Dissolution of CaO in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 Slag in Si Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
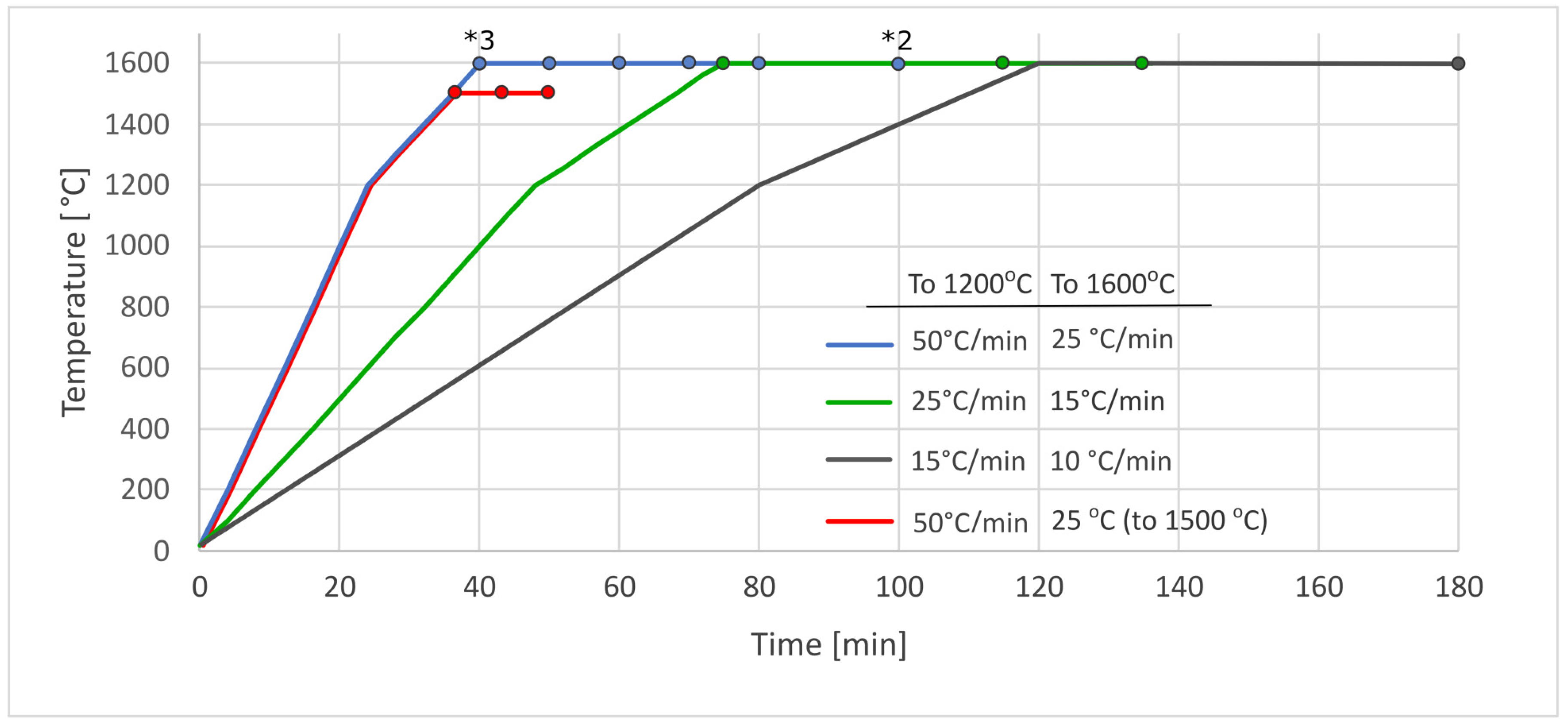
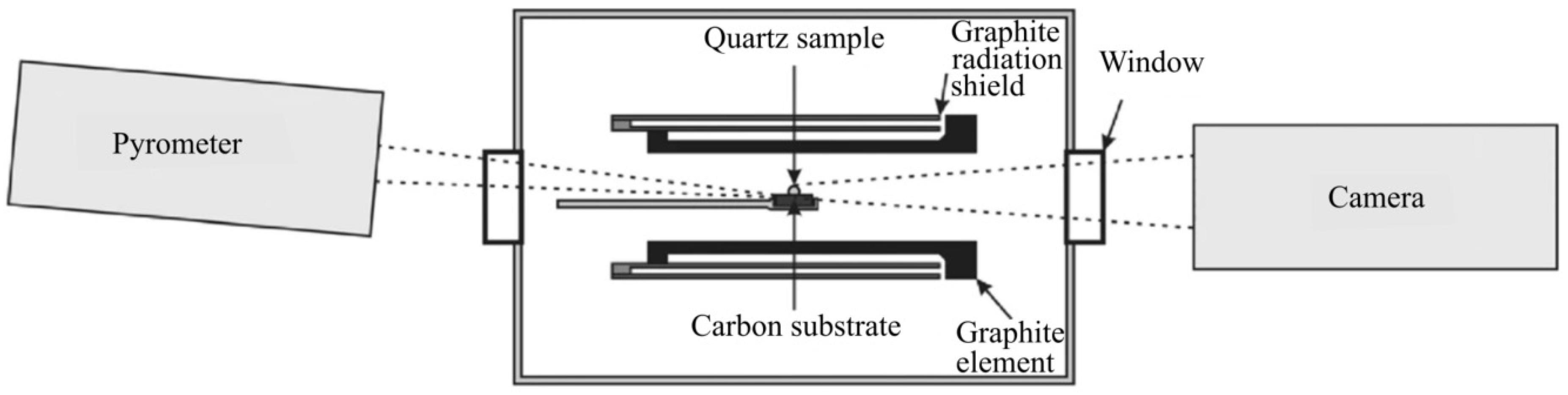
