 2001, 14, 877–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Natarajan, K.A. Electrochemical processing of ocean manganese nodules with microbial enhancement to recover valuable metals. Min. Metall. Explor. 2002, 19, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Natarajan, K.A. Electrobioleaching of polymetallic ocean nodules. Hydrometallurgy 2001, 62, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Natarajan, K.A. Cathodic reductive dissolution and surface adsorption behavior of ocean manganese nodules. Hydrometallurgy 2002, 64, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, K.; Nitta, M.; Aomura, K. The activities of manganese nodules and manganese-iron mixed oxide for decomposition of isopropyl alcohol. J. Catal. 1978, 54, 446–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, J.; Liu, L.; Tan, W.; Hao, R.; Qiu, G. Catalytic oxidation and adsorption of Cr(III) on iron-manganese nodules under oxic conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, K.M.; Mallick, S.; Dash, S.S. Studies on manganese nodule leached residues 2. Adsorption of aqueous phosphate on manganese nodule leached residues. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2005, 290, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhawa, N.S.; Das, N.N.; Jana, R.K. Selenite adsorption using leached residues generated by reduction roasting–ammonia leaching of manganese nodules. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241–242, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, K.M.; Gorai, B.; Das, N.N. Studies on Indian ocean manganese nodules III: Adsorption of aqueous selenite on ferromanganese nodules. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 187, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Zhang, A.-B.; Sun, J.; Ye, Y.; Chen, X.-G.; Xia, M.-S. Application of ocean manganese nodules for the adsorption of potassium ions from seawater. Miner. Eng. 2013, 49, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Dash, S.S.; Parida, K.M. Adsorption of hexavalent chromium on manganese nodule leached residue obtained from NH3-SO2 leaching. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 297, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, A.; Sahu, K.K. Kinetic and isotherm studies of cadmium adsorption on manganese nodule residue. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Yue, L.; Cao, Z.; Li, Q.; Zeng, L.; Guan, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, G.; Wu, S. Selective co-extraction of critical metals from deep ocean polymetallic nodule leachate and preparation of battery-grade Ni-Co-Mn solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalcová, A.; Orlíček, M.; Novák, P. Microstructure and Properties of Natural Alloy Prepared by Aluminothermic Reduction of Deep-Sea Nodules and Processed by Rapid Solidification. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
