A Study on the Impact Toughness of the Simulated Heat-Affected Zone in Multi-Layer and Multi-Pass Welds of 1000 MPa Grade Steel for Hydroelectric Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Microstructure of the Base Metal
3.2. Impact Property
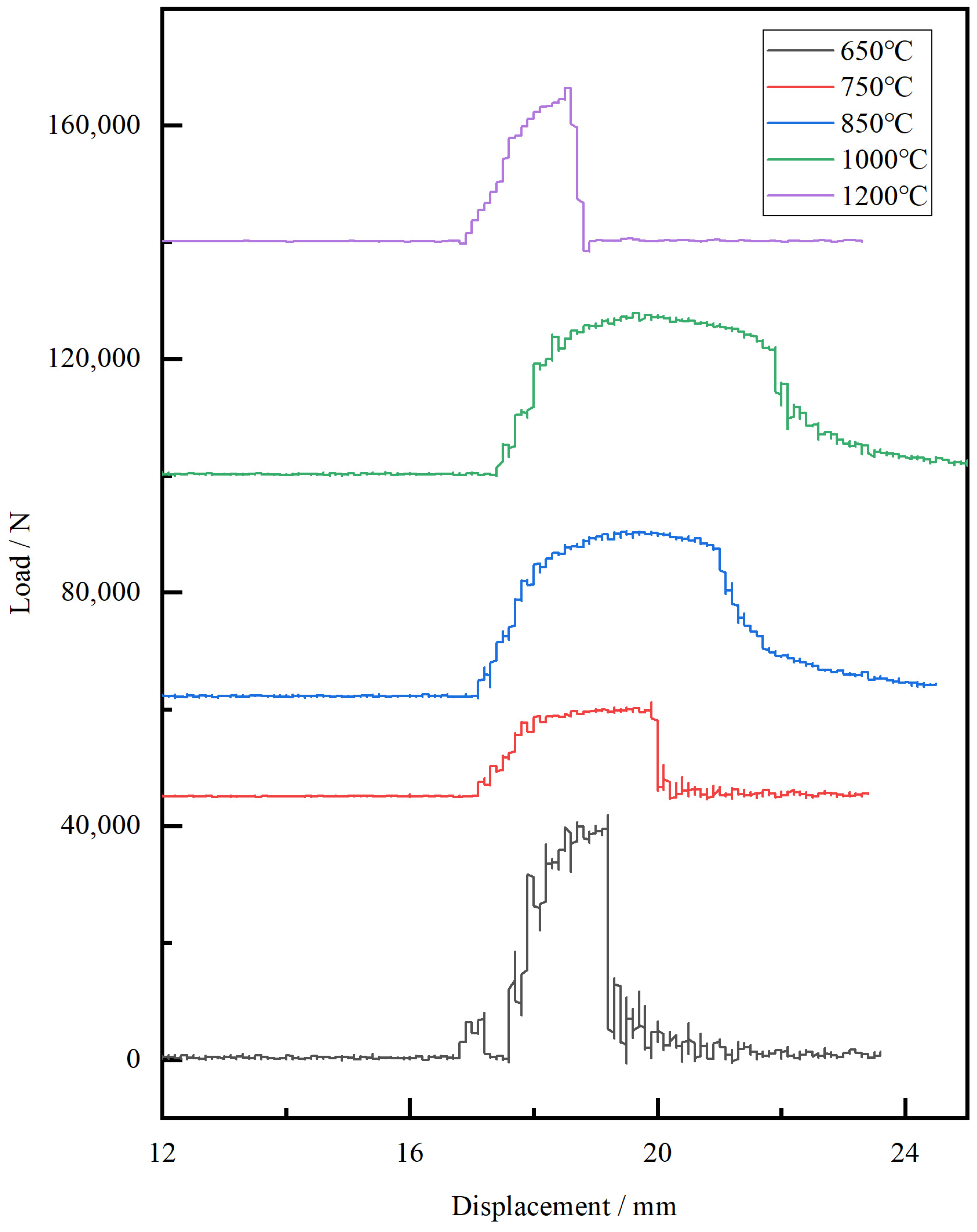
3.2.1. Oscillographic Impact Data
3.2.2. Impact Fracture Morphologies
4. Discussion
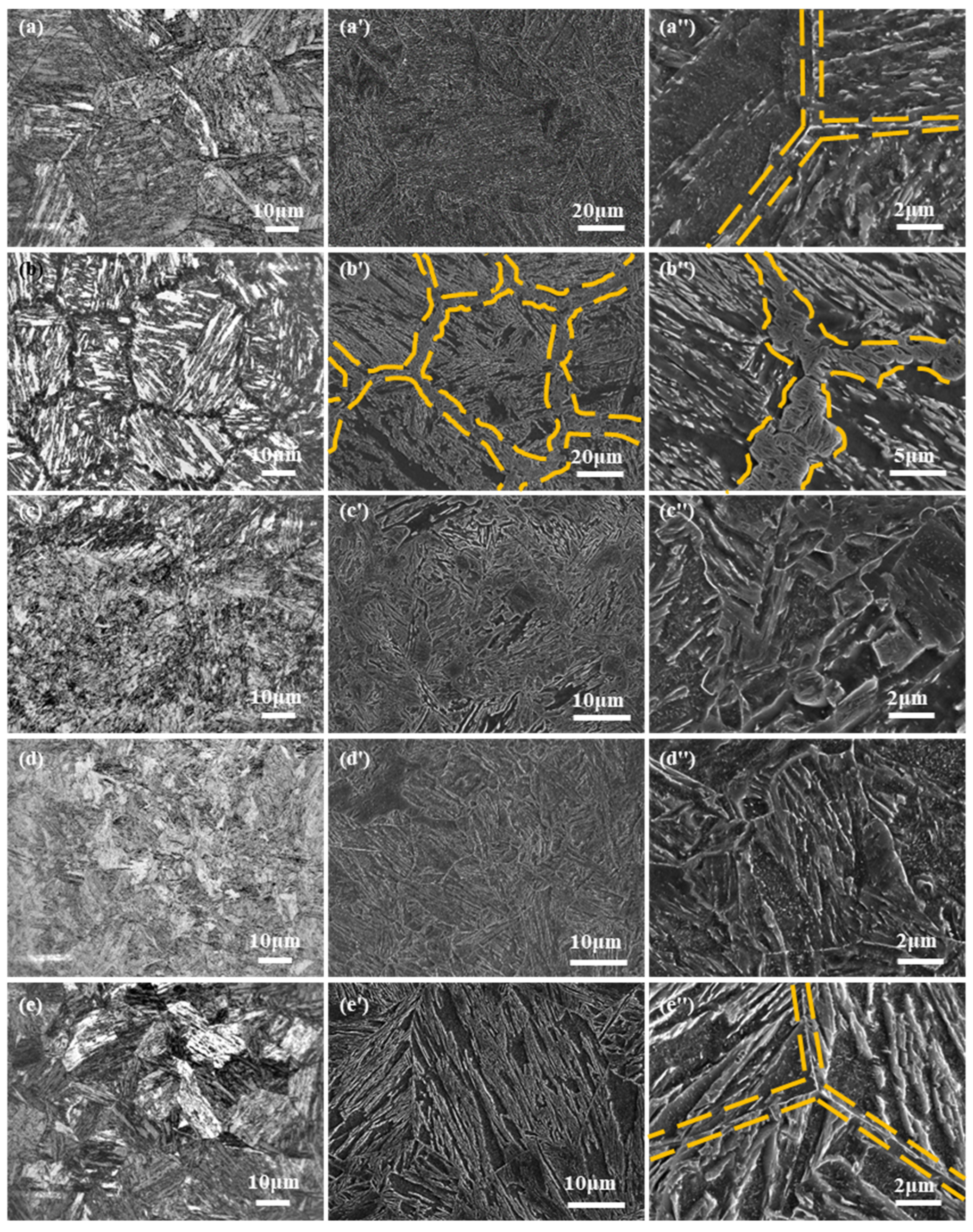
4.1. Microstructure Analysis of the HAZ at Different Secondary Peak Temperatures
4.1.1. General Characteristics of Microstructures
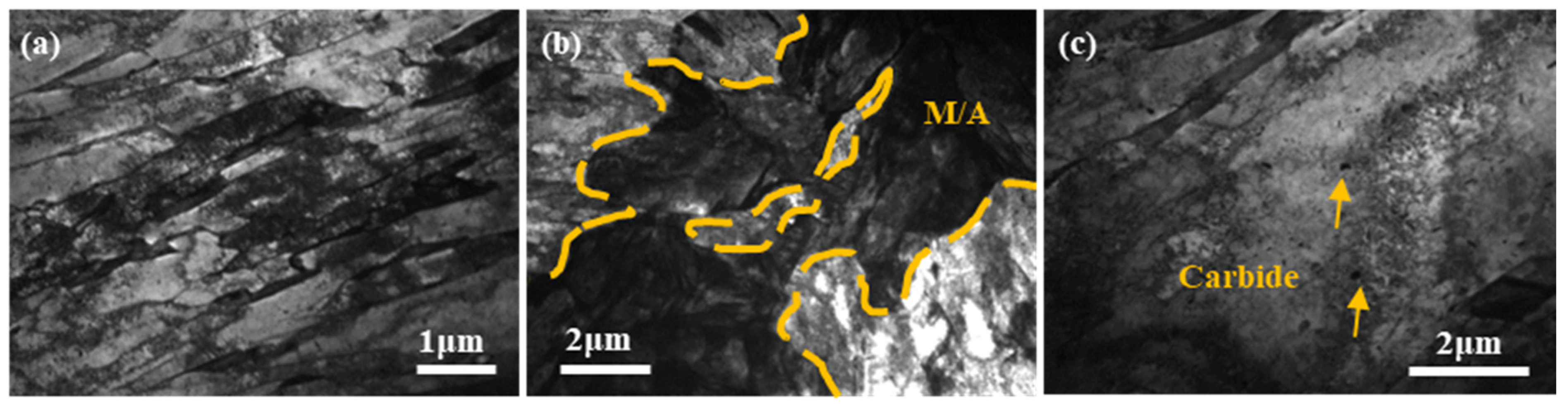
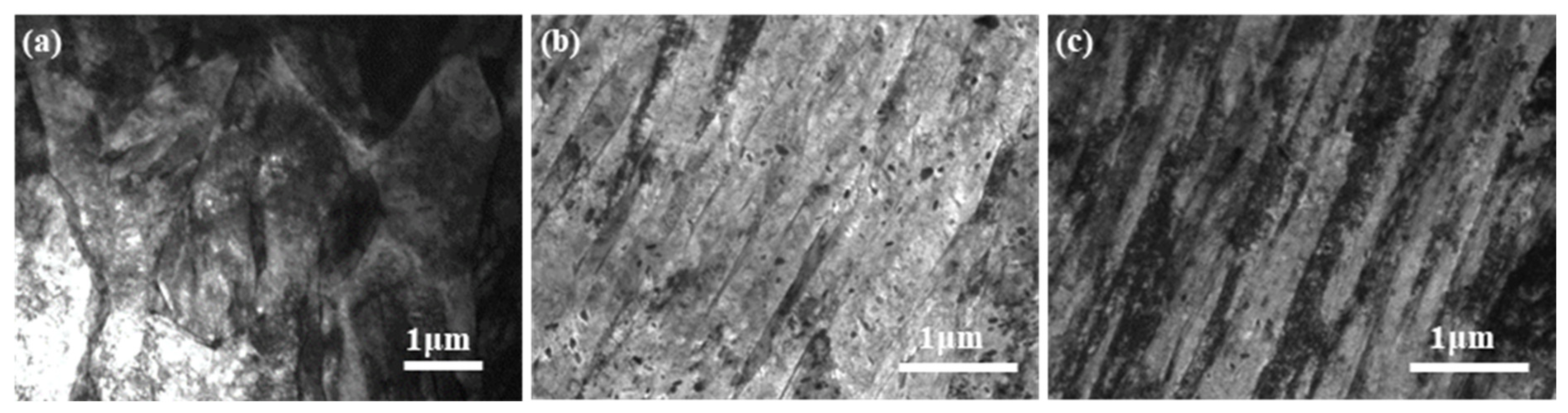
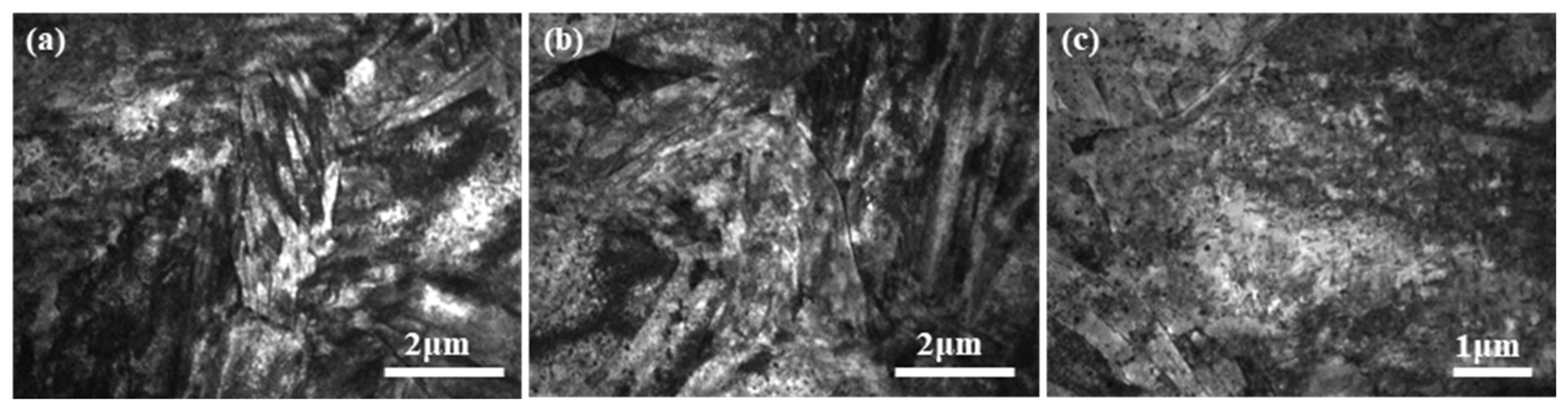
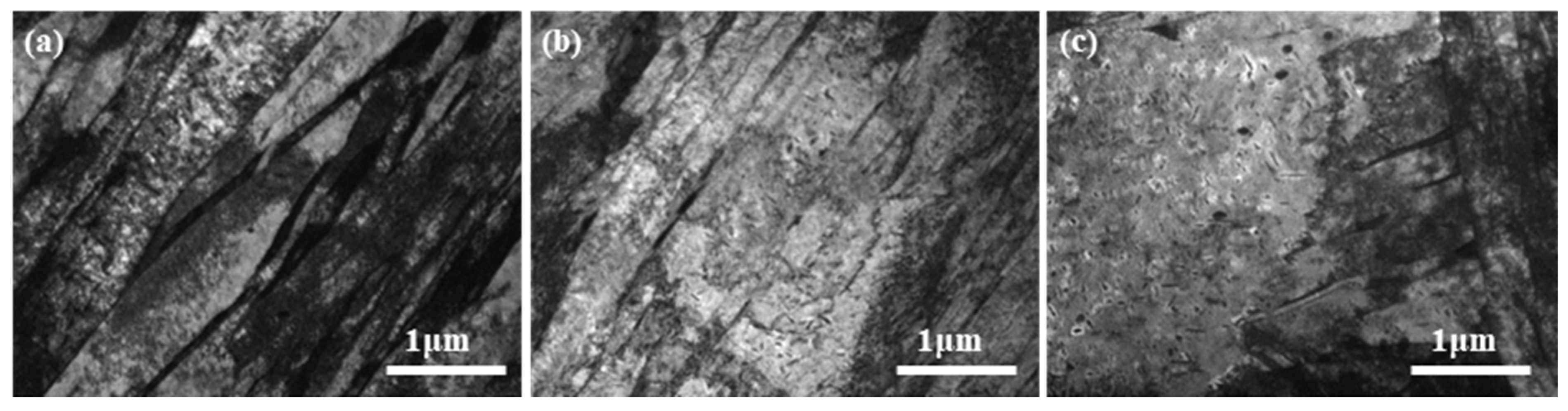
4.1.2. Fine Structure Analysis
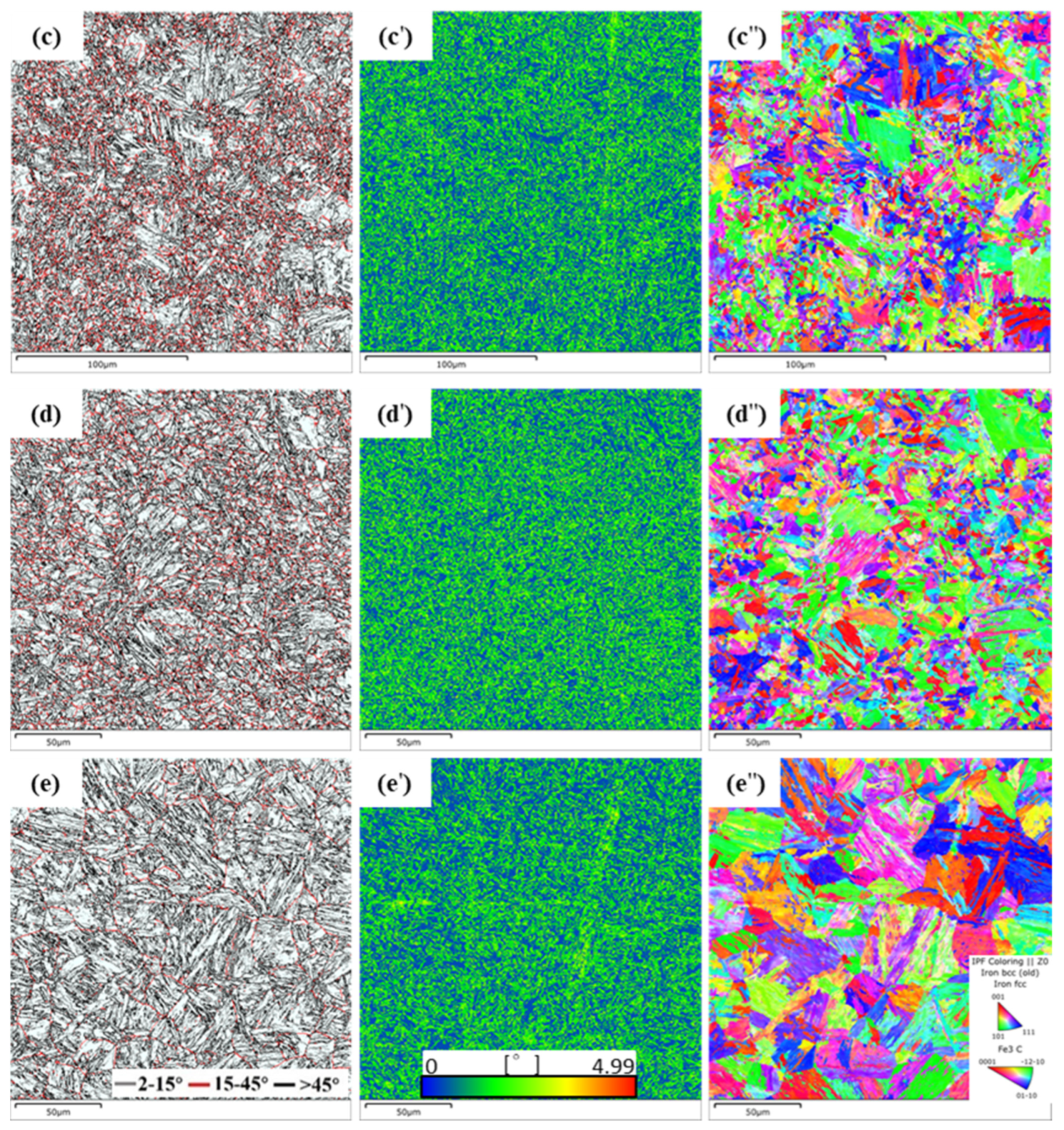
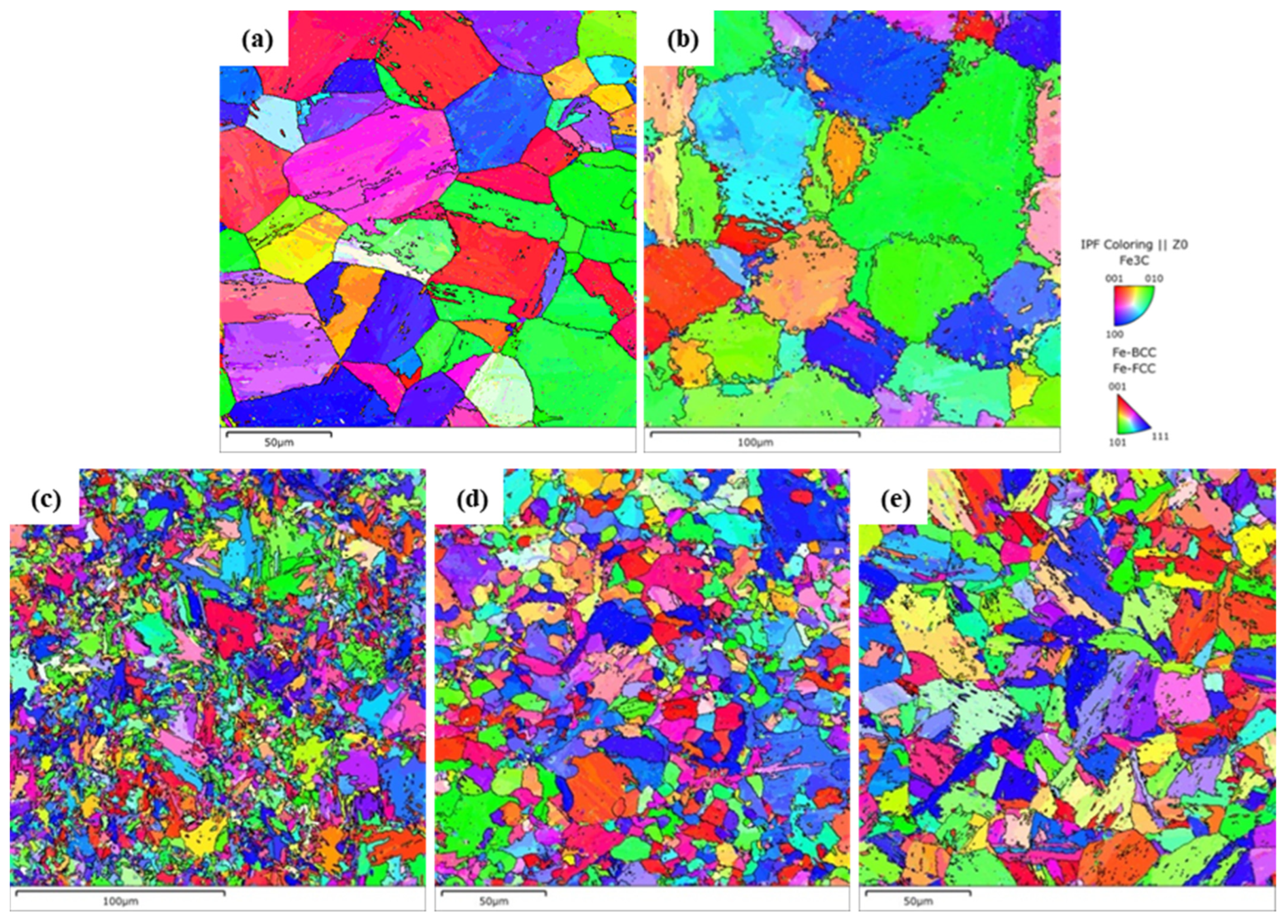
4.1.3. Crystallographic Analysis
4.1.4. Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lulu, F.; Dong, Z.; Kaiming, W.; Weiwen, Q. Study on Microstructure and properties of 1000MPa grade steel plate for hydropower station. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1637, 012072. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chen, J.; Tu, X.; Han, Y. Effect of finish rolling temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of 1000 MPa grade tempered steel plate for hydropower station. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 67, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, S.; Chen, L.; Fang, L.; Huo, S. Controlling of reheated quenching temperature of 1000 MPa grade steel plate for hydropower station. Mater. Werkst. 2019, 50, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steimbreger, C.; Gubeljak, N.; Vuherer, T. Effect of welding processes on the fatigue behaviour of ultra-high strength steel butt-welded joints. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 275, 108845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, S.; Sachin, M. A review on welding of high strength oil and gas pipeline steels. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2017, 38, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Di, X.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, C. Control strategy of reducing hydrogen enrichment in heat-affected zone during welding for ultra-high strength steels. Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf. 2024, 159, 108228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chène, O. Welding processes for the cleuson-dixence shaft. In Proceedings of the Conference on High Strength Steels for Hydropower Plants, Takasaki, Japan, 20 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Leakage Investigations at Cleuson-Dixence. Available online: https://www.waterpowermagazine.com/features/featureleakage-investigations-at-cleuson-dixence (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Hailong, C.; Xinchun, L.; Xin, W. Recent research progress on additive manufacturing of high-strength low-alloy steels: Focusing on the processing parameters, microstructures and properties. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106616. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y. Proceedings of the International Seminar on Welding of High Strength Pipeline Steel; Gray, J.M., Ed.; TMS: Araxa, Brazil, 2011; p. 435. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Bai, L.; Qian, G.; Sun, X.; Liu, G.; Xie, Z.; Shang, C. Crystallographic Study of Transformation Products of Heat-Affected Zone and Correlation with Properties of FH690 Heavy-Gauge Marine Steel by Multi-Pass Submerged Arc Welding. Metals 2024, 14, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Li, D.; Nie, J.; Wu, J. Proceedings of Recent Developments in High Strength Steels for Energy Appli Cations; Deardo, A., Ed.; MS&T: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2012; p. 892. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Shang, C. Effect of Pre-Weld Heat Treatment on the Microstructure and Properties of Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a Wind Power Steel after Simulated Welding. Metals 2024, 14, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Gao, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X. Significant influence of heat input on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of the simulated CGHAZ in a 1000 MPa grade ultra-high strength steel. Mater. Technol. 2024, 39, 2335426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Midawi, A.R.H.; Sherepenko, O.; Ramachandran, D.C.; Akbarian, S.; Shojaee, M.; Zhang, T.; Ghassemi-Armaki, H.; Worswick, M.; Biro, E. Prediction of Mechanical Properties in the Sub-Critical Heat Affected Zone of AHSS Spot Welds Using Gleeble Thermal Simulator and Hollomon-Jaffe Model. Metals 2023, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xueda, L.; Chengjia, S.; Changchai, H.; Yuran, F.; Jianbo, S. Influence of necklace-type M-A constituent on impact toughness and fracturemechanism in the heat affected zone of X100 pipeline steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2016, 52, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, L.; King, E. Cleavage initiation in the intercritically reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zone: Part I. Fractographic evidence. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1994, 25, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, P.; Solberg, K.; Karlsen, M.; Akselsen, O.M.; Østby, E. Cleavage fracture initiation at M–A constituents in intercritically Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of a HSLA steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2014, 45, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Baker, T. Effect of morphology of martensite–austenite phase on fracture of weld heat affected zone in vanadium and niobium microalloyed steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kikuta, Y.; Araki, T.; Yoneda, M.; Matsuda, Y. Micro-fracture behaviour induced by M-A constituent (Island Martensite) in simulated welding heat affected zone of HT80 high strength low alloyed steel. Acta Metall. 