Temperature-Dependent Young’s Modulus of TaC- and TiC-Strengthened Co-Re-Based Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Casting and Specimen Preparation
2.2. Experimental Determination of Young’s Modulus with Vibrating Reed
3. Results
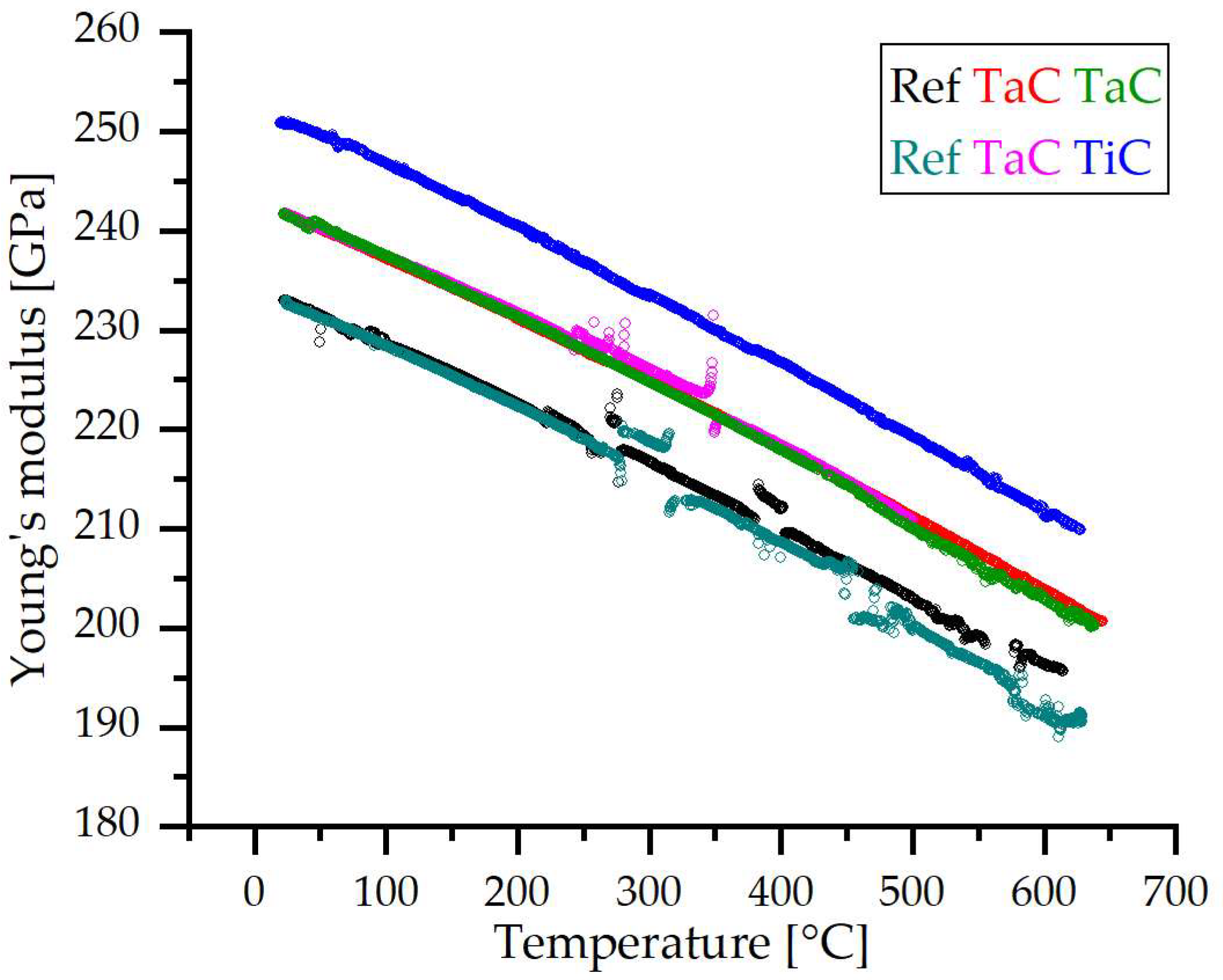
3.1. Experimental Determination of Young’s Modulus with Vibrating Reed
3.2. Temperature Dependency
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Carbides on Young’s Modulus
4.2. Temperature Dependency of Young’s Modulus
5. Conclusions
- Young’s modulus of Co-15Re-5Cr is approx. 12 % higher than that of pure Co;
- Low amounts of TaC and TiC result in a further increase in stiffness;
- The temperature dependency of Young’s modulus is weaker compared to pure Co;
- The temperature dependency of Young’s modulus for MC-free and MC-containing Co-15Re-5Cr is similar, so the CoReCr-matrix is mainly responsible for temperature dependency;
- Analytical estimations of Young’s modulus using the HS bounds are in good agreement with the experimental results obtained for the TaC-containing alloy but inaccurate for the TiC-containing variant.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perepezko, J.H. The hotter the engine, the better. Science 2009, 326, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemberg, J.A.; Ritchie, R.O. Mo-Si-B Alloys for Ultrahigh-Temperature Structural Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 23, 3445–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombola, C.; Schliephake, D.; Heilmaier, M.; Perepezko, J.H. Creep of an oxidation resistant coated Mo-9Si-8B alloy. Intermetallics 2020, 120, 106743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Paul, J.D.H.; Stark, A.; Bezold, A.; Neumeier, S.; Göken, M.; Pyczak, F. High-Temperature CoNi-Based Superalloys Strengthened by γ′-(Ni,Co)3(Cr,Al,Ti,X): The Effect of Refractory Elements. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2023, 54A, 1620–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makineni, S.K.; Sharma, A.; Pandey, P.; Chattopadhyay, K. An Overview on Co-Base Alloys for High Temperature Applications. Encycl. Mater. Met. Alloys 2020, 1, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Omori, T.; Oikawa, K.; Ohnuma, I.; Kainuma, R.; Ishida, K. Cobalt-Base High-Temperature Alloys. Science 2006, 312, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rösler, J.; Mukherji, D.; Baranski, T. Co-Re-based Alloys: A New Class of High Temperature Materials? Adv. Eng. Mater. 2007, 9, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R.; Kacprzak, L. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Seif, E.; Rösler, J. Reassessment of the Matrix Composition of Co-Re-Cr-Based Alloys for Particle Strengthening in High-Temperature Applications and Investigation of Suitable MC-Carbides. Materials 2023, 16, 4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depka, T.; Somsen, C.; Eggeler, G.; Mukherji, D.; Rösler, J. Sigma phase evolution in Co–Re–Cr-based alloys at 1100 °C. Intermetallics 2014, 48, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanderka, N.; Mousa, M.S.; Henke, P.; Korchuganova, O.; Mukherji, D.; Rösler, J.; Banhart, J. Carbides in Co–Re–Cr-based high-temperature alloys. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 7145–7155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karge, L.; Gilles, R.; Mukherji, D.; Strunz, P.; Beran, P.; Hofmann, M.; Gavilano, J.; Keiderling, U.; Dolotko, O.; Kriele, A.; et al. The influence of C/Ta ratio on TaC precipitates in Co-Re base alloys investigated by small-angle neutron scattering. Acta Mater. 2017, 132, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, E.; Rösler, J.; Werner, J.; Weirich, T.E.; Mayer, J. Investigation of TaC and TiC for Particle Strengthening of Co-Re-Based Alloys. Materials 2023, 16, 7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selle, J.E. Innere Reibung von Kobalt (Internal friction in cobalt). Kobalt 1969, 45, 163–166. [Google Scholar]