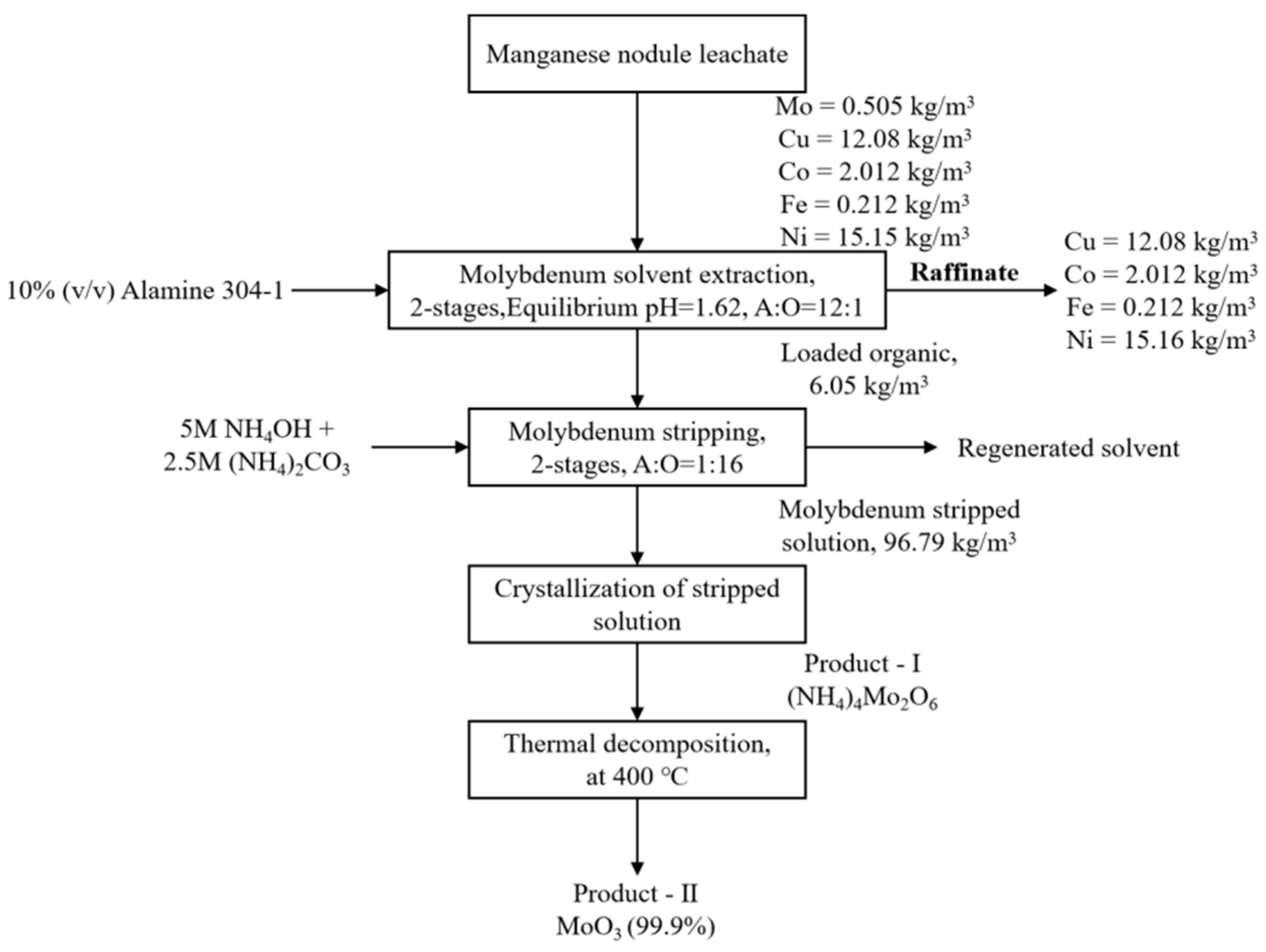
- Parhi, P.K.; Park, K.-H.; Kim, H.-I.; Park, J.-T. Recovery of molybdenum from the sea nodule leach liquor by solvent extraction using Alamine 304-I. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 105, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhi, P.K.; Park, K.H.; Nam, C.W.; Park, J.T.; Barik, S.P. Extraction of rare earth metals from deep sea nodule using H2SO4 solution. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2013, 119, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
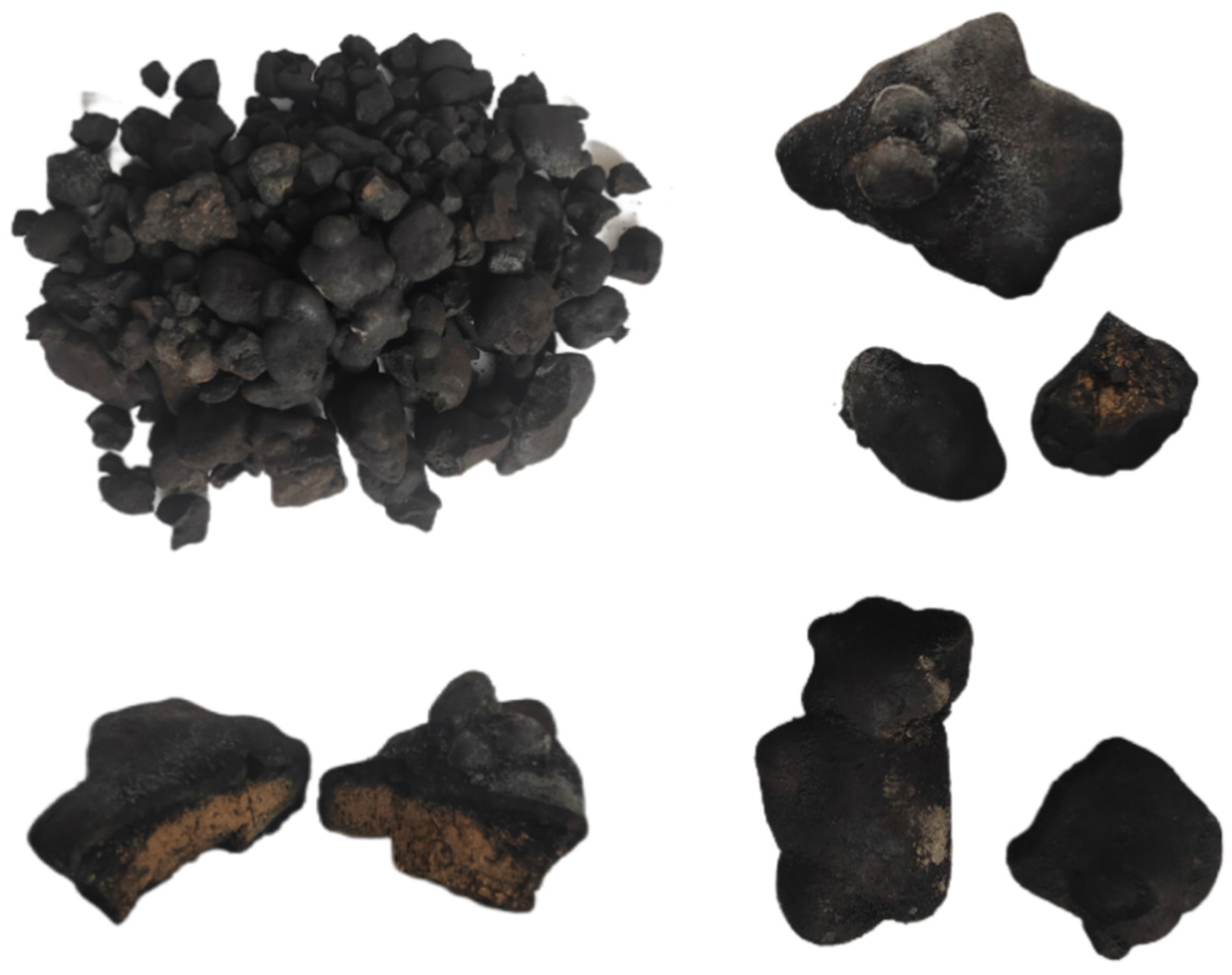




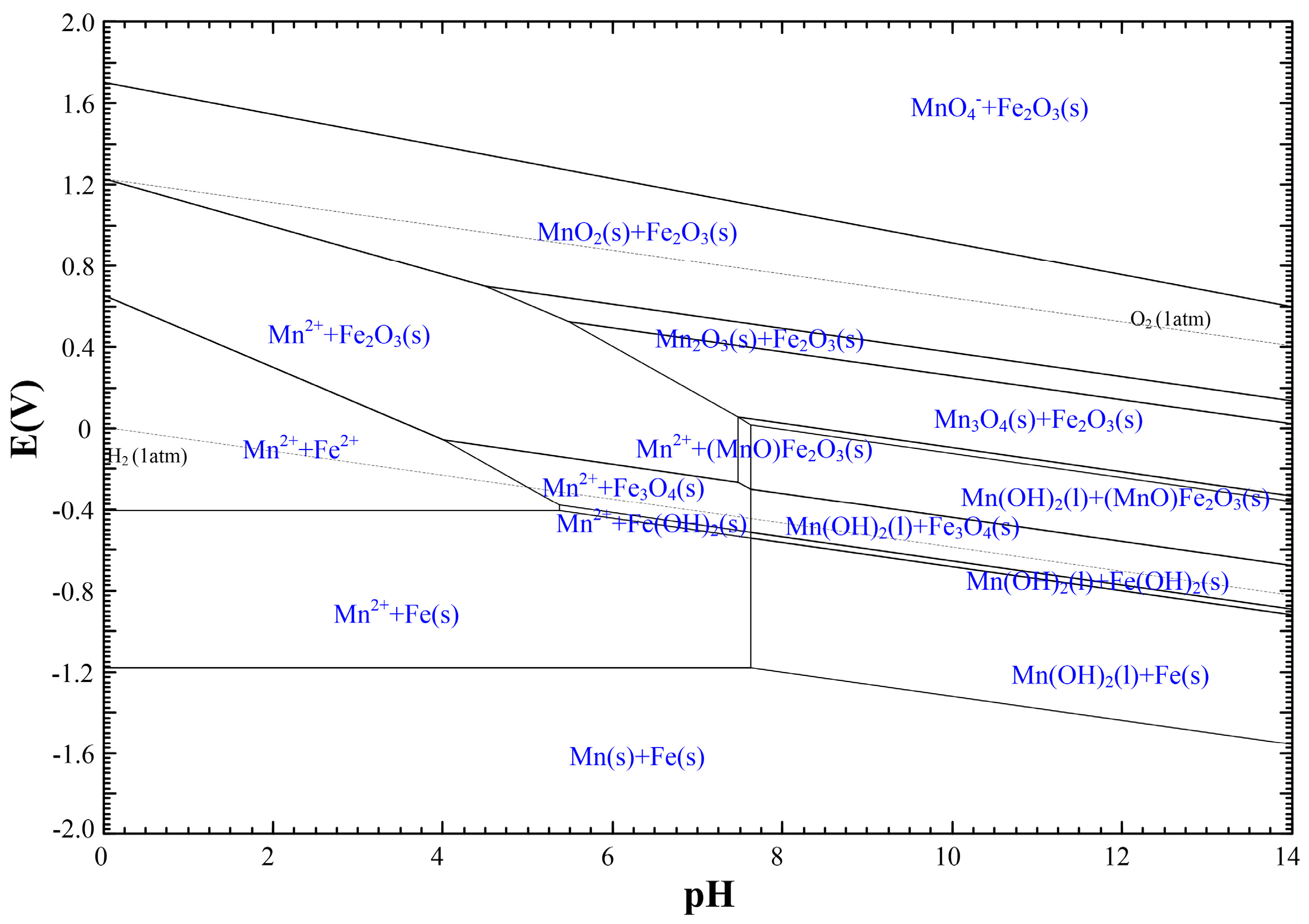

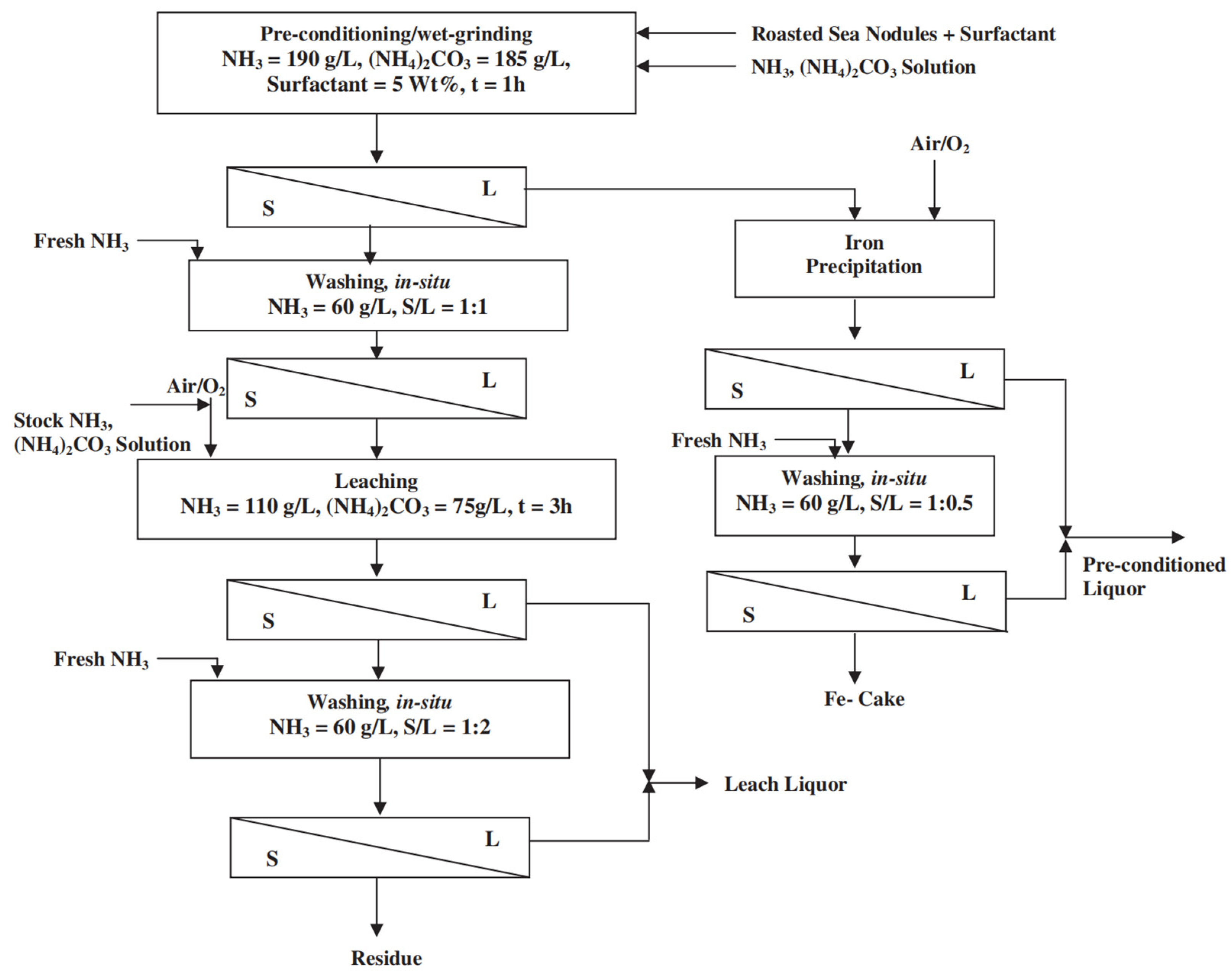
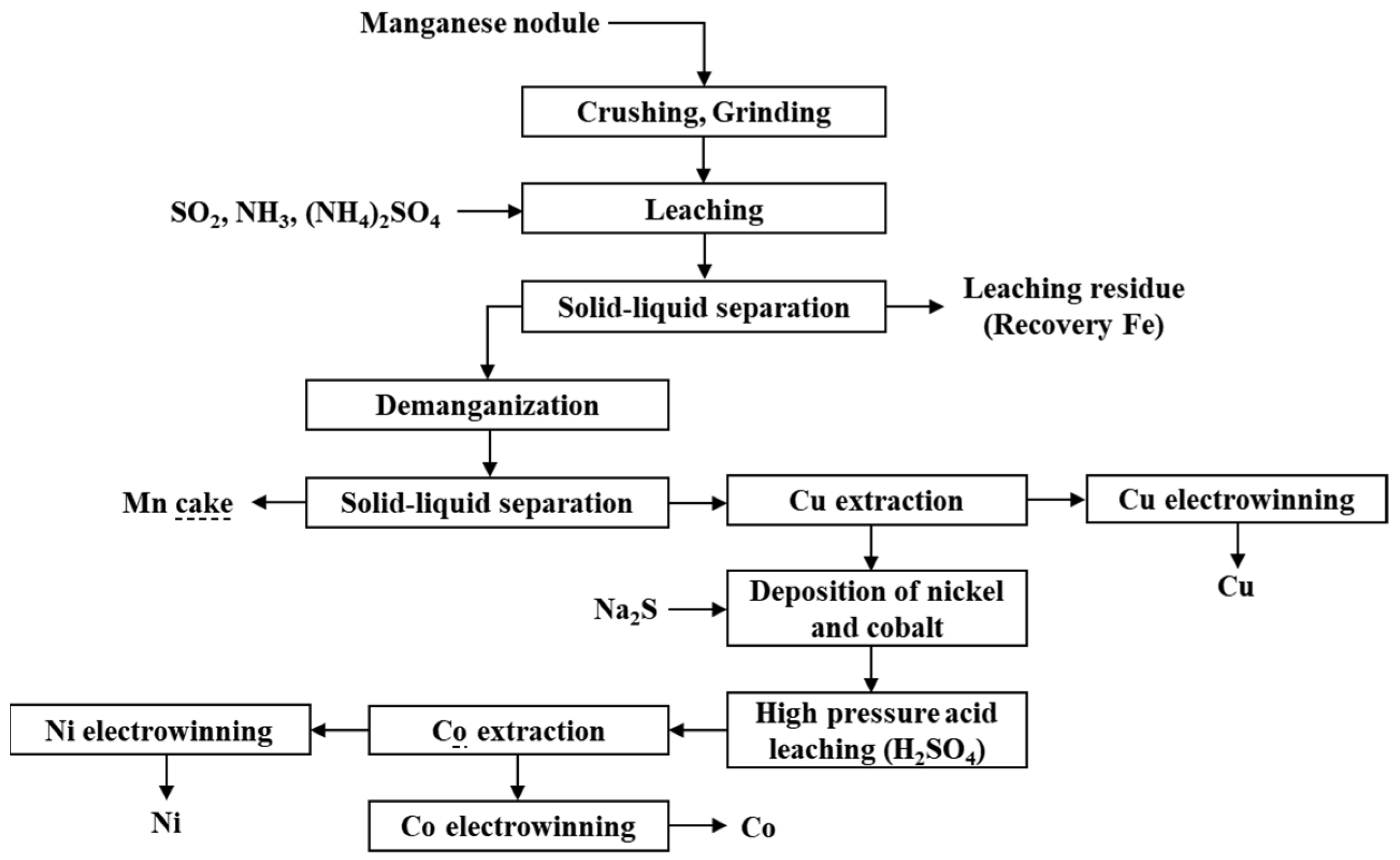


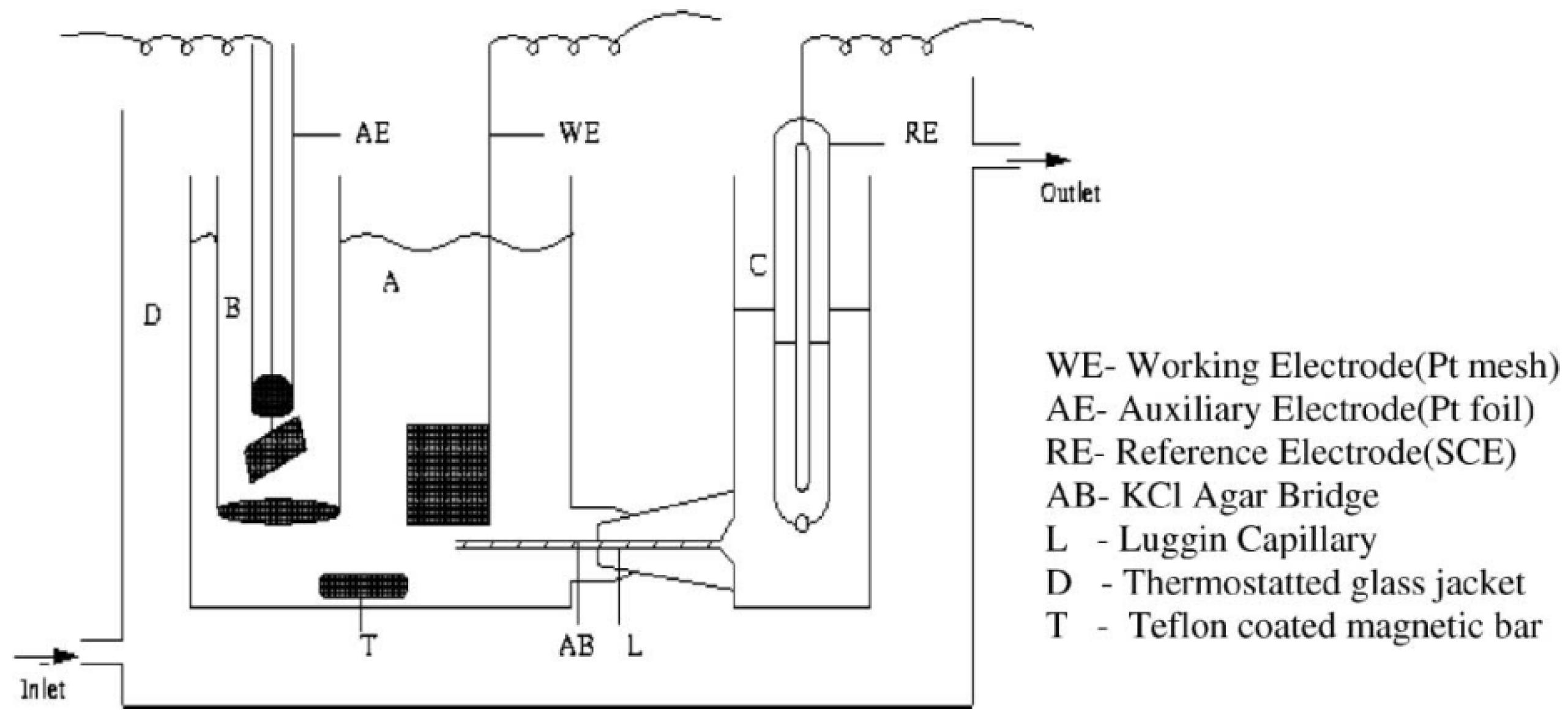


| Classification | Element |
|---|---|
| Main element (>1%) | Mn (13~27%), Fe (6~18%), SiO2 (5%), Al2O3 (1.2%), MgO (1.5%), Na2O (1.8%) |
| Minor element (600 × 10−6~1%) | Co (0.3~1.2%), Fe (1670 × 10−6~7250 × 10−6%), Cu (573 × 10−6%), Ba, Sr, Pb |
| Trace element (<600 × 10−6%) | Mo, W, Pt, Pd, Nb, Ga, Te, Sc, Y |
| O | Mn | Si | Fe | Al | Ca |
| 33 | 29.91 | 10.28 | 9.19 | 3.34 | 2.45 |
| Na | Mg | Ni | K | Cu | Cl |
