Utilization of Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue: A Sustainable Approach towards Complete Material Recycling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Analytical Methods
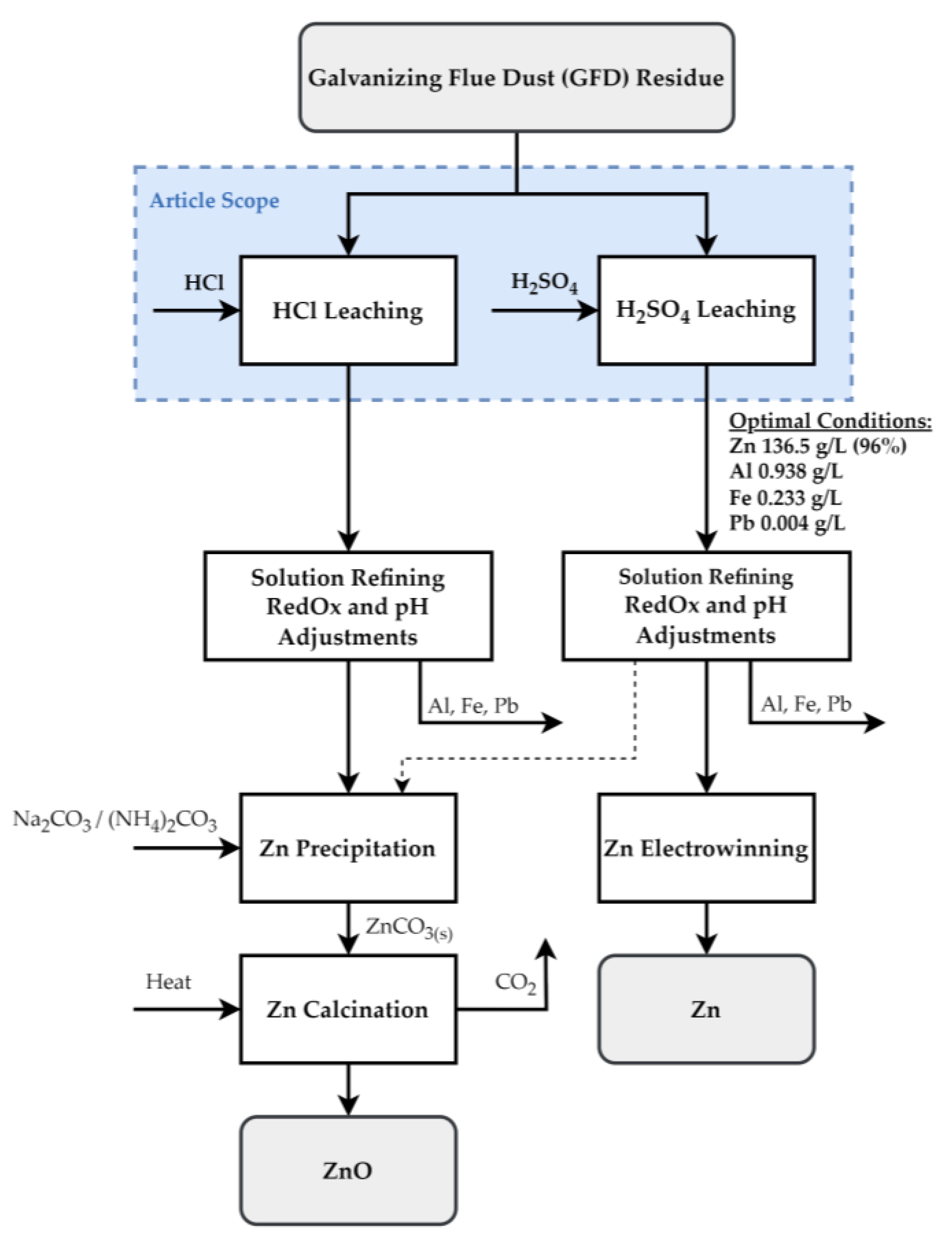
2.3. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Composition of Zinc Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue
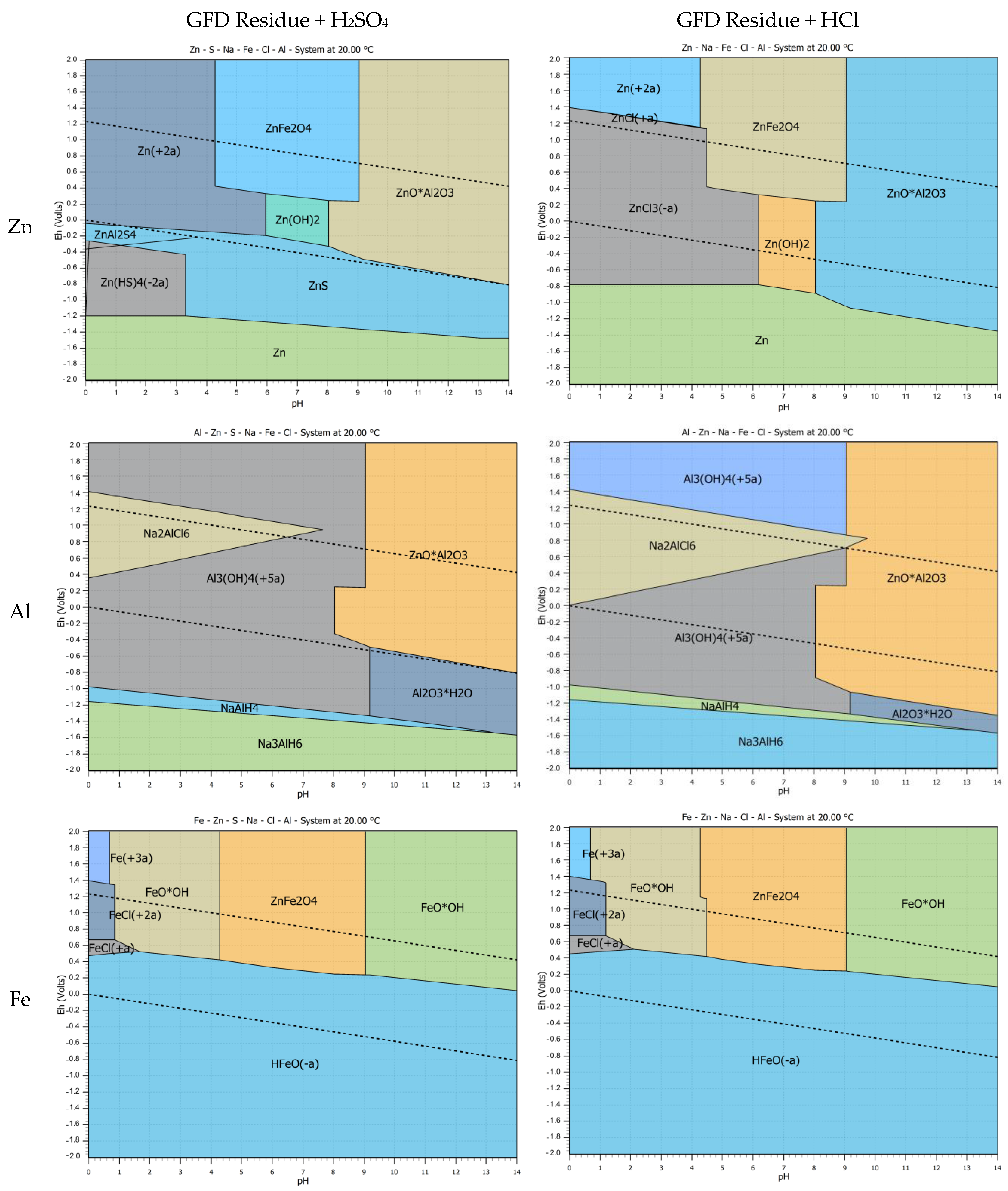
3.2. Thermodynamic Study
| ZnO(s) + H2SO4(aq) = ZnSO4(aq) + H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −121.589 KJ | (3) |
| ZnCl2(s) + H2SO4(aq) = ZnSO4(aq) + 2HCl(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −95.008 KJ | (4) |