2. Materials, Equipment and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
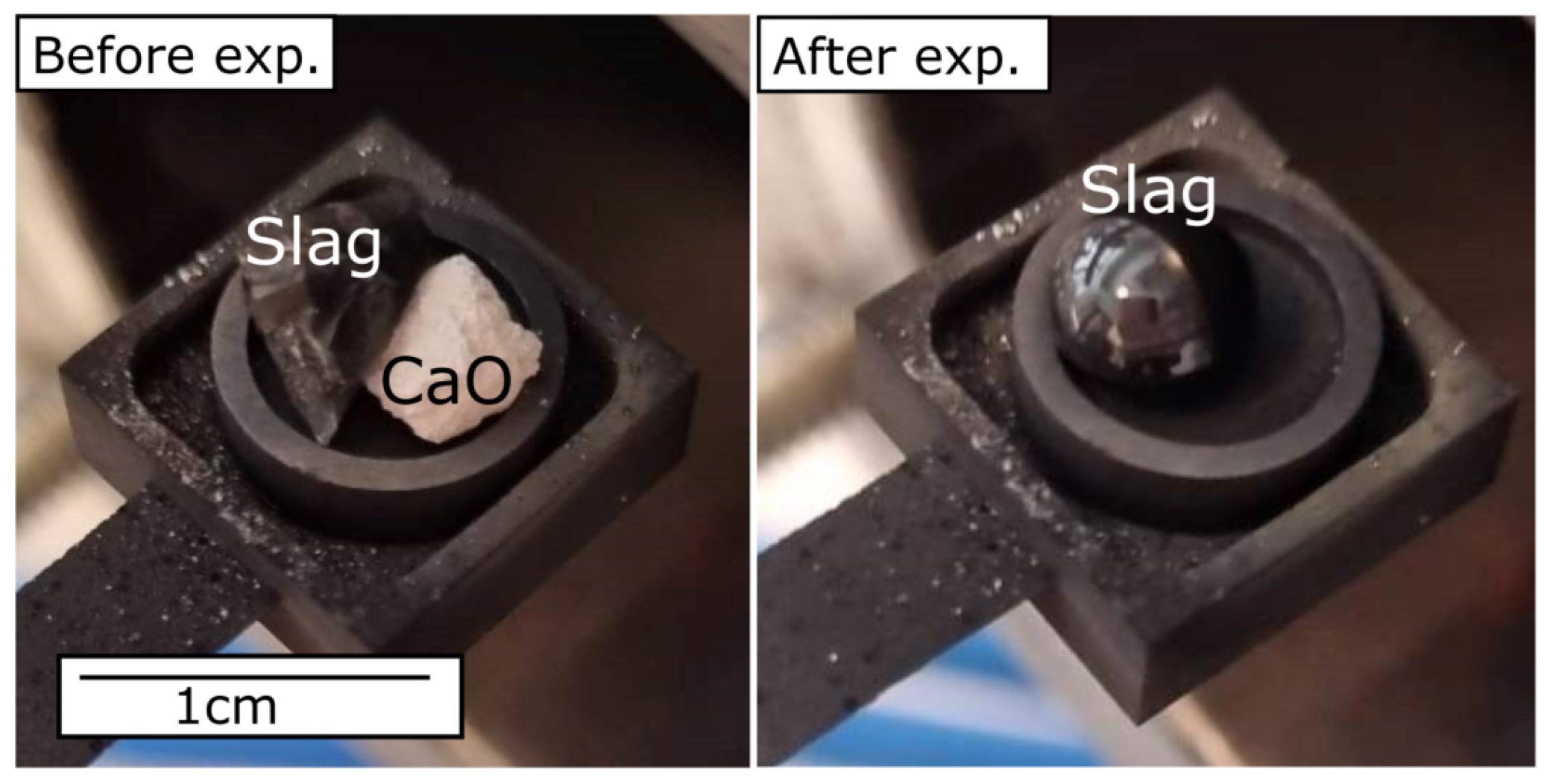
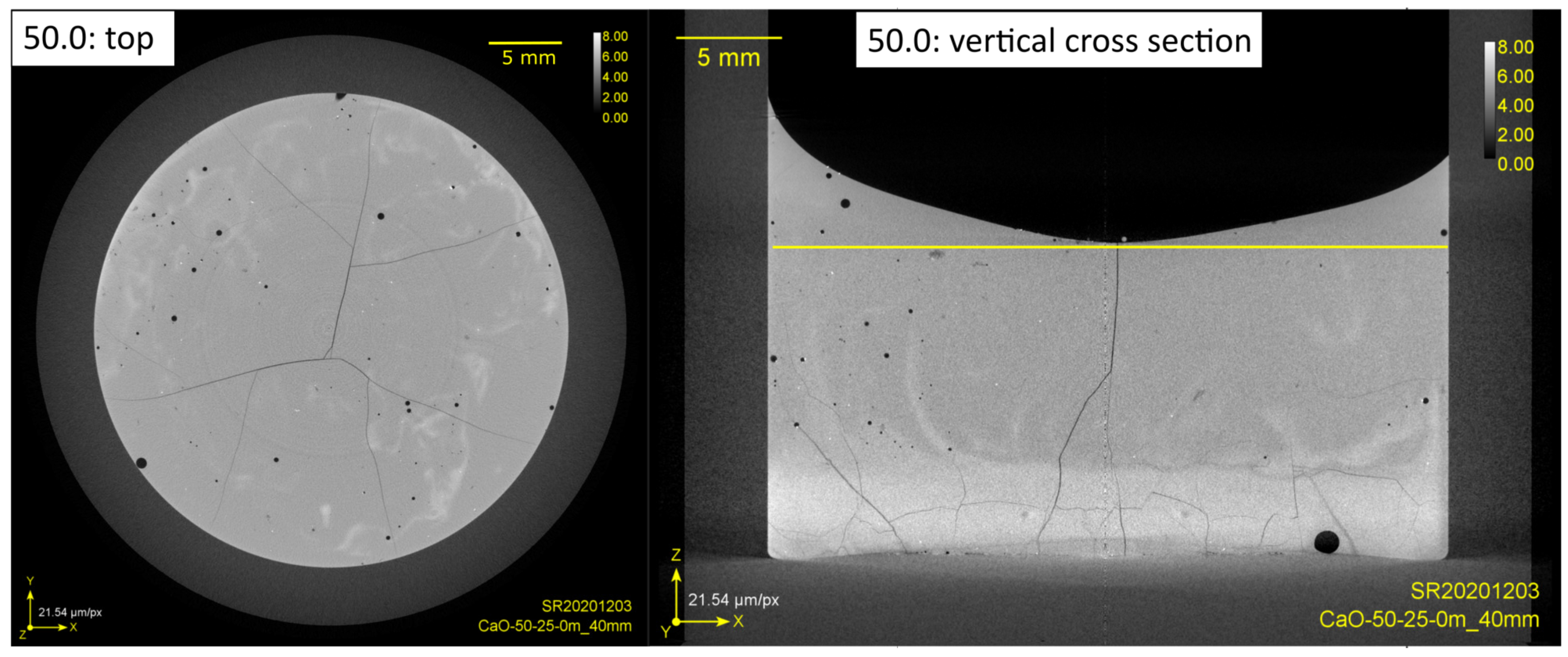
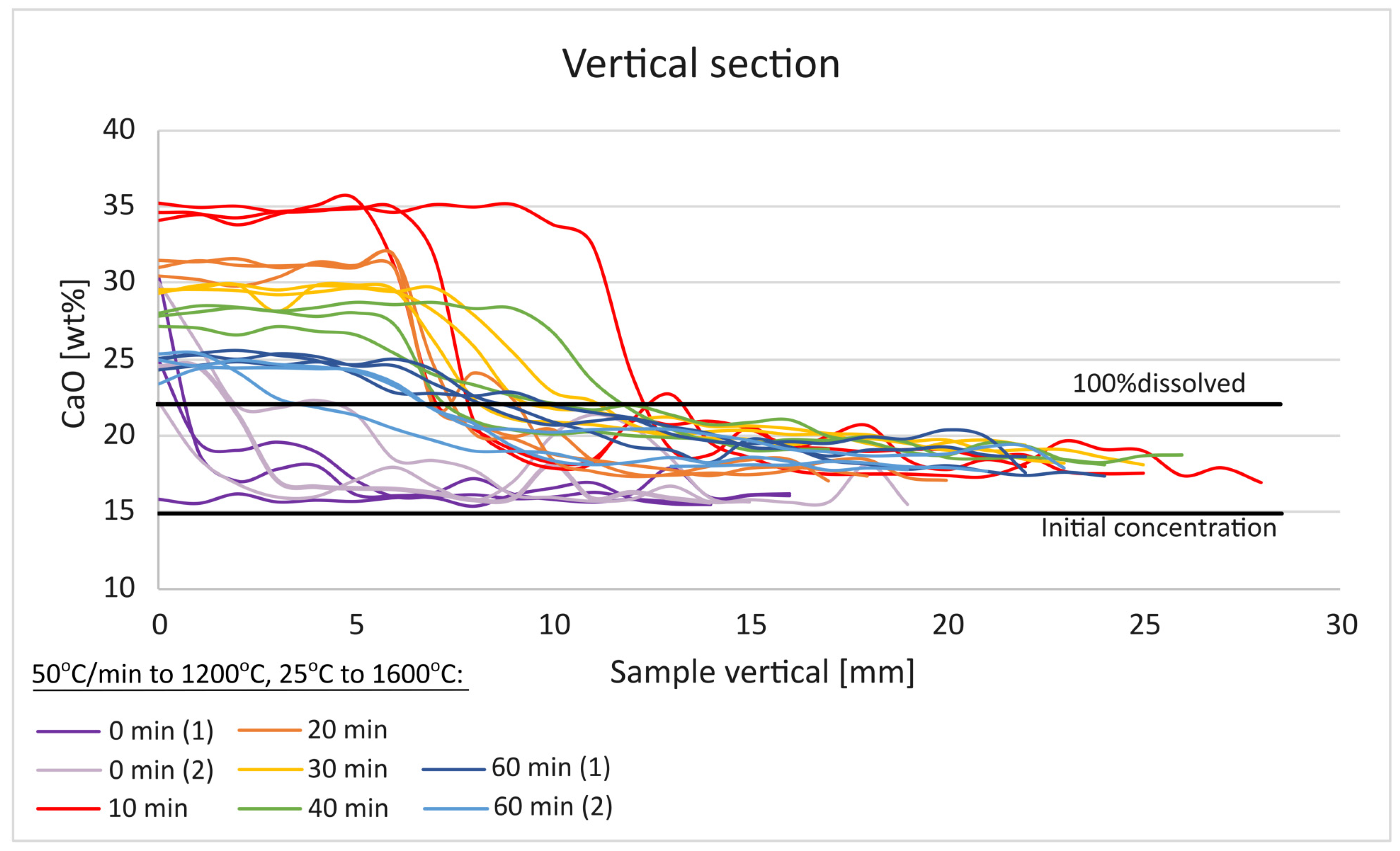