| 2.45 | 2.17 | 1.44 | 1.28 | 1.18 | 0.94 |
| Ti | Ba | Co | P | S | Zn |
| 0.68 | 0.342 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.22 | 0.144 |
| Sr | V | Mo | Pb | Ce | Zr |
| 0.0765 | 0.0707 | 0.0573 | 0.559 | 0.051 | 0.0387 |
| Tl | W | La | Y | Nb | Rb |
| 0.0335 | 0.032 | 0.023 | 0.0129 | 0.003 | 0.002 |
| Mn | Cu | Co | Ni | Na | Mg |
| 24.68 | 0.92 | 0.23 | 1.05 | 1.80 | 2.19 |
| K | Ca | Si | Fe | Al | W |
| 1.01 | 1.86 | 7.76 | 7.85 | 2.65 | 0.0072 |
| V | Mo | Pb | Zn | P | S |
| 0.04 | 0.047 | 0.052 | 0.13 | 0.30 | 0.15 |
| Phase of Mn | Manganous Silicate | Manganese Dioxide | Ferromanganese Oxide | Manganous Oxide | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 0.19 | 6.92 | 16.23 | 1.54 | 24.88 |
| Distribution/% | 0.76 | 27.81 | 65.23 | 6.19 | 100.00 |
| Phase | In Manganese Oxides | In Iron Oxides | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Content of Co/% | 0.23 | 0.0005 | 0.2305 |
| Distribution of Co/% | 99.78 | 0.22 | 100.00 |
| Content of Ni/% | 1.04 | 0.0082 | 1.0482 |
| Distribution of Ni/% | 99.22 | 0.78 | 100.00 |
| Phase of Cu | Free Copper Oxide | Bound Copper Oxide | Primary Copper Sulfide | Secondary Copper Sulfide | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content/% | 0.89 | 0.02 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.92 |