| ZnFe2O4(s) + 4H2SO4(aq) = ZnSO4(aq) + Fe2(SO4)3(ia) + 4H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −247.052 KJ | (5) |
| Al2O3(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) = Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −183.626 KJ | (6) |
| PbO(s) + H2SO4(aq) = PbSO4(s) + H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −171.653 KJ | (7) |
| ZnO(s) + 2HCl(aq) = ZnCl2(aq) + H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −181.716 KJ | (8) |
| ZnFe2O4(s) + 8HCl(aq) = ZnCl2(aq) + 2FeCl3(aq) + 4H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −438.607 KJ | (9) |
| Al2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) = 2AlCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −441.870 KJ | (10) |
| PbO(s) + 2HCl(aq) = PbCl2(aq) + H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −196.411 KJ | (11) |
| Fe2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) = 2FeCl3(aq) + 3H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −319.925 KJ | (12) |
| FeO(s) + 2HCl(aq) = FeCl2(aq) + H2O(l) | ΔG°293.15 = −145.194 KJ | (13) |
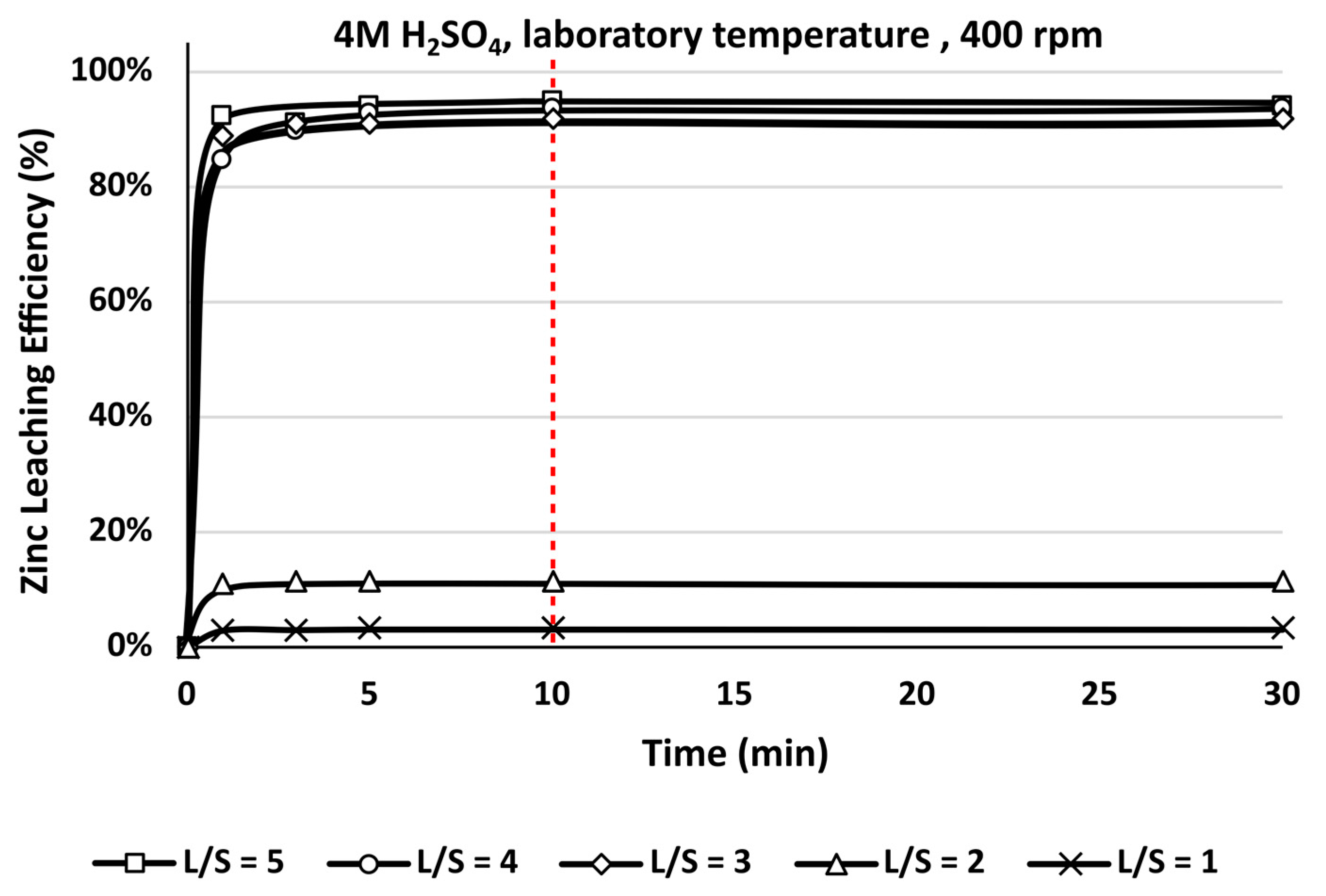
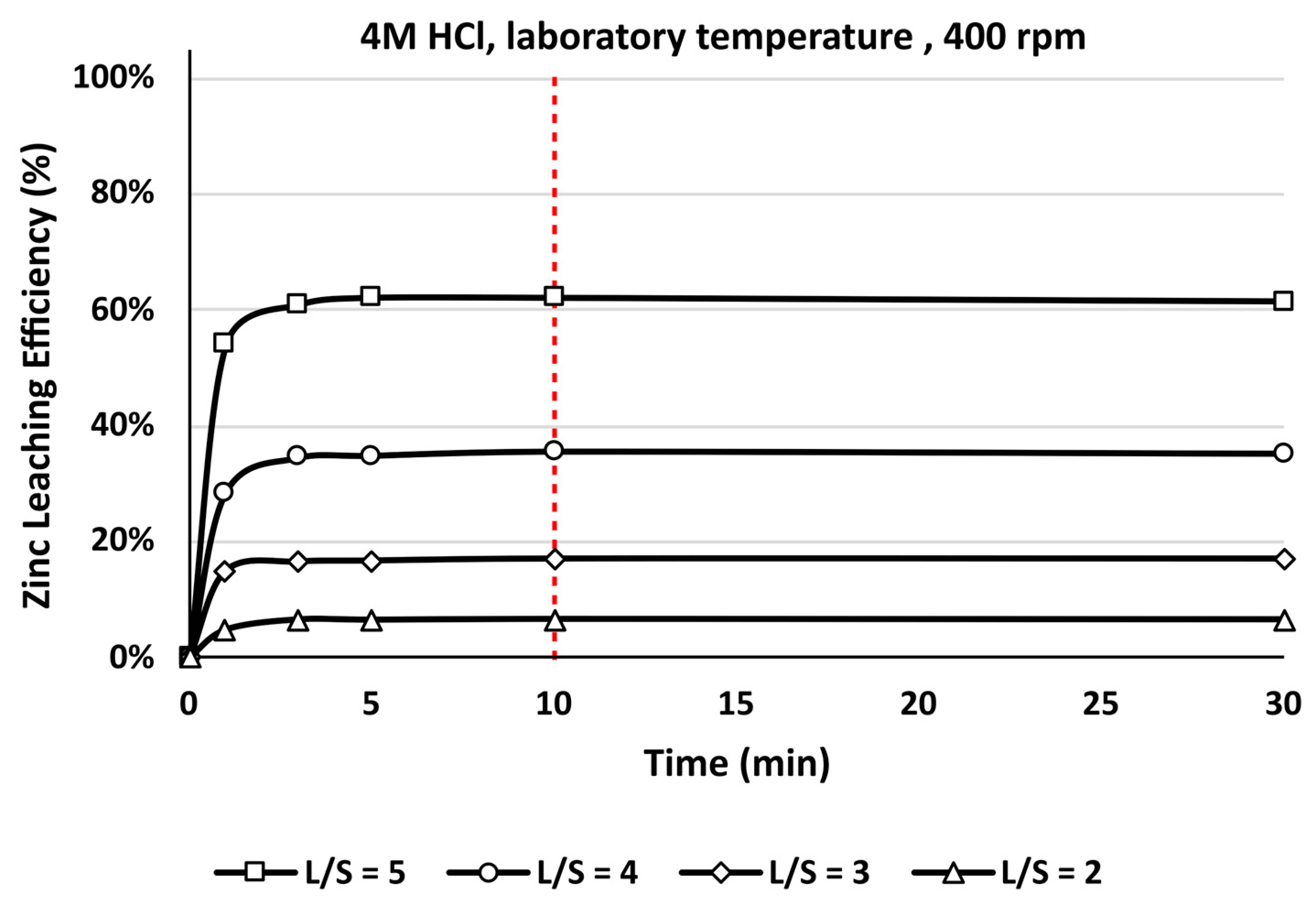
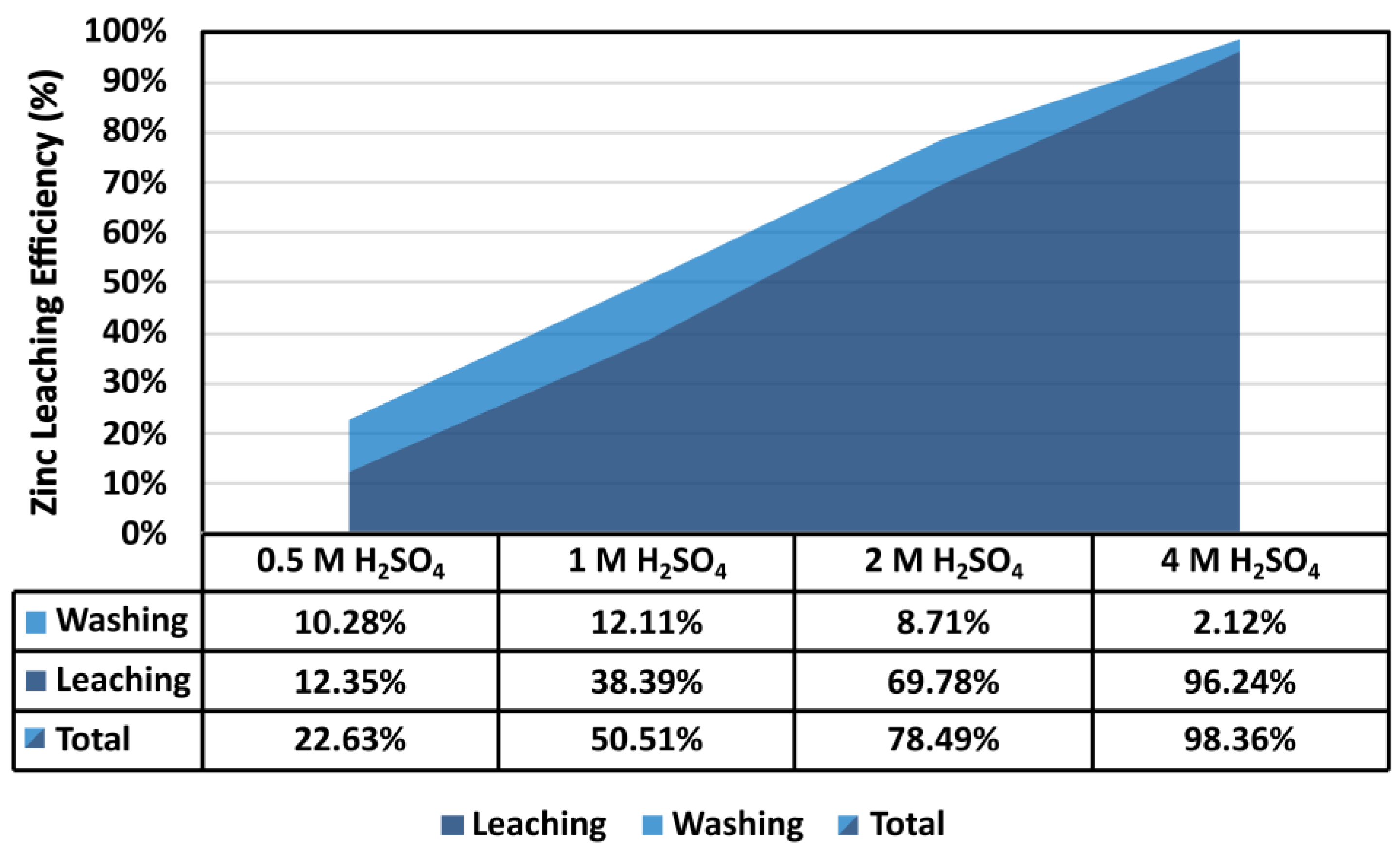
3.3. Leaching
4. Conclusions
- A thermodynamic study confirmed the leachability of the GFD residue in both investigated reagents, H2SO4, and HCl, at ambient temperatures.
- The goal of the first GFD residue leaching experiments was to achieve a high concentration of zinc in the leachate while simultaneously maintaining a high leaching efficiency, which was investigated using 4 M H2SO4 and 4 M HCl at ambient temperature by changing the L/S ratio.
- The next series of experiments investigated the possibility of reducing the concentration of H2SO4, which, however, resulted in a significant reduction in the leaching efficiency.
- The ratio L/S = 3 using 4 M H2SO4 proved to be optimal, in which the solution obtained contains 136.532 g/L of zinc, which represents 96.24% leaching efficiency of GFD residue.