1984, 32, 1779–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sungtak, L.; Byung, C.K.; Dongil, K. Correlation of microstructure and fracture propeties in weld heat-affected zones of themo-mechanically controlled processed steels. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1992, 23, 2803–2816. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, L.; King, E. Cleavage initiation in the intercritically reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zone: Part II. Failure criteria and statistical effects. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1996, 27, 3019–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, Y.; Shinohara, Y. High strength linepipe with excellent HAZ toughness and deformability. In Seminar Forum of the X100/X120 Grade High Performance Pipe Steels; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2005; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Xueda, L.; Chunyu, L.; Ning, C.; Xueqiang, L.; Jianbo, S. Crystallography of Reverted Austenite in the Intercritically Reheated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zone of High Strength Pipeline Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2021, 57, 967–976. [Google Scholar]
- Veronica, H.; Bjørn, R.; Sørås, R.; Odd, A.; Christian, T.; Erling Østby. Local mechanical properties of intercritically reheated coarse grained heat affected zone in low alloy steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 59, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L. Microstructural characteristics and impact fracture behaviors of a novel High-Strength Low-Carbon Bainitic Steel with different reheated Coarse-Grained Heat-Affected Zones. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 6258–6268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, A.; Drillet, J.; Gourgues, A.; Sturel, T.; Pineau, A. Microstructure of martensite–austenite constituents in heat affected zones of high strength low alloy steel welds in relation to toughness properties. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2000, 5, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Shangjia, J.; Wenjin, N.; Subramanian, S. Investigation on the microstructure and toughness of coarse grained heat affected zone in X-100 multi-phase pipeline steel with high Nb content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 558, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, J.; Gao, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Lin, F. Thermodynamic coupling numerical simulation and mechanical properties analysis of TC4 laser welding. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 2024, 45, 77–88+96. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Han, S.; Xie, F.; Hu, L.; Deng, D. Influence of Solid-State Phase Transformation and Softening Effect on Welding Residual Stress of Ultra-High Strength Steel. Acta Metall. Sin. 2023, 59, 1613–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, C.; Deng, D. Study on Computational Prediction About Microstructure and Hardness of Q345 Steel Welded Joint Based on SH-CCT Diagram. Acta Metall. Sin. 2021, 57, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Ma, J.; Lu, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J. Numerical simulation and mechanical properties of spray-assisted friction stir welding RAFM steel. Trans. China Weld. Inst. 2022, 43, 104–112+120. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 148-1:2016; Metallic Materials—Charpy Pendulum Impact Test—Part 1: Test Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016.