3.1. CaO Dissolution in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 Slag
3.2. Modeling the Dissolution Rate
3.3. The Effect of CaO on Slag Viscosity in Si Furnaces
4. Conclusions
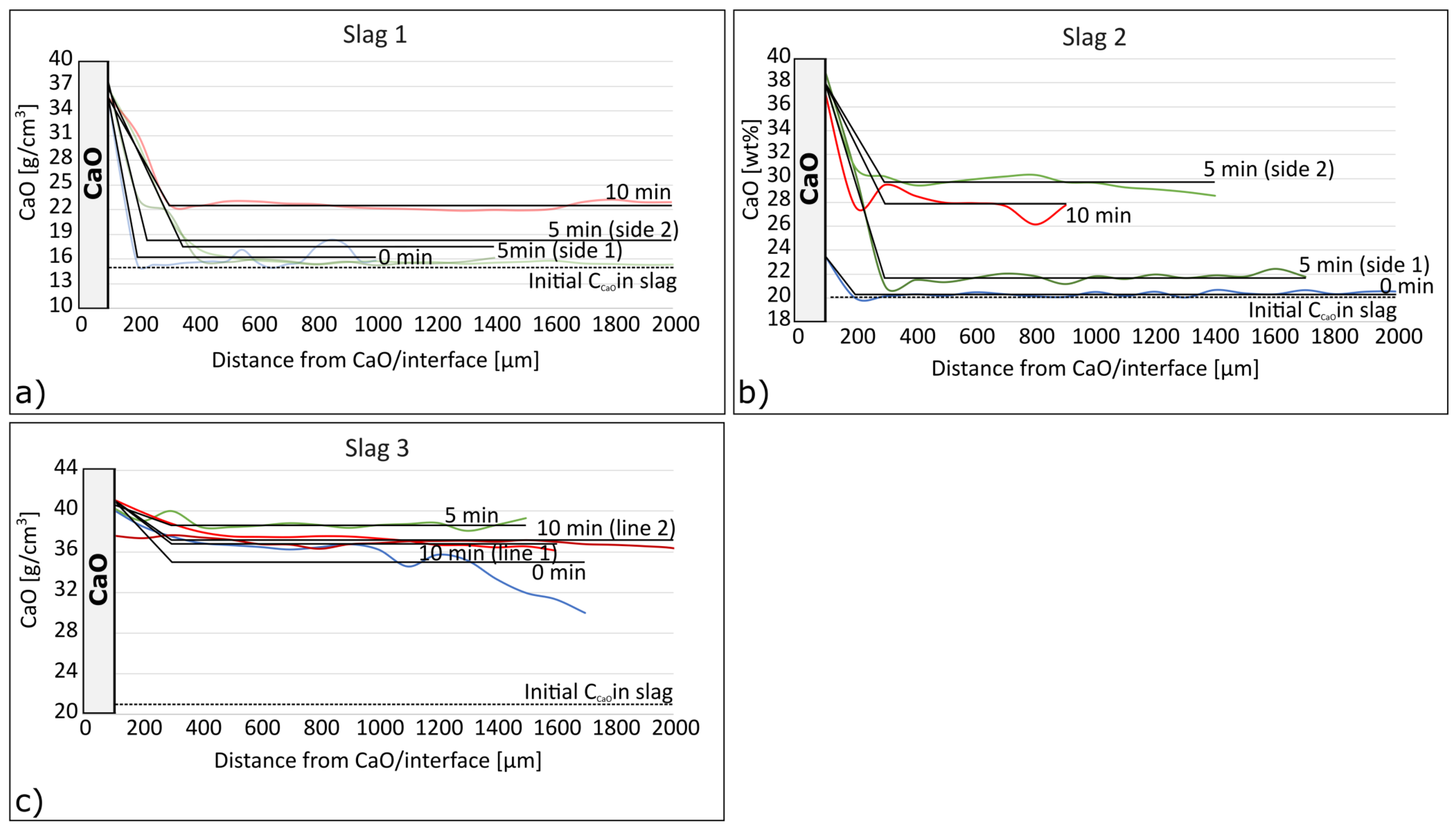
- Initial CaO disintegrates during heating before it dissolves in the slag. During the dissolution process, a layer with 35–42% CaO is formed between the CaO particle and the slag, which for slag 1 correspond to CaO·Al2O3·2SiO2, and 2CaO·Al2O3·SiO2 for slag 2 and 3. This is different from earlier research [24,25,26,27], which has found a 2CaO·SiO2 or 3CaO·SiO2 layer next to the slag at the CaO–slag interface.