- Sargent, P.M.; Ashby, M.F.; Malakondaiah, G. A Deformation Map for Cobalt. Scr. Metall. 1983, 17, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.T.; Jaffee, R.I. Further Studies of the Properties of Rhenium Metal. J. Met. 1956, 8, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karge, L.; Gilles, R.; Mukherji, D.; Beran, P.; Strunz, P.; Hoelzel, M.; Rösler, J. Beyond Ni-base superalloys: Influence of Cr addition on Co-Re base alloys strengthened by nano-sized TaC precipitates. Phys. B 2018, 551, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gorr, B.; Christ, H.-J.; Mukherji, D.; Rösler, J. Microstructure and Oxidation Mechanism Evolution of Co–17Re–25Cr–2Si in the Temperature Range 800–1100 °C. Oxid. Met. 2015, 83, 465–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, C.T. High-Temperature Materials for Aerospace and Industrial Power; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Hocker, S.; Lipp, H.; Schmauder, S.; Bakulin, A.V.; Kulkova, S.E. Ab initio investigation of Co/TaC interfaces. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 853, 156944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, S.P.; Cankurtaran, M.; James, B. Ultrasonic determination of the elastic and nonlinear acoustic properties of transition-metal carbide ceramics: TiC and TaC. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashin, Z.; Shtrikman, S. A Variational Approach to the Theory of the Elastic Behaviour of Multiphase Materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1963, 11, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, W.H.; Shimmin, K.D. Elevated Temperature Dynamic Elastic Moduli of Various Metallic Materials. 1961, US Air Force WADD Technical Report 60-438. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/4806475 (accessed on 8 November 2023).
- Whiting, R.; Jacobsen, P.H. An evaluation of the vibrating reed method for determining the mechanical properties of materials. J. Biomed. Eng. 1983, 5, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Bernhardt, J.; Faerstein, K.; Shtansky, D.; Bando, Y.; Golovin, I.S.; Sinning, H.-R.; Golberg, D. Fabrication and characteristics of melt-spun Al ribbons reinforced with nano/micro-BN phases. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 7604–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösemann, N.; Fiedler, T.; Sinning, H.-R.; Bäker, M. Determining Young’s modulus of coatings in vibrating reed experiments using irregularly shaped specimens. Results Mater. 2019, 2, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, T.; Sinning, H.-R.; Rösler, J.; Bäker, M. Temperature dependent mechanical properties of metallic HVOF coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.M.; Benaroya, H.; Wei, T. Dynamics of Transversely Vibrating Beams using four Engineering Theories. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 225, 935–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherji, A.K.; Bird, J.E.; Dorn, J.E. Experimental Correlations for High-Temperature Creep. Trans. ASM 1969, 62, 155–179. [Google Scholar]
- Sherby, O.D.; Miller, A.K. Combining Phenomenology and Physics in Describing the High Temperature Mechanical Behavior or Crystalline Solids. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 1979, 101, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, W.; Eisenlohr, P.; Breutinger, F. Understanding Creep—A Review. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33A, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösler, J.; Harders, H.; Bäker, M. Mechanisches Verhalten der Werkstoffe (Mechanical Behaviour of Materials); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; ISBN 978-3-658-26801-5. [Google Scholar]
- Köster, W. Poisson’s ratio for metals. Appl. Sci. Res. 1954, 4, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beran, P.; Mukherji, D.; Strunz, P.; Gilles, R.; Hofmann, M.; Karge, L.; Dolotko, O.; Rösler, J. Effect of Composition on the Matrix Transformation of the Co-Re-Cr-Ta-C Alloys. Met. Mater. Int. 2016, 22, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, B.; Xu, M.; Zhu, J.; Hao, Y.; Li, W.; Long, X. Elastic and thermodynamic properties of TiC from first-principles calculations. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 2011, 54, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