- The possibility of using leachate for the purposes of electrolytic extraction of metallic zinc is investigated. In addition to the electrolysis itself, the effect of the decrease in zinc concentration on the current efficiency of the electrolysis and the effect of impurities on the purity of the obtained zinc deposit is investigated in detail.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hot-Dip Galvanizing Summit: The Current Situation of Environmental Protection and Pollution Control Countermeasures in the Hot-Dip Galvanizing Industry Are Coming! Available online: https://news.metal.com/newscontent/101292420/[hotdip-galvanizing-Summit]-the-current-situation-of-environmental-protection-and-pollution-control-countermeasures-in-thehot-dip-galvanizing-industry-are-coming/ (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Bellini, C.; Iacoviello, F.; Carlino, F.; Di Cocco, V. The Influence of Hot Dip Galvanizing Process on Intermetallic Phases Formation. Mater. Des. Process. Commun. 2019, 1, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refined Zinc Production and Consumption Worldwide 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/242789/zinc-demand-and-supply/ (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Zinc Production by Country 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/264634/zinc-production-by-country/ (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Zinc: Global Reserves by Country 2022. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/273639/global-zinc-reserves-by-country/ (accessed on 30 October 2023).
- Study on the Critical Raw Materials for the EU 2023—Final Report. Available online: https://single-market-economy.ec.europa.eu/publications/study-critical-raw-materials-eu-2023-final-report_en (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Tercero Espinoza, L.A. Critical Appraisal of Recycling Indicators Used in European Criticality Exercises and Circularity Monitoring. Resour. Policy 2021, 73, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroskova, J.; Trpčevská, J.; Orac, D.; Laubertova, M.; Horvathova, H.; Holkova, B. Production of Zinc Oxide from Hazardous Waste—Sal Ammoniac Skimming. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2018, 54, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smincakova, E.; Trpcevska, J.; Piroskova, J. Kinetic Aspects of Leaching Zinc from Waste Galvanizing Zinc by Using Hydrochloric Acid Solutions. JOM 2017, 69, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piroskova, J.; Trpcevska, J.; Laubertova, M.; Smincakova, E. The influence of hydrochloric acid on the zinc extraction from flux skimming. Acta Metall. Slovaca 2015, 21, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trpčevská, J.; Hoľková, B.; Briančin, J.; Korálová, K.; Pirošková, J. The Pyrometallurgical Recovery of Zinc from the Coarse-Grained Fraction of Zinc Ash by Centrifugal Force. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2015, 143, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orac, D.; Klimko, J.; Klein, D.; Piroskova, J.; Liptai, P.; Vindt, T.; Miskufova, A. Hydrometallurgical Recycling of Copper Anode Furnace Dust for a Complete Recovery of Metal Values. Metals 2022, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orac, D.; Laubertova, M.; Piroskova, J.; Klein, D.; Bures, R.; Klimko, J. Characterization of Dusts from Secondary Copper Production. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B Metall. 2020, 56, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takacova, Z.; Piroskova, J.; Miskufova, A.; Vindt, T.; Hezelova, M.; Orac, D. Removal of Impurities from EAFD Ammonium Carbonate Leachate and Upgrading the Purity of Prepared ZnO. Materials 2023, 16, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vindt, T.; Takácová, F.; Kukurugya, F.; Havlik, T. Recycling of Used Portable Zn Batteries Optimization of Mechanical Pre-Treatment of Zn-C and Alkaline Batteries and Characterization of Obtained Active Mass. Metall 2015, 69, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Kuklík, V.; Kudláček, J. Hot-Dip Galvanizing, 1st ed.; Association of Czech and Slovak Galvanizers: Havlíčkův Brod, Czech Republic, 2014; ISBN 978-80-905298-2-3. (In Czech) [Google Scholar]
- Maaß, P. Handbook of Hot-Dip Galvanization, 1st ed.; Wily-VCH Verlag GmbH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 1–19. ISBN 978-3-527-32324-1. [Google Scholar]
- McNeeney, S.; Stephe, P. Flux and Process for Hot Dip Galvanization; European patent specification (EP1974070B1). June 2013. Available online: https://data.epo.org/publication-server/document?iDocId=4429550&iFormat=0 (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Piroskova, J.; Klimko, J.; Trpcevska, J.; Laubertova, M.; Plesingerova, B.; Liptai, P.; Vindt, T.; Orac, D. Characterization of Galvanizing Flue Dust and Recycling Possibilities. Metals 2022, 12, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, R.M.; Cole, J.A. Zaclon’s Galvanizing Handbook; Zaclon Incorporate: Cleveland, OH, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.D.N. Pickling, Rinsing and Fluxing of Steels before Galvanizing; National Metallurgical Laboratory: Jamshedpur, India, 1997; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Trpčevská, J. Zinc, Its Application, Production, and Recycling, 1st ed.; Technical University of Košice: Košice, Slovakia, 2018; ISBN 978-80-553-2997-0. (In Slovak) [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, L.; Quddus, M.; Khanam, J.; Bilkis, K.; Rahman, M. Fabrication of Zinc Oxide from Zinc Dust and Its Characterization. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 2017, 10, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisol, F. Process for Treating Metallic Dust, Mostly Oxididised Waste, in Particular Galvanising Dust and/or Steelworks Smoke; 2002. European Patent Office (EP0935005A1). Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/EP0935005A1/en (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Barakat, M.A. The Pyrometallurgical Processing of Galvanizing Zinc Ash and Flue Dust. JOM 2003, 55, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, E.E.; Hammond, W.F.; Thomas, G. Air Pollution Control Measures for Hot Dip Galvanizing Kettles. J. Air Pollut. Control Assoc. 1960, 10, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pirošková, J. Top Dross Processing Originated during Wet Hot Dip Galvanizing. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Košice, Košice, Slovakia, 2015. (In Slovak). [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA). A User-Friendly Reference Document for Hazardous Waste Listings. First Update. March 2008. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw/user-friendly-reference-document-hazardous-waste-listings (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Scottish Environment Protection Agency. European Commission 2000/532/EC1. Guidance on Using the European Waste Catalogue (EWC) to Code Waste; November 2015; p. 56. Available online: https://www.sepa.org.uk/media/163421/ewc_guidance.pdf (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Thorsen, G.; Grislingås, A.; Steintveit, G. Recovery of Zinc from Zinc Ash and Flue Dusts by Hydrometallurgical Processing. JOM 1981, 33, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roine, A. HSC Chemistry® [Software], Version 10; Outotec Research Oy: Espoo, Finland, 2021.