- Two models for the dissolution rate for the three slags in this study were made. In the first model, the CaO particle is assumed to be a smooth shrinking sphere, and the rate controlled by the rate of chemical reaction. The second model assumes that the rate is controlled by the mass transport and depends on the diffusion rate of CaO through a boundary layer at the surface of the CaO. In both models, it was found that kslag 3 > kslag 1 > kslag 2, which is consistent with proportional relationship with viscosities. The diffusion coefficients are found to be in the range of 10−6 cm2/s.
- The initial effect of increasing the CaO content in the slag from 15–21% to 25–30% gives a significant reduction in the viscosity.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schei, A.; Tuset, J.K.; Tveit, H. Production of High Silicon Alloy; Tapir: Trondheim, Norway, 1998; pp. 47–72. [Google Scholar]
- Myrhaug, E. KPN CONTROLLED TAPPING, Examples of conceptual models based on simplified COMSOL simulations. In Proceedings of the Industrial presentation from Elkem ASA, KPN Controlled Tapping Meeting 2020.03.05 regarding Conceptual Models, NTNU, Trondheim, Norway, 5 April 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Towers, H.; Paris, M.; Chipman, J. Diffusion of Calcium Ion in Liquid Slag. JOM 1953, 5, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towers, H.; Chipman, J. Diffusion of Calcium and Silicon in a Lime-Alumina-Silica Slag. JOM 1957, 9, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niwa, K. A study on the Diffusion of Calcium Ion in Molten Lime-Silica-Alumina slags by Using a Radioactive Tracer Technique. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. Mater. 1957, 21, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitô, T.; Maruya, K. Diffusion of Calcium in Liquid Slags. Res. Inst. Miner. Dress. Metall. 1958, 10, 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Goto, K.S.; Sasabe, M.; Kawakami, M. Relation between Tracer Diffusivity and Electrical Conductivity on Multi-component Oxide Slags at 900 ° to 1600 °C. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1977, 17, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Richter, F.M.; Davis, A.M.; Watson, B.E. Diffusion in silicate melts: I. Self diffusion in CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 at 1500 °C and 1 GPa. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1996, 60, 4353–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.H.; Brungs, M.P.; Ostrovski, O.; Jahanshani, S. Effects of additives and temperature on dissolution rate and diffusivity of lime in Al2O3-CaO-SiO2 based slags. Metall. Mater. Trans. B 2006, 37, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Chou, K. Diffusion Coefficient of Calcium Ion in CaO-Al2O3-SiO2 Melts. J. Iron Steel Res. 2011, 18, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.S.; Hu, X.H.; Chou, K.C. Model for diffusion coefficient estimation of calcium ions in CaO–Al2O3–SiO2 slags. Ironmak. Steelmak. 2013, 40, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verein Deutscher Eisenhüttenleute. Slag Atlas; Stahlinstitut VDEh: Düsseldorf, Germany, 1995; pp. 105–545. [Google Scholar]
- Glasstone, S.; Laidler, K.J.; Eyring, H. The Theory of Rate Processes: The Kinetics of Chemical Reactions, Viscosity, Diffusion and Electrochemical Phenomena; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1941; pp. 516–523. [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann, A.W. Diffusion in natural silicate melts: A critical review. In Physics of Magmatic Processes; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1980; pp. 385–417. [Google Scholar]
- Angell, C.A.; Cheeseman, P.A.; Tamaddon, S. Pressure Enhancement of Ion Mobilities in Liquid Silicates from Computer Simulation Studies to 800 Kilobars. Science 1982, 218, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, E.B. Calcium diffusion in a simple silicate melt to 30 kbar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1979, 43, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogan, N.; Brooks, G.A.; Rhamdhani, M.A. Kinetics of Flux Dissolution in Oxygen Steelmaking. ISIJ Int. 2009, 49, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, K.C.; Sridhar, S. Viscosities of ironmaking and steelmaking slags. Ironmak. Steelmak. 1999, 26, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstad, M.B.; Tangstad, M. SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 slags in the Si/FeSi furnaces. In Proceedings of the 16th International Ferro-Alloys Congress (INFACON XVI) 2021, Trondheim, Norway, 28–29 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jusnes, K.F.; Hjelmseth, R.; Folstad, M.B.; Ditlefsen, N.S.; Tangstad, M. Investigation of slag compositions and possible relation to furnace operation of a FeSi75 furnace. In Proceedings of the 16th International Ferro-Alloys Congress (INFACON XVI) 2021, Trondheim, Norway, 28–29 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Kristiansen, S. Dissolution Rate and Wettability of SiO2–CaO–Al2O3 Slag on Quartz. Project Work. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Trondheim, Norway, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- ThermoFisher Scientific. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/no/en/home.html (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Franzefoss Minerals AS. Available online: https://kalk.no/en/ (accessed on 8 January 2024).