- Li, X.; Ma, X.; Subramanian, S.; Shang, C.; Misra, R. Influence of prior austenite grain size on martensite–austenite constituent and toughness in the heat affected zone of 700MPa high strength linepipe steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 616, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.; Shang, C.; Chen, L.; Subramanian, S. Investigation on the crystallography of the transformation products of reverted austenite in intercritically reheated coarse grained heat affected zone. Mater. Des. 2013, 43, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouyne, E.; Flower, H.; Lindley, T.; Pineau, A. Use of EBSD technique to examine microstructure and cracking in a bainitic steel. Scr. Mater. 1998, 39, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, A.; Misra, R.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; He, X.; Jansto, S.J. An analysis of the microstructure of the heat-affected zone of an ultra-low carbon and niobium-bearing acicular ferrite steel using EBSD and its relationship to mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 6440–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, P. Development of the Local Approach to Fracture over the Past 25 years: Theory and Applications. Int. J. Fract. 2006, 138, 139–166. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, A.; Knott, J. Micromechanisms of brittle fracture. Metall. Trans. A 1993, 24, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
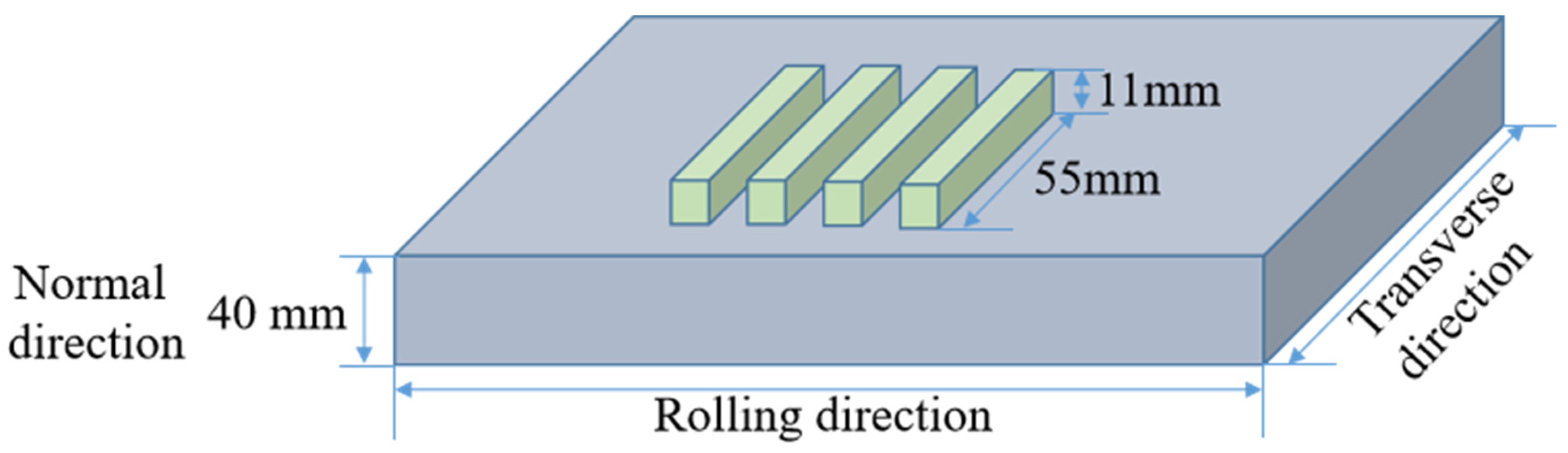
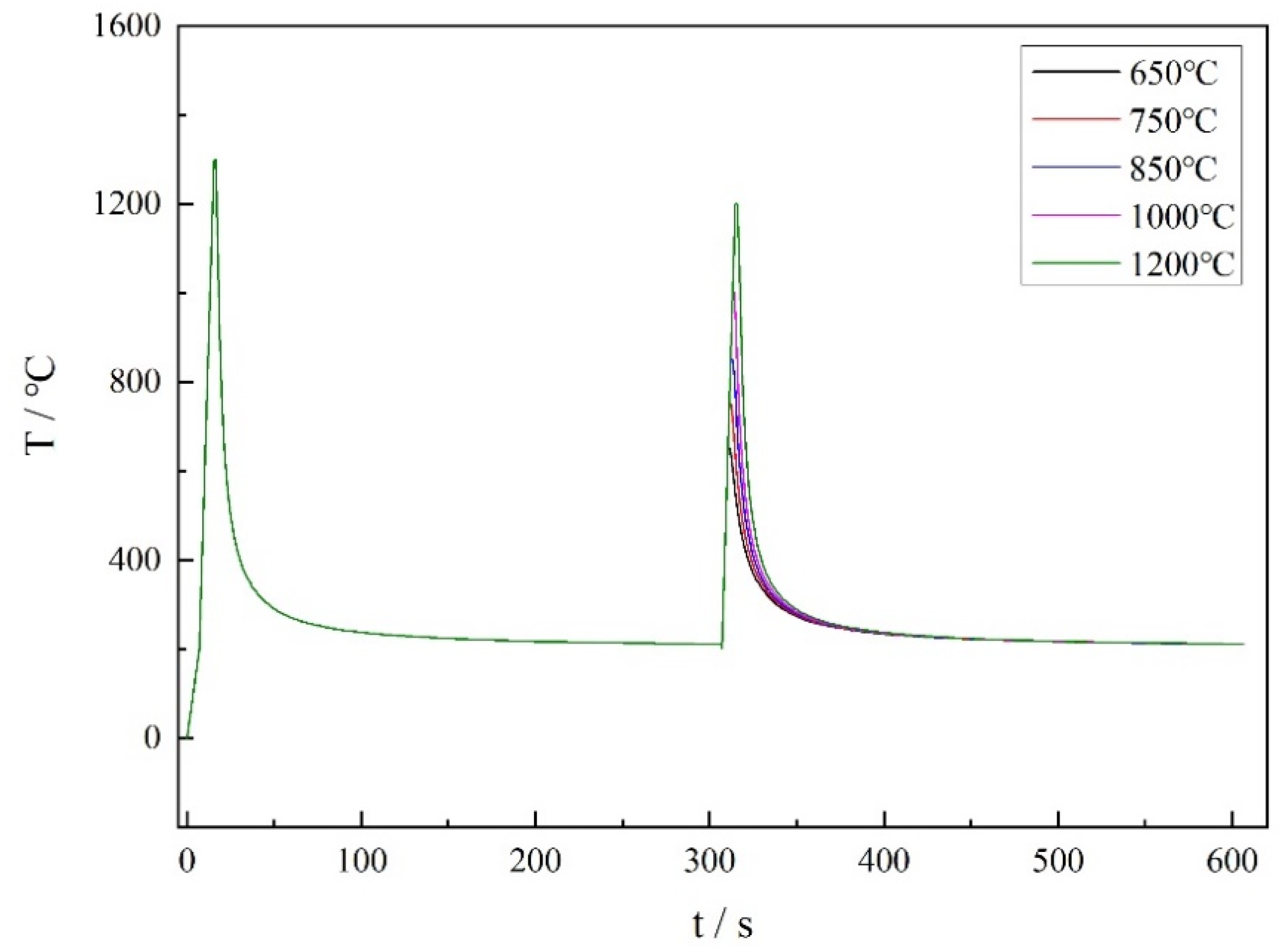