- Exchange, T.L.M. Metals|London Metal Exchange. Available online: https://www.lme.com/Metals (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- XM-Chemicals China. Available online: https://xm-chemical.en.made-in-china.com/ (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Find Quality Manufacturers, Suppliers, Exporters, Importers, Buyers, Wholesalers, Products and Trade Leads from Our Award-Winning International Trade Site. Import & Export on Alibaba.Com. Available online: https://www.alibaba.com (accessed on 31 October 2023).
- Klimko, J.; Urban, I.; Piskorova, J.; Orac, D.; Havlik, T.; Klein, D. Sustainable Development in the Tinplate Industry: Refining Tinplate Leachate with Cementation. Physicochem. Probl. Miner. Process. 2019, 56, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demčáková, S.; Hezelova, M.; Pikna, L.; Klimko, J. Selective tin recovery from tinning sludge by cementation process and chronoamperometry. J. Chem. Technol. Metall. 2021, 56, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
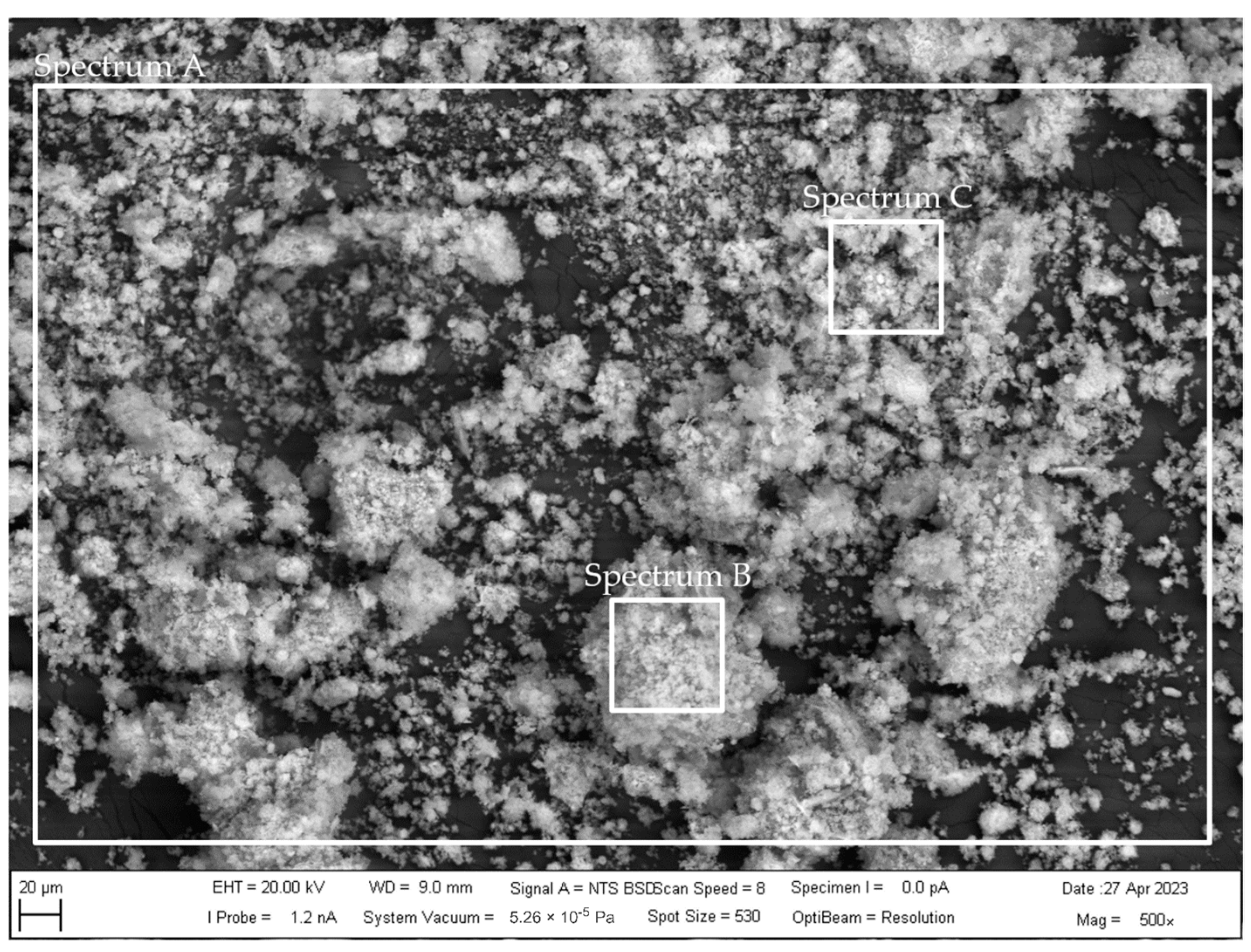
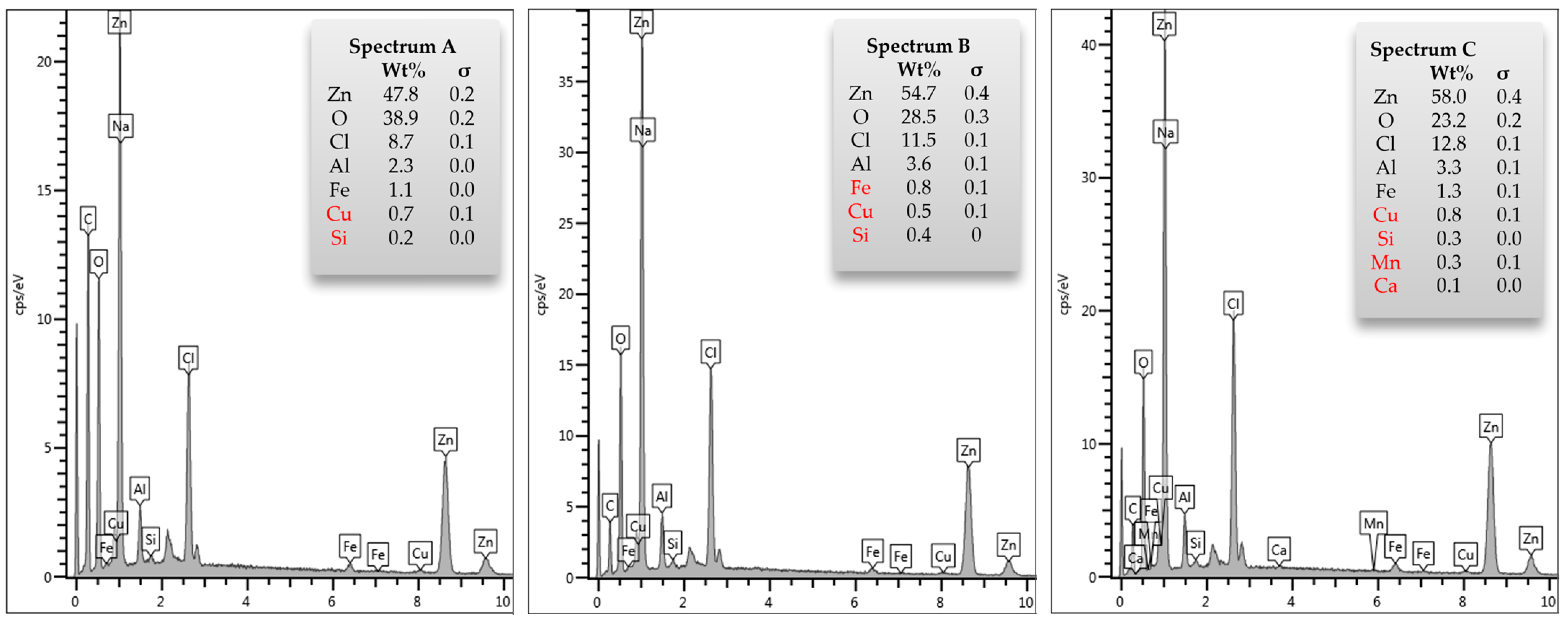
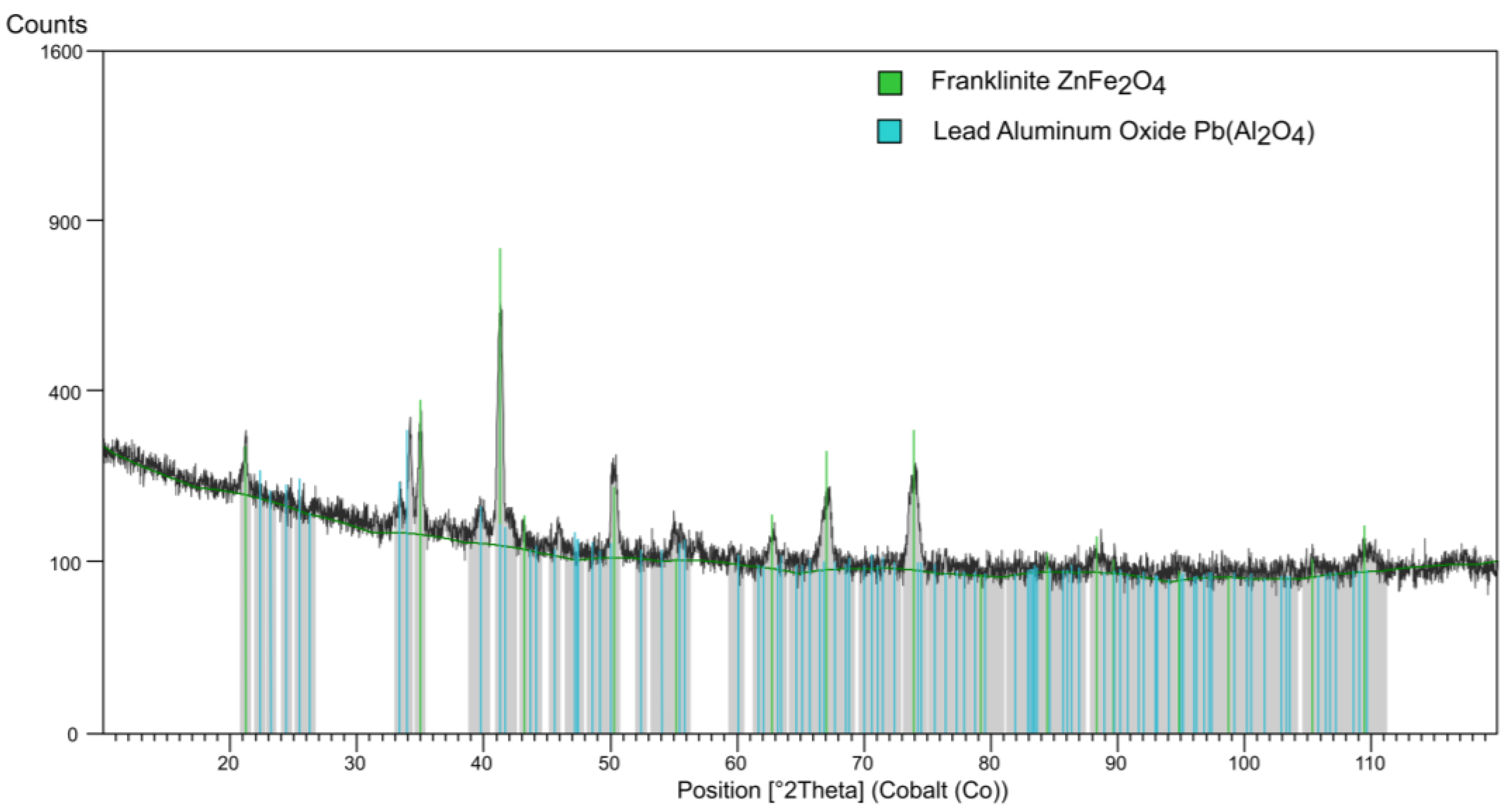

| Element | Zn | Al | Fe | Cu | Si | Pb | Mn | Ca | Cl− ** | Residue |