| Distribution/% | 96.74 | 2.17 | 0.54 | 0.54 | 100.00 |
| Reaction | ∆G/kcal·mol−1 |
|---|---|
| −34.2 | |
| −3.8 | |
| −33.44 | |
| −2.05 | |
| −54.53 | |
| −3.23 | |
| +31.38 | |
| −62.72 | |
| −13.76 | |
| −20.47 | |
| −10.4 |
| Reductant/Auxiliary | Leaching Condition | Leaching Efficiency/% | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| SO2 | Manganese nodules from CCZ, −0.2 mm particles accounted for 86%, temperature 343~353 k | In total, 92% of Cu, 96% of Ni, 92% of Co, 96% of Mn | [82] |
| SO2 | Manganese nodules from Indian Ocean, liquid/solid 10:1, 10 mL 1 M H2SO4 added per 100 mL, SO2 concentration 5% (wt/v), leaching time 15 min, temperature 31 °C | Over 85% of Mn, Ni, and Co, over 75% of Cu | [83] |
| SO2 | Manganese nodules from Cook Islands Exclusive Economic Zone, 30 °C, L/S ratio of 6:1 mL/g, H2SO4 dosage of 37.5 wt% and SO2 partial pressure of 200 kPa | In total, 98.7% of Mn, 91.4% of Fe, 95.3% of La, 99.2% of Ce, 99.3% of Ni, 95.9% of Co | [94] |
| Molasses | Manganese nodules from CCZ, concentration 31%, H2SO4 0.8 kg/kg nodule, molasses 0.12 kg/kg nodule, leaching time 60 min, temperature 140 °C | In total, 97.70% of Ni, 98.31% of Co, 91.77% of Cu, 97.99% of Zn, 97.07% of Mn, 24.54% of Fe | [81] |
| Pyrite | Manganese nodules from CCZ, concentration 35%, H2SO4 0.81 kg/kg nodule, pyrite 0.12 kg/kg nodule, leaching time 90 min, pressure 10 atm, temperature 160 °C | In total, 98.42% of Ni, 91.67% of Co, 95.98% of Cu, 96.75% of Zn, 27.52% of Mn, 27.22% of Fe | [81] |