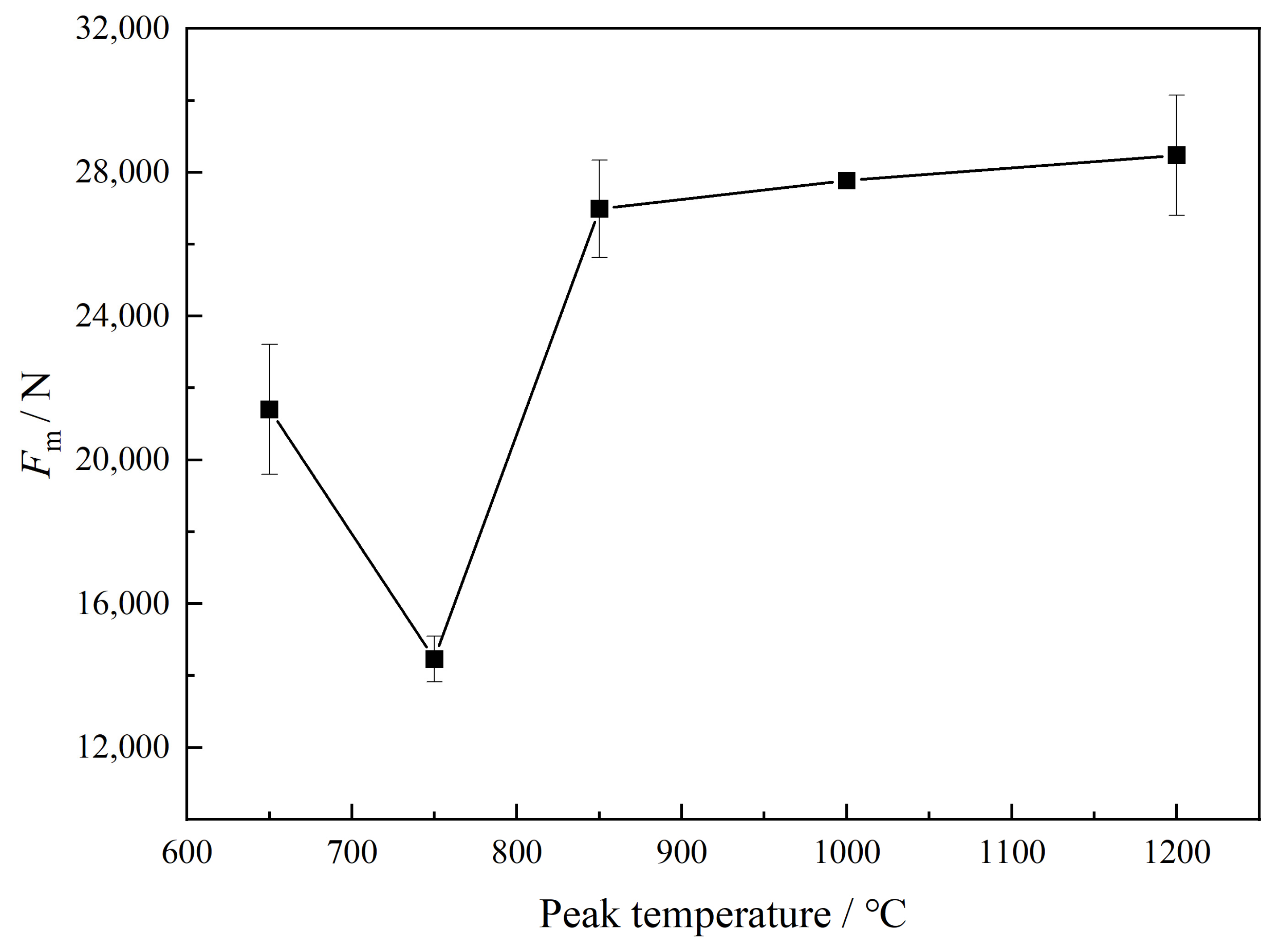
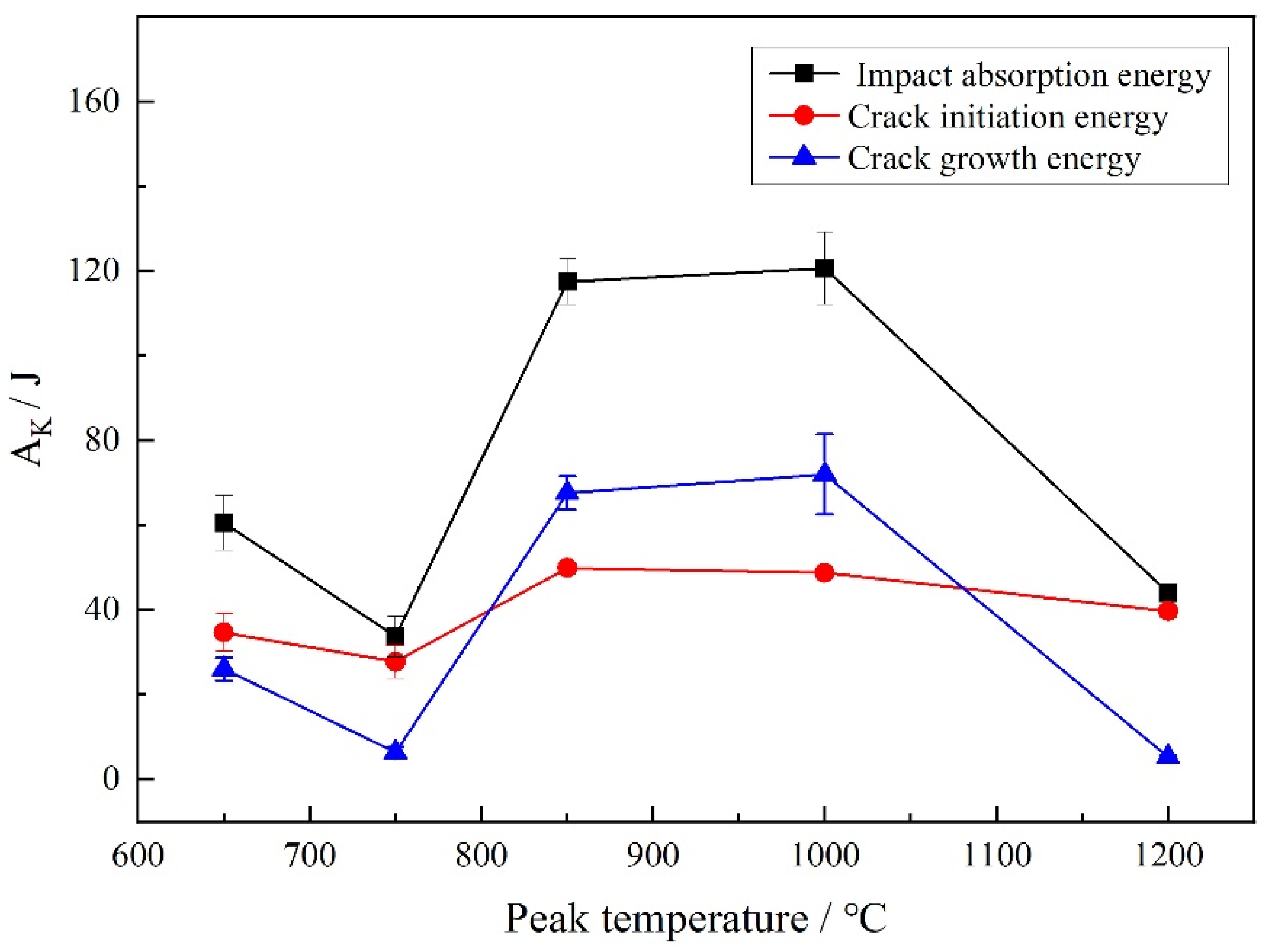




| C | Ni | Cr | Mo | Mn | Cu | Si | Al | Nb | V | Ti | B | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.11 | 2.00~2.50 | 1.00~1.50 | 0.50~1.00 | ≤1.00 | ≤0.20 | ≤0.20 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.004 | <0.02 | <0.005 | Bal. |
| Primary Thermal Cycling | Secondary Thermal Cycle | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Rate/°C/s | Peak Temperature/°C | t8/5/s | Interpass Temperature/°C | Heating Rate/°C/s | Peak Temperature/°C | t8/5/s |
| 130 | 1300 | 5 | 200 | 130 | 650 | 5 |
| 750 | ||||||
| 850 | ||||||
| 1000 | ||||||
| 1200 | ||||||
| Peak Temperatures/°C | Crack Initiation Energy/J | Crack Propagation Energy/J | Impact Energy/J |
|---|---|---|---|
| 650 | 39.1 | 28.7 | 67.0 |
| 30.2 | 23.3 | 54.0 | |
| 750 | 23.8 | 5.1 | 28.9 |
| 31.7 | 7.6 | 38.5 | |
| 850 | 51.3 | 71.5 | 122.9 |
| 48.5 | 63.7 | 112.1 | |
| 1000 | 49.0 | 62.5 | 112.1 |
| 48.5 | 81.4 | 129.2 | |
| 1200 | 41.3 | 4.9 | 45.2 |
| 38.1 | 5.7 | 42.9 |
| Peak Temperatures/°C | Grain Boundary Angle Distribution of the Original Microstructure/% | Original Grain Size/μm | Reconstructed Grain Size/μm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2°~15° | 15°~45° | >45° | |||
| 650 | 47.0 | 4.6 | 48.4 | 16.43 ± 4.03 | 36.89 ± 12.03 |
| 750 | 45.6 | 7.9 | 46.5 | 16.83 ± 4.32 | 47.22 ± 11.79 |
| 850 | 38.9 | 15.8 | 45.3 | 6.53 ± 1.78 | 7.64 ± 2.06 |
| 1000 | 41.5 | 12.7 | 45.9 | 6.90 ± 1.84 | 14.05 ± 3.98 |
| 1200 | 48.0 | 5.5 | 46.5 | 14.05 ± 3.78 | 17.38 ± 4.70 |