| Content (%) | 42.46 | 2.51 | 1.17 | <LoD * | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 0.03 | 16.42 | 36.89 |
| Element | Content (%) | Marketable Products | Price of Marketable Product 1 ($/t) | Estimated Value of Marketable Product in 1 t of GFD Residue ($/t) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 42.46 | Zn | 2425.50 | 1029.87 |
| Al | 2.51 | Al | 2236.00 | 56.12 |
| Pb | 0.2 | Pb | 2245.00 | 5.78 |
| Fe | 1.17 | FeO (Fe = 77.73%) | 40 | 0.60 |
| Mn | 0.07 | Mn | 1500 | 1.05 |
| Ca | 0.03 | CaSO4 (Ca = 29.43%) | 300 | 0.31 |
| Si | 0.25 | - | - | - |
| Element | Content (%) | L/S = 10 | L/S = 5 | L/S = 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molarity (M) | Concentration (g/L) | Molarity (M) | Concentration (g/L) | Molarity (M) | Concentration (g/L) | ||
| Zn | 42.56 | 0.651 | 42.56 | 1.302 | 85.12 | 2.17 | 141.867 |
| Fe | 1.17 | 0.021 | 1.17 | 0.042 | 2.34 | 0.07 | 3.9 |
| Al | 2.51 | 0.093 | 2.51 | 0.186 | 5.02 | 0.31 | 8.367 |
| Pb | 0.20 | 0.001 | 0.20 | 0.002 | 0.40 | 0.003 | 0.667 |
| Analyte | Zn | Fe | Al | Pb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (g/L) | 136.532 | 0.233 | 0.938 | 0.004 |
| Leaching efficiency (%) | 96.24 | 5.97 | 11.22 | 0.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirošková, J.; Klimko, J.; Ružičková, S.; Laubertová, M.; Marcinov, V.; Múdra, E.; Vojtko, M.; Oráč, D. Utilization of Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue: A Sustainable Approach towards Complete Material Recycling. Metals 2024, 14, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030253
Pirošková J, Klimko J, Ružičková S, Laubertová M, Marcinov V, Múdra E, Vojtko M, Oráč D. Utilization of Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue: A Sustainable Approach towards Complete Material Recycling. Metals. 2024; 14(3):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030253
Chicago/Turabian StylePirošková, Jana, Jakub Klimko, Silvia Ružičková, Martina Laubertová, Vladimír Marcinov, Erika Múdra, Marek Vojtko, and Dušan Oráč. 2024. "Utilization of Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue: A Sustainable Approach towards Complete Material Recycling" Metals 14, no. 3: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030253
APA StylePirošková, J., Klimko, J., Ružičková, S., Laubertová, M., Marcinov, V., Múdra, E., Vojtko, M., & Oráč, D. (2024). Utilization of Galvanizing Flue Dust Residue: A Sustainable Approach towards Complete Material Recycling. Metals, 14(3), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030253