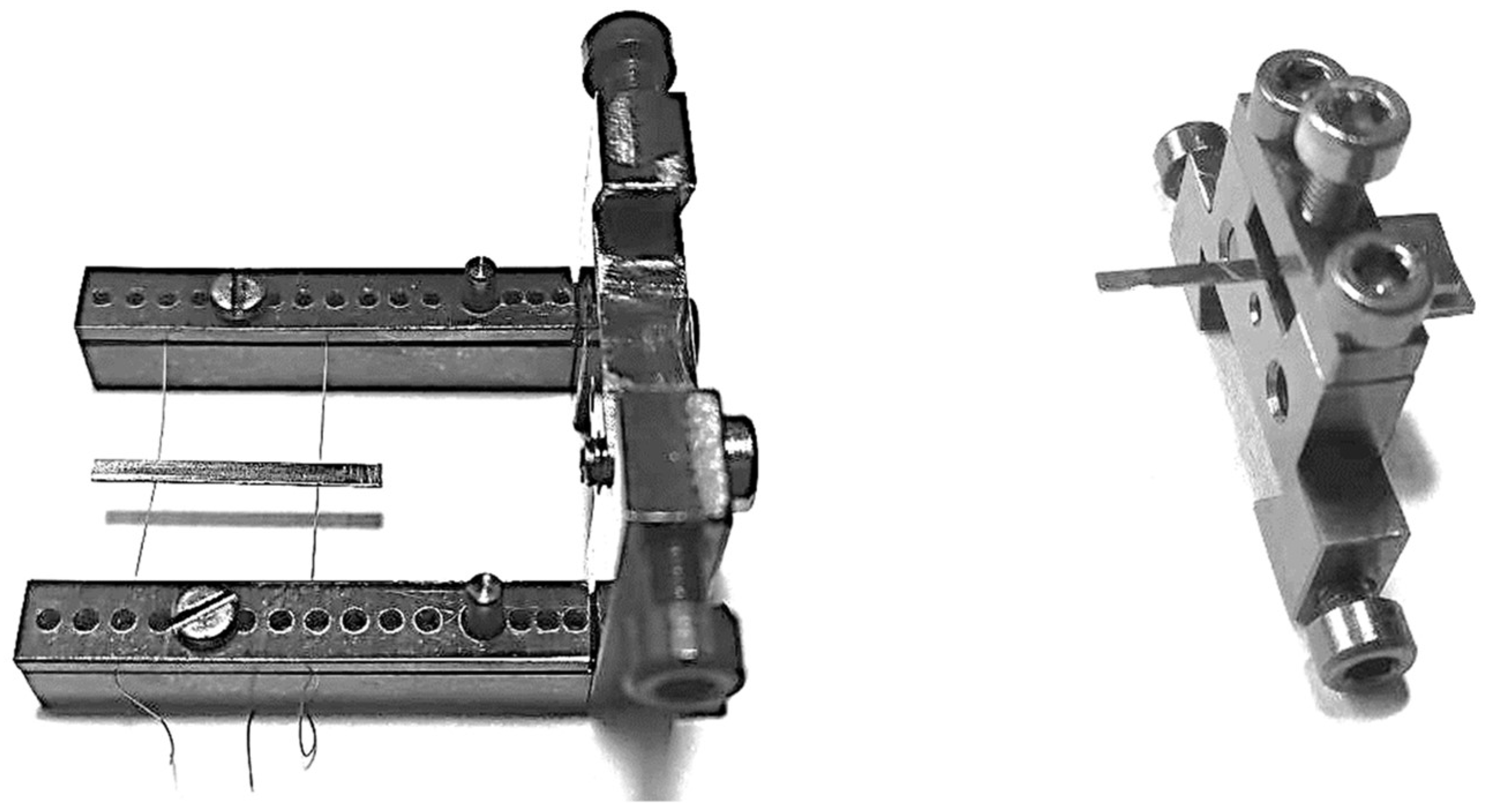
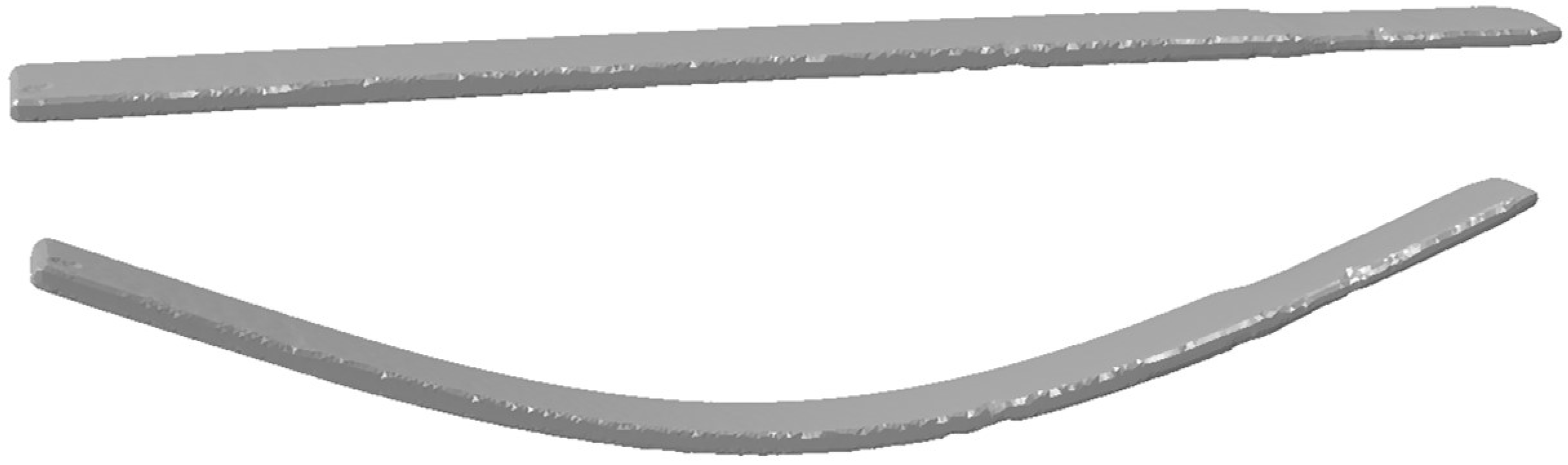

| Alloy | Co | Re | Cr | Ta | Ti | C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | Bal. | 15 | 5 | - | - | - |
| TaC | Bal. | 15 | 5 | 1.8 | - | 1.8 |
| TiC | Bal. | 15 | 5 | - | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Alloy | Frequency [1/s] | Density [g/cm3] | Young’s Modulus [GPa] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ref | 5022 | 11.33 | 233 |
| TaC | 4569 | 11.43 | 242 |
| TiC | 5002 | 11.42 | 252 |
| CoReCr-Matrix | TiC | TaC | |
|---|---|---|---|
| E [GPa] | 233.4 (this work) | 436 [21] | 567 [21] |
| ν [-] | 0.32 [33] | 0.215 [21] | 0.187 [21] |
| Alloy | Lattice Parameters [nm] | Calculated Volume Fraction of Carbides | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| a Matrix | c Matrix | a Carbides | ||
| TiC | 0.2552 [34] | 0.4121 [34] | 0.433 [35] | 0.032 |
| TaC | 0.2552 [34] | 0.4121 [34] | 0.4444 [12] | 0.034 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiedler, T.; Seif, E.; Sinning, H.-R.; Rösler, J. Temperature-Dependent Young’s Modulus of TaC- and TiC-Strengthened Co-Re-Based Alloys. Metals 2024, 14, 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030324
Fiedler T, Seif E, Sinning H-R, Rösler J. Temperature-Dependent Young’s Modulus of TaC- and TiC-Strengthened Co-Re-Based Alloys. Metals. 2024; 14(3):324. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030324
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiedler, Torben, Eugen Seif, Hans-Rainer Sinning, and Joachim Rösler. 2024. "Temperature-Dependent Young’s Modulus of TaC- and TiC-Strengthened Co-Re-Based Alloys" Metals 14, no. 3: 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030324
APA StyleFiedler, T., Seif, E., Sinning, H.-R., & Rösler, J. (2024). Temperature-Dependent Young’s Modulus of TaC- and TiC-Strengthened Co-Re-Based Alloys. Metals, 14(3), 324. https://doi.org/10.3390/met14030324