| Peak Temperatures/°C | Local Misorientation/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0°~1° | 1°~2° | 2°~3° | 3°~4° | 4°~5° | |
| 650 | 49.8 | 40.5 | 8.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| 750 | 42.2 | 44.7 | 10.9 | 1.8 | 0.3 |
| 850 | 48.1 | 41.3 | 9.1 | 1.3 | 0.2 |
| 1000 | 44.4 | 43.8 | 10.2 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| 1200 | 49.2 | 41.1 | 8.4 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Chang, J. A Study on the Impact Toughness of the Simulated Heat-Affected Zone in Multi-Layer and Multi-Pass Welds of 1000 MPa Grade Steel for Hydroelectric Applications. Metals 2024, 14, 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121455
Li Y, Li Y, Chang J. A Study on the Impact Toughness of the Simulated Heat-Affected Zone in Multi-Layer and Multi-Pass Welds of 1000 MPa Grade Steel for Hydroelectric Applications. Metals. 2024; 14(12):1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuwei, Yuanbo Li, and Jianxiu Chang. 2024. "A Study on the Impact Toughness of the Simulated Heat-Affected Zone in Multi-Layer and Multi-Pass Welds of 1000 MPa Grade Steel for Hydroelectric Applications" Metals 14, no. 12: 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121455
APA StyleLi, Y., Li, Y., & Chang, J. (2024). A Study on the Impact Toughness of the Simulated Heat-Affected Zone in Multi-Layer and Multi-Pass Welds of 1000 MPa Grade Steel for Hydroelectric Applications. Metals, 14(12), 1455. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14121455