| Water | Manganese nodules from Indian Ocean, −250 μm particles accounted for 100%, concentration 15% (wt/v), H2SO4 0.46 g/g nodule, leaching time 4 h, oxygen partial pressure 0.55 MPa, temperature 423 K | Nearly 100% of Cu and Ni, 88% of Co, 28% of Mn, 5.7% of Fe | [84] |
| CTAB | Manganese nodules from Indian Ocean, −100 μm particles accounted for 100%, concentration 10% (wt/v), H2SO4 5% (v/v), leaching time 2 h, CTAB at critical micelle concentration, temperature 160 °C | In total, 99% of Mn, Cu, Co, and Ni | [85] |
| FeC | Manganese nodules from the Blake Plateau in the Atlantic Ocean, particle size of −140 + 100 μm, liquid/solid 100:1, FeC/MnO2 2:1, H2SO4 0.1 mol/L, leaching time 20 min, room temperature | In total, 97% of Mn | [86] |
| FeSO4 | Manganese nodules from CCZ, particle size of −1000 μm, liquid/solid 7:1, FeSO4 at stoichiometric amount, H2SO4 at 1.6 times stoichiometric amount, leaching time 30 min, temperature 90 °C | More than 85% of Co, over 90% of Ni, Co, Mn | [87] |
| Phenols | Manganese nodules from the central Pacific Basin, −74 μm particles accounted for 77%, phenol 0.25~0.4 g/g nodules, H2SO4 0.925g/g nodules, liquid/solid 4:1, leaching time 10~20 min, room temperature | Over or nearly 95% of Mn, Co, Ni, Cu | [91] |