- Amini, S.; Brungs, M.; Ostrovski, O. Dissolution of Dense Lime in Molten Slags under Static Conditions. ISIJ Int. 2007, 47, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, D.; Kubota, R.; Nishimoto, A.; Kubota, M.; Matsuda, H. Kinetic Study on Dissolution of CaO Particle into CaO-SiO2-Al2O3 Molten Slag from Simulated Municipal Solid Wastes Melting. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 2017, 50, 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Yanagase, T.; Noguchi, F.; Ueda, Y. Studies on the Mechanism of CaO Dissolution into Slag Melts. J. Jpn. Inst. Met. 1974, 38, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, A.R., Jr.; Kingery, W.D. Dissolution in Ceramic Systems: I, Molecular Diffusion, Natural Convection, and Forced Convection Studies of Sapphire Dissolution in Calcium Aluminum Silicate. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1964, 47, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkamp, R.G.; Welch, B.J.; Metson, J.B. Models of Alumina Dissolution in Cryolite. ECS Proc. Vol. 1992, 1996-16, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabi, A.; Mayor, G.; Burbidge, A.; Wallach, R.; Saguy, I.S. Assessing dissolution kinetics of powders by a single particle approach. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 139, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, M.; Yadoomaru, S.; Mori, K.; Kawai, Y. A Fundamental Study on the Dissolution Rate of Solid Lime into Liquid Slag. Trans. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 1977, 17, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamura, S. Dissolution Behavior of Lime into Steelmaking Slag. ISIJ Int. 2017, 57, 1670–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Sun, Z.H.I.; Van Dyck, J.; Guo, M.; Blanpain, B. In Situ Observation on Lime Dissolution in Molten Metallurgical Slags–Kinetic Aspects. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 6325–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folstad, M. Slag and Its Effect on Si and FeSi Production. Ph.D. Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2023. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11250/3096091 (accessed on 8 January 2024).




| Authors | Slag Composition | Temperature | D | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | ||||
| [wt%] | [°C] | [cm2/s] | ||||
| Towers et al. [3] (1953) | 40 | 40 | 20 | 1450 | 1 × 3 × 10−6 | Radioactive Tracer Technique, Ca45 |
| Towers and Chipman [4] (1957) | 40 | 39 | 21 | 1430 | 1 × 10−6 | Radioactive Tracer Technique, Ca45 |
| Niwa [5] (1957) | 40 | 40 | 20 | 1350 | 3.3 × 10−7 | Radioactive Tracer Technique, Ca45 |
| 1400 | 6.2 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1450 | 1.3 × 10−7 | |||||
| 39 | 43 | 18 | 1350 | 5.2 × 10−7 | ||
| 1400 | 6.4 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1450 | 9.5 × 10−7 | |||||
| 71 | 11 | 18 | 1350 | 0.39 × 10−7 | ||
| 1400 | 3.2 × 10−7 | |||||
| Saitô and Maruya [6] (1958) | 41 | 40 | 19 | 1350 | 3.9 × 10−7 | Semi-infinite medium, Ca45 |
| 1395 | 6.9 × 0−7 | |||||
| 1440 | 10 × 10−7 | |||||
| 37 | 43 | 20 | 1440 | 8 × 10−7 | ||
| 1510 | 10 × 10−7 | |||||
| 39 | 49 | 12 | 1440 | 11.5 × 10−7 | ||
| 1510 | 17 × 10−7 | |||||
| 36 | 45 | 19 | 1510 | 8.5 × 10−7 | ||
| 1530 | 9.9 × 10−7 | |||||
| 34 | 46 | 20 | 1440 | 3.8 × 10−7 | ||
| 1485 | 7.1 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1510 | 8.4 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1530 | 10.3 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1575 | 13.0 × 10−7 | |||||
| 31 | 48 | 20 | 1540 | 5.5 × 10−7 | ||
| 1565 | 8.1 × 10−7 | |||||
| Goto et al. [7] (1977) | 40 | 40 | 20 | 1400 | 9.2 × 10−7 | Calculated values from Nernst–Einstein relation |
| 1450 | 1.6 × 10−6 | |||||
| 1500 | 2.6 × 10−6 | |||||
| Liang et al. [8] (1996) | 60 | 30 | 10 | 1500 | 7.41 × 10−7 | Isotope tracer method, Ca40 and Ca42 |
| 55 | 25 | 20 | 5.18 × 10−7 | |||
| 65 | 20 | 15 | 3.3 × 10−7 | |||
| 65 | 25 | 10 | 4.78 × 10−7 | |||
| 55 | 30 | 15 | 7.12 × 10−7 | |||
| 60 | 20 | 20 | 3.66 × 10−7 | |||
| 60 | 25 | 15 | 4.5 × 10−7 | |||
| 45 | 35 | 20 | 9.32 × 10−7 | |||
| 40 | 40 | 20 | 1.34 × 10−6 | |||
| Amini et al. [9] (2006) | 8 | 50 | 42 | 1500–1600 | In the range 10−5–10−4 | Calculated from forced convection dissolution rate data using known mass-transfer correlations |
| Zhang and Chou [10] (2011) | 40 | 40 | 20 | 1350 | 9.0 × 10−7 | Calculated values from Nernst–Einstein relation |
| 1400 | 1.3 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1450 | 1.9 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1500 | 2.8 × 10−7 | |||||
| Ren et al. [11] (2013) | 25 | 46 | 29 | 1350 | 3.74 × 10−7 | Model from relation between diffusion activation energy and optical basicity |
| 1395 | 6.13 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1440 | 9.8 × 10−7 | |||||
| 27 | 49 | 24 | 1440 | 8.80 × 10−7 | ||
| 1510 | 18.90 × 10−7 | |||||
| 45 | 45 | 10 | 1350 | 3.14 × 10−7 | ||
| 1400 | 5.72 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1450 | 10.6 × 10−7 | |||||
| 44 | 47 | 9 | 1350 | 8.39 × 10−7 | ||
| 1400 | 11.43 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1450 | 15.28 × 10−7 | |||||
| 25 | 49 | 26 | 1350 | 2.64 × 10−7 | ||
| 1500 | 16.67 × 10−7 | |||||
| 1540 | 25.88 × 10−7 | |||||
| Product | Supplier | Purity |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | ThermoFisher Scientific (ThermoFisher, Trondheim, Norway) [22] | >99.9% |
| Limestone (CaCO3) | Franzefoss Minerals AS (Franzefoss AS, Inderøy, Norway) [23] | >99.7% |
| Al2O3 | ThermoFisher Scientific [22] | >99.9% |
| Slag | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | Tliquidus | Tsolidus | Λcorr | Viscosity [Poise] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [wt%] | [wt%] | [wt%] | [°C] | [°C] | 1500 °C | 1550 °C | ||
| 1 | 56 | 15 | 29 | 1490 | 1170 | 0.50 | 456 | 250 |
| 2 | 38 | 20 | 42 | 1550 | 1385 | 0.50 | - | 48 |
| 3 | 56 | 21 | 23 | 1420 | 1170 | 0.52 | 180 | 108 |
| Shrinking Sphere | Mass Transport | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Slag (SiO2-CaO-Al2O3) | k1 | k2 | D |
| [wt%] | [g/s·cm2] | [cm/s] | [cm2/s] |
| 1: 56-15-29 | 1.2 × 10−4 | 5.5 × 10−5 | 1.7 × 10−6 |
| 2: 38-20-42 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 4.0 × 10−5 | 1.2 × 10−6 |
| 3: 56-21-23 | 2.9 × 10−4 | 1.4 × 10−4 | 4.2 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Folstad, M.B.; Einarsrud, K.E.; Tangstad, M. Dissolution of CaO in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 Slag in Si Production. Metals 2024, 14, 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020243
Folstad MB, Einarsrud KE, Tangstad M. Dissolution of CaO in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 Slag in Si Production. Metals. 2024; 14(2):243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020243
Chicago/Turabian StyleFolstad, Marit Buhaug, Kristian Etienne Einarsrud, and Merete Tangstad. 2024. "Dissolution of CaO in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 Slag in Si Production" Metals 14, no. 2: 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020243
APA StyleFolstad, M. B., Einarsrud, K. E., & Tangstad, M. (2024). Dissolution of CaO in SiO2-CaO-Al2O3 Slag in Si Production. Metals, 14(2), 243. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14020243