| Aromatic amines | Manganese nodules from the central Pacific Basin, −74 μm particles accounted for 77%, aromatic amines 0.3 g/g nodules, H2SO4 0.925 g/g nodules, liquid/solid 4:1, leaching time 10~20 min, room temperature | Over 97% of Mn, Co, Ni, Cu | [92] |
| Sawdust | Manganese nodules from Indian Ocean, −100 μm particles accounted for 100%, pulp concentration 10% (wt/v), sawdust 0.5 g/g nodules, H2SO4 5% (v/v), leaching time 2 h, temperature 105 °C | In total, 99.5% of Mn, 99.1% of Cu, 99.6% of Ni, 93% of Co, 64.6% of Fe | [93] |
| Paper | Manganese nodules from Indian Ocean, −150 μm particles accounted for 100%, pulp concentration 20% (wt/v), paper 0.3 g/g nodules, H2SO4 7.56% (v/v), leaching time 2 h, temperature 90 °C | In total, 97.28% of Cu, 98.66% of Ni, 97.90% of Co and 99.00% of Mn | [95] |
| Glycerol | Manganese nodules from Indian Ocean, −150 μm particles accounted for 100%, pulp concentration 10% (wt/v), glycerol 1% (v/v), H2SO4 10% (v/v), leaching time 1 h, temperature 80 °C | Over 95% of Ni, over 98% of Cu, Co, Mn | [96] |
| Reaction | ΔG° (kJ) |
|---|---|
| −163.37 | |
| −261.30 | |
| −199.52 |
| Reaction | ∆Gθ (kcal) | Temp (°K) |
|---|---|---|
| −14.9 | 1100 | |
| −8.3 | ||
| −23.2 | ||
| +8.2 | 1200 | |
| −20.0 | ||
| −11.8 | ||
| +3.0 | 1200 | |
| −10.7 | ||
| +7.7 | ||
| +4.1 | 1200 | |
| −2.9 | ||
| +1.2 | ||
| +3.16 | 1200 | |
| +50.62 | ||
| +53.78 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Qin, W.; Li, M.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, C. Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules and Advances in Extraction Technology of Valuable Elements from Manganese Nodules. Metals 2024, 14, 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121359
Wang X, Qin W, Li M, Liu X, Cheng Y, Chen S, Yang C. Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules and Advances in Extraction Technology of Valuable Elements from Manganese Nodules. Metals. 2024; 14(12):1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121359
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xu, Wenqing Qin, Maolin Li, Xueduan Liu, Yangrui Cheng, Shiping Chen, and Congren Yang. 2024. "Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules and Advances in Extraction Technology of Valuable Elements from Manganese Nodules" Metals 14, no. 12: 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121359
APA StyleWang, X., Qin, W., Li, M., Liu, X., Cheng, Y., Chen, S., & Yang, C. (2024). Mineralogy of Deep-Sea Manganese Nodules and Advances in Extraction Technology of Valuable Elements from Manganese Nodules. Metals, 14(12), 1359. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121359









